Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
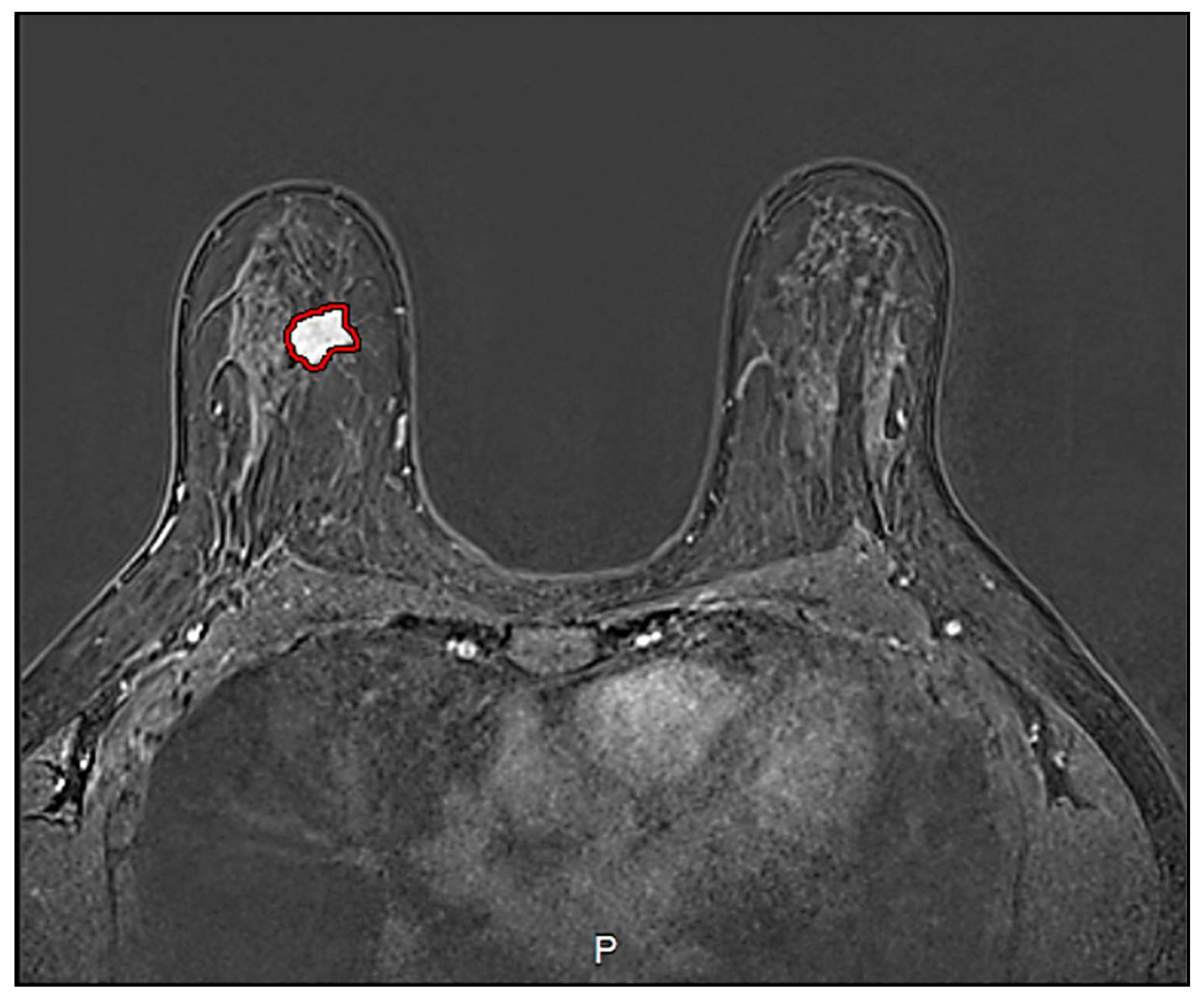
2.4. Image Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Univariate Analysis
2.5.2. Multivariate Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AIOM. I Numeri del Cancro in Italia; AIOM: Milano, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2019–2020; American Cancer Society Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; Available online: www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/documents/document/acspc-030975.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Schwab, F.D.; Huang, D.J.; Schmid, S.M.; Schötzau, A.; Güth, U. Self-detection and clinical breast examination: Comparison of the two “classical” physical examination methods for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heywang-Köbrunner, S.; Viehweg, P.; Heinig, A.; Küchler, C. Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: Accuracy, value, controversies, solutions. Eur. J. Radiol. 1997, 24, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dromain, C.; Thibault, F.; Muller, S.; Rimareix, F.; Delaloge, S.; Tardivon, A.; Balleyguier, C. Dual-energy contrast-enhanced digital mammography: Initial clinical results. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 21, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dromain, C.; Thibault, F.; Diekmann, F.; Fallenberg, E.M.; A Jong, R.; Koomen, M.; Hendrick, R.E.; Tardivon, A.; Toledano, A. Dual-energy contrast-enhanced digital mammography: Initial clinical results of a multireader, multicase study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczynska, E.; Heinze-Paluchowska, S.; Dyczek, S.; Blecharz, P.; Ryś, J.; Reinfuss, M. Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography: Comparison with Conventional Mammography and Histopathology in 152 Women. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.K.; Lobbes, M.; Lewin, J. Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography: A Review. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2018, 39, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessouky, B.; Elsaid, N.; Shaaban, Y. Role of contrast-enhanced digital mammography in evaluation of breast lesions. Menoufia Med. J. 2017, 30, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.C.; Patel, B.K.; Pizzitola, V.J. Navigating contrast-enhanced digital mammography. Appl. Radiol. 2017, 46, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, V.; Houssami, N.; Ghirardi, M.; Ferrari, A.; Speziani, M.; Bellarosa, S.; Remida, G.; Gasparotti, C.; Galligioni, E.; Ciatto, S. Evidence of the effect of adjunct ultrasound screening in women with mammography-negative dense breasts: Interval breast cancers at 1year follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, M.R. Imaging the dense breast. Appl. Radiol. 2004, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Saslow, D.; Boetes, C.; Burke, W.; Harms, S.; Leach, M.O.; Lehman, C.D.; Morris, E.; Pisano, E.; Schnall, M.; Sener, S.; et al. American Cancer Society Guidelines for Breast Screening with MRI as an Adjunct to Mammography. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2007, 57, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglogiannis, I.; Zafiropoulos, E.; Anagnostopoulos, I. An intelligent system for automated breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis using SVM based classifiers. Appl. Intell. 2007, 30, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Breitenseher, M.; Amann, G.; Dominkus, M. Are signal intensity and homogeneity useful parameters for distinguishing between benign and malignant soft tissue masses on MR images? Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 26, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, C.E.; Chen, W.-P.; Nie, K.; Su, M.-Y. Prediction of Malignant Breast Lesions from MRI Features. Acad. Radiol. 2009, 16, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, R.N.; Adams, A.E.; Horne, C.H.; Angus, B.; Smith, A.F.; Sherbet, G.V.; Lennard, T.W. Prediction of nodal metastasis and prognosis in breast cancer: A neural model. Anticancer Res. 1997, 17, 2735–2741. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, D.; Nie, K.; Chen, J.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Yu, H.J.; Nalcioglu, O.; Su, M.-Y. Selection of diagnostic features on breast MRI to differentiate between malignant and benign lesions using computer-aided diagnosis: Differences in lesions presenting as mass and non-mass-like enhancement. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 20, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Lucas-Quesada, F.A.; DeBruhl, N.D.; Sayre, J.; Farria, D.; Gorczyca, D.P.; Bassett, L.W. Multifeature analysis of Gd-enhanced MR images of breast lesions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 7, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzacheva, A.A.; Najarian, K.; Brockway, J.P. Breast cancer detection in gadolinium-enhanced MR images by static region descriptors and neural networks. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnaghi, D.; Monti, A.; Setti, E.; Musumeci, R. A use of a neural network to evaluate contrast enhancement curves in breast magnetic resonance images. J. Digit. Imaging 2001, 14, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomweg, T.W.; Buscema, P.M.; Kauczor, H.U.; Teifke, A.; Intraligi, M.; Terzi, S.; Heussel, C.P.; Achenbach, T.; Rieker, O.; Mayer, D.; et al. Improved artificial neural networks in prediction of malignancy of lesions in contrast-enhanced MR-mammography. Med. Phys. 2003, 30, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Baloch, S.; Englander, S.; Schnall, M.D.; Shen, D. Segmentation and Classification of Breast Tumor Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. MICCAI 2007, 10, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Englander, S.; Baloch, S.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Fan, Y.; Schnall, M.D.; Shen, D. STEP: Spatiotemporal enhancement pattern for MR-based breast tumor diagnosis. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 3192–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K. Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumbas, K. Pattern Recognition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Granata, V.; Catalano, O.; Amato, D.M.; Di Bonito, M.; D’Aiuto, M.; Capasso, I.; Rinaldo, M.; et al. Integration of DCE-MRI and DW-MRI Quantitative Parameters for Breast Lesion Classification. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 237863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, D.J.; Geetha, K. Mass classification in breast DCE-MR images using an artificial neural network trained via a bee colony optimization algorithm. Science 2013, 39, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, J.; Geetha, K. Experimental Investigation of Classification Algorithms for Predicting Lesion Type on Breast DCE-MR Images. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, D.M.; Hylton, N.M.; Kinkel, K.; Hochman, M.G.; Kuhl, C.K.; Kaiser, W.A.; Weinreb, J.C.; Smazal, S.F.; Degani, H.; Viehweg, P.; et al. Development, standardization, and testing of a lexicon for reporting contrast-enhanced breast magnetic resonance imaging studies. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Petrillo, A.; Sansone, C. A Multiple Classifier System for Classification of Breast Lesions Using Dynamic and Morphological Features in DCE-MRI. Comput. Vis. 2012, 7626, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhard, A.; Tanner, C.; Hayes, C.; Hawkes, D.J.; O Leach, M. The UK MRI Breast Screening Study Comparison between radiological and artificial neural network diagnosis in clinical screening. Physiol. Meas. 2002, 23, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Bonilha, L.; Li, L.; Cendes, F. Texture analysis of medical images. Clin. Radiol. 2004, 59, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1973, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, G.; Kiessling, F.; Lucht, R.; Darai, S.; Wasser, K.; Delorme, S. Microcirculation and microvasculature in breast tumors: Pharmacokinetic analysis of dynamic MR image series. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, M.; Fusco, R.; Petrillo, A.; Petrillo, M.; Bracale, M. An expectation-maximisation approach for simultaneous pixel classification and tracer kinetic modelling in dynamic contrast enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 49, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Maffei, S.; Raiano, N.; Petrillo, A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in breast cancer: A comparison between distributed and compartmental tracer kinetic models. J. Biomed. Graph. Comput. 2012, 2, p23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Petrillo, M.; Petrillo, A. Influence of parameterization on tracer kinetic modeling in DCEMRI. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2014, 34, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Sansone, C.; Petrillo, A. Segmentation and classification of breast lesions using dynamic and textural features in Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2012 25th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rome, Italy, 20–22 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmaleki, P.; Buadu, L.D.; Murayama, S.; Murakami, J.; Hashiguchi, N.; Yabuuchi, H.; Masuda, K. Neural network analysis of breast cancer from MRI findings. Radiat. Med. 1998, 15, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmaleki, P.; Buadu, L.D.; Naderimansh, H. Feature extraction and classification of breast cancer on dynamic magnetic resonance imaging using artificial neural network. Cancer Lett. 2001, 171, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agner, S.C.; Soman, S.; Libfeld, E.; McDonald, M.; Thomas, K.; Englander, S.; Rosen, M.A.; Chin, D.; Nosher, J.; Madabhushi, A. Textural Kinetics: A Novel Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE)-MRI Feature for Breast Lesion Classification. J. Digit. Imaging 2010, 24, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbach, L.; Stolpen, A.; Reinhardt, J.M. Classification of breast MRI lesions using a backpropagation neural network (BNN). In Proceedings of the 2004 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Macro to Nano (IEEE Cat No. 04EX821), Arlington, VA, USA, 18 April 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhuijs, K.G.A.; Giger, M.L.; Bick, U. Computerized analysis of breast lesions in three dimensions using dynamic magnetic-resonance imaging. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntu, J.; Sijbers, J.; De Backer, S.; Rajan, J.; Van Dyck, D. Machine learning study of several classifiers trained with texture analysis features to differentiate benign from malignant soft-tissue tumors in T1-MRI images. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Moon, W.K. Characterizing time-intensity curves for spectral morphometric analysis of intratumoral enhancement patterns in breast DCE-MRI: Comparison between differentiation performance of temporal model parameters based on DFT and SVD. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Boston, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, N.; Park, J.S.; Yang, Z.; Jung, Y.S.; Moon, W.K. Multilevel analysis of spatiotemporal association features for differentiation of tumor enhancement patterns in breast DCE-MRI. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 3940–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinsinger, G.; Schlossbauer, T.; Scherr, M.; Lange, O.; Reiser, M.; Wismuller, A. Cluster analysis of signal-intensity time course in dynamic breast MRI: Does unsupervised vector quantization help to evaluate small mammographic lesions? Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levman, J.; Leung, T.; Causer, P.; Plewes, D.; Martel, A.L. Classification of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance breast lesions by support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2008, 27, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levman, J.; Martel, A.L. Computer-aided diagnosis of breast cancer from magnetic resonance imaging examinations by custom radial basis function vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 30 August–4 September 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 2010, pp. 5577–5580. [Google Scholar]
- Lucht, R.E.; Knopp, M.V.; Brix, G. Classification of signal-time curves from dynamic MR mammography by neural networks. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 19, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, R.; Delorme, S.; Brix, G. Neural network-based segmentation of dynamic MR mammographic images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 20, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Petrillo, A. Breast contrast-enhanced MR imaging: Semiautomatic detection of vascular map. Breast Cancer 2014, 23, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The MathWorks Inc. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Vallières, M.; Freeman, C.R.; Skamene, S.; El Naqa, I. A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 5471–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Im-age-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twellmann, T.; Saalbach, A.; Gerstung, O.; O Leach, M.; Nattkemper, T.W. Image fusion for dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Biomed. Eng. Online 2004, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedegärtner, U.; Bick, U.; Wörtler, K.; Rummeny, E.; Bongartz, G. Differentiation between benign and malignant findings on MR-mammography: Usefulness of morphological criteria. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Carone, G.; Amato, D.M.; Sansone, C.; Petrillo, A. Pattern Recognition Approaches for Breast Cancer DCE-MRI Classification: A Systematic Review. J. Med Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. The lasso Method for Variable Selection in the Cox Model. Statist. Med. 1997, 16, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Statist. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 112, p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, P.; Bruce, A. Practical Statistics for Data Scientists; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Angelov, P.P.; Soares, E.A. A self-adaptive synthetic over-sampling technique for imbalanced classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, T.; Xia, X.; Xu, H.; Ding, S. A synthetic neighborhood generation based ensemble learning for the imbalanced data classification. Appl. Intell. 2017, 48, 2441–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1322–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from Imbalanced Data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R-Tools Technology Inc. Available online: https://www.r-tt.com/ (accessed on 15 October 2020).
| Settings | DCE-MRI | Units |
|---|---|---|
| TR/TE/FA | 5.08/2.39/15 | ms/ms/deg |
| Pulse sequence | T1-weighted 3D FLASH | - |
| Plane | Coronal | - |
| FOV | 500 × 500 | mm2 |
| Matrix size | 384 × 384 | pixel |
| Pixel spacing | 0.885 × 0.885 | mm2 |
| Slice thickness | 1.60 | mm |
| Gap between slices | 0 | mm |
| No. of slices | 128 | - |
| Benign (35 Lesions) | Number | Percentage Value (%) |
| Fibrosis | 5 | 14.29 |
| Ductal hyperplasia | 14 | 40.00 |
| Fibroadenoma | 10 | 28.57 |
| Dysplasia | 2 | 5.71 |
| Adenosis | 3 | 8.57 |
| Other | 1 | 2.86 |
| Malignant (56 Lesions) | Number | Percentage Value (%) |
| Infiltrating lobular carcinoma | 14 | 25.00 |
| Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | 13 | 23.21 |
| Ductal carcinoma in situ | 24 | 42.86 |
| Intraductal papilloma | 2 | 3.57 |
| Tubular carcinoma | 1 | 1.79 |
| Papillary carcinoma | 2 | 3.57 |
| Acronym | Description |
|---|---|
| AUC | Area under curve: total amount of contrast agent absorbed, computed with the trapezoidal approximation |
| AUCWIN | Area under wash-in phase |
| AUCWOUT | Area under wash-out phase |
| MSD | Maximum signal difference |
| ME | Maximum enhancement; it is determined by the ratio between the MSD and the signal intensity at the basal level—pre-contrast injection |
| WIN | Angular coefficient of linearized approximation of time–intensity curve (TIC) from time 0 to time to peak (TTP)—time elapsed since contrast injection to ME |
| WOUT | Angular coefficient of linearized approximation of TIC from time TPP to last time |
| q2 | Wash-in intercept |
| q3 | Wash-out intercept |
| Classifier | Configuration Settings |
|---|---|
| LDA | Covariance structure: full; optimizer options: hyperparameter options disabled |
| Decision tree | Fine Tree; maximum number of splits: 100; split criterion: Gini’s diversity index; surrogate decision splits: off; optimizer options: hyperparameter options disabled |
| K-nearest neighbors | Fine KNN; number of neighbors: 100; distance metric: Euclidean; distance weight: equal; standardize data: true; optimizer options: hyperparameter options disabled |
| Support vector machine | Linear SVM; kernel function: linear; kernel scale: automatic; box constraint level: 1; multiclass method: one-vs-one; standardize data: true; optimizer options; hyperparameter options disabled |
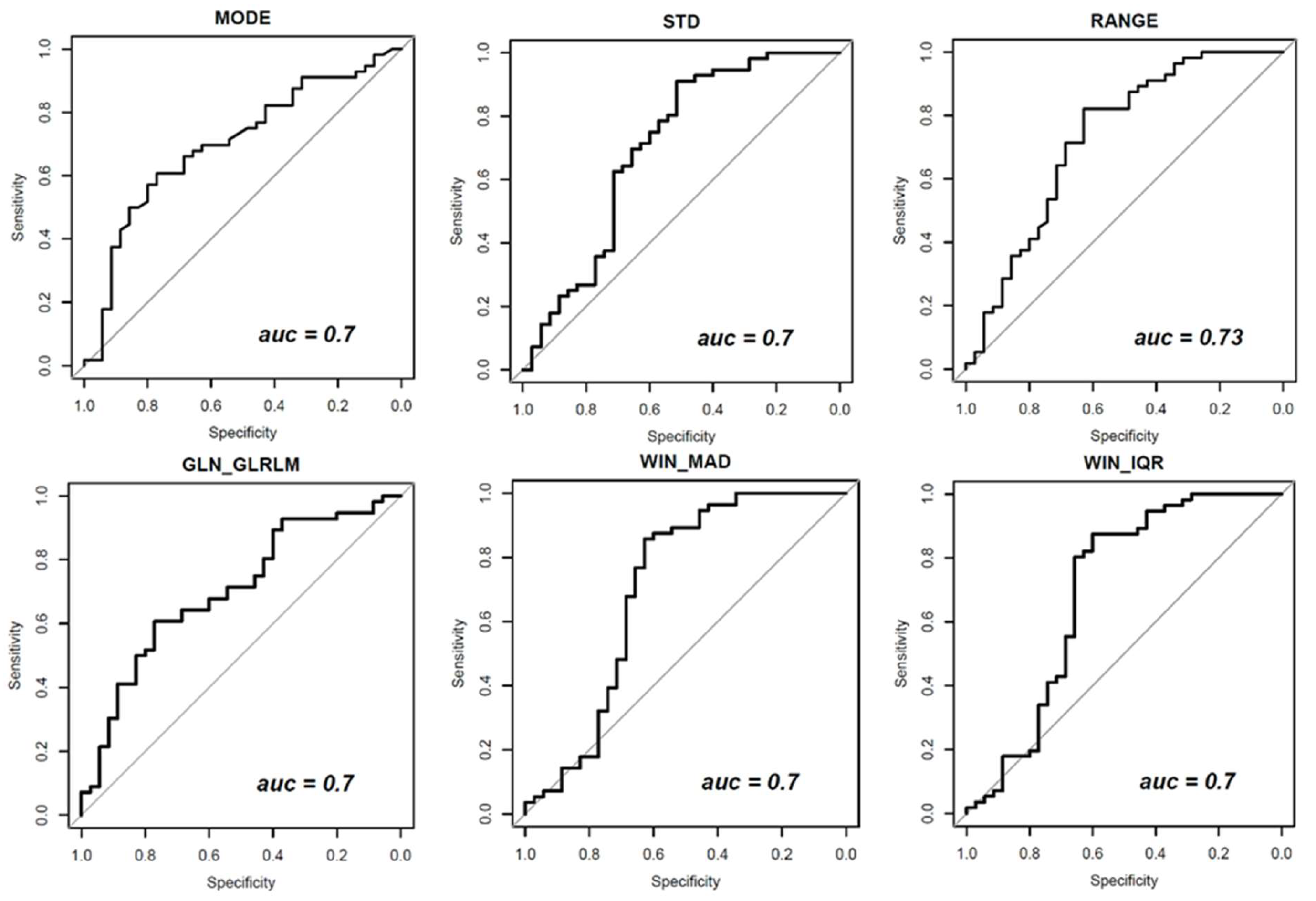
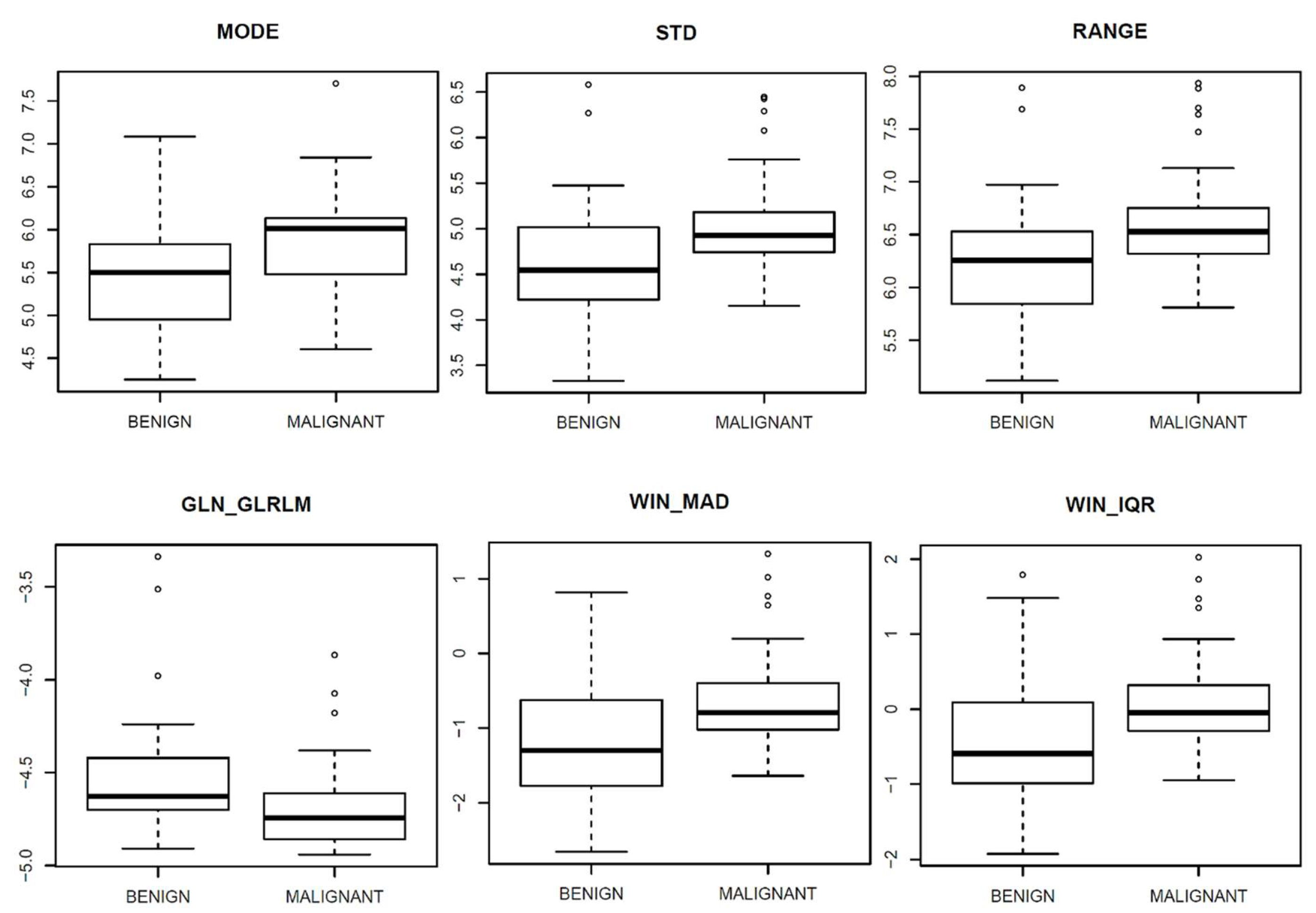
| Textural Parameters | Symbol | AUC Values | p-Value | |
| First-order gray-level statistics | MODE | - | 0.7 | 0.001 |
| STANDARD DEVIATION | STD | 0.7 | 0.001 | |
| RANGE | - | 0.73 | 0.000 | |
| Gray-Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM) | Gray-Level Non-Uniformity | GLN_GLRLM | 0.7 | 0.001 |
| Dynamic Parameters | Symbol | AUC Values | p-Value | |
| MAD of wash-in | WIN_MAD | 0.70 | 0.001 | |
| IQR of wash-in | WIN_IQR | 0.70 | 0.002 | |
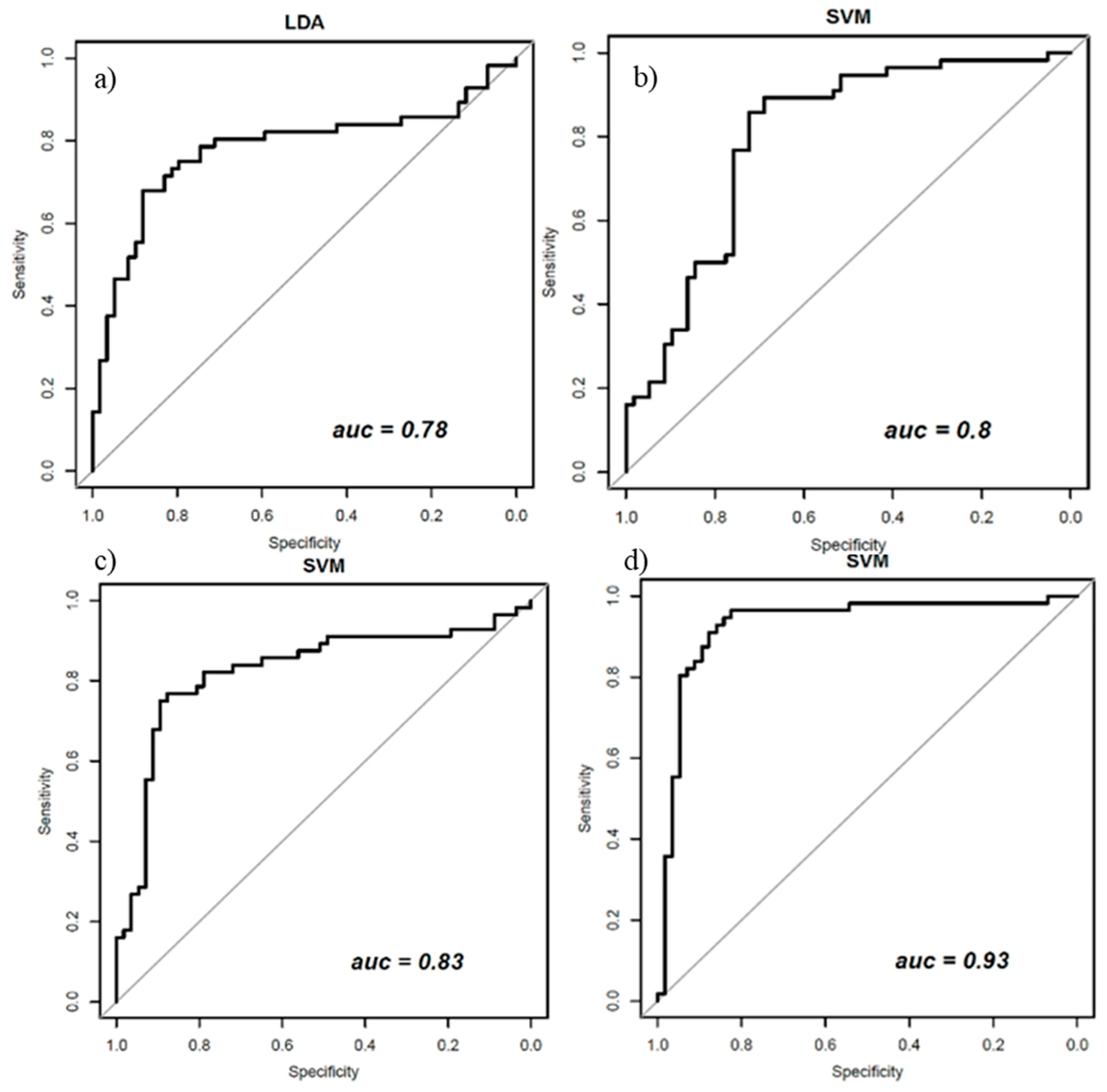
| Classifier | ACC | SENS | SPEC | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance for classifiers trained with balanced data (with ADASYN function) and all 48 textural features | ||||||
| LDA | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.78 |
| Performance for classifiers trained with balanced data (with ADASYN function) and a subset of five robust morphological features | ||||||
| SVM | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.80 |
| Performance for classifiers trained with balanced data (with ADASYN function) and a set of 21 robust dynamic features | ||||||
| SVM | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.85 |
| Performance for classifiers trained with balanced data (with ADASYN function) and a set of 37 robust features | ||||||
| SVM | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusco, R.; Piccirillo, A.; Sansone, M.; Granata, V.; Vallone, P.; Barretta, M.L.; Petrosino, T.; Siani, C.; Di Giacomo, R.; Di Bonito, M.; et al. Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041880
Fusco R, Piccirillo A, Sansone M, Granata V, Vallone P, Barretta ML, Petrosino T, Siani C, Di Giacomo R, Di Bonito M, et al. Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041880
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusco, Roberta, Adele Piccirillo, Mario Sansone, Vincenza Granata, Paolo Vallone, Maria Luisa Barretta, Teresa Petrosino, Claudio Siani, Raimondo Di Giacomo, Maurizio Di Bonito, and et al. 2021. "Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041880
APA StyleFusco, R., Piccirillo, A., Sansone, M., Granata, V., Vallone, P., Barretta, M. L., Petrosino, T., Siani, C., Di Giacomo, R., Di Bonito, M., Botti, G., & Petrillo, A. (2021). Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041880






