Generation of Decoy Signals Using Optical Amplifiers for a Plug-and-Play Quantum Key Distribution System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
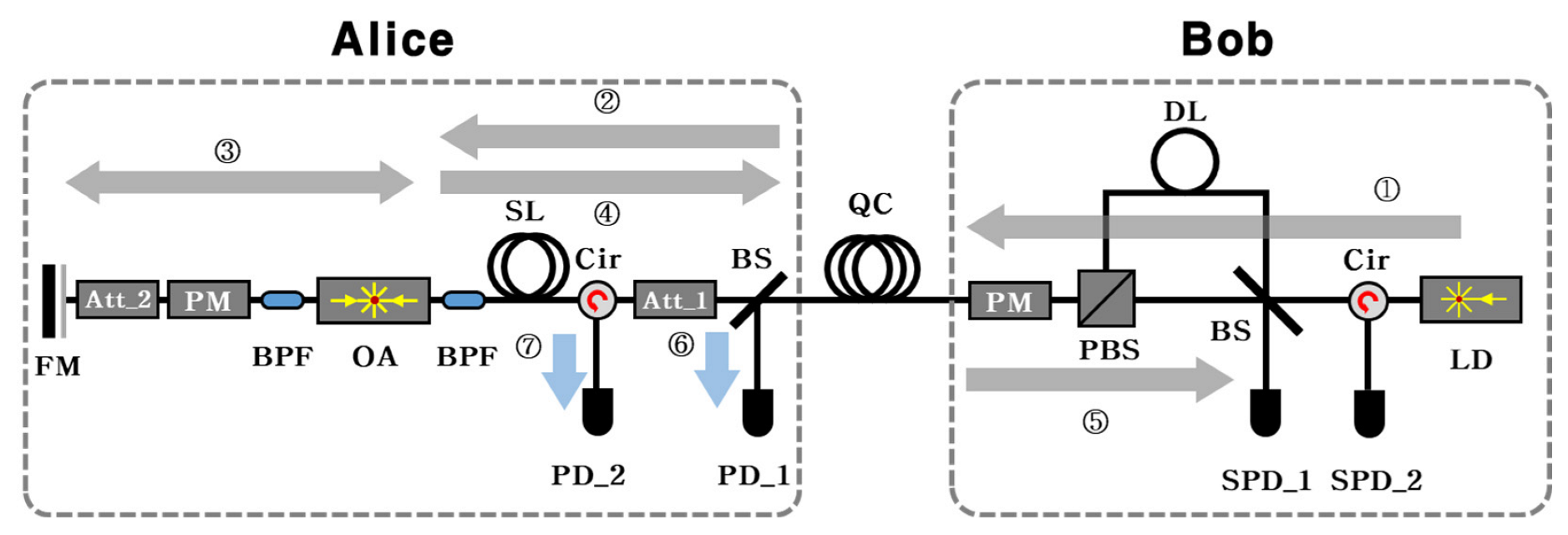
2. PnP QKD Decoy System with Amplification Structure
- ①
- Bob generates a strong laser pulse (1550.92 nm) with a gain-switched laser. Then, the pulse passes through the asymmetric Mach–Zehnder interferometer and is divided into a time-bin pulse and transmitted to Alice. Now, in our scheme, has horizontal polarization, while has vertical polarization.
- ②
- After passing through the QC, some part of the strong pulse that reaches Alice branches to ⑥. The rest goes to an attenuator (Att_1) forward-directed circulator (Cir), storage line (SL), bandpass filter, and OA.
- ③
- The OA amplifies the intensity of the pulse. Noise from the OA is reduced by a bandpass filter. Subsequently arriving at the phase modulator (PM), which is used for phase encoding and randomization, the pulse is then attenuated at Att_2, reflected from the Faraday mirror (FM), and proceeded backward to OA. Then, it is amplified once again in OA.
- ④
- The pulse proceeds in reverse order of ②. At this point, most of the pulse power is delivered in the circulator’s forward direction, ⑦. The only rest weak power of the pulse is transmitted to att_1, and it is fine-tuned to a single-photon level at Alice’s output.
- ⑤
- The single-photon level pulse passes through the QC and reaches Bob’s PM. Decoding starts through this PM. After passing Bob’s asymmetric Mach–Zehnder interferometer, it reaches the beam splitter (BS) and interferes. The results of the interference can be known from the measurement results of the single-photon detectors (SPDs).
- ⑥
- A pulse that splits from the BS of Alice reaches photo diode_1 (PD_1). This pulse enables the timing control of Alice’s device. Moreover, measuring the intensity of the pulse may help to adjust the intensity of Bob’s initial laser pulse.
- ⑦
- This is the forward flow of the circulator. It is connected to PD_2, and the output pulse can be monitored through PD_2.
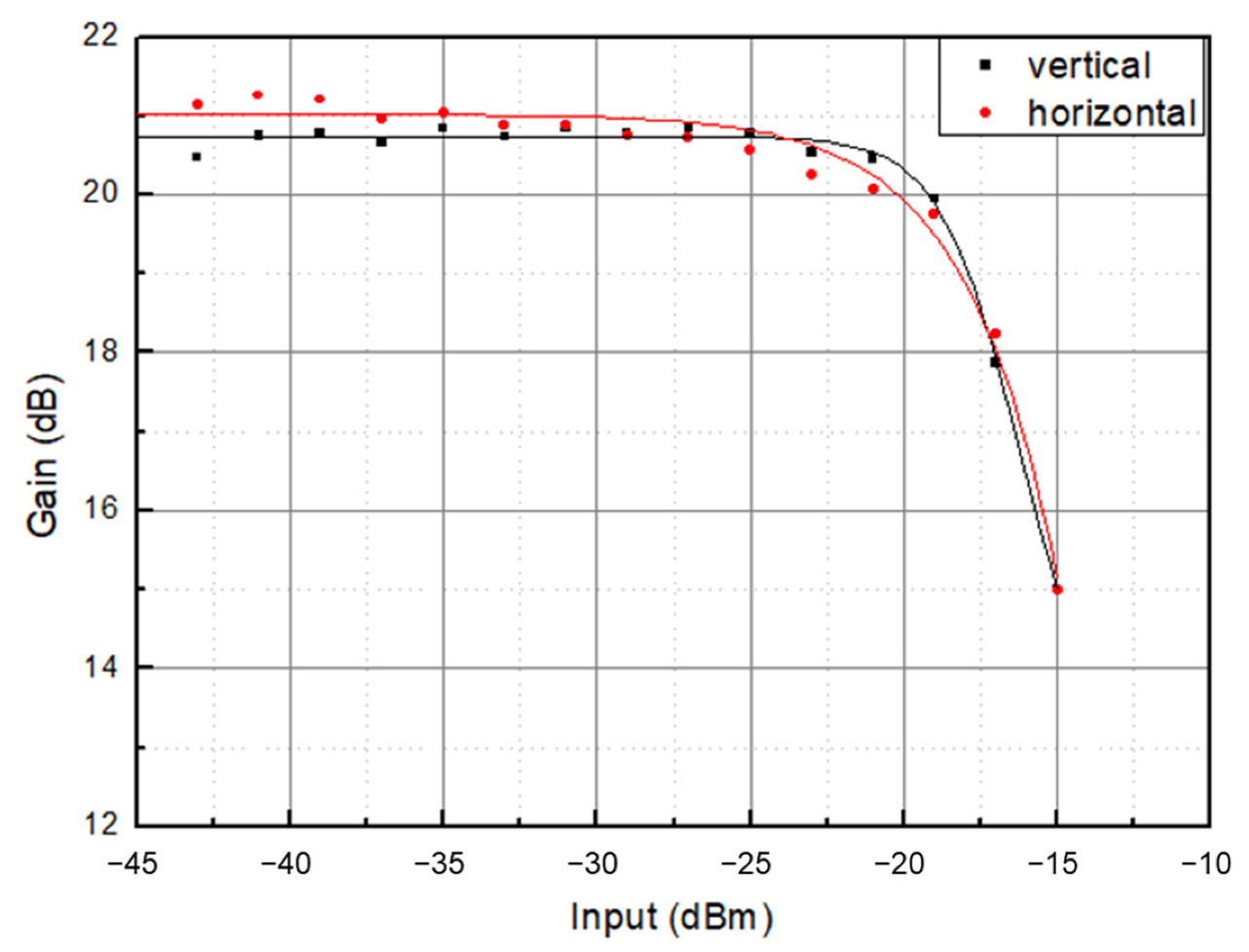
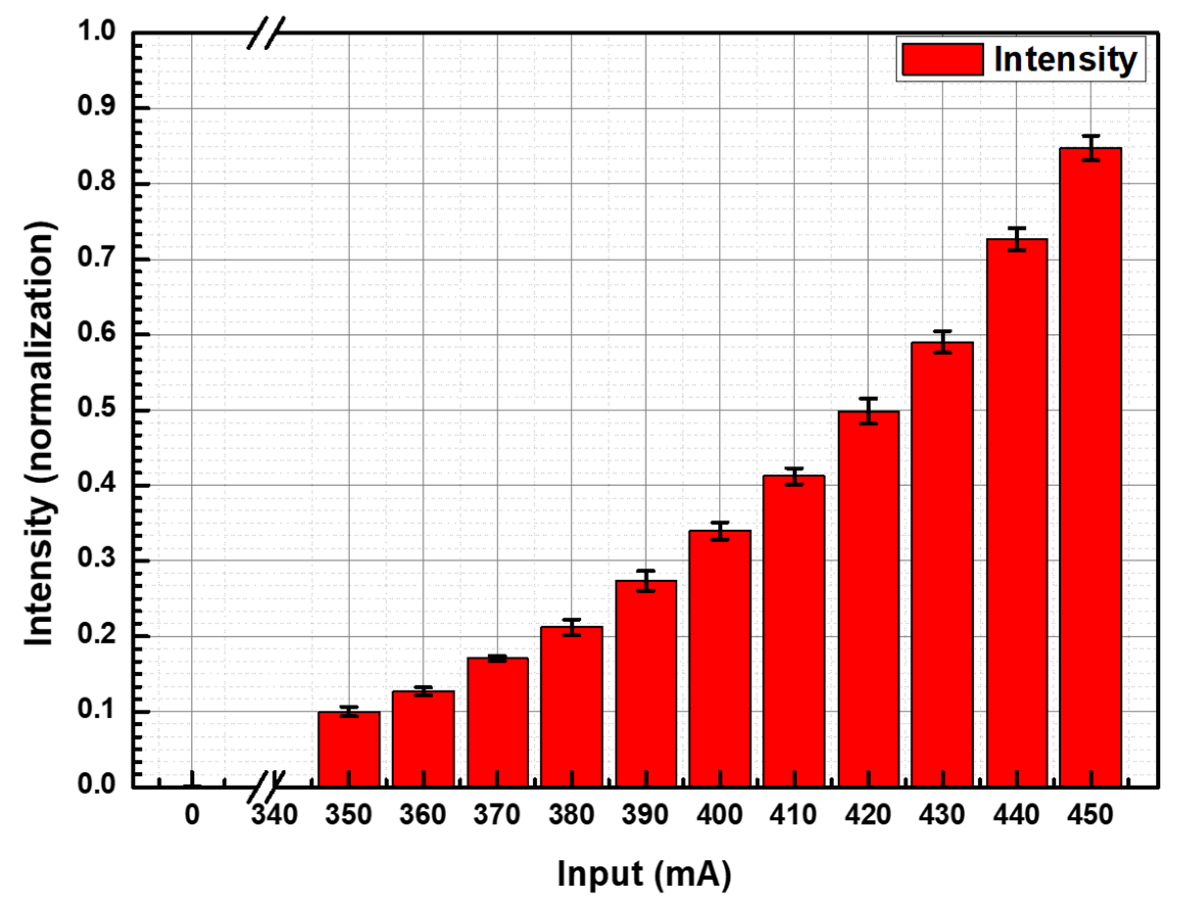
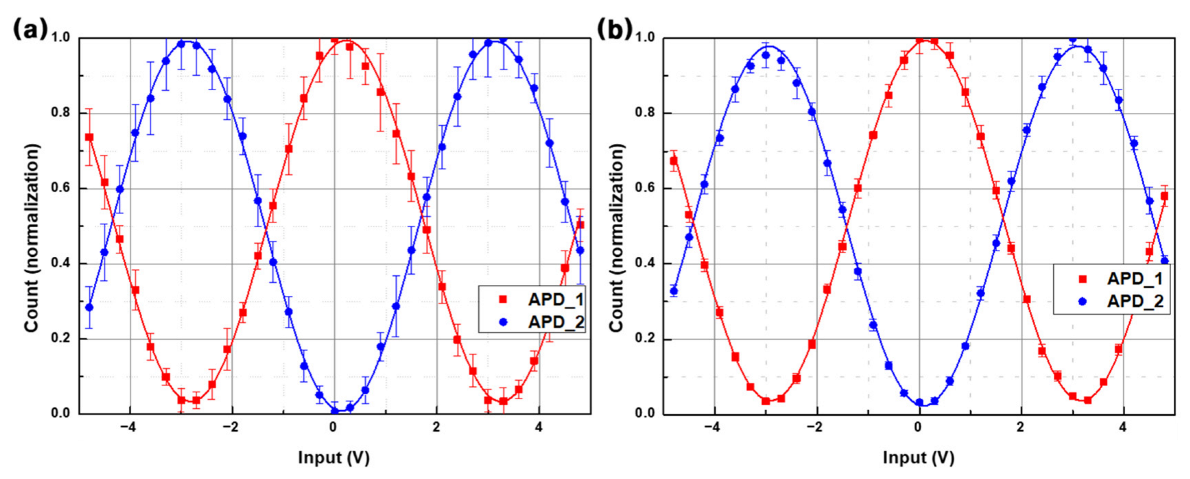
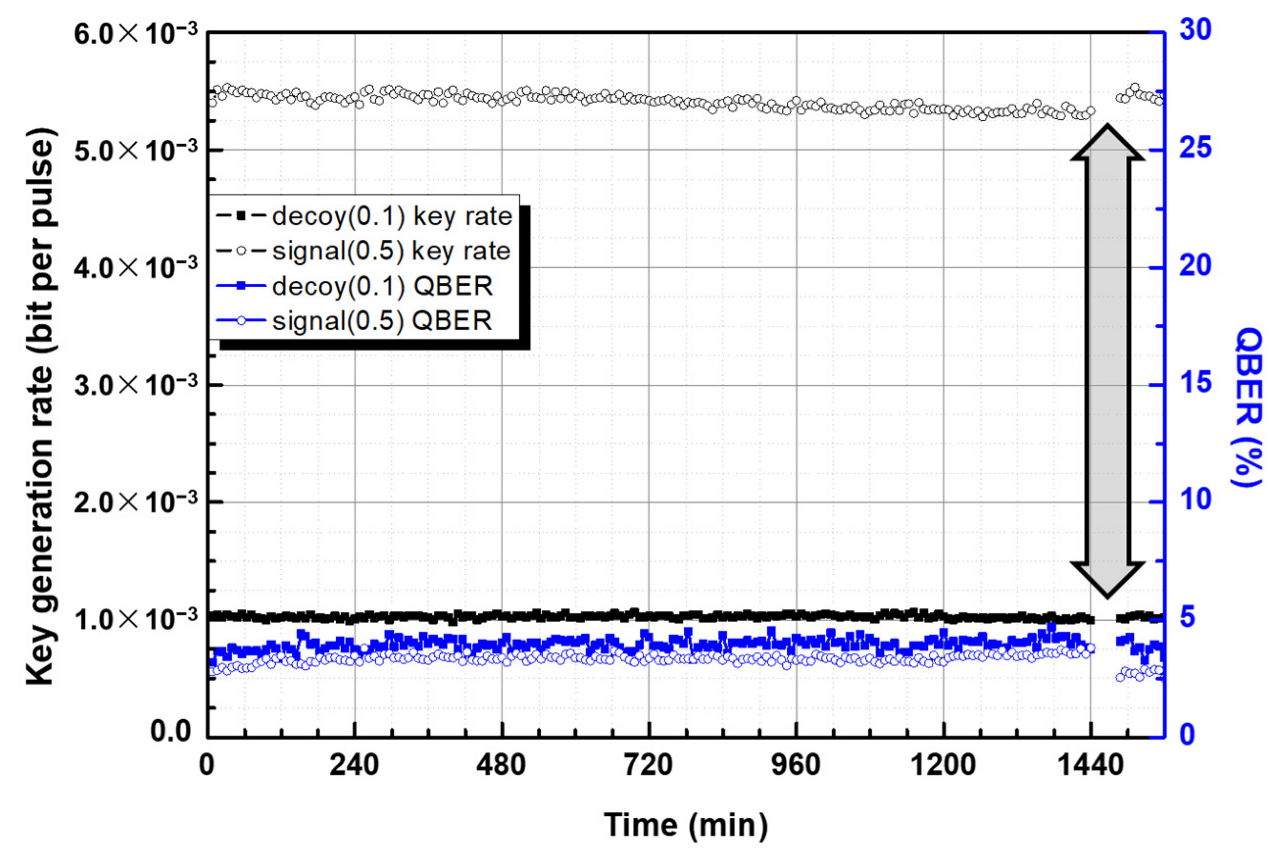
3. Method and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Modern Phy. 2002, 74, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.-K.; Zhao, Y. Quantum cryptography. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0803.2507. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Computer Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 10–12 December 1984; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.-J.; Han, Z.-Y.; Ma, S.-Z.; Hu, X.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Liu, H.; et al. Twin-field quantum key distribution over a 511 km optical fibre linking two distant metropolitan areas. Nat. Photon. 2021, 15, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.K.; Cai, W.Q.; Handsteiner, J.; Liu, B.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Rauch, D.; Fink, M.; Ren, J.G.; Liu, W.Y.; et al. Satellite-Relayed Intercontinental Quantum Network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frohlich, B.; Dynes, J.F.; Lucamarini, M.; Sharpe, A.W.; Yuan, Z.; Shields, A.J. A quantum access network. Nature 2013, 501, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibson, P.; Erven, C.; Godfrey, M.; Miki, S.; Yamashita, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Sasaki, M.; Terai, H.; Tanner, M.G.; Natarajan, C.M.; et al. Chip-based quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, H.T.; Zou, M.; Yu, Z.W.; Hu, X.L.; Xu, H.; Ma, S.; Han, Z.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Field Test of Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution through Sending-or-Not-Sending over 428 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 250502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Fujiwara, M.; Ishizuka, H.; Klaus, W.; Wakui, K.; Takeoka, M.; Miki, S.; Yamashita, T.; Wang, Z.; Tanaka, A. Field test of quantum key distribution in the Tokyo QKD Network. Opt. Exp. 2011, 19, 10387–10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunandar, D.; Lentine, A.; Lee, C.; Cai, H.; Long, C.M.; Boynton, N.; Martinez, N.; DeRose, C.; Chen, C.; Grein, M.; et al. Metropolitan Quantum Key Distribution with Silicon Photonics. Phy. Rev. X 2018, 8, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, A.; Herzog, T.; Huttner, B.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H.; Gisin, N. “Plug and play” systems for quantum cryptography. Appl. Phy. Lett. 1997, 70, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.Y. Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 057901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.K.; Ma, X.; Chen, K. Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 230504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.B. Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 230503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Yang, K.-X.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Li, S.-L.; Hu, X.-L.; Abulizi, M.; Li, C.-L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.-C.; et al. Long-Distance Free-Space Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 260503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, Z.-W.; Wang, X.-B. Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 042324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-B.; Yu, Z.-W.; Hu, X.-L. Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 062323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.H.; Woo, M.K.; Park, B.K.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, Y.-W.; Kim, S.; Han, S.-W.; Moon, S. Practical Plug-and-Play Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Polarization Division Multiplexing. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58587–58593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K.; Park, B.K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, Y.-W.; Jung, H.; Lim, H.-T.; Kim, S.; Moon, S.; Han, S.-W. One to Many QKD Network System Using Polarization-Wavelength Division Multiplexing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194007–194014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Hwang, W.-Y.; Kim, J.-J. Origin of direct current drift in electro-optic polymer modulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 70, 2796–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Minakata, M. DC drift phenomena in LiNbO3 optical waveguide devices. Jap. J. Appl. Phy. 1981, 20, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisin, N.; Fasel, S.; Kraus, B.; Zbinden, H.; Ribordy, G. Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phy. Rev. A 2006, 73, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, N.; Stiller, B.; Khan, I.; Makarov, V.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Risk analysis of Trojan-horse attacks on practical quantum key distribution systems. IEEE J. Selected Topics Quant. Electron. 2014, 21, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.K.; Lee, M.S.; Woo, M.K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Han, S.-W.; Moon, S. QKD system with fast active optical path length compensation. Sci. Chi. Phy. Mech. Astro. 2017, 60, 060311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, M.-K.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, S.; Han, S.-W. Generation of Decoy Signals Using Optical Amplifiers for a Plug-and-Play Quantum Key Distribution System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136491
Woo M-K, Park C-H, Kim S, Han S-W. Generation of Decoy Signals Using Optical Amplifiers for a Plug-and-Play Quantum Key Distribution System. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136491
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Min-Ki, Chang-Hoon Park, Sangin Kim, and Sang-Wook Han. 2022. "Generation of Decoy Signals Using Optical Amplifiers for a Plug-and-Play Quantum Key Distribution System" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136491
APA StyleWoo, M.-K., Park, C.-H., Kim, S., & Han, S.-W. (2022). Generation of Decoy Signals Using Optical Amplifiers for a Plug-and-Play Quantum Key Distribution System. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136491






