DriNet: Dynamic Backdoor Attack against Automatic Speech Recognization Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We explored a novel dynamic backdoor attack paradigm in the audio domain (a challenge rarely explored). In our threat model, dynamic triggers are used to attack automatic speech recognition systems, enjoying rich attack styles and greater stealth.
- We introduce a dynamic trigger generation method via the generative adversarial network (GAN) jointly trained with a discriminative model. The effectiveness of backdoor attacks with dynamic triggers is successfully demonstrated.
- Experimental results on two benchmark datasets show the superiority of our method compared to the baseline BadNets. Moreover, an extensive analysis verifies the resistance of the proposed method to the state-of-the-art defense.
2. Related Work
2.1. Automatic Speech Recognition
2.2. Backdoor Attack
2.3. Defense for Backdoor Attack
3. Design of Dynamic Backdoor Attacks
3.1. Treat Model
3.2. Problem Formulation
3.3. Overview of Dynamic Backdoor Attack
3.4. Dynamic Trigger Generation
3.5. DriNet Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Joint training of the target victim model and the trigger generation model |
| Input:
The training dataset Q, the epochs, the loss function , the uniform distribution function (random), the target label l, the backdoor add function , the weight Output: D, G
|
3.6. Poisoning
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Results
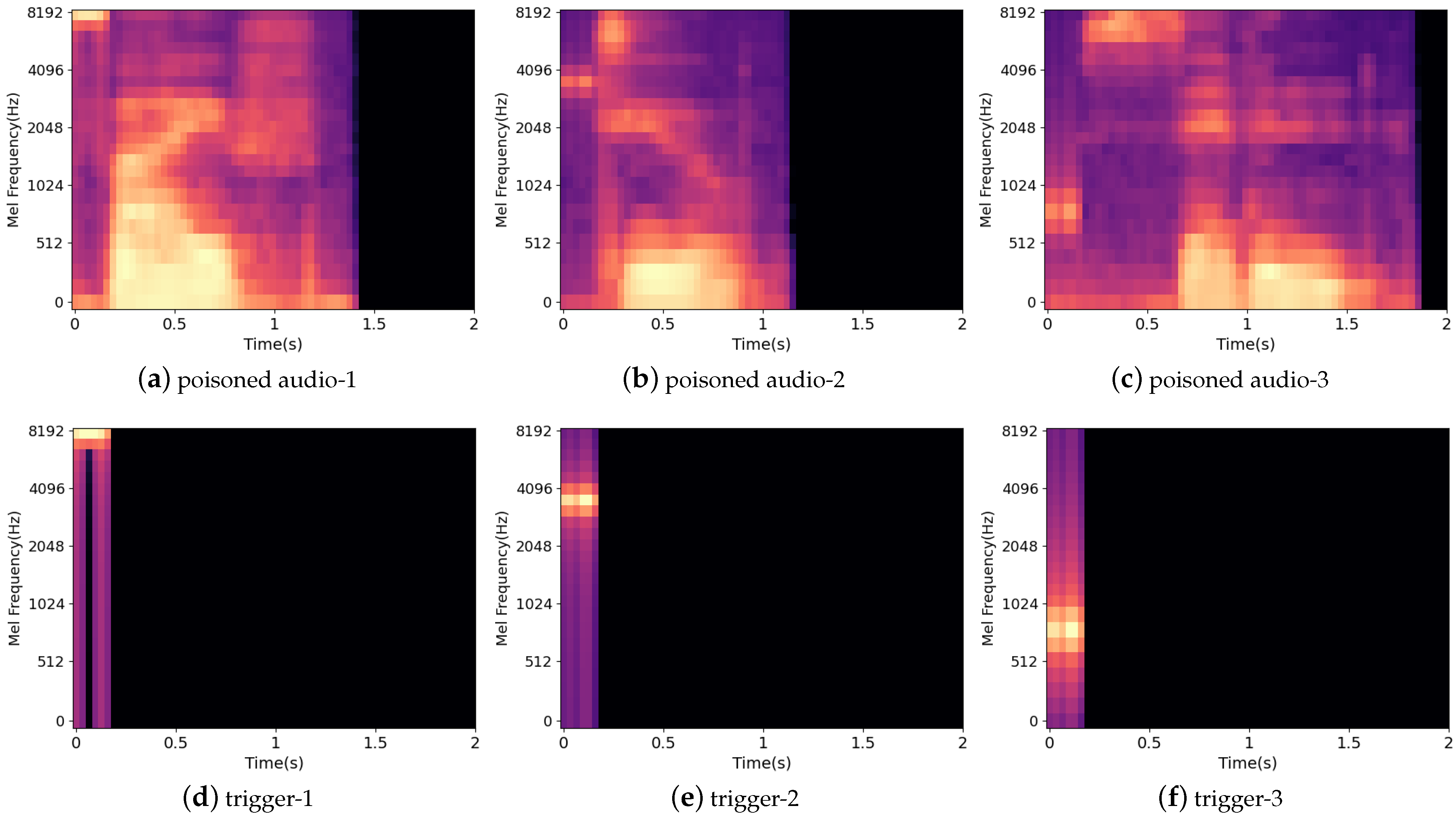
4.4. Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, H.; Warren, K.; Bindschaedler, V.; Papernot, N.; Traynor, P. Sok: The faults in our asrs: An overview of attacks against automatic speech recognition and speaker identification systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 May 2021; pp. 730–747. [Google Scholar]
- Kurakin, A.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Bengio, S. Adversarial examples in the physical world. In Artificial Intelligence Safety and Security; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.; Bhagavatula, S.; Bauer, L.; Reiter, M.K. Accessorize to a crime: Real and stealthy attacks on state-of-the-art face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 1528–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, S.T. Backdoor attack against speaker verification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2560–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, S.T. Backdoor learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.08745. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Liu, K.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Badnets: Evaluating backdooring attacks on deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47230–47244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Bailey, J.; Lu, F. Reflection backdoor: A natural backdoor attack on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 182–199. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, A.; Wen, R.; Backes, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic backdoor attacks against machine learning models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.03675. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, X.; Zheng, X.; Bailey, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.G. Clean-label backdoor attacks on video recognition models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 14443–14452. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.Y. Latent backdoor attacks on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 2041–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.; Tsipras, D.; Madry, A. Clean-Label Backdoor Attacks. Available online: https://people.csail.mit.edu/madry/lab/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Shan, S.; Li, H.; Viswanath, B.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.Y. Neural cleanse: Identifying and mitigating backdoor attacks in neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; pp. 707–723. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Nepal, S. Strip: A defence against trojan attacks on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, San Juan, PR, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Doan, B.G.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Fu, A.; Nepal, S.; Kim, H. Backdoor attacks and countermeasures on deep learning: A comprehensive review. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.10760. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shaughnessy, D. Automatic speech recognition: History, methods and challenges. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 2965–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Aafer, Y.; Lee, W.; Zhai, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Trojaning Attack on Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, NDSS 2018, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Tran, A. Input-aware dynamic backdoor attack. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 3454–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, J. Adversarial audio: A new information hiding method and backdoor for dnn-based speech recognition models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.03829. [Google Scholar]
- Koffas, S.; Xu, J.; Conti, M.; Picek, S. Can You Hear It? Backdoor Attacks via Ultrasonic Triggers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.14569. [Google Scholar]
- Aghakhani, H.; Schönherr, L.; Eisenhofer, T.; Kolossa, D.; Holz, T.; Kruegel, C.; Vigna, G. VenoMave: Targeted Poisoning against Speech Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.10682. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Huo, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. A Novel Trojan Attack against Co-learning Based ASR DNN System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Dalian, China, 5–7 May 2021; pp. 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, S.; Ackermann, M.; Lapuschkin, S.; Müller, K.R.; Samek, W. Interpreting and explaining deep neural networks for classification of audio signals. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03418. [Google Scholar]
- Warden, P. Speech commands: A dataset for limited-vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03209. [Google Scholar]
- Jati, A.; Hsu, C.C.; Pal, M.; Peri, R.; AbdAlmageed, W.; Narayanan, S. Adversarial attack and defense strategies for deep speaker recognition systems. Comput. Speech Lang. 2021, 68, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust dnn embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, P. The mel scale. J. Music Theory 1965, 9, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, F.R. The influence curve and its role in robust estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Layers Type | Input | Filter | Stride | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv1d | 1 | ReLU | ||
| FC | n | - | ReLU | |
| FC | 64 | - | ReLU | |
| Dropout | - | - | - | - |
| FC | 128 | - | ReLU | |
| Dropout | - | - | - | - |
| FC | 128 | - | ReLU | |
| Dropout | - | - | - | - |
| Reshape | - | sigmoid |
| Dataset | Zero | One | Two | Three | Four | Five | Six | Seven | Eight | Nine | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AudioMNIST | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 30,000 |
| Speech Commands | 4052 | 3890 | 3880 | 3727 | 3728 | 4052 | 3860 | 3998 | 3787 | 3934 | 38,908 |
| AudioMNIST | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Poisoning Rate | Trigger Size | |||||
| (1 × 5) | (2 × 5) | (3 × 5) | |||||
| ACC | ASR | ACC | ASR | ACC | ASR | ||
| 1D CNN | 0.005 | 0.998 | 0.697 | 0.998 | 0.758 | 1 | 0.864 |
| 0.01 | 0.999 | 0.87 | 0.998 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.984 | |
| 0.03 | 0.999 | 0.983 | 0.999 | 0.988 | 0.999 | 0.989 | |
| 0.05 | 0.998 | 0.984 | 0.999 | 0.994 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| 0.1 | 0.998 | 0.987 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.995 | |
| 0.2 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.997 | |
| X-vector | 0.005 | 0.997 | 0.676 | 0.997 | 0.516 | 0.997 | 0.633 |
| 0.01 | 0.998 | 0.857 | 0.999 | 0.968 | 0.999 | 0.926 | |
| 0.03 | 0.998 | 0.983 | 0.998 | 0.957 | 0.998 | 0.977 | |
| 0.05 | 0.998 | 0.987 | 0.998 | 0.984 | 0.998 | 0.994 | |
| 0.1 | 0.997 | 0.985 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.997 | |
| 0.2 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.997 | |
| Speech Commands | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Poisoning Rate | Trigger Size | |||||
| (1 × 5) | (2 × 5) | (3 × 5) | |||||
| ACC | ASR | ACC | ASR | ACC | ASR | ||
| 1D CNN | 0.03 | 0.927 | 0.211 | 0.936 | 0.341 | 0.946 | 0.455 |
| 0.05 | 0.917 | 0.411 | 0.926 | 0.467 | 0.924 | 0.541 | |
| 0.1 | 0.877 | 0.484 | 0.893 | 0.559 | 0.906 | 0.629 | |
| 0.2 | 0.834 | 0.617 | 0.852 | 0.662 | 0.871 | 0.722 | |
| 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.68 | 0.825 | 0.753 | 0.847 | 0.778 | |
| 0.4 | 0.79 | 0.762 | 0.815 | 0.81 | 0.845 | 0.824 | |
| 0.5 | 0.782 | 0.812 | 0.822 | 0.842 | 0.844 | 0.866 | |
| X-vector | 0.03 | 0.931 | 0.105 | 0.941 | 0.342 | 0.949 | 0.522 |
| 0.05 | 0.915 | 0.287 | 0.932 | 0.52 | 0.939 | 0.574 | |
| 0.1 | 0.891 | 0.466 | 0.905 | 0.627 | 0.92 | 0.705 | |
| 0.2 | 0.835 | 0.636 | 0.875 | 0.755 | 0.892 | 0.756 | |
| 0.3 | 0.812 | 0.727 | 0.851 | 0.797 | 0.863 | 0.807 | |
| 0.4 | 0.797 | 0.795 | 0.841 | 0.847 | 0.862 | 0.868 | |
| 0.5 | 0.811 | 0.861 | 0.84 | 0.888 | 0.861 | 0.898 | |
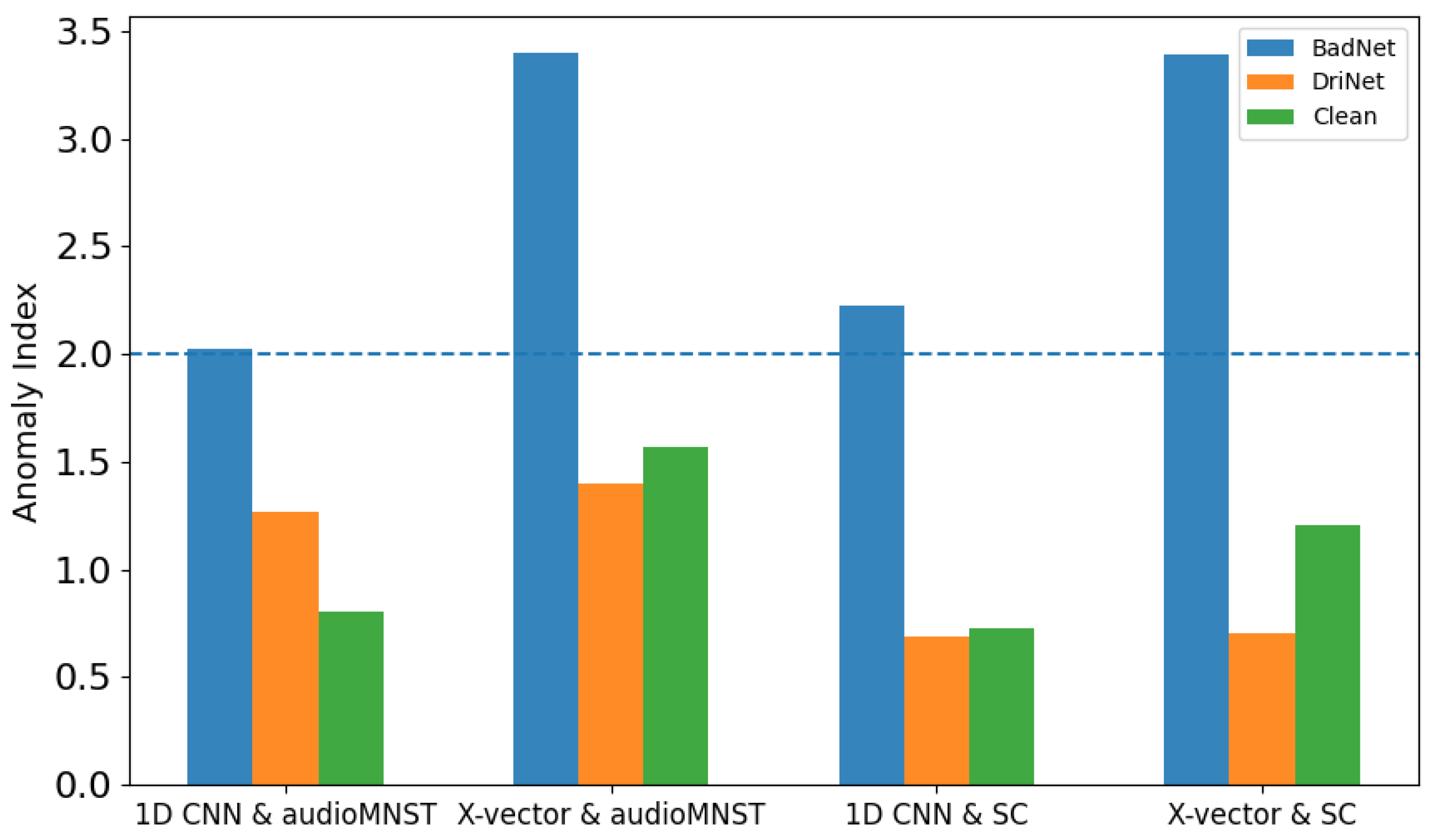
| Attack Method | Victim Model | AudioMNIST | Speech Commands | Neural Cleanse | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | ASR | ACC | ASR | |||
| BadNets | 1D CNN | 0.999 | 0.956 | 0.912 | 0.677 | × |
| X-vector | 0.999 | 0.949 | 0.915 | 0.658 | ||
| DriNet | 1D CNN | 0.999 | 0.984 | 0.906 | 0.629 | √ |
| X-vector | 0.999 | 0.945 | 0.920 | 0.705 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Liu, X.; You, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, B. DriNet: Dynamic Backdoor Attack against Automatic Speech Recognization Models. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5786. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125786
Ye J, Liu X, You Z, Li G, Liu B. DriNet: Dynamic Backdoor Attack against Automatic Speech Recognization Models. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5786. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125786
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jianbin, Xiaoyuan Liu, Zheng You, Guowei Li, and Bo Liu. 2022. "DriNet: Dynamic Backdoor Attack against Automatic Speech Recognization Models" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5786. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125786
APA StyleYe, J., Liu, X., You, Z., Li, G., & Liu, B. (2022). DriNet: Dynamic Backdoor Attack against Automatic Speech Recognization Models. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5786. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125786






