Learning Robust Shape-Indexed Features for Facial Landmark Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
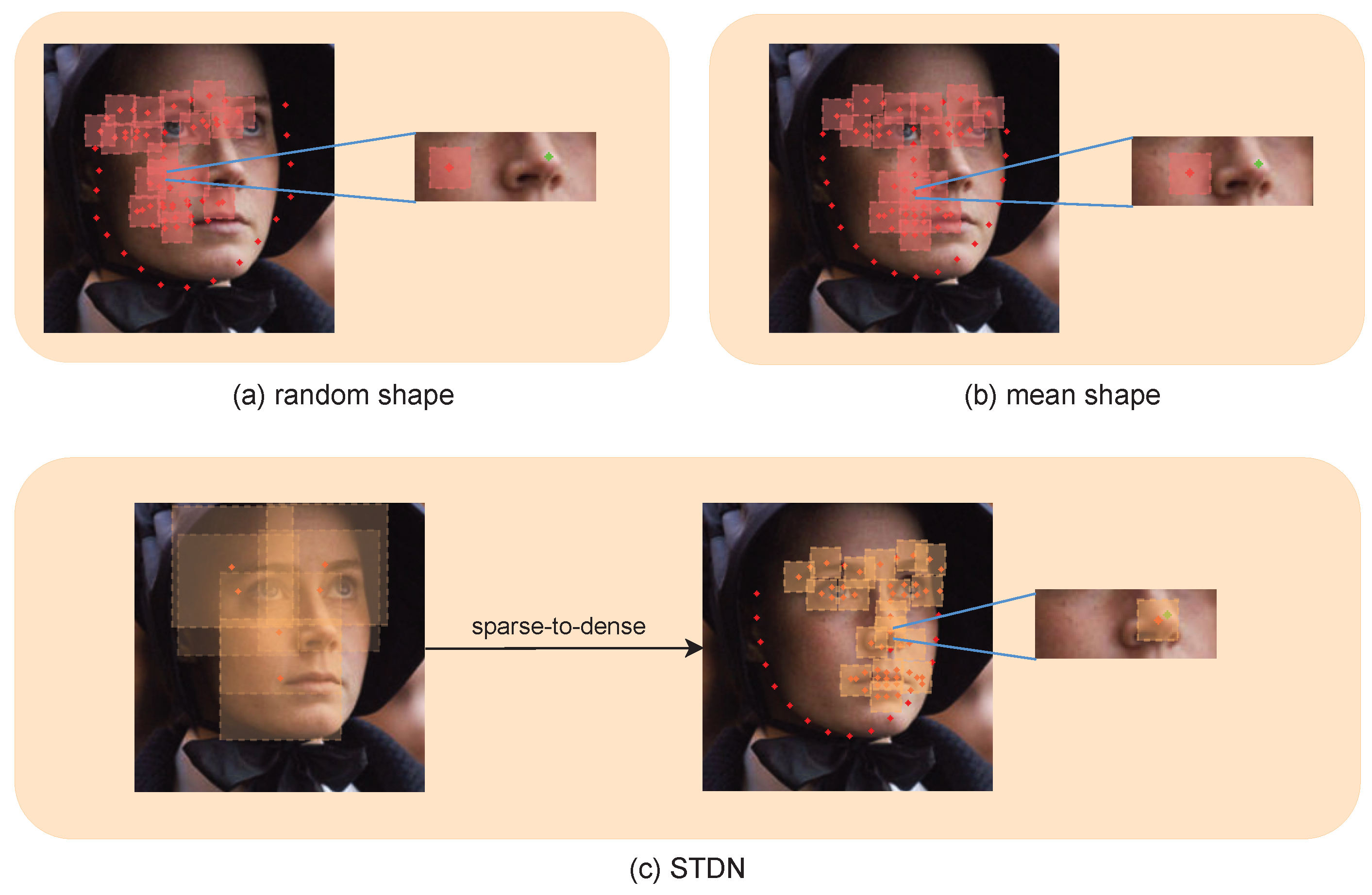
- We propose a sparse-to-dense network (STDN), a two-stage framework, to reduce the noise data with large pose variations and address the severe occlusion problem;
- We suggest a sparse to dense patch sampling strategy to efficiently improve the quality of the cropped local patches with large pose variations;
- We take advantage of a group-relational module to handle the severe occlusion problem, which learns the geometric relations between facial components to enhance the shape constraint against occlusion.
2. Related Work
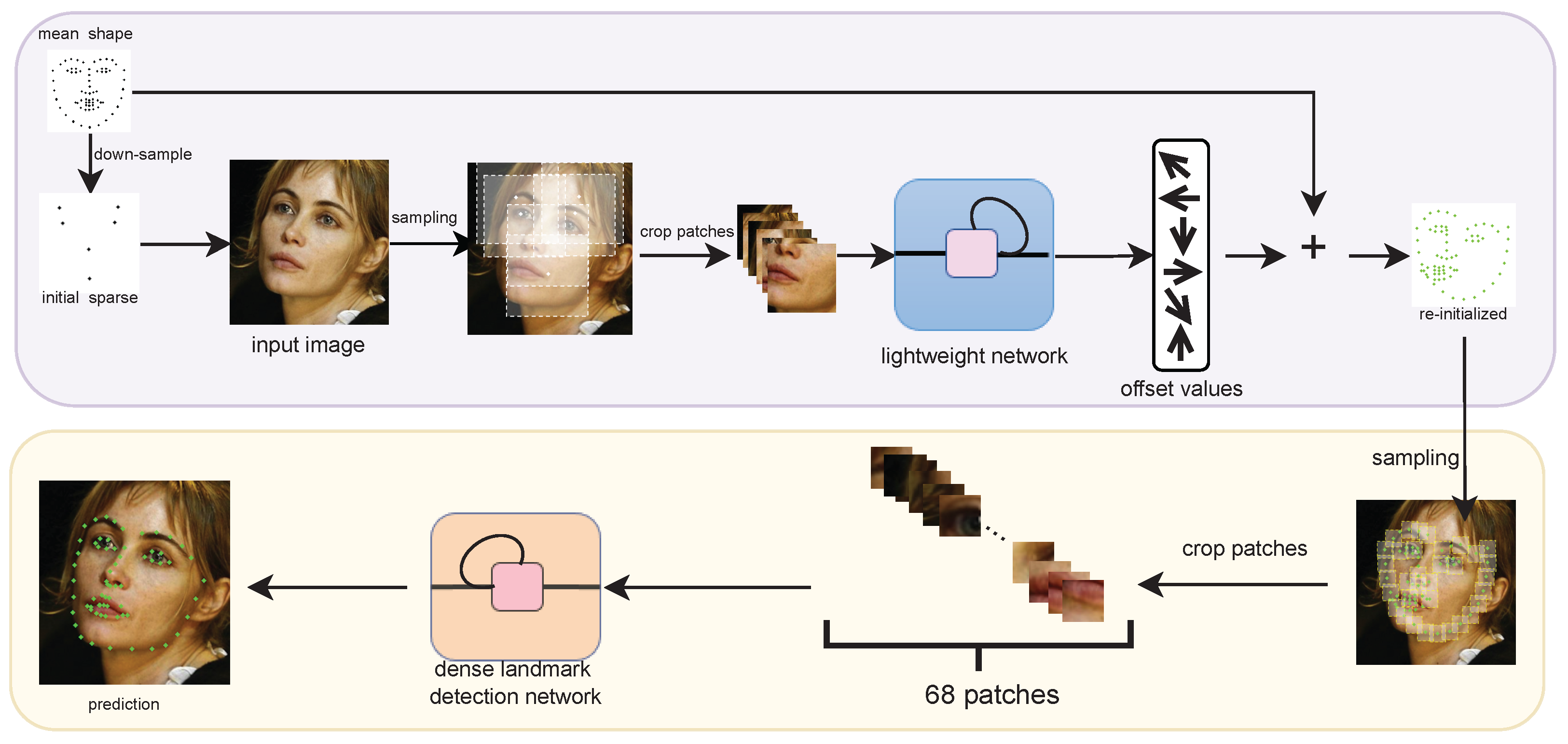
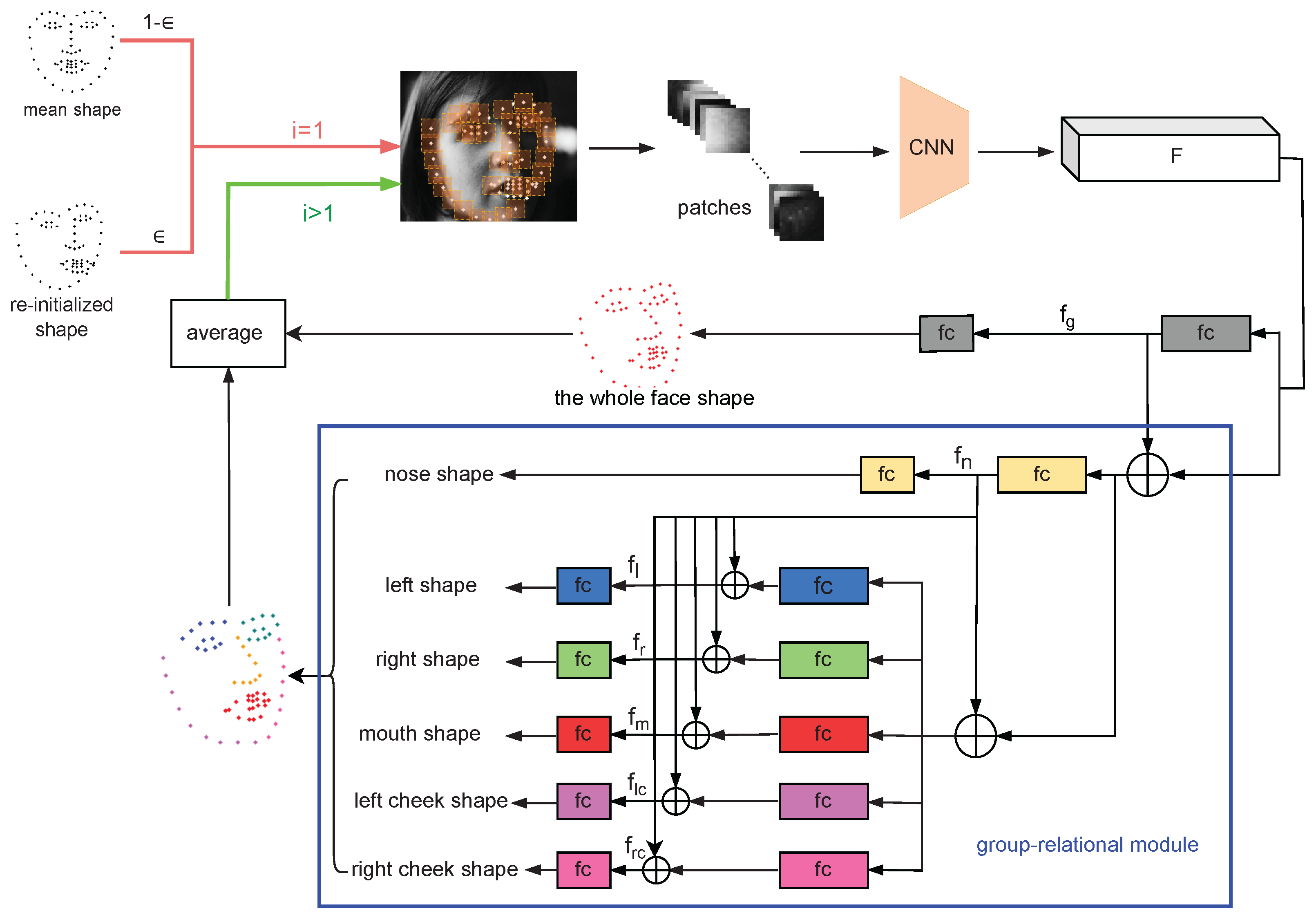
3. Methods
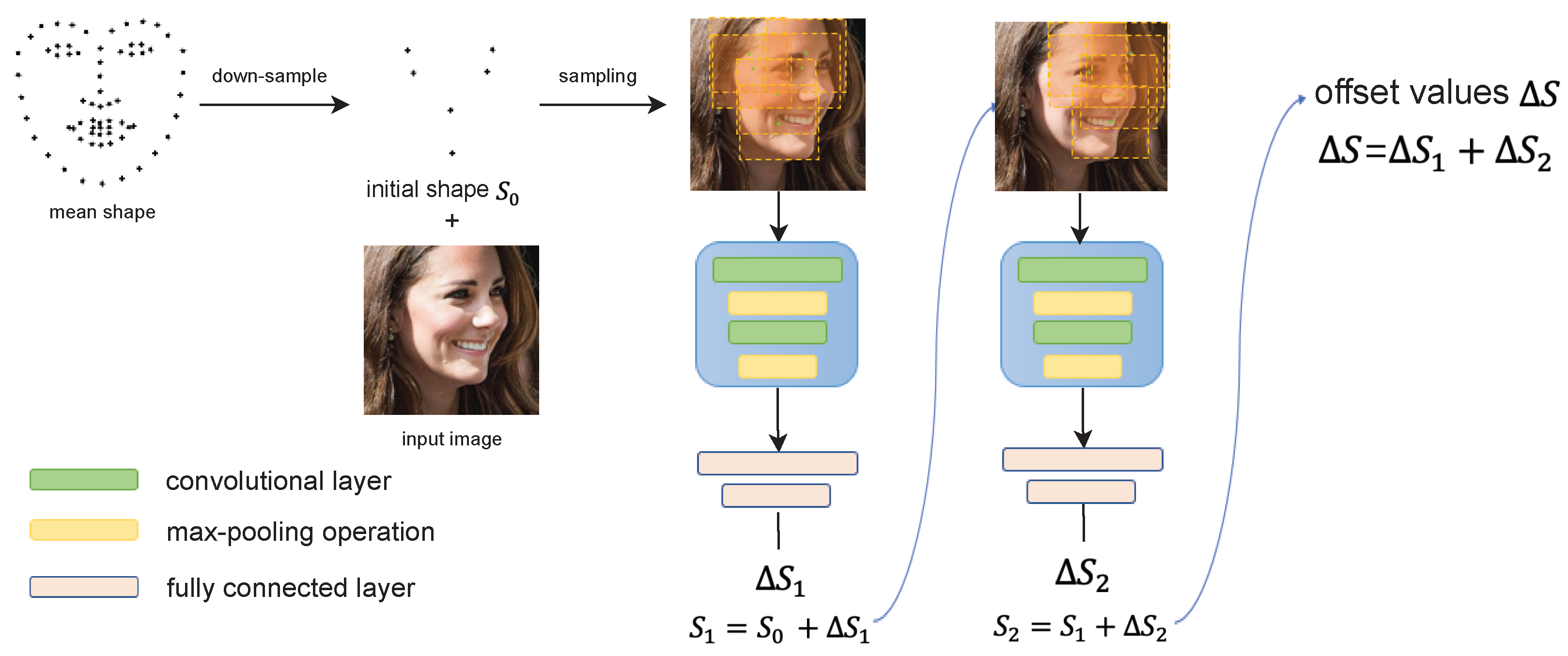
3.1. Patch Resampling Stage
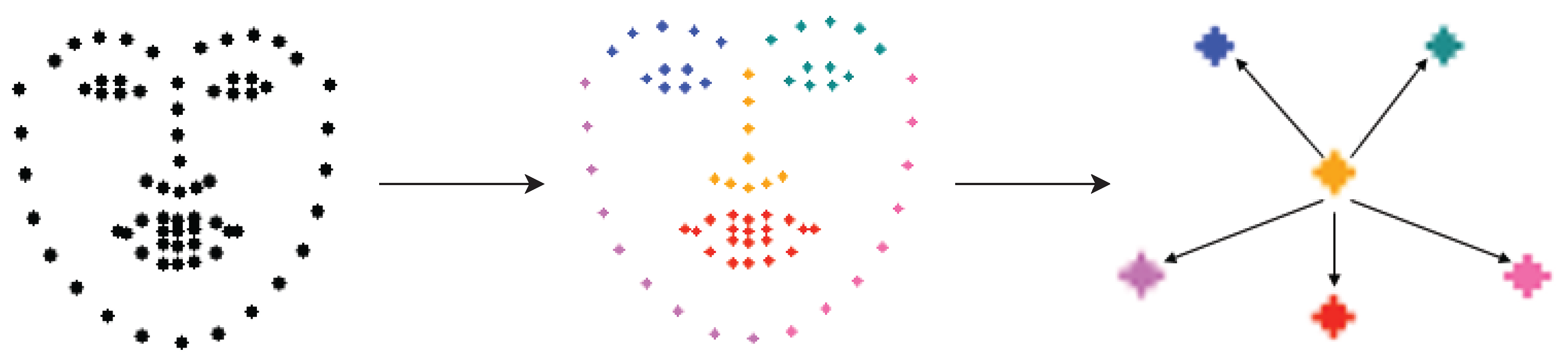
3.2. Relation Reasoning Stage
4. Experimentation
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
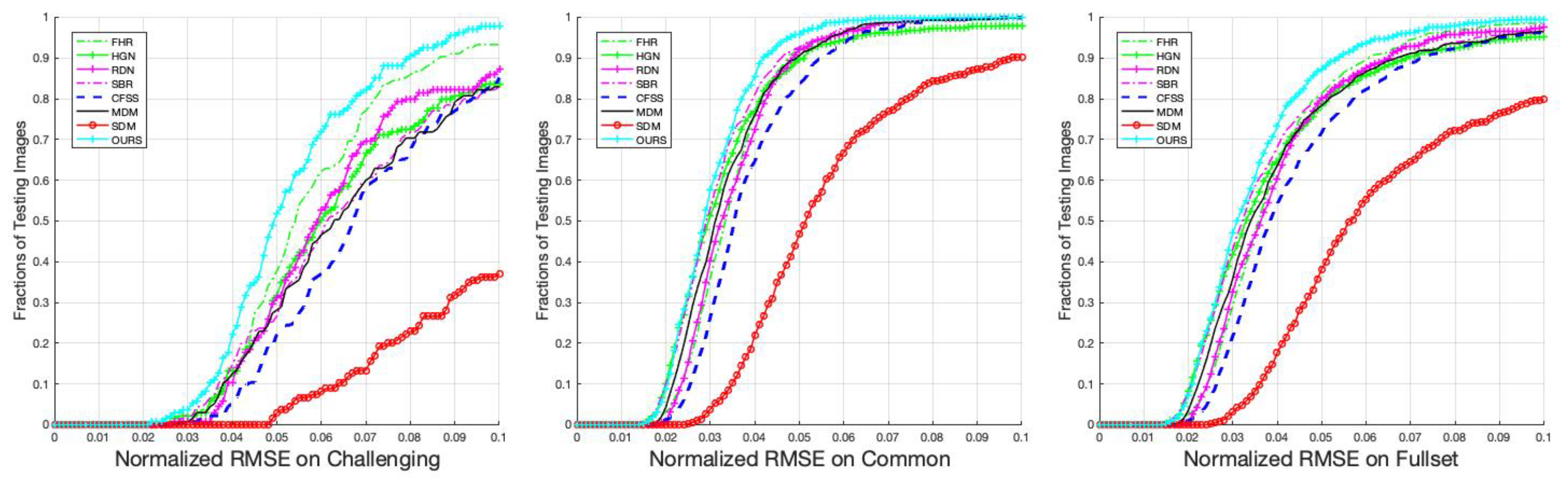
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
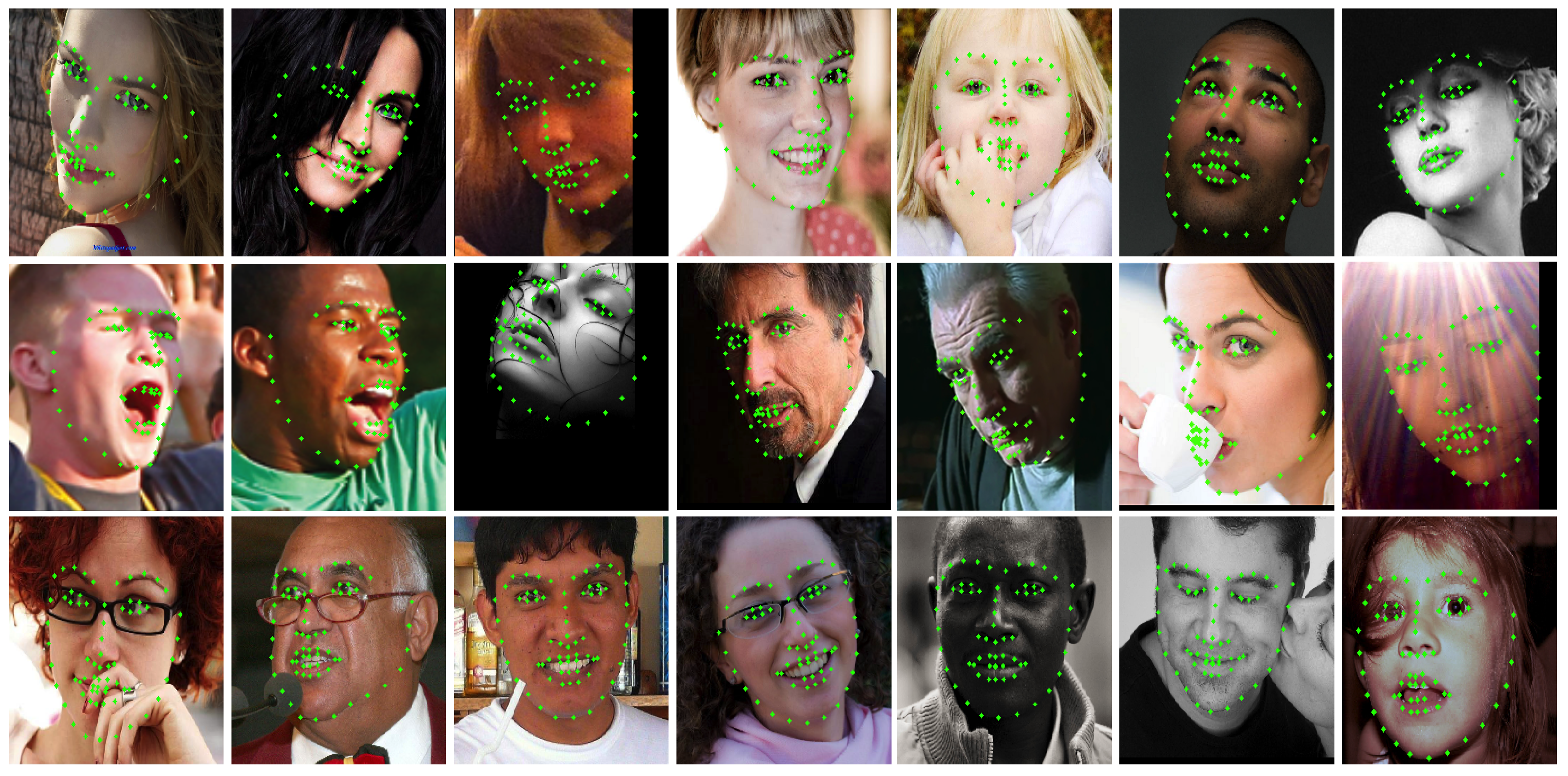
4.3.1. Evaluation on the 300 W Dataset
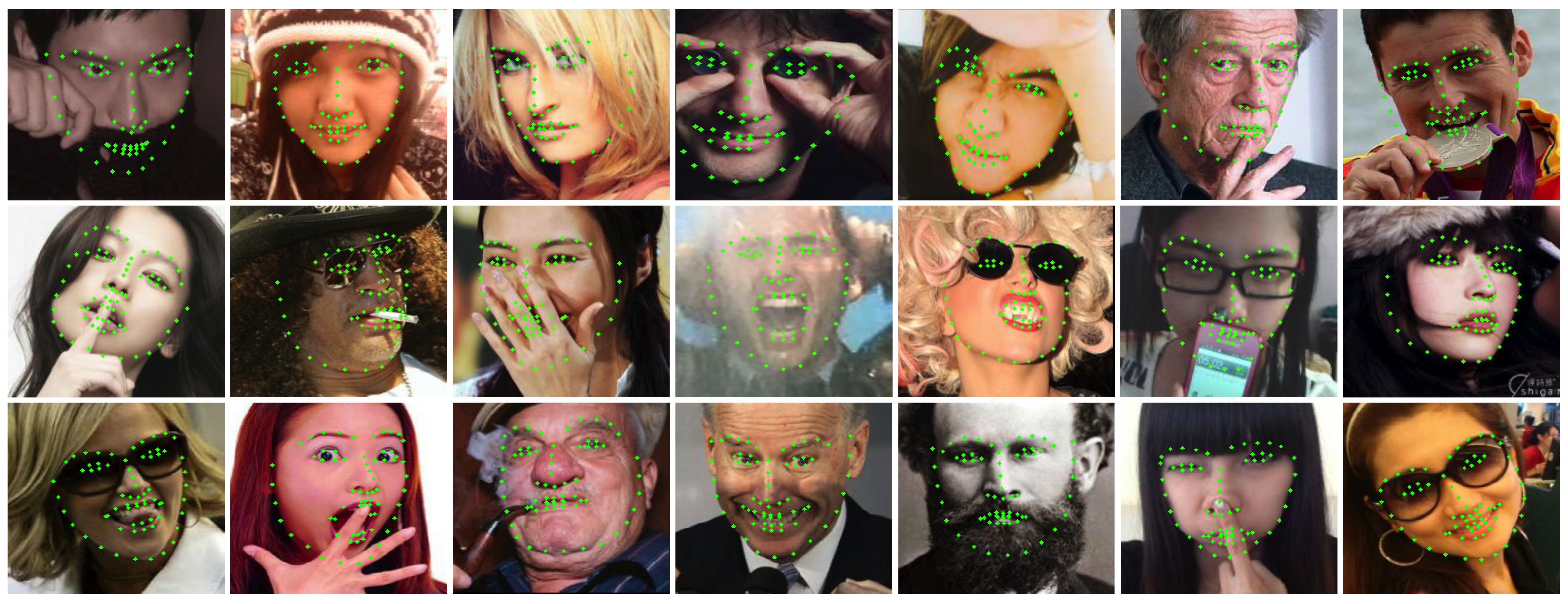
4.3.2. Evaluation on COFW68 Dataset
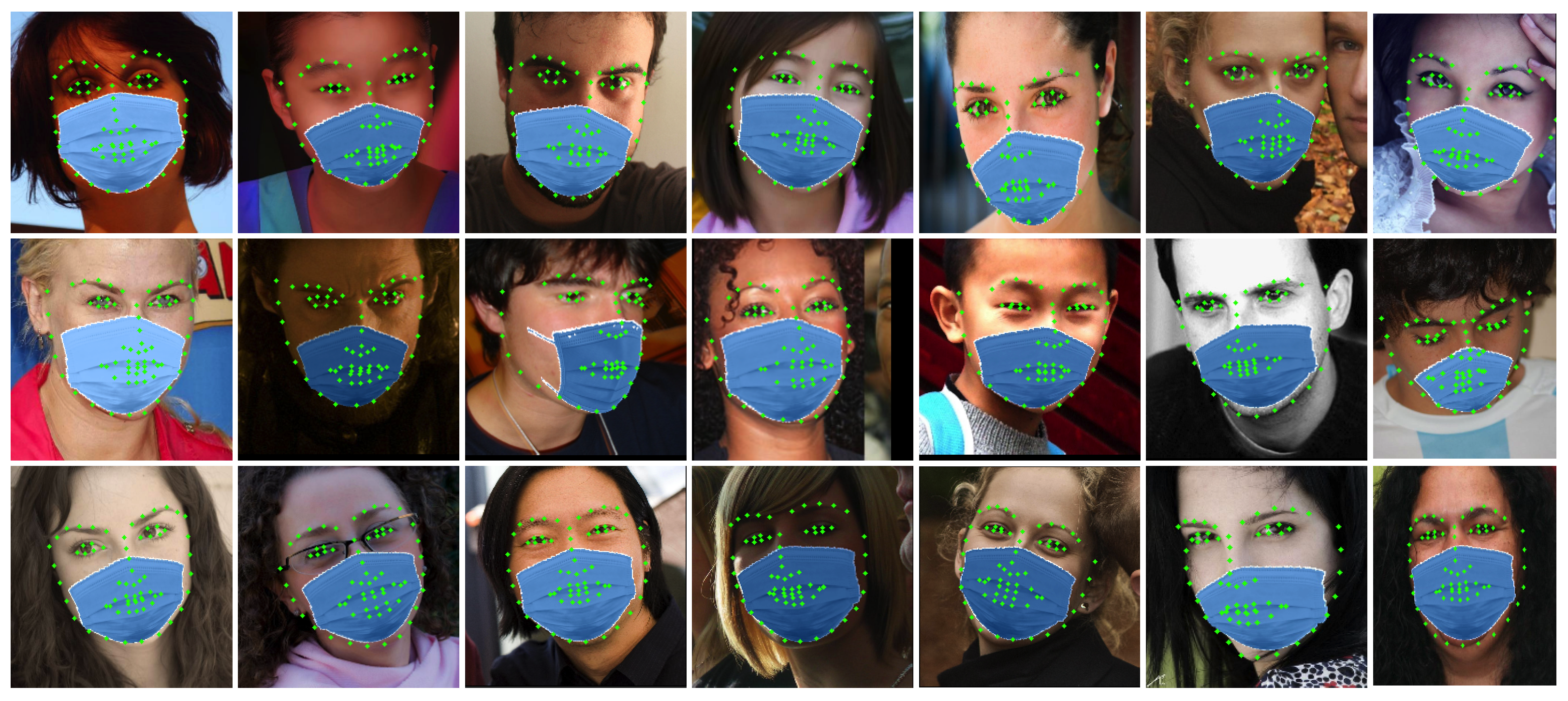
4.3.3. Evaluation on Masked 300 W Dataset
4.3.4. Analysis
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Investigation of the Effectiveness of the Two Stages
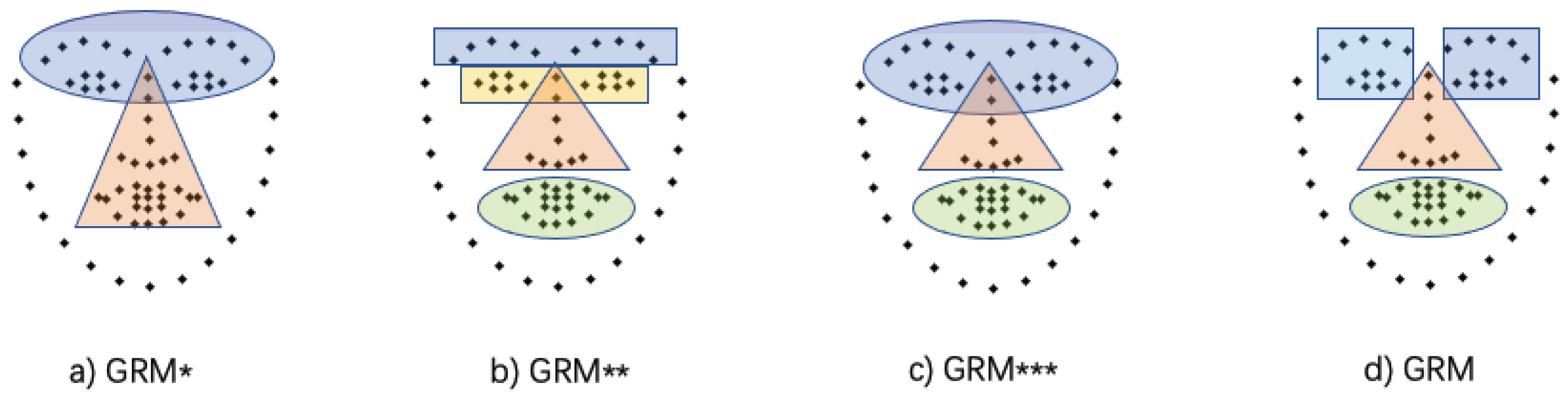
4.4.2. Investigation of Different Group Strategies
4.4.3. Investigation of Hyperparameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, F.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.T.; Wu, J. Ecml: An ensemble cascade metric-learning mechanism toward face verification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 1736–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoud, A.; Oumane, A.; Ouafi, A.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. Multimodal 2d+ 3d multi-descriptor tensor for face verification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 23071–23092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Nagpal, S.; Singh, R.; Vatsa, M. Disguise resilient face verification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z. Identity–expression dual branch network for facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 13, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lai, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.-F. Infrared facial expression recognition via gaussian-based label distribution learning in the dark illumination environment for human emotion detection. Neurocomputing 2020, 409, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, D.K.R.; Ansari, M.D.; Vuppala, S.; Gunjan, V.K.; Sati, M.M. Human facial emotion detection using deep learning. In ICDSMLA 2020; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 1417–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Cao, G.; Zhou, F.; Liu, B.; Duan, J.; Qiu, G. Towards disentangling latent space for unsupervised semantic face editing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, H.; Shen, L.; Lai, Z.; Wan, J. Guidedstyle: Attribute knowledge guided style manipulation for semantic face editing. Neural Netw. 2022, 145, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Khan, M.; Ansari, M.D. Face recognition algorithm based on stack denoising and self-encoding lbp. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 31, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talab, M.A.; Awang, S.; Ansari, M.D. A novel statistical feature analysis-based global and local method for face recognition. Int. J. Opt. 2020, 2020, 4967034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. Look at boundary: A boundary-aware face alignment algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2129–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Trigeorgis, G.; Snape, P.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Antonakos, E.; Zafeiriou, S. Mnemonic descent method: A recurrent process applied for end-to-end face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4177–4187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Dai, S.; Tong, W. Reasoning structural relation for occlusion-robust facial landmark localization. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 122, 108325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cootes, T.F.; Taylor, C.J.; Cooper, D.H.; Graham, J. Active shape models-their training and application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1995, 61, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgos-Artizzu, X.P.; Perona, P.; Dollár, P. Robust face landmark estimation under occlusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1513–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, E.; Cao, Z. Coarse-to-fine face alignment with multi-scale local patch regression. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.04901. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Face alignment with deep regression. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 29, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Tao, D. Adaptive cascade regression model for robust face alignment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-H.; Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, I.-J. Face alignment using a deep neural network with local feature learning and recurrent regression. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 89, 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Shao, X.; Xing, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, X. A deep regression architecture with two-stage re-initialization for high performance facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3317–3326. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.-H.; Kittler, J.; Christmas, W.; Huber, P.; Wu, X.-J. Dynamic attention-controlled cascaded shape regression exploiting training data augmentation and fuzzy-set sample weighting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2481–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Wei, Y.; Wen, F.; Sun, J. Face alignment by explicit shape regression. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2887–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Ji, Q. Shape augmented regression method for face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Feng, J.; Xing, J.; Lai, H.; Yan, S.; Kassim, A. Robust facial landmark detection via recurrent attentive-refinement networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, Y. Style aggregated network for facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Peng, X.; Geng, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, S.; Metaxas, D. Quantized densely connected u-nets for efficient landmark localization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 339–354. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, H. Face alignment by discriminative feature learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 2204–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bo, L.; Fuxin, L. Adaptive wing loss for robust face alignment via heatmap regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 6971–6981. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiang, W. Residual neural network and wing loss for face alignment network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 14th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE), Dalian, China, 14–16 November 2019; pp. 1093–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, P.; Bradley, D.; Gross, M.; Beeler, T. Attention-driven cropping for very high resolution facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5861–5870. [Google Scholar]
- Browatzki, B.; Wallraven, C. 3fabrec: Fast few-shot face alignment by reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6110–6120. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Chellappa, R. Disentangling 3d pose in a dendritic cnn for unconstrained 2d face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 430–439. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, D.; Zheng, M.; Sadiq, M. Robust facial landmark detection via occlusion-adaptive deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3486–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Marks, T.K.; Mou, W.; Wang, Y.; Jones, M.; Cherian, A.; Koike-Akino, T.; Liu, X.; Feng, C. Luvli face alignment: Estimating landmarks’ location, uncertainty, and visibility likelihood. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8236–8246. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Lai, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhou, J.; Gao, C.; Xiao, G.; Hou, X. Robust facial landmark detection by cross-order cross-semantic deep network. Neural Netw. 2021, 136, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Chang, J.; Wan, J.; Ma, J. Multi-task adversarial autoencoder network for face alignment in the wild. Neurocomputing 2021, 437, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Dai, S. Improving robustness of facial landmark detection by defending against adversarial attacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11751–11760. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.; Du, B.; Wu, J.; Wan, J.; Xiao, Y. Robust face alignment by dual-attentional spatial-aware capsule networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, R.; Zhou, J.; Tao, L.; Kwan, H.K. Multistage model for robust face alignment using deep neural networks. Cogn. Comput. 2022, 14, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.P.; Mahoor, M.H. Facial landmark points detection using knowledge distillation-based neural networks. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 215, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagonas, C.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Zafeiriou, S.; Pantic, M. 300 faces in-the-wild challenge: The first facial landmark localization challenge. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 December 2013; pp. 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Fowlkes, C.C. Occlusion coherence: Localizing occluded faces with a hierarchical deformable part model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2385–2392. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Sun, K.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Jia, J. Aggregation via separation: Boosting facial landmark detector with semi-supervised style translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 10153–10163. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Guan, W.; Li, P.; Ikeda, N.; Hirasawa, K.; Lu, H. Residual multi-task learning for facial landmark localization and expression recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Face alignment by coarse-to-fine shape searching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4998–5006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Guo, M.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J. Learning reasoning-decision networks for robust face alignment. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 42, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; De la Torre, F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yu, S.-I.; Weng, X.; Wei, S.-E.; Yang, Y.; Sheikh, Y. Supervision-by-registration: An unsupervised approach to improve the precision of facial landmark detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, L.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, F.; Chen, Y. Towards highly accurate and stable face alignment for high-resolution videos. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8893–8900. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Niu, Z.; Huang, J.; Hu, W.; Yan, S. Towards multi-view and partially-occluded face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1829–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Learning deep representation for face alignment with auxiliary attributes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.; Cao, X.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Face alignment via regressing local binary features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G. How far are we from solving the 2d & 3d face alignment problem? (and a dataset of 230,000 3d facial landmarks). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Deng, Z.; Sun, X. Learning spatial-temporal deformable networks for unconstrained face alignment and tracking in videos. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Layers | Input Shape | Output Shape | Kernel |
|---|---|---|---|
| conv1 | |||
| pool1 | |||
| conv2 | |||
| pool2 | |||
| fc1 | - | ||
| fc2 | - |
| Layers | Input Shape | Output Shape | Kernel |
|---|---|---|---|
| conv1 | |||
| pool1 | |||
| conv2 | |||
| pool2 | |||
| conv3 | |||
| pool3 | |||
| fc1 | - | ||
| fc2 | - |
| Method | Challenging | Common | Full | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heatmap regression | LAB [11] (2018) | 5.19 | 2.98 | 3.41 |
| SAN [26] (2018) | 6.60 | 3.34 | 3.98 | |
| DFL [28] (2019) | 7.20 | 4.11 | 4.72 | |
| RWAN [30] (2019) | 7.37 | 3.21 | 3.97 | |
| ADC [31] (2020) | 7.04 | 2.83 | 4.23 | |
| 3FabRec [32] (2020) | 5.74 | 3.36 | 3.82 | |
| MTAAE [37] (2021) | 7.48 | 4.30 | 5.30 | |
| Coordinate regression | MDM [12] (2016) | 7.48 | 4.03 | 4.46 |
| DR [18] (2016) | 13.80 | 4.51 | 6.31 | |
| TR-DRN [21] (2017) | 7.56 | 4.36 | 4.99 | |
| ODN [34] (2019) | 6.67 | 3.56 | 4.17 | |
| AVS [44] (2019) | 6.49 | 3.21 | 3.86 | |
| SRN [13] (2021) | 5.86 | 3.08 | 3.62 | |
| RMTL [45] (2021) | 5.50 | 3.00 | 3.49 | |
| mnv2 [41] (2022) | 6.13 | 3.56 | 4.06 | |
| STDN (Ours) | 5.33 | 3.02 | 3.44 |
| Method | NME | FR (0.1) |
|---|---|---|
| HPM [43] (2014) | 7.46 | - |
| OSRD [52] (2014) | 9.27 | - |
| TCDCN [53] (2015) | 8.05 | 6.31 |
| LBF [54] (2016) | 13.7 | - |
| CRASM [19] (2016) | 8.02 | - |
| MDM [12] (2016) | 6.32 | 4.31 |
| LAB [11] (2018) | 4.62 | 2.17 |
| ODN [34] (2019) | 5.87 | 2.84 |
| STDN (Ours) | 4.64 | 1.97 |
| Method | Challenging | Common | Full |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFSS [46] (2015) | 19.98 | 11.73 | 13.35 |
| MDM [12] (2016) | 15.66 | 8.42 | 9.83 |
| SHG [49] (2016) | 13.52 | 8.17 | 9.22 |
| FAN [55] (2017) | 10.81 | 7.36 | 8.02 |
| SBR [50] (2018) | 15.28 | 9.72 | 10.65 |
| DHGN [56] (2020) | 12.19 | 8.98 | 9.61 |
| STDN (Ours) | 9.64 | 6.51 | 7.12 |
| Method | Challenging | Common | Full |
|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 6.31 | 3.23 | 3.82 |
| baseline + PRS | 5.55 | 3.07 | 3.55 |
| baseline + GRM | 5.58 | 3.05 | 3.54 |
| baseline + PRS + GRM | 5.33 | 3.02 | 3.44 |
| Method | Challenging | Common | Full |
|---|---|---|---|
| STDN with GRM* | 5.57 | 3.09 | 3.57 |
| STDN with GRM** | 5.53 | 3.06 | 3.54 |
| STDN with GRM*** | 5.48 | 3.04 | 3.51 |
| STDN with GRM | 5.33 | 3.02 | 3.44 |
| ϵ | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| NME | 7.28 | 5.41 | 5.40 | 5.41 | 5.38 | 5.33 | 5.41 | 5.45 | 5.46 | 5.59 | 5.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Learning Robust Shape-Indexed Features for Facial Landmark Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125828
Wan X, Wu Y, Li X. Learning Robust Shape-Indexed Features for Facial Landmark Detection. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125828
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Xintong, Yifan Wu, and Xiaoqiang Li. 2022. "Learning Robust Shape-Indexed Features for Facial Landmark Detection" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125828
APA StyleWan, X., Wu, Y., & Li, X. (2022). Learning Robust Shape-Indexed Features for Facial Landmark Detection. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125828






