The Influences of Projectile Material and Environmental Temperature on the High Velocity Impact Behavior of Triaxial Braided Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ballistic Impact Test
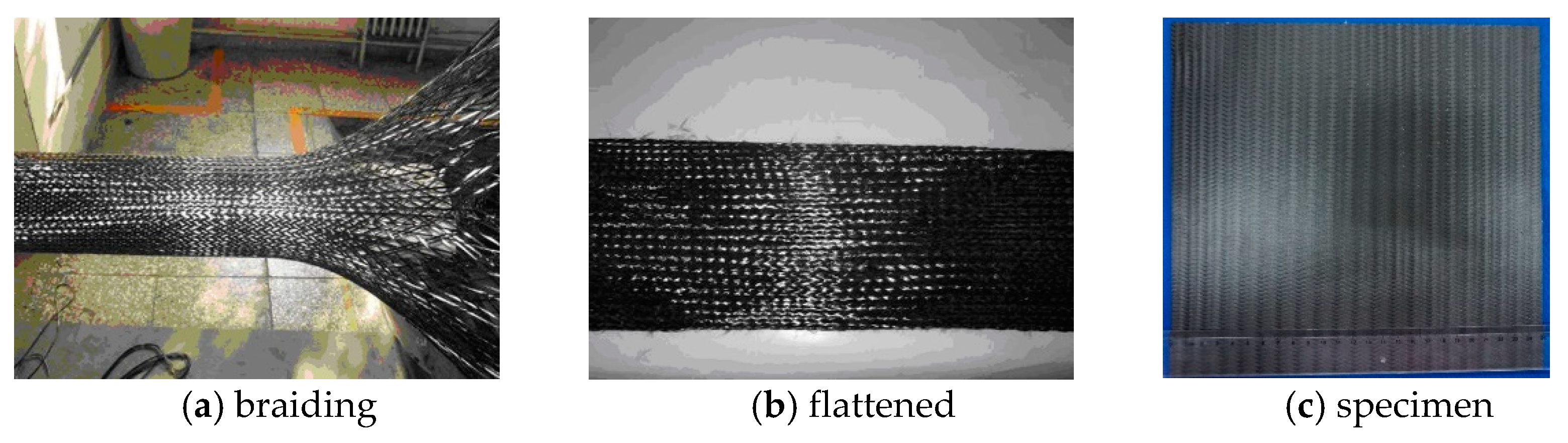
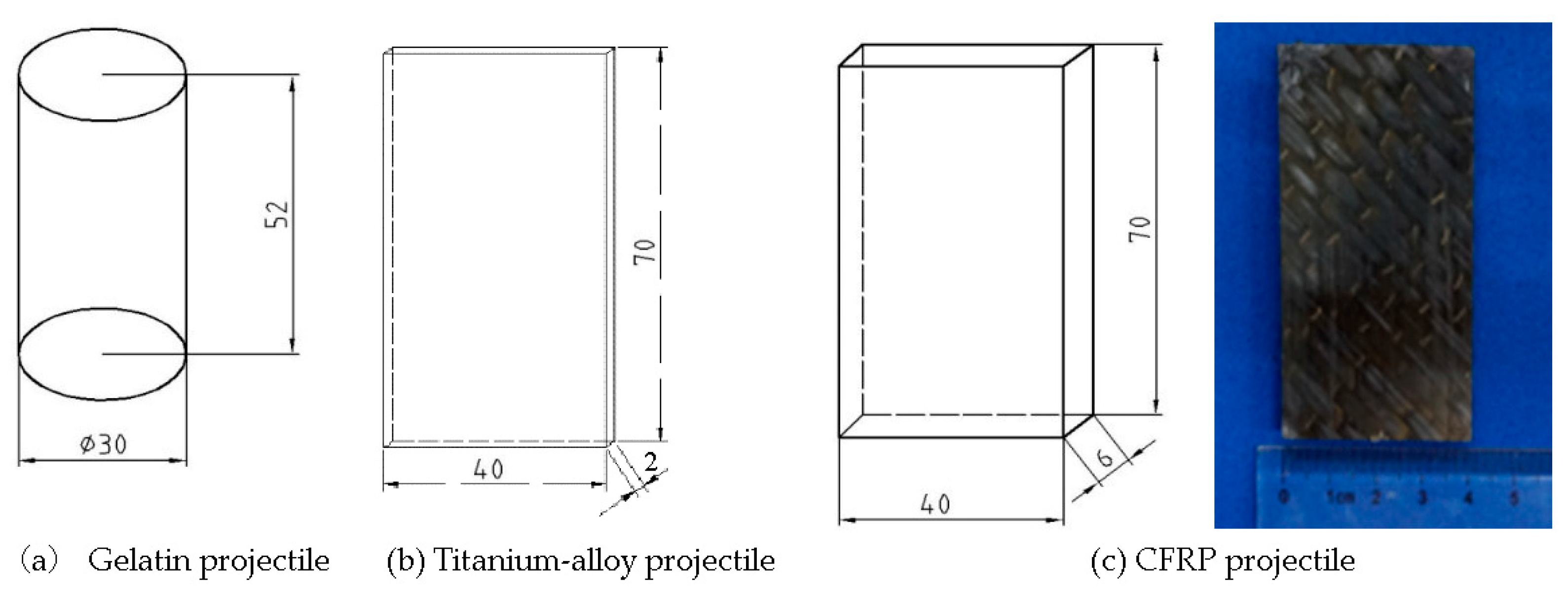
2.1. Test Specimen
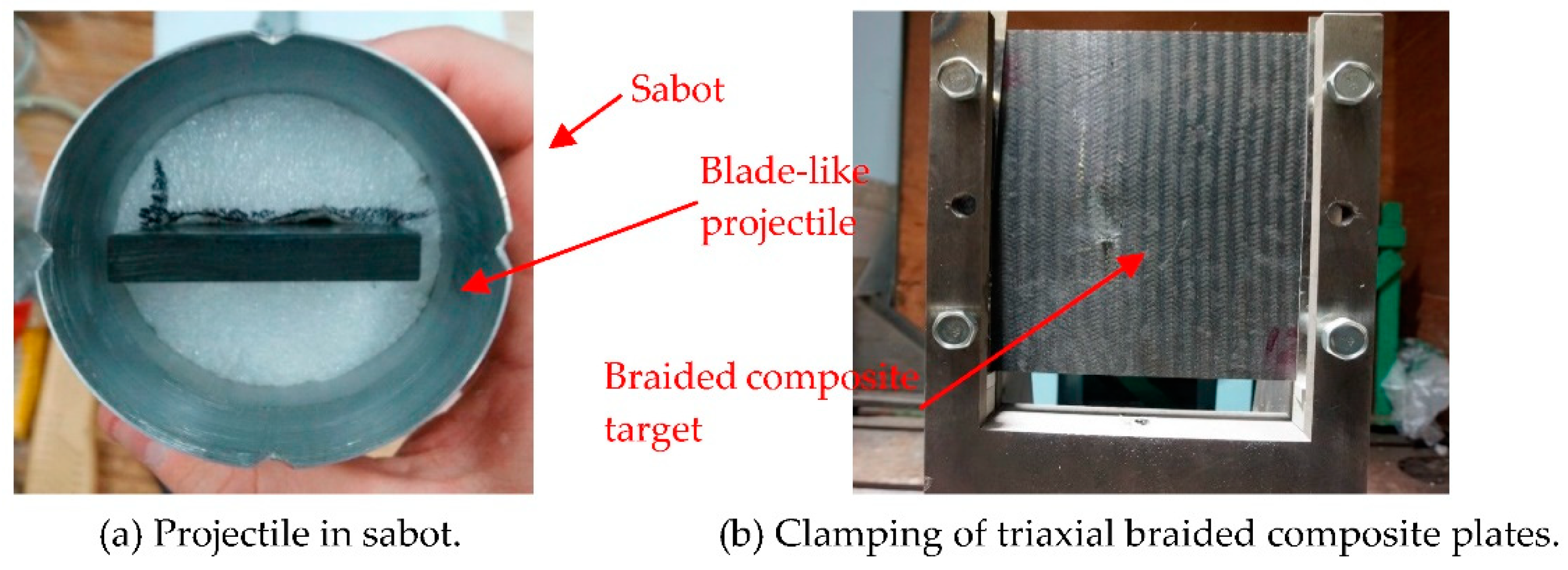
2.2. Testing Device
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Projectile Material
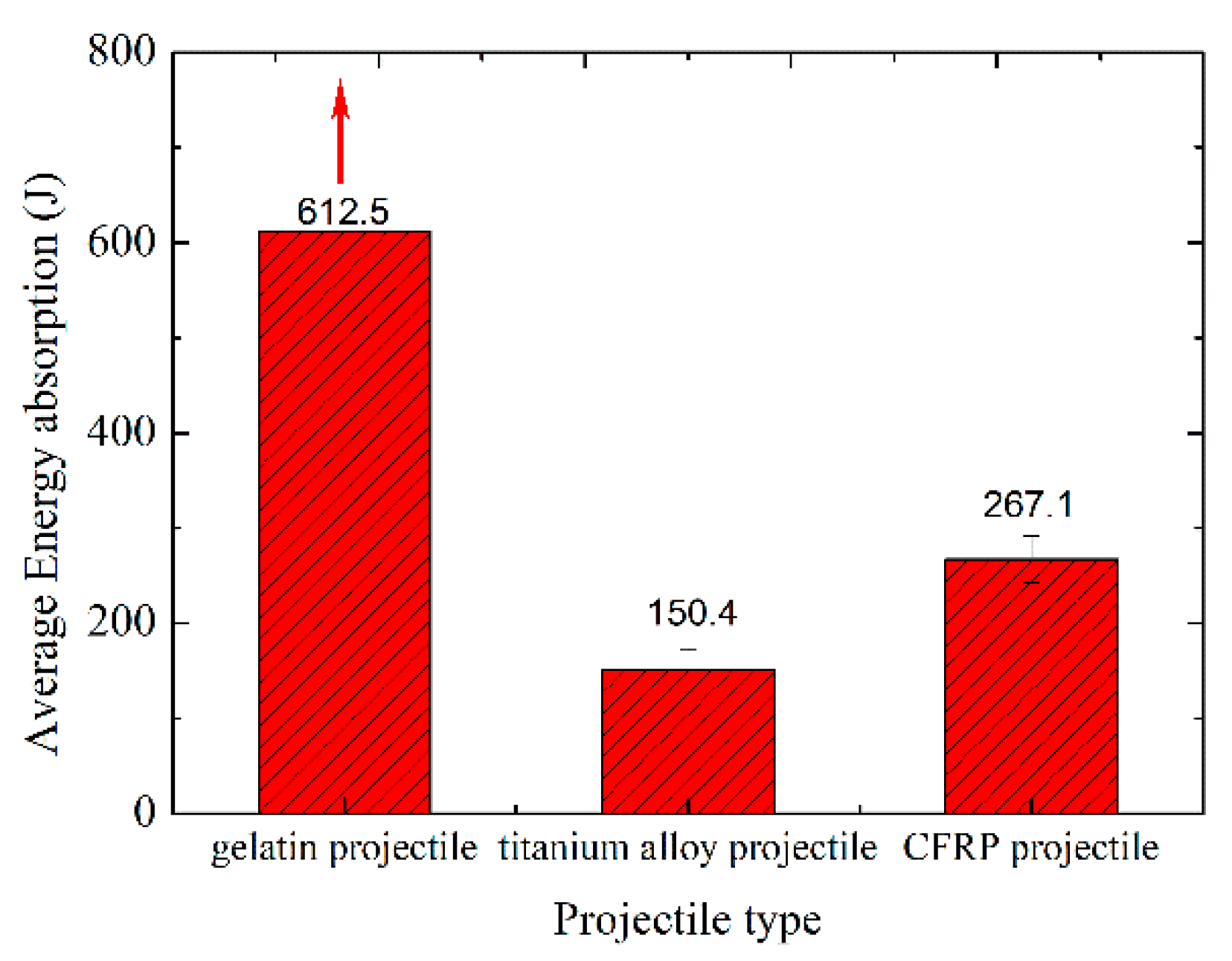
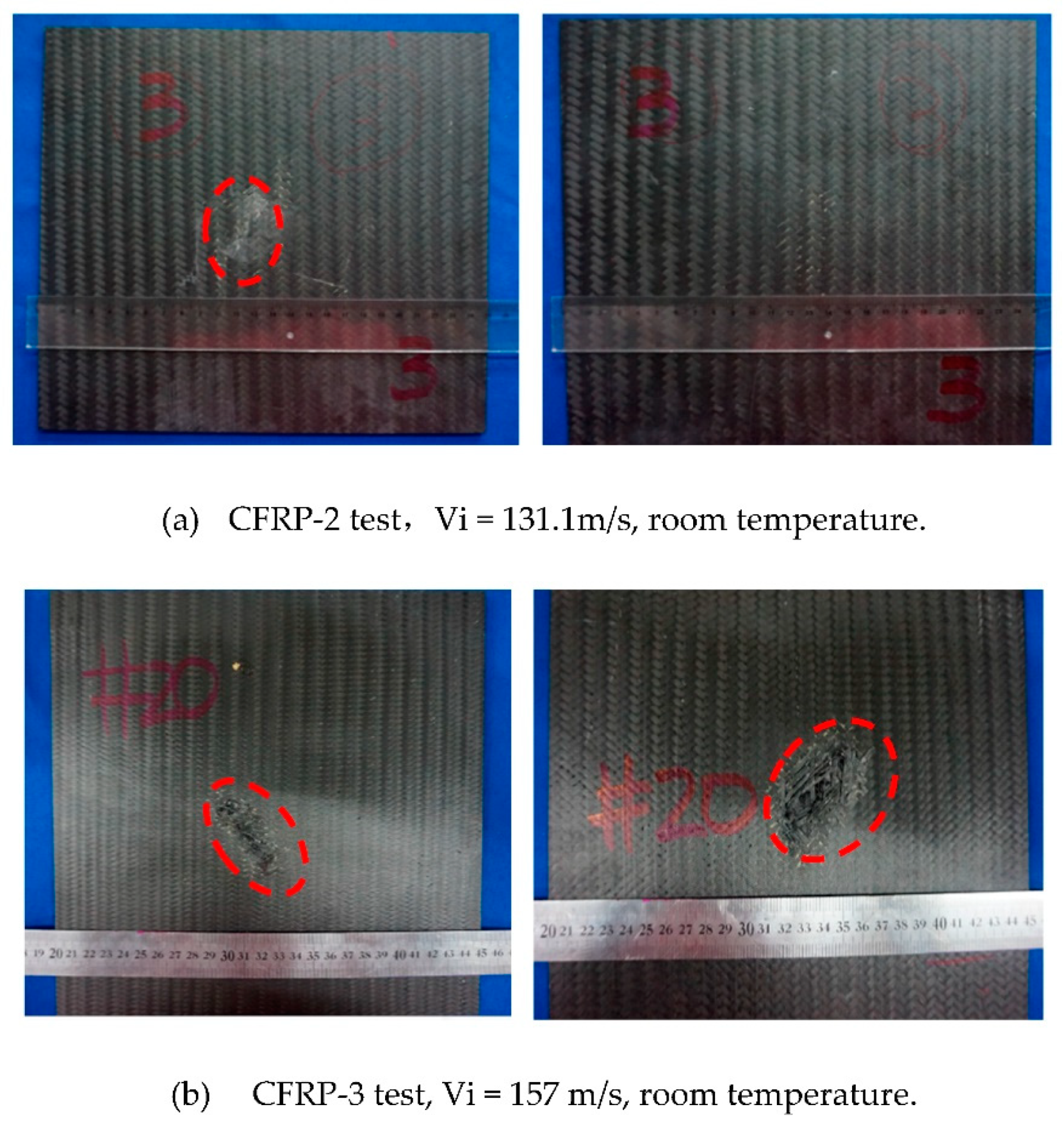
3.1.1. Energy Absorption
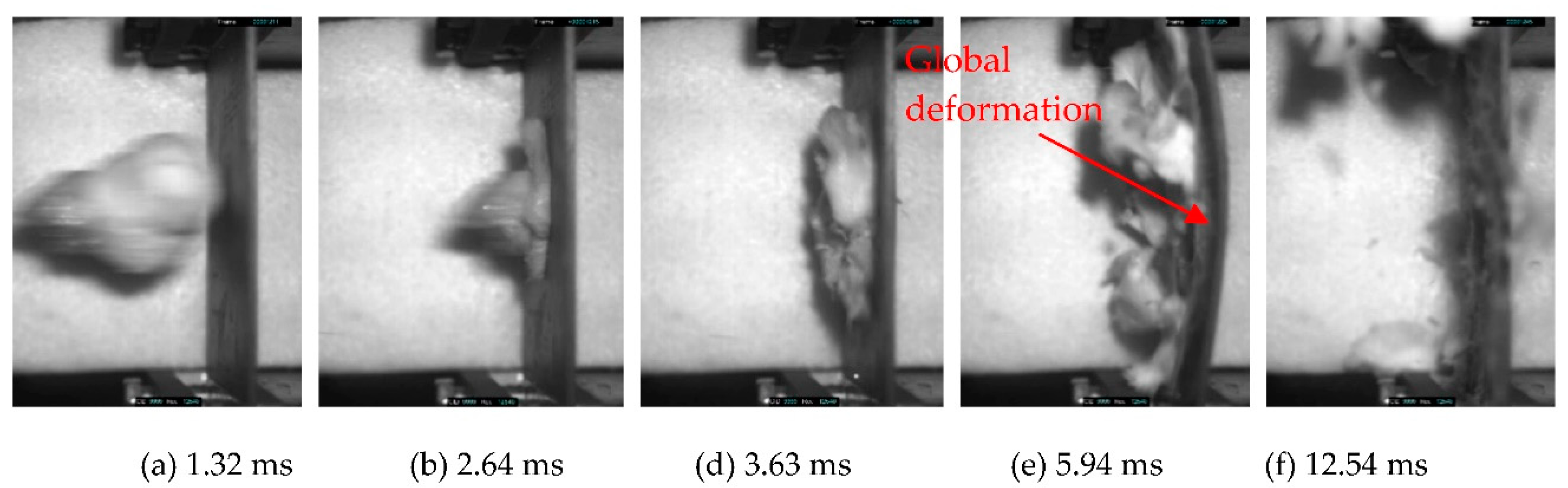
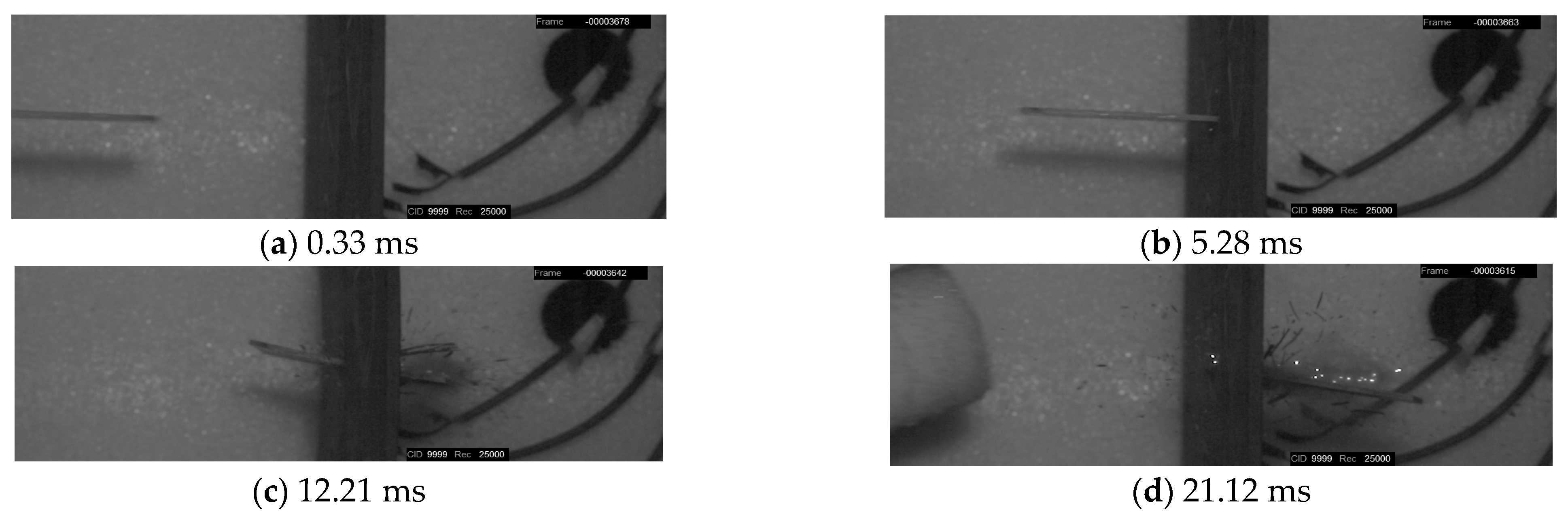
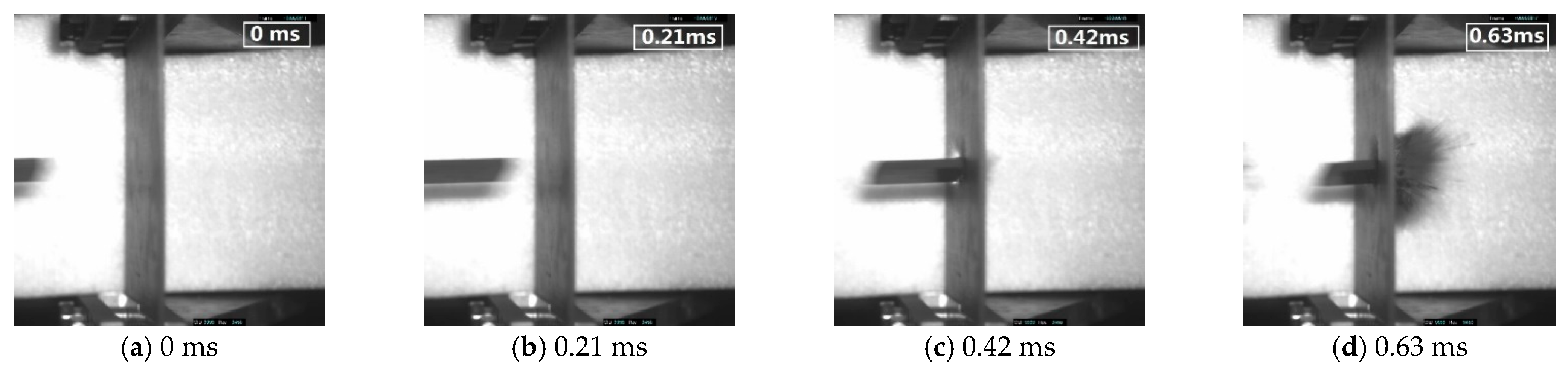
3.1.2. Impact Process
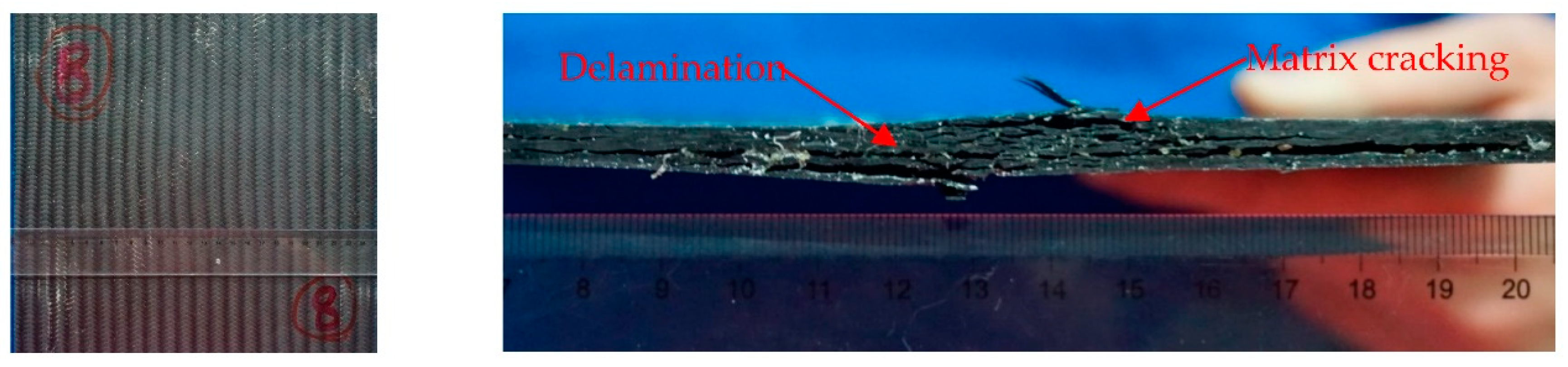
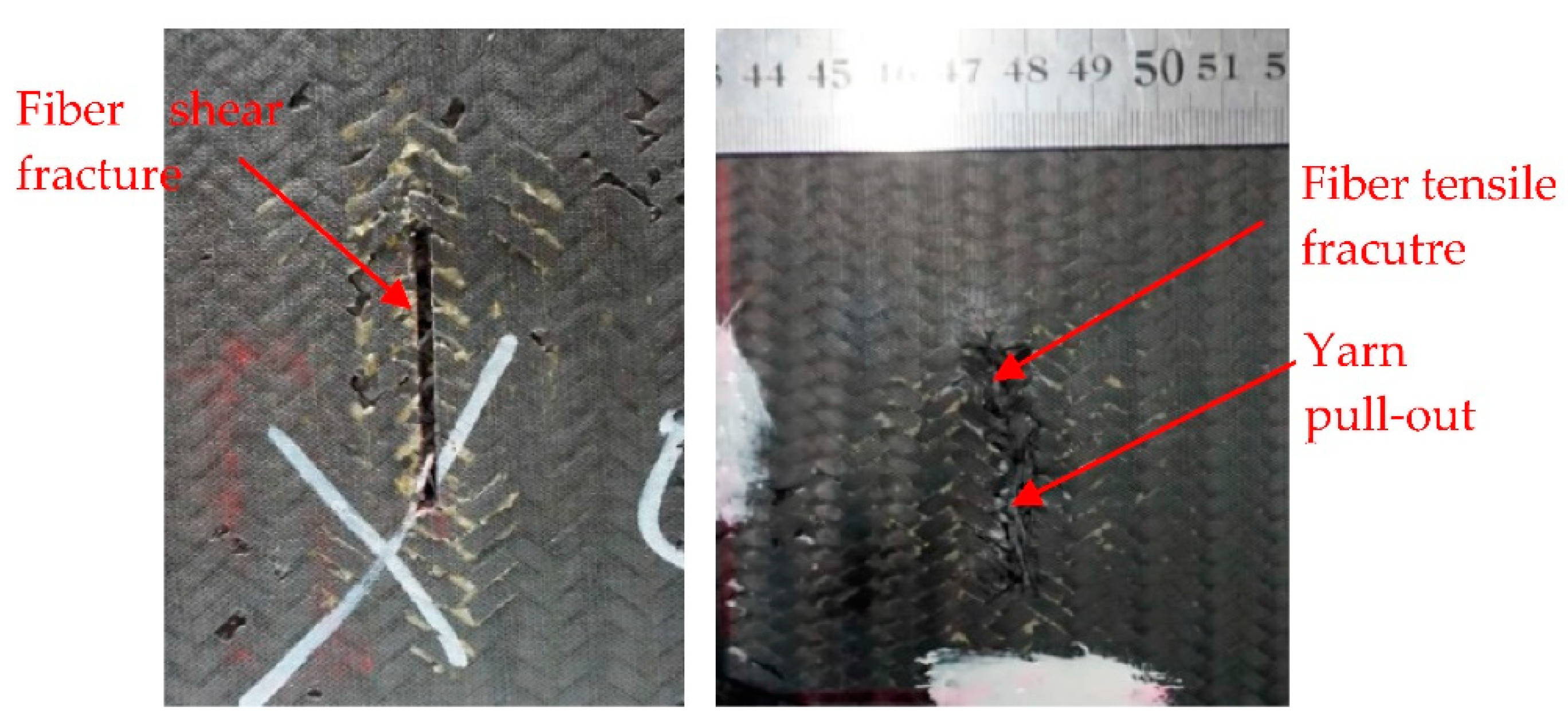
3.1.3. Damage Morphology
3.2. Impact Characteristics under Cryogenic and High Temperatures
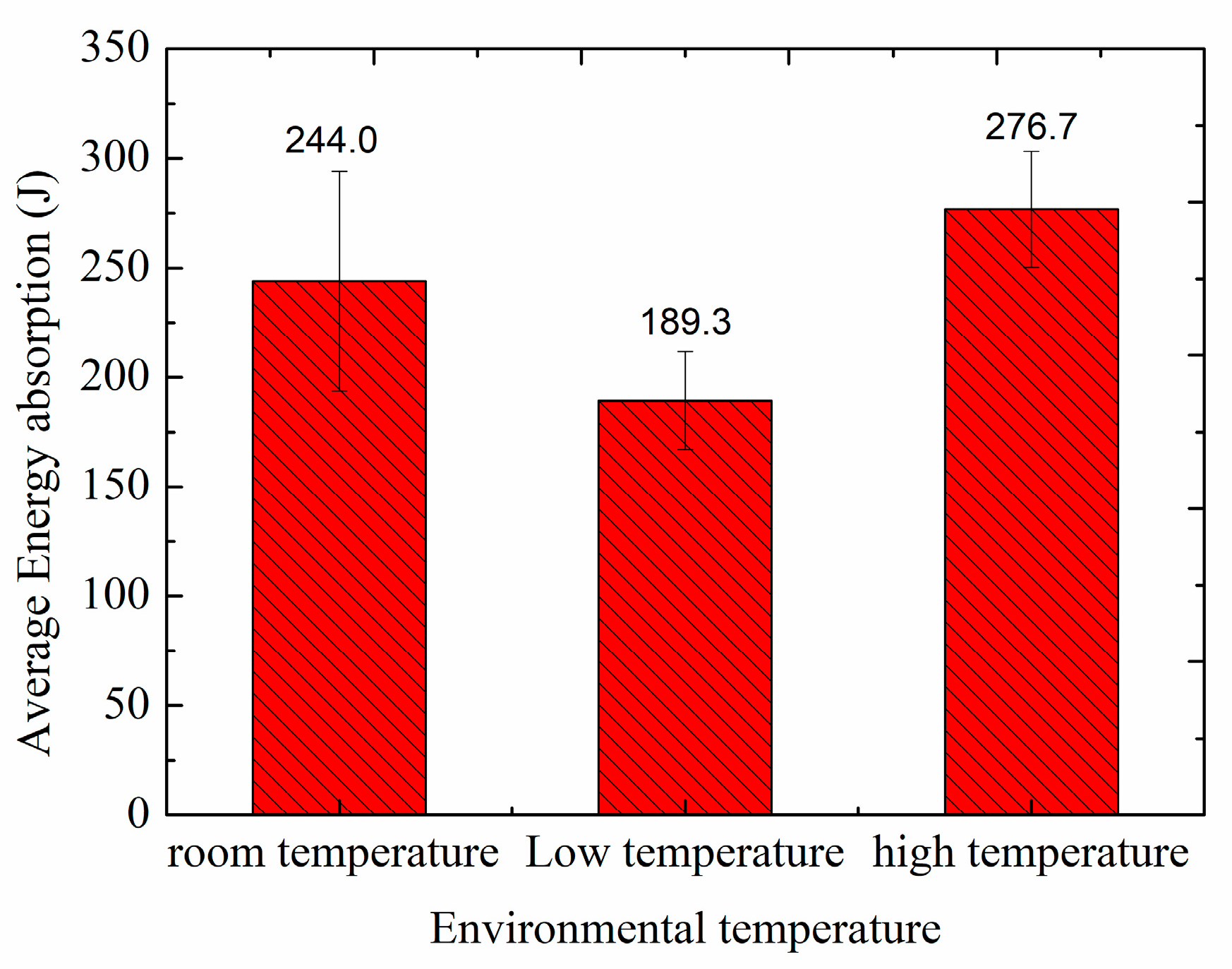
3.2.1. Energy Absorption
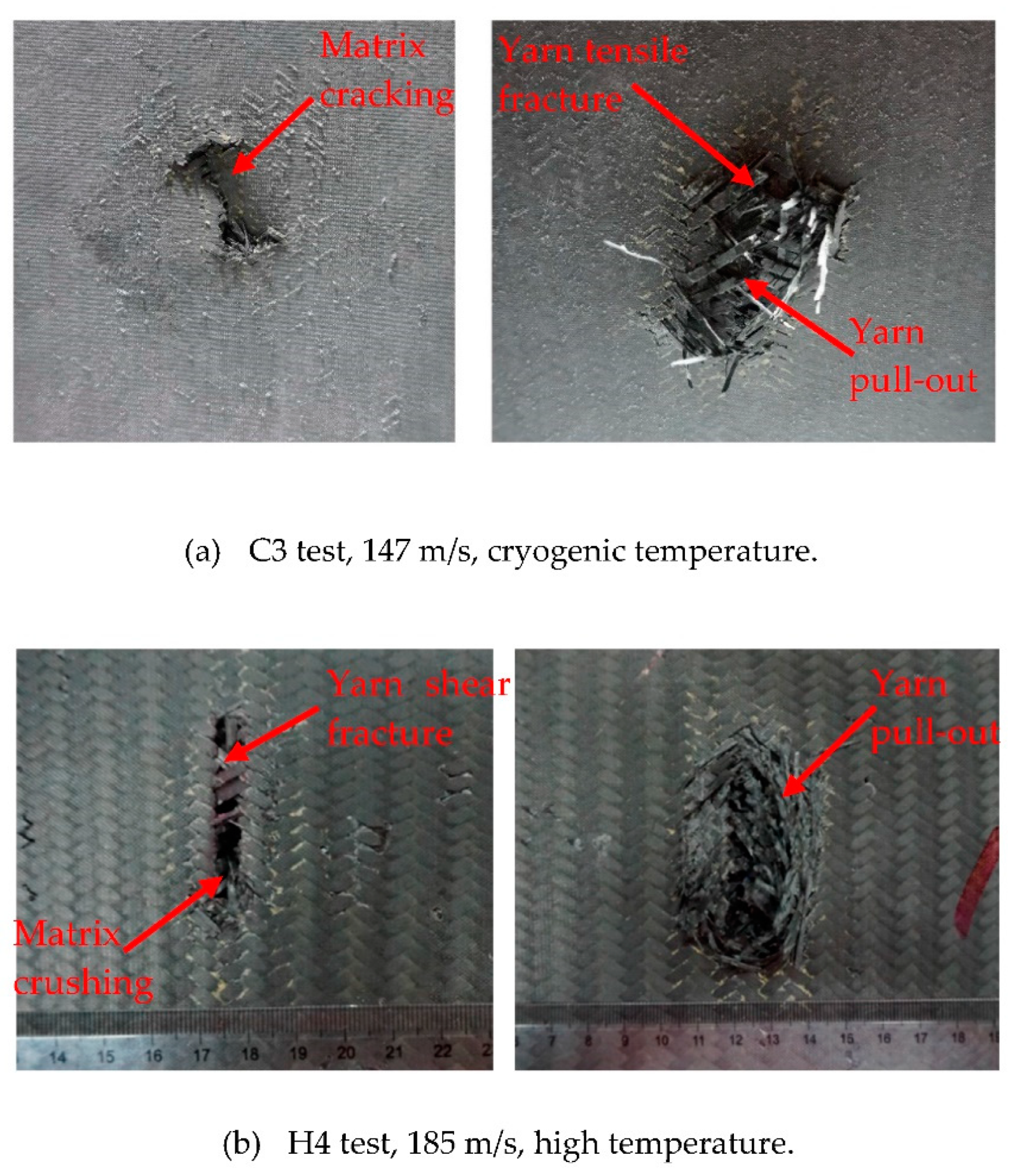
3.2.2. Damage Morphology
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Given the fluid behavior of gelatin projectiles under impact load, the triaxial braided composite target impacted with a gelatin projectile undergoes global deformation and therefore absorbs much more energy than when impacted by CFRP or titanium projectiles. Upon impact with a gelatin projectile, delamination, matrix cracking, and slight fiber breakage appear in the through-thickness direction of the target.
- (2)
- Triaxial braided composites impacted by CFRP and titanium-alloy blade-like projectiles produce similar damage patterns. A rectangular opening appears at the impact surface and an elliptically shaped damage area appears at the exit surface with massive fiber breakage, yarn pull-out, and severe matrix cracking and delamination. The average energy absorption of the triaxial braided composite when perforated by a CFRP projectile is 77.59% greater than that perforated by a titanium-alloy projectile. When the composite target is impacted by a titanium-alloy projectile, its main damage has a shear pattern, and barely global bending deformation occurs to dissipate energy. Therefore, the usage of composite fan blades is very important, because compared to titanium alloy blades, the application of composite blades could not only reduce the weight of the blade itself, but also further reduce the weight of the composite casing, which will bring enormous economic benefits.
- (3)
- Cryogenic temperatures deteriorate the impact resistance of 2D triaxial braided composite material while high temperature improves its impact resistance. This result is attributed mainly to the decreased flexibility of the 2D triaxial braided composite target plate at cryogenic temperature, which permits less global deformation under impact load. The temperature affects the damage pattern of the 2D triaxial braided composites. Therefore, in the design and analysis of the composite containment casing, it is necessary to consider the influence of the working environment temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khezri, M.; Rasmussen, K.J.R. An energy-based approach to buckling modal decomposition of thin-walled members with arbitrary cross sections, Part 1: Derivation. Thin Wall. Struct. 2019, 138, 496–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, J.J.; Srinivasan, S.M.; Arockiarajan, A.; Dhakal, H.N. Parameters influencing the impact response of fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite materials: A critical review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 224, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dang, H.; Liu, P.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. On the impact failure behavior of triaxially braided composites subjected to metallic plate projectile. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 186, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xuan, H.; Bai, C.; Song, M.; Zhu, Z. Containment of soft wall casing wrapped with Kevlar fabric. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Z. Containment Ability of Kevlar 49 Composite Case under Spinning Impact. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 31, 04017096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xie, Z.; Xuan, H.; Liu, L.; Hong, W. Multi-blade effects on aero-engine blade containment. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xuan, H.; Liu, L.; Hong, W.; Wu, R. Perforation of aero-engine fan casing by a single rotating blade. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 25, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.H.; Karuppanan, S.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Sajid, Z. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites: A review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Tong, L.; Li, Y. A new analytical method for progressive failure analysis of two-dimensional triaxially braided composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 186, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Modeling the transverse tensile and compressive failure behavior of triaxially braided composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 172, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carpintero, A.; Van den Beuken, B.N.G.; Haldar, S.; Herráez, M.; González, C.; Lopes, C.S. Fracture behaviour of triaxial braided composites and its simulation using a multi-material shell modelling approach. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 188, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrkamp-Richter, T.; De Carvalho, N.V.; Pinho, S.T. A meso-scale simulation framework for predicting the mechanical response of triaxial braided composites. Compos. Part A. Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2018, 107, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yu, G. Multi-scale analysis for mechanical properties of fiber bundle and damage characteristics of 2D triaxially braided composite panel under shear loading. Thin Wall. Struct. 2018, 132, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrkamp-Richter, T.; De Carvalho, N.V.; Pinho, S.T. Predicting the non-linear mechanical response of triaxial braided composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2018, 114, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, S.C.; Waas, A.M.; Shahwan, K.W.; Agaram, V. Compressive response and failure of braided textile composites. Part 1: Experiments. Int. J. NonLin. Mech. 2004, 39, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Baudry, F.; Van Den Broucke, B.; Lomov, S.V.; Xie, H.; Verpoest, I. Failure analysis of triaxial braided composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.R.; Anders, D.; Weinberg, K. Influence of strain rate on fracture behavior of sandwich composite T-joints. Eur. J. Mech. A Solid 2019, 78, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, M.P.F.; Aceves, C.M.; Stronge, W.J.; Choudhry, R.S.; Scott, A.E. Moderate speed impact damage to 2D-braided glass–carbon composites. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.P.; Pereira, J.M.; Ruggeri, C.R.; Roberts, G.D. High-speed infrared thermal imaging during ballistic impact of triaxially braided composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 3549–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.P.; Taylor, H.R.; Wilbeck, J.S. Bird Impact Forces and Pressures on Rigid and Compliant Targets; Technical Report AFFDL-TR-77-60; Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory: Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, J.P.; Fry, P.F.; Klyce, J.M.; Taylor, H.R. Impact of Soft Bodies on Jet Engine Fan Blades; AFML-TR-77-29; University of Dayton Research Institute: Dayton, OH, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Gao, D. Foreign Object Damage to Fan Rotor Blades of Aeroengine Part I: Experimental Study of Bird Impact. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2007, 5, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Luo, G.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X. Dynamic behavior and damage mechanism of 3D braided composite fan blade under bird impact. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5906078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.D.; Pereira, J.M., Jr.; Revilock, D.M.; Binienda, W.K.; Xie, M.; Braley, M. Ballistic impact of braided composite with a soft projectile. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 18, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, J. Material Modeling of Strain Rate Dependent Polymer and 2D Triaxially Braided Composites. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Akron, Akron, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, R.K.; Blinzler, B.J.; Binienda, W.K. Modification of a Macromechanical Finite-Element Based Model for Impact Analysis of triaxially braided composites. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2012, 25, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Roberts, G.D.; Ruggeri, C.R.; Gilat, A.; Matrka, T. Experimental Techniques for Evaluating the Effects of Aging on Impact and High Strain Rate Properties of Triaxial Braided Composite Materials; NASA/TM—2010-216763; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Glenn Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2010.
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Luo, G. Influence of pre-tension on ballistic impact performance of multi-layer Kevlar 49 woven fabrics for gas turbine engine containment systems. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xie, Z.; Xuan, H.; Hong, W. Ballistic testing and theoretical analysis for perforation mechanism of the fan casing and fragmentation of the released blade. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 91, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Revilock, D.M.; Ruggeri, C.R.; Emmerling, W.C.; Altobelli, D.J. Ballistic Impact Testing of Aluminum 2024 and Titanium 6Al-4V for Material Model Development. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2014, 27, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, W.; Guan, Y.; Gao, D. Study on Titanium Alloy TC4 Ballistic Penetration Resistance. Part I: Ballistic Impact Tests. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Shuang, C.; Luo, G. An experimental investigation on high velocity impact behavior of hygrothermal aged CFRP composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xuan, H.; He, Z.; Niu, D.; Xing, J.; Hong, W. Containment capability of 2D triaxial braided tape wound composite casing for aero-engine. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N.; Feng, Y.; Hong, W. Impact response and damage evolution of triaxial braided carbon/epoxy composites. Part I: Ballistic impact testing. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xuan, H.; Zhang, N.; Chen, G.; Feng, Y.; Hong, W. Impact response and damage evolution of triaxial braided carbon/epoxy composites. Part II: Finite element analysis. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xuan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z.; Guan, Y. Modified Subcell Model Using Solid Elements for Triaxial Braided Composite under Ballistic Impact. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 29, 04016028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Liu, L.; Guan, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z. A simplified delamination modelling methodology for triaxial braided composites with macro-scale solid finite-element models. Int. J. Crashworthines. 2019, 24, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yun, G.; Li, Y. A multi-scale modeling framework for impact damage simulation of triaxially braided composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2018, 110, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.G.; Handschuh, K.M.; Sinnott, M.J.; Kohlman, L.W. Materials, Manufacturing, and Test Development of a Composite Fan Blade Leading Edge Subcomponent for Improved Impact Resistance; NASA/TM—2015-218340; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Glenn Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2015.
- Amoo, L.M. On the design and structural analysis of jet engine fan blade structures. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2013, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Majid, M.S.A.; Khasri, A.; Basaruddin, K.S.; Gibson, A.G. Effect of moisture exposure and elevated temperatures on impact response of Pennisetum purpureum/glass-reinforced epoxy (PGRE) hybrid composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, L.; de Vasconcellos, D.S.; D’Auria, M.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J. Effect of temperature on static and low velocity impact properties of thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 113, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S. Influence of temperature on the impact behavior of woven-ply carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 185, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashaba, U.A.; Othman, R. Low-velocity impact of woven CFRE composites under different temperature levels. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 108, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Neto, M.A. Experimental study of temperature effects on composite laminates subjected to multi-impacts. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 98, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekantha Reddy, T.; Rama Subba Reddy, P.; Madhu, V. Low velocity impact studies of E-glass/epoxy composite laminates at different thicknesses and temperatures. Def. Technol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Jia, Z.; Kintak, L.; Leng, J.; Hui, D. Impact properties of glass fiber/epoxy composites at cryogenic environment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 92, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, A.; Kubota, R.; Takayama, K. High-velocity impact characteristic of carbon fiber reinforced plastic composite at low temperature. J. Strain Anal. Eng. 2012, 47, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.K. Composite Materials Manufacturing Processes. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 110–116, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.E., Jr.; Hohler, V.; Walker, J.D.; Stilp, A.J. The influence of projectile hardness on ballistic performance. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1999, 22, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Xu, Z.; Shen, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on the impact load of internally supported gelatin bird projectiles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 124, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Testing Number | Projectile Weight m (g) | Impact Velocity Vi (m/s) | Residual Velocity Vr (m/s) | Testing Results | Energy Absorption Ea (J) | Average Energy Absorption (J) | Standard Deviation (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin-1 | 25.6 | 169 | – | Projectile fragmentation | 365.58 | – | – |
| Gelatin-2 | 27 | 213 | – | Projectile fragmentation | 612.48 | ||
| Ti-1 | 25 | 105 | 23 | Perforation | 131.2 | 150.4 | 22.58 |
| Ti-2 | 24.3 | 146 | 83 | Perforation | 175.29 | ||
| Ti-3 | 24.8 | 160 | 118 | Perforation | 144.78 | ||
| CFRP1 | 27.8 | 118 | 0 | Rebound | 193.54 | 267.1 | 24.38 |
| CFRP2 | 27.3 | 131 | 0 | Rebound | 234.25 | ||
| CFRP3 | 26.1 | 157 | 45 | Perforation | 295.24 | ||
| CFRP5 | 27.1 | 170 | 101 | Perforation | 253.37 | ||
| CFRP6 | 28.2 | 172 | 108 | Perforation | 252.67 |
| Test Number | Temperature T (°C) | Projectile Weight (g) | Initial Velocity Vi (m/s) | Residual Velocity Vr (m/s) | Result | Energy Absorbed Ea (J) | Average Energy (J) | Standard Deviation (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −49.9 | 27.8 | 70.5 | −22.7 | Rebound | 61.92 | 189.3 | 22.36 |
| C2 | −47.2 | 26.7 | 130 | 62.5 | Perforation | 173.47 | ||
| C3 | −47.5 | 27.2 | 147 | 80.8 | Perforation | 205.09 | ||
| H1 | 139.5 | 26.9 | 130 | – | Rebound | 227.31 | 276.7 | 26.52 |
| H2 | 143 | 28.3 | 146 | −45.5 | Rebound | 272.33 | ||
| H3 | 149 | 27.3 | 170 | 100 | Perforation | 257.98 | ||
| H4 | 149.5 | 27.4 | 185 | 112.5 | Perforation | 295.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Yin, S.; Luo, G.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W. The Influences of Projectile Material and Environmental Temperature on the High Velocity Impact Behavior of Triaxial Braided Composites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083466
Liu L, Yin S, Luo G, Zhao Z, Chen W. The Influences of Projectile Material and Environmental Temperature on the High Velocity Impact Behavior of Triaxial Braided Composites. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083466
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lulu, Shikai Yin, Gang Luo, Zhenhua Zhao, and Wei Chen. 2021. "The Influences of Projectile Material and Environmental Temperature on the High Velocity Impact Behavior of Triaxial Braided Composites" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083466
APA StyleLiu, L., Yin, S., Luo, G., Zhao, Z., & Chen, W. (2021). The Influences of Projectile Material and Environmental Temperature on the High Velocity Impact Behavior of Triaxial Braided Composites. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083466






