Differences in Fitness and Academic Attainment between Obese, and Non Obese School-Age Adolescent Handball Players: An Explorative, Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Approach to the Problem
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Testing Schedule
2.3.1. Anthropometry
2.3.2. Physical Performance
- Squat (SJ) and Counter Movement Jump (CMJ) Tests
- Sprint Tests
- Ability to Change Direction (T-Half Tests)
- Medicine Ball Overhead Throw
- The Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level 1 (Yo-Yo IR1)
2.3.3. Academic Attainment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intrarater Reliability
3.2. Normal Distribution and Variance Homogeneity
3.3. Age and Anthropometric Data
3.4. Physical Fitness
3.5. Academic Performance
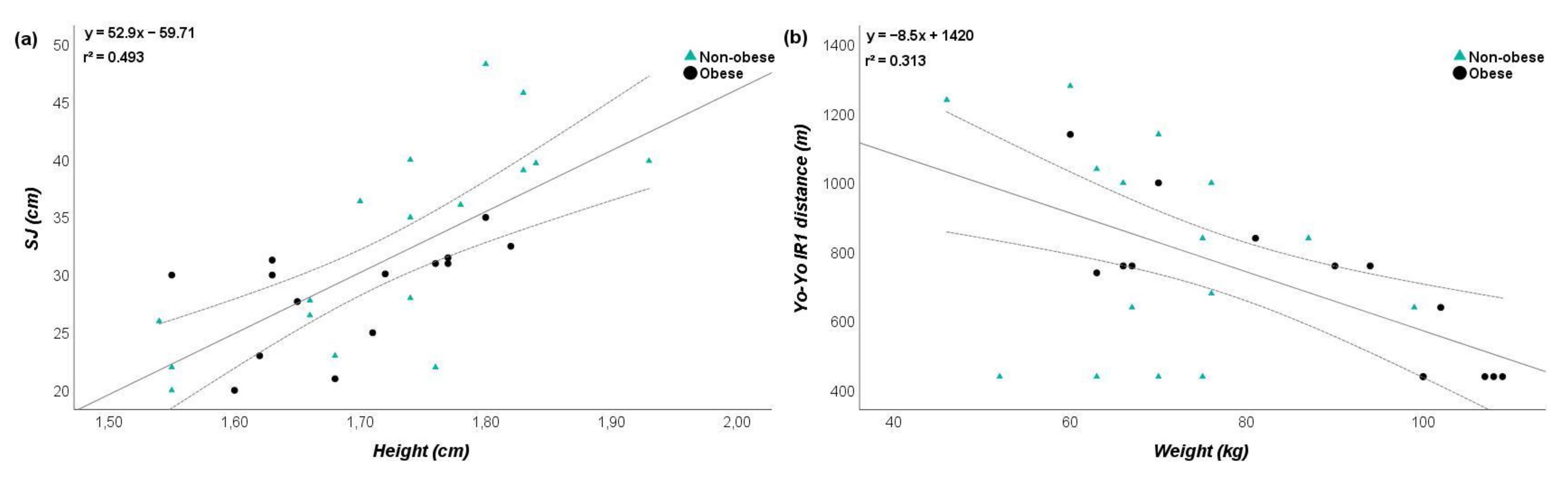
3.6. Relationships between Parameters
4. Discussions
4.1. Physical Performance
4.2. Academic Performance
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Páez-Maldonado, J.A.; Reigal, R.E.; Morillo-Baro, J.P.; Carrasco-Beltrán, H.; Hernández-Mendo, A.; Morales-Sánchez, V. Physical Fitness, Selective Attention and Academic Performance in a Pre-Adolescent Sample. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelantado-Renau, M.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Beltran-Valls, M.R.; Ponce-González, J.G.; Chiva-Bartoll, Ó.; Moliner-Urdiales, D. Fitness and academic performance in adolescents. The mediating role of leptin: DADOS study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, F.; Törpel, A.; Hamacher, D.; Budde, H.; Gronwald, T. A discussion on different approaches for prescribing physical interventions—Four roads lead to Rome, but which one should we choose? J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, D.R.; Gejl, A.K.; Tarp, J.; Wedderkopp, N.; Kramer, A.F.; Hillman, C.H.; Bugge, A. Associations between aerobic fitness and cognitive control in adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Santos, D.A.; Hillman, C.H.; Sardinha, L.B. How does academic achievement relate to cardiorespiratory fitness, self-reported physical activity and objectively reported physical activity: A systematic review in children and adolescents aged 6-18 years. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth Vedøy, I.; Skulberg, K.R.; Anderssen, S.A.; Tjomsland, H.E.; Thurston, M. Physical activity and academic achievement among Norwegian adolescents: Findings from a longitudinal study. Prev. Med. Rep. 2021, 21, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, M.L.; De Groot, R.H.; Savelberg, H.H.; Van Acker, F.; Kirschner, P.A. The association between objectively measured physical activity and academic achievement in Dutch adolescents: Findings from the GOALS study. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2014, 36, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ansari, W.; Stock, C. Is the health and wellbeing of university students associated with their academic performance? Cross sectional findings from the United Kingdom. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2010, 7, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.W.; Brown, D.D.; Laurson, K.R.; Coleman, M.M. Physical fitness and academic performance in middle school students. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Y.C.; Kirkpatrick, K.; Dolan, G.M.S.; Wouldes, T.A.; Grant, C.C.; Cave, T.L.; Wild, C.E.K.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Cuffield, W.S.; Hofman, P.L. Do changes in weight status affect cognitive function in children and adolescents with obesity? A secondary analysis of a clinical trial. Bmj Open 2019, 9, e021586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Lehrer, S.F.; Rosenquist, J.N.; Audrain-McGovern, J. The impact of poor health on academic performance: New evidence using genetic markers. J. Health Econ. 2009, 28, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Greene, J.L.; Gibson, C.A.; Sullivan, D.K.; Hansen, D.M.; Hillman, C.H.; Poggio, J.; Mayo, M.S.; Smith, B.K.; Lambourne, K.; et al. Physical activity and academic achievement across the curriculum (A + PAAC): Rationale and design of a 3-year, cluster-randomized trial. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Hillman, C.H.; Castelli, D.; Etnier, J.L.; Lee, S.; Tomporowski, P.; Lambourne, K.; Szabo-Reed, A.N. Physical activity, fitness, cognitive function, and academic achievement in children: A systematic review. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2016, 48, 1197–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinert, K.R.; Po’e, E.K.; Barkin, S.L. The relationship between executive function and obesity in children and adolescents: A systematic literature review. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 820956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Facchini, S.; Stubbs, B.; Luchini, C.; Solmi, M.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Maggi, S.; Cosco, T.; Fontana, L. Weight loss is associated with improvements in cognitive function among overweight and obese people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecka-Tendera, E.; Mazur, A. Childhood obesity: A pandemic of the twenty-first century. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30 (Suppl. 2), S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.L.; Cooper, S. Fitness, fatness, cognition, behavior, and academic achievement among overweight children: Do cross-sectional associations correspond to exercise trial outcomes? Prev. Med. 2011, 52, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B.; Castillo, R.; Martin-Matillas, M.; Kwak, L.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G. Physical activity, fitness, weight status, and cognitive performance in adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, E.; Andersen, L.B.; Skrede, T.; Ekelund, U.; Anderssen, S.A.; Resaland, G.K. Reproducibility of objectively measured physical activity and sedentary time over two seasons in children; comparing a day-by-day and a week-by-week approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Tejero-Gonzalez, C.M.; Martinez-Gomez, D.; Cabanas Sanchez, V.; Fernandez-Santos, J.R.; Conde-Caveda, J.; Sallis, J.F.; Veiga, O.L.; UP & Down Study Group. Objectively measured physical activity has a negative but weak association with academic performance in children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, e501–e506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Westfall, D.R.; Parks, A.C.; Pontifex, M.B.; Hillman, C.H. Muscular and aerobic fitness, working memory, and academic achievement in children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomitz, V.R.; Slining, M.M.; McGowan, R.J.; Mitchell, S.E.; Dawson, G.F.; Hacker, K.A. Is there a relationship between physical fitness and academic achievement? Positive results from public school children in the northeastern United States. J. Sch. Health 2009, 79, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, L.; Kremers, S.P.; Bergman, P.; Ruiz, J.R.; Rizzo, N.S.; Sjöström, M. Associations between physical activity, fitness, and academic achievement. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittberg, R.A.; Northrup, K.L.; Cottrell, L.A. Children’s aerobic fitness and academic achievement: A longitudinal examination of students during their fifth and seventh grade years. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 2303–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Migueles, J.H.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Henriksson, P.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Molina-Garcia, P.; Löf, M.; Labayen, I.; Hillmann, C.H.; et al. Fitness, physical activity and academic achievement in overweight/obese children. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedewa, A.L.; Ahn, S. The effects of physical activity and physical fitness on children’s achievement and cognitive outcomes: A meta-analysis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport. 2011, 82, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchison, W.C.; Bloodgood, E.A.; Minton, C.P.; Thompson, N.J.; Collins, M.A.; Hunter, S.C.; Dai, H. Body mass index and percentage of body fat as indicators for obesity in an adolescent athletic population. Sports Health 2011, 3, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.; Cartwright, L.; Corish, C.; Sugrue, S.; Wood-Martin, R. The body composition, nutritional knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, and future education needs of senior schoolboy rugby players in Ireland. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.A.; Leon, J.F.; Seron, R.; Mesana, M.I.; Fleta, J. Body composition in young male football (soccer) players. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cöte, J.; Baker, J.; Abernethy, B. Practice and play in the development of sport expertise. In Handbook of Sport Psychology, 3rd ed.; Eklund, R.C., Tenenbaum, G., Eds.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.S.; Oliver, J.L.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Howard, R.; De Ste Croix, M.B.; Williams, C.A.; Best, T.M.; Alvar, B.A.; Micheli, L.J.; Thomas, D.P.; et al. Long-term athletic development- part 1: A pathway for all youth. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mesa, J.; Gonzales-Chica, D.A.; Duquia, R.P.; Bonamigo, R.R.; Bastos, J.L. Sampling: How to select participants in my research study? An. Bras. Dermatol. 2016, 91, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermassi, S.; Hayes, L.D.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Schwesig, R. Physical fitness and academic performance in normal weight, overweight and obese schoolchild handball players in Qatar: A pilot study. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 616671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, S.; Laudner, K.G.; Schwesig, R. Playing level and position differences in body characteristics and physical fitness performance among male team handball players. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Womersley, J.; Durnin, J.V. An experimental study on variability of measurements of skinfold thickness on young adults. Hum. Biol. 1973, 2, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Heyward, V.H.; Gibson, A.L. Assessing body composition. In Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription, 7th ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 219–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sassi, R.H.; Dardouri, W.; Yahmed, M.H.; Gmada, N.; Mahfoudhi, M.E.; Gharbi, Z. Relative and absolute reliability of a modified agility t-test and its relationship with vertical jump and straight sprint. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, R.J.; Hanney, W.J.; Kolber, M.J.; Davies, G.J.; Ansley, M.K.; McBride, A.B.; Overstreet, A.L. Reliability, minimal detectable change, and normative values for tests of upper extremity function and power. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3318–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M.; Amstrup, T.; Rysgaard, T.; Johansen, J.; Steensberg, A.; Pedersen, P.K.; Bangsbo, J. The yo-yo intermittent recovery test: Physiological response, reliability, and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.S.; Tsai, J.R.; Chang, S.H.; Ho, J.Y.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, P.H.; Sung, Y.T.; Hung, T.M. The subject-dependent, cumulative, and recency association of aerobic fitness with academic performance in Taiwanese junior high school students. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, P.P.; Stenneberg, M.S.; Lucas, C.; van Trijffel, E. Intraexaminer reliability of hand-held dynamometry in the upper extremity: A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2444–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portney, L.G.; Watkins, M.P. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W. Measures of reliability in sports medicine and science. Sports Med. 2000, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopker, J.; Myers, S.; Jobson, S.A.; Bruce, W.; Passfield, L. Validity and reliability of the Wattbike cycle ergometer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortz, J. Basic Principle of One-Factorial Analysis of Variance, in Statistics for Social Scientists; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.T.E. Eta squared and partial eta squared as measures of effect size in educational 416 research. Educ. Res. Rev. 2011, 6, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. The effect size. In Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1988; pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hermassi, S.; van den Tillaar, R.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Schwesig, R. The Associations between physical performance and anthropometric characteristics in obese and non-obese schoolchild handball players. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 580991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruschitz, R.; Wallner-Liebmann, S.J.; Hamlin, M.J.; Moser, M.; Ludvik, B.; Schnedl, W.J.; Tafeit, E. Detecting body Fat–A weighty problem BMI versus subcutaneous fat patterns in athletes and non-athletes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, S.; Chelly, M.S.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Shephard, R.J.; Schwesig, R. In-season weightlifting training exercise in healthy male handball players: Effects on body composition, muscle volume, maximal strength, and ball-throwing velocity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vänttinen, T.; Blomqvist, M.; Nyman, K.; Häkkinen, K. Changes in body composition, hormonal status, and physical fitness in 11-, 13-, and 15-year-old Finnish regional youth soccer players during a two-year follow up. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 3342–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.K.; Ho, S.Y.; Lo, W.S.; Thomas, G.N.; McManus, A.M.; Day, J.R.; Lam, T.H. Health-related physical fitness and weight status in Hong Kong adolescents. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artero, E.G.; Espana-Romero, V.; Ortega, F.B.; Jimenez-Pavon, D.; Ruiz, J.R.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Bueno, M.; Marcos, A.; Gomez-Martinez, S.; Urzanqui, A.; et al. Health-related fitness in adolescents: Underweight, and not only overweight, as an influencing factor. The AVENA study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butte, N.F.; Puyau, M.R.; Vohra, F.A.; Adolph, A.L.; Mehta, N.R.; Zakeri, I. Body size, body composition, and metabolic profile explain higher energy expenditure in overweight children. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2660–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Fanari, P.; Fontana, M.; Buontempi, L.; Saezza, A.; Baudo, S.; Miserocci, G.; Longhini, E. Oxygen uptake and cardiac performance in obese and normal subjects during exercise. Respiration 1999, 66, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hraste, M.; De Giorgio, A.; Jelaska, P.M.; Padulo, J.; Granić, I. When mathematics meets physical activity in the school-aged child: The effect of an integrated motor and cognitive approach to learning geometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhalter, T.M.; Hillman, C.H. A narrative review of physical activity, nutrition, and obesity to cognition and scholastic performance across the human lifespan. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 201S–206S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, F. Childhood obesity and academic performance: The role of working memory. Front. Psychol. 2017, 19, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, K.; Khan, N.A.; Pontifex, M.B.; Scudder, M.R.; Drollette, E.S.; Raine, L.B.; Evans, E.M.; Castelli, D.M.; Hillman, C.H. The relation of adiposity to cognitive control and scholastic achievement in preadolescent children. Obesity 2012, 20, 2406–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Matheson, B.E.; Kaye, W.H.; Boutelle, K.N. Neurocognitive correlates of obesity and obesity-related behaviors in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrigas, C.; Fragoso, I. Obesity, academic performance and reasoning ability in Portuguese students between 6 and 12 years old. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2012, 44, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dusen, D.P.; Kelder, S.H.; Kohl, H.W., 3rd; Ranjit, N.; Perry, C.L. Associations of physical fitness and academic performance among schoolchildren. J. Sch. Health 2011, 81, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswat, K.A.; Al-Shehri, A.D.; Aljuaid, T.A.; Alzaidi, B.A.; Alasmari, H.D. The association between body mass index and academic performance. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauner, R.R.; Walters, R.W.; Avery, M.; Wanser, T.J. Evidence that aerobic fitness is more salient than weight status in predicting standardized math and reading outcomes in fourth- through eighth-grade students. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, S.; Foumier, M.; Pagani, L.; Janosz, M. Predicting academic and cognitive outcomes from weight status trajectories during childhood. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krukowski, R.A.; West, D.S.; Perez, A.P.; Bursac, Z.; Phillips, M.M.; Raczynski, J.M. Overweight children, weight-based teasing and academic performance. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2009, 4, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrijos-Nino, C.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V.; Pardo-Guijarro, M.J.; Garcia-Prieto, J.C.; Arias-Palencia, N.M.; Sánchez-López, M. Physical fitness, obesity, and academic achievement in schoolchildren. J. Pediatr. 2014, 65, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datar, A.; Sturm, R. Childhood overweight and elementary school outcomes. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, Q.; Jackson, J.C.; Zhang, J. Overweight is associated with decreased cognitive functioning among school-age children and adolescents. Obesity 2008, 16, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test | Session One Mean ± SD | Session Two Mean ± SD | ICC (95% CI) | CV (%) (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 m sprint (s) | 2.75 ± 0.29 | 2.81 ± 0.29 | 0.98 (0.82–0.99) | 1.9 (1.4–2.8) |
| 30 m sprint (s) | 5.07 ± 0.75 | 5.03 ± 0.77 | 0.94 (0.88–0.97) | 6.9 (5.4–10.7) |
| Agility T-half test (s) | 7.10 ± 0.58 | 7.13 ± 0.58 | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) |
| CMJ (cm) | 34.8 ± 5.32 | 33.6 ± 5.33 | 0.99 (0.31–1.00) | 1.4 (1.1–2.1) |
| SJ (cm) | 30.8 ± 7.43 | 30.1 ± 7.31 | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 1.1 (0.8–1.6) |
| Medicine ball throw (m) | 7.92 ± 0.90 | 7.76 ± 0.93 | 0.98 (0.89–1.00) | 1.2 (0.9–1.8) |
| Non-Obese (n = 17) | Obese (n = 14) | Observed Power | ANOVA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ηp2 | ||||
| Age (years) | 15.4 ± 1.33 | 15.5 ± 0.94 | 0.055 | 0.836 | 0.002 |
| Anthropometric parameters | |||||
| Body height (m) | 1.73 ± 0.11 | 1.69 ± 0.08 | 0.138 | 0.382 | 0.027 |
| Body mass (kg) | 70.3 ± 13.4 | 86.9 ± 18.4 | 0.802 | 0.007 | 0.226 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 5.06 | 30.5 ± 7.18 | 0.838 | 0.005 | 0.243 |
| Body fat (%) | 21.5 ± 3.81 | 32.4 ± 1.96 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.766 |
| Bicipital skinfold (mm) | 12.8 ± 5.73 | 32.6 ± 11.4 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.575 |
| Tricipital skinfold (mm) | 15.9 ± 5.53 | 34.1 ± 6.83 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.697 |
| Subscapular (mm) | 16.1 ± 6.74 | 39.5 ± 6.36 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.770 |
| Suprailiac (mm) | 15.4 ± 6.67 | 39.5 ± 6.36 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.770 |
| Non-obese (n = 17) | Obese (n = 14) | Observed Power | ANOVA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ηp2 | ||||
| Physical performance parameters | |||||
| 15 m sprint (s) | 2.64 ± 0.28 | 2.88 ± 0.26 | 0.668 | 0.019 | 0.175 |
| 30 m sprint (s) | 4.89 ± 0.62 | 5.28 ± 0.87 | 0.282 | 0.163 | 0.066 |
| Agility T-half test (s) | 6.82 ± 0.52 | 7.45 ± 0.46 | 0.931 | 0.001 | 0.305 |
| CMJ (cm) | 37.9 ± 3.80 | 31.0 ± 4.45 | 0.994 | <0.001 | 0.425 |
| SJ (cm) | 32.7 ± 8.85 | 28.5 ± 4.53 | 0.339 | 0.121 | 0.081 |
| Yo-Yo IR1 distance (m) | 824 ± 293 | 686 ± 225 | 0.287 | 0.160 | 0.067 |
| Medicine ball overhead throw (m) | 7.75 ± 0.93 | 8.12 ± 0.86 | 0.200 | 0.258 | 0.044 |
| Academic performance parameters | |||||
| Science | 87.4 ± 11.0 | 75.9 ± 13.2 | 0.726 | 0.013 | 0.195 |
| Mathematics | 91.4 ± 9.98 | 71.4 ± 16.8 | 0.977 | <0.001 | 0.367 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermassi, S.; Hayes, L.D.; Schwesig, R. Differences in Fitness and Academic Attainment between Obese, and Non Obese School-Age Adolescent Handball Players: An Explorative, Cross-Sectional Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094185
Hermassi S, Hayes LD, Schwesig R. Differences in Fitness and Academic Attainment between Obese, and Non Obese School-Age Adolescent Handball Players: An Explorative, Cross-Sectional Study. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094185
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermassi, Souhail, Lawrence D. Hayes, and René Schwesig. 2021. "Differences in Fitness and Academic Attainment between Obese, and Non Obese School-Age Adolescent Handball Players: An Explorative, Cross-Sectional Study" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094185
APA StyleHermassi, S., Hayes, L. D., & Schwesig, R. (2021). Differences in Fitness and Academic Attainment between Obese, and Non Obese School-Age Adolescent Handball Players: An Explorative, Cross-Sectional Study. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094185








