A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Routing Issues and Challenges for VANETs
2.2. Cluster-Based Routing Schemes
2.3. Reliability-Based Routing Schemes
2.4. Link Connectivity Metric for Cluster-Based Routing Schemes
3. Connectivity Models for Vehicular Communications
3.1. System Model
3.2. Vehicle Connectivity Models
3.3. Strongly Connected (STC) Route Selection
4. Proposed Connectivity-Based Clustering Schemes
4.1. Vehicular Connectivity to VANET Graphs
- The value of link connectivity is added to the th position of adjacency matrix if vehicle and are connected.
- If a link represents the same connectivity in both directions, i.e., , then we add 1 value for connectivity.
- The term “otherwise” in Equation (7) is considered when the first two conditions failed. When two vehicles are not connected, we add 0 in that case. The adjacency matrix representing the inter-connectivity of vehicles can be calculated as below:
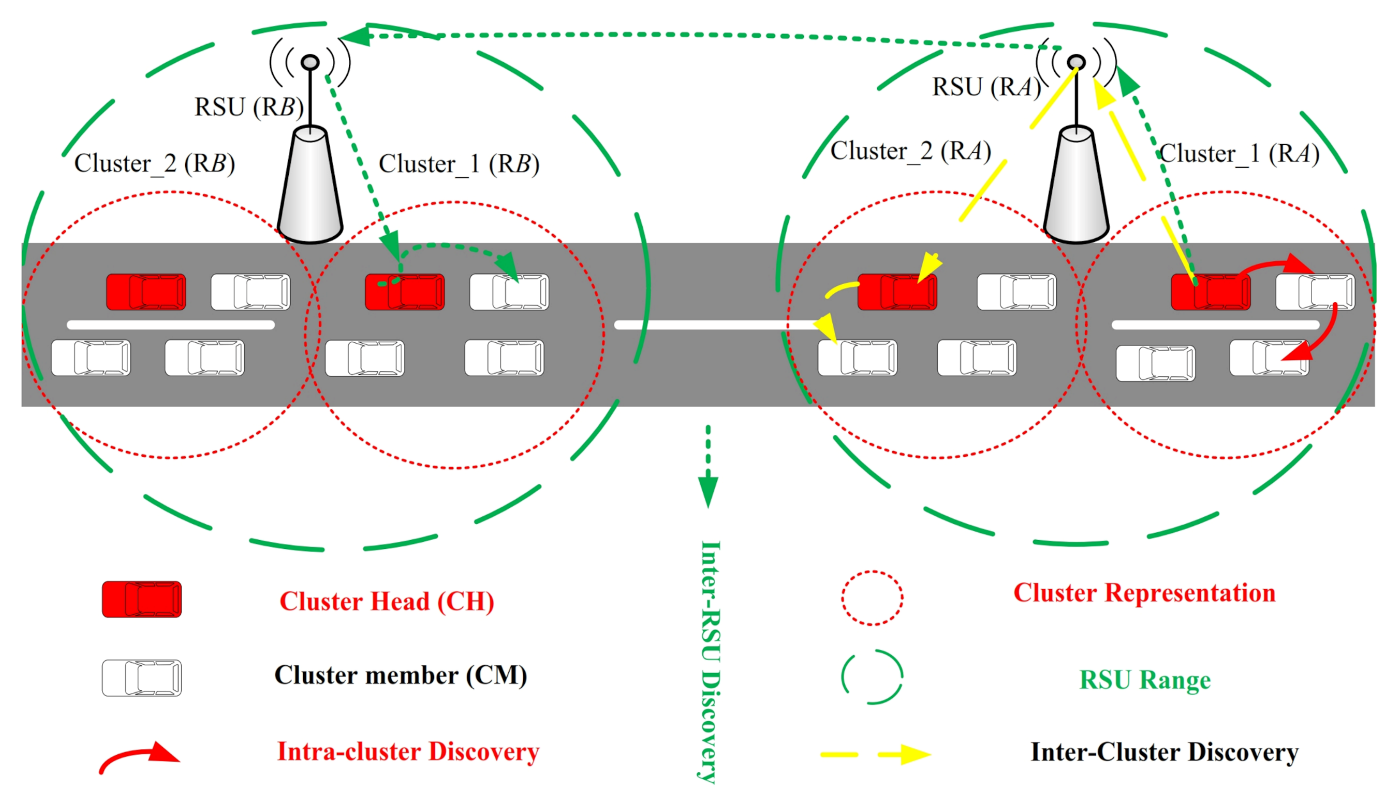
4.2. Cluster Formation and Cluster Head Selection in the Suggested Routing Scheme
5. Route Discovery in the Suggested Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme
5.1. Route Discovery in Intra-Cluster to the Destination
5.2. Route Discovery in Inter-Cluster to the Destination
- FAP enables each CH to obtain cluster reachability information from RSU. The reachability information refers to the list of connected nodes to a particular RSU and/or CH. It is similar to a routing table that stores information of all accessible nodes.
- Next, RSU propagates the reachability information to all CHs.
6. Simulation Results and Discussion
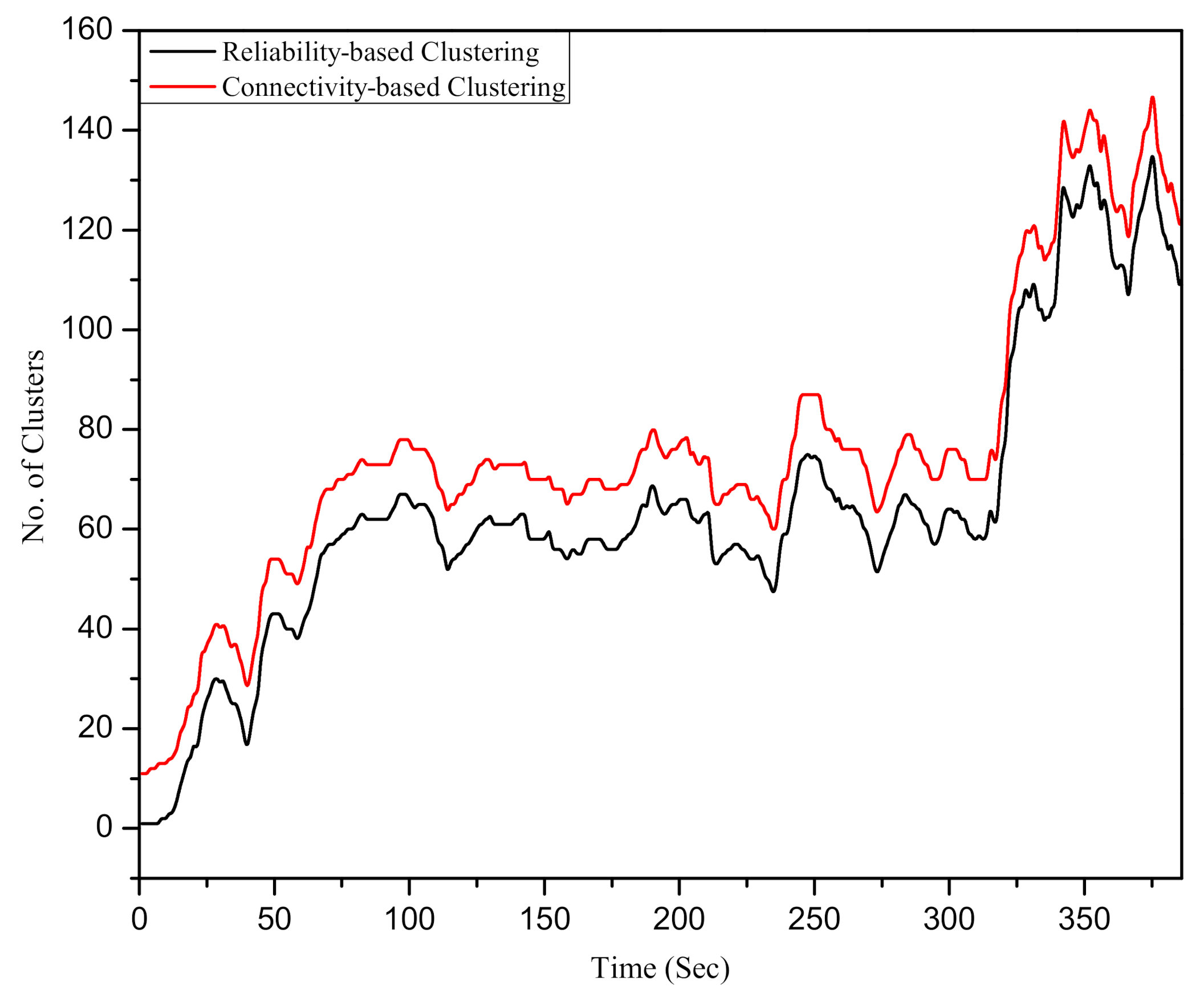
6.1. Assessment of the Dynamic Number of Clusters
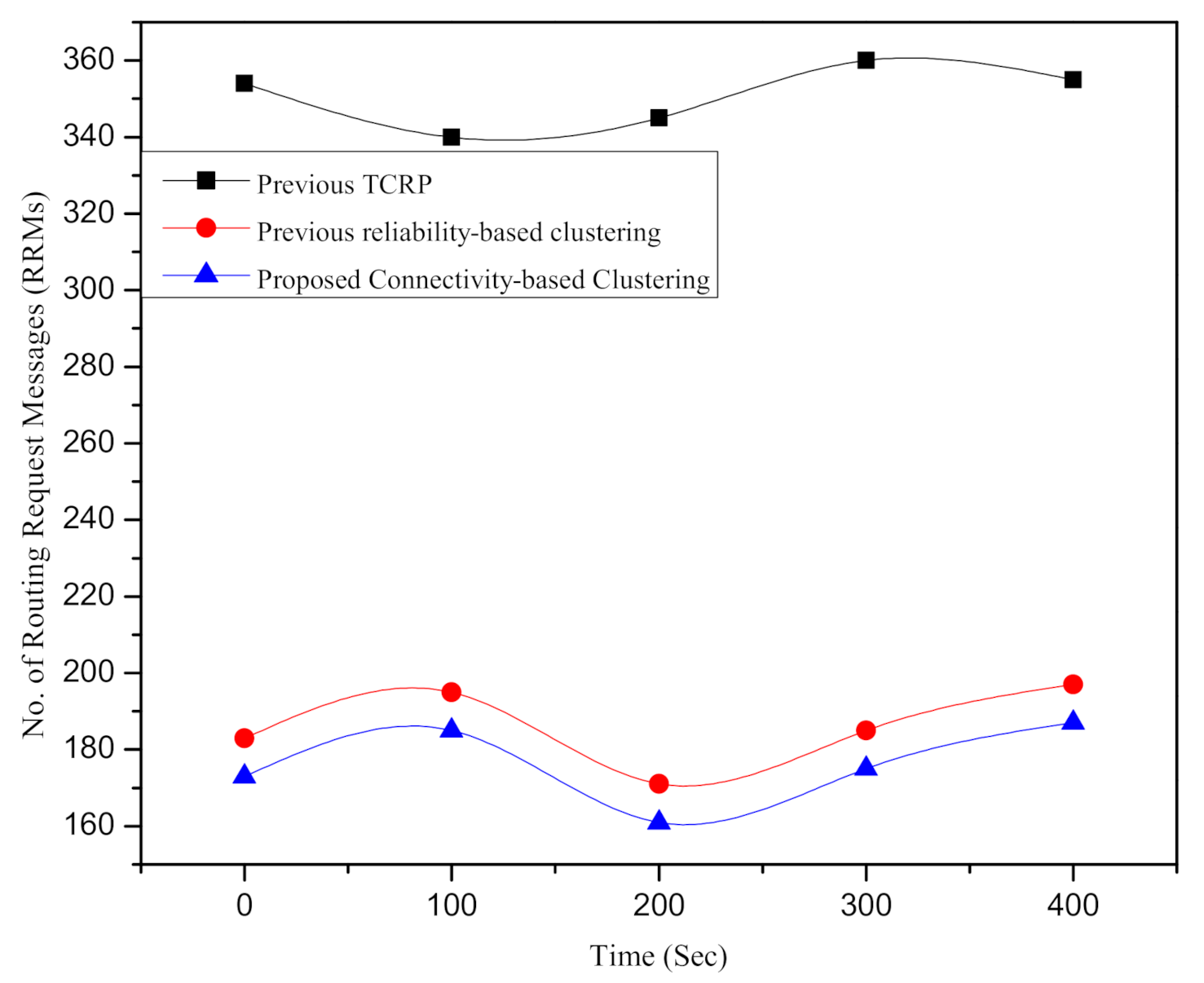
6.2. Assessment of the Connectivity-Based Clustering Overhead
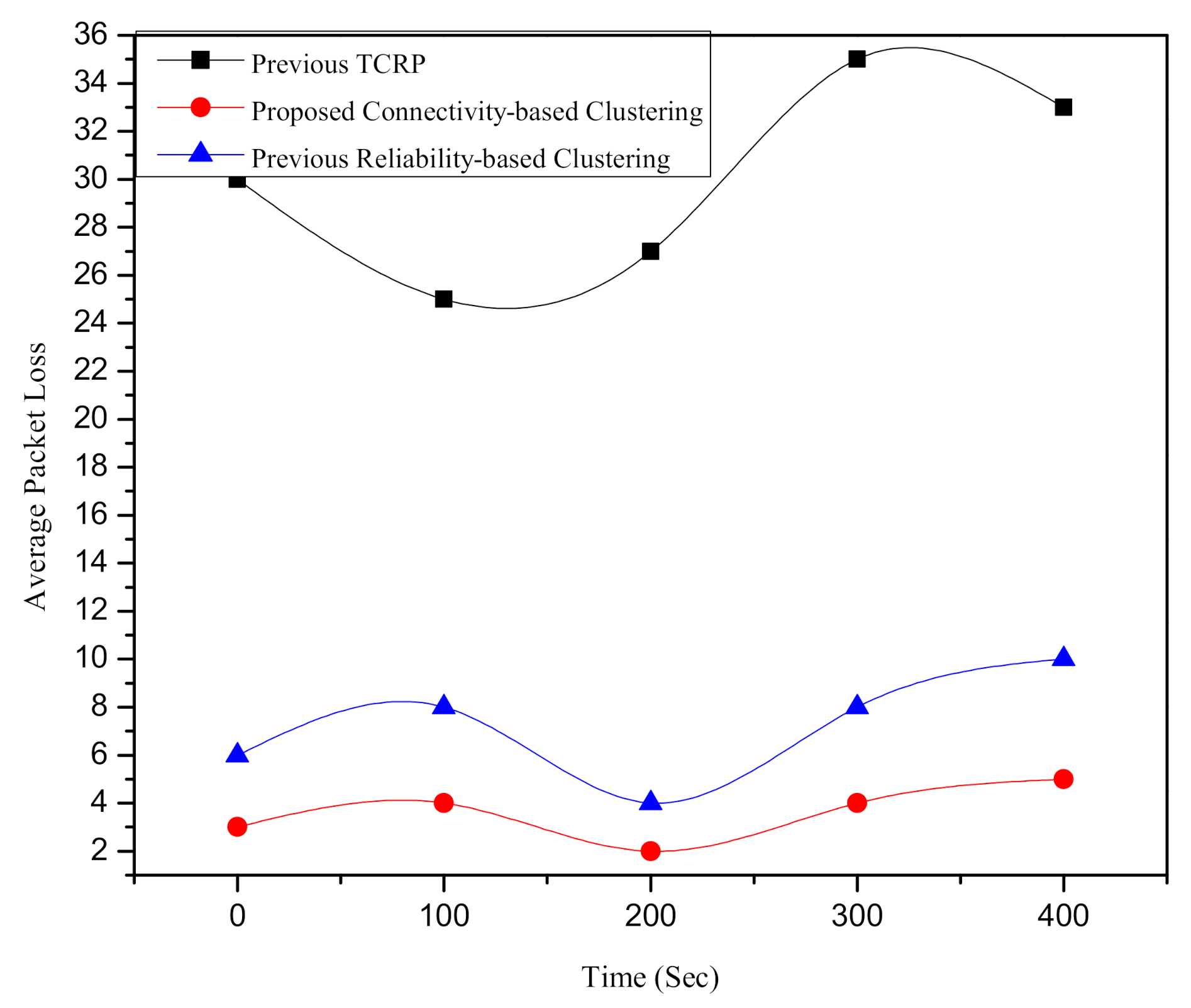
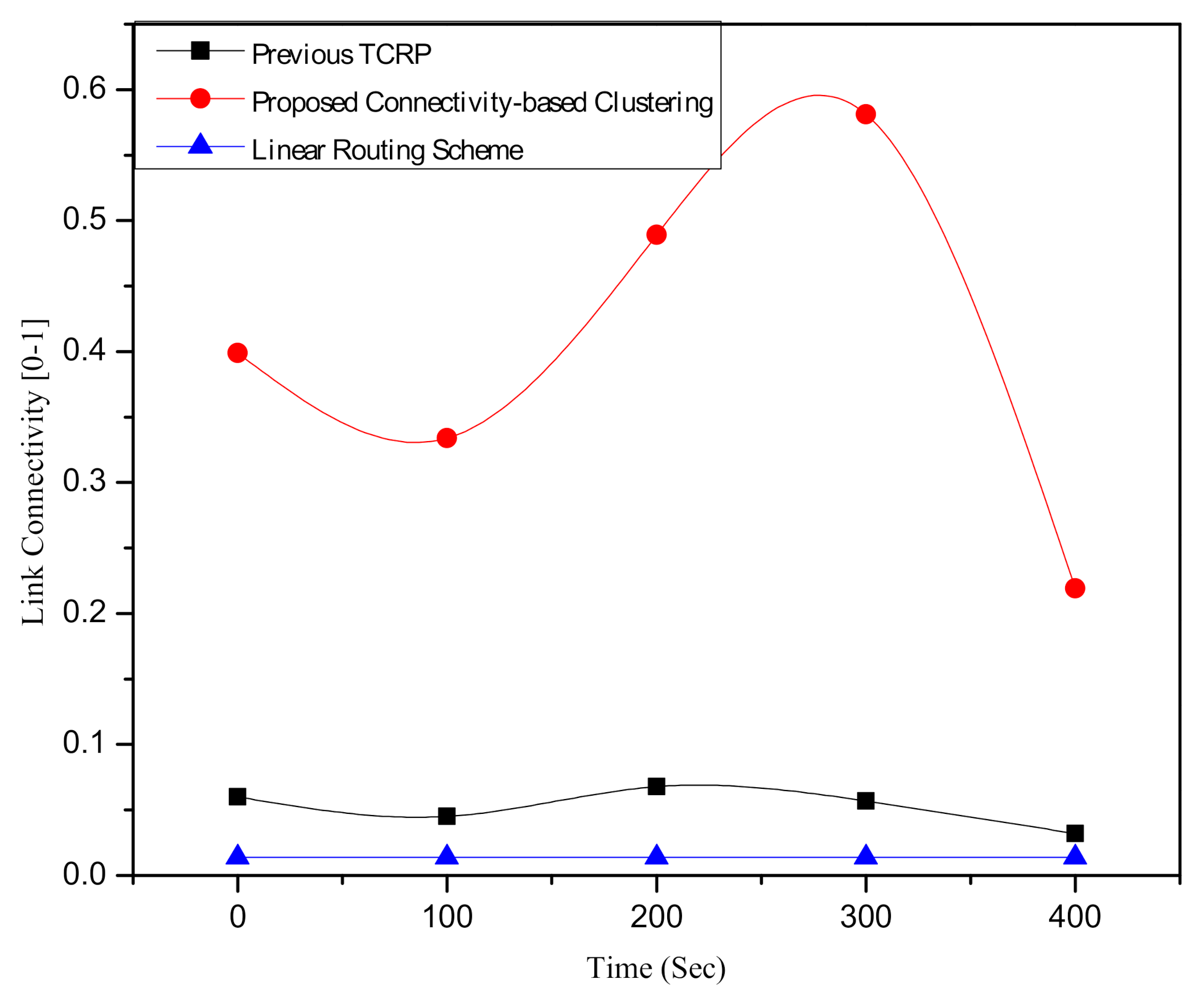
6.3. Assessment of the Route Connectivity of the Proposed Clustering Scheme
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, Z.; Fan, P. A novel triple cluster based routing protocol (TCRP) for VANETs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wahid, I.; Ikram, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, S.; Ali, A. State of the art routing protocols in VANETs: A review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 130, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fan, P.; Fang, S.; Abbas, F. An Unsupervised Cluster-Based VANET-Oriented Evolving Graph (CVoEG) Model and Associated Reliable Routing Scheme. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 3844–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fan, P. A multi-hop moving zone (MMZ) clustering scheme based on cellular-V2X. China Commun. 2018, 15, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiza, M.H.; Ni, Q. An evolving graph-based reliable routing scheme for VANETs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fan, P.; Abbas, F.; Chen, H.; Fang, S. Two-level cluster based routing scheme for 5G V2X communication. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16194–16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kang, J.; Squicciarini, A.; Wu, Y.; Gurung, S.; Tonguz, O. MoZo: A moving zone based routing protocol using pure V2V communication in VANETs. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 16, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fang, S.; Koubaa, A.; Fan, P.; Abbas, F.; Farman, H. Street-centric routing scheme using ant colony optimization-based clustering for bus-based vehicular ad-hoc network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 86, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Liu, G.; Fan, P.; Khan, Z. An Efficient Cluster Based Resource Management Scheme and Its Performance Analysis for V2X Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87071–87082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Franklin, D.; Ros, M.; Safaei, F.; Abolhasan, M. A comparative survey of VANET clustering techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 19, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fan, P.; Fang, S. On the connectivity of vehicular ad hoc network under various mobility scenarios. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22559–22565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qi, N.; Chen, J.; Dong, C.; Huang, Z. Enhancing clustering stability in VANET: A spectral clustering based approach. China Commun. 2020, 17, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, V.; Gross, T.R. Connectivity-aware routing (CAR) in vehicular ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2007—26th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, Anchorage, AK, USA, 6–12 May 2007; pp. 1919–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Viriyasitavat, W.; Tonguz, O.K.; Bai, F. UV-CAST: An urban vehicular broadcast protocol. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonguz, O.; Wisitpongphan, N.; Bai, F.; Mudalige, P.; Sadekar, V. Broadcasting in VANET. In Proceedings of the 2007 Mobile Networking For Vehicular Environments, Anchorage, AK, USA, 11 May 2007; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Abichar, Z.; Chang, J.M. Roadside-aided routing (RAR) in vehicular networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Istanbul, Turkey, 11–15 June 2006; Volume 8, pp. 3602–3607. [Google Scholar]
- Khakpour, S.; Pazzi, R.W.; El-Khatib, K. Using clustering for target tracking in vehicular ad hoc networks. Veh. Commun. 2017, 9, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiamoorthy, J.; Ramakrishnan, B. Design of a proficient hybrid protocol for efficient route discovery and secure data transmission in CEAACK MANETs. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2017, 36, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, N.; Shen, X. i CAR-II: Infrastructure-Based Connectivity Aware Routing in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 4231–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yu, H.; Fan, G.; Sun, H.; Chen, L. Efficient and reliable cluster-based data transmission for vehicular ad hoc networks. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Leng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Vinel, A.; Jonsson, M. Performance analysis of connectivity probability and connectivity-aware MAC protocol design for platoon-based VANETs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 5596–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Li, T.; Khan, Z.; Khurshid, F.; Ahmad, M. A novel connectivity-based LEACH-MEEC routing protocol for mobile wireless sensor network. Sensors 2018, 18, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, M.; Zhang, J.; Khoukhi, L.; Labiod, H.; Vèque, V. A unified framework of clustering approach in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 19, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, S.; Lynn, C.; Seo, K. Secure border gateway protocol (S-BGP). IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2000, 18, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrisch, M.; Bieker, L.; Erdmann, J.; Krajzewicz, D. SUMO–simulation of urban mobility: An overview. In Proceedings of the SIMUL 2011, The Third International Conference on Advances in System Simulation ThinkMind, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kabrane, M.; Krit, S.; Elmaimouni, L.; Bendaoud, K.; Oudani, H.; Elasikri, M.; Karimi, K.; El Bousty, H. Smart cities: Energy consumption in wireless sensor networks for road trafile modeling using simulator SUMO. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS), Monastir, Tunisia, 8–10 May 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length of road | 2 km |
| Number of lanes | 3 |
| Length of vehicle | 5 m |
| Mean velocity | [60–100] km/h |
| Junctions | 2 |
| Traffic lights | 2 |
| Traffic arrival | Poison distribution (continuous) |
| Number of nodes | Depends on arrival rate |
| Mobility duration | 400 s |
| Road type | Highway |
| Road surface | Asphalt |
| Traffic departure | Poison distribution |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transmission range R | 300 m |
| Performance metrics | route request messages (RRMs), link connectivity, number of clusters |
| MAC protocol | IEEE 802.11p |
| Packet size | 2000 bytes |
| Bit rate | 128 kb/s |
| Number of simulation run | 5 |
| Routing | CEG-Dijkstra |
| Metric for clustering | Link connectivity |
| Minimum clustering criteria | |
| RSU range | 1 km |
| Number of RSUs | Equal distance installation |
| CH selection | Max. Eigen centrality |
| Route discovery types | Inter and intra-discovery |
| Intra-clustering discovery | CEG-Dijkstra |
| Inter-clustering discovery | FAP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, Z.; Koubaa, A.; Fang, S.; Lee, M.Y.; Muhammad, K. A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052413
Khan Z, Koubaa A, Fang S, Lee MY, Muhammad K. A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052413
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Zahid, Anis Koubaa, Sangsha Fang, Mi Young Lee, and Khan Muhammad. 2021. "A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052413
APA StyleKhan, Z., Koubaa, A., Fang, S., Lee, M. Y., & Muhammad, K. (2021). A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052413






