Acoustic Sensing and Noise Identification of a Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Unit: Industrial Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
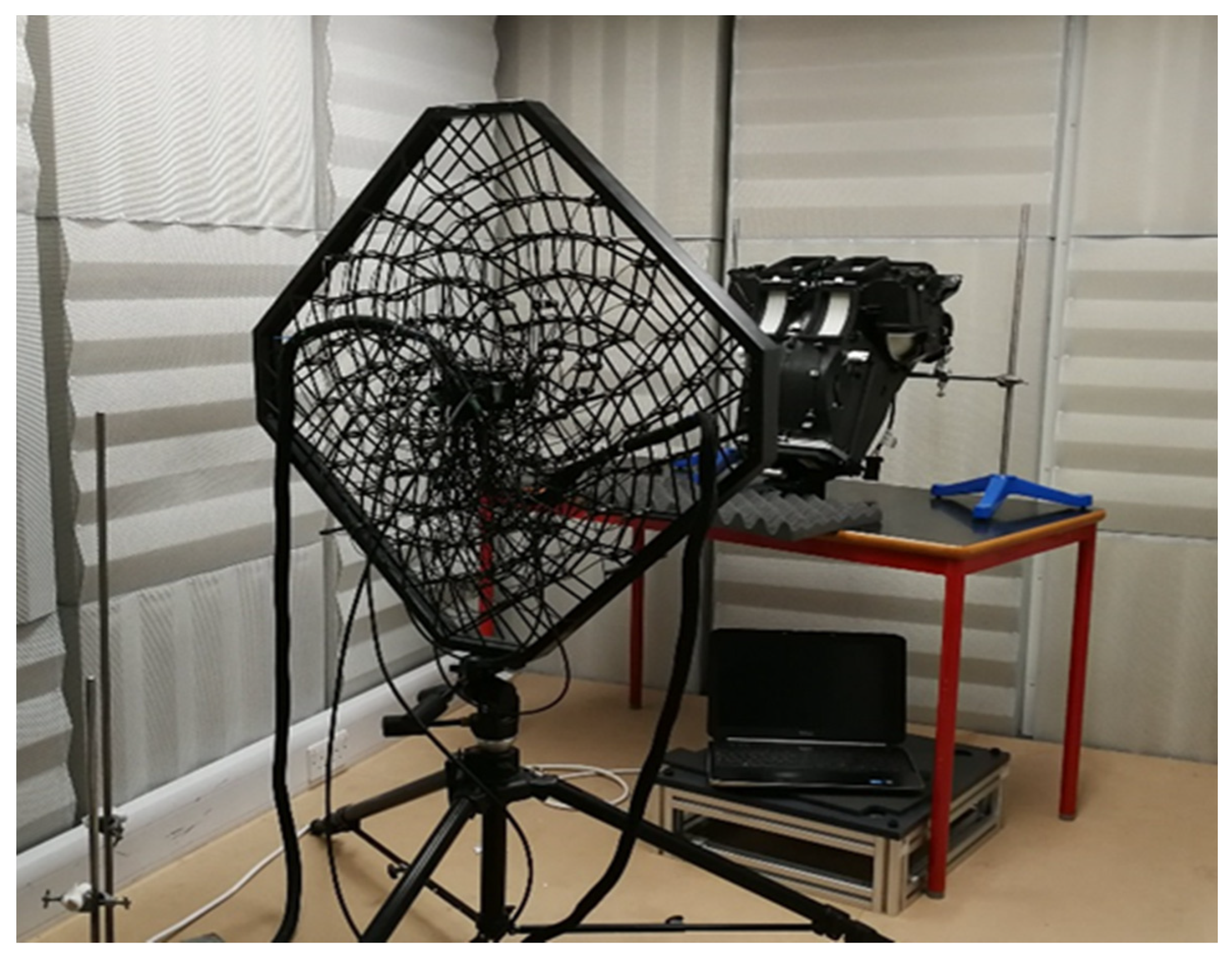
2.1. Test Setup
2.2. Maintaining Observations during Testing
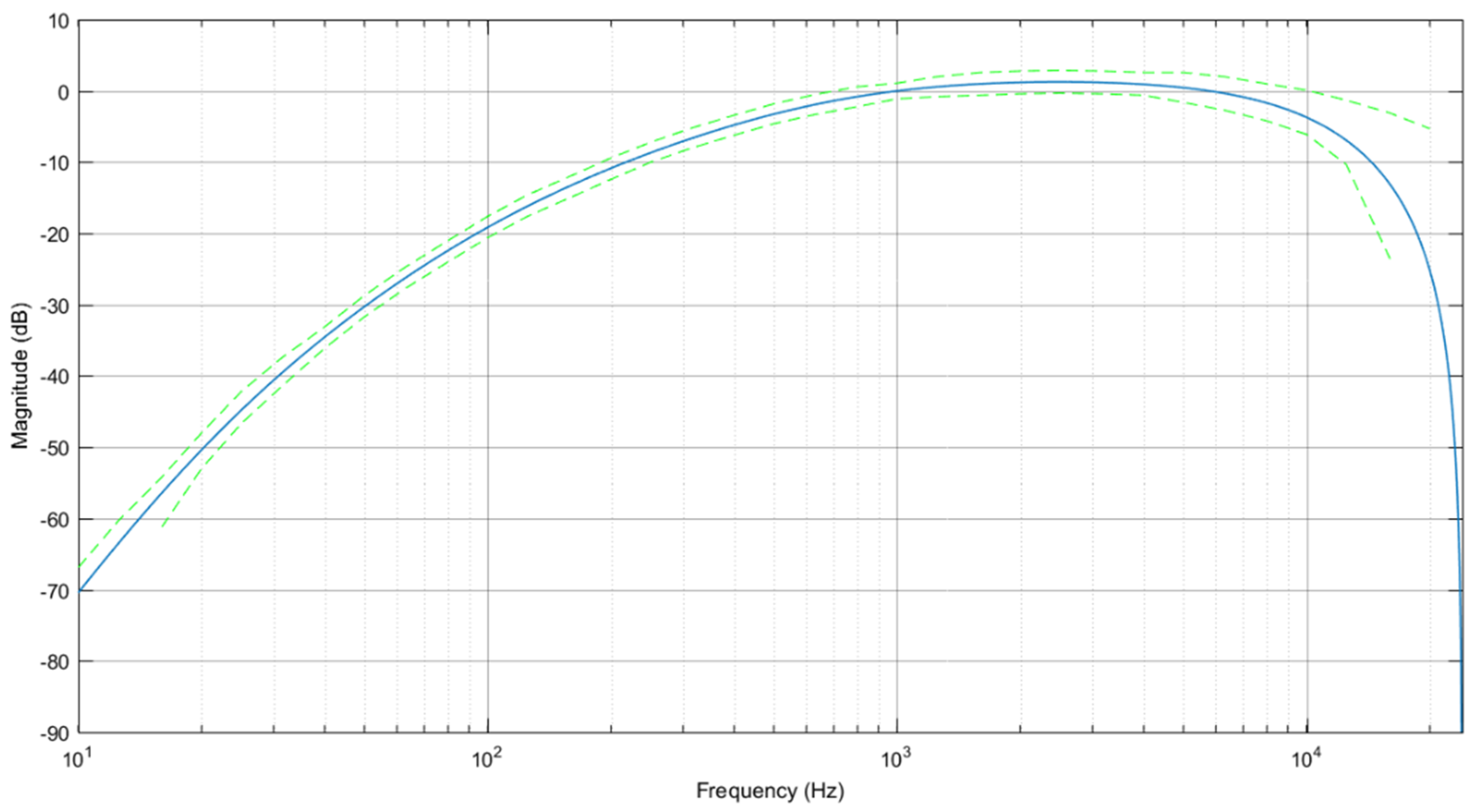
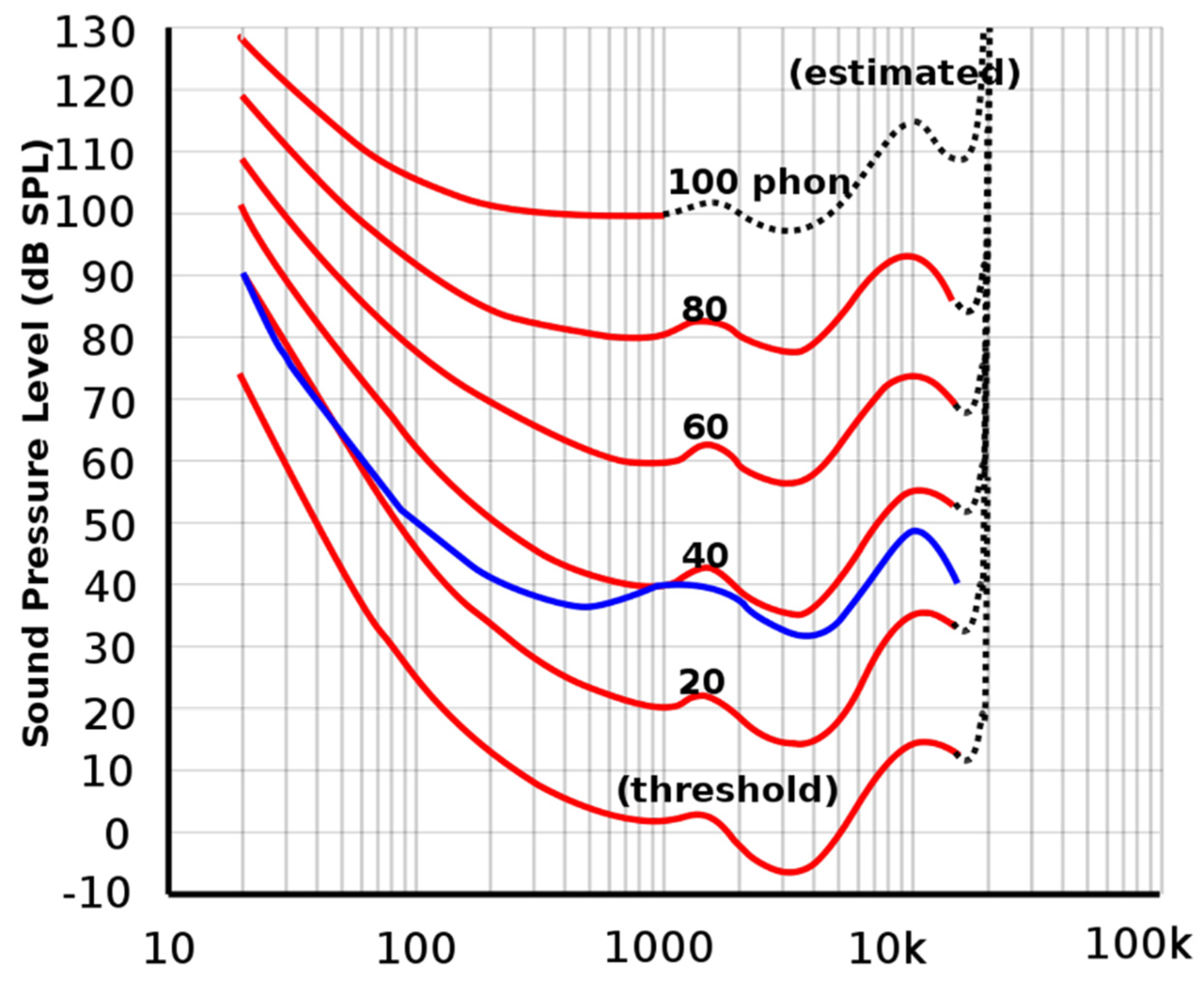
2.3. Psychoacoustic Metrics
- Sound pressure level
- 2.
- A-weighted sound pressure level
- 3.
- Loudness
- 4.
- Sharpness
3. Results
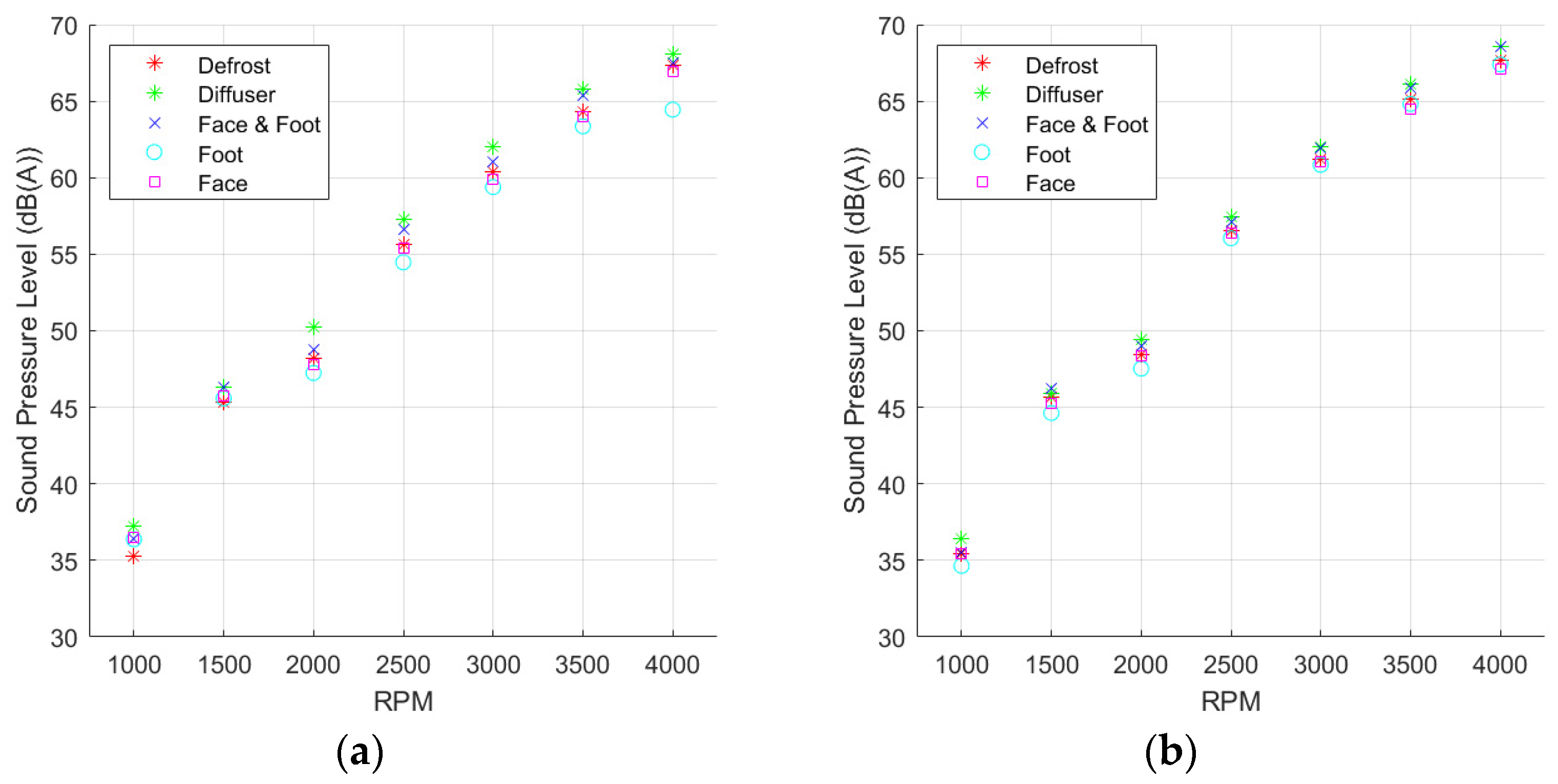
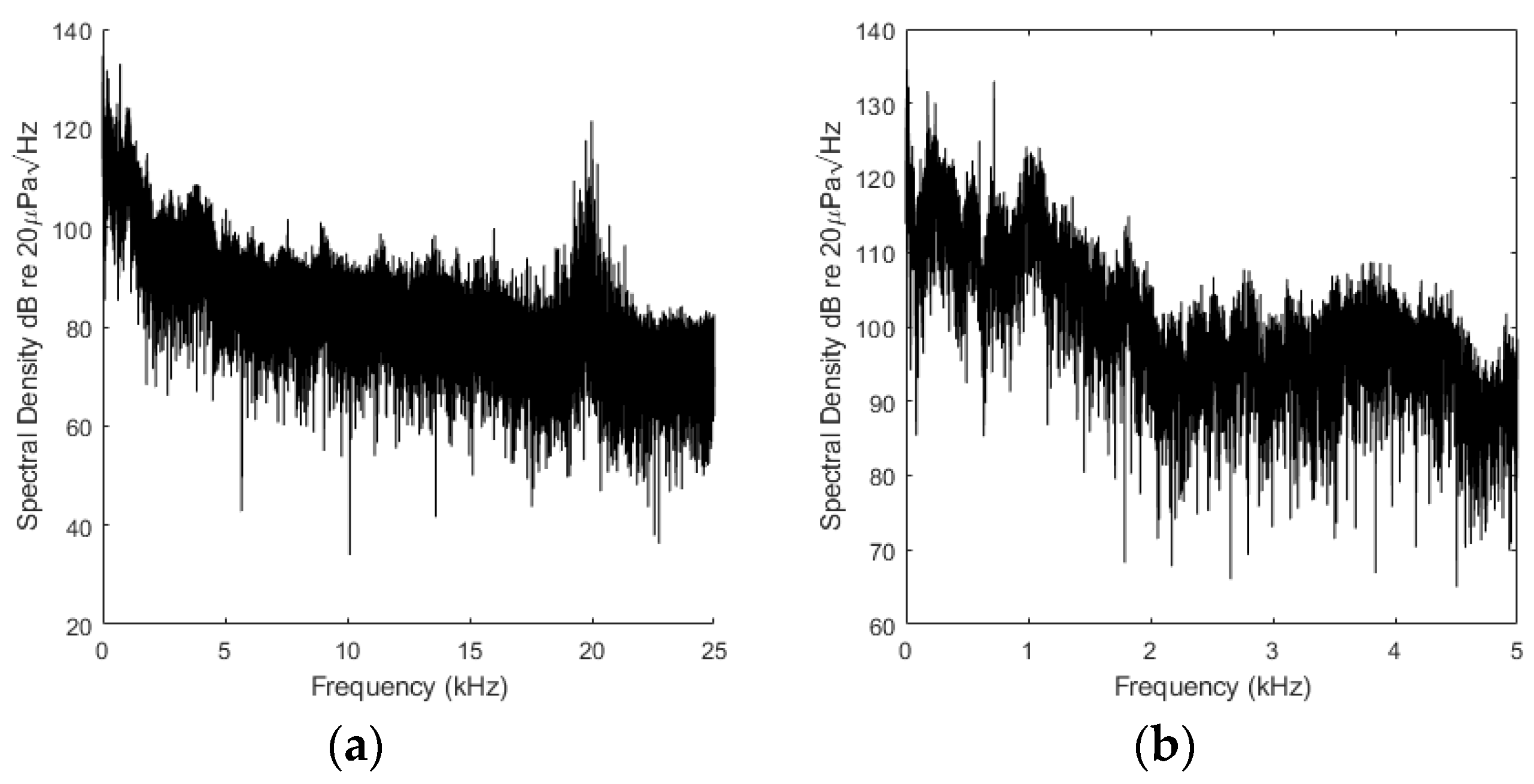
3.1. A-Weighted Sound Pressure Level
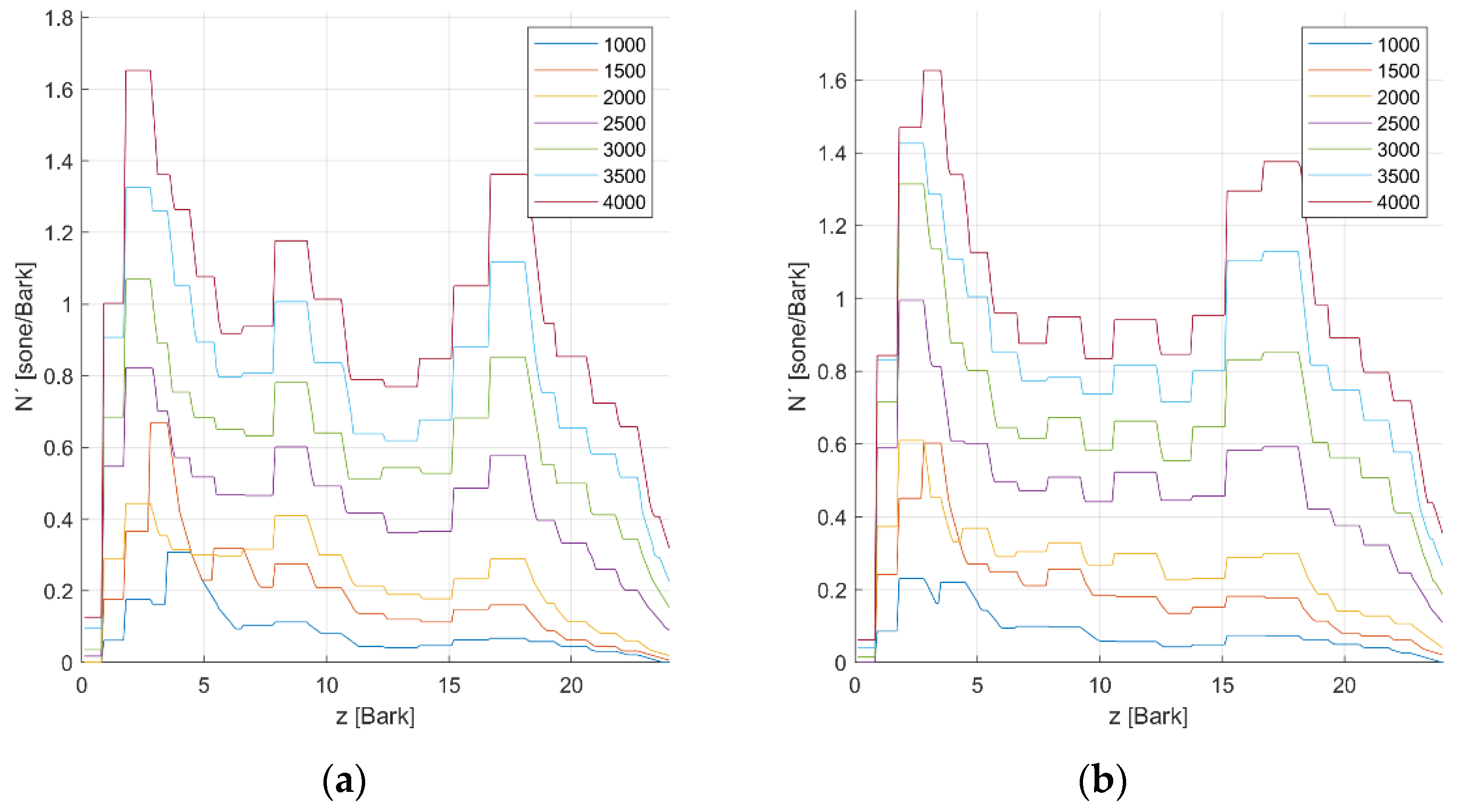
3.2. Loudness
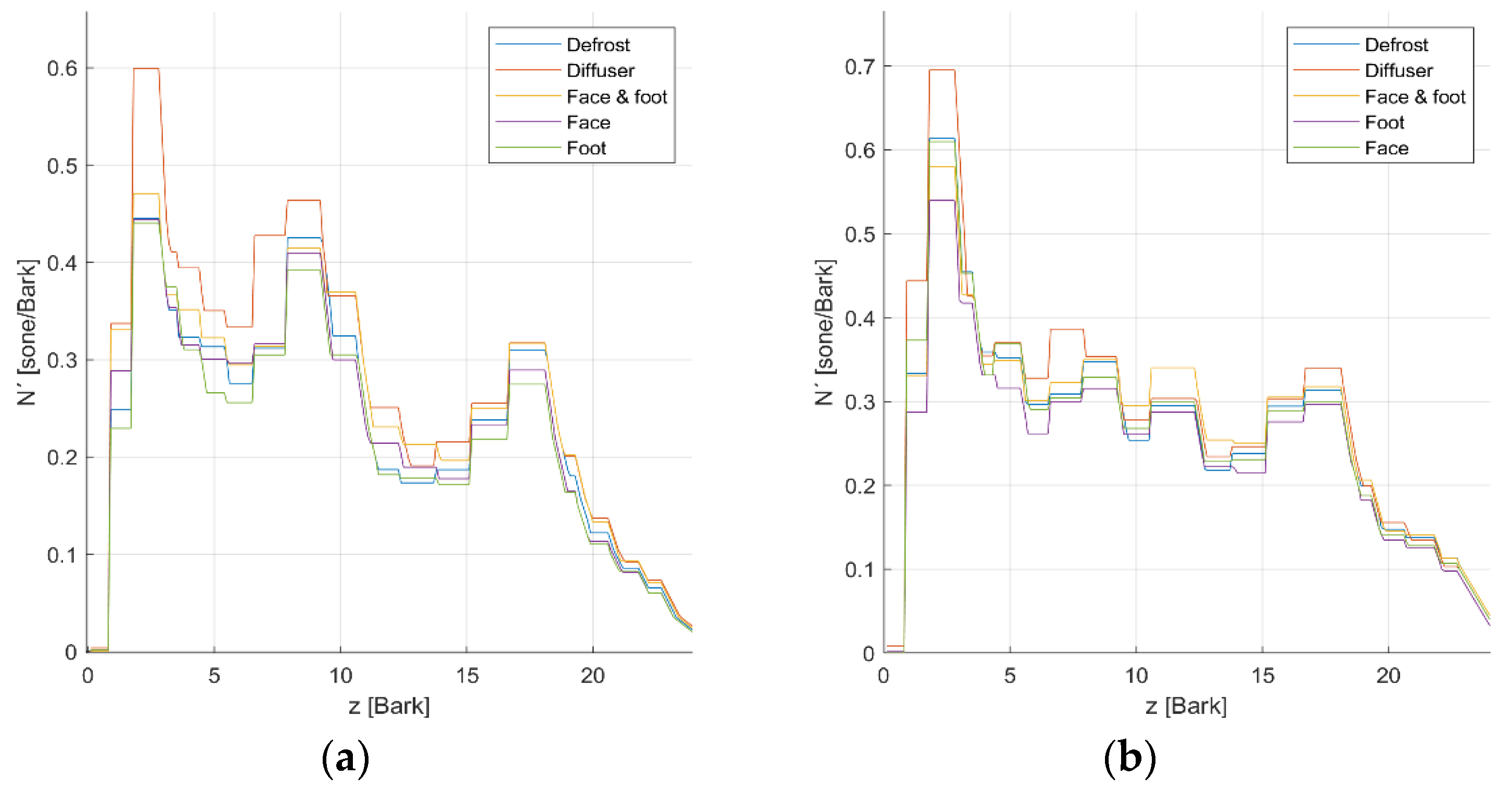
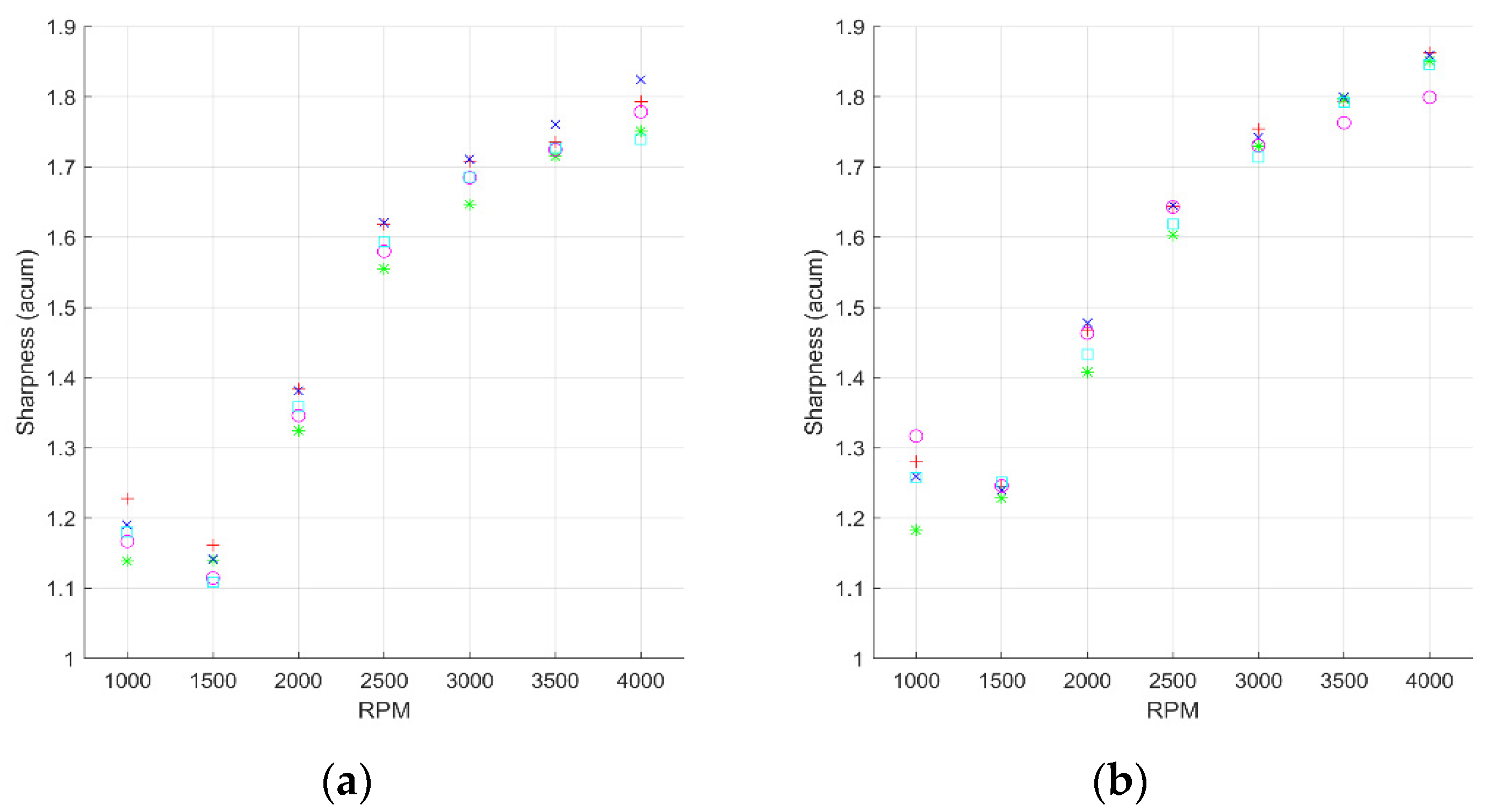
3.3. Sharpness
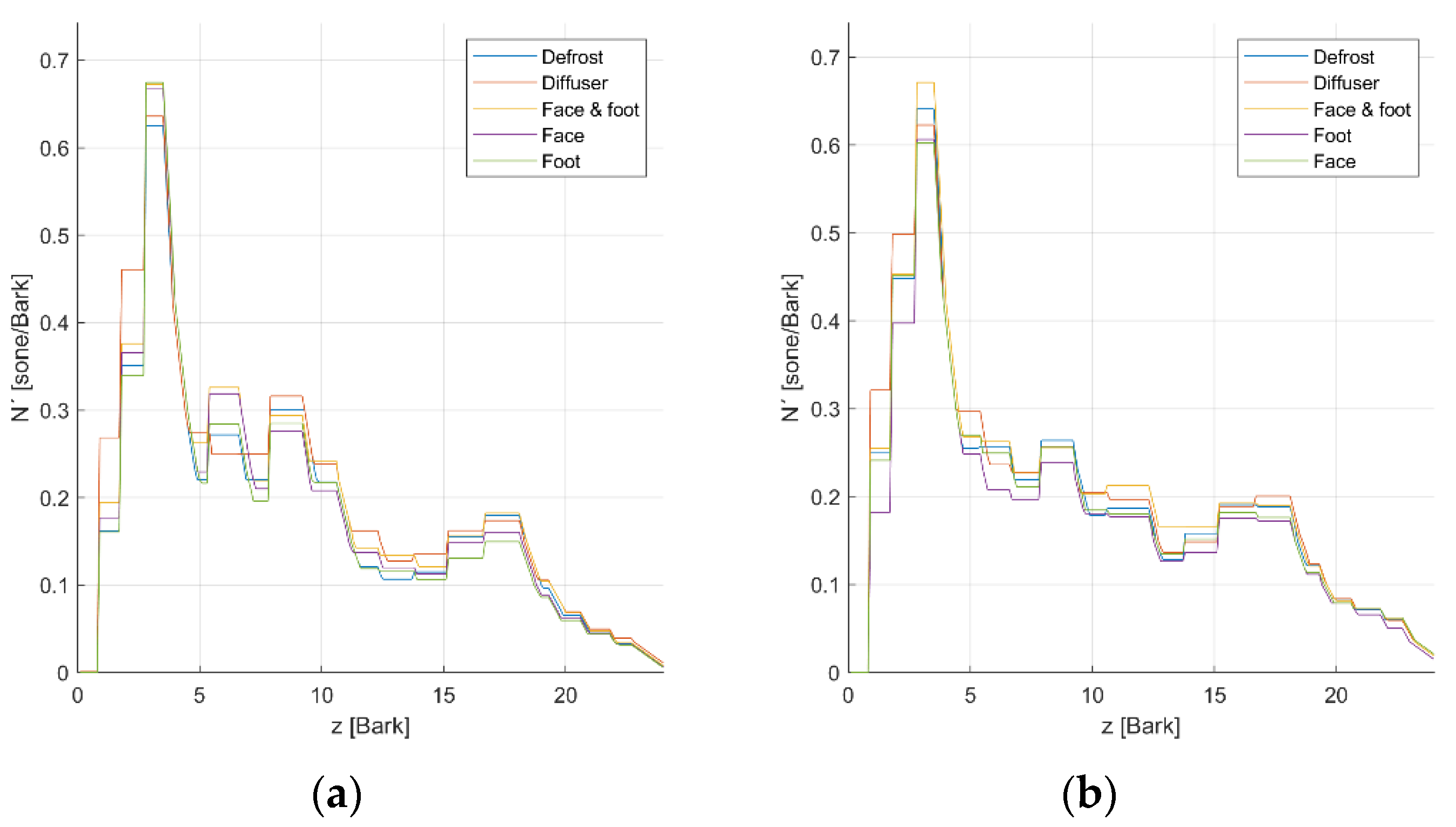
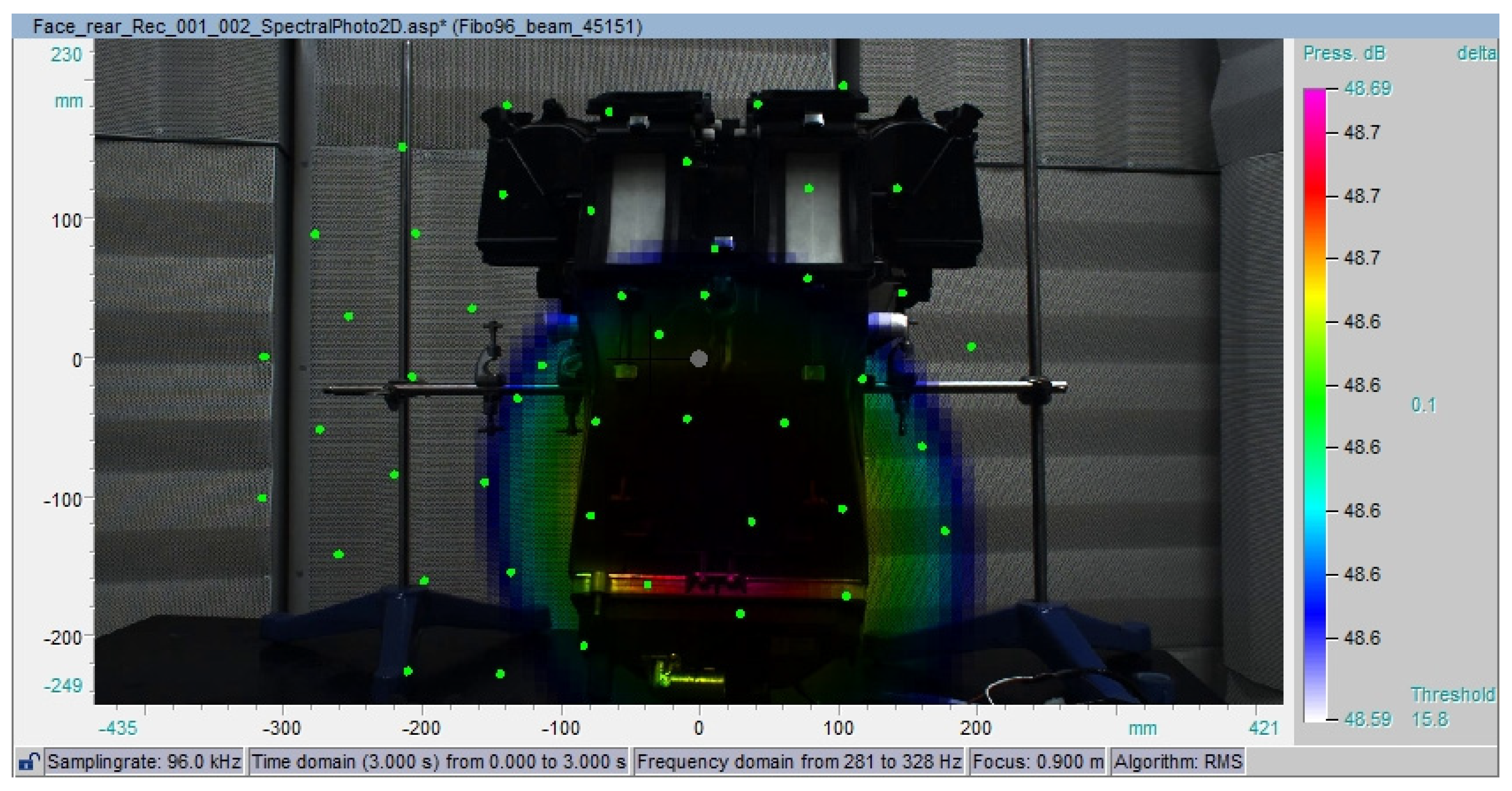
3.4. Acoustic-Camera Noise Localization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennings, P.A.; Dunne, G.; Williams, R.; Giudice, S. Tools and techniques for understanding the fundamentals of automotive sound quality. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2010, 224, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Payne, S.R.; Jennings, P.A. Toward a Methodology for Assessing Electric Vehicle Exterior Sounds. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, N.; Priebsch, H.H. The prediction of low-and mid-frequency internal road vehicle noise: A literature survey. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2007, 221, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, R.P.; Paul, S.; Gerges, S.N. A sound quality-based investigation of the HVAC system noise of an automobile model. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Elliott, S.J.; Cheer, J. Local active control of road noise inside a vehicle. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 121, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, S.; Abom, M. Fan Noise Control Using Microperforated Splitter Silencers. J. Vib. Acoust. 2014, 136, 031017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, S.; Abom, M. Noise control for cooling fans on heavy vehicles. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2012, 60, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Yang, I.-H.; Jeong, J.-E.; Park, S.-G.; Oh, J.-E. Reliability improvement of a sound quality index for a vehicle HVAC system using a regression and neural network model. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neise, W. Noise reduction in centrifugal fans: A literature survey. J. Sound Vib. 1976, 45, 375–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neise, W. Review of Noise Reduction Methods for Centrifugal Fans. J. Eng. Ind. 1982, 104, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-D.; Bai, M.R. Application of feed forward adaptive active-noise control for reducing blade passing noise in centrifugal fans. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 239, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde-Suárez, S.; Ballesteros-Tajadura, R.; Hurtado-Cruz, J.P.; Santolaria-Morros, C. Experimental determination of the tonal noise sources in a centrifugal fan. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 295, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Envia, E. Fan noise reduction: An overview. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2002, 1, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M. Noise Attenuating Device for a Heating-Ventilation-Cooling System of a Motor Vehicle. U.S. Patent No. 8,166,775, 1 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I.H.; Kwon, O.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, J.-E. Sound quality evaluation for the vehicle HVAC system after active noise control. In Proceedings of the ASME 2008 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Boston, MA, USA, 31 October–6 November 2008; pp. 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Crocker, M.J. Recent trends in porous sound-absorbing materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, T.; Sato, S.; Shimokura, R.; Ando, Y. Measurement of temporal and spatial factors of a flushing toilet noise in a downstairs bedroom. J. Temporal Des. Arch. Environ. 2002, 2, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Beranek, L.L. Criteria for Office Quieting Based on Questionnaire Rating Studies. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, L. Noise and Vibration Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Beranek, L.L. Balanced noise-criterion (NCB) curves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazier, W.E. Revised noise criterion for application in the acoustical design and rating of HVAC systems. Noise Control. Eng. J. 1981, 162, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazier, W.E. Sound quality consideration in rating noise from heating, ventilating and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems in buildings. Noise Control Eng. J. 1995, 43, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazier, W.E. RC Mark II: A refined procedure for rating the noise of heating, ventilating, and airconditioning (HVAC) systems in buildings. Noise Control Eng. J. 1997, 45, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomer, P.D. Proposed revisions to room noise criteria. Noise Control Eng. J. 2000, 48, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomer, P.D.; Bradley, J.S. A test of proposed revisions to room noise criteria curves. Noise Control Eng. J. 2000, 48, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, S.; Kuwano, S. Psychological study on Leq as a measure of loudness of various kinds of noises. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E) 1984, 5, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuwano, S.; Namba, S.; Miura, H. Advantages and disadvantages of A-weighted sound pressure level in relation to subjective impression of environmental noises. Noise Control. Eng. J. 1989, 33, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayr, U.; Cirillo, E.; Fato, I.; Martellotta, F. A new approach to assessing the performance of noise indices in buildings. Appl. Acoust. 2003, 64, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryter, K. The Effects of Noise on Man; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D. Towards a unified system of noise assessment. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 14, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.; Henner, M.; Casalino, D.; Gullbrand, J.; Iaccarino, G.; Wang, M. Toward the prediction of low-speed fan noise. In Proceedings of the Summer Program, 9 July–4 August 2006; Center for Turbulence Research: Stanford, CA, USA, 2006; p. 519. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.B.; Huang, X.R.; Yang, M.L.; Lim, T.C.; Ding, W.P. Identification of vehicle interior noise sources based on wavelet transform and partial coherence analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 109, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, T. (Ed.) Springer Handbook of Acoustics; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Acoustics—Normal Equal-Loudness Contours; ISO 226; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Marui, A.; Martens, W.L. Predicting perceived sharpness of broadband noise from multiple moments of the specific loudness distribution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, EL7–EL13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigg, S.; Al-Shibaany, Z.Y.A.; Pearson, M.R.; Pullin, R.; Calderbank, P. Acoustic Sensing and Noise Identification of a Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Unit: Industrial Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9811. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219811
Grigg S, Al-Shibaany ZYA, Pearson MR, Pullin R, Calderbank P. Acoustic Sensing and Noise Identification of a Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Unit: Industrial Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):9811. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219811
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigg, Stephen, Zeyad Yousif Abdoon Al-Shibaany, Matthew Robert Pearson, Rhys Pullin, and Paul Calderbank. 2021. "Acoustic Sensing and Noise Identification of a Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Unit: Industrial Case Study" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 9811. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219811
APA StyleGrigg, S., Al-Shibaany, Z. Y. A., Pearson, M. R., Pullin, R., & Calderbank, P. (2021). Acoustic Sensing and Noise Identification of a Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Unit: Industrial Case Study. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 9811. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219811






