F127/Cisplatin Microemulsions: In Vitro, In Vivo and Computational Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Cell Lines, and Culture Conditions
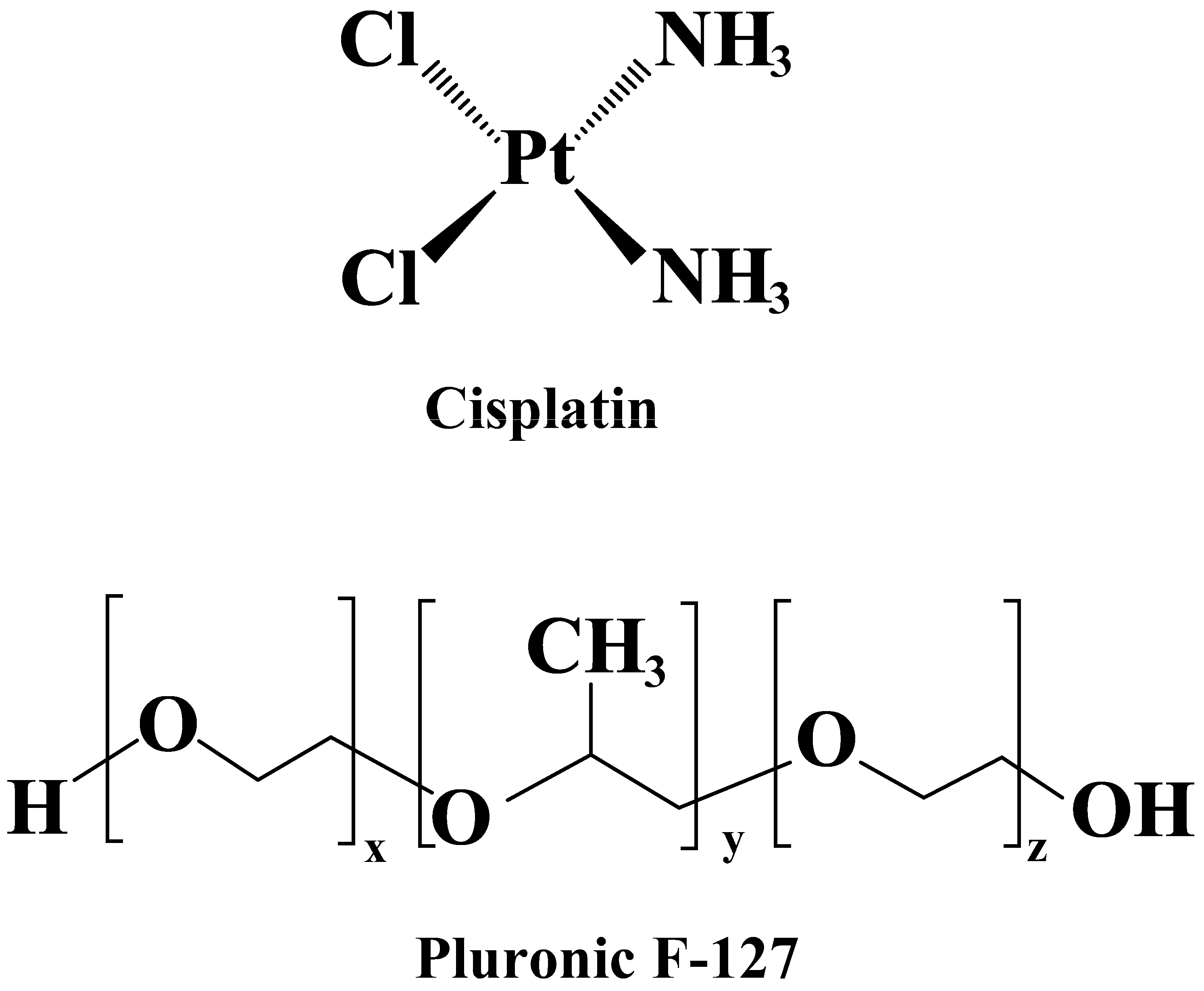
2.2. Formulation of Cis-Incorporated Microemulsions
2.3. Characterization of Cis-Loaded Microemulsions by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4. Cytotoxicity and Morphology Evaluations
2.5. In Vivo Experiments
2.5.1. Treatments and Experimental Design
2.5.2. Determination of Biochemical Parameters
2.5.3. Histological Examination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Quantum Mechanics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CisMicroemulsions
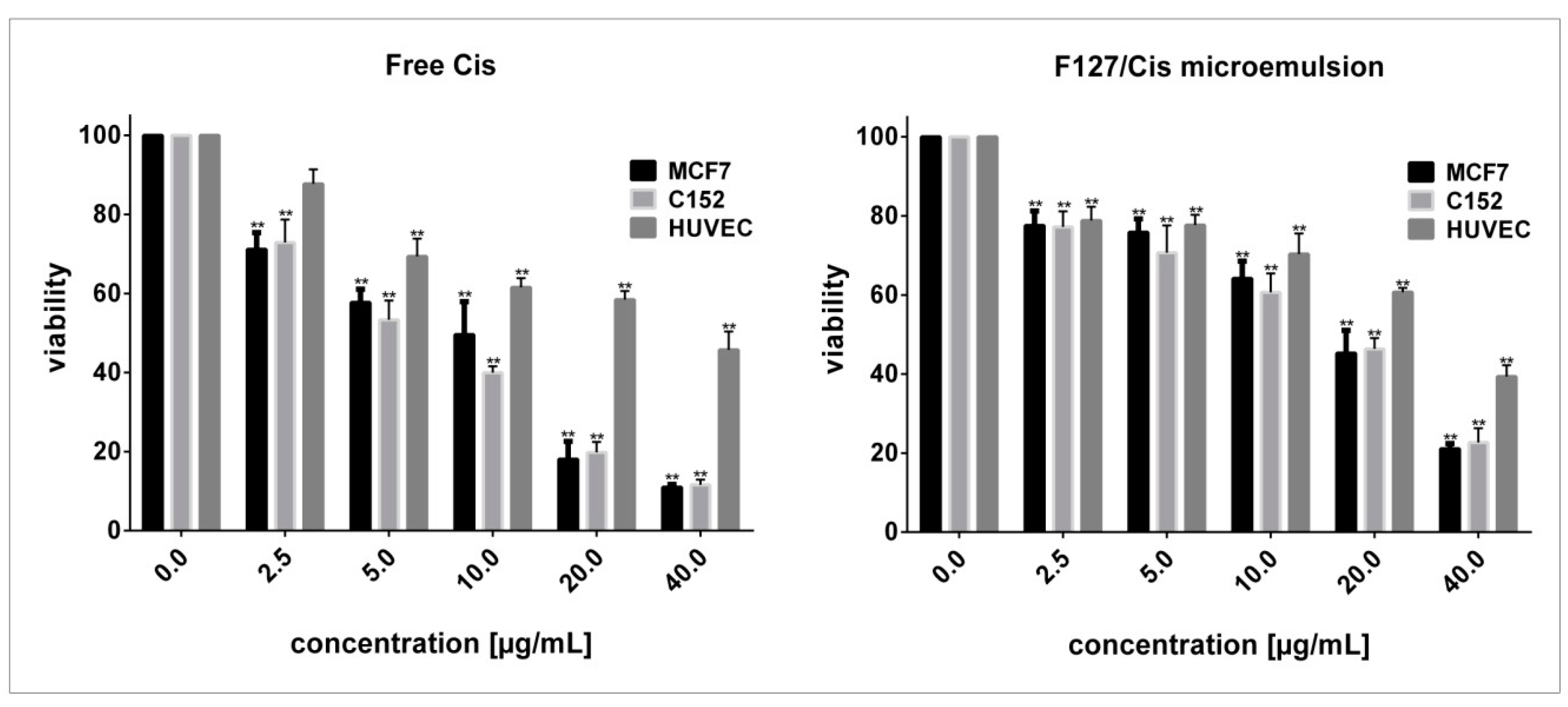
3.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3.3. Biochemical Analysis
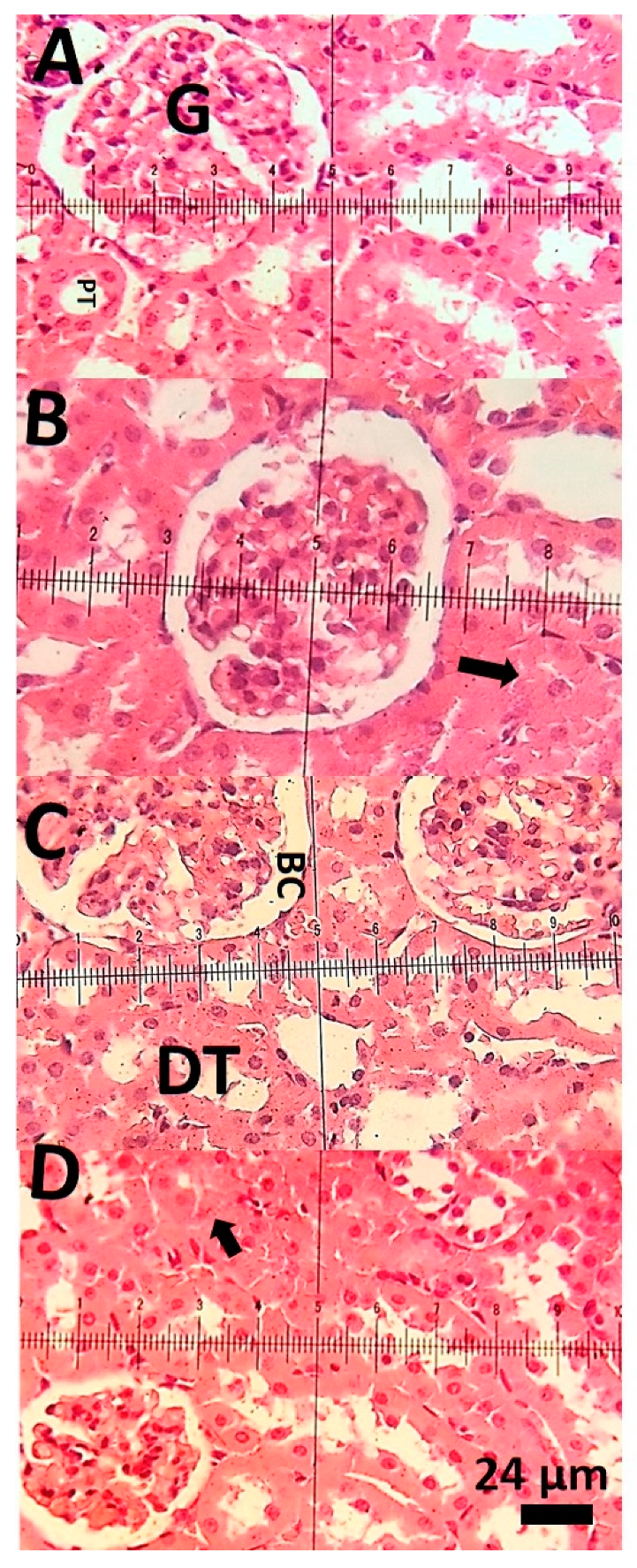
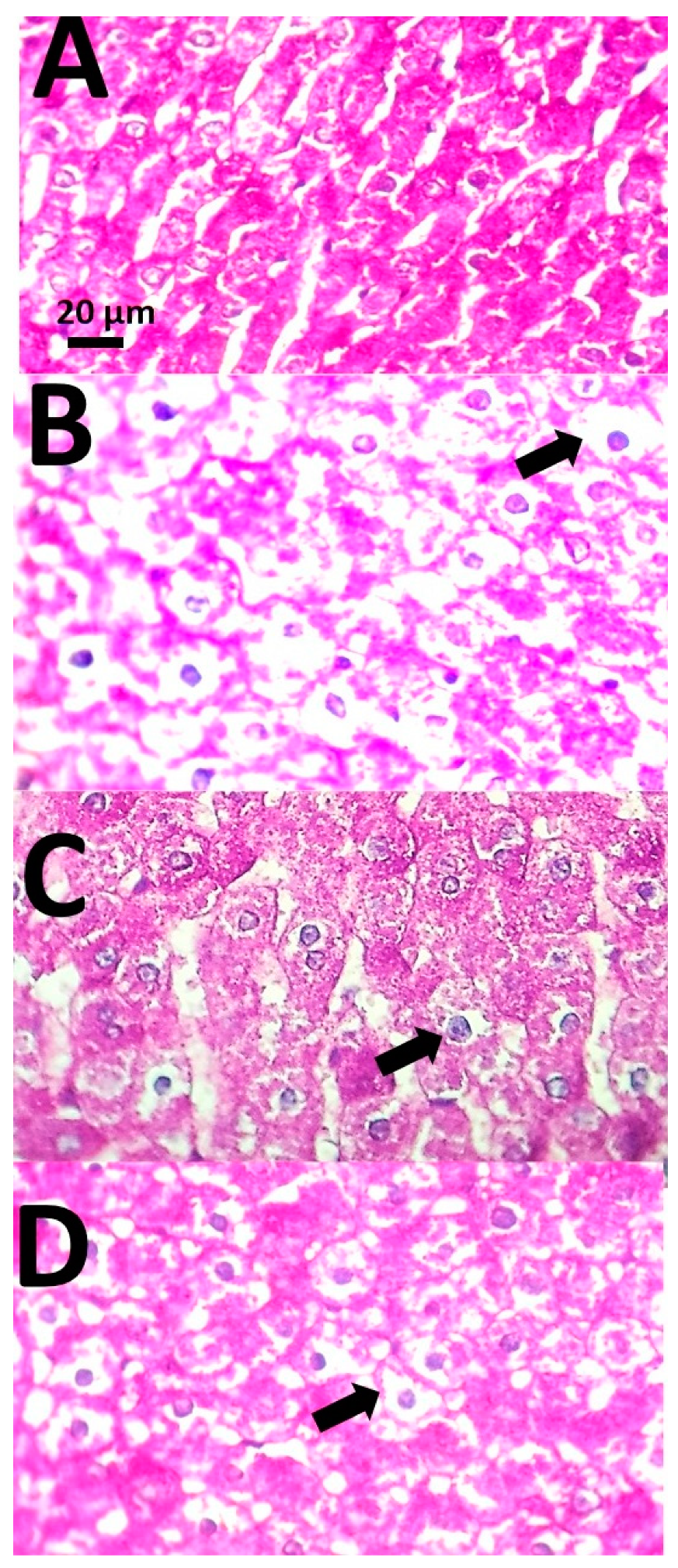
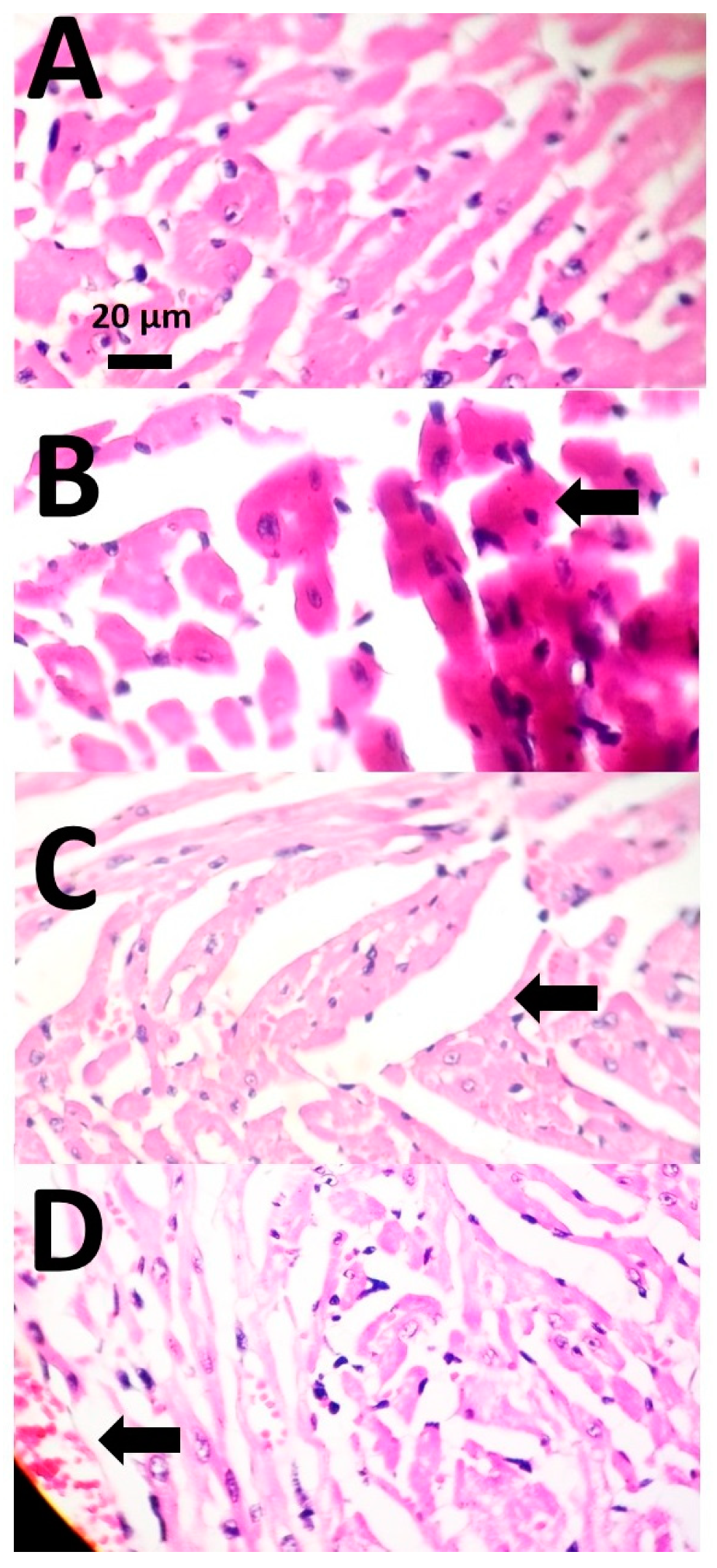
3.4. Histopathological Examinations
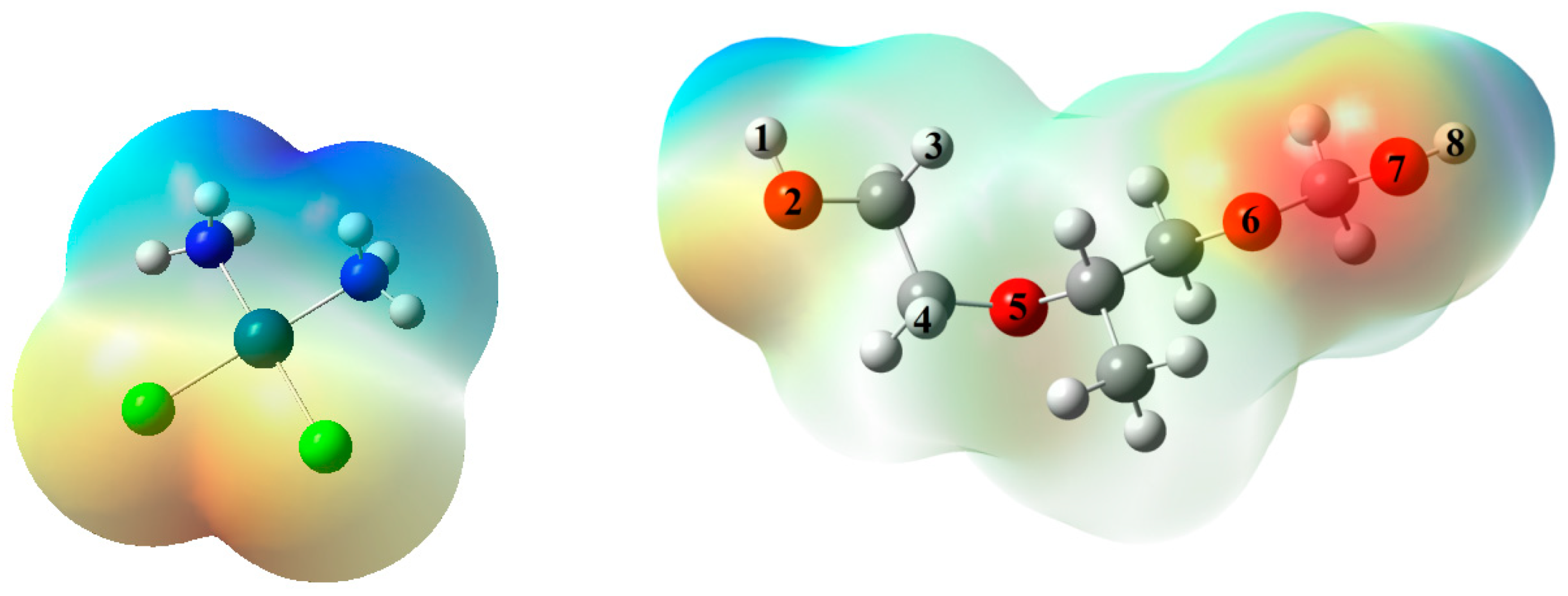
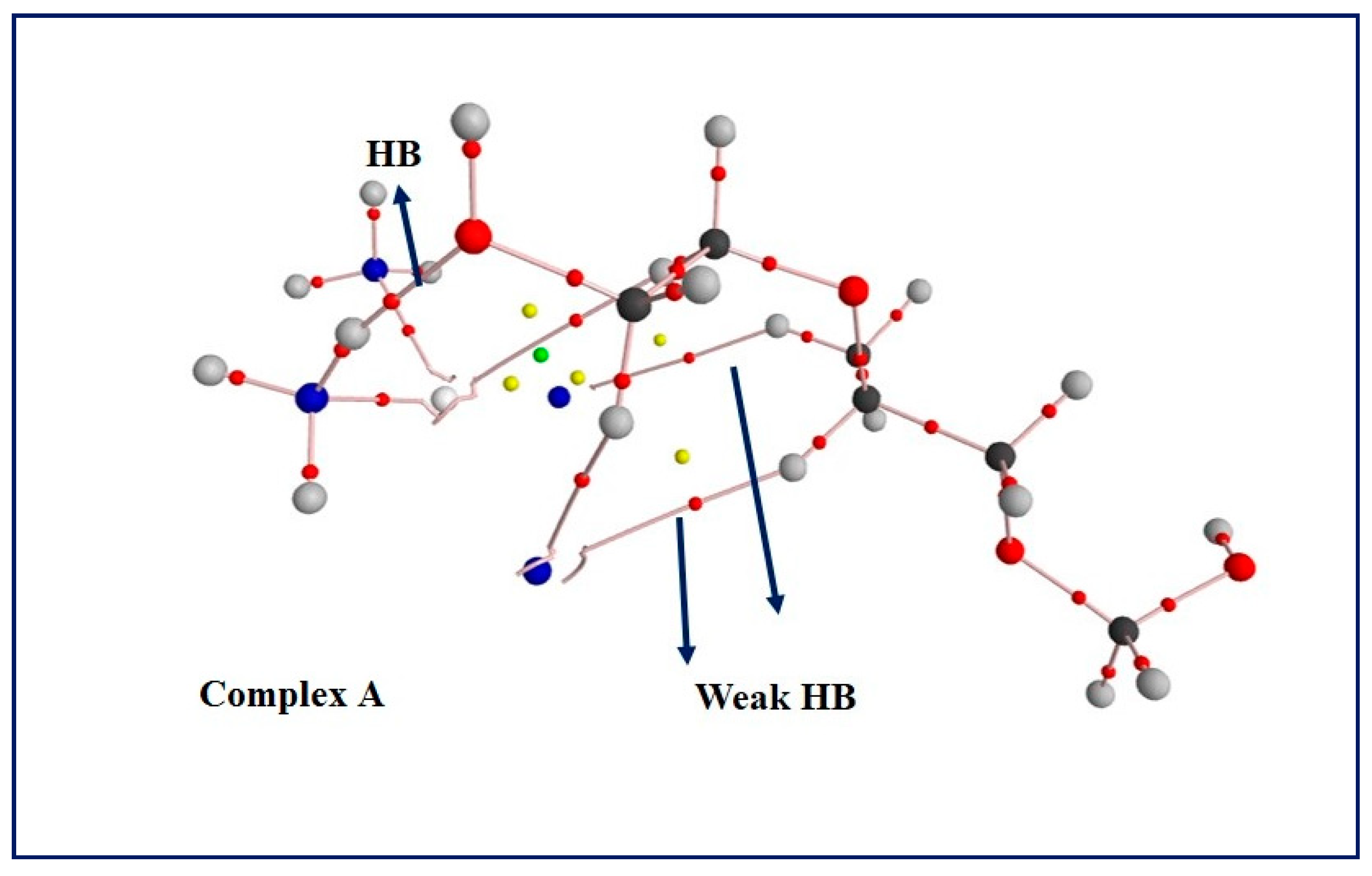
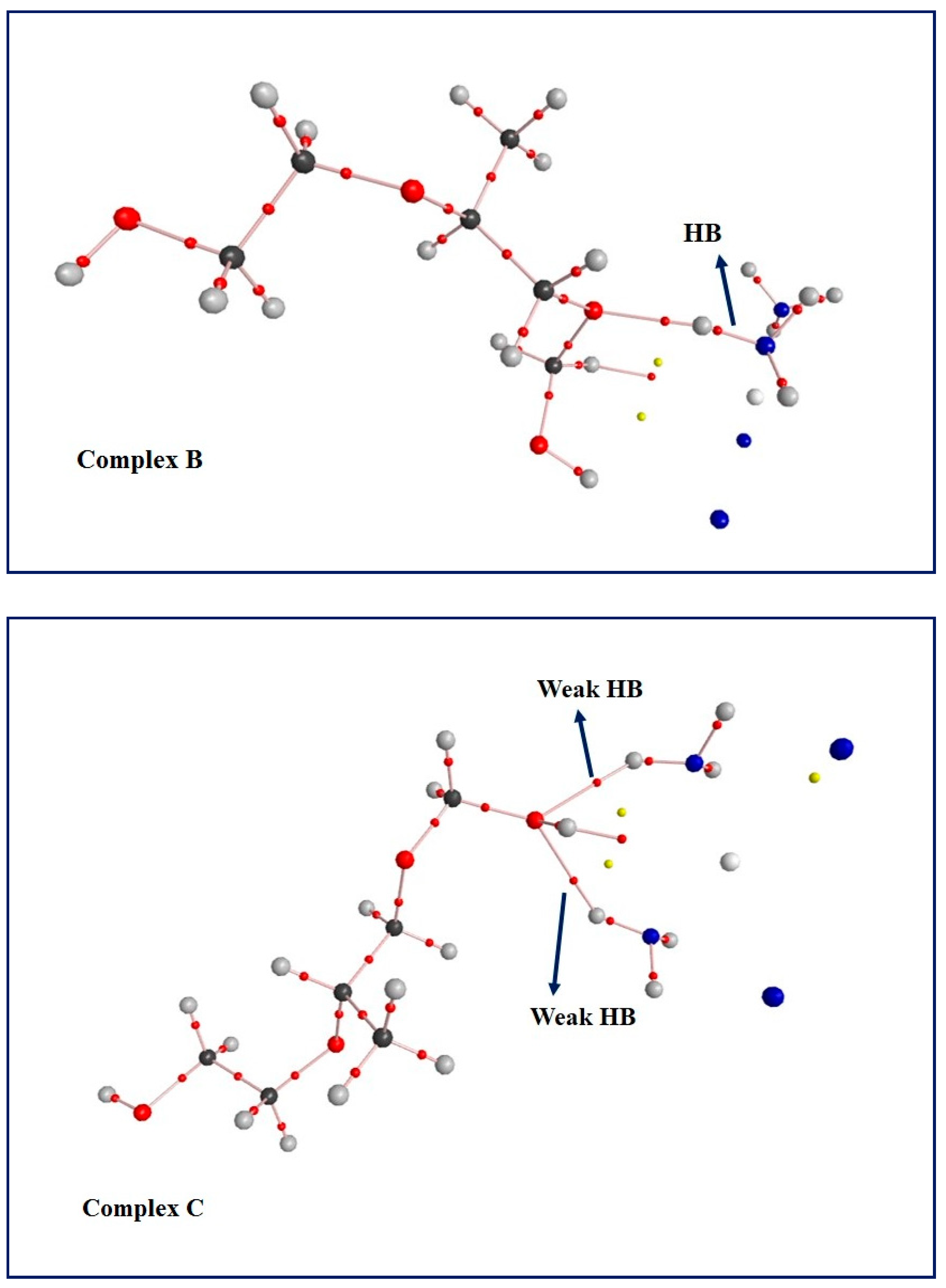
3.5. Computational Results: The Interplay between Cis and Surfactant F127
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Definitions |
| FDA | Food and drug administration |
| Cis | Cisplatin |
| MTT | 3-( 4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| HB | Hydrogen bonding |
| CRT1 | Copper transporter 1 |
| MDR | Multi-drug resistance |
| EPR | Enhanced permeability and retention effect |
| O/W | Oil in water |
| W/O | Water in oil |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| HUVECs | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ARF | Autocorrelation function |
| MEP | Molecular electrostatic potential |
| HOMO | Highest occupied molecular orbital |
| LUMO | Lowest unoccupied molecular orbital |
| EG | Energy gap |
| CT | Charge transfer |
| BCPs | Bond critical points |
References
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Wani, W.A.; Saleem, K.; Haque, A. Platinum compounds: A hope for future cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.-L.; Fang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Fang, J.-Y. Permeation enhancer-containing water-in-oil nanoemulsions as carriers for intravesicalcisplatin delivery. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taber, A.; Christensen, E.; Lamy, P.; Nordentoft, I.; Prip, F.; Lindskrog, S.V.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Okholm, T.L.H.; Knudsen, M.; Pedersen, J.S. Molecular correlates of cisplatin-based chemotherapy response in muscle invasive bladder cancer by integrated multi-omics analysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.A.; Xiao, H.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Jing, X.; Lin, J. Rational design of multifunctional upconversionnanocrystals/polymer nanocomposites for cisplatin (IV) delivery and biomedical imaging. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4898–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varbanov, H.; Valiahdi, S.M.; Legin, A.A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Roller, A.; Galanski, M.; Keppler, B.K. Synthesis and characterization of novel bis (carboxylato) dichloridobis (ethylamine) platinum (IV) complexes with higher cytotoxicity than cisplatin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Ríos, R.; Sánchez-Ramírez, D.R.; Ruiz-Saray, K.; Oceguera-Basurto, P.E.; Almada, M.; Juárez, J.; Zepeda-Moreno, A.; del Toro-Arreola, A.; Topete, A.; Daneri-Navarro, A. Cisplatin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for HER2 targeted ovarian cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Z.; Du, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, J. Rational design of polyion complex nanoparticles to overcome cisplatin resistance in cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Kolishetti, N.; Lippard, S.J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Targeted delivery of a cisplatinprodrug for safer and more effective prostate cancer therapy in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callender, S.P.; Mathews, J.A.; Kobernyk, K.; Wettig, S.D. Microemulsion utility in pharmaceuticals: Implications for multi-drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y. Stimuli-responsive microemulsions: State-of-the-art and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 49, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.S.; Delmarre, D.; Gao, D. Stable drug encapsulation in micelles and microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 345, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Boutonnet, M.; Solans, C. A novel approach to metal and metal oxide nanoparticle synthesis: The oil-in-water microemulsion reaction method. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biruss, B.; Valenta, C. The advantage of polymer addition to a non-ionic oil in water microemulsion for the dermal delivery of progesterone. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Nasri, S.; Beyzaei, H.; Barani, M.; Trant, J.F. The synthesis of methotrexate-loaded F127 microemulsions and their in vivo toxicity in a rat model. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Kazemi, S.; Askari, F. Pluronic as nano-carier for drug delivery systems. Nanomed. Res. J. 2018, 3, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Al Khateb, K.; Ozhmukhametova, E.K.; Mussin, M.N.; Seilkhanov, S.K.; Rakhypbekov, T.K.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. In situ gelling systems based on Pluronic F127/Pluronic F68 formulations for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James-Smith, M.A.; Shekhawat, D.; Cheung, S.; Moudgil, B.M.; Shah, D.O. Role of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide groups of pluronics in binding of fatty acid to pluronics in microemulsions. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2008, 11, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Sargazi, S.; Bilal, M.; Barani, M.; Karimi, P.; Kyzas, G.Z. Biochemical effects of deferasirox and deferasirox-loaded nanomicellesin iron-intoxicated rats. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, R.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Fan, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. Enhancement of cisplatin efficacy by lipid–CaO 2 nanocarrier-mediated comprehensive modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4260–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akartas, I.; Karasulu, H.Y. Preparation and characterization of self-microemusifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of cisplatin for oral use in ovarian cancer treatment. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2020, 77, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, I.D.; Doijad, R.C.; Mohite, S.K.; Manjappa, A.S. Preparation and Characterization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, H.; Song, Y.; Wu, R.; Tang, C.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z. Preparation and optimization lipid nanocapsules to enhance the antitumor efficacy of cisplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Morey, T.E.; Shah, D.O.; Flint, J.A.; Moudgil, B.M.; Seubert, C.N.; Dennis, D.M. Pluronicmicroemulsions as nanoreservoirs for extraction of bupivacaine from normal saline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5108–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W. Dynamic Light Scattering: The Method and Some Applications; Clarendon Press: Bolton, ON, Canada, 1993; Volume 49. [Google Scholar]
- Rahdar, A.; Almasi-Kashi, M.; Khan, A.M.; Aliahmad, M.; Salimi, A.; Guettari, M.; Kohne, H.E.G. Effect of ion exchange in NaAOT surfactant on droplet size and location of dye within Rhodamine B (RhB)-containing microemulsion at low dye concentration. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 252, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Amini, N.; Askari, F.; Susan, M.; Hasan, A.B. Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential measurements: Effective techniques to characterize therapeutic nanoparticles. J. Nanoanal. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A. The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules: From Solid State to DNA and Drug Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendening, E.D.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Weinhold, F. NBO Version 3.1; Gaussian Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; He, C.; Kron, S.J.; Lin, W. Nanoparticle formulations of cisplatin for cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarimboli, G. Membrane transporters as mediators of cisplatin side-effects. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Miao, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. Unmodified drug used as a material to construct nanoparticles: Delivery of cisplatin for enhanced anti-cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, A.; Nitta, N.; Ohta, S.; Nitta-Seko, A.; Morikawa, S.; Tabata, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K. Controlled release and antitumor effect of pluronic F127 mixed with cisplatin in a rabbit model. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, D.K. Engineering of nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; Chang, L.-C.; Wu, P.-C. Co-Delivery of Cisplatin and Gemcitabine via Viscous Nanoemulsion for Potential Synergistic Intravesical Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahdar, A.; Aliahmad, M.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Samani, M. Xanthan gum-stabilized nano-ceria: Green chemistry based synthesis, characterization, study of biochemical alterations induced by intraperitoneal doses of nanoparticles in rat. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1173, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Hamishekar, H.; Ghamkhari, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Copolymer/graphene oxide nanocomposites as potential anticancer agents. Polym. Bull. 2020, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Taboada, P.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Barani, M.; Beyzaei, H. Effect of tocopherol on the properties of Pluronic F127 microemulsions: Physico-chemical characterization and in vivo toxicity. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Treatment * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Cisplatin Bulk | F127/Cis Microemulsion 7 mg/kg | F127/Cis Microemulsion 14 mg/kg | |
| Liver MDA (nmol/mg protein) | 117.0 ± 11.3 | 144.9 * ± 21.4 | 125.8 ± 23.4 | 142.3 * ± 14.2 |
| AST (U/L) | 56.8 ± 19.4 | 86.8 *** ± 13.3 | 75.9 * ± 13.5 | 80.6 ** ± 13.8 |
| ALT (U/L) | 44.8 ± 13 | 78.9 *** ± 17.5 | 69.6 * ± 22.9 | 71.1 * ± 18.9 |
| ALP (U/L) | 19.5 ± 6.3 | 38.9 *** ± 8.1 | 25.3 ± 6.2 | 30.8 ** ± 7.1 |
| BUN (mg/dl) | 16 ± 4.9 | 24.5 * ± 8.7 | 21.8 ± 5.3 | 23.9 *± 5.7 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 0.71 ± 0.11 | 1.1 *** ± 0.21 | 0.9 ± 0.06 | 1.07 ** ± 0.26 |
| LDH (U/dl) | 117.8 ± 12.9 | 134.8 * ± 12.3 | 118.5 ± 5.3 | 125.2 ± 9 |
| EHOMO | ELUMO | EG | qO | qH | qN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cis | −6.272 | −1.901 | 4.372 | - | 0.363 | −0.883 |
| F127 | −6.990 | 1.288 | 8.278 | * | - | - |
| complex A | −6.225 | −1.739 | 4.486 | −0.567 | 0.457 | −0.916 |
| complex B | −6.383 | −1.927 | 4.455 | −0.413 | 0.463 | −0.918 |
| complex C | −6.166 | −1.711 | 4.455 | −0.548 | 0.391 | −0.890 |
| Concentration | 2.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * ∆G | −3.486 | 328.313 | 988.026 | 2304.883 | 4937.124 |
| * ∆H | 10.139 | 337.308 | 993.932 | 2308.857 | 4940.136 |
| ** ∆S | 0.046 | 0.03 | 0.020 | 0.013 | 0.010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sargazi, S.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Baino, F.; Karimi, P.; Pandey, S. F127/Cisplatin Microemulsions: In Vitro, In Vivo and Computational Studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073006
Sargazi S, Hajinezhad MR, Barani M, Mukhtar M, Rahdar A, Baino F, Karimi P, Pandey S. F127/Cisplatin Microemulsions: In Vitro, In Vivo and Computational Studies. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSargazi, Saman, Mohammad Reza Hajinezhad, Mahmood Barani, Mahwash Mukhtar, Abbas Rahdar, Francesco Baino, Pouya Karimi, and Sadanand Pandey. 2021. "F127/Cisplatin Microemulsions: In Vitro, In Vivo and Computational Studies" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073006
APA StyleSargazi, S., Hajinezhad, M. R., Barani, M., Mukhtar, M., Rahdar, A., Baino, F., Karimi, P., & Pandey, S. (2021). F127/Cisplatin Microemulsions: In Vitro, In Vivo and Computational Studies. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073006










