Identification of Key Components of CNC Lathe Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
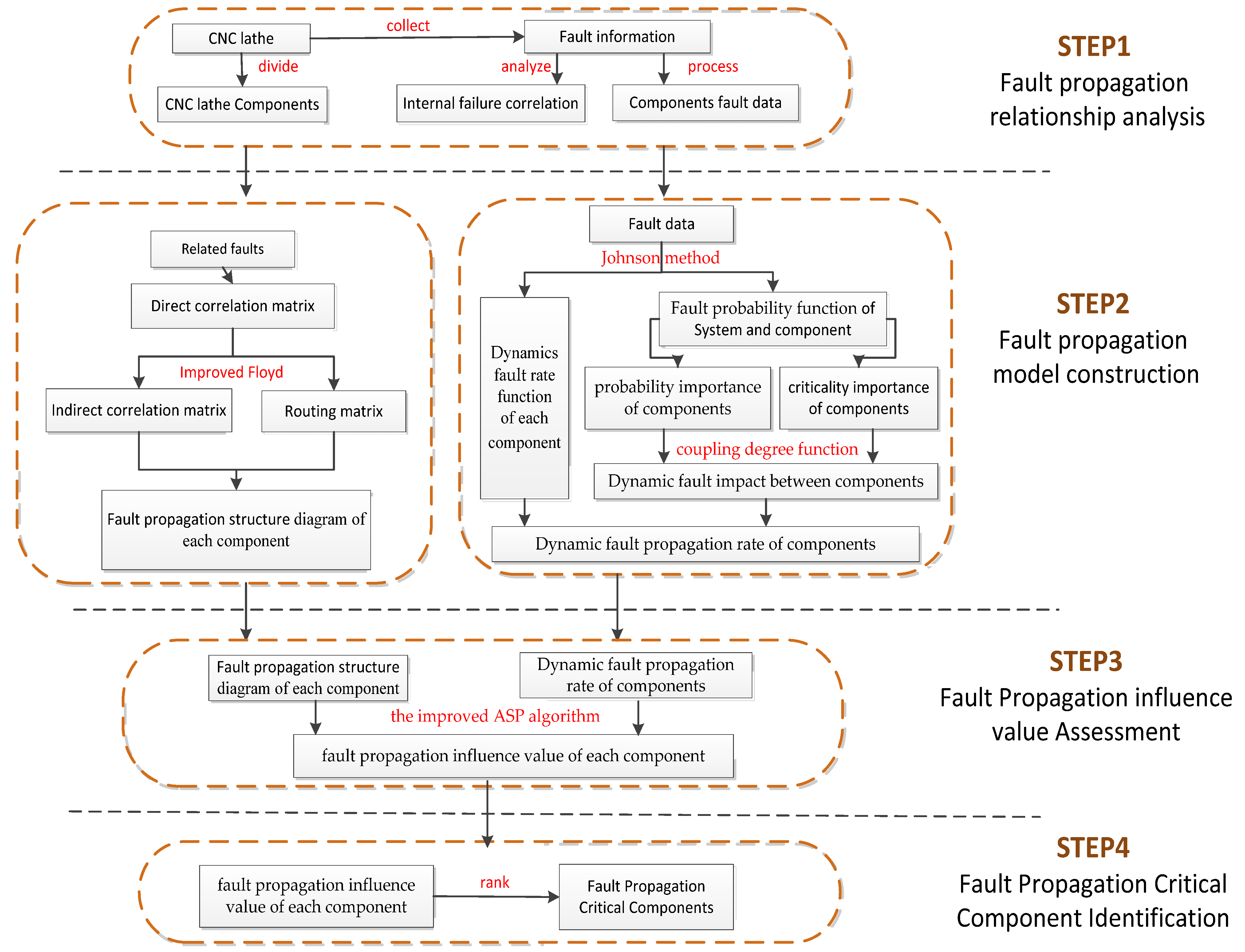
2. Identification Method of Key Components of CNC Lathe
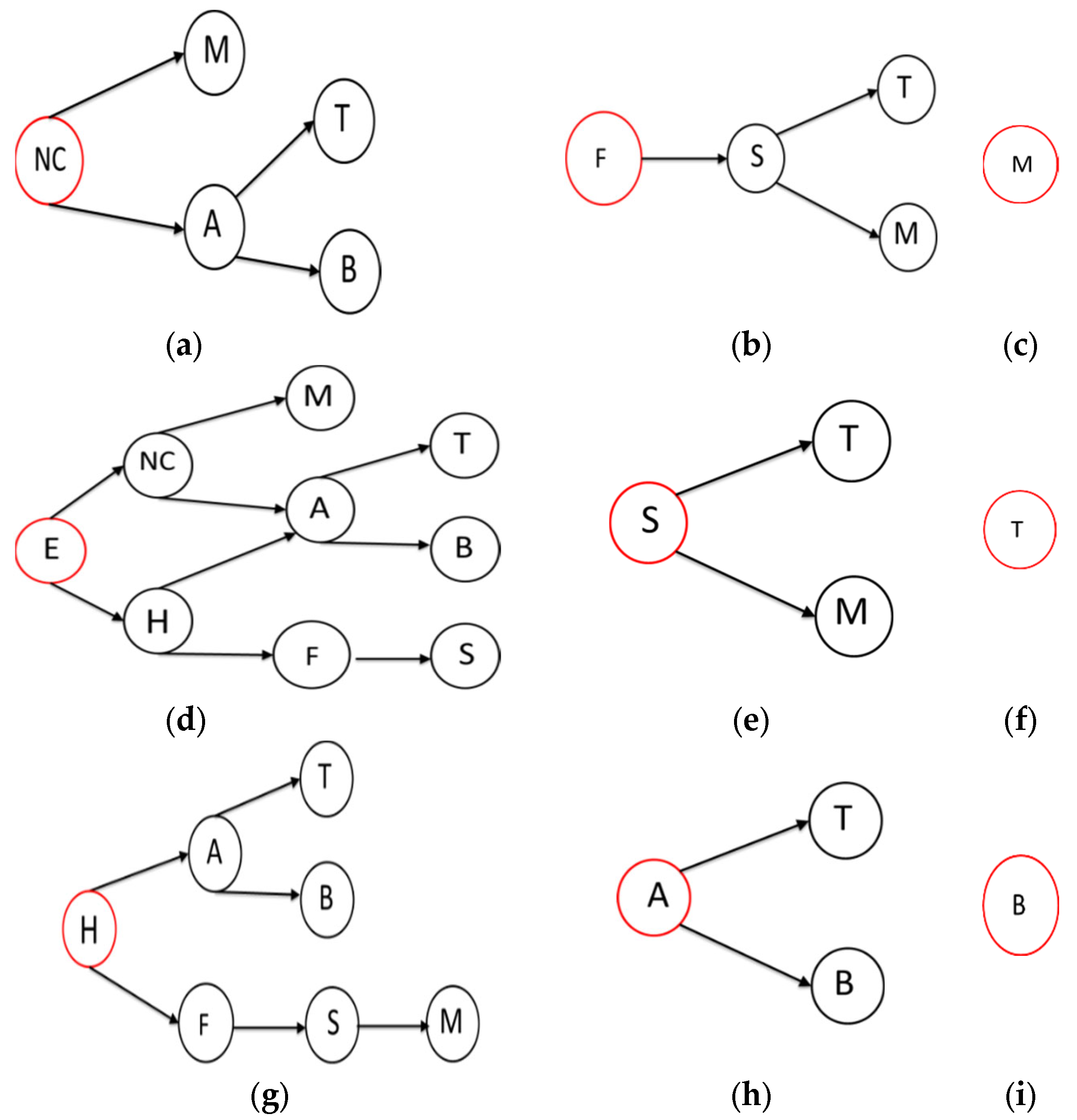
2.1. Construction of the Fault Propagation Structure Model of Components
2.2. Calculation of Fault Propagation Rate of CNC Lathe Components
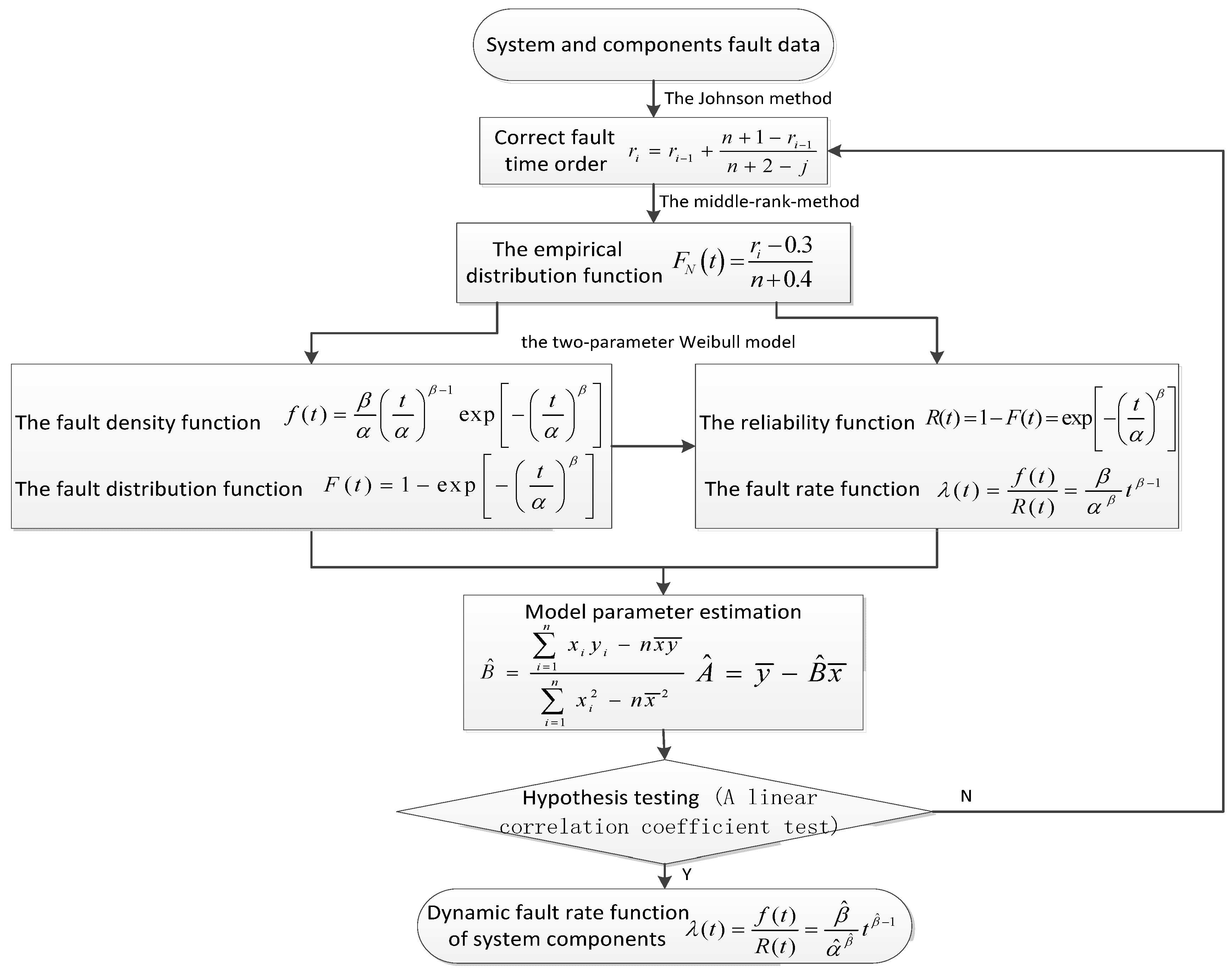
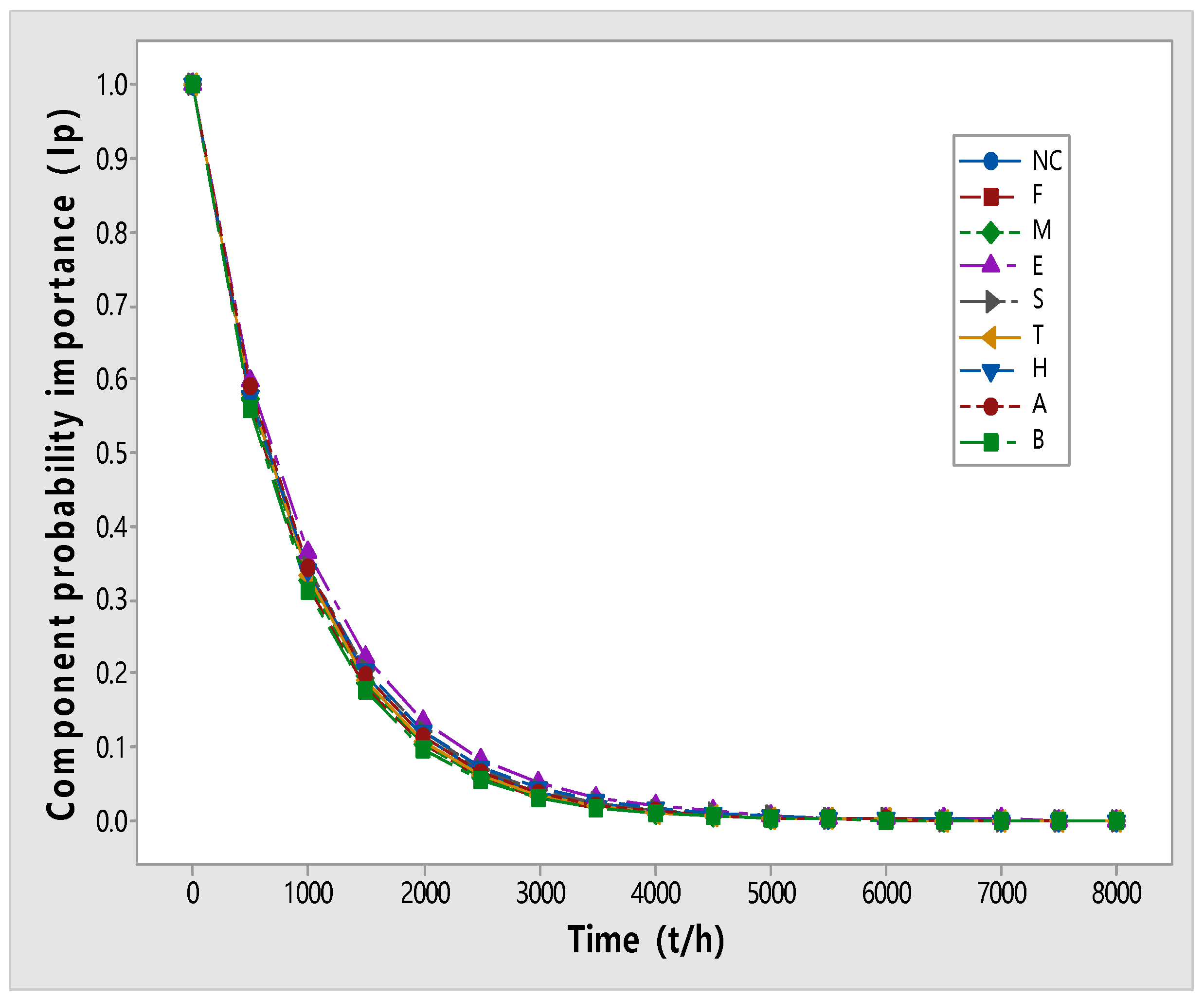
2.2.1. Calculation of Dynamic Fault Rate of Components
2.2.2. Determination of the Dynamic Influence Degree between Components
2.2.3. Calculation of Dynamic Fault Propagation Rate of Components
2.3. Identification of Key Components of System Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation
3. Case Application
4. Comparison Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinova, L.I.; Martinov, G.M. Prospects for CNC machine tools. Russ. Eng. Res. 2019, 39, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peukert, B.W.; Archenti, A. Dynamic interaction between precision machine tools and their foundations. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2020, 14, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daqing, L.; Yinan, J.; Rui, K.; Havlin, S. Spatial correlation analysis of cascading failures: Congestions and blackouts. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Jia, L.-M.; Wang, Y.-H. Identification of critical components of high-speed train system based on interval-value intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy set. Control Theory Appl. 2019, 36, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ruijters, E.; Stoelinga, M. Fault tree analysis: A survey of the state-of-the-art in modeling, analysis and tools. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2015, 15, 29–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, Z. Risk assessment of chemical process considering dynamic probability of near misses based on Bayesian theory and event tree analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 68, 104280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Chen, Y. Reliability evaluation and component importance measure for manufacturing systems based on failure losses. J. Intell. Manuf. 2017, 28, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Kang, R.; Zhang, Y. Resilience-based component importance measures. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2020, 30, 4244–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziuła, P.; Navarro, J. Birnbaum importance measure for reliability systems with dependent components. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2019, 68, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Linking component importance to optimisation of preventive maintenance policy. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 146, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dui, H.; Si, S.; Zuo, M.J.; Sun, S. Semi-Markov process-based integrated importance measure for multi-state systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2015, 64, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Duan, J.; Bai, J. Identification of Key Nodes in a Power Grid Based on Modified PageRank Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, J. Identification of critical nodes for cascade faults of grids based on electrical PageRank. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2021, 4, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Olaf, S. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X. Node importance evaluation in dynamic convergence complex networks. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2017, 49, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Benzi, M.; Klymko, C. On the limiting behavior of parameter-dependent network centrality measures. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2015, 36, 686–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Manoj, B.S. GFT centrality: A new node importance measure for complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 487, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P.; Lloyd, P. Eigenvector centrality and structural zeroes and ones: When is a neighbor not a neighbor? Soc. Netw. 2015, 43, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S. Identifying Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Neighborhood Entropy Centrality. Comput. J. 2021, 64, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terdenge, L.M.; Heisel, S.; Schembecker, G.; Wohlgemuth, K. Agglomeration degree distribution as quality criterion to evaluate crystalline products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 133, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmouch, S.; Aroui, T.; Koubaa, Y. Statistical neural networks for induction machine fault diagnosis and features processing based on principal component analysis. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 16, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y. Identifying key component in high-speed train based on complex network. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Traffic Engineering and Transportation System, Dalian, China, 21–23 August 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 587, p. 012047. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Hang, Z. Multi-Attribute Decision Making Method for Node Importance Metric in Complex Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, F.; Lian, J. Comprehensive evaluation model of abnormal production data based on Entropy Weight Method and TOPSIS Method. Int. J. Front. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ren, M.; Wang, J. Interval number multi-attribute decision-making method based on TOPSIS. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 5059–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Application of Grey Relation Analysis Theory to Choose High Reliability of the Network Node. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1237, 032056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Wang, S.; Ren, F. A novel risk assessment and analysis method for correlation in a complex system based on multi-dimensional theory. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; He, M.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Q. A novel layered fuzzy Petri nets modelling and reasoning method for process equipment failure risk assessment. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 62, 103953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiren, S.; Kai, W. Floyd algorithm for the shortest path planning of mobile robot. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 30, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.R.; Cao, M. Study on the Improvement of Floyd Algorithm and its Application in Network Plan. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 3488, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Pan, C.; Qian, M. Manufacturing/Remanufacturing Logistics Network Optimization Based on Floyd Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1288, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Dai, B.C.; Zhang, L. Dynamic importance analysis of components with known failure contribition of complex systems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8534065. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Coit, D.W.; Feng, Q.M. Component reliability criticality or importance measures for systems with degrading components. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2012, 61, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.L.; Liu, H.M.; Li, G.D. International progress and evaluation on interactive coupling effects between urbanization and the eco-environment. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1081–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, F.; Song, J. Dynamic Analysis Method for Fault Propagation Behaviour of Machining Centres. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Run, R.; Song-Yang, L.; Jun-De, W.; Liang, B.; Lu-Lin, H. An improved evaluating method of node spreading influence in complex network based on information spreading probability. Acta Phys. Sin. 2017, 66, 208901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.H.; Christakis, N.A. Dynamic spread of happiness in a large social network: Longitudinal analysis over 20 years in the Framingham Heart Study. BMJ 2008, 337, a2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, J.T.; Shen, G.X.; Long, Z.; Sun, S.G. Reliability evaluation of machine center components based on cascading failure analysis. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
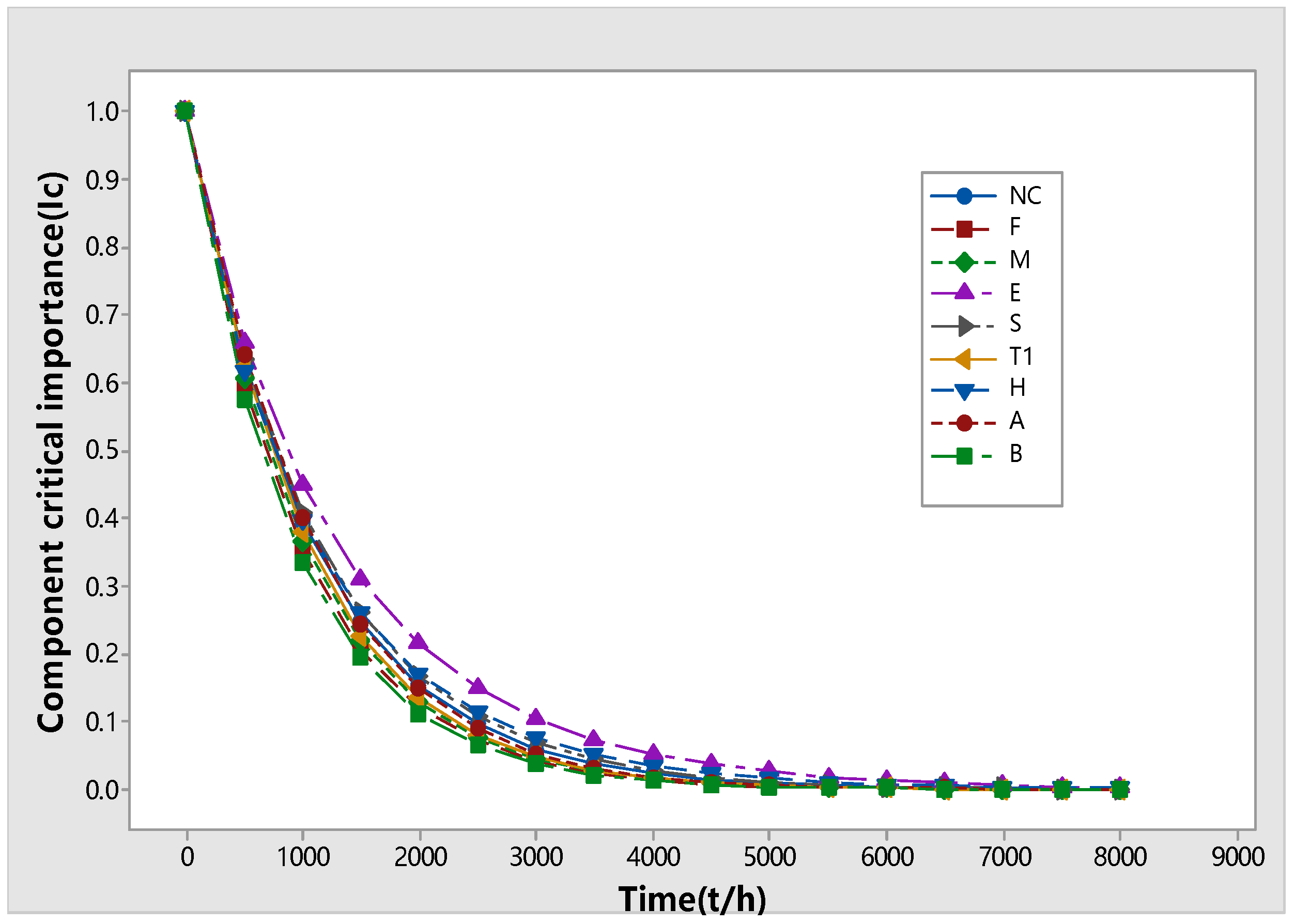
| Element Code and Name | Fault Time (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical control | 29.54 | 99.31 | 172.53 | 235.26 | 348.63 | 406.73 |
| system (NC) | 609.18 | 725.92 | 971.39 | 1058.25 | 1189.59 | 1363.59 |
| 1564.23 | 1853.46 | 2111.67 | ||||
| Feed system (F) | 52.49 | 135.57 | 309.27 | 589.69 | 726.11 | 868.53 |
| 1276.37 | 1486.23 | 2275.64 | ||||
| Electrical system (E) | 30.75 | 80.74 | 126.85 | 160.85 | 219.37 | 319.75 |
| 333.39 | 435.97 | 581.55 | 683.86 | 689.83 | 750.35 | |
| 784.27 | 957.84 | 1015.73 | 1146.33 | 1268.24 | 1305.53 | |
| 1496.54 | 1596.24 | 1812.53 | 1856.96 | 2073.36 | 2546.35 | |
| 2943.71 | ||||||
| Tool holder (M) | 58.63 | 72.63 | 116.78 | 348.36 | 420.75 | 551.71 |
| 1029.27 | 1116.58 | 1531.33 | 1860.67 | 2755.26 | ||
| Servo system (S) | 28.53 | 116.36 | 174.64 | 246.59 | 275.57 | 333.53 |
| 406.36 | 449.63 | 592.73 | 707.59 | 896.47 | 1160.36 | |
| 1264.74 | 1408.49 | 1643.68 | 1785.24 | 1972.74 | 2465.46 | |
| Main driving system (T) | 43.57 | 58.35 | 103.57 | 161.47 | 219.63 | 278.54 |
| 420.47 | 565.97 | 841.977 | 1334.44 | 1667.38 | 1986.96 | |
| Hydraulic system (H) | 67.45 | 143.53 | 246.52 | 297.68 | 347.53 | 406.86 |
| 464.49 | 551.41 | 638.83 | 826.5 | 1015.58 | 1102.09 | |
| 1256.36 | 1580.56 | 1972.47 | 2436.37 | |||
| Auxiliary system (A) | 15.82 | 42.57 | 92.75 | 169.53 | 195.46 | 284.38 |
| 363.36 | 498.75 | 652.85 | 797.3 | 975.35 | 1029.86 | |
| 1276.29 | 1421.96 | 1940.47 | 2812.5 | |||
| Base piece (B) | 89.75 | 278.93 | 568.27 | 758.53 | 1136.57 | 2264.43 |
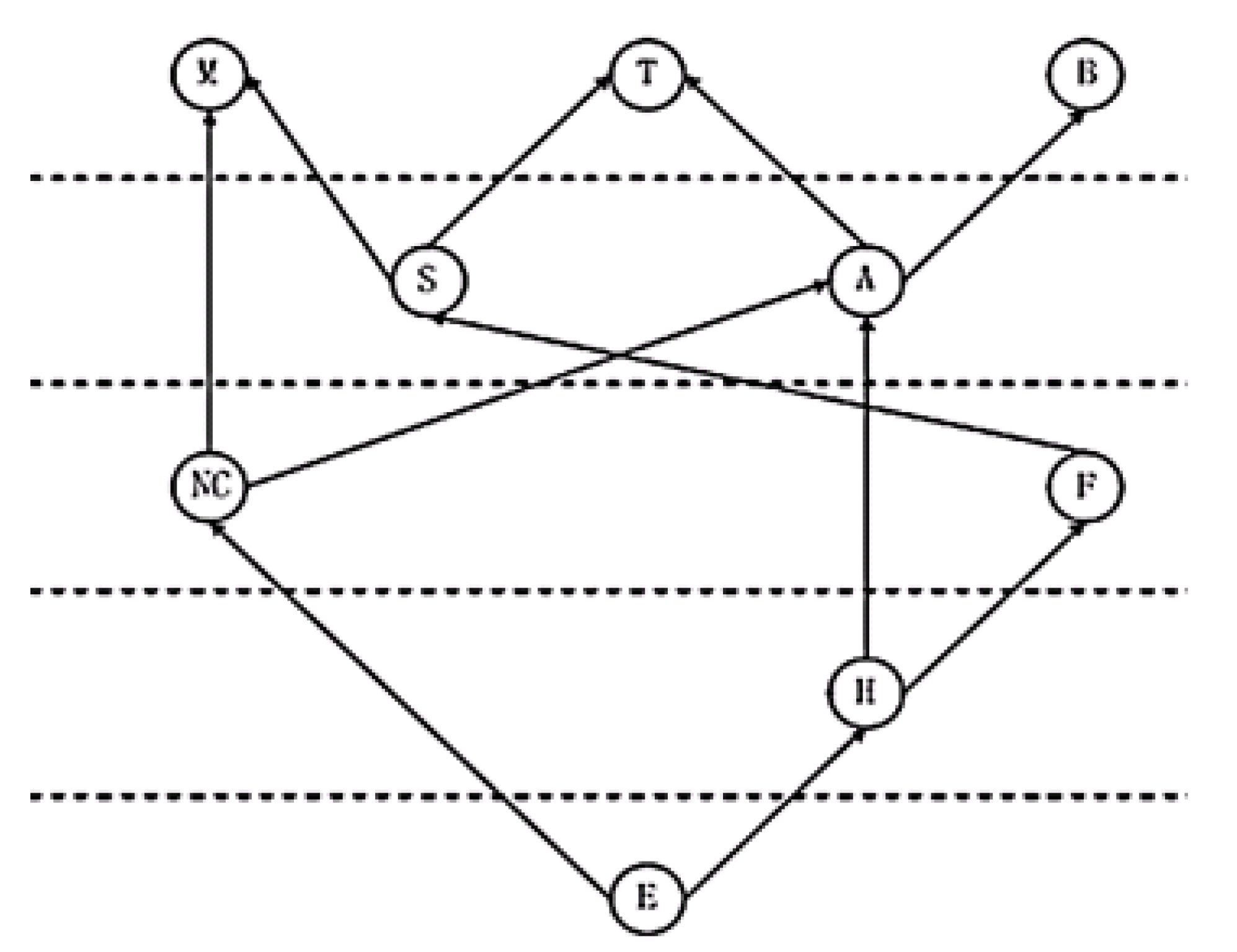
| Antecedent Component | Subsequent Component | Antecedent Component | Subsequent Component |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | M | E | A |
| NC | T | E | B |
| NC | A | S | M |
| NC | B | S | T |
| F | S | H | F |
| E | NC | H | M |
| E | F | H | A |
| E | M | H | B |
| E | T | A | T |
| E | H | A | B |
| Component Code | Dynamics Fault Rate Function |
|---|---|
| NC | |
| F | |
| M | |
| E | |
| S | |
| T | |
| H | |
| A | |
| B |
| Component Code | Fault Probability Function |
|---|---|
| NC | |
| F | |
| M | |
| E | |
| S | |
| T | |
| H | |
| A | |
| B |
| Propagation Path | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (E as a starting point) | ||||
| E→NC | 0.918448361 | 0.000254995 | 0.796881103 | 0.000231419 |
| E→H | 0.977647161 | 0.000271431 | 0.956705067 | 0.000277833 |
| H→A | 0.956717540 | 0.000221941 | 0.848962399 | 0.000211872 |
| H→F | 0.909115084 | 0.000210898 | 0.766856527 | 0.000191382 |
| NC→M | 0.981947229 | 0.000141439 | 0.955113065 | 0.000137078 |
| NC→A | 0.995526834 | 0.000143395 | 0.982569130 | 0.000141019 |
| A→B | 0.979554928 | 0.000098696 | 0.969648730 | 0.000091128 |
| A→T | 0.996958535 | 0.000100450 | 0.994247429 | 0.000093440 |
| F→S | 0.945228319 | 0.000078409 | 0.875293970 | 0.000071674 |
| (NC as a starting point) | ||||
| NC→A | 0.995526834 | 0.000143395 | 0.982569130 | 0.000141019 |
| NC→M | 0.981947229 | 0.000141414 | 0.955113065 | 0.000137078 |
| A→B | 0.979554928 | 0.000098696 | 0.969648730 | 0.000091128 |
| A→T | 0.996958535 | 0.000100450 | 0.994247429 | 0.000093440 |
| (F as a starting point) | ||||
| F→S | 0.945228319 | 0.000078409 | 0.875293970 | 0.000071674 |
| S→T | 0.963840493 | 0.000169284 | 0.902043089 | 0.000160421 |
| S→M | 0.958919595 | 0.000168419 | 0.898204379 | 0.000159738 |
| (S as a starting point) | ||||
| S→T | 0.963840493 | 0.000169284 | 0.902043089 | 0.000160421 |
| S→M | 0.958919595 | 0.000168419 | 0.898204379 | 0.000159738 |
| (A as a starting point) | ||||
| A→T | 0.996958535 | 0.000100450 | 0.994247429 | 0.000093440 |
| A→B | 0.979554928 | 0.000098696 | 0.969648730 | 0.000091128 |
| (H as a starting point) | ||||
| H→F | 0.909115084 | 0.000210898 | 0.766856527 | 0.000191382 |
| H→A | 0.956717540 | 0.000221941 | 0.848962399 | 0.000211872 |
| F→S | 0.945228319 | 0.000078409 | 0.875293970 | 0.000071674 |
| S→M | 0.958919595 | 0.000168419 | 0.898204379 | 0.000159738 |
| A→T | 0.996958535 | 0.000100450 | 0.994247429 | 0.000093440 |
| A→B | 0.979554928 | 0.000098696 | 0.969648730 | 0.000091128 |
| Component Code | Rank | Rank | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 0.000284891 | 4 | 0.000278149 | 4 |
| F | 0.000078462 | 6 | 0.000071720 | 6 |
| M | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 0.000538541 | 1 | 0.000509605 | 1 |
| S | 0.000337703 | 3 | 0.000320159 | 3 |
| T | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| H | 0.000434398 | 2 | 0.000404833 | 2 |
| A | 0.000199146 | 5 | 0.000184567 | 5 |
| B | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| Directed Edge | Fault Propagation Intensity Value (4000 h) | Fault Propagation Intensity Value (6000 h) |
|---|---|---|
| E→NC | 0.17773814 | 0.165807 |
| E→H | 0.26106422 | 0.262317 |
| H→A | 0.20396607 | 0.200436 |
| H→F | 0.22417257 | 0.216161 |
| NC→M | 0.12332509 | 0.128086 |
| NC→A | 0.16248011 | 0.168651 |
| A→B | 0.13769959 | 0.141097 |
| A→T | 0.11370514 | 0.117754 |
| F→S | 0.24395299 | 0.246486 |
| S→M | 0.18203743 | 0.18273 |
| S→T | 0.16985866 | 0.170474 |
| Component Code | Fault Probability | Fault Propagation Strength (4000 h) | Rank | Fault Probability | Fault Propagation Strength (6000 h) | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 0.440846 | 0.285805 | 4 | 0.580568 | 0.296737 | 4 |
| F | 0.290179 | 0.243953 | 6 | 0.398005 | 0.246486 | 6 |
| M | 0.322855 | 0 | 7 | 0.430764 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 0.632003 | 0.438802 | 1 | 0.79164 | 0.428125 | 1 |
| S | 0.494166 | 0.351896 | 3 | 0.644833 | 0.353204 | 3 |
| T | 0.335338 | 0 | 7 | 0.436309 | 0 | 7 |
| H | 0.544449 | 0.428139 | 2 | 0.718822 | 0.416597 | 2 |
| A | 0.385268 | 0.251405 | 5 | 0.493773 | 0.258851 | 5 |
| B | 0.246186 | 0 | 7 | 0.350279 | 0 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, L.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, G. Identification of Key Components of CNC Lathe Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126187
Luan L, Shen G, Zhang Y, Guo G. Identification of Key Components of CNC Lathe Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Lan, Guixiang Shen, Yingzhi Zhang, and Guiming Guo. 2022. "Identification of Key Components of CNC Lathe Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126187
APA StyleLuan, L., Shen, G., Zhang, Y., & Guo, G. (2022). Identification of Key Components of CNC Lathe Based on Dynamic Influence of Fault Propagation. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126187







