Characterization of Neurochemical Signature Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EAE Induction
2.2. Whole-Mount Staining
2.3. Human Gut Tissue Samples
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
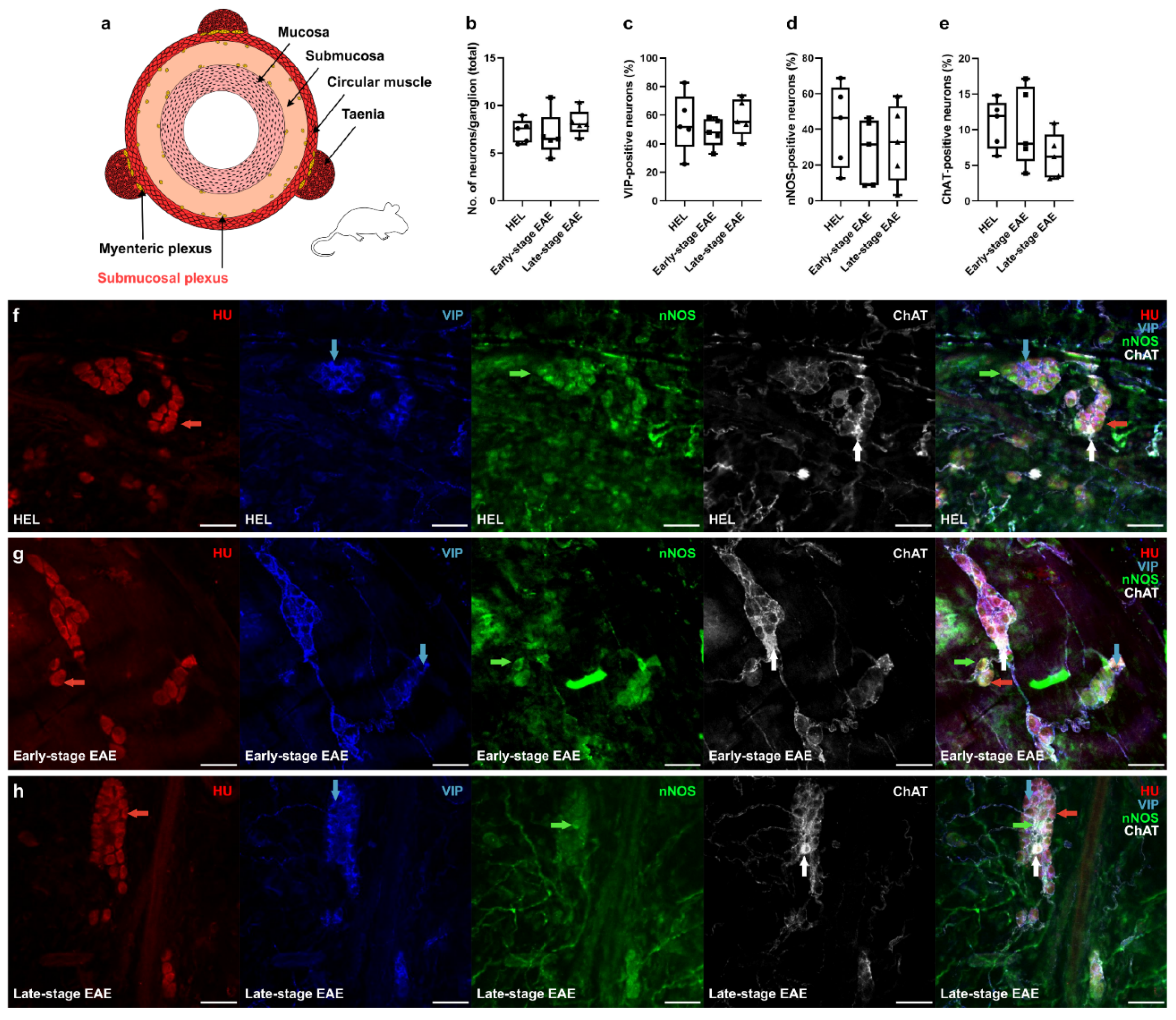
3.1. Decrease in the Percentage of ChAT+ Neurons in the MP of Early- and Late-Stage EAE Mice
3.2. Decrease in the Percentage of the ANO1+ Area in the MP of Late-Stage EAE Mice
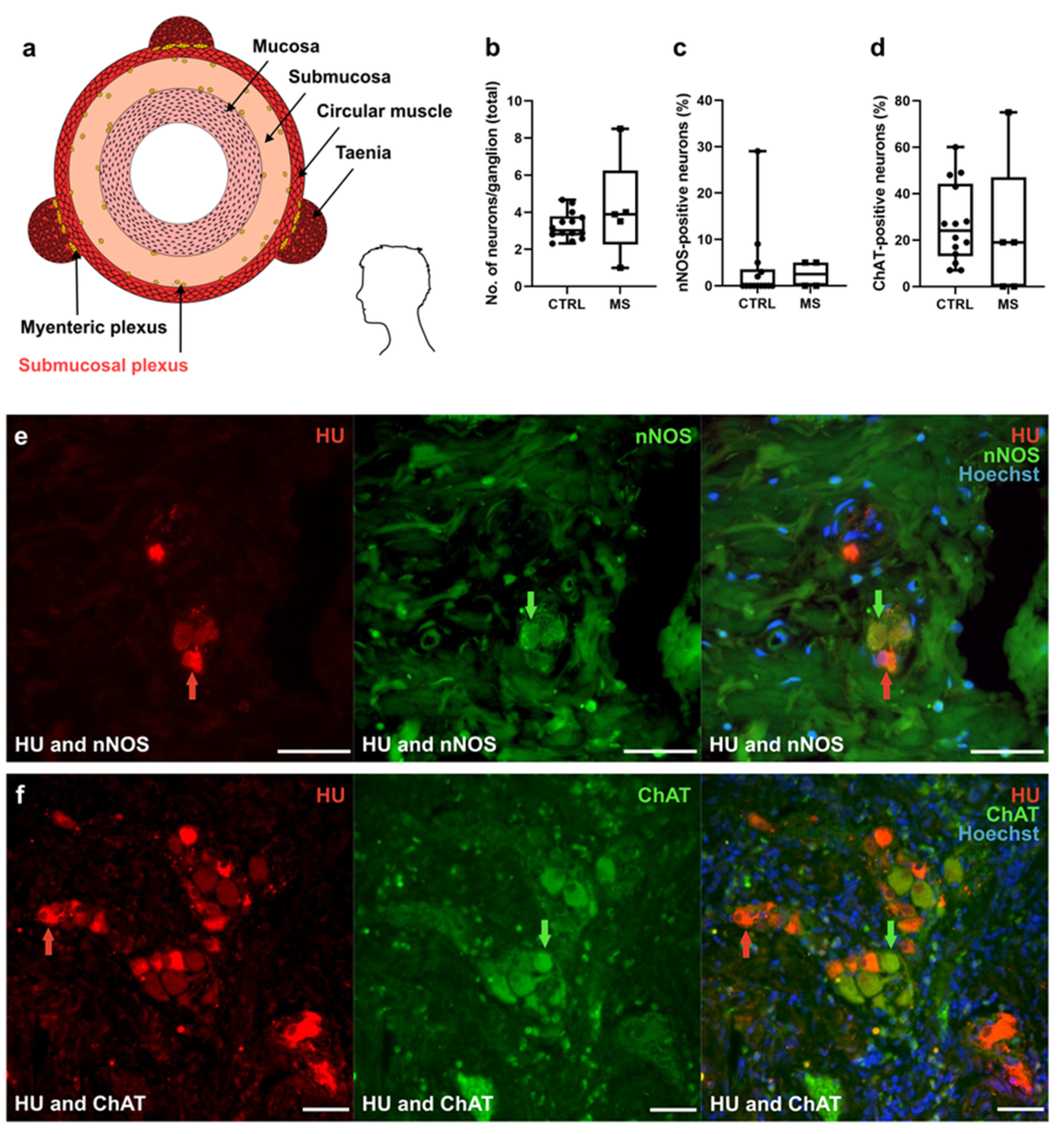
3.3. Increase in the Percentage of ChAT+ Neurons in the MP of Patients with MS
3.4. Significant Increase in the Area of ANO1+ ICCs in Relation to the Area of Muscle Tissue in Patients with MS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Multiple Sclerosis International Federation Atlas of MS, 3rd ed.; 2020; Available online: https://www.atlasofms.org/map/global/epidemiology/number-of-people-with-ms (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple Sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.P.; Eidelman, B.H.; Wald, A. Prevalence of bowel dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, D.J.; Rahman, A.; Nusrat, S.; O’Leary, M.; Heyman, R.; Bielefeldt, K. Adding to the Burden: Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Syndromes in Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2013, 2013, 319201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziosi, G.; Raptis, D.A.; Raeburn, A.; Thiruppathy, K.; Panicker, J.; Emmanuel, A. Gut dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis and the role of spinal cord involvement in the disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.N.; Silvernale, C.; Kuo, B.; Staller, K. Bowel symptoms predate the diagnosis among many patients with multiple sclerosis: A 14-year cohort study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D.; Grundy, D. Little Brain—Big Brain V. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 1998, 10, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System; Blackwell Pub: Malden, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 15, 29–30, 84–85, 135–136. ISBN 978-1-4051-3376-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss, W.M.; Starling, E.H. The movements and innervation of the small intestine. J. Physiol. 1899, 24, 99–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, F.P. A Study of the Intestinal Contraction. Johns Hopkins Hosp. Rep. 1896, 1, 37–75. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, R.K.; Hirano, I. The Enteric Nervous System. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Schlabrakowski, A.; Schrödl, F.; Neuhuber, W.; Brehmer, A. ChAT and NOS in human myenteric neurons: Co-existence and co-absence. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 338, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.M.A.; Defontgalland, D.; Costa, M.; Brookes, S.; Wattchow, D.A. Quantification of subclasses of human colonic myenteric neurons by immunoreactivity to Hu, choline acetyltransferase and nitric oxide synthase. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.-S.; Montes-Adrian, N.A.; Mahns, D.; Gladman, M.A. Quantification and neurochemical coding of the myenteric plexus in humans: No regional variation between the distal colon and rectum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 30, e13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.; Wattchow, D.; Brookes, S.; Costa, M. The neurochemical coding and projections of circular muscle motor neurons in the human colon. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; Alex, G.; Clark, M.J.; Lal, V.V. Morphologies and projections of defined classes of neurons in the submucosa of the guinea-pig small intestine. Anat. Rec. 2003, 272A, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.J.; Kimberg, D.V.; Sheerin, H.E.; Field, M.; Said, S.I. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Stimulation of Adenylate Cyclase and Active Electrolyte Secretion in Intestinal Mucosa. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 54, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, J.P.P.; Tough, I.; Cox, H.; Bornstein, J. Properties of cholinergic and non-cholinergic submucosal neurons along the mouse colon. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Gibbons, S.J.; Bardsley, M.R.; Lorincz, A.; Pozo, M.J.; Pasricha, P.J.; Van de Rijn, M.; West, R.B.; Sarr, M.G.; Kendrick, M.L.; et al. Ano1 is a selective marker of interstitial cells of Cajal in the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1370–G1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, R.M.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Hamdy, H. Interstitial cells of Cajal, the Maestro in health and disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3239–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Torres-Landa, S.; Valdovinos, M.; Coss-Adame, E.; Campo, L.A.M.D.; Torres-Villalobos, G. New insights into the pathophysiology of achalasia and implications for future treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7892–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neunlist, M.; Aubert, P.; Toquet, C.; Oreshkova, T.; Barouk, J.; Lehur, P.A.; Schemann, M.; Galmiche, J.P. Changes in chemical coding of myenteric neurones in ulcerative colitis. Gut 2003, 52, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanacci, V.; Bassotti, G.; Nascimbeni, R.; Antonelli, E.; Cadei, M.; Fisogni, S.; Salerni, B.; Geboes, K. Enteric nervous system abnormalities in inflammatory bowel diseases. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, C.E.; Gibbons, S.J.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Lurken, M.S.; Schmalz, P.F.; Roeder, J.L.; Linden, D.; Cima, R.R.; Dozois, E.J.; Larson, D.W.; et al. Effect of age on the enteric nervous system of the human colon. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 746-e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.J.; Kieffer, E.J.; Powley, T.L. Aging of the myenteric plexus: Neuronal loss is specific to cholinergic neurons. Auton. Neurosci. 2003, 106, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancola, F.; Torresan, F.; Repossi, R.; Bianco, F.; Latorre, R.; Ioannou, A.; Guarino, M.; Volta, U.; Clavenzani, P.; Mazzoni, M.; et al. Downregulation of neuronal vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in Parkinson’s disease and chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 29, e12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaram, C.; Ashraf, W.; Gaumnitz, E.A.; Torbey, C.; Sengupta, A.; Pfeiffer, R.; Quigley, E.M. Dopaminergic defect of enteric nervous system in Parkinson’s disease patients with chronic constipation. Lancet 1995, 346, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, M.; Jabari, S.; Voussen, B.; Enders, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Cossais, F.; Wedel, T.; Boettner, M.; Schwarz, A.; Weyer, L.; et al. The enteric nervous system is a potential autoimmune target in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.A.; McFarland, H.I.; Nye, S.H.; Cofiell, R.; Wilson, T.M.; Wilkins, J.A.; Squinto, S.P.; Matis, L.A.; Mueller, J.P. Treatment of experimental encephalomyelitis with a novel chimeric fusion protein of myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerten, S.; Lichtenegger, F.S.; Faas, S.; Angelov, D.N.; Tary-Lehmann, M.; Lehmann, P.V. MBP-PLP fusion protein-induced EAE in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 177, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, E.T.; Holt, E.A.; Joyce, E.J.; Haag, M.M.; Mawe, G.; Hennig, G.W.; Lavoie, B.; Applebee, A.M.; Teuscher, C. Altered gastrointestinal motility involving autoantibodies in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of multiple sclerosis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving Bioscience Research Reporting: The ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, C.; Neuhuber, W.L.; Wörl, J. Development of neuromuscular junctions in the mouse esophagus: Morphology suggests a role for enteric coinnervation during maturation of vagal myoneural contacts. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 475, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörl, J.; Mayer, B.; Neuhuber, W.L. Nitrergic innervation of the rat esophagus: Focus on motor endplates. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1994, 49, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.D.; Barlow-Anacker, A.J.; Pierre, J.F.; Touw, K.; Erickson, C.S.; Furness, J.B.; Epstein, M.L.; Gosain, A. Deletion of choline acetyltransferase in enteric neurons results in postnatal intestinal dysmotility and dysbiosis. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4744–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattchow, D.; Brookes, S.; Murphy, E.; Carbone, S.; De Fontgalland, D.; Costa, M. Regional variation in the neurochemical coding of the myenteric plexus of the human colon and changes in patients with slow transit constipation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Skull Base 2016, 36, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira, C.; Sandgren, K.; Kessaris, N.; Richardson, W.; Potocnik, A.; Berghe, P.V.; Pachnis, V. Glial cells in the mouse enteric nervous system can undergo neurogenesis in response to injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, S.; Obata, Y.; Fourli, E.; Boeing, S.; Peddie, C.J.; Xu, Q.; Horswell, S.; Kelsh, R.N.; Collinson, L.; Wilkinson, D.; et al. Enteric glia as a source of neural progenitors in adult zebrafish. eLife 2020, 9, e56086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkind-Gerson, J.; Graham, H.K.; Reynolds, J.; Hotta, R.; Nagy, N.; Cheng, L.; Kamionek, M.; Shi, H.N.; Aherne, C.M.; Goldstein, A.M. Colitis promotes neuronal differentiation of Sox2+ and PLP1+ enteric cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Giorgio, R.; Guerrini, S.; Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; De Ponti, F.; Corinaldesi, R.; Moses, P.L.; Sharkey, K.; Mawe, G.M. Inflammatory neuropathies of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, K.; Kaji, N.; Kurosawa, T.; Aikiyo, S.; Hori, M. Hyperglycemia in the early stages of type 1 diabetes accelerates gastric emptying through increased networks of interstitial cells of Cajal. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xue, R.; Jia, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Gu, C.; Yang, J. Involvement of interstitial cells of Cajal in bladder dysfunction in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.M.; Gibbons, S.J.; Roeder, J.L.; Lurken, M.S.; Zhu, J.; Wouters, M.M.; Miller, S.M.; Szurszewski, J.H.; Farrugia, G. Regulation of interstitial cells of Cajal in the mouse gastric body by neuronal nitric oxide. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiong, C.-J.; Sun, H.-M.; Li, X.-S.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Wu, B.; Zhou, D.-S. The distribution of HCN2-positive cells in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. J. Anat. 2012, 221, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Patient ID | Sex | Age (Years) | Reason for Surgery | Tissue Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 25 | I | Appendix |
| 2 | F | 46 | I | Neoileocolic anastomosis |
| 3 | M | 67 | C | Colon |
| 4 | M | 68 | C | Ileum and rectum |
| 5 | F | 37 | O | Ileum and colon |
| 6 | F | 63 | O | Colon |
| 7 | F | 65 | O | Colon |
| Patient ID | Sex | Age (Years) | Reason for Surgery | Tissue Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 61 | I | Ascending colon |
| 2 | M | 52 | I | Ascending colon |
| 3 | M | 61 | I | Colon |
| 4 | F | 56 | I | Ileum |
| 5 | M | 42 | I | Ileum |
| 6 | F | 25 | I | Sigmoid colon |
| 7 | F | 35 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 8 | F | 67 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 9 | F | 32 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 10 | M | 54 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 11 | M | 74 | C | Descending colon |
| 12 | M | 58 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 13 | F | 38 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| 14 | M | 69 | C | Sigmoid colon |
| Analysis | MS | CTRL | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChAT and HU (in MP), nNOS and HU | |||
| (in MP), nNOS and HU (in SP) | |||
| Number of patients (patient IDs) | 4 (1, 2, 3, 4) | 14 (all) | |
| Age, years—median (min-max) | 56.5 (25–68) | 55 (25–74) | 0.9399 * |
| Sex—% female | 50 | 50 | 1 † |
| Reason for surgery—% C/% I | 50/50 | 57/43 | 1 † |
| ChAT and HU (in SP) | |||
| Number of patients (patient IDs) | 5 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) | 14 (all) | |
| Age, years—median (min-max) | 46 (25–68) | 55 (25–74) | 0.8056 * |
| Sex—% female | 60 | 50 | 1 † |
| Reason for surgery—% C/% I | 40/40 (20% other) | 57/43 | 1 † |
| ANO1-positive ICCs | |||
| Number of patients (patient IDs) | 5 (1, 2, 4, 6, 7) | 10 (3–7, 9, 10, 12–14) | |
| Age, years—median (min-max) | 63 (25–68) | 48 (25–69) | 0.3866 * |
| Sex—% female | 80 | 50 | 0.5804 † |
| Reason for surgery—% C/% I | 20/40 (40% other) | 60/40 | 0.5594 † |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kicherer, J.; Weier, A.; Enders, M.; Neuhuber, W.; Heider, T.; Kuerten, S. Characterization of Neurochemical Signature Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125974
Kicherer J, Weier A, Enders M, Neuhuber W, Heider T, Kuerten S. Characterization of Neurochemical Signature Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125974
Chicago/Turabian StyleKicherer, Julia, Alicia Weier, Michael Enders, Winfried Neuhuber, Thorsten Heider, and Stefanie Kuerten. 2022. "Characterization of Neurochemical Signature Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125974
APA StyleKicherer, J., Weier, A., Enders, M., Neuhuber, W., Heider, T., & Kuerten, S. (2022). Characterization of Neurochemical Signature Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125974







