Experimental Testing of Passive Linear TMD for Postural Tremor Attenuation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
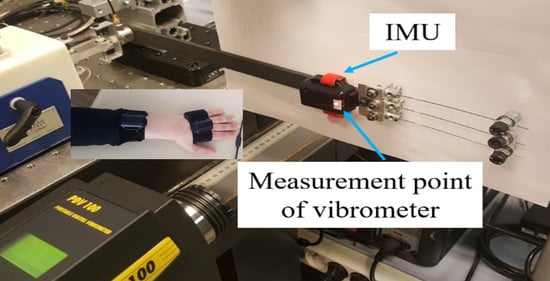
2.1. Experimental Arm
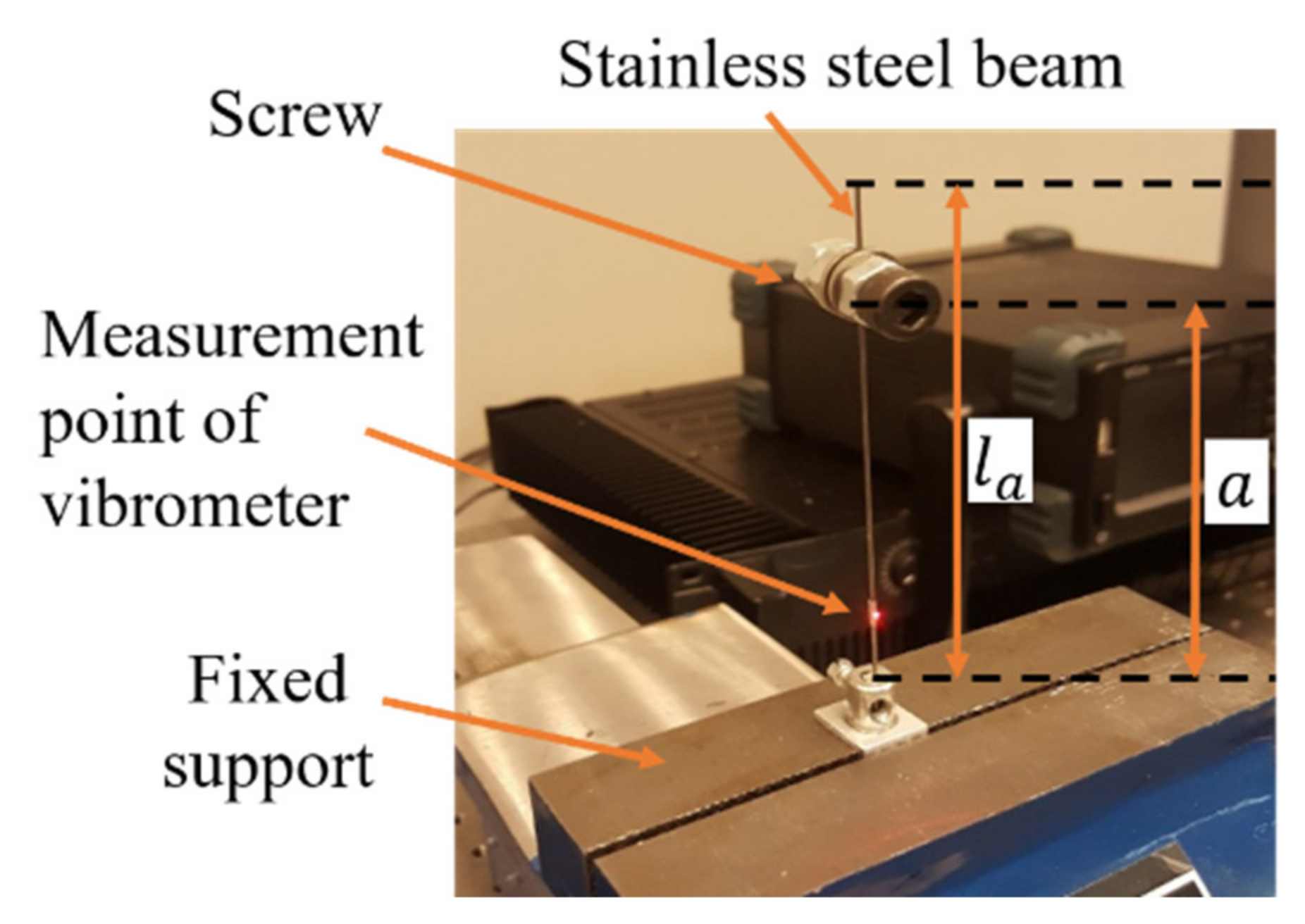
2.2. Passive Tuned Mass Damper
3. Results
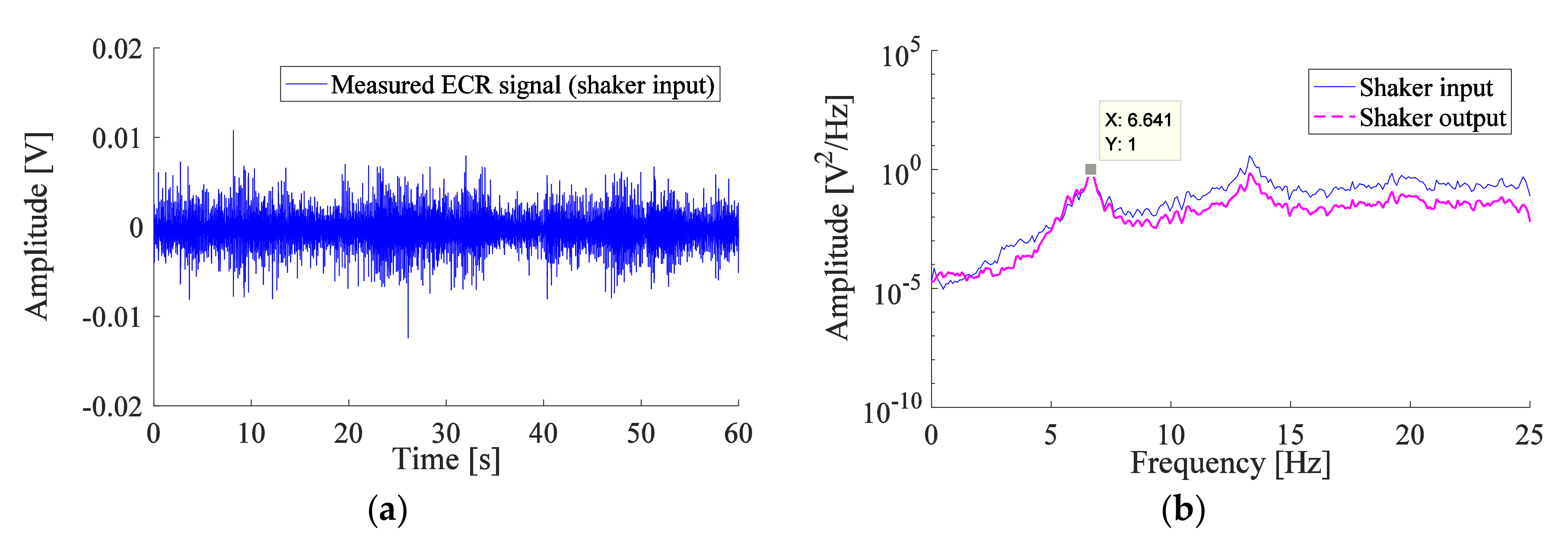
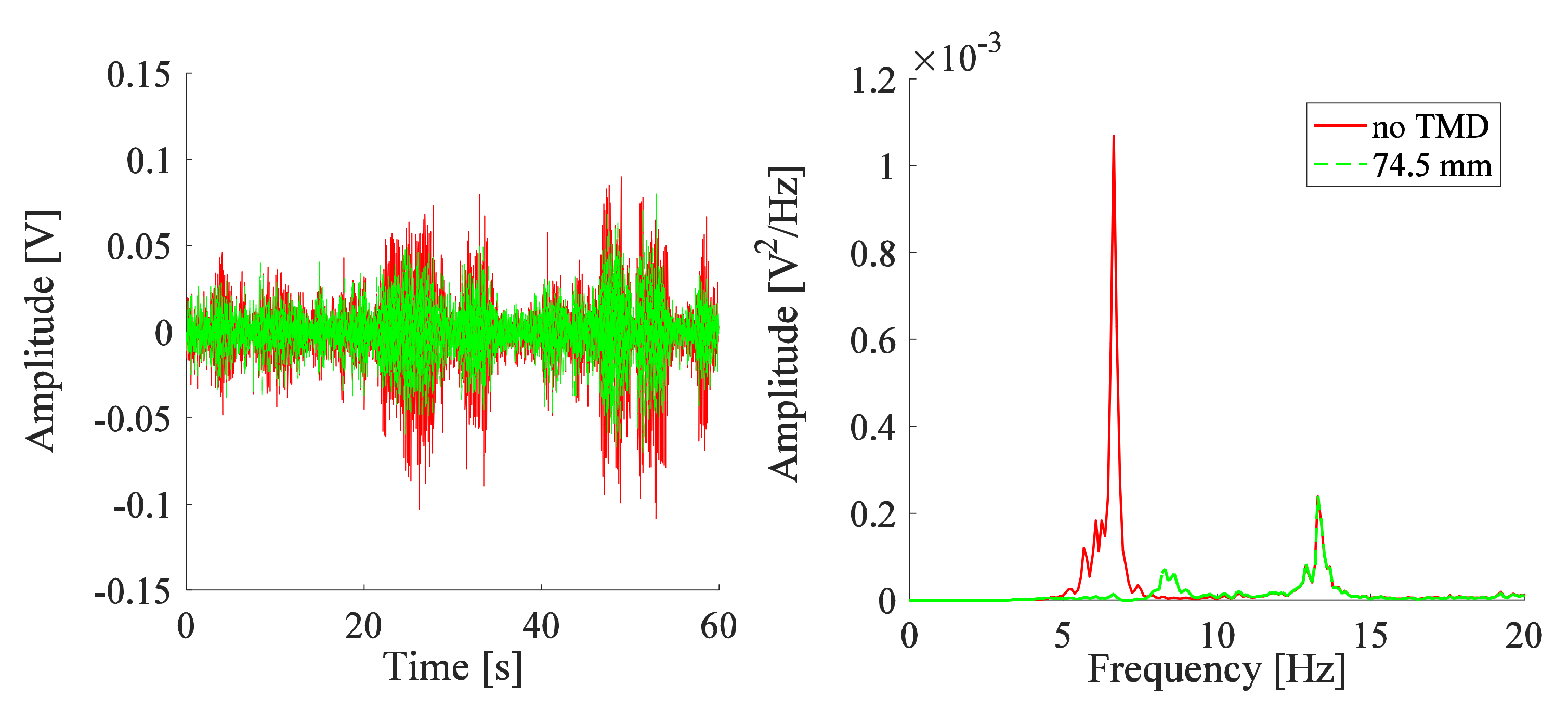
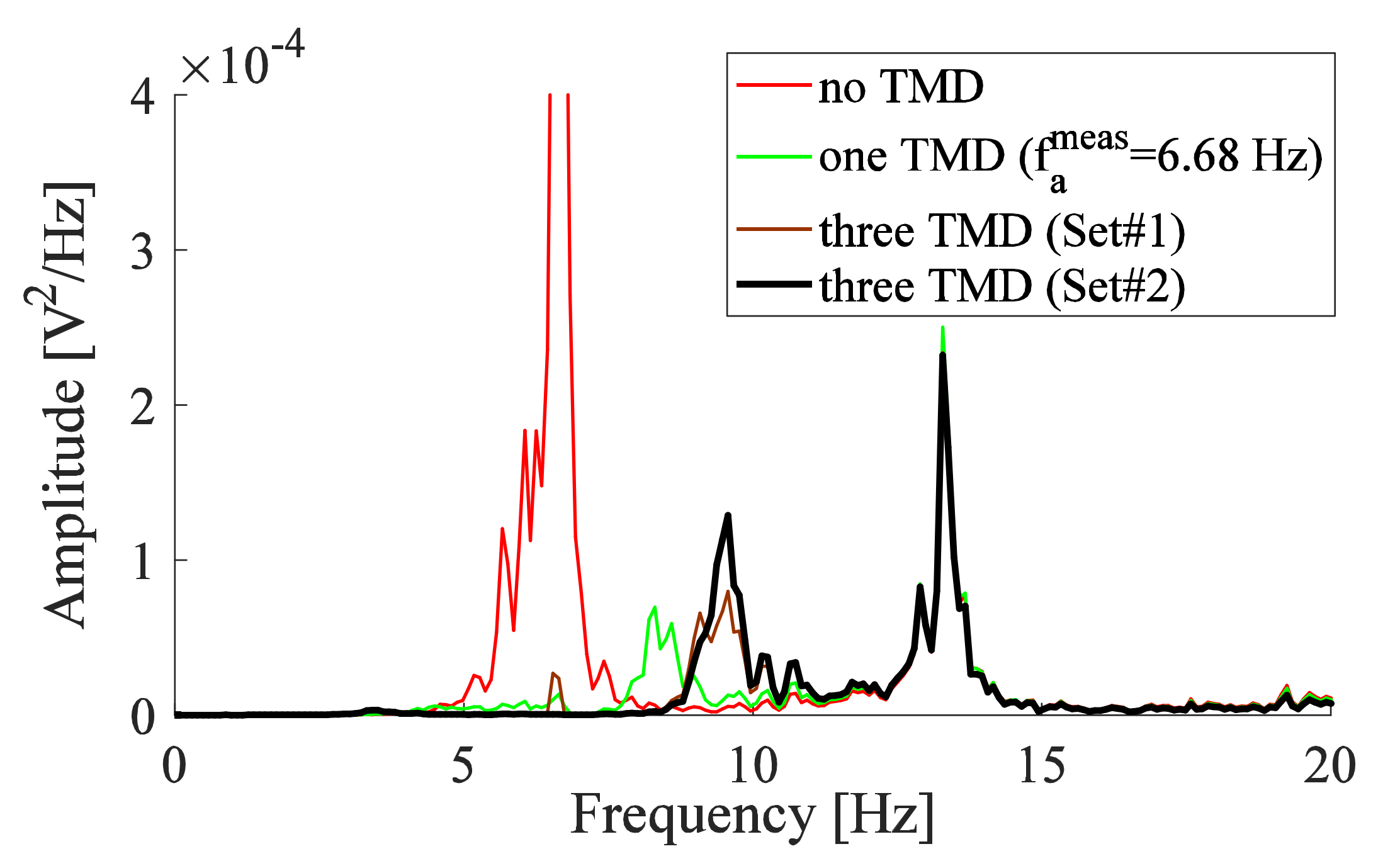
3.1. Measurements for the TMD
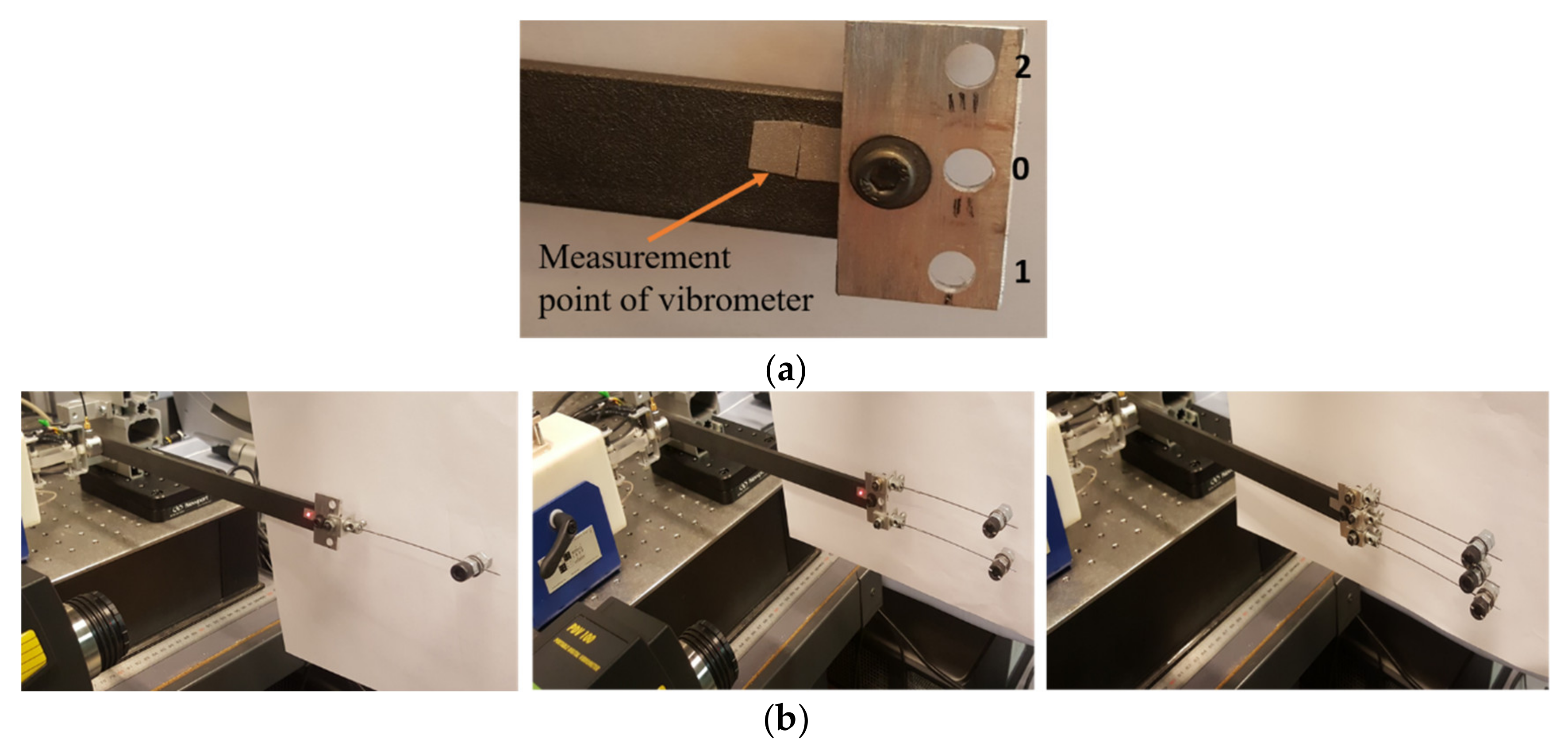
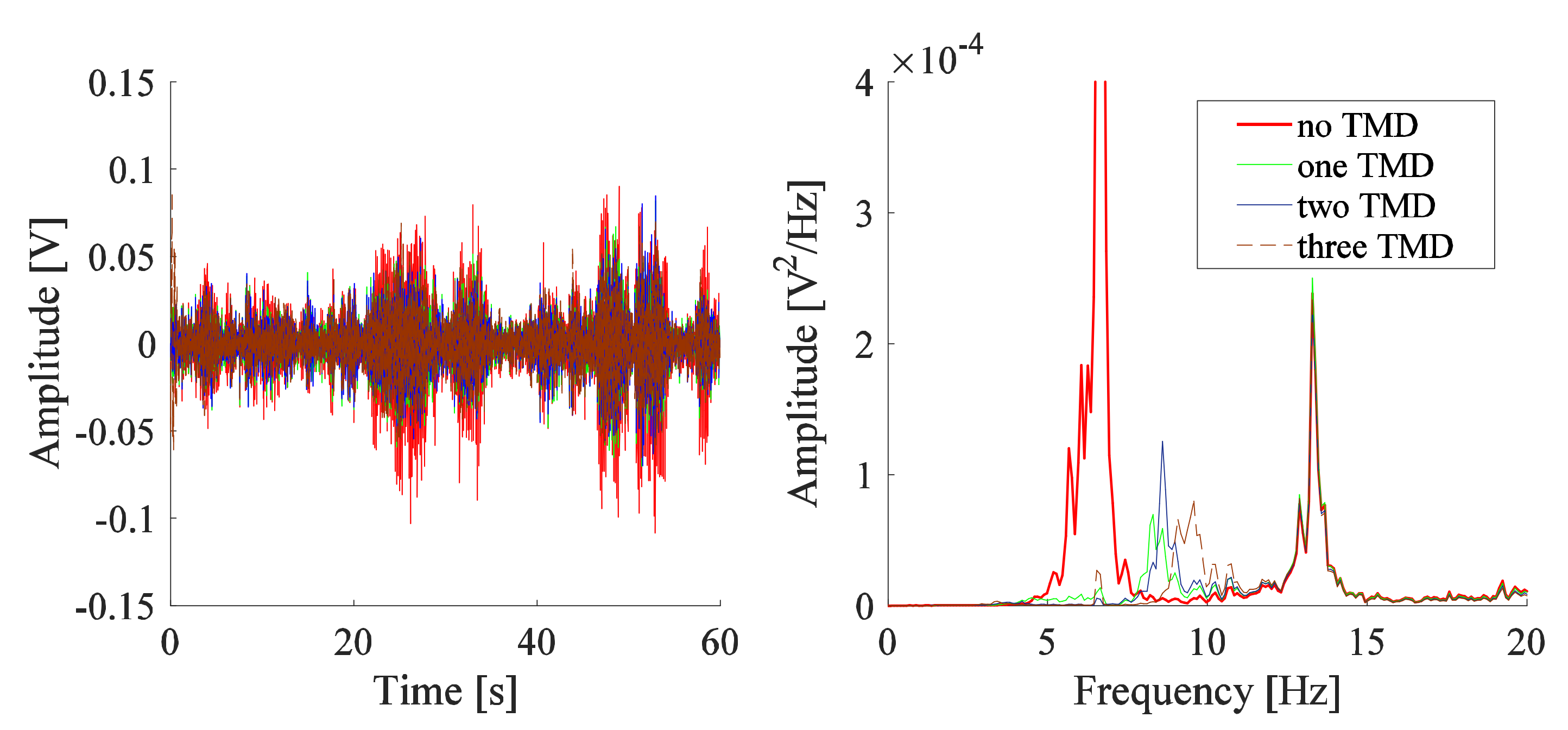
3.2. TMD Added to the System
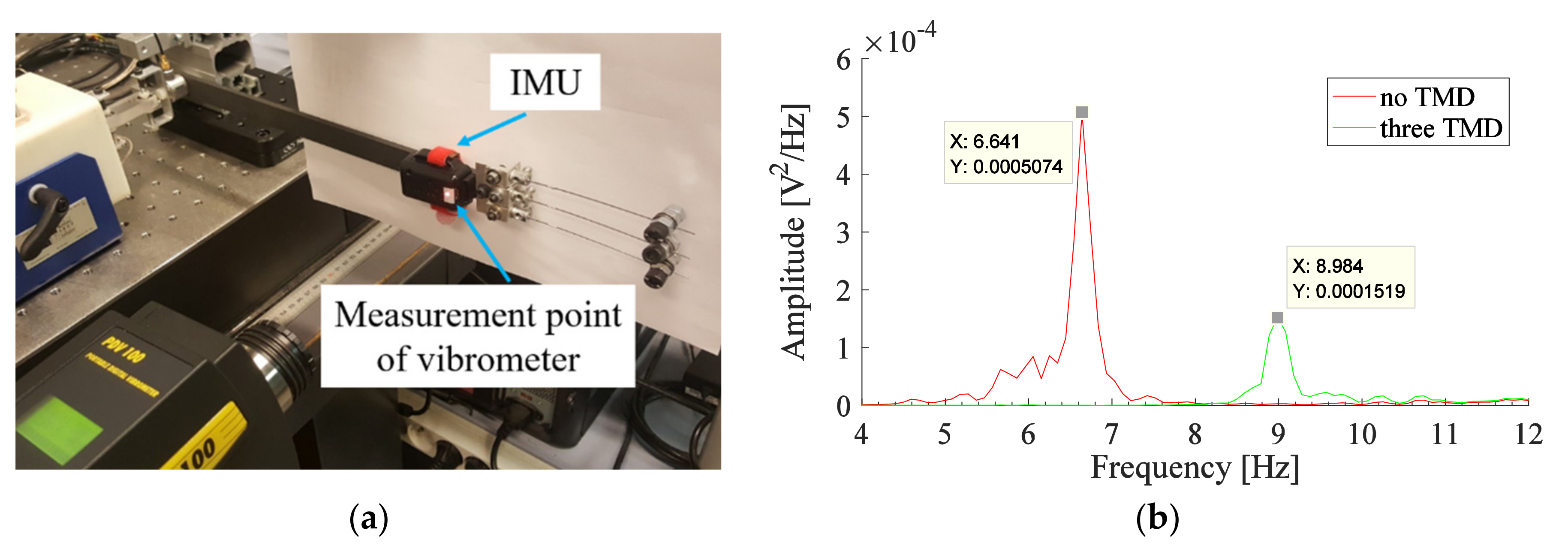
3.3. IMU Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, E.D. Clinical practice. Essential tremor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubchinsky, L.L.; Kuznetsov, A.S.; Wheelock, V.L.; Sigvardt, K.A. Tremor. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhidayasiri, R. Differential diagnosis of common tremor syndromes. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 81, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fromme, N.P.; Camenzind, M.; Riener, R.; Rossi, R.M. Need for mechanically and ergonomically enhanced tremor-suppression orthoses for the upper limb: A systematic review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castrillo-Fraile, V.; Peña, E.C.; Gabriel y Galán, J.M.T.; Delgado-López, P.D.; Collazo, C.; Cubo, E. Tremor control devices for essential tremor: A systematic literature review. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.; Kaiser, K.; White, R.D. Autotuning of A PID Controller for an Active Vibration Suppression Device for the Treatment of Essential Tremor. In Proceedings of the ASME 2006 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Dynamic Systems and Control, Parts A and B, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 November 2006; pp. 855–861. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, C.J.; Bicho, E.; Rocha, L.A.; Gago, M.F. A self-tunable dynamic vibration absorber: Parkinson’s Disease’s tremor suppression. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 3rd Portuguese Meeting in Bioengineering, Braga, Portugal, 20–23 February 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Buki, E.; Katz, R.; Zacksenhouse, M.; Schlesinger, I. Vib-bracelet: A passive absorber for attenuating forearm tremor. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudraraju, S.; Nguyen, T. Wearable Tremor Reduction Device (TRD) for Human Hands and Arms. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Phan Van, H.; Ngo, H.Q.T. Developing an Assisting Device to Reduce the Vibration on the Hands of Elders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, M.; Kmanzi, S.; Wang, H.; Mohammadi, H. Design and fabrication of a novel passive hand tremor attenuator. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2021, 1936673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, D.; Arjmand, N.; Plamondon, A.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Larivière, C. An improved multi-joint EMG-assisted optimization approach to estimate joint and muscle forces in a musculoskeletal model of the lumbar spine. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corie, T.H.; Charles, S.K. Simulated tremor propagation in the upper limb: From muscle activity to joint displacement. J. Biomech. Eng. 2019, 141, 11–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inman, D.J. Engineering Vibration, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 377–419. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, C.W.; Pullman, S.L. Tremor: Clinical phenomenology and assessment techniques. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2012, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, J.; Häussler, S.; Lauk, M.; Lücking, C.H. Pathological tremors: Deterministic chaos or nonlinear stochastic oscillators? Chaos 2000, 10, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresty, M.; Buckwell, D. Spectral analysis of tremor: Understanding the results. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1990, 53, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebai, S.; Hammoud, M.; Hallal, A.; Khachfe, H. Tremor Reduction at the Palm of a Parkinson’s Patient Using Dynamic Vibration Absorber. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B. A correction of the half-power bandwidth method for estimating damping. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2014, 85, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argoul, P.; Le, T.P. Instantaneous indicators of structural behaviour based on the continuous Cauchy wavelet analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2003, 17, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, G.; Bachmann, H. Vibration Problems in Structures, 2nd ed.; Birkhäuser Basel: Zürich, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Gebai, S. Optimization of Passive Cantilever-Type Tuned Mass Damper to Reduce the Hand Postural Tremor. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Est, Paris, France, 8 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.; Nayfeh, S.A. Optimization of the Individual Stiffness and Damping Parameters in Multiple-Tuned-Mass-Damper Systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 2005, 127, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

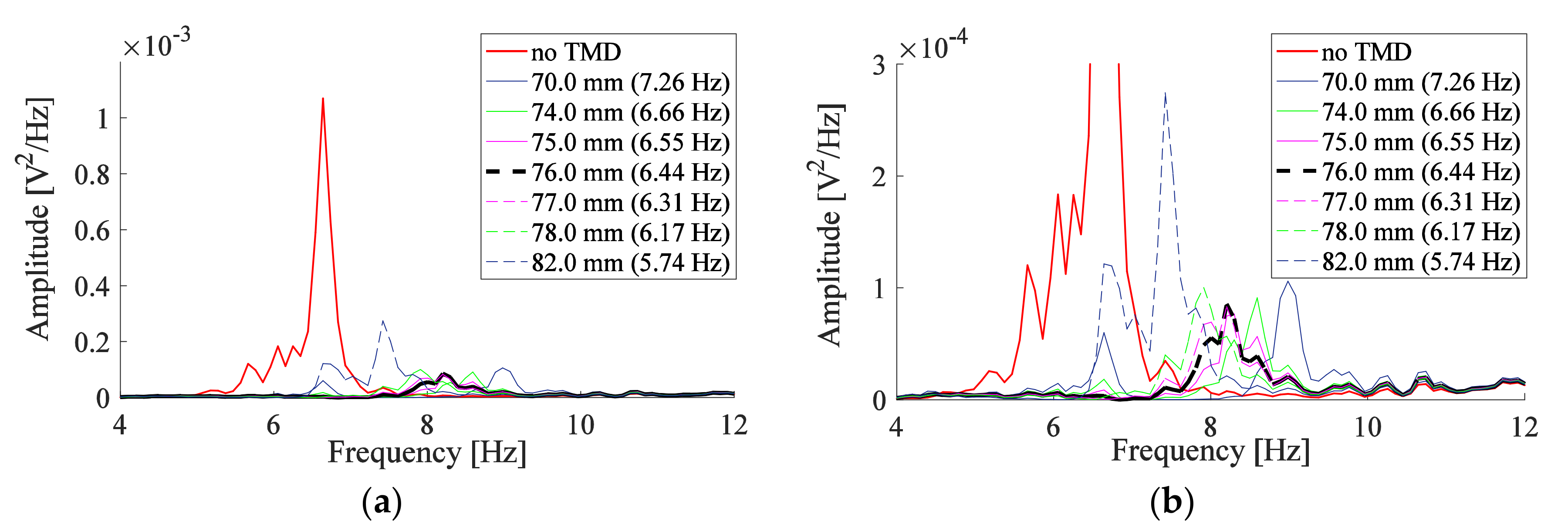

| [mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Graphically | Half-Power Bandwidth Method | Continuous Wavelet Method |
| 66.0 | 7.57 | 0.32 | 0.20 |
| 68.0 | 7.42 | 0.38 | 0.20 |
| 70.0 | 7.26 | 0.39 | 0.22 |
| 72.0 | 6.95 | 0.36 | 0.21 |
| 73.0 | 6.80 | 0.32 | 0.21 |
| 74.0 | 6.66 | 0.38 | 0.22 |
| 75.0 | 6.55 | 0.38 | 0.21 |
| 76.0 | 6.44 | 0.27 | 0.20 |
| 77.0 | 6.31 | 0.34 | 0.20 |
| 78.0 | 6.17 | 0.26 | 0.17 |
| 79.0 | 6.06 | 0.36 | 0.23 |
| 80.0 | 5.96 | 0.33 | 0.23 |
| 81.0 | 5.83 | 0.26 | 0.20 |
| 82.0 | 5.74 | 0.32 | 0.21 |
| 83.0 | 5.67 | 0.29 | 0.22 |
| 84.0 | 5.52 | 0.27 | 0.20 |
| Number of TMDs | One TMD | Two TMD | Three TMD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical study | [mm] | 74.9 | 76.8 | 75.6 | 79.1 | 77.0 | 75.9 |
| [Hz] | 6.69 | 6.23 | 6.44 | 6.15 | 6.41 | 6.55 | |
| Experimental work | Position | ‘0’ | ‘1’ | ‘2’ | ‘1’ | ‘0’ | ‘2’ |
| [mm] | 73.0 | 79.0 | 76.0 | 79.5 | 76.0 | 75.0 | |
| [Hz] | 6.68 | 6.21 | 6.41 | 6.18 | 6.41 | 6.52 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebai, S.; Hammoud, M.; Cumunel, G.; Foret, G.; Roze, E.; Hainque, E. Experimental Testing of Passive Linear TMD for Postural Tremor Attenuation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219809
Gebai S, Hammoud M, Cumunel G, Foret G, Roze E, Hainque E. Experimental Testing of Passive Linear TMD for Postural Tremor Attenuation. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):9809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219809
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebai, Sarah, Mohammad Hammoud, Gwendal Cumunel, Gilles Foret, Emmanuel Roze, and Elodie Hainque. 2021. "Experimental Testing of Passive Linear TMD for Postural Tremor Attenuation" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 9809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219809
APA StyleGebai, S., Hammoud, M., Cumunel, G., Foret, G., Roze, E., & Hainque, E. (2021). Experimental Testing of Passive Linear TMD for Postural Tremor Attenuation. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 9809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219809