Three-Component Microseismic Data Denoising Based on Re-Constrain Variational Mode Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2. Re-Constraint of Variational Mode Decomposition
- Load the initial three-component microseismic data.
- Expend the data using a mirror image against the boundary effect, and perform the Fourier transform for the original data. The related parameters of the subsequent processing are initialized.
- Update the vertical component variable using VMD updated formulas as Formula (2).
- Update the parameters of the horizontal components using updated re-constrain VMD formula as in Formula (6).
- Judge whether the end condition of iteration is satisfied. The end condition is determined by the maximum number of iterations. If the condition is not satisfied, repeat Step 3.
- Perform the inverse Fourier transform for the previous output, and remove the mirror data. Then, the final result is obtained.
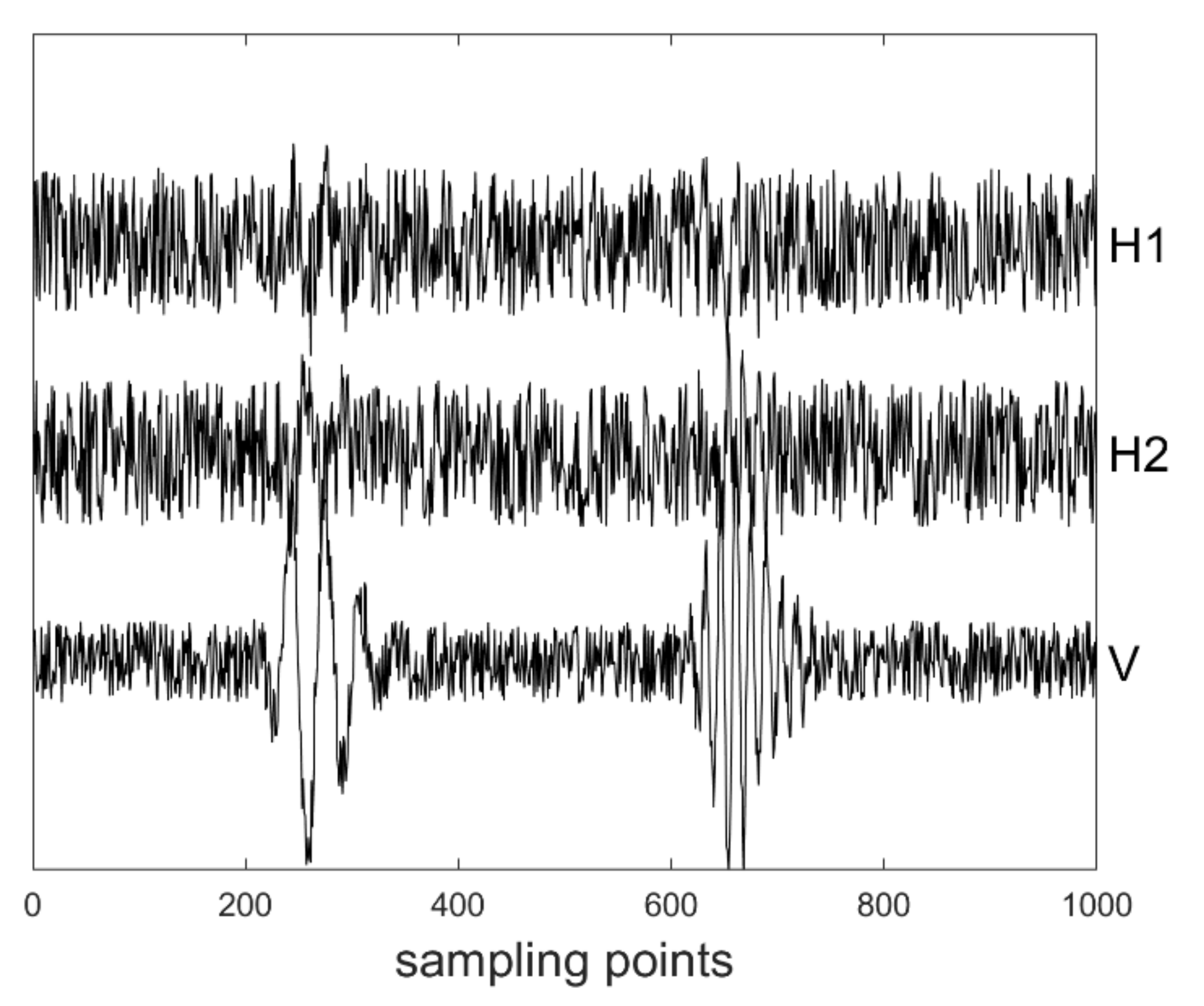
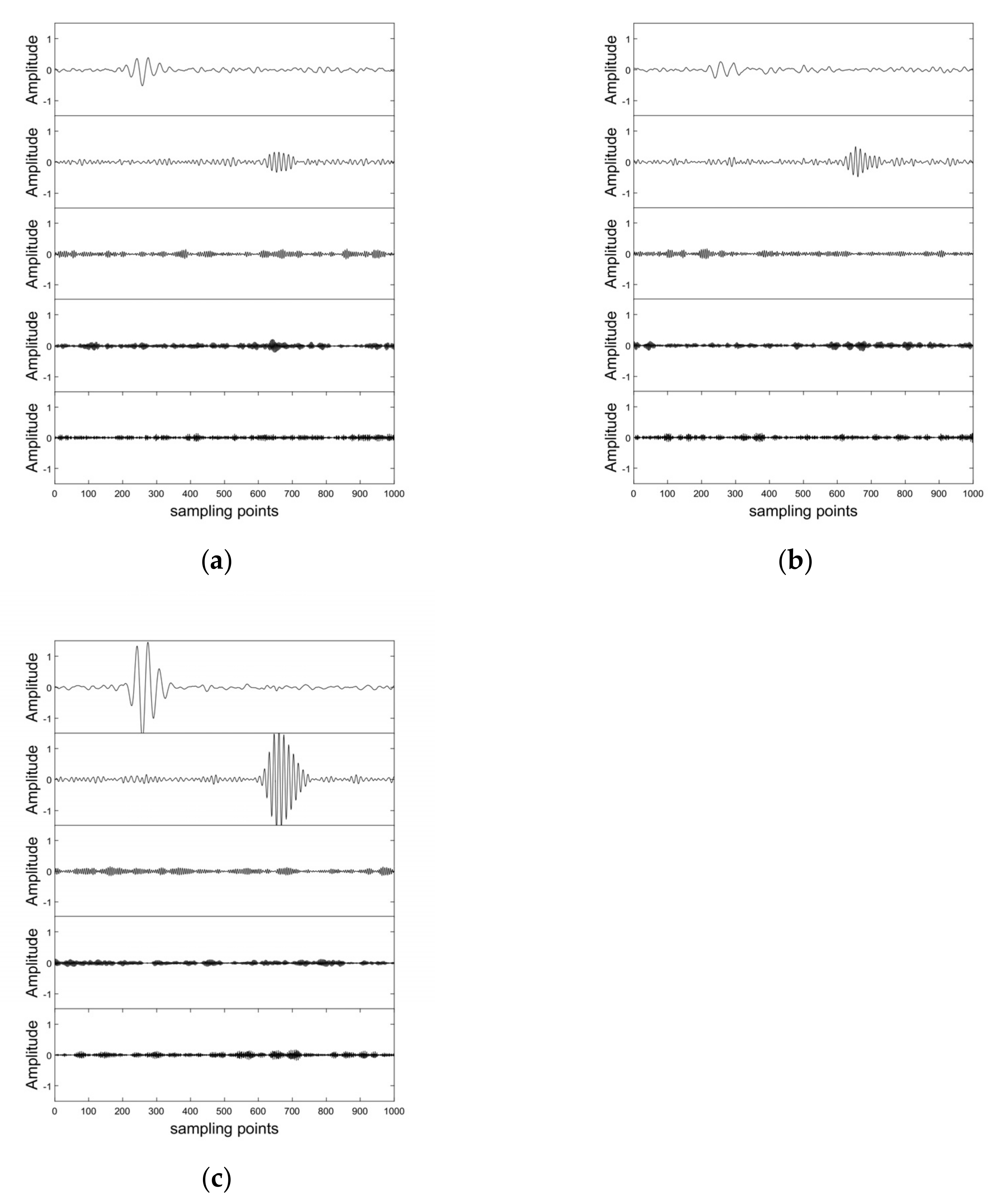
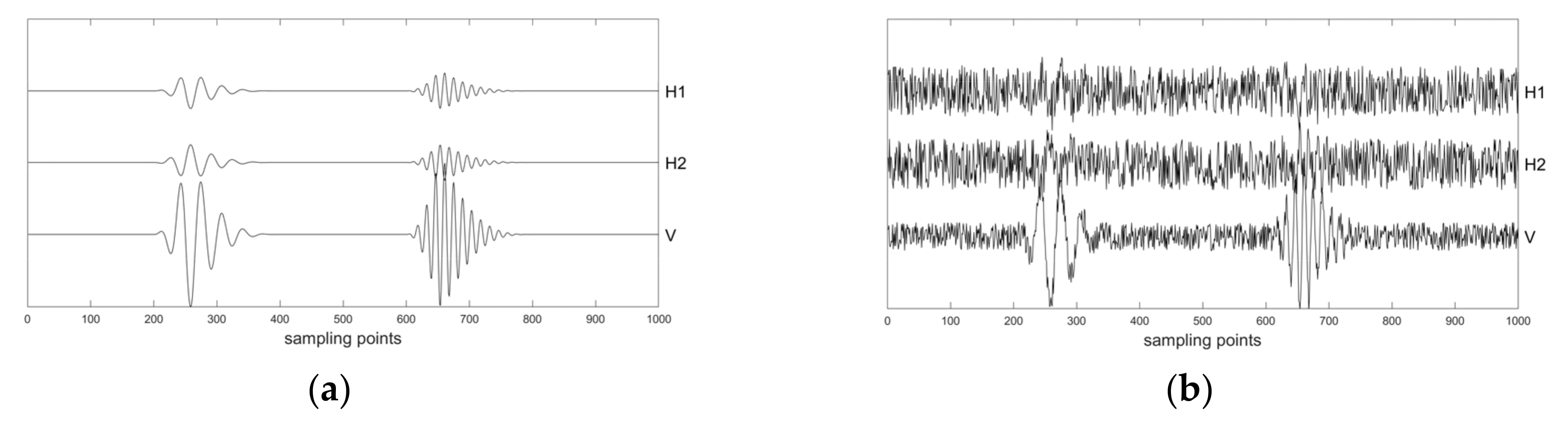
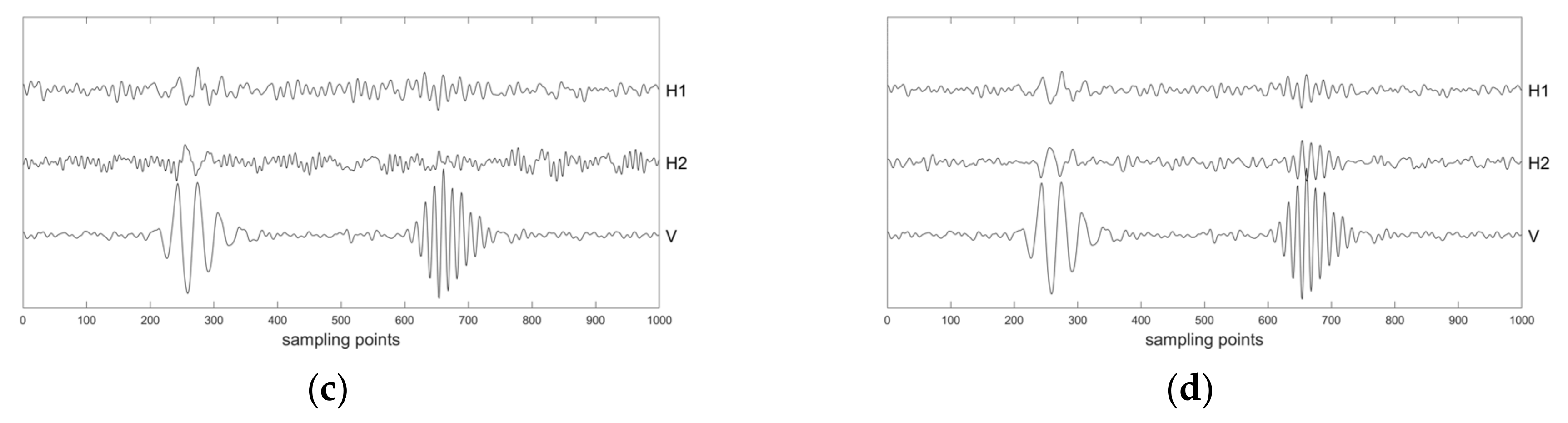
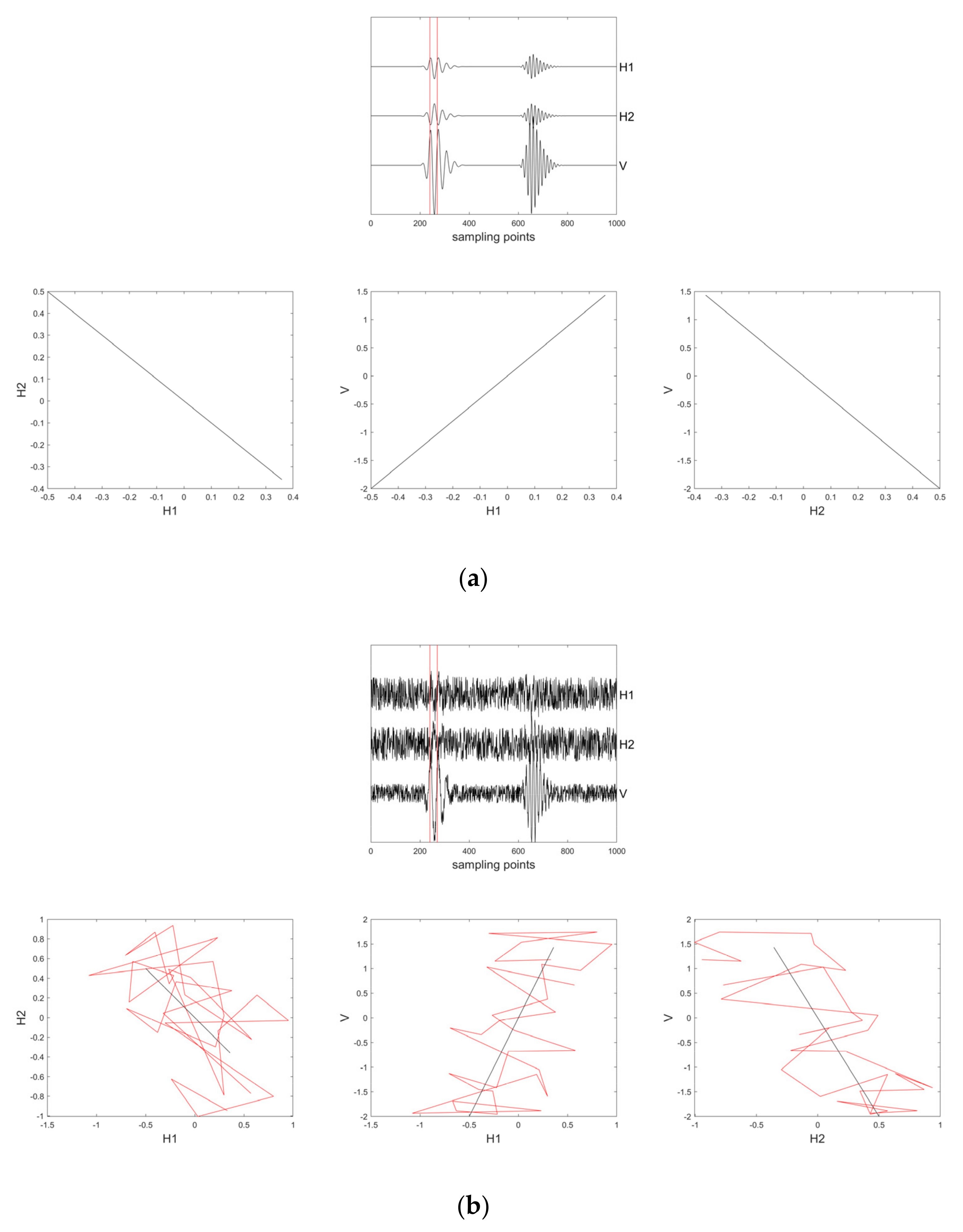
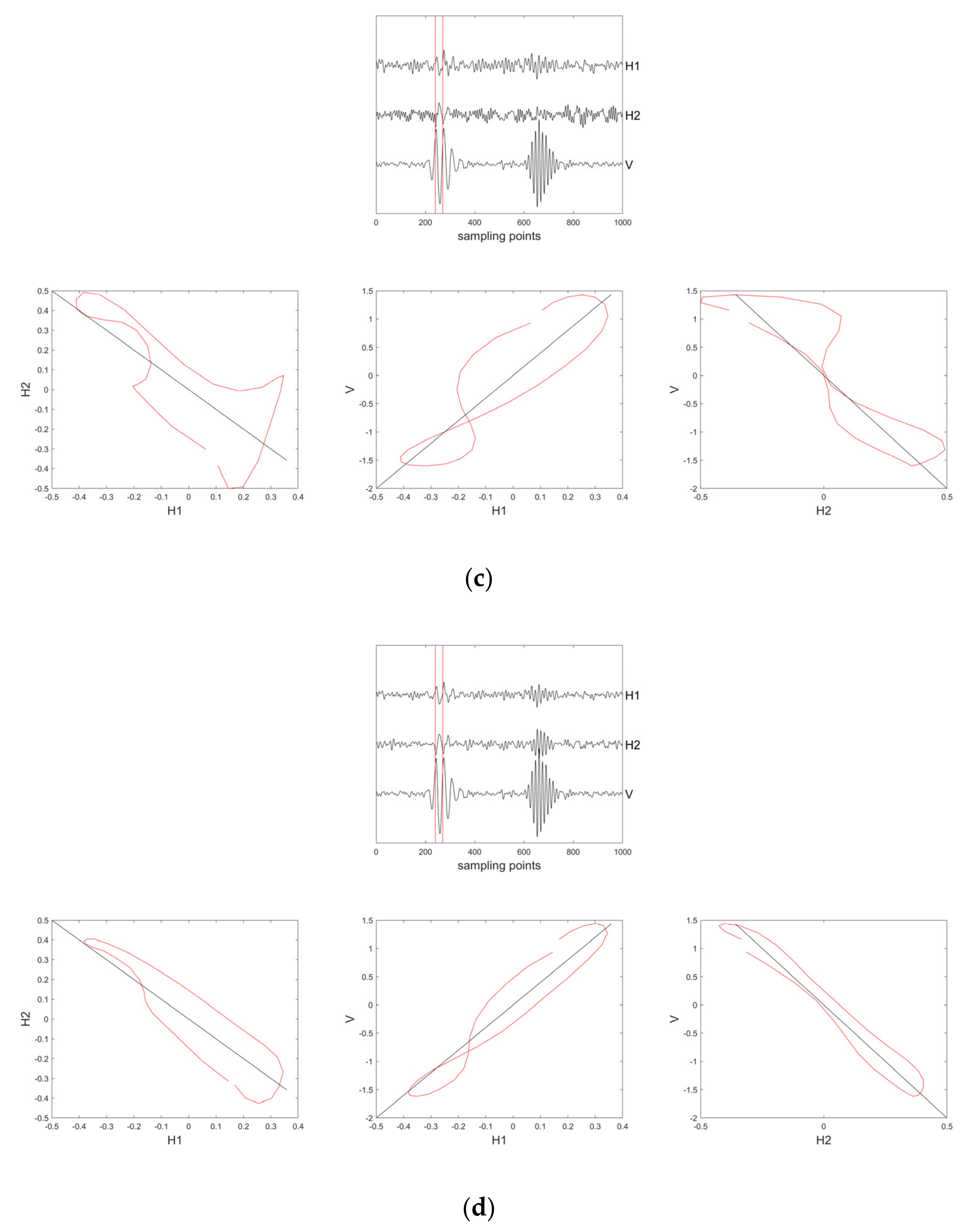
3. Synthetic Data
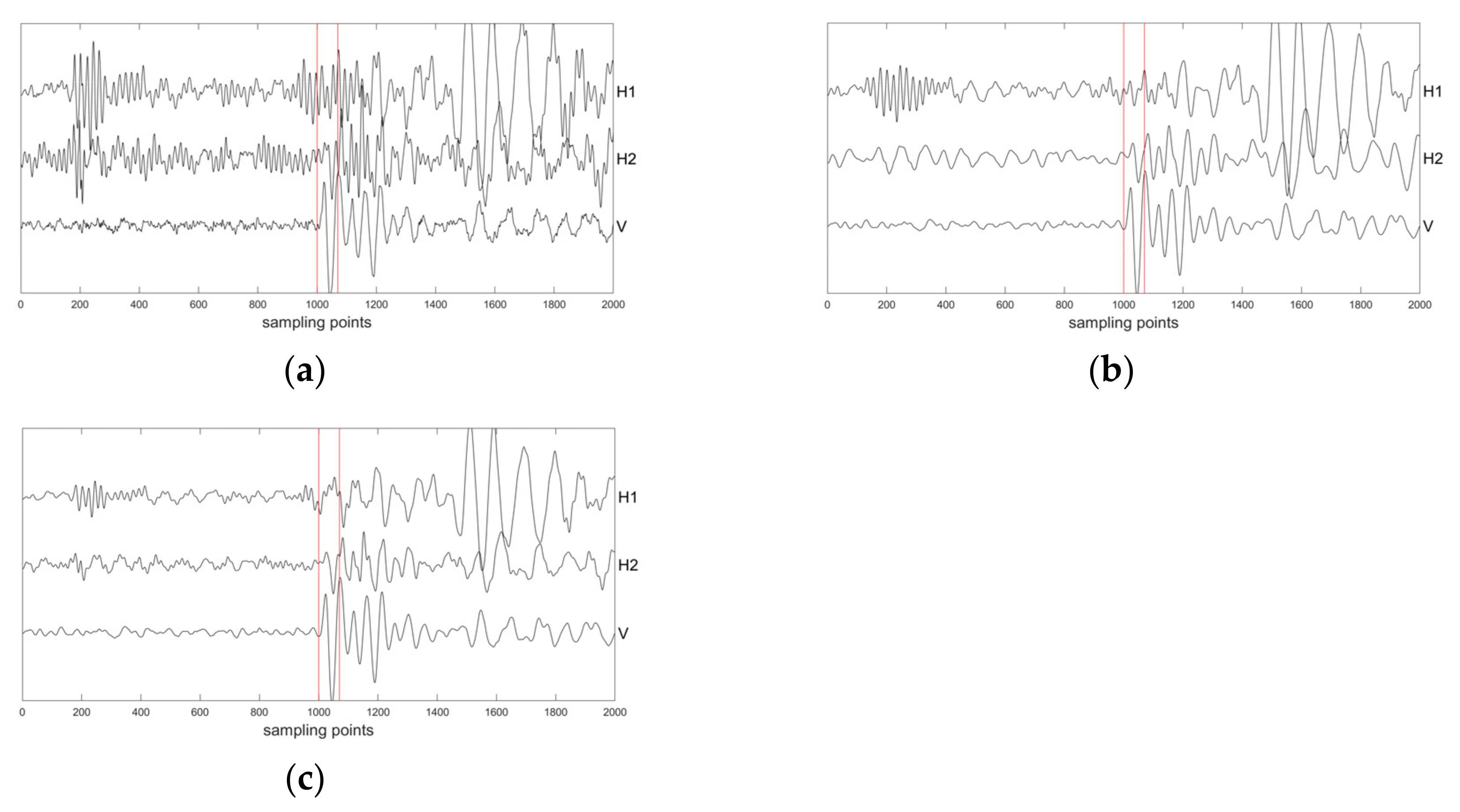
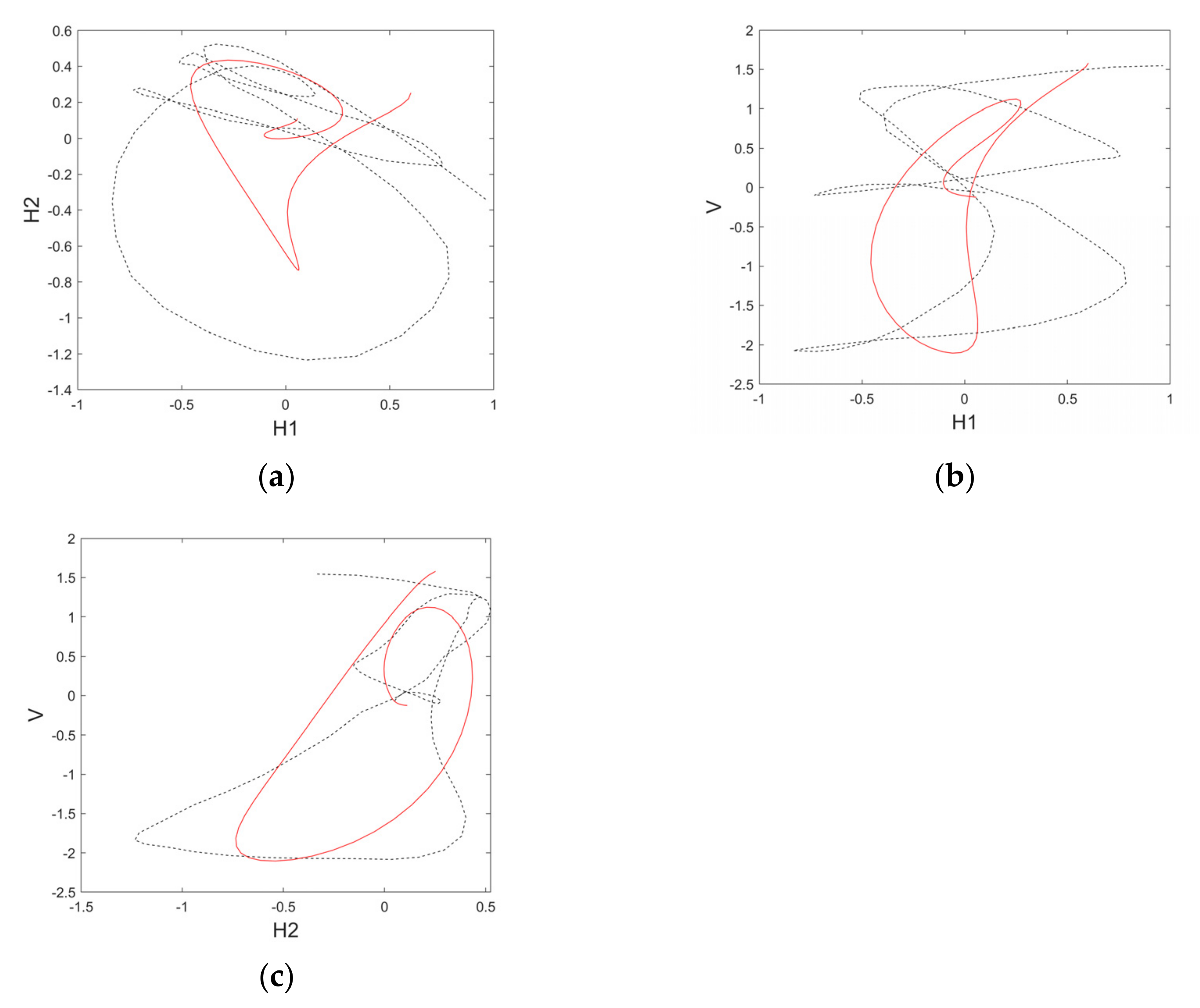
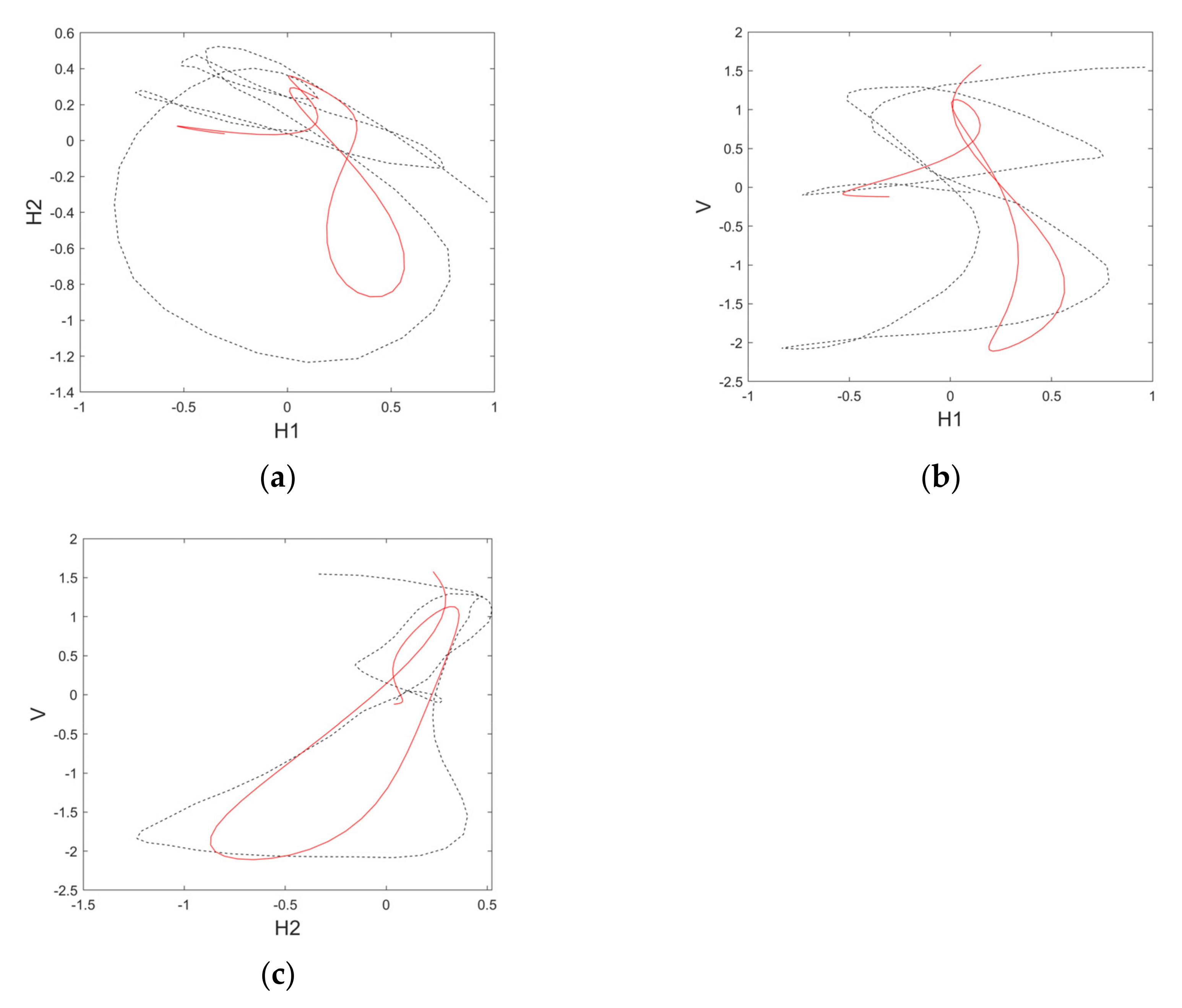
4. Field Microseismic Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyer, B.C.; Schanz, U.; Ladner, F.; Häring, M.O.; Spillman, T. Microseismic imaging of a geothermal reservoir stimulation. Lead. Edge 2008, 27, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellouch, A.; Lindsey, N.J.; Ellsworth, W.L.; Biondi, B.L. Comparison between Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Geophones: Downhole Microseismic Monitoring of the FORGE Geothermal Experiment. Seism. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 3256–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, B.; Kang, Y. A Modified Bursting Energy Index for Evaluating Coal Burst Proneness and Its Application in Ordos Coalfield, China. Energies 2020, 13, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwan, F.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Liang, B.; et al. Sichuan Shale Gas Microseismic Monitoring: Acquisition, Processing, and Integrated Analyses. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Fang, J.; Chen, Y. Self-training and learning the waveform features of microseismic data using an adaptive dictionary. Geophysics 2020, 85, KS51–KS61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiang, K. Separation of simultaneous sources using a structural-oriented median filter in the flattened dimension. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 86, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Van Der Baan, M. Multicomponent microseismic data denoising by 3D shearlet transform. Geophysics 2018, 83, A45–A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y. Nonstationary Least-Squares Decomposition With Structural Constraint for Denoising Multi-Channel Seismic Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10437–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Okaya, D. Frequency-time decomposition of seismic data using wavelet-based methods. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Langston, C.; Horton, S.P. Automatic microseismic denoising and onset detection using the synchrosqueezed continuous wavelet transform. Geophysics 2016, 81, V341–V355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H. Single-channel and multi-channel seismic random noise suppression based on the regularized non-stationary decomposition. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 175, 103986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekara, M.; Van Der Baan, M. Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition. Geophysics 2009, 74, V89–V98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, J. Random noise attenuation by f-x empirical-mode decomposition predictive filtering. Geophysics 2014, 79, V81–V91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, D.P.; Rehman, N.U.; Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Time-Frequency Analysis of Multivariate Signals: The Power of Adaptive Data Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; van der Baan, M. Microseismic and seismic denoising via ensemble empirical mode decomposition and adaptive thresholding. Geophysics 2015, 80, KS69–KS80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. Random noise reduction using a hybrid method based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. J. Seism. Explor. 2017, 26, 227–249. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D. Signal enhancement based on complex curvelet transform and complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 144, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-R.; Shieh, J.-S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.-Q.; Sun, H.-M.; Mao, Q.-C.; Liu, X.-Y.; Jia, R.-S. Noise Suppression Method of Microseismic Signal Based on Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Wavelet Packet Threshold. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 176504–176513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Guo, H.; Shang, X. EEMD and Multiscale PCA-Based Signal Denoising Method and Its Application to Seismic P-Phase Arrival Picking. Sensors 2021, 21, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cao, S.; Chen, Y. Applications of variational mode decomposition in seismic time-frequency analysis. Geophysics 2016, 81, V365–V378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Verma, S.; Marfurt, K.J. Seismic signal denoising using thresholded variational mode decomposition. Explor. Geophys. 2018, 49, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bao, H.; Qi, X. Seismic Random Noise Attenuation Method Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Correlation Coefficients. Electronics 2018, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z. A hybrid method for noise suppression using variational mode decomposition and singular spectrum analysis. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 161, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, N.; Sun, F.; Jiang, X. Random noise suppression of seismic data by time–frequency peak filtering with variational mode decomposition. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 50, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Duan, Z. Seismic Signal Denoising Using f-x Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, L.; Xu, N. Noise Suppression of Microseismic Signals via Adaptive Variational Mode Decomposition and Akaike Information Criterion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jin, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, S. Noise reduction method of microseismic signal of water inrush in tunnel based on variational mode method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 2021, 6497–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukuhira, Y.; Poliannikov, O.V.; Fehler, M.C.; Moriya, H. Low-SNR Microseismic Detection Using Direct P-Wave Arrival Polarization. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2020, 110, 3115–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. A multi-window algorithm for automatic picking of microseismic events on 3-C data. In Proceedings of the 2005 SEG Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 6–11 November 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera Rodriguez, I.; Bonar, D.; Sacchi, M. Microseismic data denoising using a 3C group sparsity constrained time-frequency transform. Geophysics 2012, 77, V21–V29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Wang, P.; Gui, Z.; Mao, Q. Three-Component Microseismic Data Denoising Based on Re-Constrain Variational Mode Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210943
Chen Z, Wang P, Gui Z, Mao Q. Three-Component Microseismic Data Denoising Based on Re-Constrain Variational Mode Decomposition. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210943
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhili, Peng Wang, Zhixian Gui, and Qinghui Mao. 2021. "Three-Component Microseismic Data Denoising Based on Re-Constrain Variational Mode Decomposition" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210943
APA StyleChen, Z., Wang, P., Gui, Z., & Mao, Q. (2021). Three-Component Microseismic Data Denoising Based on Re-Constrain Variational Mode Decomposition. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210943





