Abstract
Surgery is a compelling application field for collaborative control robots. This paper proposes a gesture recognition method applied to a medical assistant robot delivering instruments to collaborate with surgeons to complete surgeries. The key to assisting the surgeon in passing instruments in the operating room is the ability to recognize the surgeon’s hand gestures accurately and quickly. Existing gesture recognition techniques suffer from poor recognition accuracy and low rate. To address the existing shortcomings, we propose an improved lightweight convolutional neural network called E-MobileNetv2. The ECA module is added to the original MobileNetv2 network model to obtain more useful features by computing the information interactions between the current channel and the adjacent channels and between the current channel and the distant channels in the feature map. We add R6-SELU activation function to enhance the network’s ability to extract features. By adjusting the shrinkable hyper-parameters, the number of parameters of the network is reduced to improve the recognition speed. The improved network model achieves excellent performance on both the self-built dataset Gesture_II and the public dataset Jester. The recognition accuracy of the improved model is 96.82%, which is 3.17 % higher than that of the original model, achieving an increase in accuracy and recognition speed.
1. Introduction
Medical assistant robots have made a significant impact in the operating room due to their dexterity and intelligence []. Due to the efforts of many academic institutions and leading surgical robot companies in medical robotics, medical assistant robots applied in different scenarios have gradually emerged []. In recent years, the demand for medical assistant robots is increasing rapidly due to the overload problem in the health care system caused by population growth []. We propose a medical assistant robot applied in the operating room for collaborative surgery through the information of the doctor’s gestures. The doctor only needs to place one hand on the recognition platform of the medical assistant robot, and the robot will start to detect the gesture category. When there is no change within one second, the robot will deliver the surgical instrument corresponding to the recognition result to the doctor’s hand, according to the prescribed route. The doctor can get the instrument with one hand and continue the surgery, and the robot starts waiting for new gesture input. The gesture recognition technology allows robots to replace nurses for medical mechanical delivery, not only improving the efficiency of medical treatment and saving healthcare resources, but also providing a sterile environment, thus avoiding the spread of infection []. Despite the rapid and accurate recognition of various gestures made by doctors, the existing technologies still face many challenges [].
Gesture recognition technology has been a hot research topic in human-machine interaction. Gesture communication can provide a more natural and efficient interaction experience because of its advantages such as easy expression, rich information, and no contact []. Gesture recognition methods based on machine learning mainly rely on manual feature extraction and gesture segmentation []. Huang et al. [] used Gabor feature extractor and SVM classifier for the gesture recognition task. Tarvekar et al. [] proposed a skin threshold segmentation method to recognize and classify gestures by segmenting the hand region in the image and extracting color and edge features from it using SVM classifier. Gesture recognition methods based on machine learning generally need to extract features before classification, which not only has complex operations but also low efficiency and poor generalization ability [].
In recent years, deep neural networks have achieved great success in the field of image classification, and gesture recognition based on deep learning has become the mainstream direction []. Convolutional neural networks in deep learning can learn the features of input information layer by layer and classify it more accurately []. Oyedotum et al. [] first performed a binarization preprocessing operation on the image, then set a threshold to localize the gesture, and finally used a convolutional neural network to recognize the gesture. Fang et al. [] proposed a CNN-based gesture recognition system, a deep convolutional generative adversarial network (DCGAN), to solve the overfitting problem. They used fewer samples for training and achieved better results. Molchanov et al. [] fused the collected image and radar information into the convolutional neural network for gesture classification. ElBadawy et al. [] sent normalized images into a 3D convolutional neural network for gesture recognition, and the recognition rate reached 90% on average. Carreira et al. [] proposed a new 2D convolutional neural network model (I3D) for gesture recognition. Koller O et al. [] used Inception-v1 of GoogLeNet [] to extract millions of weakly labeled data from sign language videos and input them into HMM to obtain gesture recognition results. In order to improve the recognition accuracy of deep neural networks, researchers deepened the depth of the model while making it more and more complex. However, the complex model depth and the huge number of model parameters require high computing power, which is not conducive to practical applications. Firstly, the model is too large and faces the problem of insufficient memory, and, secondly, some special scenarios have requirements such as low latency and fast response time for gesture recognition, which makes it difficult to apply gesture recognition to practical deployment []. In recent years, lightweight networks such as GhostNet [], ShuffleNetv1 [], MobileNetv1 [], MobileNetv2 [], ShuffleNetv2 [], SqueezeNet [], and IGCv3 [] have been proposed successively, whose recognition effect is comparable to that of deep neural networks while greatly reducing the network model parameters, among which the MobileNet series is more representative. In MobileNetv1, depthwise separable convolution is proposed instead of standard convolution to reduce the parameter calculation. MobileNetv2 proposes a linear bottleneck structure and inverted residual structure on this basis to solve the gradient disappearance problem and enhance the feature expression capability. Compared with deep neural networks, MobileNet series network models require less memory, occupy fewer resources, less computation, and fast computation, and can be run on mobile devices and embedded devices. Therefore, the emergence of lightweight networks provides a new direction for gesture recognition. However, when the network structure of the MobileNet series is applied to the gesture recognition task, due to its internal network design, optimization strategy and activation function, negative-valued feature information in input information will be ignored, which may be the key point of gesture recognition []. Therefore, it makes its feature extraction ability insufficient and affects its classification accuracy.
To address this problem, we propose an improved MobileNetv2 model, called E-MobileNetv2, which uses the MobileNetv2 architecture as the basic skeleton of the model and adds an adaptive channel attention module, ECA [], which avoids dimensionality reduction while also effectively capturing cross-channel interaction information, thus improving recognition accuracy. A new activation function R6-SELU is proposed to replace the original ReLU6 to prevent the phenomenon of neuron “death”, which causes the loss of negative-valued feature information, and further improves the network recognition accuracy. Finally, we also adjust the width multiplier and resolution multiplier of the model and use the transfer learning method to make the network model obtain better initialization weight parameters, which work together to improve the recognition accuracy of the model.
2. Related Works
In recent years, as more lightweight networks have been proposed, there has been an increasing interest on how to apply lightweight networks in real life. MobileNetv2 network, as a typical representative of lightweight networks, has the following outstanding features: (1) A depthwise separable convolution is introduced instead of ordinary convolution, which reduces the number of parameters of the model and improves the recognition speed. (2) An inverted residual structure is proposed, which enhances the feature expression ability and improves the gradient propagation efficiency compared with the ordinary residual structure. (3) A linear bottleneck structure is introduced to reduce the loss of low-dimensional features. Depthwise separable convolution is a structure composed of depthwise convolution (DW) and pointwise convolution (PW). Each depthwise separable convolution structure is followed by batch normalization (BN) [] and ReLU6 activation function []. Depthwise separable convolution structure is shown in Figure 1. The depth convolution kernel is a 1D convolution kernel, which is responsible for extracting features for a channel, and the depth of the input feature matrix does not change after the depth convolution. Pointwise convolution is ordinary convolution, and its convolution kernel is 1 × 1, which plays the role of dimensional enhancement here. Depthwise separable convolution works by extracting the channel information in-depth and associating the features of the channel point by point. We compare the computational cost of the depthwise separable convolution with that of the ordinary convolution (as in Figure 2). Where is the size of the convolution kernel, is the size of the input characteristic matrix, M is the number of input channels, and N is the number of output channels. The computational cost of the deep separable convolution is shown in Equation (1).
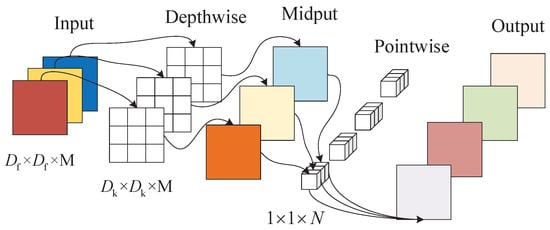
Figure 1.
Depthwise separable convolution structure.
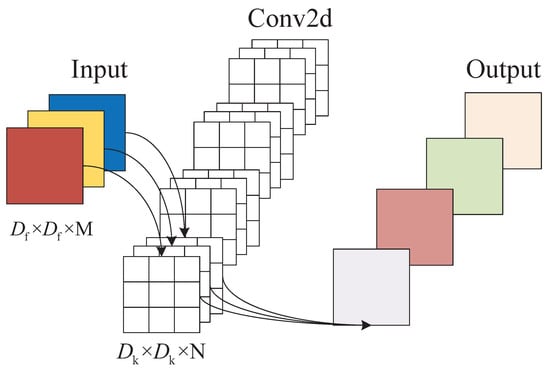
Figure 2.
Ordinary convolution structure.
The cost of ordinary convolution calculation is shown in Equation (2).
Equation (3) shows the comparison of the computational costs of two kinds of convolutions.
As can be seen from the above calculation, N is generally large. When a 3 × 3 convolution kernel is used, the result of Equation (3) is close to 1/9. Ordinary convolution is 8∼9 times the computation cost of the depthwise separable convolution.MobileNet series, adding depthwise separable convolution to build a lightweight deep neural network layer by layer, which reduces computational complexity, reduces model size, and improves model recognition speed.
The proposed two linear bottleneck structures in the MobileNetv2 network not only reduce the number of parameters but also optimize the network structure in time and space. The MobileNetv2 network is inspired by the ResNet residual network [] and proposes an inverted residual structure. The residual structure of ResNet uses the first layer of pointwise convolution for dimensionality reduction, followed by depthwise convolution, and then pointwise convolution for the dimensionality increase, which results in the loss of feature information. The inverted residual structure uses the first layer of pointwise convolution to perform the up-dimensioning operation, the second layer of depthwise convolution to extract channel features, and the third layer of pointwise convolution to downscale, and then adds shortcut connections. The network layer connection is opposite to the ResNet residual structure, so it is called an inverted residual structure. It is worth noting that only when the step size is 1 and the input characteristic matrix and output characteristic matrix are the same sizes, will there be a shortcut connection (as in Figure 3). When the step size is 2, the series structure is used and there is no shortcut. The loss of sparse features formed by this inverted residual structure is small, which not only enhances the feature extraction ability and improves gradient propagation, but also reduces the number of parameters. ReLU6 activation function is used in the linear bottleneck structure. Compared with the ordinary ReLU activation function, the maximum output is limited to 6.
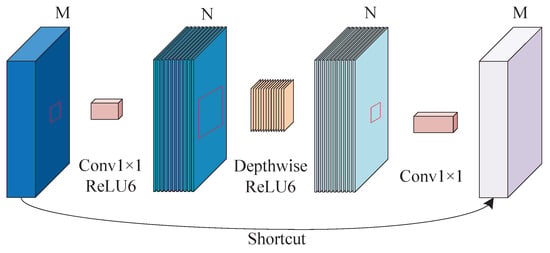
Figure 3.
The linear bottleneck with shortcut connection in MobileNetV2.
3. Model
In order to build a fast and accurate gesture recognition model, we made a series of improvements to MobileNetv2. By adding the ECA module, the network refinement ability is enhanced. The activation function was improved so as to improve the feature extraction ability of the model. The hyper-parameters of the model were adjusted to reduce the number of parameters and improve the recognition speed of the model.
3.1. Efficient Channel Attention Module
The attention mechanism can allocate limited computing resources to the part with the highest proportion of information in the image, which can better gather the attention of the network model to recognize the target and reduce the influence of irrelevant information []. In order not to increase the complexity of the model and improve the network performance, ECA proposed a local cross-channel interaction strategy without dimensionality reduction and an adaptive selection method of 1D convolution kernels size, to avoid the information loss caused by dimension reduction and, at the same time, effectively obtain the interdependent relationship between the cross channel, so as to realize the optimal performance. The structure of the ECA module is shown in Figure 4.
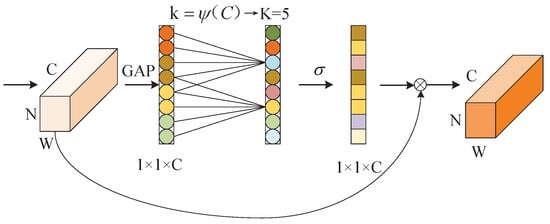
Figure 4.
The ECA module.
Firstly, the module directly carries out global average pooling (GAP) of the input feature map without dimensionality reduction to avoid the adverse impact of dimensionality reduction on channel attention learning. Then the local cross-channel information exchange for each channel and its k local channels is realized by performing a fast 1D convolution with the number of k, so as to avoid inefficient redundant information for all channels in the information exchange. Finally, the weight of each channel is obtained by the Sigmoid function, which can improve the weight of the effective channel and obtain effective information. The value of k is determined by the adaptive mapping of channel dimension C and has a proportional relationship, which can effectively avoid manually setting the size of k through cross-validation in the experiment.
Where the k represents the coverage of local cross-channel interaction, that is, how many adjacent channels are involved in the attention prediction of this channel. According to the weight-sharing characteristics of the convolutional neural network, it can be inferred that there is a certain functional relationship between channel dimension C and channel number k, which is . The linear relationship between channel dimension C and the number of 1D convolution kernel k is expressed in (4):
where C is the dimension of channels in the input feature map, the k is the number of 1D convolution kernels, is the nearest odd number t, and and b are the hyper-parameter, select = 2, b = 1.
We propose to add the ECA module into the linear bottleneck structure with stride = 1. The improved linear bottleneck structure is shown in Figure 5, and we named it Bottleneck_1. The ECA module is added to enhance the network’s ability to refine features and reduce the interference of irrelevant information, so as to realize the optimization of recognition performance.
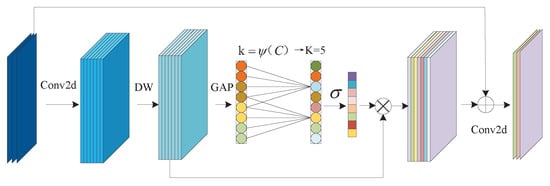
Figure 5.
The linear bottleneck with the ECA module.
3.2. Improved R6-SELU Activation Function
In a convolutional neural network, convolution and pooling are linear operations, which cannot form a complex expression space. The activation function is a kind of nonlinear mapping structure in the neural network. Adding activation function to the neural network can improve the expression ability of the neural network. ReLU, as the main function of the activation function is often used in various deep neural networks. However, with the deepening of the network, ReLU itself has great limitations, as the output range of the ReLU activation function is , which will bring some loss of accuracy; secondly, the gradient of the ReLU activation function is constant 0 when it is in negative half axis, and the neuron will appear inactivated, resulting in the parameter not being able to be updated. In the end, the mean value of the ReLU activation function output value is always greater than zero. It will ignore some key information of the negative-valued feature information and the calculation results are difficult to converge, which affects the identification effect of the network. Although in MobileNetv2, the author changed the activation function into the ReLU6 activation function, and controlled the output range at , so that the network can have a good numerical resolution during the low precision floating point operation to prevent the loss of accuracy. However, The ReLU6 activation function still has the same disadvantages as the ReLU activation function.
Aiming at the above defects, we introduce another activation function, SELU []. The SELU activation function equation is shown in Equation (5), where and are fixed values derived from the formula, , . The positive half-axis derivative of the SELU activation function is a constant , which can reduce the gradient disappearance. At the same time, the negative half axis of the function is not zero, which prevents the loss of negative-valued information and the occurrence of neuron death, and enables comprehensive learning of image features.
Combining the respective advantages of ReLU6 and SELU, we proposed an improved activation function R6-SELU, and the improved activation function expression is shown in Equation (6):
The improved activation function image is shown in Figure 6. The improved activation function is analyzed and has the following characteristics:
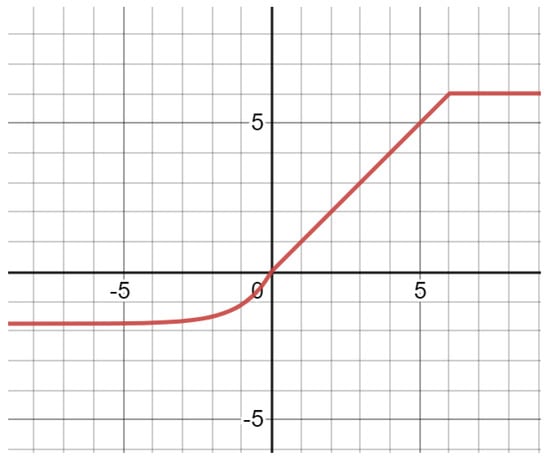
Figure 6.
R6-SELU activation function image.
- Parameters have non-zero output in both positive and negative half axes;
- The positive half axis inherits the characteristics of fast convergence and small precision loss of ReLU6 activation function;
- The negative half axis inherits the SELU activation function, non-linear correction of negative-valued characteristic information, smooth convergence, and enhances the model’s expression ability.
3.3. Setting Hyper-Parameters
There are two shrinkable hyper-parameters in MobileNet networks, width multiplier , and resolution multiplier . The function of width multiplier is to thin a network uniformly at each layer. Common values are 1, 0.75, 0.5, and 0.25. The functional relationship between the calculated parameter and the width multiplier is shown in Equation (7):
It can be seen that the calculation and parameter number of the model can be reduced to the square times of by adjusting . Table 1 shows the relationship between the accuracy (Acc), computation (Mult-Adds), and parameter number (Param) on ImageNet when Mobilenetv1 adjusts network parameters by using different width multiplier coefficients.

Table 1.
The model performance under different width multipliers.
As can be seen from the above table, with the decrease of the width multiplier , the calculation amount and parameters of the model become smaller and smaller, and the accuracy rate also decreases. When the width factor is 0.75, the accuracy is improved by 4.7% compared with that when is 0.5, but the calculation amount and parameters are doubled.
The resolution multiplier is between (0, 1). The resolution multiplier acts to multiply the size of the feature map at each layer by a certain proportion to make the feature matrix smaller. The resolution multiplier does not change the number of parameters, but only changes the calculation amount of the model. When the resolution multiplier is 1, the accuracy is 70.6%, which is the highest among other values. In order to balance accuracy and network performance, we chose to sacrifice a small amount of accuracy and keep the computational amount and parameters at a low level. The width multiplier of MobileNetv2 was set as 0.5 and the resolution multiplier was set as 1. Other optimization strategies are used to improve the accuracy of the network so that the network can ensure high accuracy under the premise of being lightweight.
3.4. Establishment of the E-MobileNetv2 Model
Because aiming for the MobileNetv2 network structure feature extraction ability is not enough, and it is easy to ignore negative-valued feature information, this paper proposes an improved MobileNetv2 network structure gesture recognition method, namely E-Mobilenetv2. E-MobileNetv2 takes MobileNetv2 as the network skeleton, adds the ECA module into the inverted residual structure, and improves the original activation function ReLU6, which is replaced by the improved activation function R6-SELU. The specific operation is as follows: Insert the ECA module after the depthwise convolution of a linear bottleneck structure of stride = 1. R6-SELU activation function is added after the first convolution and the second depthwise convolution of the two linear bottleneck structures, respectively, and the nonlinear activation functions at the remaining positions remain unchanged. The ECA module is added to enhance the network’s capability of feature refinement and reduce the interference of irrelevant information. The improved R6-SELU activation function retained the diversity of feature information and enhanced the expression ability of the target features. The improved inverted residual structure is shown in Figure 7. It can bring a significant performance gain and significantly reduce the model complexity while keeping the network lightweight.
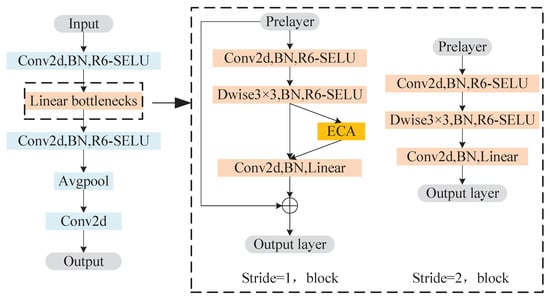
Figure 7.
The overall framework of the network.
The improved E-MobileNetv2 network structure is shown in Table 2. The operator indicates the processing method of the input feature map, t indicates the extension factor, c indicates the number of channels, n indicates the number of repetitions, and s indicates the size of the step. The linear Bottleneck structure with the ECA module is named Bottleneck_1. When n is greater than 1, the step size of the convolution in the first Bottleneck of each group is the value in the table, and the other step size is 1.

Table 2.
The layer structure of the E-Mobilenetv2.
Finally, the transfer learning method is used to learn the weights in similar tasks to avoid the model learning from zero, so that the model can obtain better initial weight parameters. In this study, the pre-training weights of MobileNetv2 in the ImageNet dataset were used to optimize the initial weight parameters of the model and enhance the generalization performance of the model to improve the recognition accuracy of the model.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Environment and Parameter Setting
The computer was configured with Windows 10, a 64-bit operating system, GTX 1650 Ti GPU, pytorch1.3 deep learning framework, Python version 3.6, and all experiments were completed based on the above. The data set was divided into the training set and test set according to the ratio of 9:1. The image size of the input model was 224 × 224, Adam was selected as the model optimizer, the learning rate was set to 0.001, and cross-entropy was used in the loss function. We set the batch size to 32 and iteration times to 100 epochs. All experiments in this paper are completed based on the above experimental environment.
4.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
The training of deep neural networks requires a large number of samples as training sets. The data set of this experiment mainly includes self-constructed Gesture_II and public datasets. By searching the data on medical instrument sign language, six kinds of commonly used medical instrument sign language in the operating room were developed, including scalpel, scissors, gauze, retractor, bone hammer, and hemostatic forceps, as shown in Figure 8.
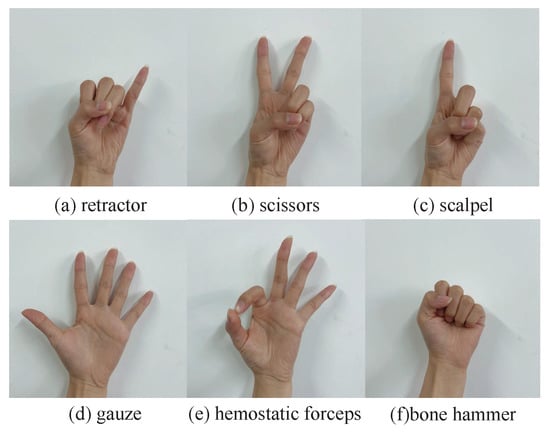
Figure 8.
Six kinds of hand gestures.
The gestures of 30 test subjects were collected. Two pictures were collected for each gesture in a single background and three pictures were collected for each gesture in complex background. In addition, in order to simulate the real scene in the operation, we collected 6 gestures of wearing medical gloves, and some of the gestures were painted red (to simulate blood), and 10 of each gesture were collected. The collected images were preprocessed: (1) the collected pictures were rotated clockwise at 90°, 180°, and 270° to simulate different shooting angles of the camera. (2) We randomly enhanced and weakened the brightness to simulate different light recognition scenes in the operating room. (3) By scaling, flipping, blurring, and other operations, the robustness of the model’s recognition effect at different angles and the expansion of the data set can be increased. After data preprocessing, the dataset was expanded to images.
In addition, we performed network performance verification on the Jester public dataset. There are a large number of RGB gesture video samples and a variety of gesture categories in the Jester data set. RGB gesture images are obtained by intercepting adjacent frames, and then the data set is screened and sent to the network for classification and recognition. The partial Jester dataset for the experiment is shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Part of the Jester dataset.
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.3.1. Ablation Experiment
To verify the network optimization effect of the proposed E-MobileNetv2 modules, we carried out ablation experiments and compared the accuracy of the algorithm and the number of model parameters under various structural combinations. In order to verify that the ECA module improves the model accuracy, we add the ECA module into the linear bottleneck structure with stride = 1. In order to verify that the improved activation function can improve the feature extraction ability of the model and thus improve the recognition accuracy, we replace all ReLU6 activation functions in the linear bottleneck structure with R6-SELU. In order to prove that reducing the number of parameters can improve the reasoning speed of the model, we set the hyper-parameters. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of ablation experiment.
ECA indicates the embedding of the ECA module in a linear bottleneck; R-S indicates adding the R6-SELU activation function into the network model; H-p indicates setting the hyper-parameters. The analysis of the ablation experiment results shows that the recognition accuracy of the model is increased by 2.19% after the addition of ECA, and the introduced parameters can almost be ignored. The R6-SELU activation function is introduced to enhance the extraction of negative-valued features, and the recognition accuracy of the model is increased by 1.14%, without increasing the parameters of the model. Finally, for the setting of hyper-parameters, although the recognition accuracy is reduced by 2.52%, the number of parameters is reduced by half, which improves the recognition speed. It can be seen that the proposed network improves the accuracy by 3.17% and reduces the number of parameters by about 30% compared with the unimproved network. Each additional module contributes to the model identification accuracy and parameter reduction.
4.3.2. Comparative Experiment
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, the improved network E-MobileNetv2 and the unimproved network MobileNetv2 are trained on the self-built dataset Gesture_II, During the training process, the accuracy of the test set and the training loss value of the model are recorded for every iteration cycle. To grasp the training situation of the model in time, we ensure that each model is in the state of convergence to complete the training. The change curve of loss value and accuracy rate in the training process are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively.
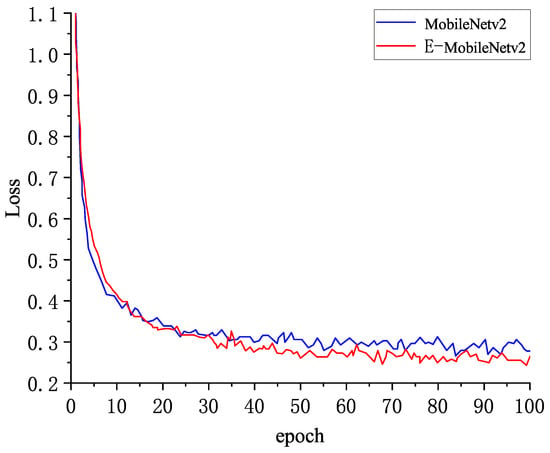
Figure 10.
Training loss.
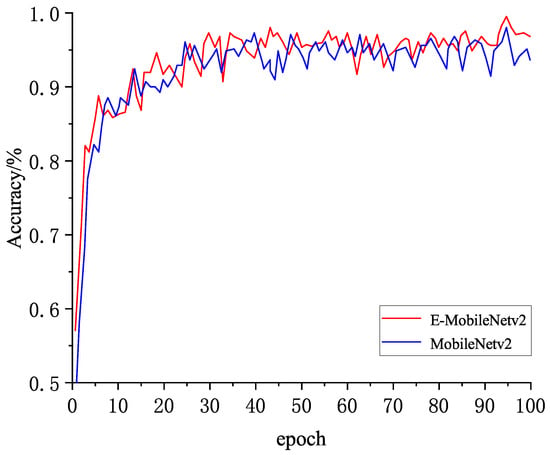
Figure 11.
Test accuracy.
It can be seen from the loss change curve that the loss function of the two models decreases rapidly in the initial training period, indicating that the model is rapidly fitting and the learning efficiency of the model is high. When the epoch of the improved model was 30, the decrease rate of the loss value of the model began to slow down; when the epoch was 60, the loss curve gradually flattened, the loss value fluctuated around 0.2 after stabilization, and the model converged. The loss value of the original MobileNetv2 declined slowly in the 40th epoch and then stabilized gradually. It can be seen that the loss value of the improved model is faster than that of the original model, and the loss value of the improved model is smaller after it is stabilized.
After the 20th epoch, the accuracy values of the two models both reached about 90%, and gradually increased with the increase of iterations. Among them, the original MobileNetv2 has great fluctuation in the process of convergence, and the accuracy reaches 93.6% after training, while the improved MobileNetv2 reaches 96.8% after training. Through the comparison of loss and precision experiments, it can be seen that the improved model performs better than the original model in both accuracy change and loss change, and the improved model has better convergence speed than the original model and is more stable. When iteration stops, it has higher accuracy and lower loss value, which verifies the reliability and effectiveness of the proposed improved method.
To verify the competitiveness of the improved E-MobileNetv2, the improved network structure is compared with the existing advanced network models. We chose EfficientNetb0, ShuffleNetv2, ResNet101, and GoogLeNet as the comparison models, and then compared and analyzed the four models in terms of accuracy, number of parameters, and recognition time by training and testing on self-built and public data sets, respectively.The experimental environment and parameter settings are described in Section 3.1. The result is shown in Table 4, where Ts is the single image recognition time on the CPU.

Table 4.
Comparison of results of different network models.
The experimental results show that the improved algorithm has the highest accuracy in self-built data, compared with the other two lightweight networks EfficientNetb0 and ShuffleNetv2. The number of parameters and the single image recognition speed are also better. The improved algorithm was 2.65% more accurate than GoogLeNet, a large network. The accuracy of the improved algorithm is second only to ResNet101 on public data sets, which proves that the improved algorithm has certain generalization ability and robustness. The recognition accuracy of the improved algorithm is only 1.7% less than that of ResNet101, but the number of parameters is 1/20 of that of ResNet101, and the single image recognition time on the CPU is only about 1/4 of that of ResNet101. The main reason for this phenomenon is that ResNet101 has deep network layers, a complex model, good feature extraction ability, and can achieve a better learning effect on large data sets. However, ResNet101 consumes huge memory and computing resources, and its reasoning speed is too slow to meet the requirements of gesture recognition.
To evaluate the accuracy of the model, we performed a model evaluation on the test set, and obtained a confusion matrix, as shown in Figure 12. From the experimental results, it can be seen that the recognition accuracy of gesture (d) and gesture (c) reaches 100%. Gesture (f) has a poor recognition effect because it has a high similarity with gesture (a) and is easily confused, and the average recognition accuracy of the model reaches 95.3%. Gesture recognition results of the model are shown in Figure 13. The model can recognize gestures quickly and accurately in both single and complex environments. Therefore, the improved algorithm meets the requirements of accuracy and reasoning speed.
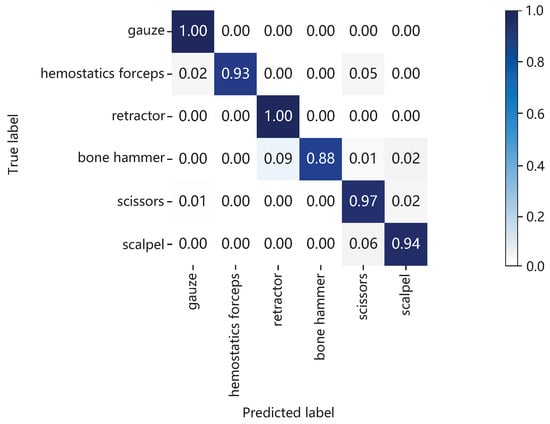
Figure 12.
Confusion matrix of the improved model.

Figure 13.
Result of the part of the gestures.
5. Conclusions
In this study, an improved E-MobileNetv2 network model is proposed based on MobileNetv2 as the network backbone, which is applied to the gesture recognition technology of medical assistants. By analyzing the shortcomings of the original model, three improvements are proposed. Firstly, in view of the insufficient feature extraction ability of the model, we added ECA to enhance the network’s feature refining ability and reduce the interference of irrelevant information, so as to achieve the optimization of recognition performance. Secondly, considering that the activation function used in the original model is prone to lead to neuron inactivation, affecting parameter updating and insufficient extraction of negative information, we designed a new activation function R6-SELU to enhance the network feature extraction ability and further improve the recognition accuracy by integrating SELU activation function. Finally, in order to reduce the parameters of the model and improve the recognition speed, we adjusted the width multiplier and resolution multiplier of the model, and the improved model achieved a good balance between recognition accuracy and model complexity. Compared with the original model, the accuracy is increased by 3.17%, the number of parameters is reduced by about 30%, and the network identification performance is still excellent compared with other networks. In conclusion, the model proposed in this study can be well applied to the gesture recognition of medical assistants, meeting the requirements of gesture recognition accuracy and speed in the operating room.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. M.H. made the primary contributions to the conception or design of the work. W.W. made optimization of the software architecture and concept reconsideration. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by X.W., H.S. and J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51905405, Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi under Grant No. 2022GY-248 and 2022GY-276, Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi under Grant No. 2021TD-29, Applied Technology Research and development project in Beilin District of Xi’an under Grant No. GX2149.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
References
- Mišeikis, J.; Caroni, P.; Duchamp, P.; Gasser, A.; Marko, R.; Mišeikienė, N.; Zwilling, F.; De Castelbajac, C.; Eicher, L.; Früh, M.; et al. Lio-a personal robot assistant for human-robot interaction and care applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5339–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, E.; Khosravian, F.; Wang, W.; Armand, M.; Dargahi, J.; Zadeh, M. Towards skill transfer via learning-based guidance in human-robot interaction: An application to orthopaedic surgical drilling skill. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 98, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, X. Medical robotics in bone fracture reduction surgery: A review. Sensors 2019, 19, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukui, S.; Kawai, T.; Nishizawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Nakamura, T.; Iwamoto, N.; Horise, Y.; Masamune, K. Locally operated assistant manipulators with selectable connection system for robotically assisted laparoscopic solo surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Song, A.; Xiong, P.; Yi, P.; Xu, X.; Li, H. Egocentric-vision based hand posture control system for reconnaissance robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 87, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, J.; Ni, T. Research and Application of Multifeature Gesture Recognition in Human-Computer Interaction Based on Virtual Reality Technology. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 3603693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ray, S.; Rajanna, V.; Hammond, T. Evaluating the Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms in Gaze Gesture Recognition Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 10, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Y.; Hu, W.C.; Chang, S.H. Gabor filter-based hand-pose angle estimation for hand gesture recognition under varying illumination. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 6031–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvekar, M.P. Hand gesture recognition system for touch-less car interface using multiclass support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 1929–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, M.A.; Miah, A.S.M.; Sayeed, A.; Shin, J. Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Optimal Segmentation in Human-Computer Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Innovation and Invention (ICKII), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 21–23 August 2020; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, W.Q.; Wen, C. Research on optimization of static gesture recognition based on convolution neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE), Hohhot, China, 25–27 October 2019; pp. 398–3982. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, I.J.; Perico, D.H.; Homem, T.P.D.; da Costa Bianchi, R.A. Deep Reinforcement Learning for a Humanoid Robot Soccer Player. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 102, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedotun, O.K.; Khashman, A. Deep learning in vision-based static hand gesture recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sheng, J. Gesture recognition based on CNN and DCGAN for calculation and text output. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28230–28237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, P.; Gupta, S.; Kim, K.; Pulli, K. Multi-sensor system for driver’s hand-gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- ElBadawy, M.; Elons, A.; Shedeed, H.A.; Tolba, M. Arabic sign language recognition with 3d convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Information Systems (ICICIS), Cairo, Egypt, 5–7 December 2017; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Koller, O.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Deep hand: How to train a cnn on 1 million hand images when your data is continuous and weakly labelled. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3793–3802. [Google Scholar]
- Jahandad; Sam, S.M.; Kamardin, K.; Sjarif, N.N.A.; Mohamed, N. Offline signature verification using deep learning convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures GoogLeNet inception-v1 and inception-v3. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, A. Self-Selection Salient Region-Based Scene Recognition Using Slight-Weight Convolutional Neural Network. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 102, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50× fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Igcv3: Interleaved low-rank group convolutions for efficient deep neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00178. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Lai, J.; Hu, Q. Fruit image classification based on Mobilenetv2 with transfer learning technique. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Application Engineering, Sanya, China, 22–24 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the ICML, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klambauer, G.; Unterthiner, T.; Mayr, A.; Hochreiter, S. Self-normalizing neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; Curran Associates Inc.: Hook, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).