Reduced Graphene Oxide-Metalloporphyrin Sensors for Human Breath Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
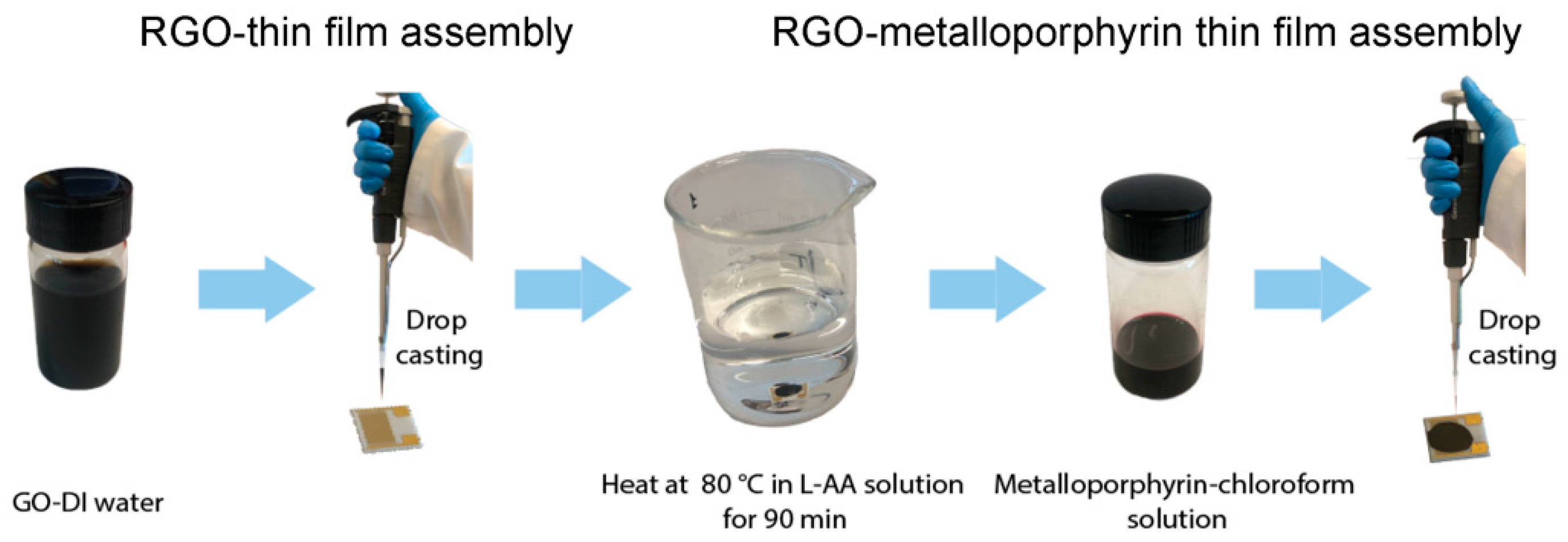
2.2. Sensor Fabrication
2.3. Material Characterization
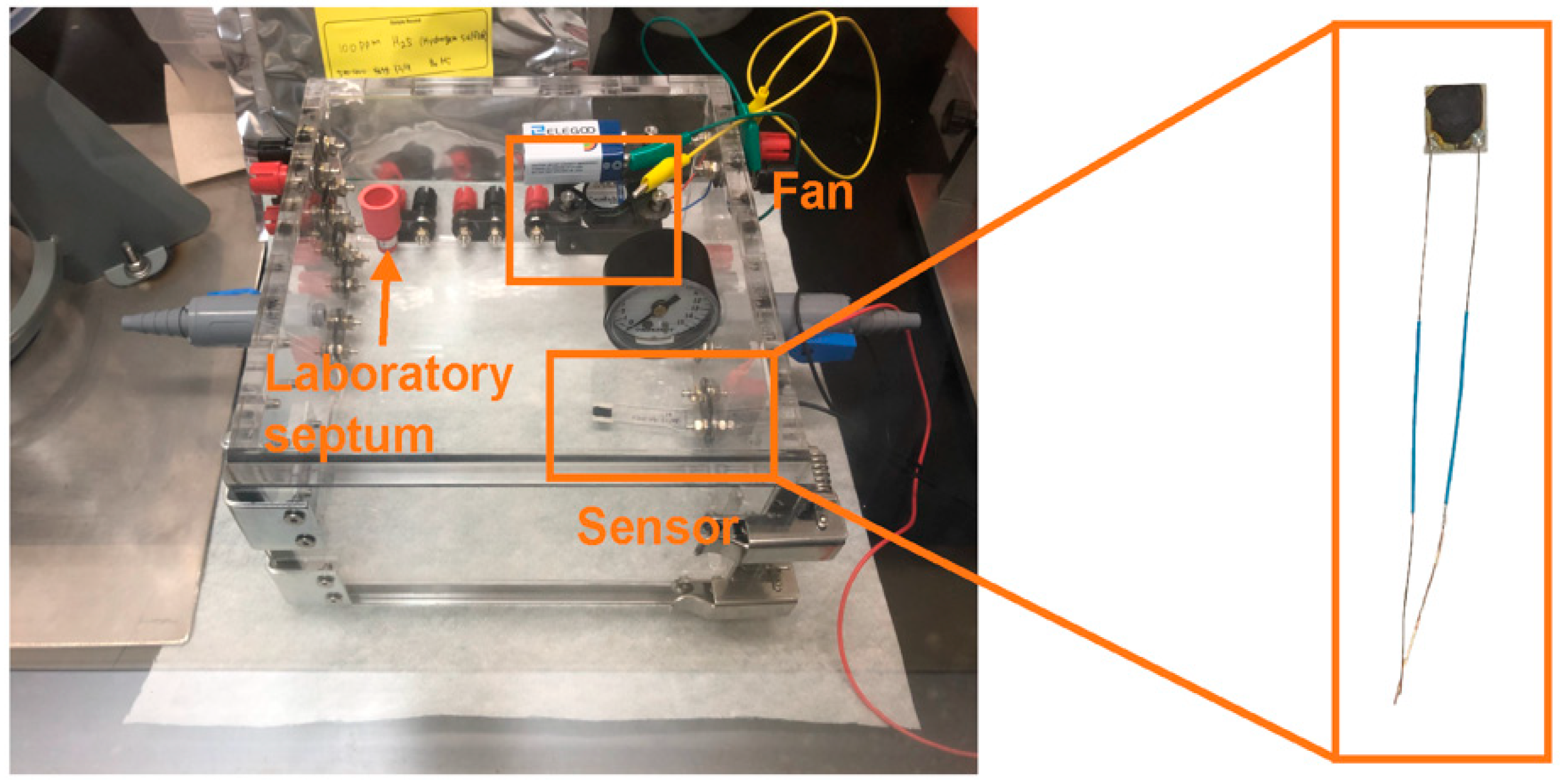
2.4. VOC-Sensing Characterization
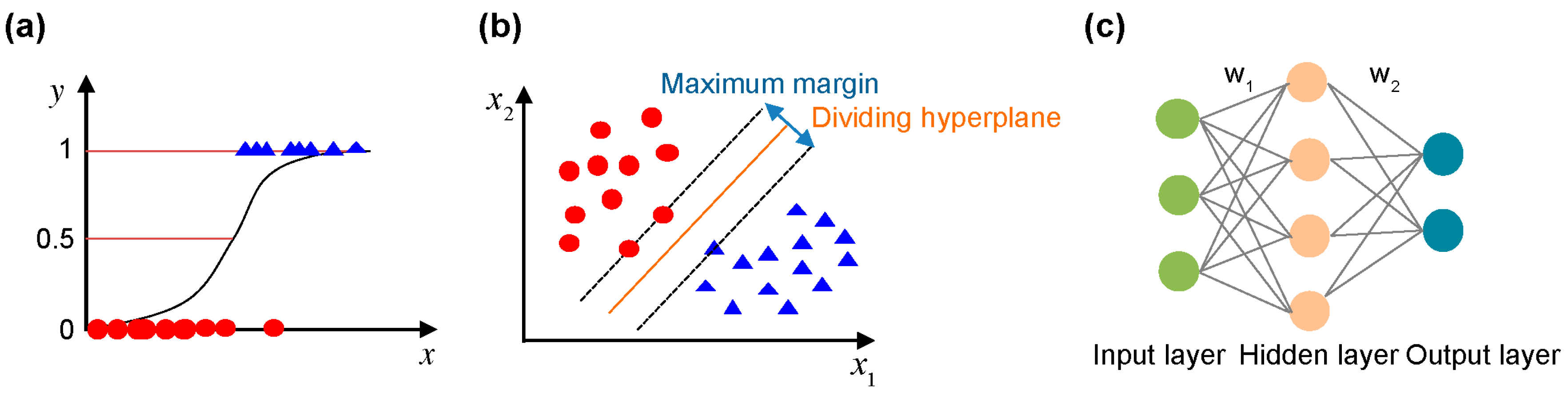
2.5. VOC-Sensing Pattern Recognition
2.6. Healthy and Unhealthy Discrimination
3. Results
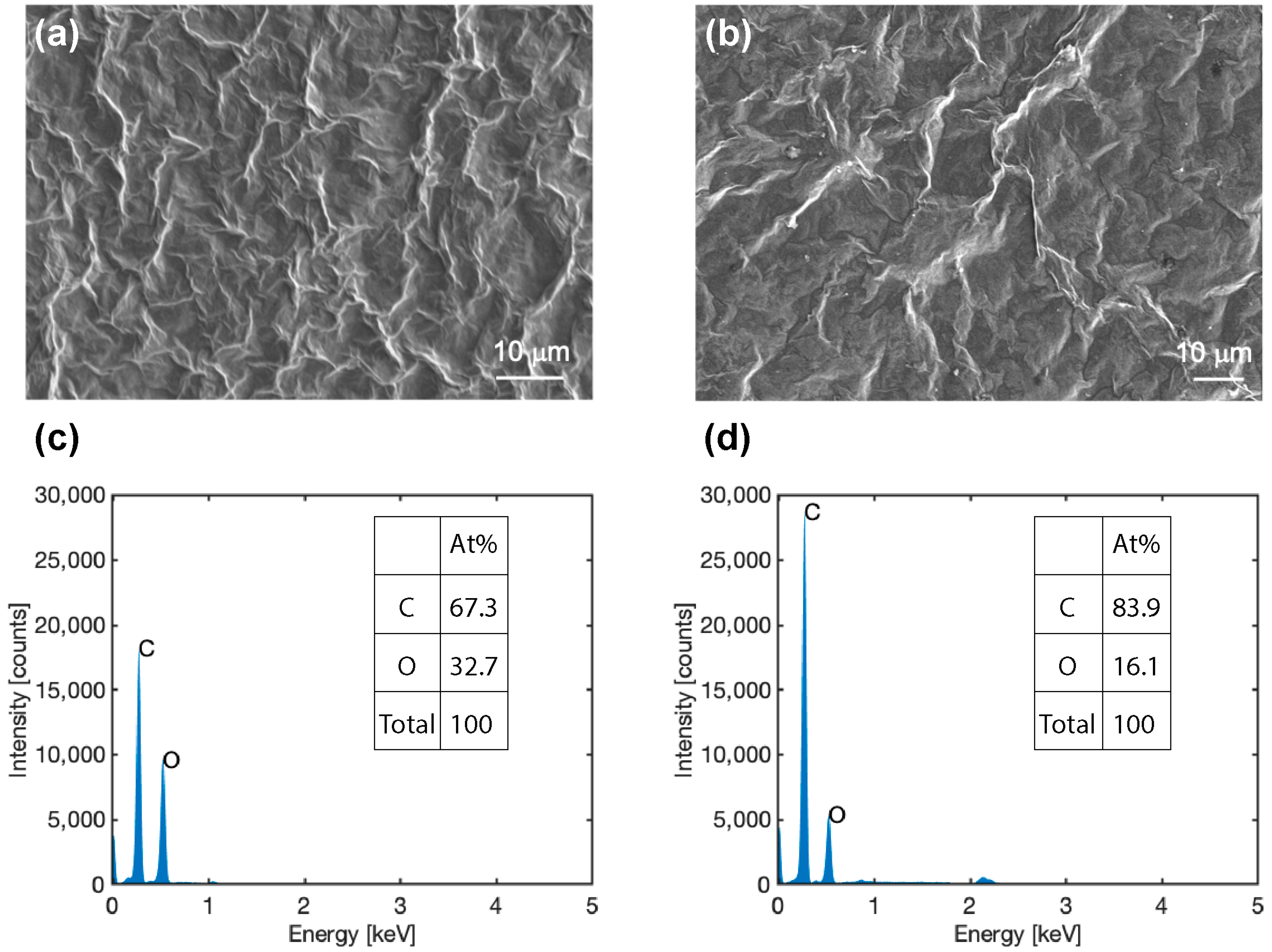
3.1. A GO Thin Film Was Chemically Reduced to Form an RGO Thin Film Using L-AA
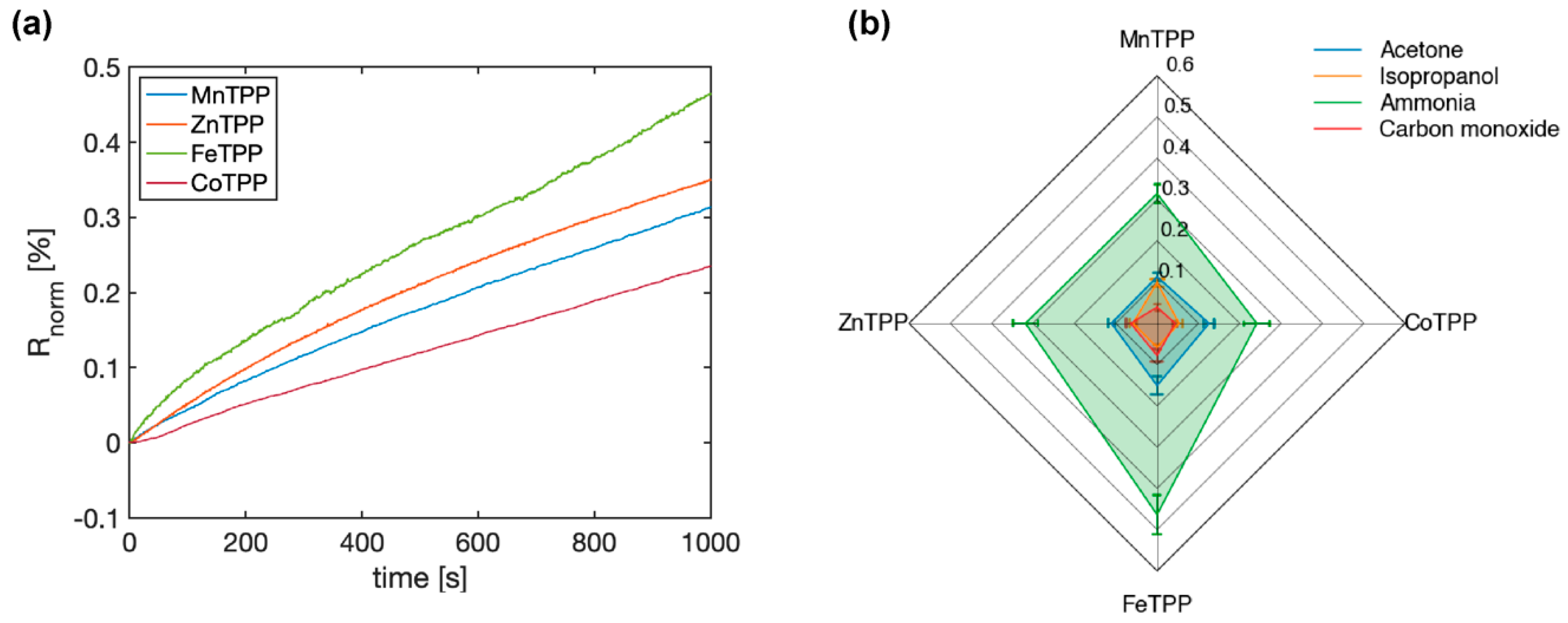
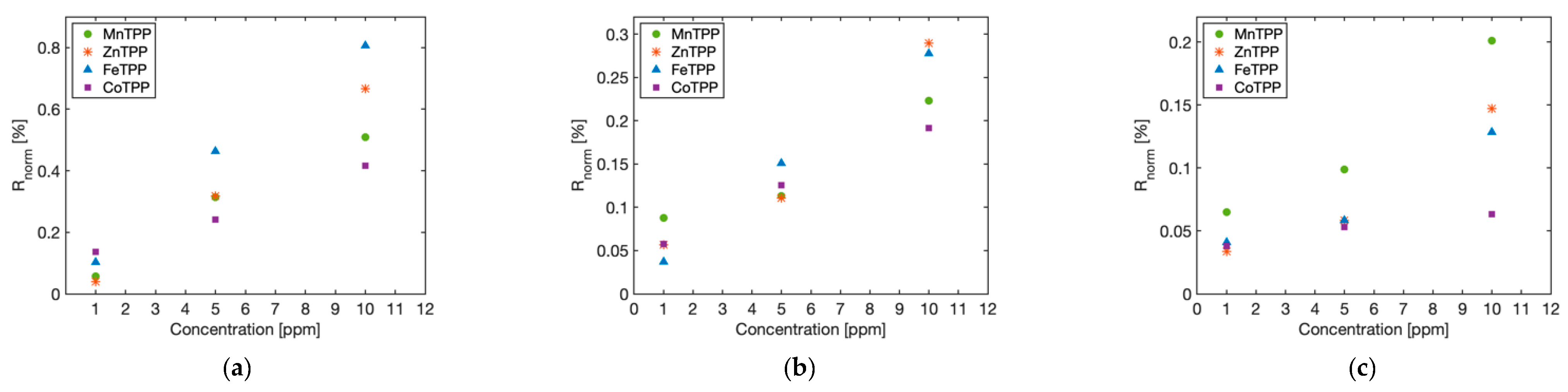
3.2. RGO–Metalloporphyrin Sensors Showed Unique Sensing Responses upon Exposure to VOCs
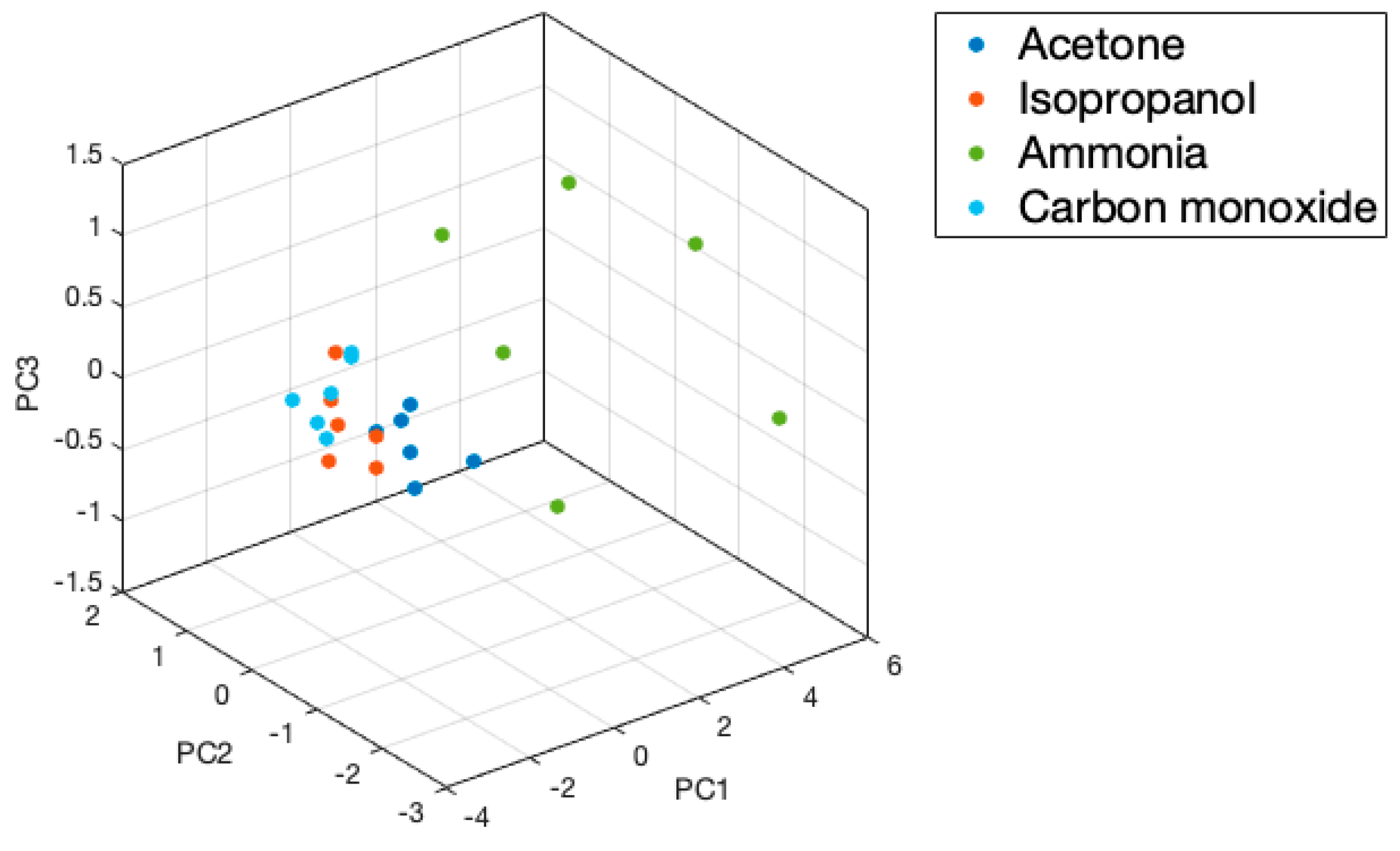
3.3. RGO Sensors Enabled Accurate VOC Classification Using Machine Learning
3.4. RGO Sensors with ML Algorithms Can Discriminate the Healthy and Unhealthy Samples with 91.7% Accuracy
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Lacy Costello, B.; Amann, A.; Al-Kateb, H.; Flynn, C.; Filipiak, W.; Khalid, T.; Osborne, D.; Ratcliffe, N.M. A review of the volatiles from the healthy human body. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pal, S.; Mitra, M. Significance of exhaled breath test in clinical diagnosis: A special focus on the detection of diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Condos, R.; Erickson, G.A.R.; Greenberg, J.; La Bombardi, V.; Munawar, M.I.; Tietje, O. Volatile biomarkers of pulmonary tuberculosis in the breath. Tuberculosis 2007, 87, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeyama, H.; Wang, T.; Ichinose, M.; Ansai, T.; Lee, S.-W. Identification of volatile metabolites in human saliva from patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma via zeolite-based thin-film microextraction coupled with GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1104, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, X.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Y. Discovery of potential biomarkers in exhaled breath for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on GC-MS with metabolomics. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25430–25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.; Prazeller, P.; Mayr, D.; Jordan, A.; Rieder, J.; Fall, R.; Lindinger, W. Human breath isoprene and its relation to blood cholesterol levels: New measurements and modeling. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smolinska, A.; Bodelier, A.G.L.; Dallinga, J.W.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.; Van Schooten, F.-J.; Pierik, M.J. The potential of volatile organic compounds for the detection of active disease in patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.-D.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Jang, J.-S. Exhaled Breath Sensors. In KAIST Research Series; Springer: Singapore, 2015; pp. 19–49. [Google Scholar]
- Amal, H.; Haick, H. Chapter 14-Point of care breath analysis systems. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Inexpensive Gas Microsensors; Llobet, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 315–334. [Google Scholar]
- El Manouni el Hassani, S.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; Bosch, S.; Benninga, M.A.; De Boer, N.K.H.; De Meij, T.G.J. Application of fecal volatile organic compound analysis in clinical practice: Current state and future perspectives. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Huang, J.; Abbassi-Ghadi, N.; Spanel, P.; Smith, D.; Hanna, G.B. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry analysis of exhaled breath for volatile organic compound profiling of esophago-gastric cancer. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6121–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, M.; Hoeschen, C.; Oeh, U. Multidimensional statistical analysis of PTR-MS breath samples: A test study on irradiation detection. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 295, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapthorn, C.; Pullen, F.; Chowdhry, B.Z. Ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) of small molecules: Separating and assigning structures to ions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2013, 32, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.-A.; Li, M.; Knipp, R.J.; Nantz, M.H.; Bousamra, M. Noninvasive detection of lung cancer using exhaled breath. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolesse, R.; Nardis, S.; Monti, D.; Stefanelli, M.; Di Natale, C. Porphyrinoids for chemical sensor applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 2517–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Jang, M.; Suslick, K.S. Preoxidation for Colorimetric sensor array detection of VOCs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16786–16789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penza, M.; Cassano, G.; Aversa, P.; Cusano, A.; Cutolo, A.; Giordano, M.; Nicolais, L. Carbon nanotube acoustic and optical sensors for volatile organic compound detection. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, H.; Joseph, A.; Park, J.; Emadi, A. Advanced micro- and nano-gas sensor technology: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, F.; Tian, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Chen, W. Stable Cu2O nanocrystals grown on functionalized graphene sheets and room temperature H2S gas sensing with ultrahigh sensitivity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Laskowski, D.; Deffenderfer, O.; Burch, T.; Zheng, S.; Mazzone, P.J.; Mekhail, T.; Jennings, C.; Stoller, J.K.; Pyle, J.; et al. Detection of lung cancer by sensor array analyses of exhaled breath. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vishinkin, R.; Haick, H. Nanoscale sensor technologies for disease detection via volatolomics. Small 2015, 11, 6142–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Fa, H.; Yang, M.; Luo, X. Colorimetric artificial nose for identification of breath volatile organic compounds of patients with lung cancer. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomi, D.; Abud, M.; Liran, O.; Bar, J.; Gai-Mor, N.; Ilouze, M.; Onn, A.; Ben-Nun, A.; Haick, H.; Peled, N. Detection of lung cancer and EGFR mutation by electronic nose system. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Tisch, U.; Bunn, P.A.; Hirsch, F.R.; Haick, H. Classification of lung cancer histology by gold nanoparticle sensors. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Lee, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Kim, S.; Yun, M. Detection and identification of breast cancer volatile organic compounds biomarkers using highly-sensitive single nanowire array on a chip. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srimathi, U.; Nagarajan, V.; Chandiramouli, R. Germanane nanosheet as a novel biosensor for liver cirrhosis based on adsorption of biomarker volatiles–A DFT study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Billan, S.; Tisch, U.; Peng, G.; Dvrokind, I.; Marom, O.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosis of head-and-neck cancer from exhaled breath. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salehi, S.; Nikan, E.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. Highly sensitive carbon nanotubes–SnO2 nanocomposite sensor for acetone detection in diabetes mellitus breath. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; Covington, J.; Harmston, C.; Nwokolo, C.U. Review article: Next generation diagnostic modalities in gastroenterology-gas phase volatile compound biomarker detection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marom, O.; Nakhoul, F.; Tisch, U.; Shiban, A.; Abassi, Z.; Haick, H. Gold nanoparticle sensors for detecting chronic kidney disease and disease progression. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisch, U.; Schlesinger, I.; Ionescu, R.; Nassar, M.; Axelrod, N.; Robertman, D.; Tessler, Y.; Azar, F.; Marmur, A.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease from exhaled breath using nanomaterial-based sensors. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xue, Z.; Chen, X.-Y.; Huang, C.; Bai, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T. Nanomaterial-based gas sensors used for breath diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3231–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Farha, F.; Li, Q.; Wan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ning, H. Review on smart gas sensing technology. Sensors 2019, 19, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.H.; Feng, L.; Kemling, J.W.; Musto, C.J.; Suslick, K.S. An optoelectronic nose for the detection of toxic gases. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buff, W. SAW sensors. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 1992, 30, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Yoon, J.-W.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.-H. Dual role of multiroom-structured Sn-doped NiO microspheres for ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of xylene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16605–16612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.F.; Moh, L.C.H.; Swager, T.M. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube–Metalloporphyrin chemiresistive gas sensor arrays for volatile organic compounds. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3560–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güder, F.; Ainla, A.; Redston, J.; Mosadegh, B.; Glavan, A.; Martin, T.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based electrical respiration sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5727–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Silva, K.K.H.; Huang, H.-H.; Yoshimura, M. Progress of reduction of graphene oxide by ascorbic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Resistance-based H2S gas sensors using metal oxide nanostructures: A review of recent advances. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 357, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Logistic Regression; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schlkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support. Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; The MIT Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, K.M. Confusion Matrix. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning; Sammut, C., Webb, G.I., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Schönermarck, U.; Dengler, C.; Gmeinwieser, A.; Praun, S.; Schelling, G.; Fischereder, M.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Dolch, M.E. Exhaled breath volatile organic and inorganic compound composition in end-stage renal disease. Clin. Nephrol. 2016, 86, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, L.; Razal, J.M.; Wallace, G.; Chen, J. Metal porphyrin intercalated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite utilized for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Green Energy Environ. 2017, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Lamm, W.J.E.; Hlastala, M.P. Measuring airway exchange of endogenous acetone using a single-exhalation breathing maneuver. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Duan, Y. Exhaled isopropanol: New potential biomarker in diabetic breathomics and its metabolic correlations with acetone. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17480–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- E Jones, A.; Summers, R.L. Detection of isopropyl alcohol in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis. J. Emerg. Med. 2000, 19, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.T.; Devadhasan, J.P.; Kim, S. Recent analytical approaches to detect exhaled breath ammonia with special reference to renal patients. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 409, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Sethi, J.M. Exhaled carbon monoxide as a biomarker of inflammatory lung disease. J. Breath Res. 2007, 1, 026004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, S.; Deveci, F.; Açik, Y.; Ozan, A. The measurement of exhaled carbon monoxide in healthy smokers and non-smokers. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trefz, P.; Obermeier, J.; Lehbrink, R.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W.; Fischer, D.-C. Exhaled volatile substances in children suffering from type 1 diabetes mellitus: Results from a cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Panigrahi, S.; Logue, C.M.; Marchello, M.; Doetkott, C.; Gu, H.; Sherwood, J.; Nolan, L. Spoilage identification of beef using an electronic nose system. Trans. ASAE 2004, 47, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; Damico, A. Metalloporphyrins based artificial olfactory receptors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minitha, C.R.; Anithaa, V.S.; Subramaniam, V.; Kumar, R.T.R. Impact of oxygen functional groups on reduced graphene oxide-based sensors for ammonia and toluene detection at room temperature. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4105–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.; Ahlers, S.; Bosch-V.Braunmühl, C.; Müller, G.; Kiesewetter, O. Gas sensing properties of thin- and thick-film tin-oxide materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 77, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K.J.; Lewis, N.S.; Schauer, C.L.; Sotzing, G.A.; Stitzel, S.E.; Vaid, T.; Walt, D.R. Cross-reactive chemical sensor arrays. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2595–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, N.; Clarke, C. Nanostructured chemiresistive gas sensors for medical applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Li, G.; Qin, Y.; Freeman, W.J. A pattern recognition method for electronic noses based on an olfactory neural network. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-J.; Choi, S.-J.; Jang, J.-S.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, I.-D. Innovative nanosensor for disease diagnosis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.; Lee, K.; Pyo, S.; Kim, J. Fabrication and characterization of VOC sensor array based on SnO2 and ZnO nanoparticles functionalized by metalloporphyrins. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. A room temperature VOCs gas sensor based on a layer by layer multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly-ethylene glycol composite. Sensors 2018, 18, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Guo, X.; Duan, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, L.; Peng, C.; Zhang, S. Electronic nose feature extraction methods: A review. Sensors 2015, 15, 27804–27831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Detecting internal quality of peanuts during storage using electronic nose responses combined with physicochemical methods. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Evans, E.D.; Wu, Y.-C.M.; Voll, C.-C.A.; McDonald, B.R.; Savagatrup, S.; Swager, T.M. Chemiresistive sensor array and machine learning classification of food. ACS Sen. 2019, 4, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-R.; Kuo, W.-J.; Chang, R.-F.; Moon, W.K.; Lee, C.C. Use of the bootstrap technique with small training sets for computer-aided diagnosis in breast ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tian, F.; Liang, Z.; Sun, T.; Yu, B.; Yang, S.X.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Sensor array optimization of electronic nose for detection of bacteria in wound infection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7350–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Exhaled Biomarkers | Healthy (ppb) | Disease (ppb) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes | Acetone | 500–2000 [2] | 2200–21,000 [2] |
| Isopropanol | 784 (287–8963) [53] | 1223 (481–15,011) [53] | |
| Chronic kidney disease | Ammonia | 356 (290–412) [45] | 3863 (828–11,570) [45] |
| Smoking status | Carbon monoxide | 3610 ± 2150 (healthy non-smoker) [52] | 17,130 ± 8500 (healthy smoker) [52] |
| Acetone | Isopropanol | Ammonia | Carbon Monoxide | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | SVM | NN | LR | SVM | NN | LR | SVM | NN | LR | SVM | NN | |
| Recall | 0.813 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.802 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.952 | 0.857 | 1.0 |
| Accuracy | 0.792 | 0.958 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.917 | 0.833 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.917 | 0.958 | 0.875 |
| F1 | 0.871 | 1.0 | 0.857 | 0.837 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.944 | 0.857 | 0.923 |
| Precision | 0.944 | 1.0 | 0.75 | 0.889 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.944 | 0.857 | 0.857 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.M.; Eetemadi, A.; Tagkopoulos, I. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Metalloporphyrin Sensors for Human Breath Screening. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311290
Lee BM, Eetemadi A, Tagkopoulos I. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Metalloporphyrin Sensors for Human Breath Screening. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Bo Mi, Ameen Eetemadi, and Ilias Tagkopoulos. 2021. "Reduced Graphene Oxide-Metalloporphyrin Sensors for Human Breath Screening" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311290
APA StyleLee, B. M., Eetemadi, A., & Tagkopoulos, I. (2021). Reduced Graphene Oxide-Metalloporphyrin Sensors for Human Breath Screening. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311290






