Influence of Edentulous Conditions on Intraoral Scanning Accuracy of Virtual Interocclusal Record in Quadrant Scan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. Trueness and Precision
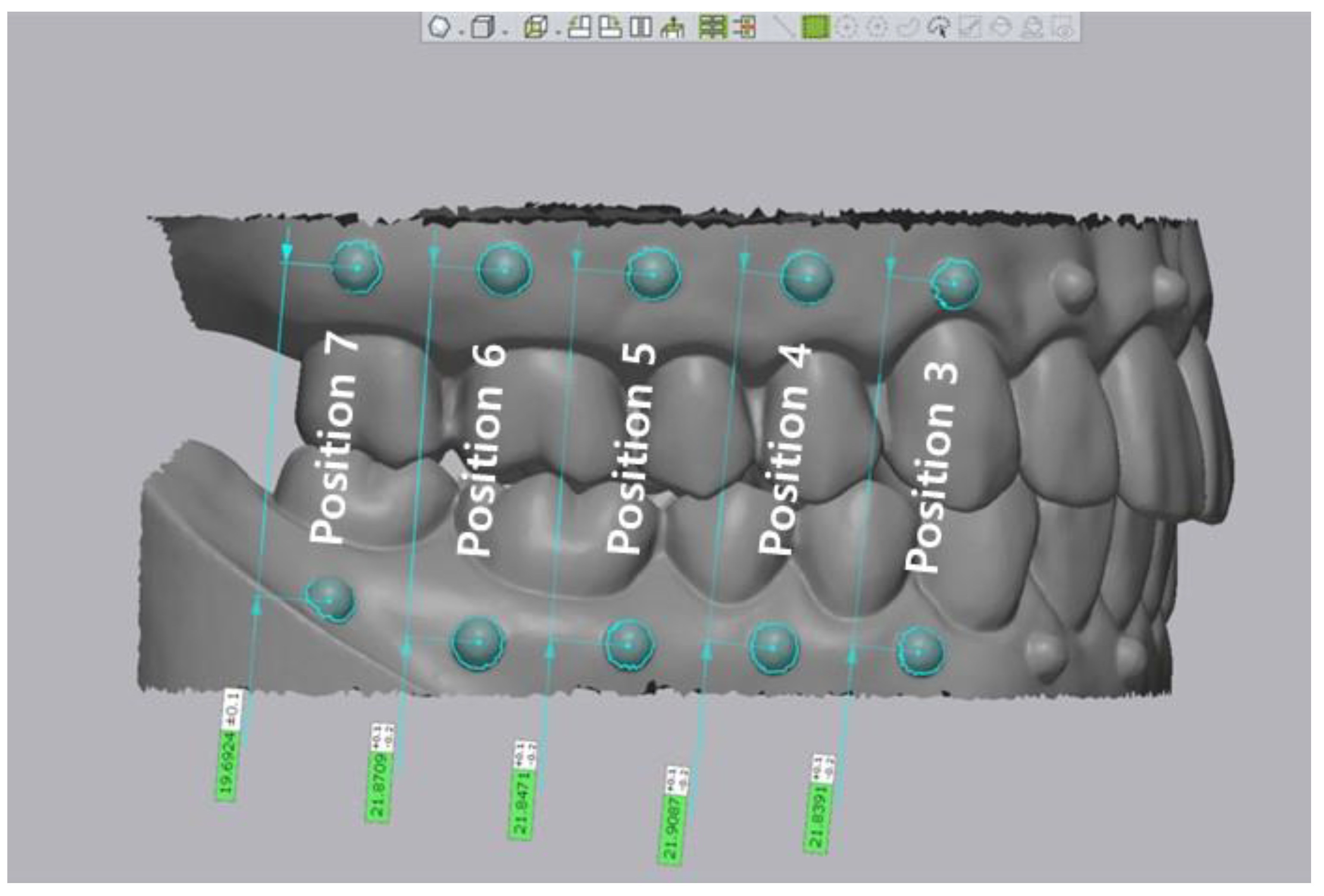
2.3. Linear Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
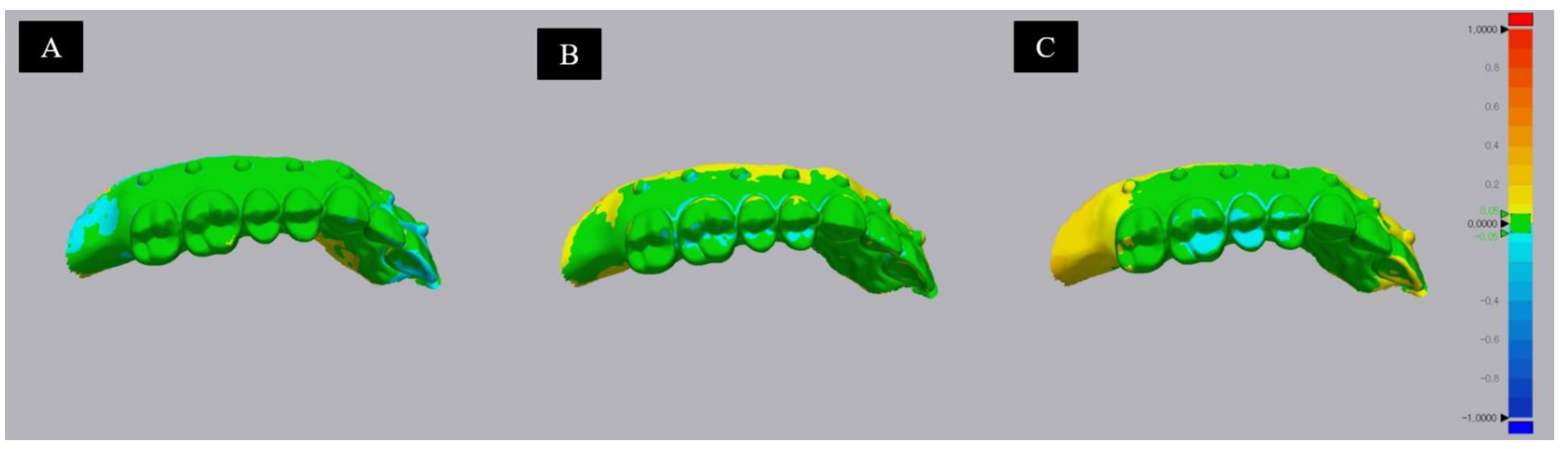
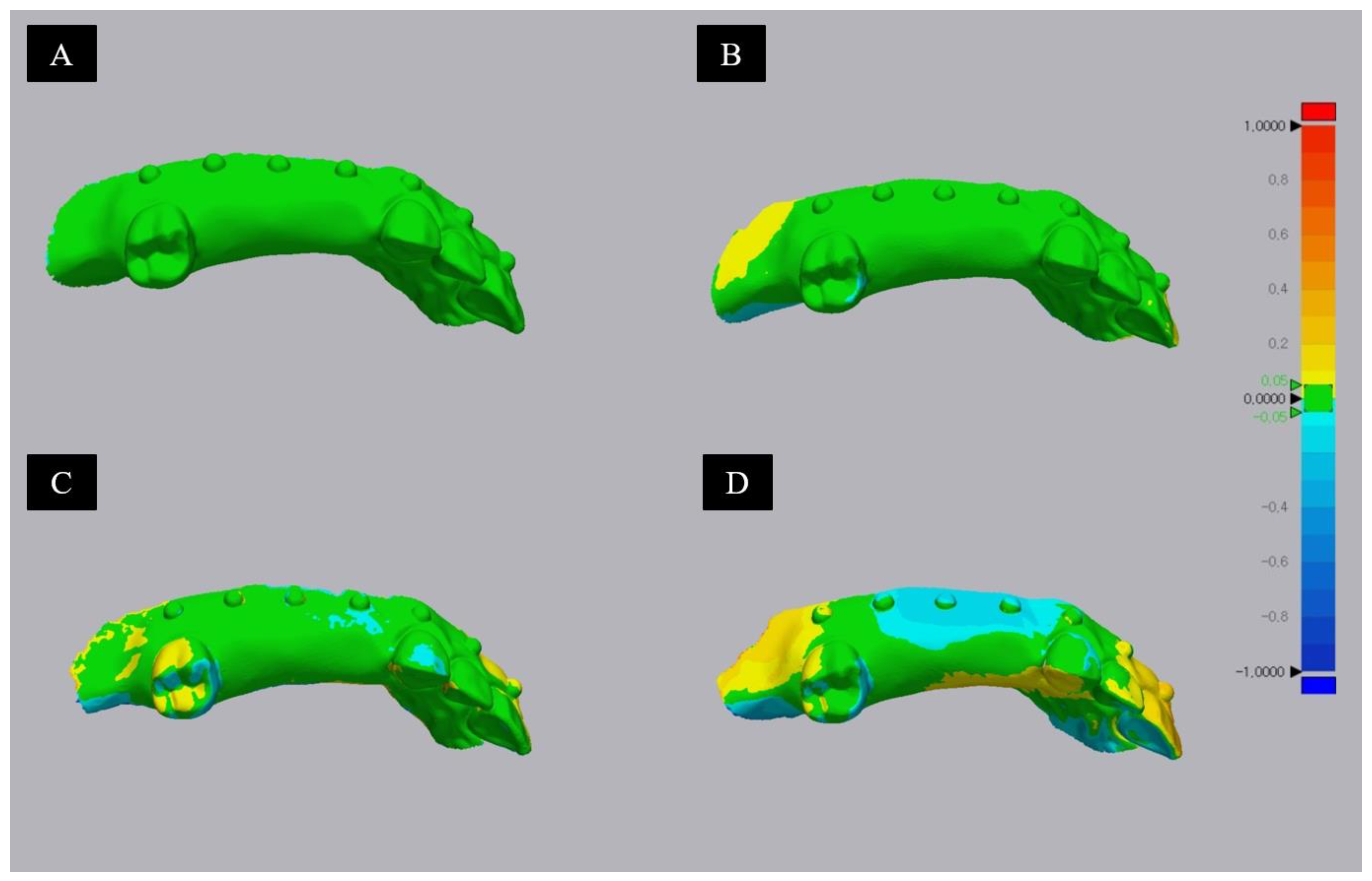
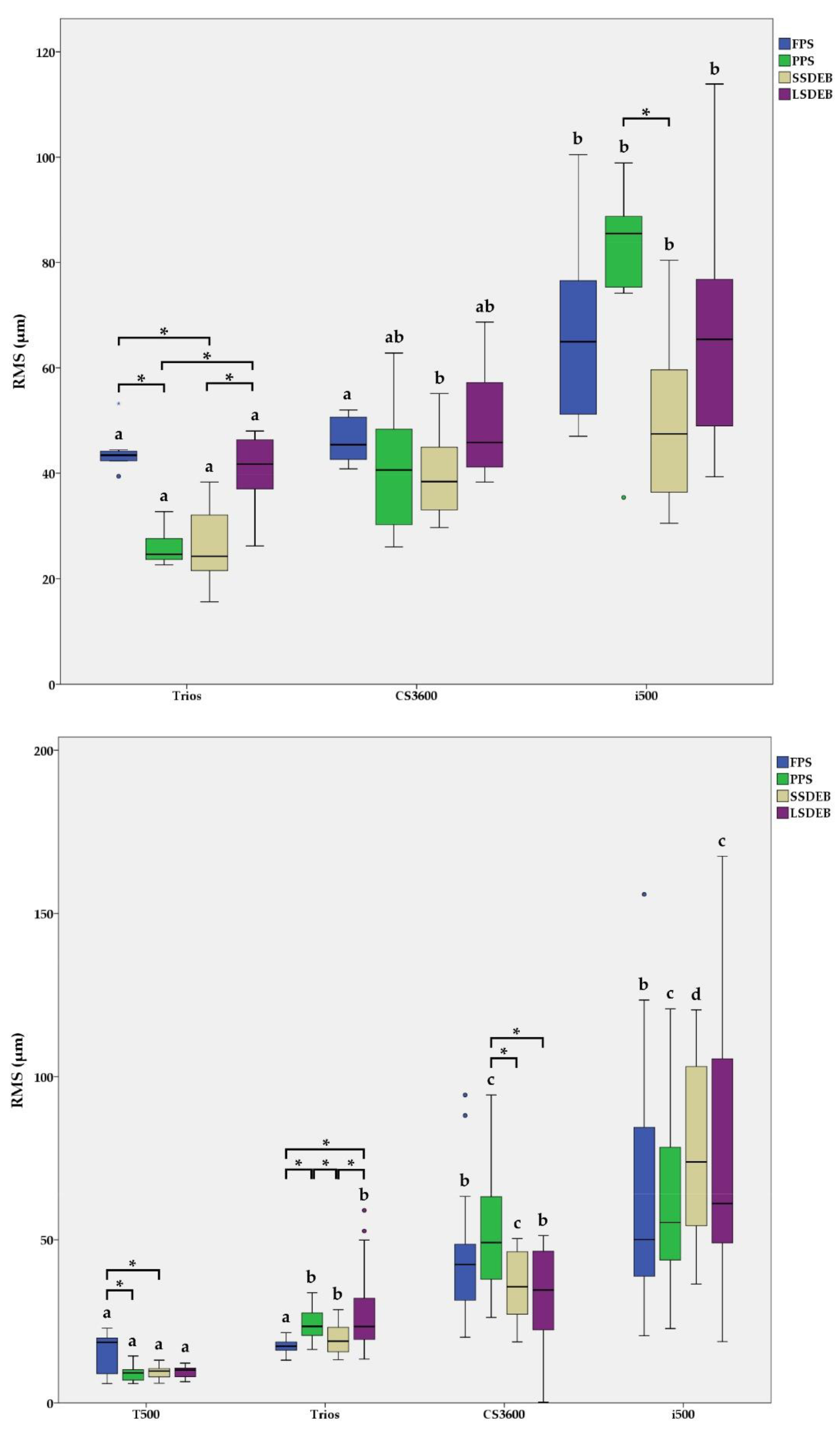
3.1. Trueness and Pricison
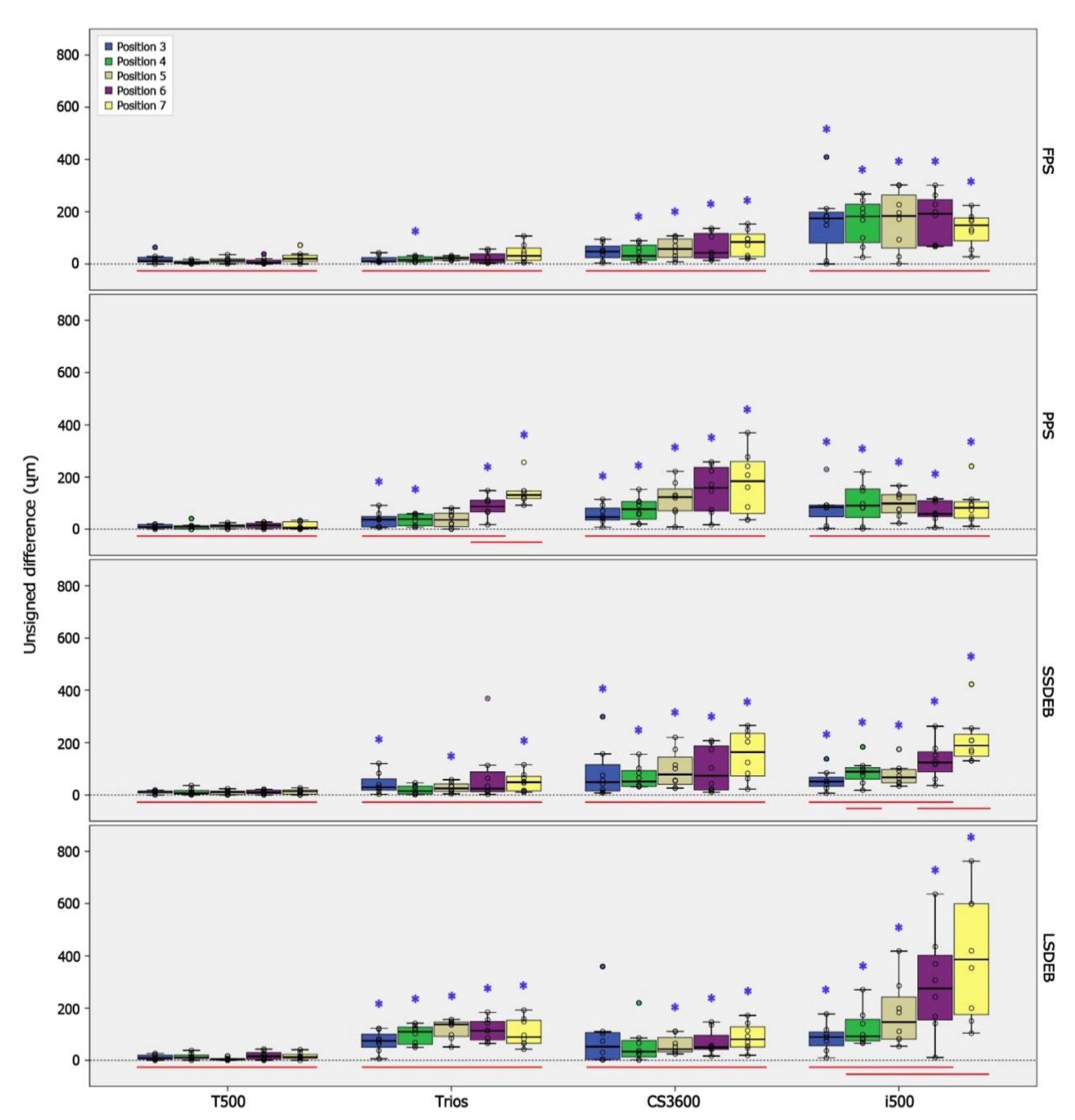
3.2. Linear Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The registration of the VIR using IOSs in quadrant scans with two or more missing teeth is less predictable than laboratory scanners.
- In identical edentulous conditions, there are differences in the occlusal relationship records between different IOSs.
- In the same scanner, there are differences in the accuracy of the VIR according to the edentulous condition.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, K.Y.; Esguerra, R.J.; Chia, V.A.P.; Tan, Y.H.; Tan, K.B.C. Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Digital Static Interocclusal Registration by Three Intraoral Scanner Systems. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logozzo, S.; Zanetti, E.M.; Franceschini, G.; Kilpelä, A.; Mäkynen, A. Recent advances in dental optics—Part I: 3D intraoral scanners for restorative dentistry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 54, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.G.; Hauschild, U.; Veronesi, G.; Imburgia, M.; Mangano, C.; Admakin, O. Trueness and precision of 5 intraoral scanners in the impressions of single and multiple implants: A comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patzelt, S.B.M.; Emmanouilidi, A.; Stampf, S.; Strub, J.R.; Att, W. Accuracy of full-arch scans using intraoral scanners. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.; Gandolfi, A.; Luongo, G.; Logozzo, S. Intraoral scanners in dentistry: A review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ender, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Attin, T.; Mehl, A. In vivo precision of conventional and digital methods for obtaining quadrant dental impressions. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlholm, P.; Sipilä, K.; Vallittu, P.; Jakonen, M.; Kotiranta, U. Digital Versus Conventional Impressions in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freilich, M.A.; Altieri, J.V.; Wahle, J.J. Principles for selecting interocclusal records for articulation of dentate and partially dentate casts. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 68, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Ender, A.; Attin, T.; Mehl, A. Accuracy of Buccal Scan Procedures for the Registration of Habitual Intercuspation. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.C. Registration of occlusion by buccal scan in Cerec software version 3.80. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2010, 13, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edher, F.; Hannam, A.G.; Tobias, D.L.; Wyatt, C.C.L. The accuracy of virtual interocclusal registration during intraoral scanning. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintaute, A.; Keeling, A.J.; Osnes, C.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Ferrari, M.; Joda, T. Precision of maxillo-mandibular registration with intraoral scanners in vitro. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Morton, D.; Lin, W.S. Accuracy of virtual interocclusal records for partially edentulous patients. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, Y.; Wakabayashi, N.; Igarashi, Y. Dimensional Accuracy of Optical Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations. Oper. Dent. 2013, 38, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaberrieta, E.; Arias, A.; Brizuela, A.; Garikano, X.; Pradies, G. Determining the requirements, section quantity, and dimension of the virtual occlusal record. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Yun, J.; Han, J.; Yeo, I.L.; Yoon, H. Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andriessen, F.S.; Rijkens, D.R.; Van der Meer, W.J.; Wismeijer, D.W. Applicability and accuracy of an intraoral scanner for scanning multiple implants in edentulous mandibles: A pilot study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 111, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Benedickt, C.R.; Schlenz, M.A.; Rehmann, P.; Wöstmann, B. Torsion and linear accuracy in intraoral scans obtained with different scanning principles. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, A.; Chen, Y.W.; Hayashi, J.; Sadr, A. Accuracy of CAD/CAM Digital Impressions with Different Intraoral Scanner Parameters. Sensors 2020, 20, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Amelya, A.; Shin, Y.; Shim, J.S. Accuracy of intraoral digital impressions using an artificial landmark. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsei, B.; Joós-Kovács, G.; Borbély, J.; Hermann, P. Comparison of the accuracy of direct and indirect three-dimensional digitizing processes for CAD/CAM systems—An in vitro study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flügge, T.V.; Schlager, S.; Nelson, K.; Nahles, S.; Metzger, M.C. Precision of intraoral digital dental impressions with iTero and extraoral digitization with the iTero and a model scanner. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, A.; Wu, J.; Ferrari, M. Confounding factors affecting the marginal quality of an intra-oral scan. J. Dent. 2017, 59, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

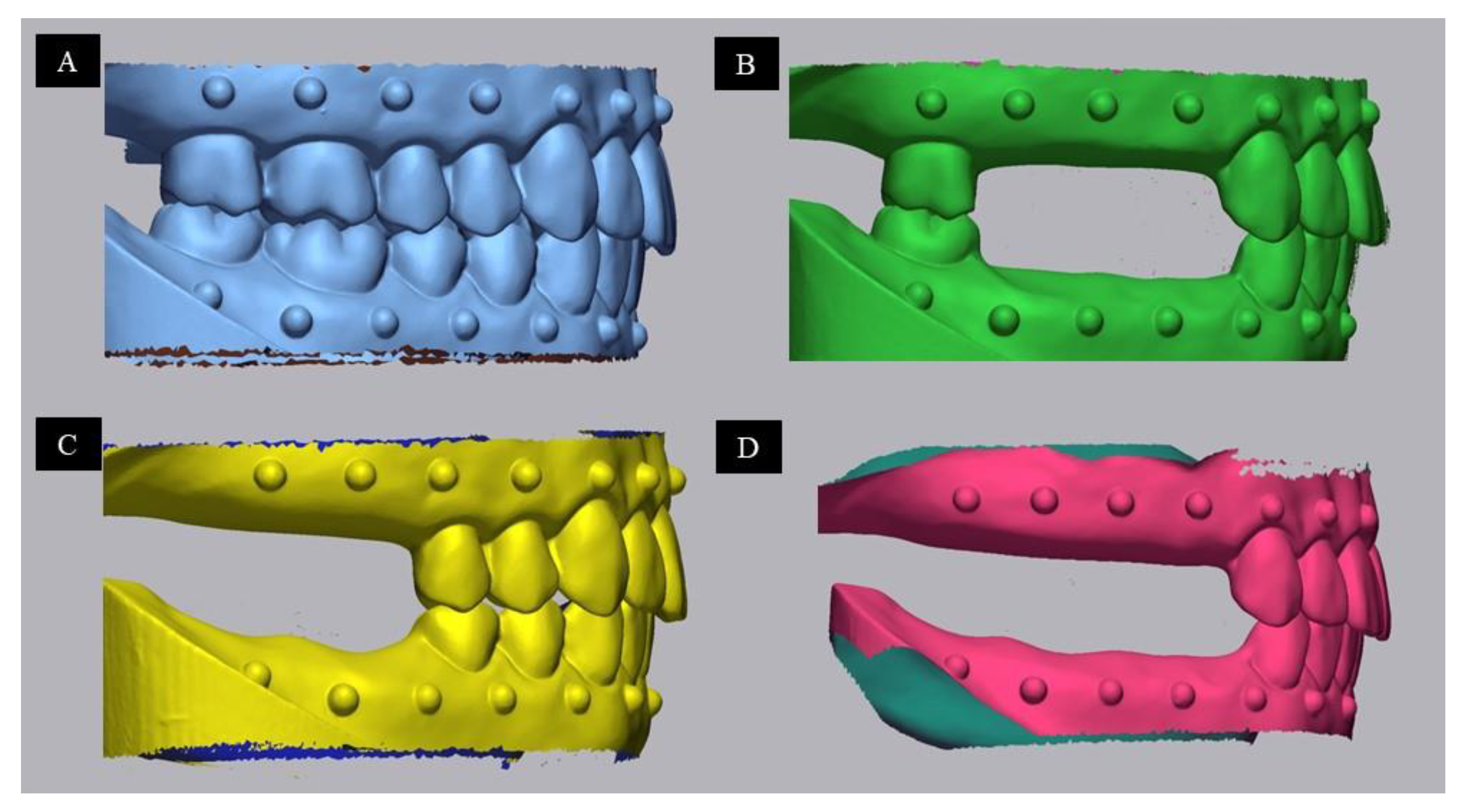

| Type | Producer | Acquisition Method | Powder | Color | |
| T500® | Laboratory scanner | Medit Corp, Seoul, Korea | Phase-shifting optical triangulation with Blue light scanning technology™ | No | Yes |
| Trios3 wireless® | Intraoral scanner | 3shape A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark | Structured light-Confocal microscopy and Ultrafast optical scanning™ | No | Yes |
| CS3600® | Intraoral scanner | Carestream Dental LLC, Atlanta, GA, USA | Structured light-Active speed 3d video™ | No | Yes |
| I500® | Intraoral scanner | Medit Corp, Seoul, Korea | 3D-in-motion video technology™ and rapid video-based scan | No | Yes |
| T500 | Trios | CS3600 | i500 | |||||||||||||
| Median | Q1 | Q3 | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | ||
| FPS | P3 | 7.6 | 3.6 | 18.4 | −7.1 a | −23.0 | 2.4 | 0.11 | −41.3 | −51.3 | −7.6 | 0.07 | 174.6 | 79.8 | 198.4 | 0.02 * |
| P4 | −0.9 | −10.9 | 2.9 | 6.8 ab | −20.6 | 12.8 | 0.38 | −15.7 | −53.6 | −4.1 | 0.16 | 182.0 | 45.0 | 228.6 | 0.01 * | |
| P5 | 2.5 | −9.4 | 16.6 | −15.0 ab | −22.0 | 19.9 | 0.28 | −19.3 | −95.6 | 25.1 | 0.57 | 183.9 | 46.0 | 263.9 | 0.05 * | |
| P6 | −3.6 | −8.0 | −0.4 | 1.1 ab | −5.3 | 38.1 | 0.38 | −30.4 | −117.3 | 19.7 | 0.38 | 192.3 | 69.3 | 246.1 | 0.00 * | |
| P7 | 9.1 | −7.3 | 33.2 | 31.2 b | 14.5 | 60.7 | 0.13 | −26.2 | −114.6 | 28.0 | 0.44 | 148.0 | 88.9 | 175.8 | 0.00 * | |
| PPS | P3 | −5.2 | −14.4 | −2.4 | 21.1 a | −9.1 | 49.0 | 0.20 | −16.1 | −71.0 | 37.8 | 0.96 | 84.6 a | 47.8 | 92.5 | 0.00 * |
| P4 | −4.1 | −11.8 | 0.4 | 38.9 a | 2.6 | 57.4 | 0.07 | −41.1 | −99.6 | 38.5 | 0.38 | 90.6 a | 45.4 | 153.9 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | −10.7 | −14.1 | 2.3 | 34.3 a | 0.7 | 61.6 | 0.07 | −70.6 | −123.2 | 70.0 | 0.38 | 98.4 a | 37.3 | 132.6 | 0.02 * | |
| P6 | −14.7 | −22.8 | −2.7 | 86.7 ab | 66.4 | 111.5 | 0.00 * | −69.9 | −158.9 | 116.3 | 0.23 | 56.6 ab | 17.4 | 83.2 | 0.03 * | |
| P7 | −4.1 | −18.4 | 0.7 | 131.3 b | 117.6 | 146.7 | 0.00 * | −61.2 | −184.2 | 120.4 | 0.11 | −82.3 b | −105.0 | −43.5 | 0.00 * | |
| SSDEB | P3 | 6.6 | −7.4 | 14.6 | 29.2 | 18.3 | 61.2 | 0.02 * | 1.8 | −47.5 | 49.3 | 0.88 | −51.8 a | −68.4 | −23.5 | 0.02 * |
| P4 | −6.5 | −17.4 | 1.2 | 6.7 | −3.0 | 25.7 | 0.11 | −0.7 | −51.5 | 67.2 | 0.96 | −89.0 ab | −105.0 | −60.4 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | 11.2 | 0.4 | 14.7 | 17.7 | −7.1 | 33.8 | 0.57 | 40.4 | −37.4 | 115.2 | 0.11 | −67.5 ab | −97.5 | −46.4 | 0.00 * | |
| P6 | −4.8 | −14.1 | 5.0 | −6.0 | −73.5 | 12.4 | 0.80 | 32.8 | 13.6 | 138.7 | 0.02 * | −124.4 ab | −165.1 | −76.6 | 0.01 * | |
| P7 | −5.8 | −16.8 | 3.3 | −15.7 | −71.5 | 17.7 | 0.51 | 93.7 | −30.0 | 224.4 | 0.11 | −189.7 b | −231.7 | −148.1 | 0.01 * | |
| LSDEB | P3 | 3.7 | −3.6 | 15.6 | −67.2 | −79.5 | −15.8 | 0.04 * | −3.5 | −66.1 | 37.7 | 0.44 | −88.8 a | −108.1 | −42.0 | 0.02 * |
| P4 | 8.8 | 2.8 | 13.1 | −109.6 | −127.2 | −58.5 | 0.01 * | 2.3 | −30.2 | 47.8 | 0.88 | −91.6 ab | −156.5 | −74.4 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 6.6 | −137.2 | −146.8 | −74.4 | 0.01 * | 32.7 | −42.7 | 42.9 | 0.11 | −146.7 ab | −242.0 | −81.3 | 0.00 * | |
| P6 | 15.0 | −1.3 | 29.7 | −113.1 | −149.0 | −75.5 | 0.01 * | 12.5 | −45.2 | 54.1 | 0.96 | −275.3 ab | −401.9 | −154.4 | 0.00 * | |
| P7 | −7.9 | −20.0 | 6.5 | −80.9 | −153.2 | −53.6 | 0.01 * | 44.3 | −51.0 | 102.8 | 0.44 | −386.4 b | −599.2 | −175.0 | 0.01 * | |
| T500 | Trios | CS3600 | i500 | |||||||||||||
| Median | Q1 | Q3 | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p | ||
| FPS | P3 | 11.6 | 7.3 | 25.2 | 10.5 | 7.1 | 24.1 | 0.80 | 47.5 | 23.7 | 68.7 | 0.08 * | 174.6 | 79.8 | 198.4 | 0.03 * |
| P4 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 10.9 | 15.5 | 8.2 | 27.1 | 0.02 * | 31.1 | 14.8 | 72.1 | 0.01 * | 182.0 | 82.0 | 228.6 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | 12.9 | 5.7 | 19.1 | 22.0 | 15.0 | 26.9 | 0.08 * | 57.4 | 25.1 | 95.6 | 0.01 * | 183.9 | 60.6 | 263.9 | 0.01 * | |
| P6 | 4.9 | 2.1 | 15.1 | 15.7 | 4.8 | 38.1 | 0.23 | 42.5 | 22.3 | 117.3 | 0.00 * | 192.3 | 69.3 | 246.1 | 0.00 * | |
| P7 | 19.9 | 9.1 | 33.2 | 31.2 | 14.5 | 60.7 | 0.38 | 84.2 | 28.0 | 114.6 | 0.02 * | 148.0 | 88.9 | 175.8 | 0.00 * | |
| PPS | P3 | 8.1 | 4.9 | 18.2 | 37.0 a | 9.1 | 49.0 | 0.04 * | 47.1 | 35.7 | 81.1 | 0.00 * | 84.6 | 47.8 | 92.5 | 0.02 * |
| P4 | 9.2 | 0.4 | 13.8 | 38.9 a | 13.8 | 57.4 | 0.02 * | 77.0 | 38.5 | 106.1 | 0.00 * | 90.6 | 45.4 | 153.9 | 0.02 * | |
| P5 | 13.4 | 6.6 | 16.6 | 35.8 a | 10.6 | 61.6 | 0.11 | 123.2 | 70.6 | 154.1 | 0.00 * | 98.8 | 63.4 | 132.6 | 0.00 * | |
| P6 | 14.7 | 4.9 | 22.8 | 86.7 ab | 66.4 | 111.5 | 0.00 * | 158.9 | 69.9 | 236.6 | 0.00 * | 59.2 | 48.8 | 109.3 | 0.00 * | |
| P7 | 6.9 | 2.2 | 29.3 | 131.3 b | 117.6 | 146.7 | 0.00 * | 184.2 | 61.2 | 259.4 | 0.00 * | 82.3 | 43.5 | 105.0 | 0.00 * | |
| SSDEB | P3 | 13.1 | 7.4 | 14.6 | 29.2 | 18.3 | 61.2 | 0.04 * | 49.3 | 15.5 | 116.2 | 0.04 * | 51.8 a | 33.4 | 68.4 | 0.04 * |
| P4 | 6.5 | 3.4 | 17.4 | 15.1 | 3.9 | 34.0 | 0.44 | 51.5 | 32.8 | 93.1 | 0.00 * | 89.0 ab | 60.4 | 105.0 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | 11.2 | 2.0 | 14.7 | 25.0 | 13.7 | 42.3 | 0.04 * | 78.5 | 40.4 | 144.5 | 0.00 * | 67.5 a | 46.4 | 97.5 | 0.00 * | |
| P6 | 9.9 | 5.0 | 18.6 | 24.0 | 12.4 | 88.6 | 0.11 | 73.6 | 19.5 | 188.0 | 0.01 * | 124.4 ab | 88.8 | 165.1 | 0.01 * | |
| P7 | 13.2 | 3.3 | 19.4 | 48.8 | 15.7 | 71.5 | 0.04 * | 163.8 | 72.9 | 235.9 | 0.00 * | 189.7 b | 148.1 | 231.7 | 0.00 * | |
| LSDEB | P3 | 8.6 | 3.6 | 19.5 | 74.6 | 50.4 | 99.9 | 0.00 * | 52.1 | 3.5 | 105.9 | 0.20 | 88.8 a | 55.5 | 108.1 | 0.00 * |
| P4 | 11.0 | 6.6 | 19.8 | 109.6 | 61.6 | 127.2 | 0.00 * | 33.3 | 13.2 | 75.8 | 0.16 | 91.6 ab | 74.4 | 156.5 | 0.00 * | |
| P5 | 3.8 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 137.2 | 91.3 | 146.8 | 0.00 * | 42.9 | 32.7 | 87.1 | 0.00 * | 146.7 ab | 81.3 | 242.0 | 0.00 * | |
| P6 | 15.0 | 4.0 | 29.7 | 113.1 | 78.3 | 149.0 | 0.00 * | 49.9 | 41.9 | 96.2 | 0.01 * | 275.3 ab | 154.4 | 401.9 | 0.00 * | |
| P7 | 12.0 | 7.9 | 22.4 | 88.6 | 65.4 | 153.2 | 0.00 * | 80.6 | 51.0 | 128.2 | 0.00 * | 386.4 b | 175.0 | 599.2 | 0.00 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, N.-E.; Shin, S.-H.; Lim, J.-H.; Lee, K.-W.; Shim, J.-S. Influence of Edentulous Conditions on Intraoral Scanning Accuracy of Virtual Interocclusal Record in Quadrant Scan. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041489
Lee Y-C, Kim J-E, Nam N-E, Shin S-H, Lim J-H, Lee K-W, Shim J-S. Influence of Edentulous Conditions on Intraoral Scanning Accuracy of Virtual Interocclusal Record in Quadrant Scan. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041489
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ye-Chan, Jong-Eun Kim, Na-Eun Nam, Seung-Ho Shin, Jung-Hwa Lim, Keun-Woo Lee, and June-Sung Shim. 2021. "Influence of Edentulous Conditions on Intraoral Scanning Accuracy of Virtual Interocclusal Record in Quadrant Scan" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041489
APA StyleLee, Y.-C., Kim, J.-E., Nam, N.-E., Shin, S.-H., Lim, J.-H., Lee, K.-W., & Shim, J.-S. (2021). Influence of Edentulous Conditions on Intraoral Scanning Accuracy of Virtual Interocclusal Record in Quadrant Scan. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041489






