Abstract
Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4-MSNs) were successfully synthesized with a relatively high surface area of 568 m2g−1. Fe3O4-MSNs were then modified with poly(2-diethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) (PDEAEMA) brushes using surface-initiated ARGET atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) (Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA). Since the charge of PDEAEMA is externally regulated by solution pH, tertiary amines in the polymer chains were quaternized using 2-iodoethanol to obtain cationic polymer chains with a permanent positive charge (Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA). The intensity of the C−O peak in the C1s X-ray photoelectron spectrum increased after reaction with 2-iodoethanol, suggesting that the quaternization process was successful. The applicability of the synthesized materials on the removal of methyl orange (MO), and sunset yellow (E110) dyes from an aqueous solution was examined. The effects of pH, contact time, and initial dyes concentrations on the removal performance were investigated by batch experiments. The results showed that the Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA sample exhibited a weak adsorption performance toward both MO and E110, compared with Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA at a pH level above 5. The maximum adsorption capacities of MO and E110 using Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA were 294 mg g−1 and 194.8 mg g−1, respectively.
1. Introduction
According to recent United Nations projections, the world’s population will increase by more than a third by 2050. Currently, many countries worldwide suffer from a shortage of water, and therefore, achieving sustainable water management is a major challenge for such countries. Sustainable water management contains industrial wastewater treatment [1,2]. In recent decades, industrial wastewater treatment has become increasingly complex. Increased population growth has led to an increase in industrialization and, consequently, an increase in the release of pollutants into wastewater, which threatens health and the environment [3,4,5,6,7].
Among these pollutants are dyes that are widely used in the most common industries, such as textiles, paper, and plastics [8,9,10,11]. Dyes are considered as one of the major pollutants because of their complex molecular structure, stability, and effect on plant photosynthesis, as well as having low biodegradability, high toxicity, and cancerous properties [12,13,14]. Most dyes can be positively or/and negatively charged and could change regarding the pH. Moreover, they can also combine with metal ions in wastewater to form complex pollutants. Several methods are used to remove these complex structures such as precipitation [15], membrane filtration [16,17], photocatalytic reduction [18], electrocoagulation [19], biological treatment [20], electrochemical removal [21], and adsorption [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. In the past few decades, great attention has been paid to the adsorption process due to its ease of application on a large scale and its efficiency [29,30,31,32,33,34].
Recently, several conventional adsorbents (e.g., activated carbons [35], ordered mesoporous carbons [36], metal–organic frameworks [37], carbon nanotubes [38], graphene-based nanocomposites [39], activated carbons [40] and natural clay [41] have been used for the removal of dyes from contaminated water solutions. However, most of these solid adsorbents are not widely practiced due to poor selectivity, high cost, difficult disposal, and complex preparation processes. Therefore, it is of great importance to find an adsorbent that is highly efficient, economic, and selective toward organic dyes.
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are one of the most widely used adsorbent materials in water purification due to their non-toxicity, high adsorption capacity, tunable pore structures, pore size, shorter equilibrium time, and abundant surface functional groups [42,43]. To increase the adsorption efficiency of the porous silica particles, their surfaces have been modified with different functional groups such as amine, carboxyl, thiol, and epoxy [44,45,46]. The contaminants are often removed through electrostatic interactions between the target analytes and the functional groups present on the surface of the nanoparticles.
To bind these functional groups on the surface of the silica, the self-assembly technique has been widely applied [47,48]. The density of these functional groups on the surface is the crucial factor to increase the efficiency of adsorption. Furthermore, in order to improve the active sites available on the surface of the nanoparticles, surface modification with polymer brushes has been proposed [49]. Polymer brushes (surface-confined macromolecular architectures) are being increasingly used for a variety of applications and consist of a linear backbone densely grafted with polymeric side chains [50]. The confined and compact structure of the polymer brushes can provide the nanoparticle surface with remarkable properties such as stimuli responsiveness, in which the polymer can change its conformation structure by changing the surrounding environment, such as pH and temperature [51,52,53]. A variety of polymer brushes were applied to the surface of silica nanoparticles such as poly(2-(tert-butylamino) ethyl methacrylate) and poly(2-diethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) to study their responsive behaviors [54,55]. The results show that in the acidic medium, the polymer chains expand, while in the basic medium, the polymer chain collapse.
The novelty of this work is to synthesize new materials using the quaternization process for potential applications. To the best of our knowledge, there is very little work in the literature on the use of pH-responsive polymer brushes in water remediation. In this paper, we developed effective materials based on silica nanoparticles and pH-sensitive poly(2-diethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) brush for removing dyes from water. The objectives are divided into two parts. First, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) were prepared, then their surface was grafted with pH-sensitive poly(2-diethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) brush. Next, the tertiary amines were quaternized with 2-iodoethanol to eliminate the influence of pH on the adsorption performance of the material. The prepared materials were characterized by several techniques, including FTIR, XPS, SEM, and TEM. Finally, the performance of the prepared materials in removing methyl orange (MO) and sunset yellow (E110) dyes from an aqueous solution was investigated. A variety of sorption isotherms, including Langmuir and Freundlich models, as well as kinetic models, were applied to the experimental data to predict the adsorption capabilities of the synthesized adsorbents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Ethanol (99.8%, HPLC grade), methanol (99.8%, HPLC grade), isopropanol (99.8%), dichloromethane (DCM, HPLC grade), pyridine (analytical grade), n-hexane (HPLC grade), toluene (HPLC grade), 2-iodoethanol (99%), dimethylformamide (DMF, 99.9%), ammonium hydroxide (28 wt %), tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, 98%), 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES, >98%), 2-bromo-2-methylpropionyl bromide (BIBB, 98%), (2-(diethylamino) ethylmethacrylate) (PDEAEMA, 99%), N-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 98%), 2,2′-bipyridyl (bipy, 99%) ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3, >99%), sunset yellow (E110, 90%), and methyl orange (MO, 85%) were bought from Sigma-Aldrich. Copper (II) bromide (CuBr2, 98%) was bought from BDH chemicals. Iron (II) chloride (99%) and iron (III) chloride (99%) were bought from Loba Chemie. Sodium chloride and hydrochloric acid were obtained Alfa Aesar. Deionized water (DI-water) was taken from Elga Pure Nanopore System (18 Ω).
2.2. Methods of Nanoparticles Preparation
2.2.1. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4)
Iron (II) chloride (3.12 g) and iron (III) chloride (4.80 g) were dissolved in DI-water (30 mL) and stirred at 90 °C under N2 gas. Then, ammonium hydroxide (20 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and kept under stirring for 150 min. Finally, the solid was separated and washed with water and ethanol.
2.2.2. Iron Oxide Covered with Mesoporous Silica (Fe3O4@MSNs)
Iron oxide coated with mesoporous silica (Fe3O4@ MSNs) was synthesized according to previously reported studies by Beagan et al. [56]. To this end, 0.5 g of Fe3O4 was suspended in 150 mL of DI-water, followed by the addition of CTAB (1.0 g) at 38 °C. Then, ammonium hydroxide (7 mL) was added to the reaction mixture. A solution containing 5 mL of TEOS and 20 mL of n-hexane was slowly added to the reaction mixture with stirring. After 15 h, the solid was separated and washed with DI-water and ethanol.
2.2.3. Amino Functionalized Iron Oxide Coated with Mesoporous Silica (Fe3O4@MSN-NH2)
Fe3O4@MSN-NH2 nanoparticles were obtained by suspending 1.5 g Fe3O4@MSN nanoparticles in a solution containing 0.5 mL APTES and 60 mL methanol. The mixture was refluxed for 15 h. The solid was separated and washed with DI-water and ethanol.
2.2.4. ATRP Initiator Functionalized Iron Oxide Coated with Mesoporous Silica (Fe3O4@MSN-Br)
Fe3O4@MSN-Br nanoparticles were obtained by dispersing 1.0 g of Fe3O4@MSN-NH2 in a solution of 25 mL of DCM and 1.5 mL of triethylamine. To the mixture, 1.2 mL of 2-bromo-2-methylprpionyl bromide was slowly added and stirred for 48 h at room temperature. The solid was separated and washed with DCM and ethanol.
To extract CTAB, Fe3O4@MSN-Br nanoparticles were dispersed in a solution of ammonium nitrate in ethanol (10 mg/mL) and refluxed overnight with stirring. The solid was separated and washed with ethanol.
2.2.5. Poly(2-dimethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) Brushes Grafted on Iron Oxide Coated with Mesoporous Silica (Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA)
In a 25 mL round bottom flask, 0.4 g of Fe3O4@ MSN-Br was dispersed in a solution containing 4 mL of ethanol and 1 mL of DI-water and degassed for 15 min. A solution containing 2-dimethyl aminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) (2 mL), 2,2 bipy (0.0067 g), CuBr2 (0.0009 g), ethanol (8 mL), and water (2 mL) were transferred into the reaction mixture and degassed for 15 min. To the polymerization mixture, 0.0076 g of ascorbic acid was added and stirred for 5 h. The solid was separated and washed with 10 mM of HCl solution and ethanol.
2.2.6. Quaternization of PDMAEMA Grafted on Fe3O4@MSNs (Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA)
Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA (0.5 g) was dispersed in 40 mL of DMF. Then, 0.5 g of 2-iodoethanol was added to the solution under stirring and heated at 120 °C overnight. The solid was separated and washed with DMF and ethanol.
2.3. Measurement and Characterization
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images were acquired using the JEOL instrument, model JSM-7610F at 15Kv. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were acquired using the JEOL instrument, model JEM-1400 at 100 Kv. PerkinElmer Spectrum BX instrument was used to obtain infrared spectra in the region of 400–4400 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra were obtained using the JEOL instrument, model JPS-9030. The UV spectrum was obtained using SpectraMax 384 Plus UV/Vis spectrophotometer with a microplate reader. The surface zeta potential of the polymer-modified MSNs was measured using Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern. The specific surface area, pore size distribution, and pore volume of the synthesized materials were characterized using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) (Gemini VII, 2390 Surface Area, and Porosity USA). Prior to analysis, samples were degassed at 150 °C under nitrogen flow for 2 h to remove moisture and gasses. The crystalline phase of the fabricated magnetite nanoparticles was determined using powder X-ray diffraction technique, with Mini Flex II X-ray diffractometer equipped with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5405 Å) at 5°/min.
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
The adsorption behavior of the anionic dyes (MO and FCF) on the surface of Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA and Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA was explored as a function of changing the initial concentrations, exposure time, and the solution’s pHs. Generally, 10 mg of the sorbent was suspended in 15 mL of a solution containing a specific amount of the selected dye at 25 °C and a shaking rate of 150 rpm. The sorbent material was separated by centrifuge at a specific time. The amount of the chosen dye adsorbed on the surface was estimated using UV/Vis spectrophotometer. The adsorption capacity (qe) at equilibrium (mg·g−1) was calculated using Equation (1).
where C0 is the dyes’ initial concentration (mg·L−1), and Ce is the concentration of dyes at equilibrium (mg·L−1). V and m are the volume (L) and the mass of adsorbents (g), respectively.
2.4.1. Adsorption Isotherms
The adsorption data of the selected dyes on the sorbents were fitted using different isotherm models. Equation (2) presents a linear form of the Langmuir isotherm model.
where qm represents the maximum capacity (mg/g) of the anionic dyes adsorbed on the sorbents. kl is the Langmuir constant (L·mg−1).
Equation (3) presents a linear form of the Freundlich isotherm model.
where 1/n is the measure of intensity, and KF is the Freundlich constant ((mg/g)/(mg/L)1/n).
2.4.2. Adsorption Kinetics
The adsorption data of the selected dyes on the sorbents were assessed using pseudo-first- and second-order equations. Equation (4) presents the pseudo-first-order equation.
where qt is the adsorption capacity at time t (mg·g−1), and K1 is the rate coefficient of pseudo-first-order adsorption (L·min−1).
Equation (5) presents the pseudo-second-order equation.
where K2 is the rate constant of adsorption in the pseudo-second-order model (g/mg·min).
3. Results
3.1. Characterization
The co-precipitation protocol was used to synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) by mixing two types of iron salts. As shown in Figure 1A, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are nearly spherical with an average particle size of ca. 21 nm. However, Fe3O4 nanoparticles have shown agglomeration as a result of their paramagnetic property. After coating Fe3O4 nanoparticles with mesoporous silica shell using TEOS as silica source and CTAB as directing agent in a basic solution, there was an increase in the particle size from 21 nm to ca. 230 nm, with the shape of semi-sphere-like nanoparticle, as shown in Figure 1B. The presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the core of mesoporous nanomaterials is clearly seen in the TEM image (Figure 1C), indicating successful coating. The average core size was estimated to be 19 nm, which is in agreement with the SEM image of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Figure 1D,E show SEM and TEM images of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles after polymerization. There is a noticeable increase in the average diameter of Fe3O4@MSN-PDEAEMA, with ca. 20 nm, compared with none coated nanoparticles. The PDEAEMA brushes showed as a layer surrounding the modified Fe3O4@MSNs.
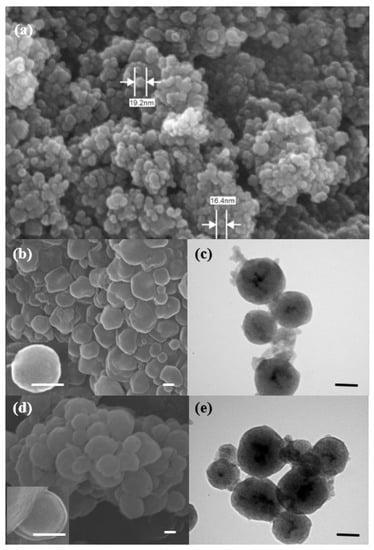
Figure 1.
Microscopic images of the synthesized nanoparticles: (a) SEM image of Fe3O4 nanoparticles; (b) SEM image of Fe3O4@MSNs; (c) TEM images of Fe3O4@MSNs; (d) SEM image of Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA; (e) TEM images of Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA.
The XRD patterns of both magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4-NPs) and magnetite-modified silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4@MSNs) are demonstrated in Figure 2. The characteristic peaks in the spectrum of Fe2O3-NPs agreed well with the standard cubic phase of magnetite Fe3O4. The observed peaks at 2θ values of 30.2°, 35.6°, 43.2°,53.9, 57.3° and 62.9°, assigned to the lattice planes (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) (JCPDS 88-0866), respectively. These peaks also appeared in the Fe3O4@MSNs sample except the peaks at 2θ values of 30.2°and 53.9°, which might be attributed to the presence of an amorphous silica shell. The sharpness and the intensity of most Fe3O4 peaks indicate that the crystalline nature of Fe3O4 was not affected by a mesoporous silica shell.
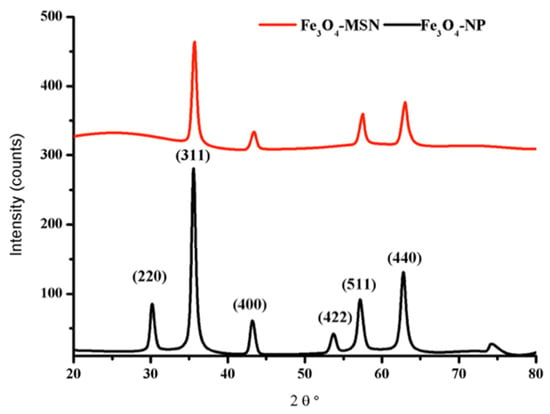
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and Fe3O4 modified by silica shell.
The nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms of Fe3O4-NPs and Fe3O4@MSNs are shown in Figure 3, and the related parameter results are listed in Table 1. It was observed that Fe3O4-NPs and Fe3O4@MSNs exhibited type-IV isotherm, which reveals the material’s mesoporous characteristics. However, a variation in the hysteresis Loops was observed for both materials, as Fe3O4@MSNs showed a typical H1 hysteresis loop, indicating the presence of a narrow range of uniform mesopores where networking effects are minimal, whereas H3 hysteresis loop was obtained for Fe3O4-NPs indicates the existence of complex pore structure and networking effects are significant. A specific surface area of 568.3 m²/g and 61.8 m²/g were obtained for Fe3O4@MSNs and Fe3O4-NPs, respectively. Fe3O4@MSNs had well-defined narrow pores size ca.5 nm, whereas Fe3O4-NPs had a broader pore size distribution of ca 20–50 nm, which could be related to the agglomeration of the magnetite NPs.
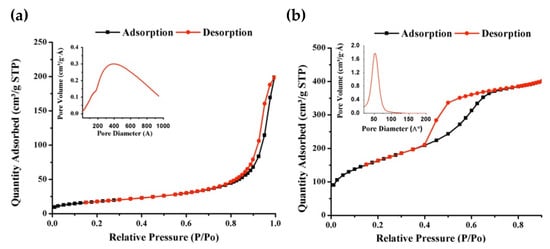
Figure 3.
N2 adsorption–desorption BET isotherm for (a) Fe3O4-NP and (b) Fe3O4@MSNs. The insets show the BJH pore size distribution.

Table 1.
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface analysis of Fe3O4-NP and Fe3O4-MSN.
Figure 4 illustrates the FTIR spectra of as made Fe3O4@MSNs, Fe3O4@MSNs (without CTAB), Fe3O4@MSN-Br, and Fe3O4@MSN-PDEAEMA. The absorption peaks of Si-O-Si bonds were observed at ~1090 and ~1240 cm−1 for all samples. The stretching absorption vibration of Si-OH was allocated at ~3460 and ~970 cm−1. The absorption peaks of C–H stretching bands were assigned at ~2940 cm−1 and ~2840 cm−1 for as made Fe3O4@MSNs, where were disappeared after the CTAB extraction process. Compared with Fe3O4@MSN-Br, a new peak was observed at ~1730 cm−1 after the polymerization process, referred to as C = O groups.
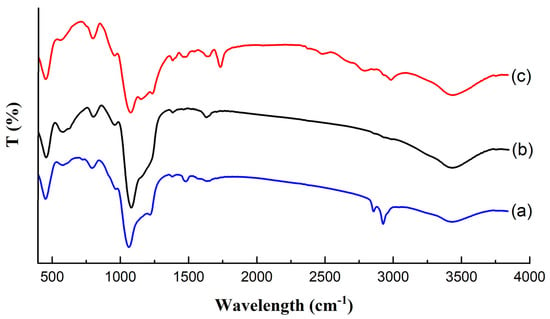
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectra: (a) as-made Fe3O4@MSN; (b) Fe3O4@MSN-Br (without CTAB); (c) Fe3O4@MSN-PDEAEMA.
The successful decoration of Fe3O4@MSNs with polymer layers was evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), as shown in Figure 5. The C1s spectrum of non-modified PDEAEMA brush on the surface of Fe3O4@MSNs was fitted with four peaks, at 285 eV, 285.9 eV, 286.8 eV, and 288.3 eV with peak-area ratios of 4.5:3.8:1:1, related to the C–H, C–N, C–O, and O = C–O, respectively. This is in good agreement with the theoretical value of 5:3:1:1 (Figure 5a). After quaternization, the tertiary amino groups in the polymer chains, the C1s spectrum was fitted with three peaks, at 285 eV, 286.3 eV, and 288.9 eV, related to the C–H, C–N/C–O, and O = C–O, respectively (Figure 5b). As expected, there was an increase in peak intensity ~286.3 eV, due to the increase in the amount of C–O bonds present in the organic layer. This observation confirmed the successful attachment of iodoethanol molecules.
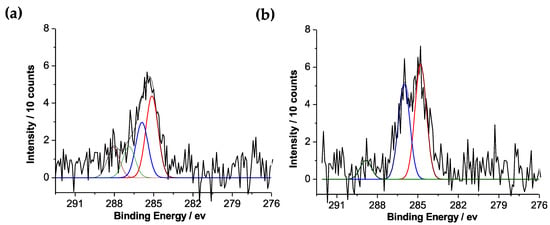
Figure 5.
C1s XPS spectra: (a) Fe3O4@MSN-PDEAEMA; (b) Fe3O4@MSN-QPDEAEMA.
The surface charges of Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA and Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA were also investigated using a zeta potential analyzer, and the results are shown in Figure 6. Both materials had similar zeta potential at pH below 7. However, above pH 7 the Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA potential remained almost constant, whereas a significant drop in the potential of Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA material was observed.
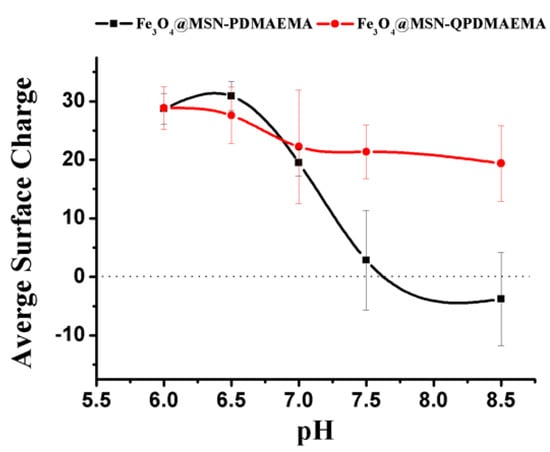
Figure 6.
Zeta potential values for Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA and Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA at different pH levels.
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Effect of pH on Adsorption
The influence of pH on the removal of two sulfonic acid-based dyes, MO and E110 by Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA and Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA were examined, (Figure 7). Each sample (10 mg) was mixed with 200 mg/cm−3 of the targeted analytes at pH ranging from 4 to 9. Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA sample exhibited a weak adsorption performance toward MO with 40% extraction efficiency at pH < 6, whereas 100% extraction efficiency was achieved using Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA. The observed behavior can be explained by knowing the actual pKa value of PDMAEMA (pKa = 6.8). As the pH increased above pKa, the polymer brush became deprotonated and collapsed. When the pH was below the pKa, the polymer was positively charged and swollen due to the protonation of the tertiary amine groups. However, previous investigations confirmed that the pKa value of PDMAEMA can be shifted to below 5 depending upon the polymer’s grafting density and thickness [57,58,59]. Therefore, it is possible that the grafting density of the sample was high, causing a significant pKa shift, especially when silane as initiator was used. Hence, it should not be surprising that Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA was less efficient in removing the negatively charged dyes, due to the deprotonation of polymer chains. E110 dye exhibited a better adsorption performance which might be attributed to the presence of two sulfonic acid moieties compared with the one in MO.
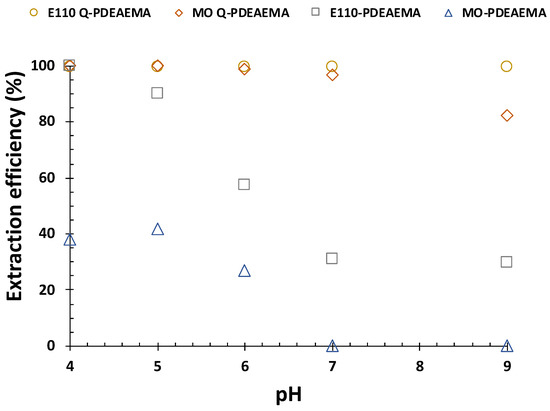
Figure 7.
Effect of pH on the adsorption of methyl orange and sunset dye by Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA and Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA at equilibrium.
3.2.2. Equilibrium Isotherms
Detailed knowledge of the equilibrium adsorption isotherm is essential in examining the interactive behavior between the adsorbent and the adsorbate in any adsorption system. Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models were employed, as shown in Figure 8. In order to study the isotherms, the concentration of the analytes was adjusted in the range of 50–250 mgL−1 and 300–1000 mgL−1 for MO and E110, respectively. The experimental parameters were performed using the optimum conditions. Langmuir isotherm assumes that a homogeneous interaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbate at the material’s adsorption sites with the formation of a monolayer of the adsorbate on the material’s surface [60]. In contrast, the Freundlich isotherm model assumes the possibility of the existence of the multilayer sorption mechanism at the surface of absorbents with a heterogeneous energy distribution of active sites. The correlation coefficient (R2) is the criterion used to assess how well the data are fit with each model. The model with a higher R2 value will be utilized to describe the adsorption mechanism. The equilibrium data of the adsorption of MO (Figure 8b) fitted well with the Langmuir model with R2 of more than 0.99, indicating the formation of a monolayer of MO molecules on the surface of the adsorbent (homogeneous interaction) with a maximum adsorption capacity of 294 mg g−1. On the other hand, the equilibrium data of the E110 adsorption fitted well with the Freundlich isotherm model, indicating the formation of multilayers of E110 molecules on the surface of the adsorbent (heterogeneous interaction) with a maximum adsorption capacity of 194.8 mg g−1. The difference between the two dyes in terms of the interaction can be attributed to the presence of two sulfonic moieties in both sides of E110 molecules, making them more electronegative compared with MO molecules, and consequently, more attraction with the positively charged adsorbent surface.
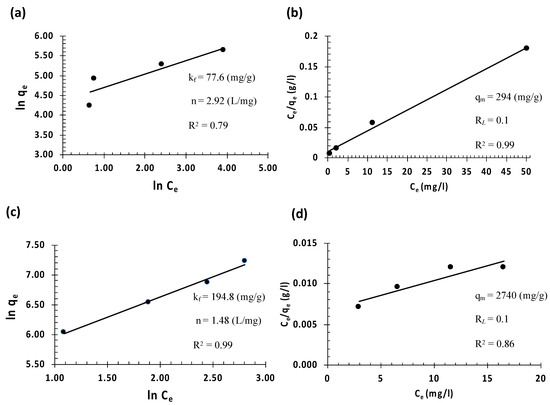
Figure 8.
Dyes adsorption at 25 oC by the synthesized Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA at equilibrium with different initial analytes concentrations: (a,b) Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms of MO uptake, respectively; (c,d) Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms of E110 uptake, respectively.
The extraction of methyl orange and sunset yellow dyes using a variety of adsorbents has been extensively studied. Table 2 demonstrates a comparative study of the maximum adsorption capacities of some adsorbents for MO and E110 along with the current work. It is obvious that the adsorption capacities of our novel material are higher than other competitive adsorbents, indicating that Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA can be considered a promising adsorbent for the removal of both dyes from aqueous solutions.

Table 2.
A list of maximum adsorption capacities for different types of adsorbents.
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorption Time and Adsorption Kinetics
A kinetic study of the removal of studied analytes is crucial to understand and describe the kinetic mechanism of Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA. Each dye (14 mL) was placed in a 15 mL centrifuge tube of fixed initial concentrations, followed by the addition of 10 mg of Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA, and the mixture was shaken at 25 °C for different time intervals. The data were then fitted with pseudo-first-order [65,66,67] and pseudo-second-order kinetic models [68] (Figure 9a–d). Along with these two models, the intraparticle diffusion model was also studied to investigate the process of the sequestration of analytes from aqueous solution onto SNPs, (Figure 9e,f). It can be shown that the uptake data of both dyes by the adsorbent fitted well with the pseudo-second-order model, indicating an inclination toward chemisorption. This implies that the rate of the analyte’s uptake depends upon the adsorption capacity and not the concentration of adsorbate [69].
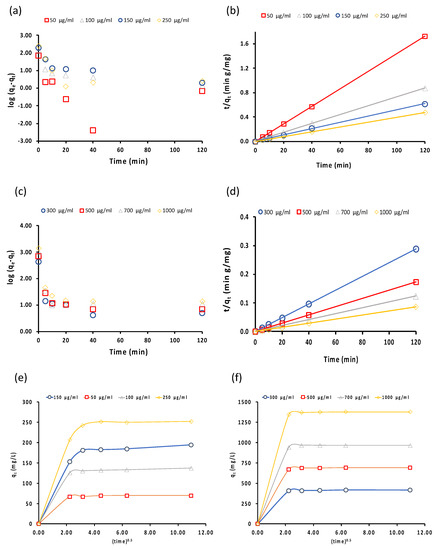
Figure 9.
(a,b) Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models of MO uptake by Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA, respectively; (c,d) pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order of E110 uptake by Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA, respectively; (e,f) intraparticle diffusion model of MO and E110 dyes uptake by Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA, respectively.
The results obtained by the intraparticle diffusion model showed that rapid removal of the MO dye at the initial stage was caused by the presence of a considerable number of free active sites on the surface of Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA that analyte molecules could bind to (boundary layer diffusion effects). A reduction in the removal rate at the second stage was observed due to a significant drop in the number of the available active sites on the sorbent’s surface. This resulted in the diffusion of the MO molecule through the pores (pore diffusion). In the case of E110 dye, a different behavior was observed, as the dye was adsorbed by the sorbent in one kinetic stage, which could be attributed to the multilayer adsorption of E110 dye on the adsorbent surface. The values of the intraparticle diffusion rate constants Kid of both dyes are summarized in Table 3. Higher Kid value indicates higher intraparticle mass transfer, which means that the kinetics of E110 uptake by Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA may be controlled by film diffusion mechanism, whereas pore diffusion was more active in the adsorption of MO.

Table 3.
Intraparticle diffusion model parameters for the removal of MO and E110 from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we reported the synthesis of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles, followed by the modification with 2-diethyl aminoethyl methacrylate (DEAEMA) using surface-initiated ARGET atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). Furthermore, the polymer chains were quaternized using 2-iodoethanol to obtain a cationic polymer that would not be affected by the solution’s pH. The synthesized materials were characterized using a variety of advanced techniques. The characterization results showed that Fe3O4 nanoparticles were spherical in shape with particles sized ca. 29 nm. When the Fe3O4 were coated with a mesoporous silica shell, the particle size was increased to 230 nm, confirming the successful loading of the silica shell. Finally, the materials were evaluated for the removal of methyl orange (MO) and sunset yellow (E110) dyes from an aqueous solution. The results showed that the Fe3O4@MSN-PDMAEMA sample exhibited a weak adsorption performance toward both MO and E110, compared with Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA. The maximum adsorption capacities of MO and E110 using Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA were 294 mg g−1 and 194.8 mg g−1, respectively. Thus, the high sorption ability, ease of applicability, abundance of the raw materials, and low price make Fe3O4@MSN-QPDMAEMA a promising adsorbent for the removal of both dyes from aqueous solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.A., H.M.A.-S., A.A.; methodology, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; software, S.A.B.; validation, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; formal analysis, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; investigation, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; data curation, K.M.A. and A.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; writing—review and editing, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; visualization, H.M.A.-S.; supervision, K.M.A. and A.M.A.; project administration, K.M.A., A.M.B. and A.M.A.; funding acquisition, A.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through Research Group No. RG-1441-304.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chowdhury, S.; Pan, S.; Balasubramanian, R.; Das, P. Date palm based activated carbon for the efficient removal of organic dyes from aqueous environment. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2019, 34, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudian, N.; Rajabi, M.; Ghaedi, M. Titanium oxide nanoparticles loaded onto activated carbon prepared from bio-waste watermelon rind for the efficient ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of congo red and phenol red dyes from wastewaters. Polyhedron 2019, 173, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Water Assessment Programme (United Nations); UN-Water. Water in a Changing World; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Shabbir, M.; Rebah, F.B. Application of functionalized nanomaterials as effective adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2020, 17, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Ghernaout, D.; Lajimi, R.H.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Rebah, F.B. Multifunctional crosslinked chitosan/nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot for wastewater treatment. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Katubi, K.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Tahoon, M.A.; Ben Rebah, F. Clay-polymer nanocomposites: Preparations and utilization for pollutants removal. Materials 2021, 14, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Rehan, M. Textile dyeing industry: Environmental impacts and remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 3803–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Aghdasinia, H.; Mohammadi, R.; Ramavandi, B. Modification of bio-hydroxyapatite gen-erated from waste poultry bone with MgO for purifying methyl violet-laden liquids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44218–44229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei-Fakhri, S.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Foroutan, R.; Arsalani, N.; Ramavandi, B. Crystal violet dye sorption over acryla-mide/graphene oxide bonded sodium alginate nanocomposite hydrogel. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esvandi, Z.; Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Akbari, A.; Ramavandi, B. Uptake of anionic and cationic dyes from water using natural clay and clay/starch/MnFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, G.; Huan, Y.; Hao, C.; Chen, W. Acrylic acid functionalized graphene oxide: High-efficient removal of cationic dyes from wastewater and exploration on adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.-L. High efficient dye removal with hydrolyzed ethanolamine-Polyacrylonitrile UF membrane: Rejection of anionic dye and selective adsorption of cationic dye. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Lei, L. Biodegradation of reactive blue 13 in a two-stage anaerobic/aerobic fluidized beds system with a Pseudomonas sp. isolate. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ng, D.H.; Liu, S. Recovery of nickel ions from wastewater by precipitation approach using silica xerogel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiong, J.; Tian, C.; Gao, B.; Wang, L.; Jia, X. The degradation of methyl orange and membrane fouling behavior in anaerobic baffled membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Lindström, T.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose-enabled membranes for water purification: Perspectives. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 1900114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Li, Q.-H.; Hou, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.-S.; Feng, P.; Bu, X. In situ synthesis of n–n Bi2MoO6 & Bi2S3 heterojunctions for highly efficient photocatalytic removal of Cr(vi). J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22580–22589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Troyer, L.D.; Catalano, J.G.; Giammar, D.E. Dynamics of chromium (VI) removal from drinking water by iron electro-coagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13502–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, W.-M.; Li, J.-L.; Day, G.S.; Drake, H.; Joseph, E.; Zhou, H.-C. Biological antagonism inspired detoxification: Removal of toxic elements by porous polymer networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14383–14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Jia, M.; Yang, Q.; Luo, K.; Chen, F.; Zhong, Y.; He, L.; Pi, Z.; Hou, K.; Wang, D.; et al. Electrochemical Cr(VI) removal from aqueous media using titanium as anode: Simultaneous indirect electrochemical reduction of Cr(VI) and in-situ precipitation of Cr(III). Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by chemically modified orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katubi, K.; Alsaiari, N.; Alzahrani, F.; Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A. Synthesis of manganese ferrite/graphene oxide magnetic nanocomposite for pollutants removal from water. Processes 2021, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, F.M.; Alzahrani, N.S.; Alsaiari, K.M.; Katubi, F.B.; Rebah, M.A. Tahoon, magnetic metal organic framework immobi-lized laccase for wastewater decolorization. Processes 2021, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Geng, L.-H.; Amiralian, N.; Martin, D.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose from Spinifex as an effective adsorbent to remove cadmium (II) from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Antoine, R.; Hsiao, B.S. Efficient removal of arsenic using zinc oxide nanocrystal-decorated regenerated microfibrillated cellulose scaffolds. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6140–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filice, S.; Bongiorno, C.; Libertino, S.; Compagnini, G.; Gradon, L.; Iannazzo, D.; La Magna, A.; Scalese, S. Structural characterization and adsorption properties of dunino raw halloysite mineral for dye removal from water. Materials 2021, 14, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filice, S.; Mazurkiewicz-Pawlicka, M.; Malolepszy, A.; Stobinski, L.; Kwiatkowski, R.; Boczkowska, A. Sulfonated pen-tablock copolymer membranes and graphene oxide addition for efficient removal of metal ions from water. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpiano, G.R.; Tocco, D.; Medda, L.; Magner, E.; Salis, A. Adsorption of malachite green and alizarin red s dyes using Fe-BTC metal organic framework as adsorbent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihlenburg, R.B.J.; Lehnen, A.-C.; Koetz, J.; Taubert, A. Sulfobetaine Cryogels for preferential adsorption of methyl orange from mixed dye solutions. Polymers 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, P.; Chiodo, A.; Macario, A.; Siciliano, C.; Nagy, B.J. Semi-continuous adsorption processes with multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the treatment of water contaminated by an organic textile dye. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Huang, W.; Niu, Y. In situ formation of 4-cyanopyridinecarboxylic acid and its polyacid doping coor-dination polymer for adsorption of organic dyes in wastewater. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 118, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, P.R.; Yeh, H.; Johnson, K.; Hsiao, B.S. Arsenic (III) removal by nanostructured dialdehyde cellulose–Cysteine microscale and nanoscale fibers. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22008–22020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, C.; Sharma, P.R.; He, H.; Sharma, S.K.; McCauley-Pearl, A.; Wang, R.; Hsiao, B.S. Rice husk based nanocellulose scaffolds for highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions from contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 3080–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, P.; Guo, J.; Barford, J.; McKay, G. Multilayer dye adsorption in activated carbons—Facile approach to exploit vacant sites and interlayer charge interaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5041–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, R.A.; Yasir, A.; Yijun, Z.; Mehdi, K.; Moses, O.T.; Shaobin, W.; Zongping, S. An adsorption–Catalysis pathway toward sustainable application of mesoporous carbon nanospheres for efficient environ-mental remediation. ACS ES T Water 2021, 1, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, X.; Song, S.; Gao, Z. Ultra-high-capacity adsorption of Rhodamine B in a carboxyl-functionalized metal–organic framework via surface adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualnaja, K.; Alprol, A.; Ashour, M.; Mansour, A. Influencing multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the removal of Ismate Violet 2R dye from wastewater: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthi, G.; Satyam, P.S.; Sushmee, B. Reusable, few-layered-MoS 2 nanosheets/graphene hybrid on cellulose paper for superior adsorption of methylene blue dye. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5489–5500. [Google Scholar]
- Maguana El, Y.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; Chikri, R. Activated carbon for dyes removal: Modeling and understanding the adsorption process. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2096834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alorabi, A.Q.; Hassan, M.S.; Alam, M.M.; Zabin, S.A.; Alsenani, N.I.; Baghdadi, N.E. Natural clay as a low-cost ad-sorbent for crystal violet dye removal and antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.J.; Song, J.; Ahmed, K.; Rahim, A.; Volpe, P.L.O.; Rehman, F. Mesoporous silica MCM-41, SBA-15 and derived bridged polysilsesquioxane SBA-PMDA for the selective removal of textile reactive dyes from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 111957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghanizad, A.; Abdolmaleki, M.K.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Dinari, M. One-pot synthesis of functionalized mesoporous fibrous silica nanospheres for dye adsorption: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswieleh, A.M. Remediation of cationic and anionic dyes from water by histidine modified mesoporous silica. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beagan, A.M. Cholesterol-functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles for removal of naphthalene from water. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-G.; Ma, Q.; Du, X.-Z.; Deng, H.-L.; Gao, J.-Z. Inorganic/organic mesoporous silica as a novel fiber coating of solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 2004, 62, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiei, A.; Mirahsani, A.; Shahbazi, A.; Younesi, H.; Alizadeh, M. Adsorptive removal of toxic dye from aqueous solution and real industrial effluent by tris(2-aminoethyl)amine functionalized nanoporous silica. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Shen, H.-Y.; Pan, S.-D.; Hu, M.-Q.; Xia, Q.-H. Preparation and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer adsorbents for removal of chromium (VI) ions. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5291–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, A.; Tirrell, M.; Lodge, T. Tethered chains in polymer microstructures. Macromol. Synth. Order Adv. Prop. 1992, 100, 31–71. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, S.T. Polymer brushes. Science 1991, 251, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, N. Polymer brushes: Applications in biomaterials and nanotechnology. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, X. Polymer brushes: Efficient synthesis and applications. ACC Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzatti, G.; Cavalie, S.; Combes, C.; Torrisani, J.; Carrere, N.; Tourrette, A. PNIPAM grafted surfaces through ATRP and RAFT polymerization: Chemistry and bioadhesion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 151, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alswieleh, A.M.; Alshahrani, M.M.; Alzahrani, K.E.; Alghamdi, H.S.; Niazy, A.A.; Alsilme, A.S.; Beagan, A.M.; Alsheheri, B.M.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Almeataq, M.S. Surface modification of pH-responsive poly(2-(tert-butylamino) ethyl methacrylate) brushes grafted on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Des. Monomers Polym. 2019, 22, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beagan, A.M.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Lahmadi, S.S.; Halwani, M.A.; Almeataq, M.S.; AlHazaa, A.N.; Alotaibi, K.M.; Alswieleh, A.M. Folic acid-terminated poly(2-Diethyl Amino Ethyl Methacrylate) brush-gated magnetic mesoporous nanoparticles as a smart drug delivery system. Polymers 2020, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, M.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.; Dang, C.C.; Parnell, A.J.; Martin, S.J.; Howse, J.R.; Jones, R.A.; Golestanian, R.; Topham, P.D.; Crook, C.J. The pH-induced swelling and collapse of a polybase brush synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesman, B.T.; Smith, E.G.; Murdoch, T.J.; Guibert, C.; Webber, G.B.; Edmondson, S.; Wanless, E.J. Polyelectrolyte brush pH-response at the silica–aqueous solution interface: A kinetic and equilibrium investigation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14502–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, L.A.; Edmondson, S.; Armes, S.P. Synthesis of pH-responsive tertiary amine methacrylate polymer brushes and their response to acidic vapour. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11773–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Altintas, B.; Arica, M.Y. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic beads containing aminated fibrous surfaces for removal of Reactive Green 19 dye: Kinetics and thermodynamic parameters. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shaheen, K.; Shah, Z.; Suo, H.; Khan, Q.; Shah, A.M.B.; Rehman, W.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; et al. Adsorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of methyl orange dye sequestration through chitosan composites films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takdastan, A.; Pourfadakari, S.; Yousefi, N.; Orooji, N. Removal of sunset yellow dye using heterogeneous catalytic degra-dation with magnetic Fe3O4/persulfate/ultrasound system. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 197, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, S.; Chinevari, A.; Ghorbani, M. Simultaneous removal of four dye pollutants in mixture using amine functionalized Kit-6 silica mesoporous magnetic nanocomposite. Silicon 2020, 12, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaś, J.; Stasicka, Z. Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group. Arsenic, metals, fibres, and dusts. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. IARC 2012, 128, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G. Application of kinetic models to the sorption of copper (II) on to peat. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyulu, S.R.; Gomathi, T.; Sudha, P. Physico-chemical characterization of cross linked chitosan-polyacrylonitrile polymer blends. Pharm. Lett. 2013, 5, 354–363. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, T.R.; Prelot, B. Chapter 7—Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: The perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. In Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 161–222. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).