The Cerebral Arterial Wall in the Development and Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Cerebral Arterial Wall Anatomy
3.1. Tunica Intima and Endothelium
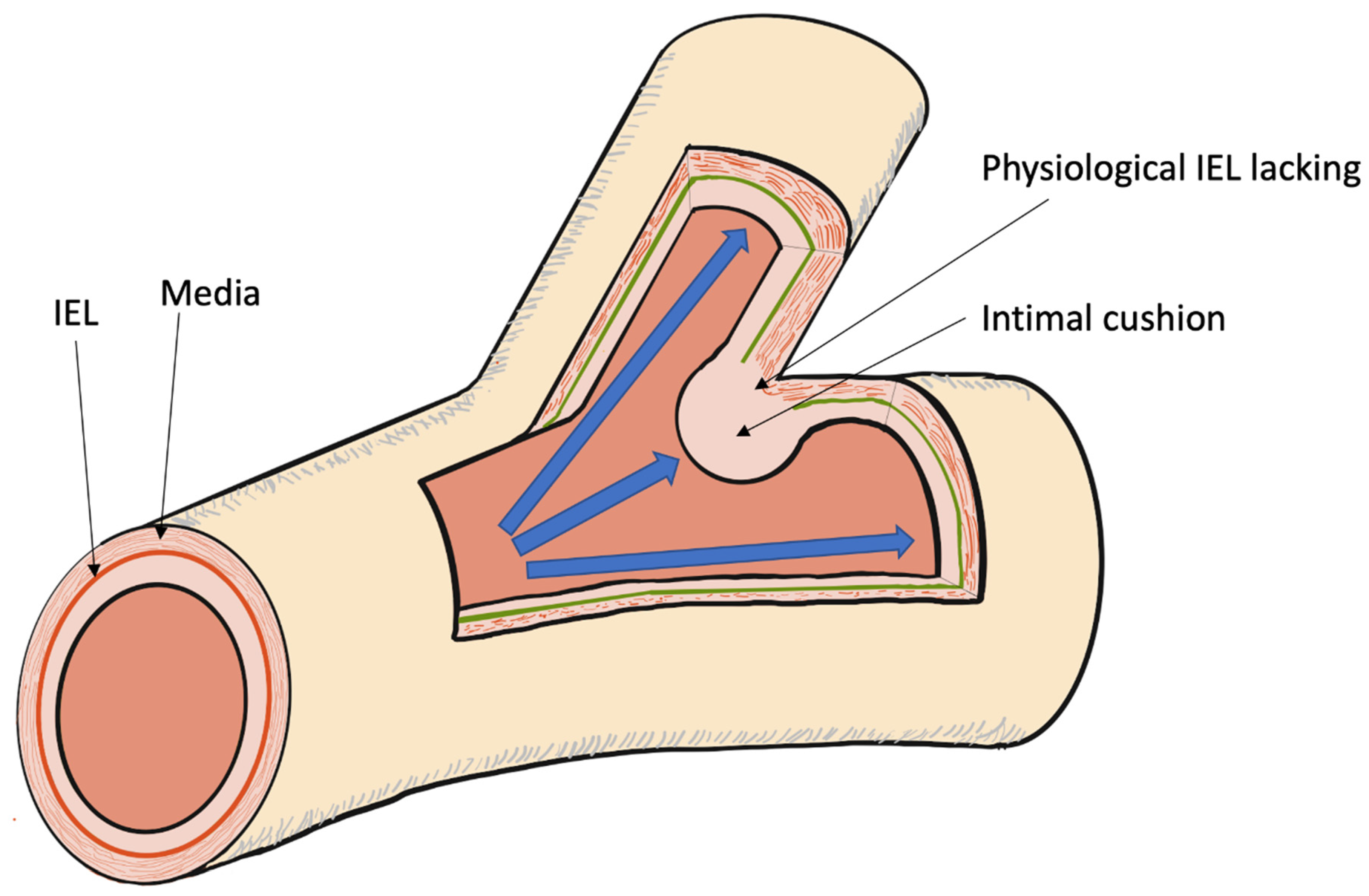
3.2. Internal Elastic Lamina (IEL)
3.3. Tunica Media
3.4. Adventitia and Vasa Vasorum
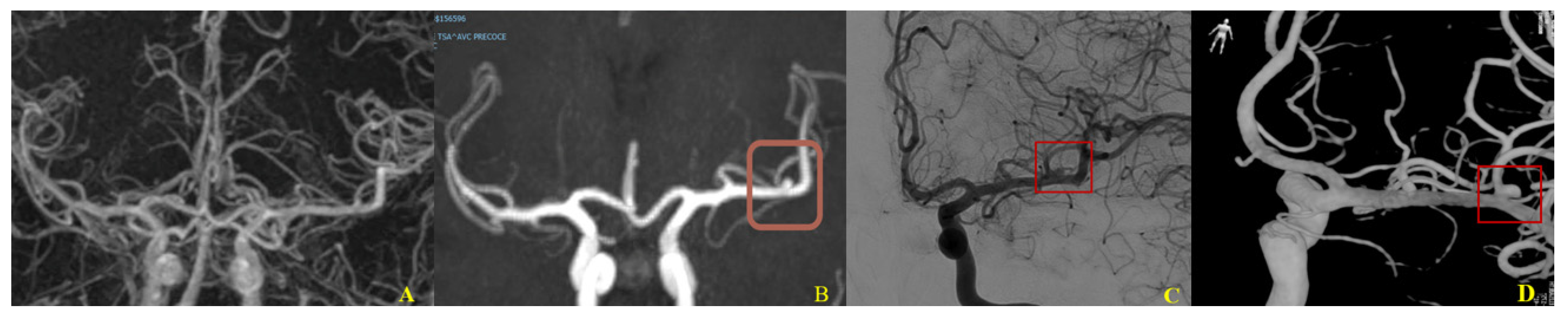
4. Different Locations
5. Birth: Development
5.1. Anatomic and Mechanical Factors
5.2. Genetic Factors
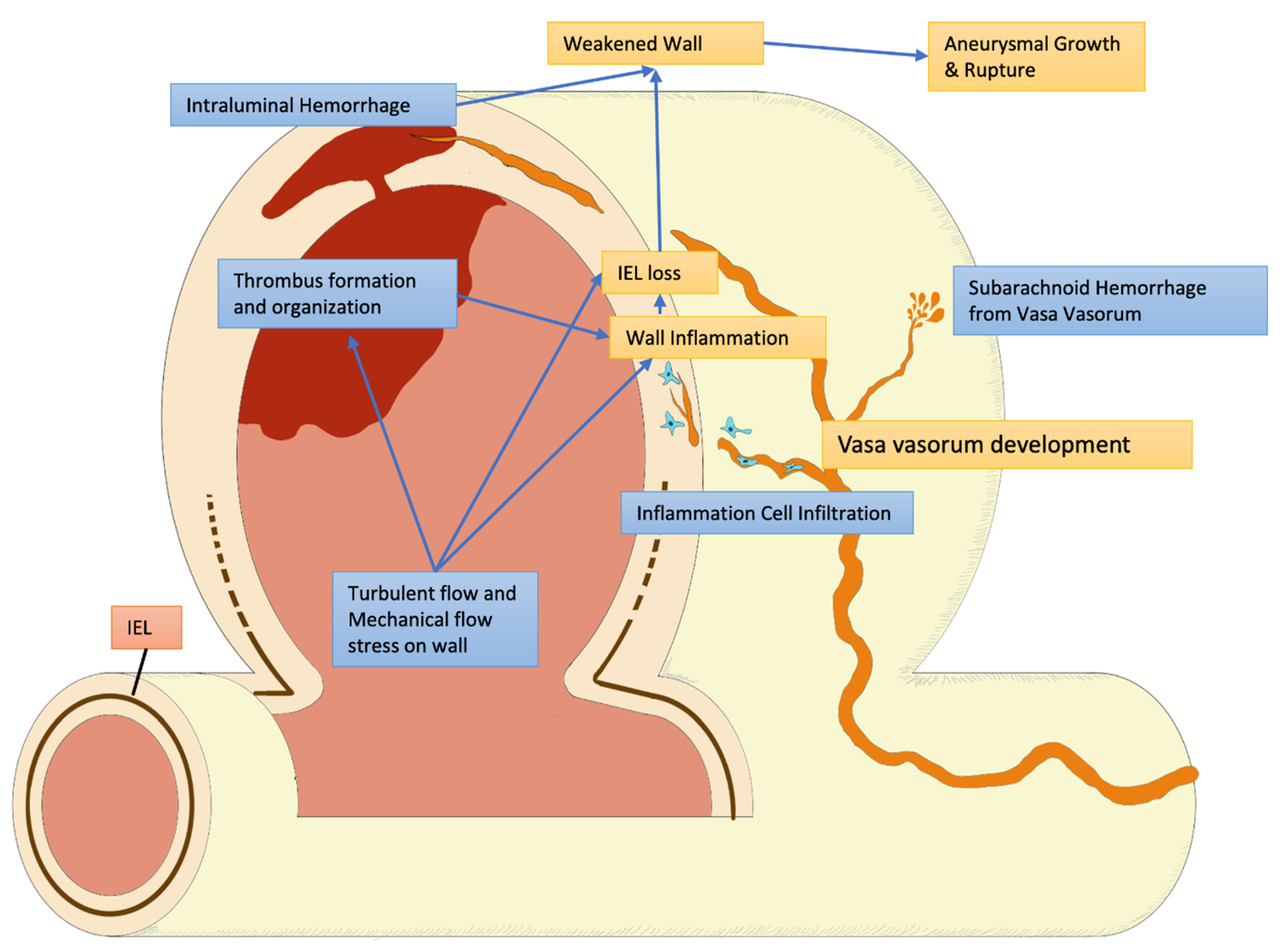
5.3. Structural Damage and Inflammatory Response
6. Growth: Modification
6.1. Flow Dynamics and Aneurysm
6.2. Hemodynamic Influence and Natural History of Aneurysm
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalouhi, N.; Hoh, B.L.; Hasan, D. Review of cerebral aneurysm formation, growth, and rupture. Stroke 2013, 44, 3613–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, G.J.; Djibuti, M.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review. Stroke 1998, 29, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordan, L.C.; Johnston, S.C.; Wu, Y.W.; Sidney, S.; Fullerton, H.J. The importance of cerebral aneurysms in childhood hemorrhagic stroke: A population-based study. Stroke 2009, 40, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.; Tomsick, T.; Huster, G.; Miller, R. The risk of subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhages in blacks as compared with whites. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labovitz, D.; Halim, A.; Brent, B.; Boden-Albala, B.; Hauser, W.; Sacco, R. Subarachnoid hemorrhage incidence among whites, blacks and Caribbean Hispanics: The northern Manhattan study. Neuroepidemiology 2006, 26, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarti, C.; Tuomilehto, J.; Salomaa, V.; Sivenius, J.; Kaarsalo, E.; Narva, E.V.; Salmi, K.; Torppa, J. Epidemiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage in Finland from 1983 to 1985. Stroke 1991, 22, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, R.A.; Kim, H.; Sidney, S.; McCulloch, C.E.; Singh, V.; Johnston, S.C.; Ko, N.U.; Achrol, A.S.; Zaroff, J.G.; Young, W.L. Ten-year detection rate of brain arteriovenous malformations in a large, multiethnic, defined population. Stroke 2010, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naggara, O.N.; White, P.M.; Guilbert, F.; Roy, D.; Weill, A.; Raymond, J. Endovascular treatment of intracranial unruptured aneurysms: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on safety and efficacy. Radiology 2010, 256, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, M.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Koroknay-Pal, P.; Bijlenga, P.; Jahromi, B.R.; Lehto, H.; Kivisaari, R.; Schaller, K.; Charbel, F.; Khan, S.; et al. Surgical clipping of very small unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A multicenter international study. Neurosurgery 2016, 78, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinaldo, L.; McCutcheon, B.A.; Murphy, M.E.; Shepherd, D.L.; Maloney, P.R.; Kerezoudis, P.; Bydon, M.; Lanzino, G. Quantitative analysis of the effect of institutional case volume on complications after surgical clipping of unruptured aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijlenga, P.; Gondar, R.; Schilling, S.; Morel, S.; Hirsch, S.; Cuony, J.; Corniola, M.V.; Perren, F.; Rüfenacht, D.; Schaller, K. PHASES score for the management of intracranial aneurysm: A cross-sectional population-based retrospective study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, R.R.; Eddleman, C.S.; Bendok, B.R.; Batjer, H.H. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms and the assessment of rupture risk based on anatomical and morphological factors: Sifting through the sands of data. Neurosurg. Focus 2009, 26, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texakalidis, P.; Sweid, A.; Mouchtouris, N.; Peterson, E.C.; Sioka, C.; Rangel-Castilla, L.; Reavey-Cantwell, J.; Jabbour, P. Aneurysm formation, growth, and rupture: The biology and physics of cerebral aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mérei, F.T.; Gallyas, F. Role of the structural elements of the arterial wall in the formation and growth of intracranial saccular aneurysms. Neurol. Res. 1980, 2, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I. Intracranial aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 2, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, K.; Denswil, N.P.; Stam, O.C.; van Lieshout, J.J.; Daemen, M.J. Cause and mechanisms of intracranial atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014, 130, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, N.; Carare, R.O. Cerebral vessels: An overview of anatomy, physiology, and role in the drainage of fluids and solutes. Front. Neurol. 2011, 11, 611485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, D.J.; Brightman, M.W. Structural and functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Prog. Drug Res. 2003, 61, 39–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, H.C.; Krizbai, I.A.; Bauer, H.; Traweger, A. “You Shall Not Pass”—Tight junctions of the blood brain barrier. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Oda, J.; Nakahara, I.; Matsumoto, S.; Suyama, Y.; Hasebe, A.; Suzuki, T.; Tanabe, J.; Suyama, K.; Hirose, Y. Experimental analysis of intra-luminal pressure by contrast injection during mechanical thrombectomy: Simulation of rupture risk of hidden cerebral aneurysm in tandem occlusion with blind alley. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, T.; Miki, Y.; Kojima, H.; Suzuki, H. Proposed classification of nonatherosclerotic cerebral fusiform and dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.M.; McCann, J.J.; Rogers, I.W.; Hickey, M.J.; Morrison, W.A.; O’Brien, B.M. A morphological study of the long-term repair process in experimentally stretched but unruptured arteries and veins. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1996, 49, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Warren, D.T. Vascular smooth muscle cell contractile function and mechanotransduction. Vessel Plus 2018, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolla, M.J. Chapter 2. Anatomy and ultrastructure. In The Cerebral Circulation; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Majesky, M.W.; Dong, X.R.; Hoglund, V.; Mahoney, W.M., Jr.; Daum, G. The adventitia: A dynamic interface containing resident progenitor cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritman, E.L.; Lerman, A. The dynamic vasa vasorum. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 75, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, X.; Shi, G.-P. Vasa vasorum in atherosclerosis and clinical significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11574–11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zervas, N.T.; Liszczak, T.M.; Mayberg, M.R.; Black, P.M. Cerebrospinal fluid may nourish cerebral vessels through pathways in the adventitia that may be analogous to systemic vasa vasorum. J. Neurosurg. 1982, 56, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, W.J.; Niu, C.B.; Zhao, H.L.; Wong, K.S.; Leung, T.W.H.; Chen, X.Y. Correlation of adventitial vasa vasorum with intracranial atherosclerosis: A postmortem study. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portanova, A.; Hakakian, N.; Mikulis, D.; Virmani, R.; Abdalla, W.M.A.; Wasserman, B.A. Intracranial vasa vasorum: Insights and implications for imaging. Radiology 2013, 267, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan-Kehoe, M.J.; Simons, M. Vasa vasorum in normal and diseased arteries. Circulation 2014, 129, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canham, P.B.; Finlay, H.M. Morphometry of medial gaps of human brain artery branches. Stroke 2004, 35, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, W.; Morgello, S.; Goldman, J.; Mohr, J.P.; Elkind, M.S.; Marshall, R.S.; Gutierrez, J. Histopathological differences between the anterior and posterior brain arteries as a function of aging. Stroke 2017, 48, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, G.; Wang, L.; Hua, Y.; Hou, H.; Zou, Q.; Wang, D.; Hu, Z.; Lu, D. Comparative morphology of the internal elastic lamina of cerebral and peripheral arteries. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.K.; Poon, W.S. Current status of computational fluid dynamics for cerebral aneurysms: The clinician’s perspective. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagbouga, M.R.; Morel, S.; Bijlenga, P.; Kwak, B.R. Role of hemodynamics in initiation/growth of intracranial aneurysms. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Tutino, V.M.; Snyder, K.V.; Meng, H. CFD: Computational fluid dynamics or confounding factor dissemination? The role of hemodynamics in intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fennell, V.S.; Kalani, M.Y.S.; Atwal, G.; Martirosyan, N.L.; Spetzler, R.F. Biology of saccular cerebral aneurysms: A review of current understanding and future directions. Front. Surg. 2016, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Dion, P.A.; Rouleau, G.A. Genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 2018, 49, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, B.; Amin, M.; Hasan, A.H. Genetics of adult onset stroke subtypes: A review of current knowledge and future prospects. J. Natl. Inst. Neurosci. Bangladesh 2021, 7, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenseil, J.E.; Mecham, R.P. Elastin in large artery stiffness and hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2012, 5, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalouhi, N.; Ali, M.S.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Koch, W.J.; Dumont, A.S. Biology of intracranial aneurysms: Role of inflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, T.; Nishimura, M. The development and the use of experimental animal models to study the underlying mechanisms of CA formation. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 535921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarins, C.K.; Runyon-Hass, A.; Zatina, M.A.; Lu, C.T.; Glagov, S. Increased collagenase activity in early aneurysmal dilatation. J. Vasc. Surg. 1986, 3, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuoka, T.; Hayashi, N.; Hori, E.; Kuwayama, N.; Ohtani, O.; Endo, S. Distribution of internal elastic lamina and external elastic lamina in the internal carotid artery: Possible relationship with atherosclerosis. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savastano, L.E.; Bhambri, A.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Pandey, A.S. Biology of cerebral aneurysm formation, growth and rupture. Chapter 2. In Intracranial Aneurysms; Ringer, A.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Boussel, L.; Rayz, V.; McCulloch, C.; Martin, A.; Acevedo-Bolton, G.; Lawton, M.; Higashida, R.; Smith, W.S.; Young, W.L.; Saloner, D. Aneurysm growth occurs at region of low wall shear stress: Patient-specific correlation of hemodynamics and growth in a longitudinal study. Stroke 2008, 39, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.A.; Putman, C.M.; Cebral, J.R. Patient-specific computational fluid dynamics modeling of anterior communicating artery aneurysms: A study of the sensitivity of intra-aneurysmal flow patterns to flow conditions in the carotid arteries. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, M.A.; Putman, C.M.; Sheridan, M.J.; Cebral, J.R. Hemodynamic patterns of anterior communicating artery aneurysms: A possible association with rupture. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, J.-J.; Chien, S. Effects of disturbed flow on vascular endothelium: Pathophysiological basis and clinical perspectives. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 327–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, C.D. The physiological principle of minimum work applied to the angle of branching of arteries. J. Gen. Physiol. 1926, 9, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, A.M.; Gunel, M.; Sumpio, B.E. The critical role of hemodynamics in the development of cerebral vascular disease: A review. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, R.R.; Linden, D.; Lücke, D.; Berlit, P. Phase relationship between cerebral blood flow velocity and blood pressure a clinical test of autoregulation. Stroke 1995, 26, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, M.; Wehrle-Wieland, E.; Grabiak, D.; Roth, M.; Guschlbauer, B.; Timmer, J.; Weiller, C.; Hetzel, A. Oscillatory cerebral hemodynamics—The macro- vs. microvascular level. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 250, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarab, M.A.; Basarad, D.A.; Konnova, N.S.; Matsievskiy, D.; Matveev, V. Analysis of chaotic and noise processes in a fluctuating blood flow using the Allan variance technique. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2016, 64, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.J.; Liu, C.A.; Huang, B.; Tseng, A.A.; Wang, D.L. Shear-induced endothelial mechanotransduction: The interplay between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) and the pathophysiological implications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, M.A.A.; Shuib, A.S.; Mohyi, M.H.H. A review of hemodynamic parameter in cerebral aneurysm. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2020, 22, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, G.G. Physical factors in the initiation, growth, and rupture of human intracranial saccular aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 1972, 37, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, G.G. Turbulence in human intracranial saccular aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 1970, 33, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, H.; Wang, Z.; Hoi, Y.; Gao, L.; Metaxa, E.; Swartz, D.D.; Kolega, J. Complex hemodynamics at the apex of an arterial bifurcation induces vascular remodeling resembling cerebral aneurysm initiation. Stroke 2007, 38, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.E.; Tu, J.; Qian, Y.; Avolio, A.P. A combination of genetic, molecular and haemodynamic risk factors contributes to the formation, enlargement and rupture of brain aneurysms. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Tutino, V.M.; Xiang, J.; Siddiqui, A. High WSS or Low WSS? Complex interactions of hemodynamics with intracranial aneurysm initiation, growth, and rupture: Toward a unifying hypothesis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Su, M.; Li, M. Association of wall shear stress with intracranial aneurysm rupture: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tremmel, M.; Dhar, S.; Levy, E.I.; Mocco, J.; Meng, H. Influence of intracranial aneurysm-to-parent vessel size ratio on hemodynamics and implication for rupture: Results from a virtual experimental study. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 622–630; discussion 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, C.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.A.; Ma, J.; Xiang, M.; Chen, P. Hypercholesterolaemic serum increases the permeability of endothelial cells through zonula occludens-1 with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 814979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.; Glomset, J.A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 295, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galis, Z.S.; Sukhova, G.K.; Lark, M.W.; Libby, P. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and matrix degrading activityin vulnerable regions of human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, R. Mechanisms of disease: Atherosclerosis—An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Wang, Z.; Kim, M.; Ecker, R.D.; Hopkins, L.N. Saccular aneurysms on straight and curved vessels are subject to different hemodynamics: Implications of intravascular stenting. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, S.; Tremmel, M.; Mocco, J.; Kim, M.; Yamamoto, J.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Hopkins, L.N.; Meng, H. Morphology parameters for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baharoglu, M.I.; Schirmer, C.M.; Hoit, D.A.; Gao, B.-L.; Malek, A.M. Aneurysm inflow-angle as a discriminant for rupture in sidewall cerebral aneurysms: Morphometric and computational fluid dynamic analysis. Stroke 2010, 41, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.M.; Hsiai, T.; Wortham, C.M.; Chen, M.; Lin, H.; Navab, M.; Demer, L.L. A complex flow pattern of low shear stress and flow reversal promotes monocyte binding to endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2001, 158, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffijberg, H.; Buskens, E.; Algra, A.; Wermer, M.J.; Rinkel, G.J. Growth rates of intracranial aneurysms: Exploring constancy. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.K.; Ball, B.Z.; Cheaney, B., II; Sweidan, A.J.; Hasjim, B.J.; Hsu, F.P.; Wang, A.S.; Lin, L.-M. Multimodal management of giant cerebral aneurysms: Review of literature and case presentation. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbate, P.M.; Hasan, A.T.M.H.; Venier, A.; Vauclin, V.; Pizzuto, S.; Sgreccia, A.; Maria, F.D.; Coskun, O.; Mizutani, K.; Rodesch, G.; et al. The Cerebral Arterial Wall in the Development and Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125964
Abbate PM, Hasan ATMH, Venier A, Vauclin V, Pizzuto S, Sgreccia A, Maria FD, Coskun O, Mizutani K, Rodesch G, et al. The Cerebral Arterial Wall in the Development and Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125964
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbate, Pasquale Marco, A. T. M. Hasibul Hasan, Alice Venier, Vincent Vauclin, Silvia Pizzuto, Alessandro Sgreccia, Federico Di Maria, Oguzhan Coskun, Katsuhiro Mizutani, Georges Rodesch, and et al. 2022. "The Cerebral Arterial Wall in the Development and Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125964
APA StyleAbbate, P. M., Hasan, A. T. M. H., Venier, A., Vauclin, V., Pizzuto, S., Sgreccia, A., Maria, F. D., Coskun, O., Mizutani, K., Rodesch, G., & Consoli, A. (2022). The Cerebral Arterial Wall in the Development and Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125964





