Source Model and Seismogenic Environment of the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan, China—Based on InSAR Observation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
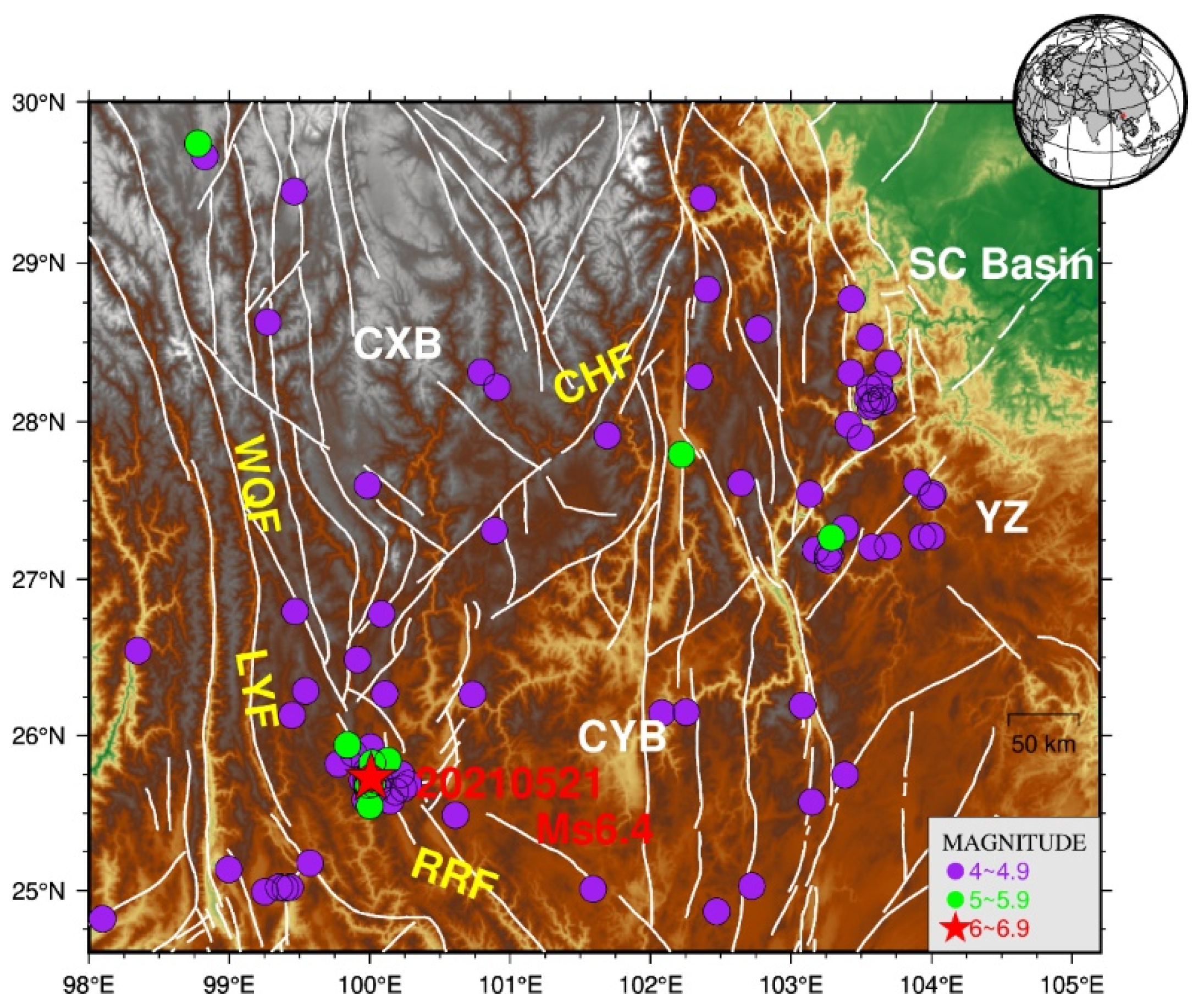
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. InSAR Observations
3.2. Coseismic Deformation
4. Slip Model Inversion
4.1. Source Parameter Inversion
4.2. Distribution Slip Inversion
5. Discussion
5.1. Seismogenic Fault
5.2. Static Coulomb Stress Changes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, G.M.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.G.; Fan, W.J.; Liu, Z.F. Characteristics of the 2021 Yangbi Ms 6.4 Earthquake Sequence and Prediction of Its Strong Aftershocks. J. Seismol. Res. 2021, 3, 309–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C.; Wang, H.L.; Duan, Y.; Sun, Z.G. Focal Mechanism Solution of the M6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan. Earthq. Res. Sichuan 2021, 12, 2852–2860. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.S.; Helmberger, D.V. Source estimation from broadband regional seismograms. Bull. Seimol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.P.; Helmberger, D.V. Advancement in source estimation techniques using broadband regional seismograms. Bull. Seimol. Soc. Am. 1996, 86, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.L.; Gan, W.J.; Liang, S.M.; Xiao, G.R.; Dai, C.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, G.Q. Coseismic displacement and slip distribution of the 2021 May 21, Ms 6.4, Yangbi Earthquake derived from GNSS observations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 2253–2266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tian, J.H. Rupture process of Yunnan Yangbi Ms 6.4 earthquake constrained by regional broadband seismograms. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 1021–1031. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.L.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Deng, Q.D.; Zhang, G.M.; Ma, J.; Gan, W.J.; Min, W.; Mao, F.Y.; Wang, Q. Strong earthquakes and active plots in mainland China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 9 (Suppl. 1), 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Ding, Z.F.; Wu, P.P.; Liu, S.; Deng, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H. The characteristics of crustal structure and seismogenic background of Yangbi Ms6.4 earthquake on May 21,2021 in Yunnan Province, China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 3083–3100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T. Relocation of the Yangbi Ms 6.4 Earthquake Squence in 2021 and Discussion of Its Seismogenic Fault. J. Seismol. Res. 2021, 3, 320–329. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Shen, Z.K.; Wang, M.; Gai, W.-J. Kinematics of Present-Day Tectonic Deformation of the Tibetan Plateau and Its Vicinities. Seismol. Geol. 2004, 26, 367–377. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Response of Channel Offsets to Sextral-Slip Movement of the Red River Fault Zone. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.R.; Gillepsie, A.R.; Han, Y.; Sieh, K.E.; Buchun, Z.; Chengnan, Z. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan province, China: Quaternary geology, slip rate and seismic hazard. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1984, 95, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Replimaz, A.; Lacassin, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Leloup, P. Large river offsets and Plio-Quaternary dextral slip rate on the Red River fault (Yunnan, China). J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.L.; Jin, M.P.; Miao, S.Q. Slip Model and Co-seismic Displacement Field of the 2021, Yangbi, Yunnan Ms 6.4 Earthquake. J. Seismol. Res. 2021, 44, 330–337. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Hu, X.L.; Zang, Y. Intensity distribution characteristics and active tectonic background in area of the 2013 Eryuan Ms5.5 earthquake. Earthq. Res. China 2014, 30, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Cai, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Deep medium environment of strong earthquakes occurrence in Yunnan region. Acta Seismol. Sin. 1999, 12, 345–356. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.P.; Han, X.M.; Gu, Y.S.; He, W.; Luo, R.L. Research on Strong Earthquakes in Yunnan Area; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.J.; He, P.; Wen, Y.M.; Liu, Y. Rencent advances InSAR interferometry and its applications. J. Geomat. 2015, 40, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Xu, C.J.; Wen, Y.M.; Wang, S.; Xu, G.Y.; Xiao, Z.H.; Fang, L.H. The 2016 Mw 6.0 Hutubi earthquake: A blind thrust event along the northern Tian Shan front. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 173, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Xu, C.J.; Xiao, Z.H.; Peng, Y. Source model for buried thrust-dominated earthquakes using partial InSAR displacements: The 2018 Lombok, Indonesia, earthquake sequence. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 229, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.M.; Xu, C.J.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.P.; Shan, X.J. Coseismic and postseismic deformation of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake from InSAR. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 1814–1824. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.J.; Qu, C.Y.; Gong, W.Y.; Zhao, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, G.H.; Song, X.G.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, G.F. Coseismic deformation field of the Jiuzhaigou Ms 7.0 earthquake from Sentinel-1A InSAR data and fault slip inversion. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 4527–4536. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Zhang, G.H.; Shan, X.J.; Qu, C.Y.; Gong, W.Y.; Jia, R.; Zhao, D.Z. Coseismic deformation and slip distribution of the M_(S)6.4 Jiashi, Xinjiang earthquake revealed by Sentinel-1A SAR imagery. Prog. Geophys. 2021, 36, 481–488. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.C. The Technic and Application of InSAR. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, P.; Spingos, I.; Kaviris, G.; Karavias, A.; Gatsios, T.; Sakkas, V.; Parcharidis, I. Combined Geodetic and Seismological Study of the December 2020 Mw = 4.6 Thiva (Central Greece) Shallow Earthquake. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshadi, Z.; Famiglietti, N.A.; Atzori, S.; Vicari, A. Surface Displacement and Source Parameters of the 2021 Bandar-e Genaveh, Iran, Earthquake Determined from InSAR Observations. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.R.; Mellors, X.T.; Wei, M.; Wessel, P. Open radar interferometry software for mapping surface deformation. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 92, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, T.G.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 81, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, K.; Shan, X.J. The seismogenic fault of the 2021 Yunnan Yangbi Ms 6.4 earthquake. Seismol. Egol. 2021, 43, 706–721. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C. Inversion Methods for the Focal Mechanisms of Small Earthquakes and the Stress Field and Their Application; Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Xie, Z.J. Present Status and Prospect of Earthquake Focal Depth Locating. Seismol. Geol. 2017, 40, 167–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Han, M. Coseismic deformation and fault slip inversion of the 2017MW7.3 Halabjah, Iraq, earthquake based on Sentinel-1A data. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2019, 41, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.P.; Li, Z.H. A novel hybrid PSO/simplex algorithm for determining earthquake source parameters using InSAR data. Prog. Geophys. 2010, 25, 1189–1196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Shan, X.J.; Qu, C.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; Xie, Z.D.; Zhao, D.Z.; Fan, X.R.; Hua, J.; Liang, S.M.; et al. Coseismic surface deformation and slip models of the 2021 Ms 6.4 Yangbi (Yunnan, China) earthquake. Seismol. Geol. 2021, 43, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Wen, Y.M.; Xu, C.J. The 21 May 2021 Ms 6.4 Yangbi (Yunnan) earthquake: A shallow strike-slip event rupturing in blind fault. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 3101–3110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.F.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, G.Y.; Xu, J. Preliminary Analysis on Seismicity of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block after the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan. Earthq. Res. Sichuan 2021, 3, 5–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.K.; Qu, Y.J.; Li, Y.L.; Zheng, J.C.; Hua, A.J.; Dai, L.; Hou, H.F. Some statistic features of aftershock sequences in Chinese mainland. Chin. J. Geophys. 2006, 49, 1110–1117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.Z.; Yang, J.Q. Microseismic detection and relocation of the 2017 Ms 4.8 and Ms 5.1 Yangbi earthquake sequence, Yunnan. Earthq. Sci. 2020, 42, 527–542. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.M.; Wu, Z.H.; Peng, G.L.; Zifeng, L.; Ruijie, L.; Xiaolong, H.; Haopeng, C. Seismogenic fault and it’s rupture characteristics of the 21 May, 2021 Yangbi Ms 6.4 earthquake: Analysis results from the relocation of the earthquake sequence. J. Geomech. 2021, 27, 662–678. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.G.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.F. Seismogenic Structure of the 2021 Yangbi, Yunnan Ms 6.4 Earthquake and Earthquake Risk Analysis in the Epicenter Area. J. Seismol. Res. 2021, 44, 380–390. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology, SSB and Seismological Bureau of Yunnan Province. Active Faults in the Northwest Yunnan Region; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 69–128. [Google Scholar]
- Freed, A.M. Earthquake triggering by static, dynamic, and postseismic stress transfer. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 335–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Tan, K. Study on the reliability of coulomb stress change induced by the 2008 Wenchuan Mw 7.9 earthquake. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 40, 692–696+707. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A. Introduction to Special Section: Stress Triggers, Stress Shadows, and Implications for Seismic Hazard. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1998, 103, 24347–24358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Simpson, R.W. Suppression of large earthquakes by stress shadows: A comparison of Coulomb and rate-and-state failure. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 24439–24451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Yu, G.H.; Ma, W.T.; Chen, W.B.; Wen, X.Z. Model of Latest Crustal Tectonic Motion of the Central Tectonic Zone on the Mainland of China. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 160–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.X.; Ji, L.Y.; Zhu, L.Y.; Wang, G.M.; Zhang, W.T.; Li, N. The Co-seismic Deformation Characteristics and Seismogenic Structure of the Yangbi Ms 6.4 Earthquake. Seismol. Geol. 2021, 43, 771–789. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Toda, S.; Stein, R.S.; Richards-Dinger, K.; Bozkurt, S.B. Forecasting the evolution of seismicity in southern California: Animations built on earthquake stress transfer. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, B05S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, L.K.; Phillips, W.S.; Mackey, K.; Begnaud, M.L.; Stead, R.J.; Rowe, C.A. Seismic tomography of crustal P and S across Eurasia. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 177, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Satellite | Master | Slave | Mode | Polar | t/d | Orbit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1A | 8 May 2021 | 1 June 2021 | IW | VV | 24 | Ascending |
| Sentinel-1A | 10 May 2021 | 22 May 2021 | IW | VV | 12 | Descending |
| Longitude/° | Latitude/° | I | II | Depth/km | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strike/° | Dip/° | Slip/° | Strike/° | Dip/° | Slip/° | ||||
| USGS | 100.01 | 25.77 | 135 | 82 | −165 | 43 | 75 | −9 | 17.5 |
| GCMT | 100.02 | 25.61 | 46 | 78 | 4 | 315 | 86 | 168 | 15 |
| GFZ | 99.92 | 25.73 | 319 | 88 | −165 | 229 | 75 | −1 | 17 |
| Wang et al. | 99.91 | 25.65 | 134.88 | 80 | −170 | 4.92 | |||
| Yang et al. | 99.934 | 25.644 | 139 | 81 | −170 | 6 | |||
| Our study | 99.87 | 25.67 | 132.4 | 76.2 | −176.3 | 13 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Yan, H. Source Model and Seismogenic Environment of the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan, China—Based on InSAR Observation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125908
Li W, Huang Y, Wang X, Jiang X, Li X, Xie X, Wang Q, Yan H. Source Model and Seismogenic Environment of the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan, China—Based on InSAR Observation. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Yutong Huang, Xiaohang Wang, Xin Jiang, Xiaotong Li, Xukang Xie, Qianwen Wang, and Haowen Yan. 2022. "Source Model and Seismogenic Environment of the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan, China—Based on InSAR Observation" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125908
APA StyleLi, W., Huang, Y., Wang, X., Jiang, X., Li, X., Xie, X., Wang, Q., & Yan, H. (2022). Source Model and Seismogenic Environment of the Ms 6.4 Yangbi Earthquake in Yunnan, China—Based on InSAR Observation. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125908







