Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Study
2.1. Materials and Properties
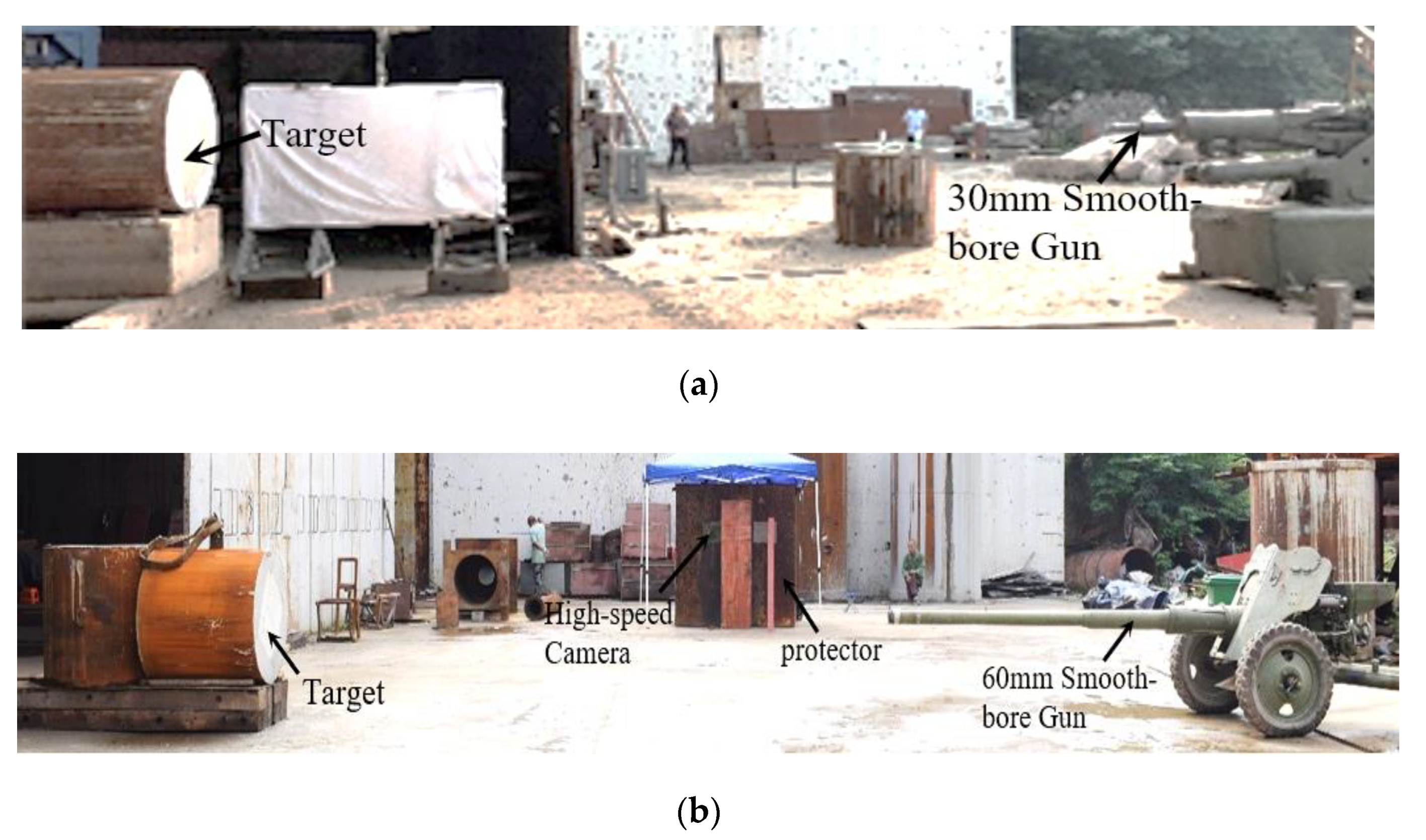
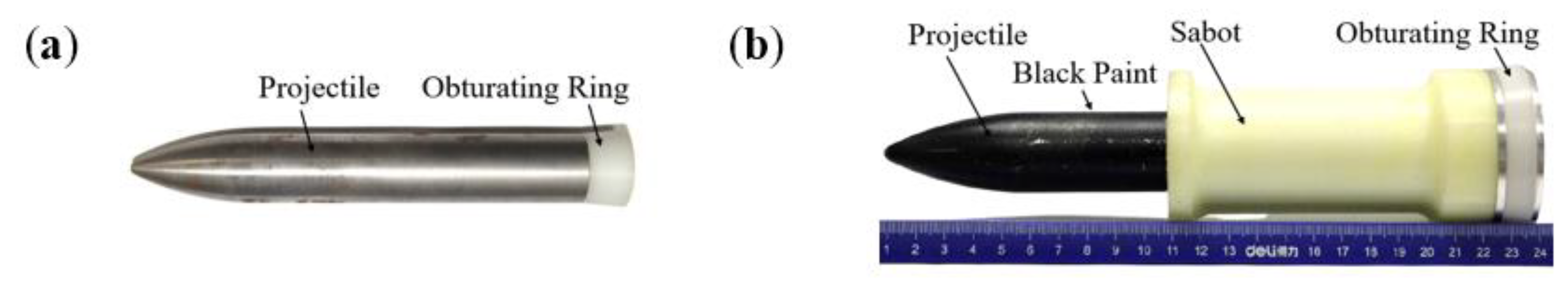
2.2. Experimental Setup
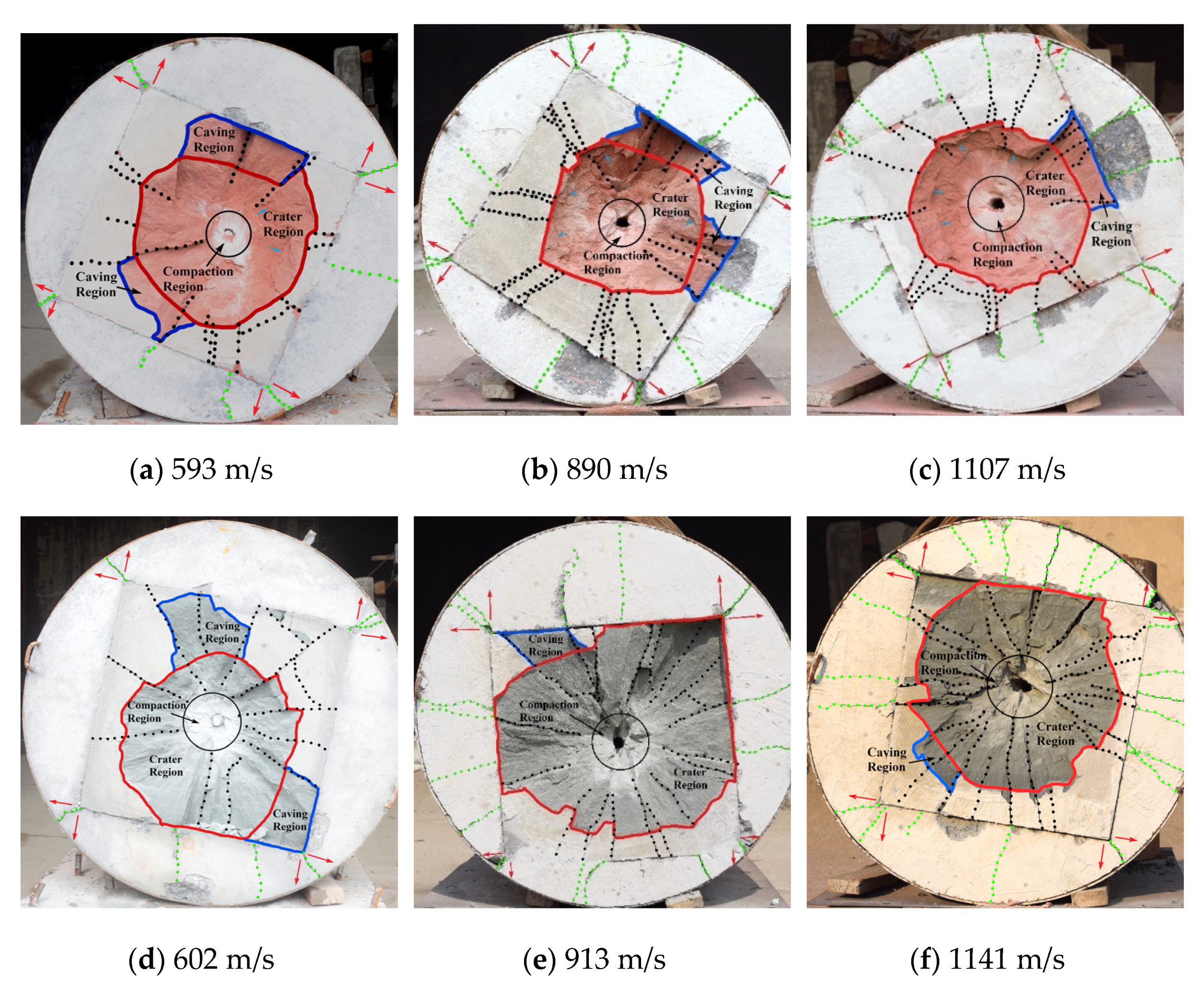
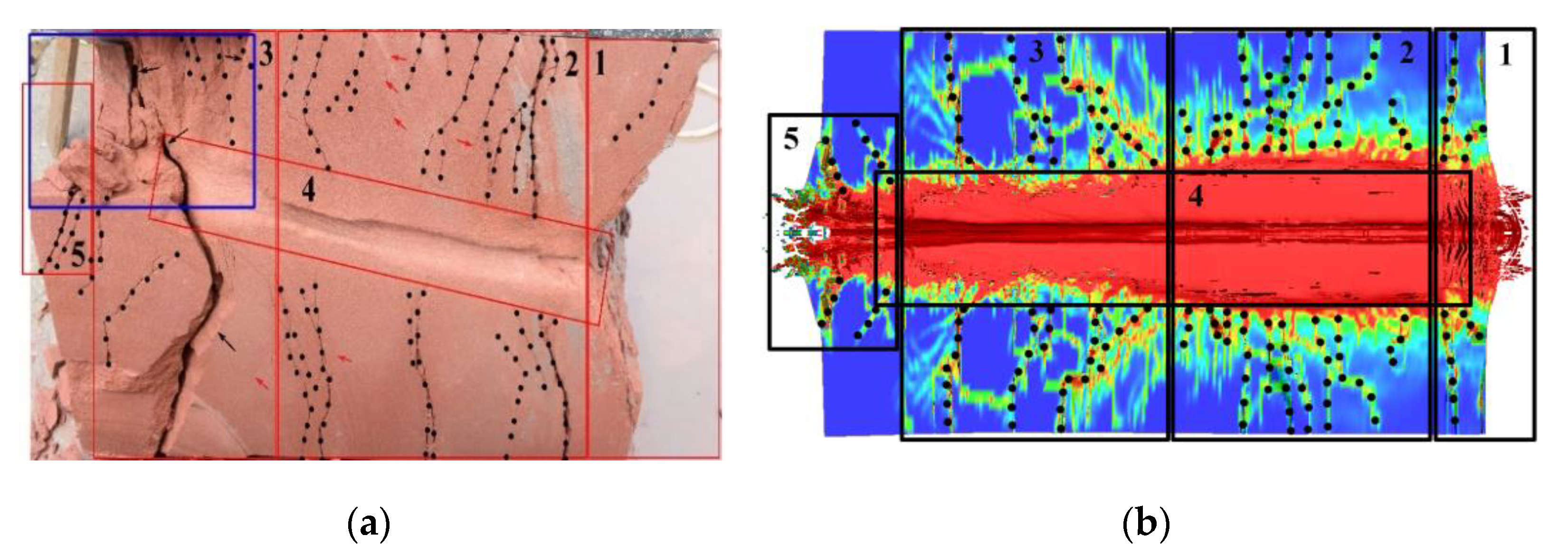
2.3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3. Numerical Simulation Analysis
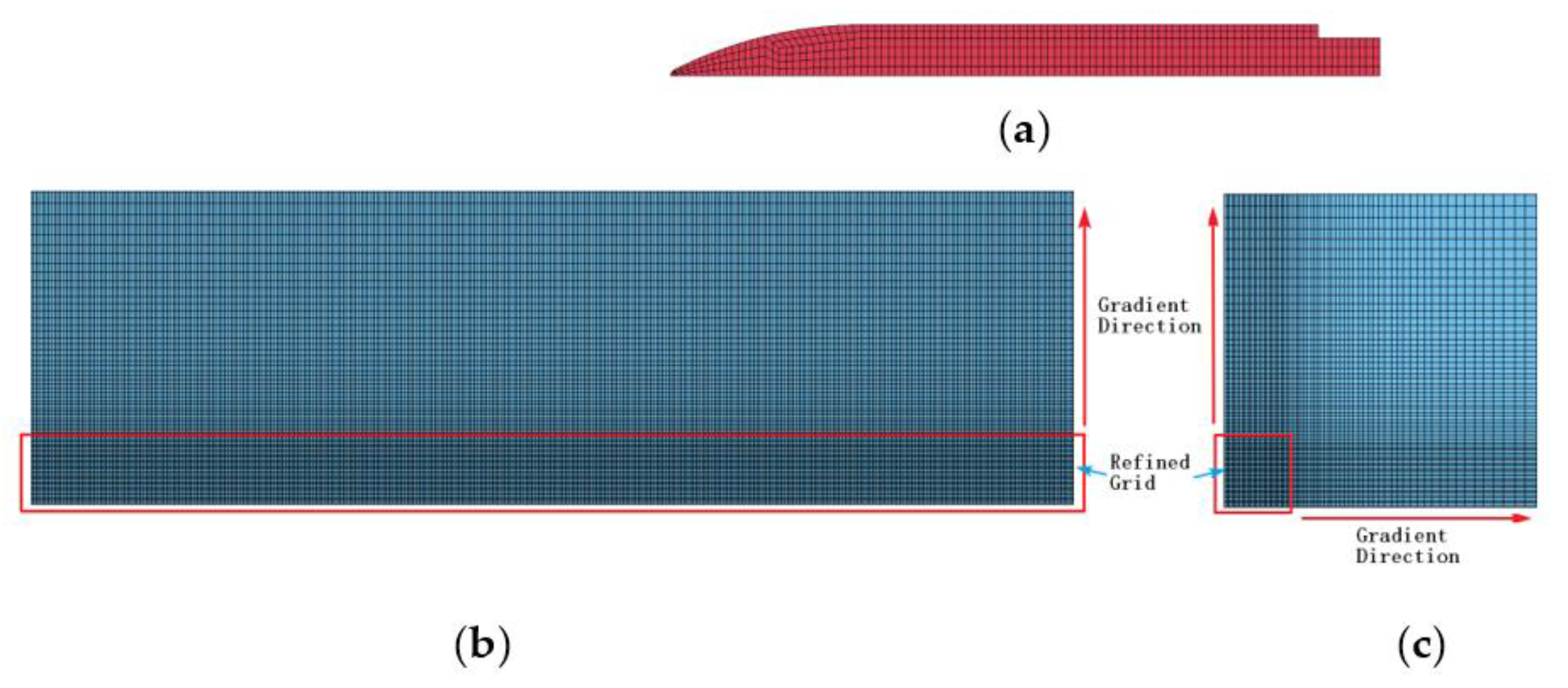
3.1. Simulation Model Setup
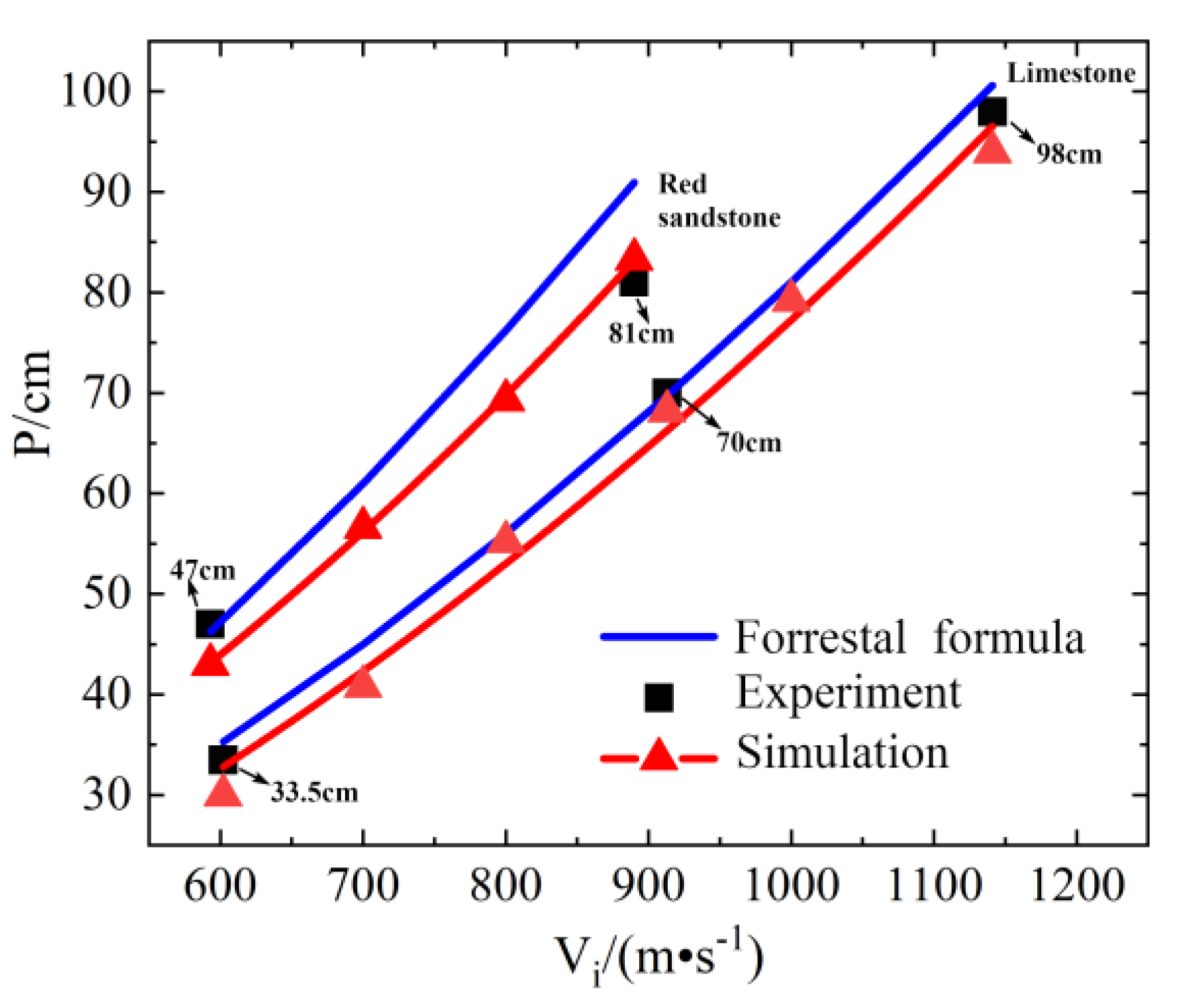
3.2. Model Verification
3.3. Parameter Analysis
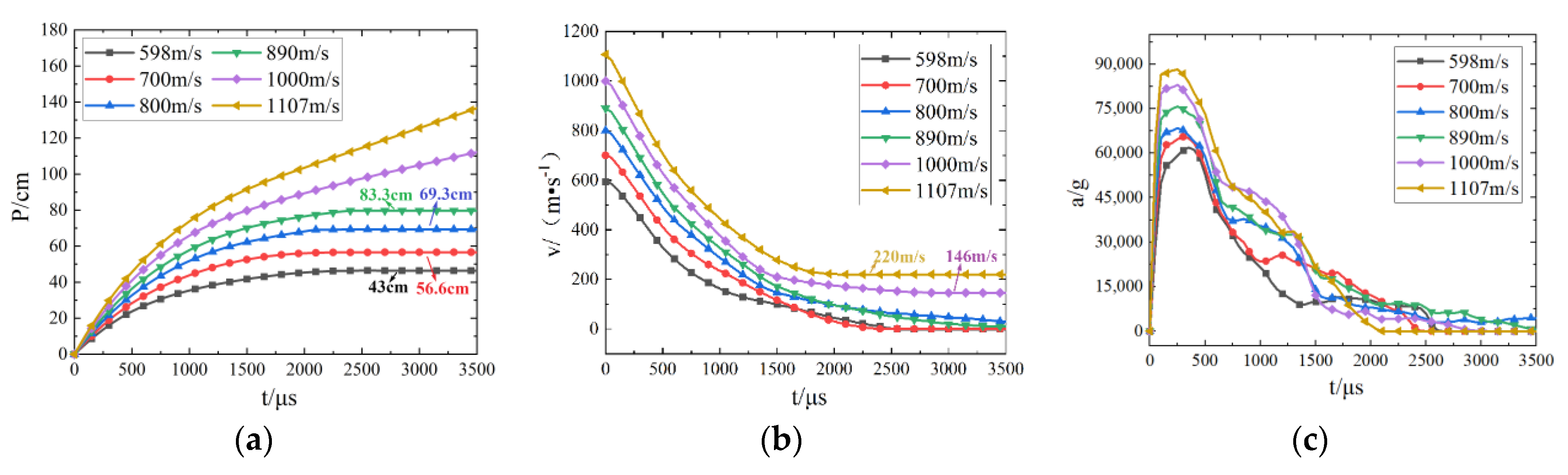
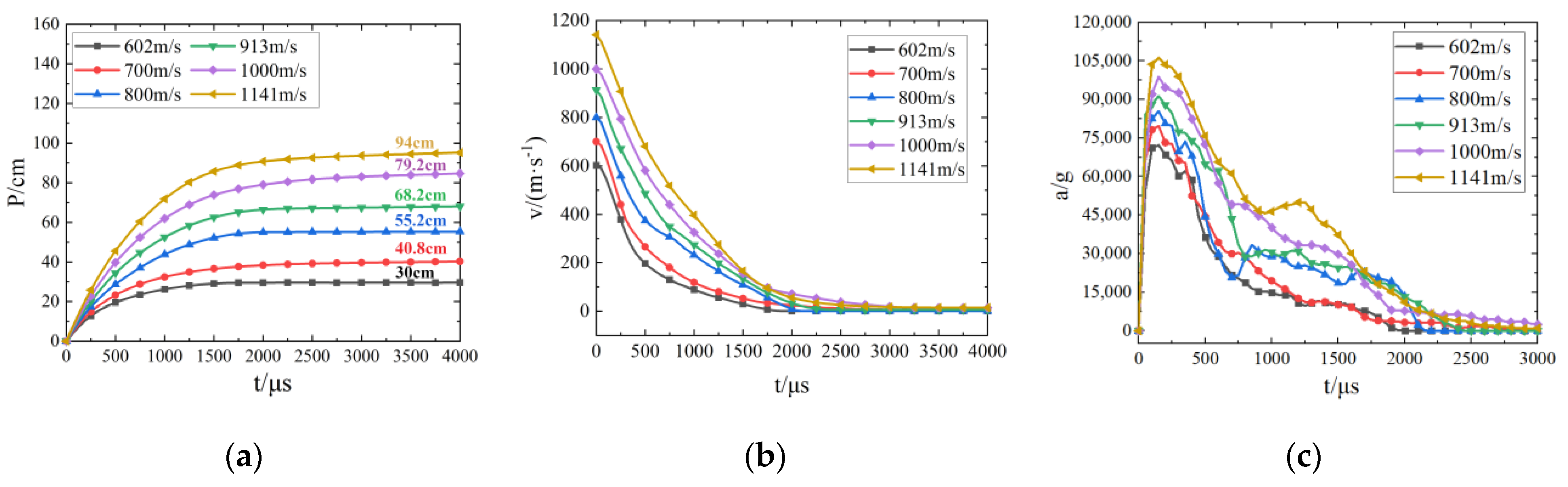
3.3.1. Effect of Impact Velocity on Penetration Performance
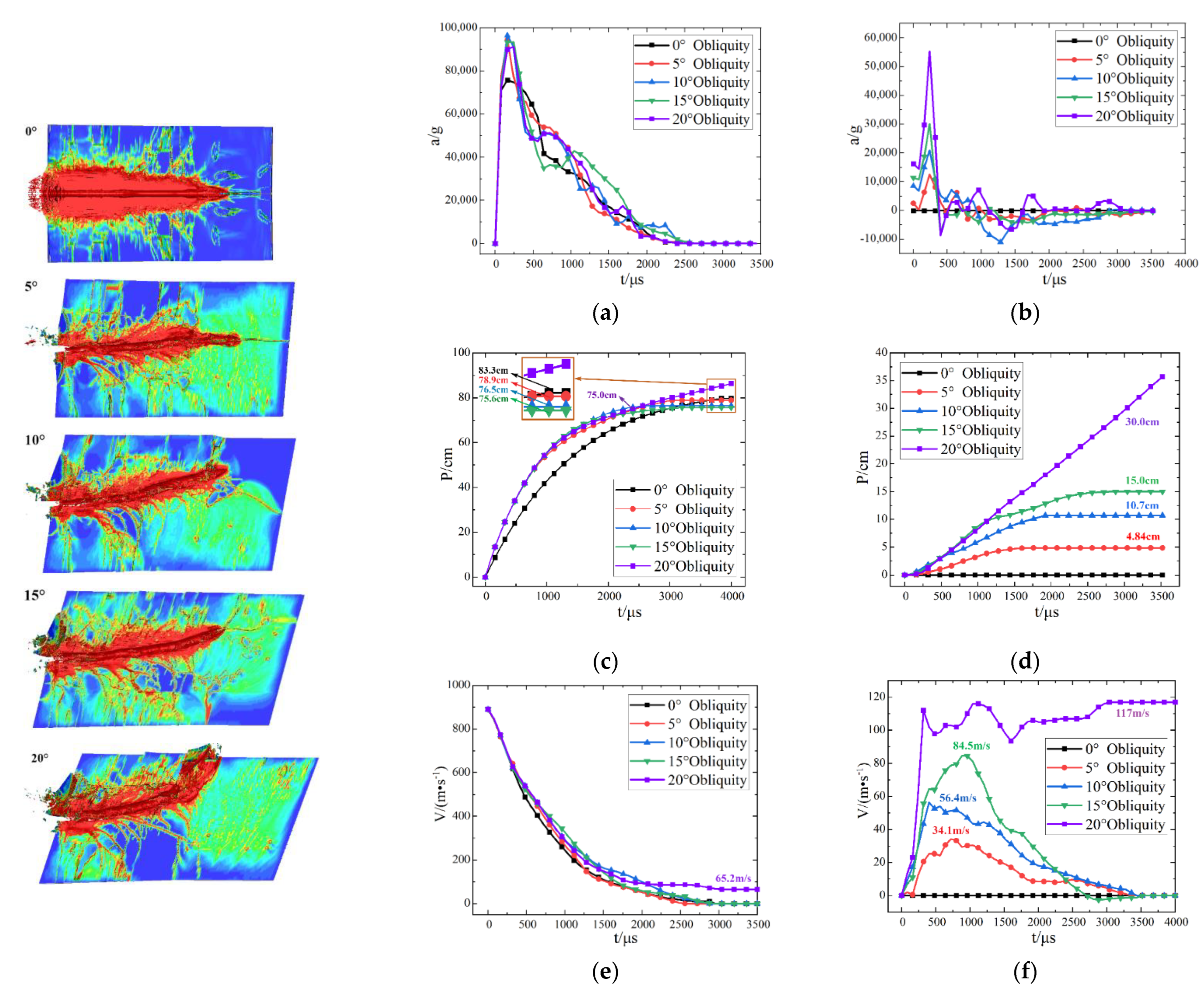
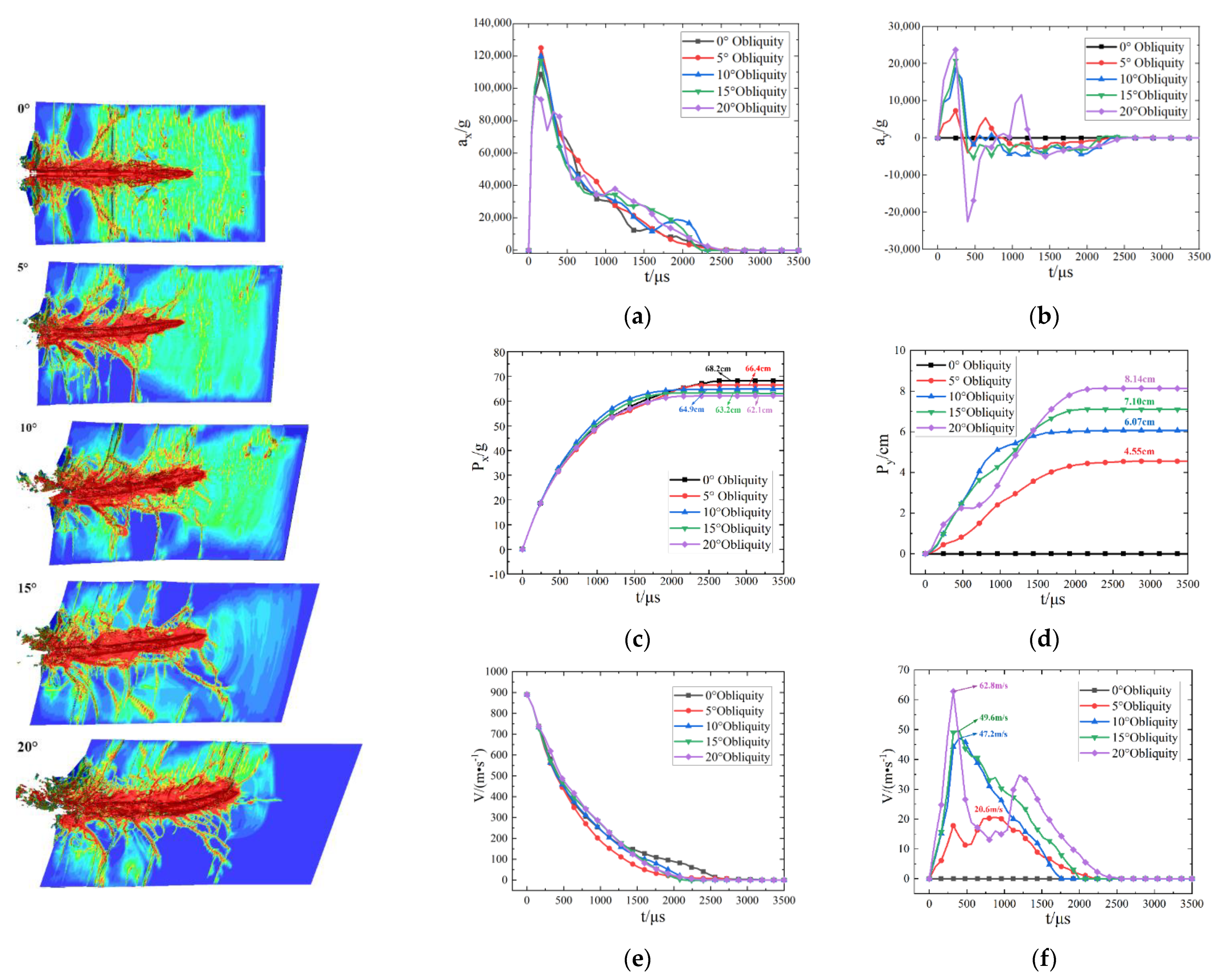
3.3.2. Effect of Impact Angle on Penetration Performance
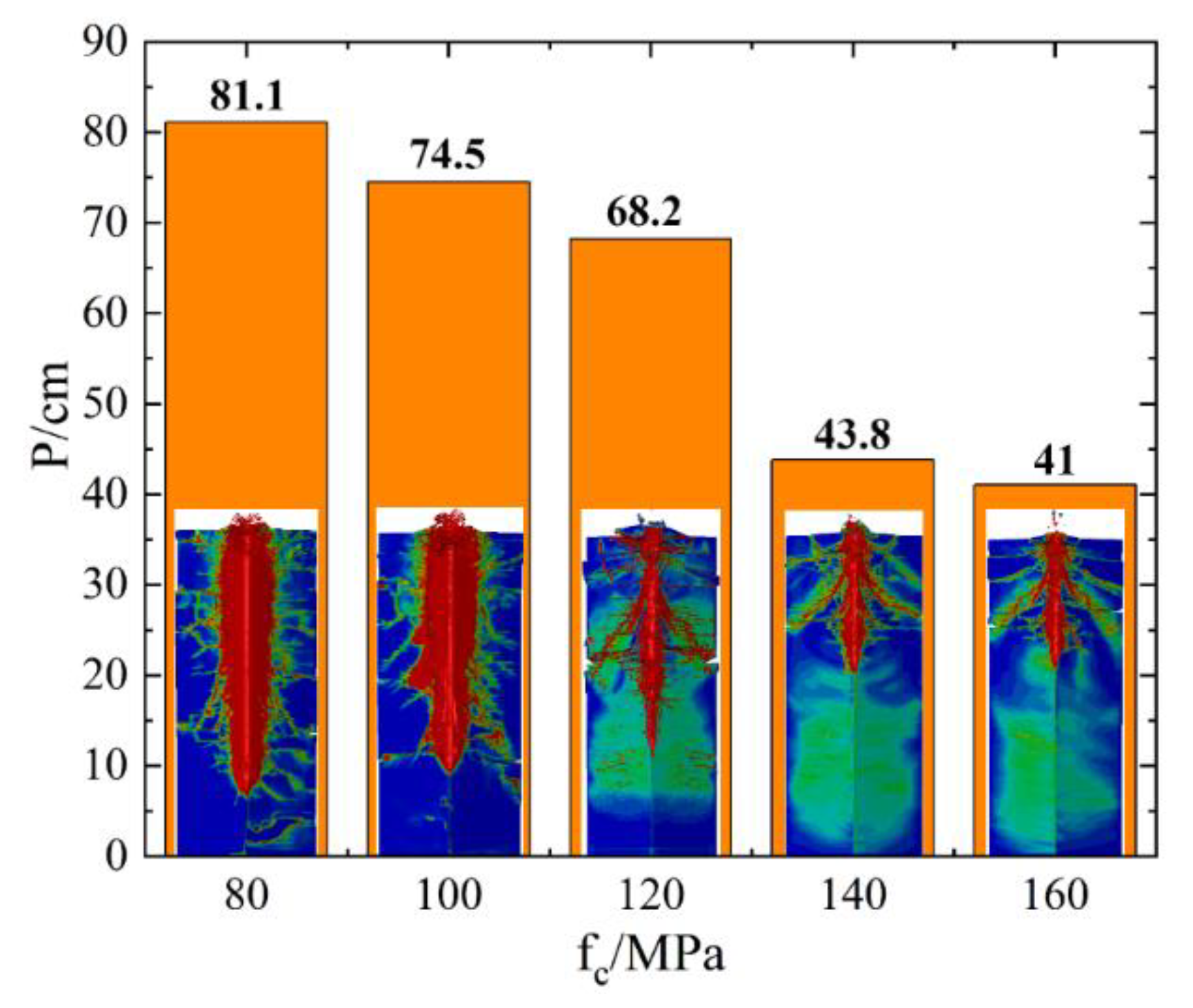
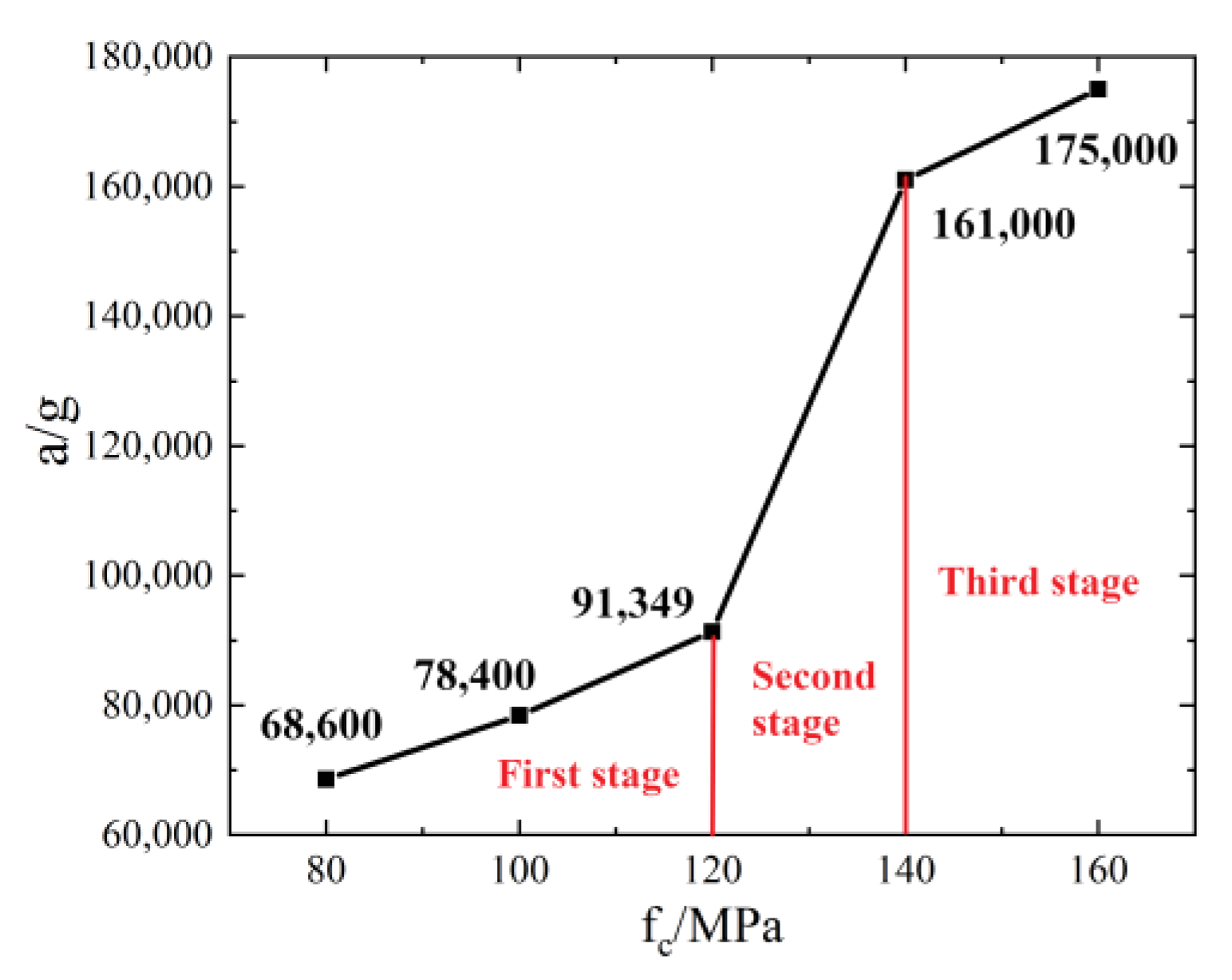
3.3.3. Effect of Target Material Strength on Penetration Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the target speed increases, the number of cracks in the same region increases. At the same speed, since the energy absorption effect of limestone is weaker than that of red sandstone, the cracks formed on the limestone target are few and wide, whereas the cracks formed on the red sandstone target are dense and fine.
- (2)
- At the same speed, the impact angle of the projectile has little effect on the axial penetration depth and acceleration but has obvious effect on the radial penetration depth and acceleration. Compared with limestone, red sandstone is more sensitive to the impact angle of the projectile.
- (3)
- The limit velocity of the projectile penetrating the 1 m-thick red sandstone target was 900–1000 m/s, whereas the limit velocity of the projectile penetrating the 1 m-thick limestone target was 1100–1200 m/s. Therefore, the penetration resistance of limestone is approximately 23.8% stronger than that of red sandstone.
- (4)
- The numerical simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results, and the error is less than 10%.
- (5)
- When the target strength changes from 80 MPa to 160 MPa, the depth of the invasion decreases in three stages (i.e., a gentle drop, a sharp drop and a gentle decline), and the invasive acceleration is a three-stage decline (i.e., a gentle rise, a sharp rise and a gentle rise).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M. Ground Penetration Damage and Engineering Protection of Ultra-High-Speed Kinetic Energy Weapons; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, K.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Second Time Penetration of Earth-penetrating Model Projectile in Rock Medium. J. PLA Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 6, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. End-Point Effects; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z. Research on Anti-Penetration Effects of Three Kinds of Rock Media. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Z.; Zhang, W. An investigation on mass loss of ogival projectiles penetrating concrete targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2011, 38, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, Y. Depth of penetration of high-speed penetrator with including the effect of mass abrasion. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Qiang, H.F.; Wang, G.; Huang, Q.Z.; Yang, Y.Q. Numerical simulation of the penetration of granite at wide-range velocities with a new SPH method. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 015220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.B.; Shou, L.F.; Zhang, J.X.; Tian, Y.; Ou, Z.C.; Zhou, G. Experiments and Numerical Analusis of Destructive Effects of Granite Target Under Impact of Projectile. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2014, 33, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, M. Theoretical and experimental studies on the phenomenon of reduction in penetration depth of hyper-velocity projectiles into granite. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Zhang, X.R.; Lin, J.D.; Tang, R.D. Penetration Experiments for Normal Impact into Granite Targets with High-strength Steel Projectile. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2005, 24, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowaili, Z.A.; Ali, A.M.; Al-Baradi, A.M.; Al-Buriahi, M.S.; Wahab, E.A.; Shaaban, K.S. A significant role of MoO3 on the optical, thermal, and radiation shielding characteristics of B2O3–P2O5–Li2O glasses. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Alomairy, S.; Sriwunkum, C.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Neutron and charged particle attenuation properties of volcanic rocks. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 184, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, J.S.; Sharma, A.; Nazrin, S.N.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Optical and radiation shielding effectiveness of a newly fabricated WO3 doped TeO2–B2O3 glass system. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 193, 109968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, J.S.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Hammoud, A.; Alomairy, S.; Sriwunkum, C.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Synthesis, physical and nuclear shielding properties of novel Pb–Al alloys. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2021, 142, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Buriahi, M.S.; Hessien, M.; Alresheedi, F.; Al-Baradi, A.M.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Kebaili, I.; Olarinoye, I.O. ZnO–Bi2O3 nanopowders: Fabrication, structural, optical, and radiation shielding properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 3464–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowaili, Z.A.; Taha, T.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Saron, K.M.A.; Sriwunkum, C.; Al-Baradi, A.M.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of B2O3-Ag3PO4-ZnO-Na2O glasses for optical and radiation shielding applications. Optik 2021, 248, 168199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kong, X.; Fang, Q.; Hong, J. Numerical simulation on ground shock wave induced by projectile hypervelocity penetration into limestone target. J. Explos. Impact. 2022, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Study on Dynamic Impact Mechanical Behavior of Porous Rock Materials Containing Water. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Prakash, V. Plate impact experiments to investigate shock-induced inelasticity in Westerly granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 60, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoerth, T.; Bagusat, F.; Hiermaier, S. Hugoniot data of Seeberger sandstone up to 7 GPa. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 99, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, X.; Shang, X. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Prefabricated Single-Cracked Red Sandstone under Uniaxial Compression. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Z.; Liu, H. Experimental Research of Physical and Mechanical Damage Evolution of Freeze-thaw Red Sandstone. Min. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Wang, M.; Qian, Q. Calculation of Penetration Depth to Consider Surface Fragmentation of Rock Target. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 1996, S1, 551–555. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Tan, K.; Wu, H.; Qian, Q. New Method of Calculation of Projectile penetration depth of earth-boring projectiles. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 28, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, P. Mechanical properties and failure mechanism of damaged limestone under uniaxial reloading. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2020, 53, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Z. Study on Triaxial Mechanical Properties of Limestone Under Different Loading Modes and Loading Rates. Min. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, X. Experimental Study on Stress Wave Propagation Characteristics in Red Sandstone under Axial Static Stress. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, Z.; Vayig, Y.; Malka-Markovitz, A.; Kositski, R. The penetration of limestone targets by rigid projectiles: Revisited. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2020, 12, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Hanchak, S.J. Penetration Limit Velocity for Ogive-Nose Projectiles and Limestone Targets. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, D.J.; Forrestal, M.J.; Hanchak, S.J. Penetration Experiments with Limestone Targets and Ogive-Nose Steel Projectiles. J. Appl. Mech. 2000, 67, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Altman, B.S.; Cargile, J.D.; Hanchak, S.J. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1994, 15, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Frew, D.J.; Hanchak, S.J.; Brar, N.S. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1996, 18, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoun, T.H.; Glenn, L.A.; Walton, O.R.; Goldstein, P.; Lomov, I.N.; Liu, B. Simulation of hypervelocity penetration in limestone. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2006, 33, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, T.L.; Hanchak, S.J.; Poormon, K.L. Penetration of limestone targets by ogive-nosed VAR 4340 steel projectiles at oblique angles: Experiments and simulations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2003, 30, 1307–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.L. Simulations of the penetration of limestone targets by ogive-nose 4340 steel projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2002, 27, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, M.F.; Greco, F.; Lonetti, P. A moving interface finite element formulation for layered structures. Compos. Part B 2016, 96, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pinna, C.; Soutis, C. Modelling impact damage in composite laminates: A simulation of intra- and inter-laminar cracking. Compos. Struct. 2014, 114, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, M.F.; Greco, F.; Lonetti, P.; Luciano, R.; Penna, R. An interface approach based on moving mesh and cohesive modeling in Z-pinned composite laminates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 135, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, C.; Castanié, B.; Bizeul, M.; Barrau, J.J. Low velocity impact modelling in laminate composite panels with discrete interface elements. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 2809–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.; Huang, R. Plastic Strain Analysis of Mineral Particles in Red Sandstone. Gold Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 557–564. Available online: https://jglobal.jst.go.jp/en/detail?JGLOBAL_ID=202002210282485785 (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Cheng, H. Lithofacies and Geochemical Characteristics of Ordovician Limestone in Shuntuguole Area. Tarim Basin D; Xi’an Shiyou University: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Lu, Y. Modifications of RHT material model for improved numerical simulation of dynamic response of concrete. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, J. Sensitivity Analysis of RHT Model Parameters under Explosive Attack. Ship Electron. Eng. 2019, 39, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.; Peng, Y.; Chen, R.; Cai, Z.; Li, F. Sensitivity Analysis of RHT Model Parameters for Rock Materials under Penetrating Condition. Vib. Impact 2021, 40, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The Study of the Broken Model for Rock Mass Blasting Based on RHT Constitutive Equation. Ph.D. Thesis, China Mining University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Li, W.; Yao, W.; Peng, H. Experimental Study on Compression and Fracture Characteristics of Two Kinds of Rocks Under Different Strain Rates. Chin. J. High Press. Phys. 2021, 35, 52–60. [Google Scholar]





| Specimen Number | Strain Rate/(s−1) | Specimen Size/mm | Compressive Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Sandstone-1 | 2 × 10−4 | 59.12 | |
| Red Sandstone-2 | 2 × 10−4 | 58.28 | |
| Red Sandstone-3 | 2 × 10−3 | 50.89 | |
| Limestone-1 | 2 × 10−4 | 110.79 | |
| Limestone-2 | 2 × 10−4 | 114.48 | |
| Limestone-3 | 2 × 10−3 | 126.80 |
| Specimen | Compression Speed/(m·s−1) | Diameter/mm | Thickness/mm | Tensile Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Sandstone-1 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 49.08 | 25.90 | 1.51 |
| Red Sandstone-2 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 49.36 | 25.80 | 1.11 |
| Red Sandstone-3 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 50.11 | 24.89 | 1.83 |
| Limestone-1 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 48.24 | 24.71 | 3.77 |
| Limestone-2 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 48.58 | 24.74 | 4.05 |
| Limestone-3 | 2.0 × 10−7 | 49.44 | 24.67 | 5.49 |
| Component | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| proportion (%) | 0.31 | 1.08 | 1.16 | 1.07 | 1.67 | 0.005 | 0.011 |
| Target Number | Target Material | Target Size(mm) | Projectile Mass (g) | Projectile Diameter (mm) | Projectile Velocity (m/s) | Launch Carrier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Red sandstone | 968.8 | 30 | 600 | 30 mm artillery | |
| R2 | 900 | 60 mm artillery | ||||
| R3 | 1200 | 60 mm artillery | ||||
| L1 | Limestone | 968.8 | 30 | 600 | 30 mm artillery | |
| L2 | 900 | 60 mm artillery | ||||
| L3 | 1200 | 60 mm artillery |
| Name | Material | Density/ | Young’s Modulus/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projectile | 30CrMnSiNi2A | 7.85 | 211 | 0.3 |
| Name | ) | B | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Sandstone | 2.575 | 56.10 | 1.48 | 0.024 | 10.5 | 0.01 | 0.0105 | 0.053 | 1 |
| Limestone | 2.651 | 117.36 | 4.44 | 0.028 | 16.7 | 0.012 | 1.6 | 0.058 | 1 |
| V(M/S) | /CM | /CM | /CM | /% | /% | /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Red Sandstone | 593 | 47 | 46.25 | 43 | 1.60 | 1.30 | 0.03 |
| 890 | 81 | 90.95 | 83.3 | 12.28 | 2.8 | 8.4 | |
| 1107 | 1 * | 129.58 | 1 * | -- | -- | -- | |
| Limestone | 602 | 33.5 | 35.3 | 31 | 5.37 | 7.46 | 12.18 |
| 913 | 70 | 69.72 | 68.2 | 0.4 | 2.57 | 2.18 | |
| 1141 | 98 | 100.61 | 94 | 2.66 | 4.08 | 6.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126120
Zhang X, Yao W, Wang X, Zhu W, Lu Z, Zhu X, Huang H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126120
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaojing, Wenjin Yao, Xiaoming Wang, Wei Zhu, Zhenyu Lu, Xintao Zhu, and Hongxin Huang. 2022. "Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126120
APA StyleZhang, X., Yao, W., Wang, X., Zhu, W., Lu, Z., Zhu, X., & Huang, H. (2022). Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126120





