A Novel Wavelet Selection Method for Seismic Signal Intelligent Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
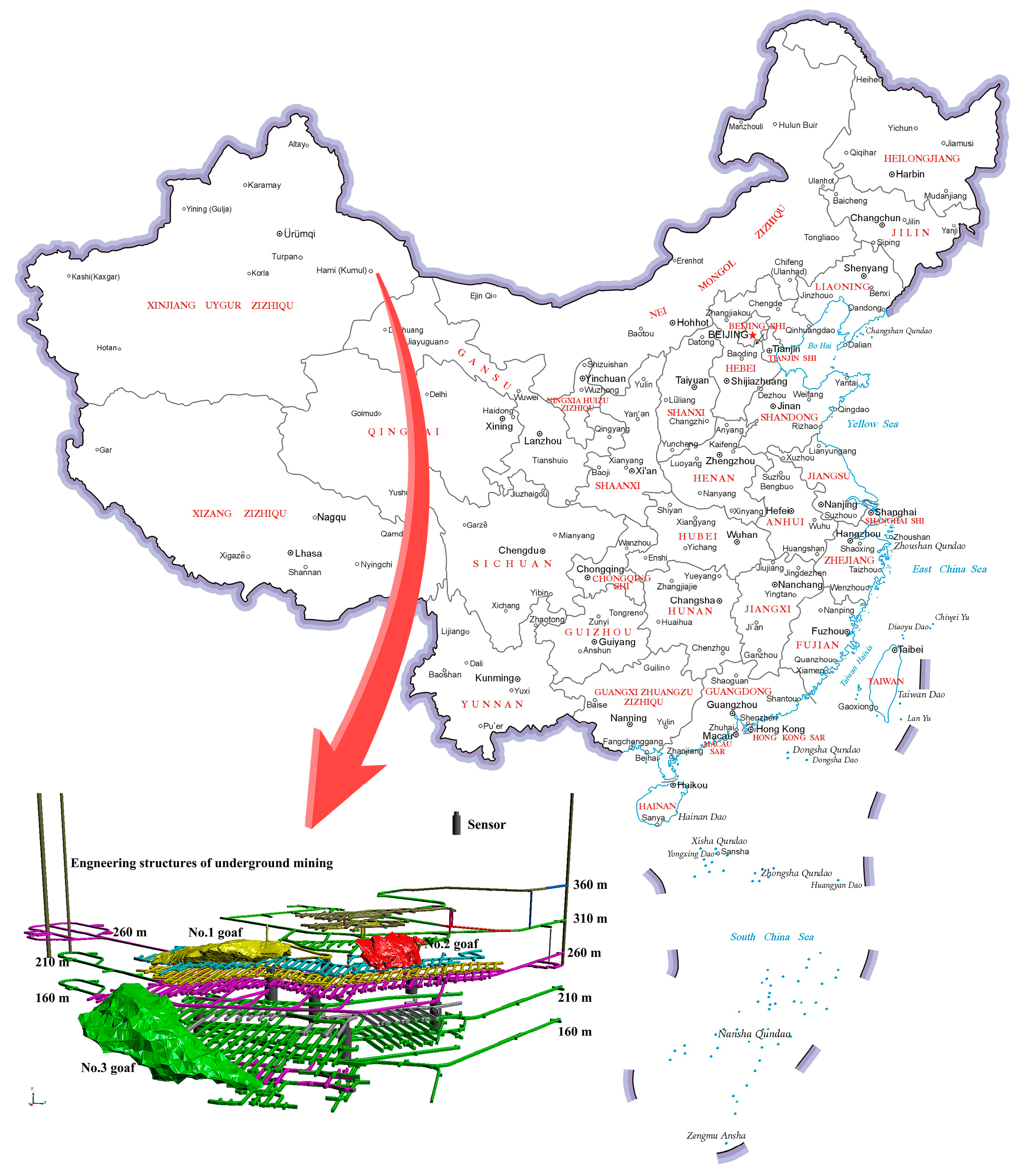
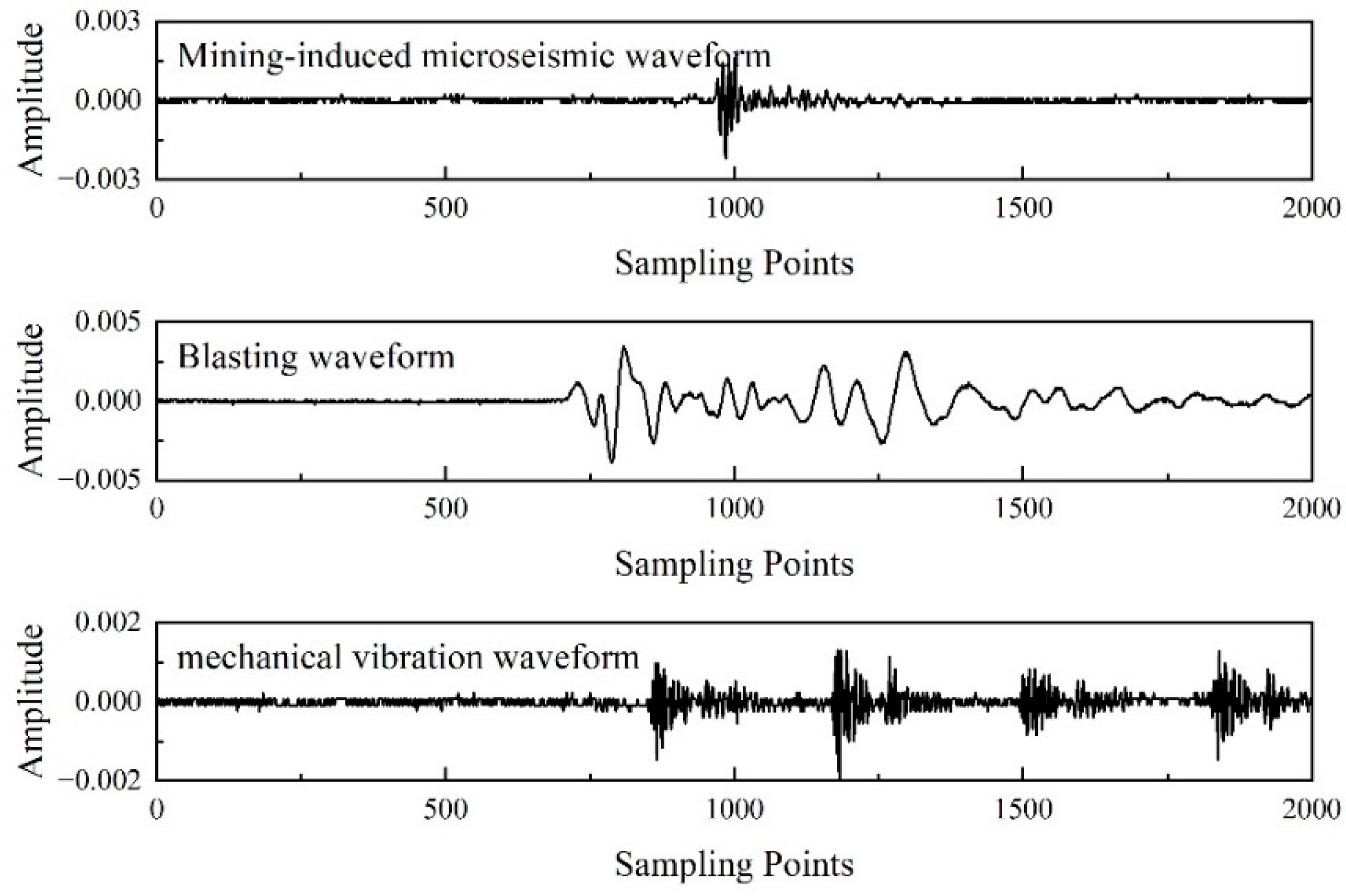
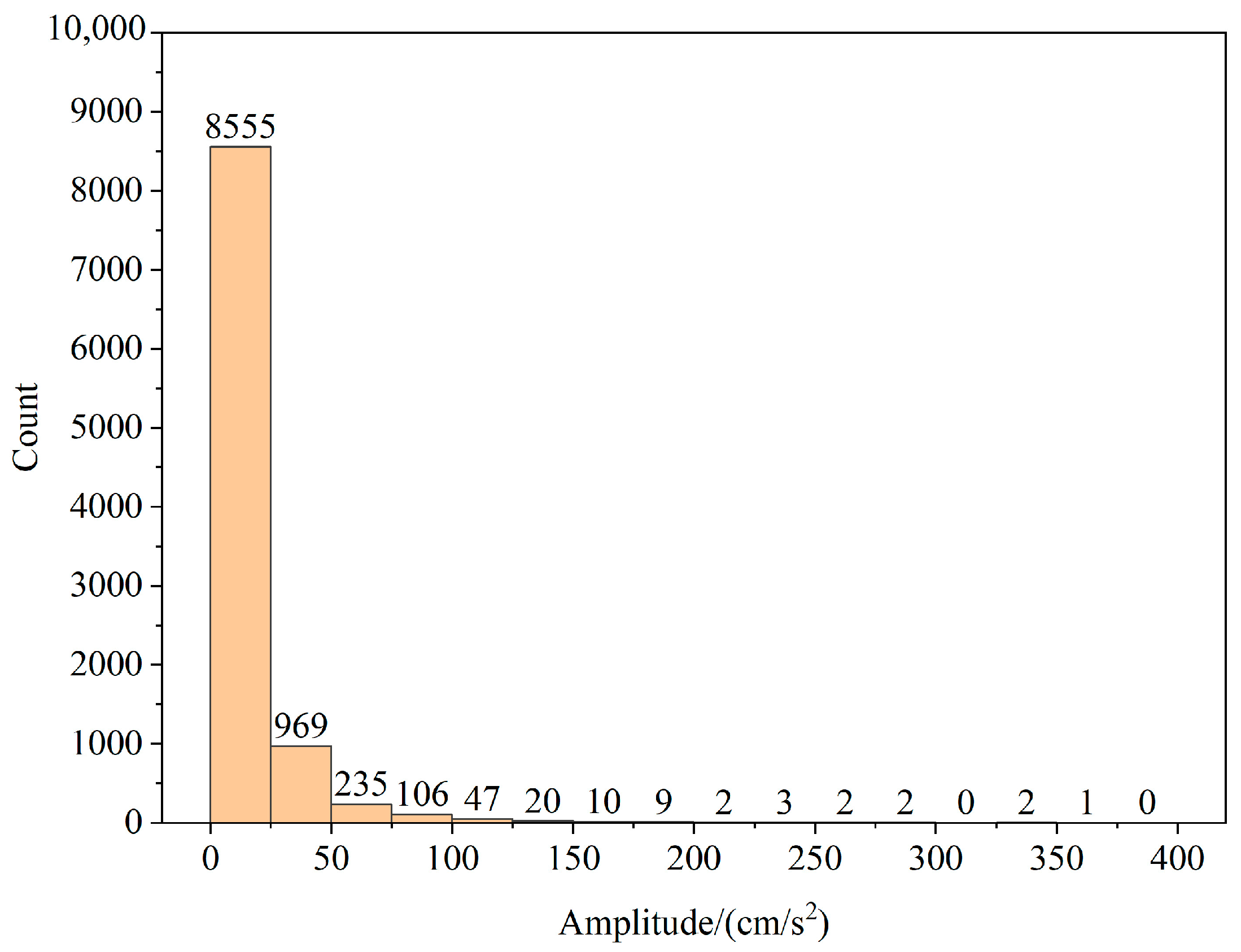
2.1. Dataset
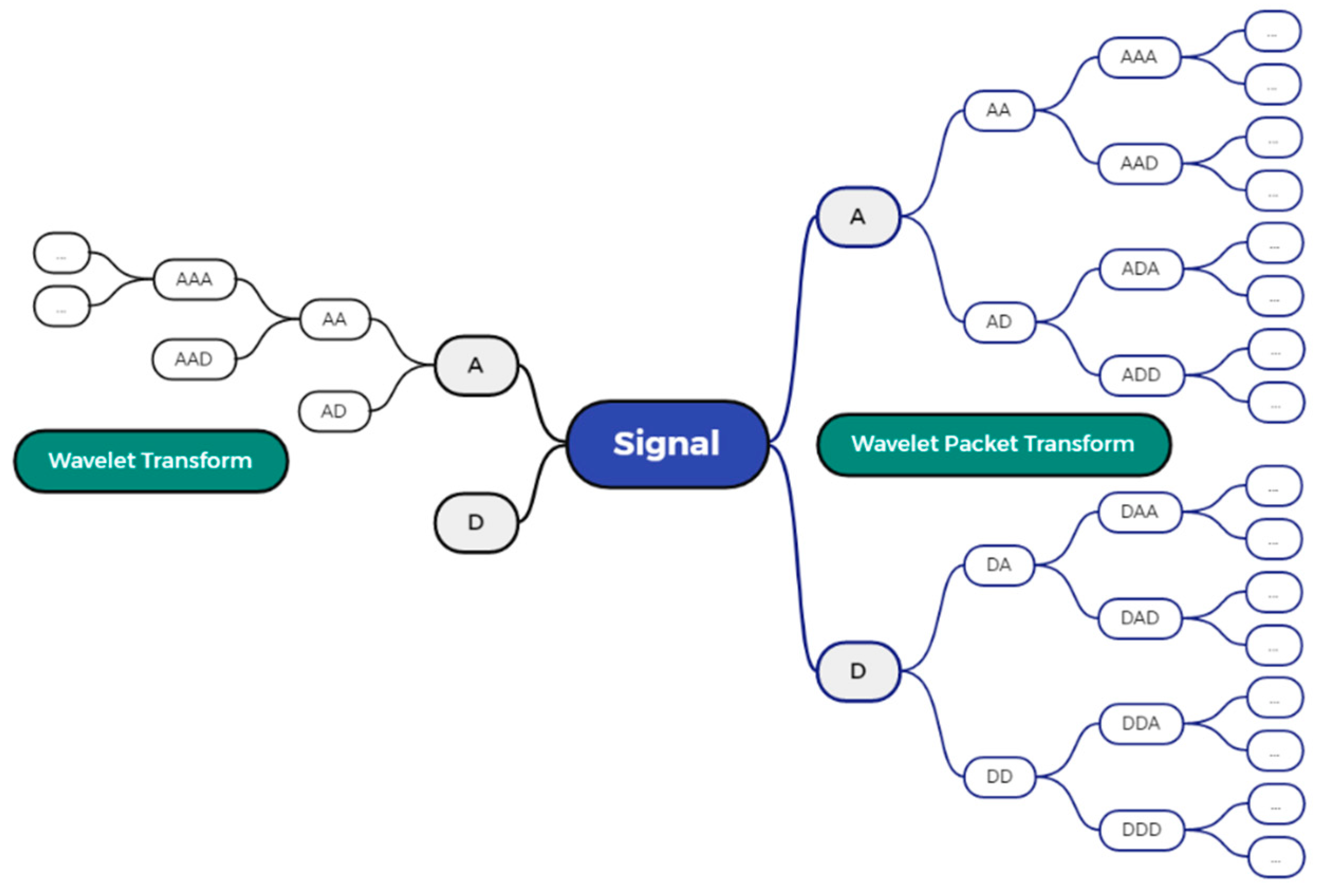
2.2. Wavelet Packet Transform
- Absolutely integrable and squarely integrable, as ;
- Offset between positives and negatives, as and , where is the Fourier transform of ;
- Meet the allowable conditions: .
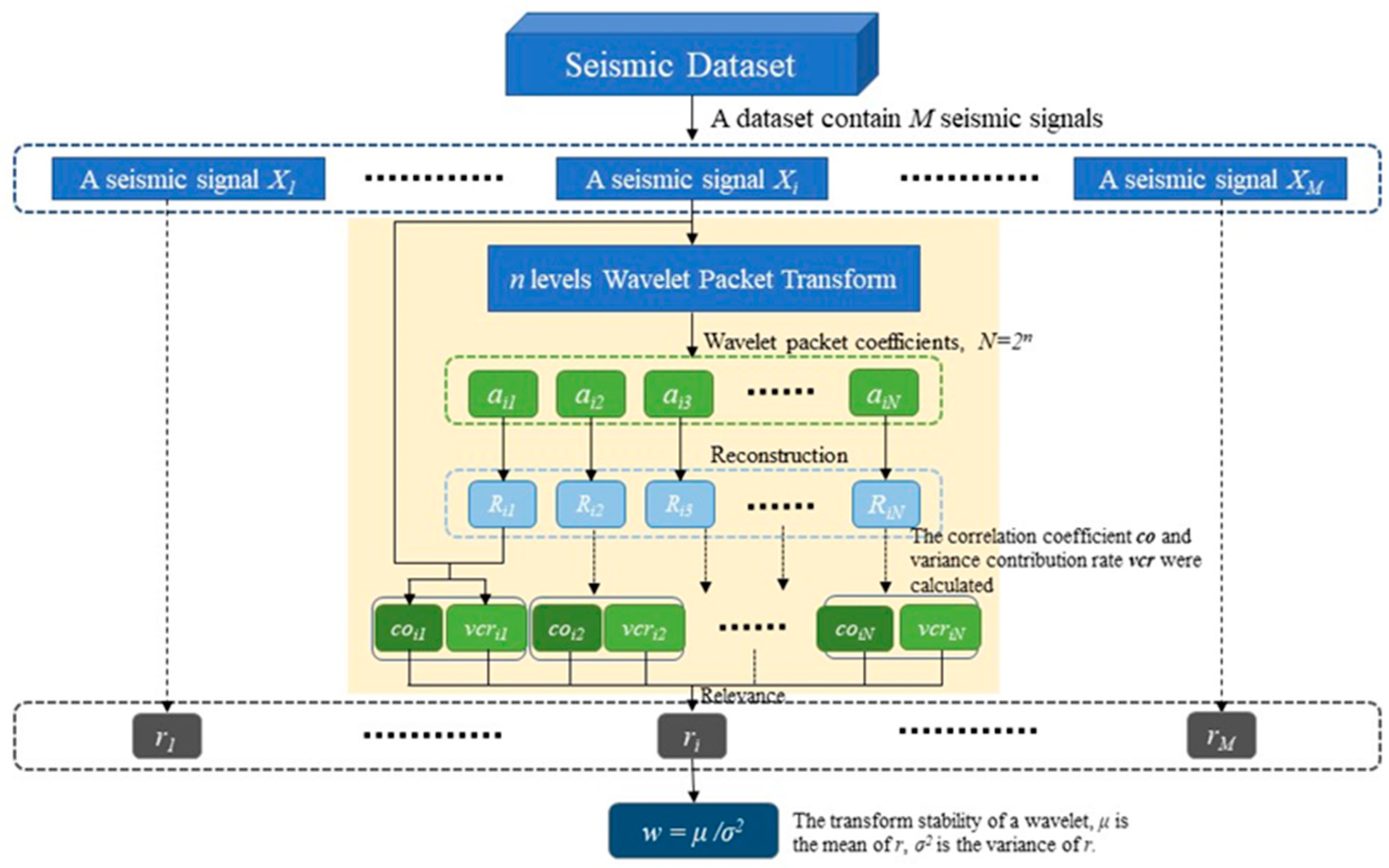
2.3. Wavelet Selection Method
- Based on this wavelet performing n levels wavelet packet decomposition of signal Xi, 2n wavelet packet coefficients are obtained.
- Each wavelet packet coefficient is reconstructed separately to obtain 2n reconstructed signals , and the correlation coefficients and variance contribution rates are calculated for each of the reconstructed signals and the original seismic signals, respectively. The formula for calculating the correlation coefficientwhere represents the correlation coefficient between and , S represents the total number of signal sampling points. The formula for calculating the variance contribution ratewhere is the variance contribution rate of , NS is the total number of sampling points.
- Calculation of relevance from correlation coefficient and variance contribution rate
- Calculate the decomposition stability of this wavelet by the mean and variance of
3. Results
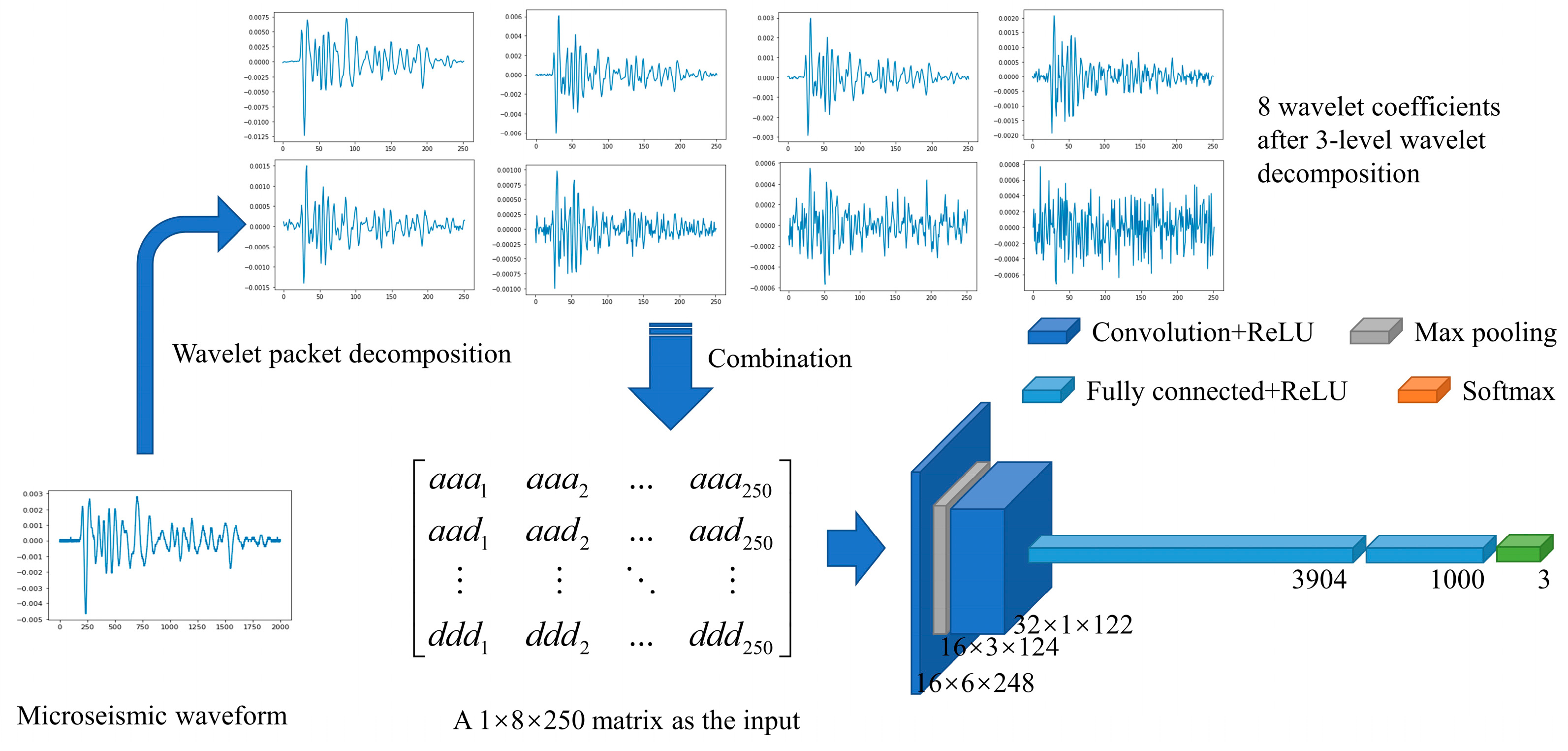
3.1. Application in Automated Mining-Induced Microseismic Events Classification
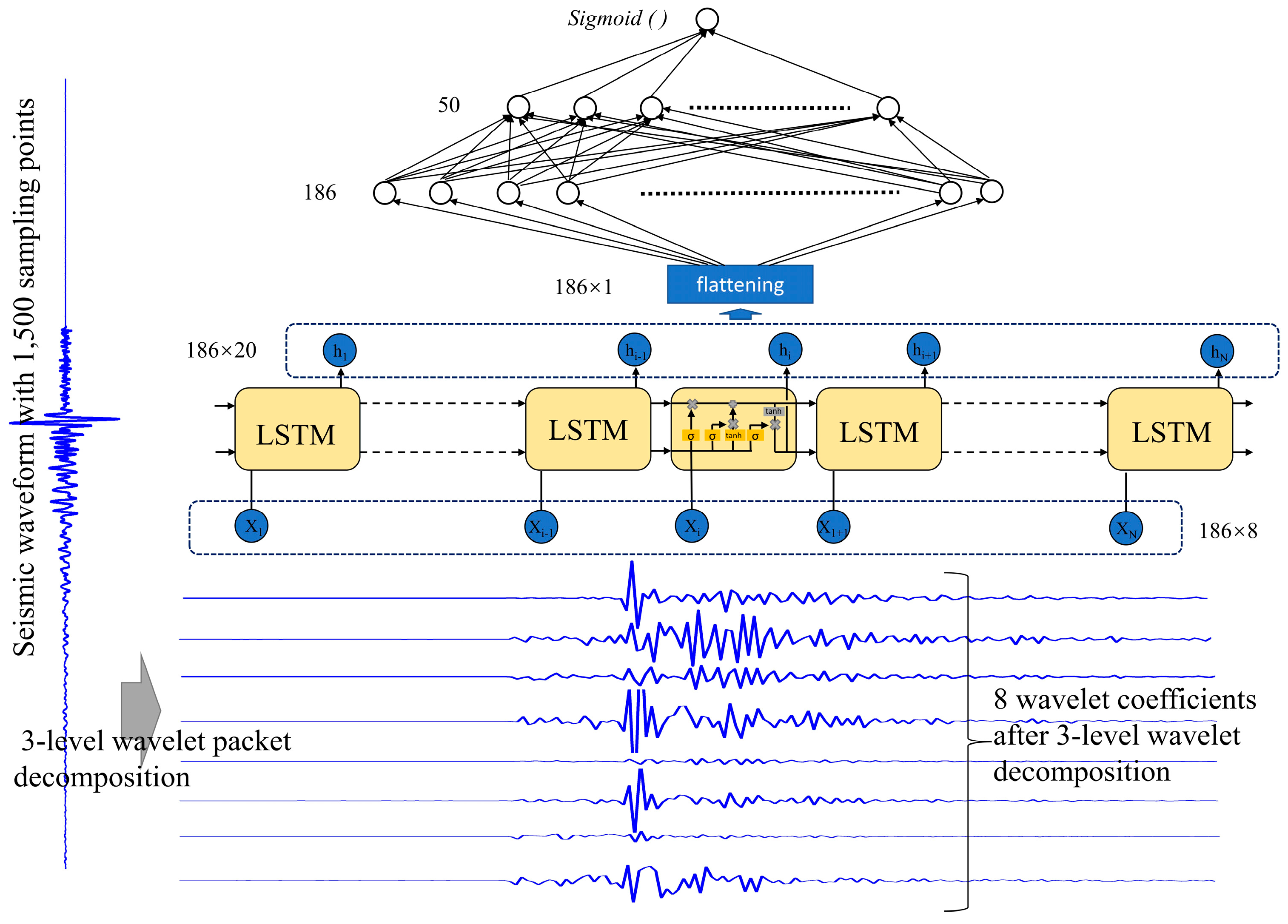
3.2. Application in Automated P Arrival Picking
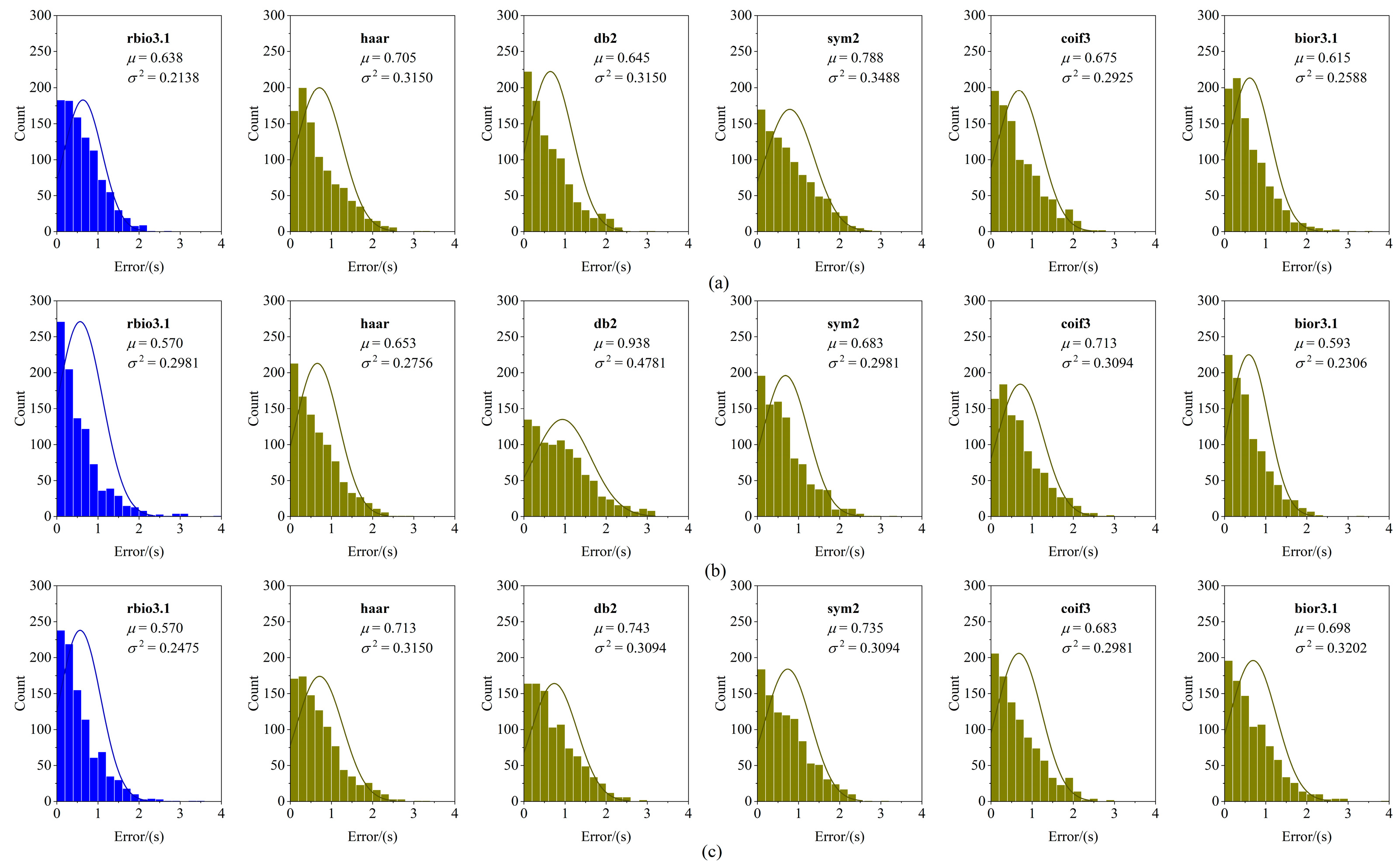
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z. Quality Control of Microseismic P-Phase Arrival Picks in Coal Mine Based on Machine Learning. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 156, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, O.; Mohebi, B.; Yakhchalian, M. Selection of Optimal Wavelet-Based Damage-Sensitive Feature for Seismic Damage Diagnosis. Measurement 2020, 154, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, B.; Liu, N.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H. Seismic Time–Frequency Analysis via Adaptive Mode Separation-Based Wavelet Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.R.; Ali, M.Z. Application of Wavelet Transform and Its Advantages Compared to Fourier Transform. J. Phys. Sci. 2009, 13, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zuo, S.; Hou, M.; Liu, W.; Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Deng, W. A Novel Adaptive Signal Processing Method Based on Enhanced Empirical Wavelet Transform Technology. Sensors 2018, 18, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Cortés, S.; Serra-Sagristà, J.; Bartrina-Rapesta, J.; Marcellin, M.W. Regression Wavelet Analysis for Near-Lossless Remote Sensing Data Compression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Su, X.; Xu, Z. Optical Remote Sensing Image Denoising and Super-Resolution Reconstructing Using Optimized Generative Network in Wavelet Transform Domain. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onifade, O.F.; Akinde, P.; Olubusola Isinkaye, F. Circular Gabor Wavelet Algorithm for Fingerprint Liveness Detection. JACST 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y. A Dynamic-Time Distance Based on Wavelet Decomposition for Subcellular Localization Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 220293–220301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wu, X.; Chen, C.; Qiu, W.; Ma, Q.; Yu, B. Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions by Fusing Various Chou’s Pseudo Components and Using Wavelet Denoising Approach. J. Theor. Biol. 2019, 462, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajani Kumari, L.V.; Padma Sai, Y.; Balaji, N. R-Peak Identification in ECG Signals Using Pattern-Adapted Wavelet Technique. IETE J. Res. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-Y. Industry Volatility and Economic Uncertainty Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Evidence from Wavelet Coherence Analysis. Financ. Res. Lett. 2020, 37, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Fei, X.; Tan, X.; Ma, H. Content Recognition of Network Traffic Using Wavelet Transform and CNN. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Cyber Security, Xi’an, China, 19–21 September 2019; Chen, X., Huang, X., Zhang, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 224–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Dai, Y.; Dai, Y.; Jin, T. Study on Processing of Wavelet Speech Denoising in Speech Recognition System. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2018, 21, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, D.A.; Natarajan, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Retinal Vessel Segmentation Using Multifractal Characterization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 94, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirsing, K.; Mili, L. Multifractal Analysis of Geomagnetically Induced Currents Using Wavelet Leaders. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 173, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholam, M.M.; Afzal, P.; Yasrebi, A.B.; Gholinejad, M.; Wetherelt, A. Detection of Geochemical Anomalies Using a Fractal-Wavelet Model in Ipack Area, Central Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 220, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Siew, W.H.; Soraghan, J.J.; Morris, E.A. A Novel Wavelet Selection Scheme for Partial Discharge Signal Detection under Low SNR Condition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Cancun, Mexico, 21–24 October 2018; pp. 498–501. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Chen, T.; Jiang, R.; Ning, L.; Jiang, Z. A Novel Approach to Wavelet Selection and Tree Kernel Construction for Diagnosis of Rolling Element Bearing Fault. J. Intell. Manuf. 2017, 28, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.P.; D’Mello, G.; Srinivasa Pai, P. Selection of Mother Wavelet for Wavelet Analysis of Vibration Signals in Machining. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2016, 6, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wan, S.; Bao, F.S. EEG-Based Seizure Detection Using Discrete Wavelet Transform through Full-Level Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Washington, DC, USA, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1596–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib, M.; Shamseldin, A.Y.; Melville, B.W. Comparative Study of Different Wavelet Based Neural Network Models for Rainfall–Runoff Modeling. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngui, W.K.; Leong, M.S.; Hee, L.M.; Abdelrhman, A.M. Wavelet Analysis: Mother Wavelet Selection Methods. AMM 2013, 393, 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Gao, R.X. Base Wavelet Selection for Bearing Vibration Signal Analysis. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut Inf. Process. 2009, 7, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, T.; Grzybowski, S.; Cheng, C. Scale Dependent Wavelet Selection for De-Noising of Partial Discharge Detection. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompusri, Y.; Dejhan, K.; Yimman, S. Mother Wavelet Selecting Method for Selective Mapping Technique ECG Compression. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Phetchaburi, Thailand, 16–18 May 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tumari, S.Z.M.; Sudirman, R.; Ahmad, A.H. Selection of a Suitable Wavelet for Cognitive Memory Using Electroencephalograph Signal. ENG 2013, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamo, F.; Andria, G.; Attivissimo, F.; Lanzolla, A.M.L.; Spadavecchia, M. A Comparative Study on Mother Wavelet Selection in Ultrasound Image Denoising. Measurement 2013, 46, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, J.; Hariharan, M.; Nadarajaw, T.; Khairunizam, W.; Yaacob, S. Optimal Selection of Mother Wavelet for Accurate Infant Cry Classification. Australas Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2014, 37, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qazzaz, N.K.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, S.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ariff, M.I. Selection of Mother Wavelets Thresholding Methods in Denoising Multi-Channel EEG Signals during Working Memory Task. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Miri, Malaysia, 8–10 December 2014; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qazzaz, N.; Hamid Bin Mohd Ali, S.; Ahmad, S.; Islam, M.; Escudero, J. Selection of Mother Wavelet Functions for Multi-Channel EEG Signal Analysis during a Working Memory Task. Sensors 2015, 15, 29015–29035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seljuq, U.; Himayun, F.; Rasheed, H. Selection of an Optimal Mother Wavelet Basis Function for ECG Signal Denoising. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Multi Topic Conference 2014, Karachi, Pakistan, 8–10 December 2014; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, C.F.F.C.; Carvalho, A.T.; Petraglia, M.R.; Lima, A.C.S. A New Wavelet Selection Method for Partial Discharge Denoising. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 125, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y. Optimal Base Wavelet Selection for ECG Noise Reduction Using a Comprehensive Entropy Criterion. Entropy 2015, 17, 6093–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijaya, D.R.; Sarno, R.; Zulaika, E. Information Quality Ratio as a Novel Metric for Mother Wavelet Selection. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 160, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Khader, A.T.; Al-Betar, M.A. Electroencephalogram Signals Denoising Using Various Mother Wavelet Functions: A Comparative Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Imaging, Signal Processing and Communication, Shenzhen, China, 17–19 November 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, N.; Zhou, H.; Guo, K.; Samuel, O.W.; Huang, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, G. Appropriate Mother Wavelets for Continuous Gait Event Detection Based on Time-Frequency Analysis for Hemiplegic and Healthy Individuals. Sensors 2019, 19, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atangana, R.; Tchiotsop, D.; Kenne, G.; Djoufack Nkengfack, L.C. Suitable Mother Wavelet Selection for EEG Signals Analysis: Frequency Bands Decomposition and Discriminative Feature Selection. SIPIJ 2020, 11, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y. Automatic Classification of Microseismic Records in Underground Mining: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17863–17876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y. Microseismic Records Classification Using Capsule Network with Limited Training Samples in Underground Mining. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Peng, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y. PickCapsNet: Capsule Network for Automatic P-Wave Arrival Picking. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, J.M.; Olhede, S.C. On the Analytic Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 4135–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Hao, H.; Li, X.; Li, J. Source Identification of Microseismic Events in Underground Mines with Interferometric Imaging and Cross Wavelet Transform. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 71, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hao, H.; Li, X.; Li, J. Micro-Seismic Monitoring in Mines Based on Cross Wavelet Transform. Earthq. Struct. 2016, 11, 1143–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chang, C.C. Structural Damage Assessment Based on Wavelet Packet Transform. J. Struct. Eng. 2002, 128, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, X. Regressive and Big-Data-Based Analyses of Rock Drillability Based on Drilling Process Monitoring (DPM) Parameters. Mathematics 2022, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Du, K.; Wang, S.; Khandelwal, M. Experimental Investigation and Theoretical Analysis of Indentations on Cuboid Hard Rock Using a Conical Pick under Uniaxial Lateral Stress. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energ. Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Hao, H.; Li, X. Micro-Seismic Event Detection and Location in Underground Mines by Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Deep Learning. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 81, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, W.A.; Al-Shuhail, A.A.; Al-Lehyani, A. A New Technique for First-Arrival Picking of Refracted Seismic Data Based on Digital Image Segmentation. GEOPHYSICS 2011, 76, V79–V89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawles, C.; Thurber, C. A Non-Parametric Method for Automatic Determination of P-Wave and S-Wave Arrival Times: Application to Local Micro Earthquakes. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, J.; Eaton, D.W. A Review and Appraisal of Arrival-Time Picking Methods for Downhole Microseismic Data. GEOPHYSICS 2016, 81, KS71–KS91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, H. STA/LTA Fractal Dimension Algorithm of Detecting the P-Wave Arrival. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2018, 108, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Peng, P. Accurate Identification of Microseismic P- and S-Phase Arrivals Using the Multi-Step AIC Algorithm. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 150, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhu, T.; Gao, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, J. AEnet: Automatic Picking of P-Wave First Arrivals Using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5293–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Peng, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y. Enhancing Seismic P-Wave Arrival Picking by Target-Oriented Detection of the Local Windows Using Faster-RCNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 141733–141747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Wavelet | Representation | Orthogonality | Biorthogonality | Support Length | Symmetry | Global Moment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haar | Haar | yes | yes | 1 | symmetry | 1 |
| Daubechies | db N | yes | yes | 2N − 1 | approximate | N |
| Symlets | sym N | yes | yes | 2N − 1 | approximate | N |
| Coiflets | coif N | yes | yes | 6N − 1 | approximate | 2N |
| BiorSplines | bior Nr.Nd | no | yes | reconstruction: 2Nr + 1 decomposition: 2Nd + 1 | asymmetry | Nr − 1 |
| ReverseBior | rbio Nr.Nd | no | yes | reconstruction: 2Nr + 1 decomposition: 2Nd + 1 | symmetry | Nr − 1 |
| Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | wavelet | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| haar | −4.78 | db10 | −5.56 | coif5 | −5.51 | bior3.5 | −9.72 | rbio2.8 | −2.25 |
| db1 | −4.78 | sym2 | −5.19 | bior1.1 | −4.77 | bior3.7 | −9.22 | rbio3.1 | −0.03 |
| db2 | −5.19 | sym3 | −5.38 | bior1.3 | −4.83 | bior3.9 | −9.16 | rbio3.3 | −0.86 |
| db3 | −5.38 | sym4 | −5.40 | bior1.5 | −4.87 | bior4.4 | −6.50 | rbio3.5 | −0.98 |
| db4 | −5.39 | sym5 | −5.41 | bior2.2 | −9.64 | bior5.5 | −3.51 | rbio3.7 | −1.04 |
| db5 | −5.44 | sym6 | −5.40 | bior2.4 | −8.47 | bior6.8 | −6.54 | rbio3.9 | −1.09 |
| db6 | −5.52 | sym7 | −5.62 | bior2.6 | −8.19 | rbio1.5 | −5.65 | rbio4.4 | −4.31 |
| db7 | −5.46 | sym8 | −5.46 | bior2.8 | −8.20 | rbio2.2 | −1.70 | rbio5.5 | −6.66 |
| db8 | −5.48 | coif3 | −5.43 | bior3.1 | −33.48 | rbio2.4 | −2.06 | rbio6.8 | −4.47 |
| db9 | −5.61 | coif4 | −5.48 | bior3.3 | −11.46 | rbio2.6 | −2.18 |
| Wavelet | rbio3.1 | haar | db2 | sym2 | coif3 | bior3.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test accuracy | 93.55% | 90.92% | 91.33% | 91.83% | 89.75% | 91.42% |
| Test accuracy | 92.75% | 91.25% | 90.67% | 91.83% | 90.58% | 91.33% |
| Test accuracy | 93.08% | 90.50% | 87.42% | 90.92% | 92.25% | 91.58% |
| Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w | Wavelet | w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| haar | −1.207 | db10 | −1.536 | coif5 | −1.533 | bior3.5 | −5.547 | rbio2.8 | 0.213 |
| db1 | −1.207 | sym2 | −1.411 | bior1.1 | −1.207 | bior3.7 | −5.010 | rbio3.1 | 10.422 |
| db2 | −1.411 | sym3 | −1.480 | bior1.3 | −1.139 | bior3.9 | −4.912 | rbio3.3 | 2.776 |
| db3 | −1.480 | sym4 | −1.486 | bior1.5 | −1.144 | bior4.4 | −2.080 | rbio3.5 | 1.858 |
| db4 | −1.496 | sym5 | −1.505 | bior2.2 | −4.874 | bior5.5 | −0.337 | rbio3.7 | 1.497 |
| db5 | −1.497 | sym6 | −1.515 | bior2.4 | −3.961 | bior6.8 | −2.152 | rbio3.9 | 1.323 |
| db6 | −1.519 | sym7 | −1.511 | bior2.6 | −3.752 | rbio1.5 | −1.648 | rbio4.4 | −0.982 |
| db7 | −1.515 | sym8 | −1.543 | bior2.8 | −3.622 | rbio2.2 | 0.824 | rbio5.5 | −2.652 |
| db8 | −1.528 | coif3 | −1.517 | bior3.1 | −25.742 | rbio2.4 | 0.388 | rbio6.8 | −0.965 |
| db9 | −1.520 | coif4 | −1.541 | bior3.3 | −7.114 | rbio2.6 | 0.269 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Peng, P. A Novel Wavelet Selection Method for Seismic Signal Intelligent Processing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136470
He Z, Ma S, Wang L, Peng P. A Novel Wavelet Selection Method for Seismic Signal Intelligent Processing. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136470
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhengxiang, Shaowei Ma, Liguan Wang, and Pingan Peng. 2022. "A Novel Wavelet Selection Method for Seismic Signal Intelligent Processing" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136470
APA StyleHe, Z., Ma, S., Wang, L., & Peng, P. (2022). A Novel Wavelet Selection Method for Seismic Signal Intelligent Processing. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136470









