A New General Type-2 Fuzzy Predictive Scheme for PID Tuning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The PID is a simple and effective controller, but in many applications the gains should be tuned. The un-tuned parameters leads to undesired performance and/or instability.
- The most of existence regulation methods such evolutionary methods impose high computational cost.
- The predictive scheme in many applications improves the control accuracy, but its implementation is more difficult than PID.
- The MPC results in good performance, but its accuracy strongly depends on the model.
2. Literature Review
- A simple practical controller is proposed based on good features of popular PID and MPC methods.
- A type-2 fuzzy approach is suggested for online modeling that improves the MPC performance.
- An online optimization scheme is presented to handle the online unpredicted disturbances.
- The better performance is shown by several simulations.
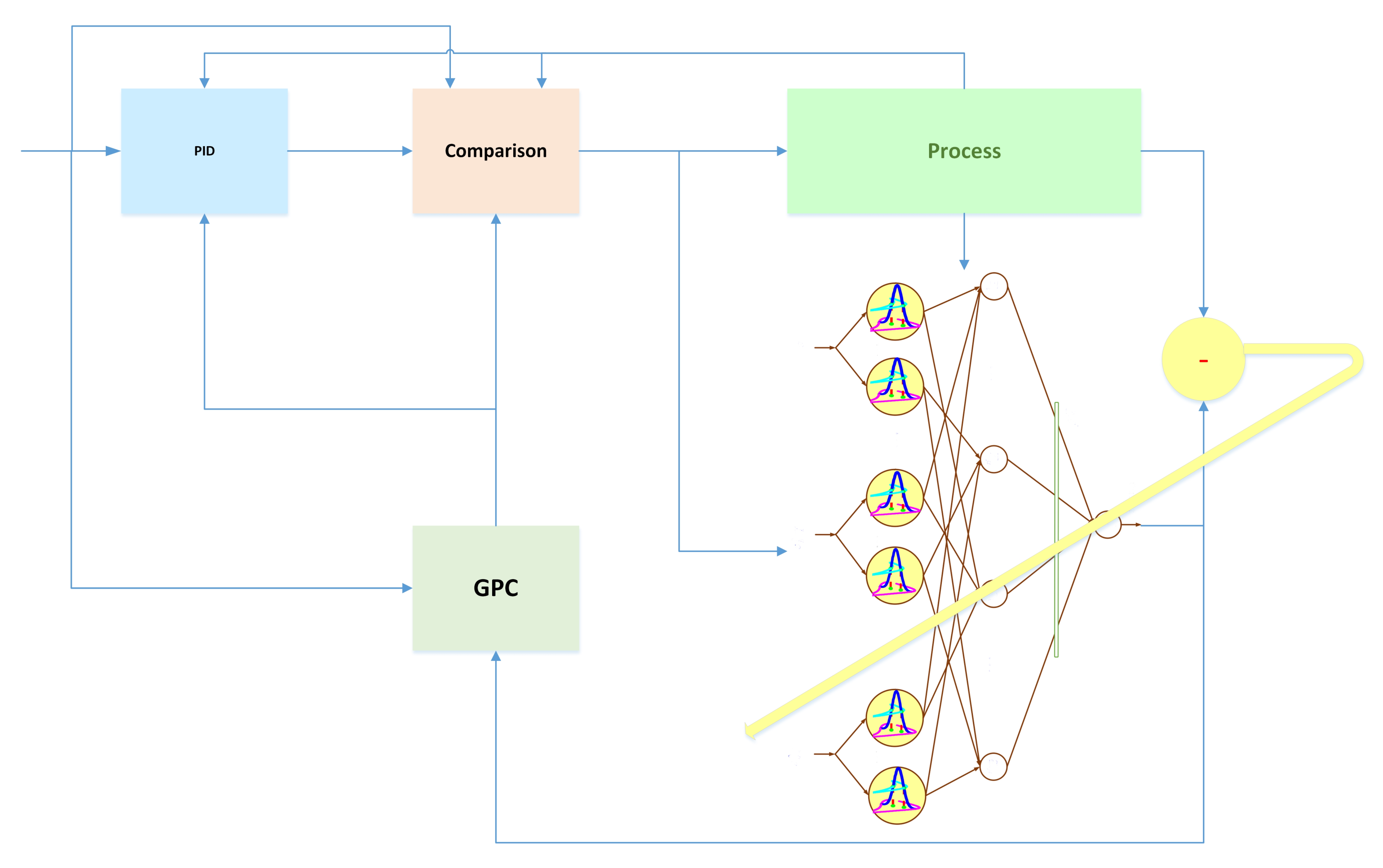
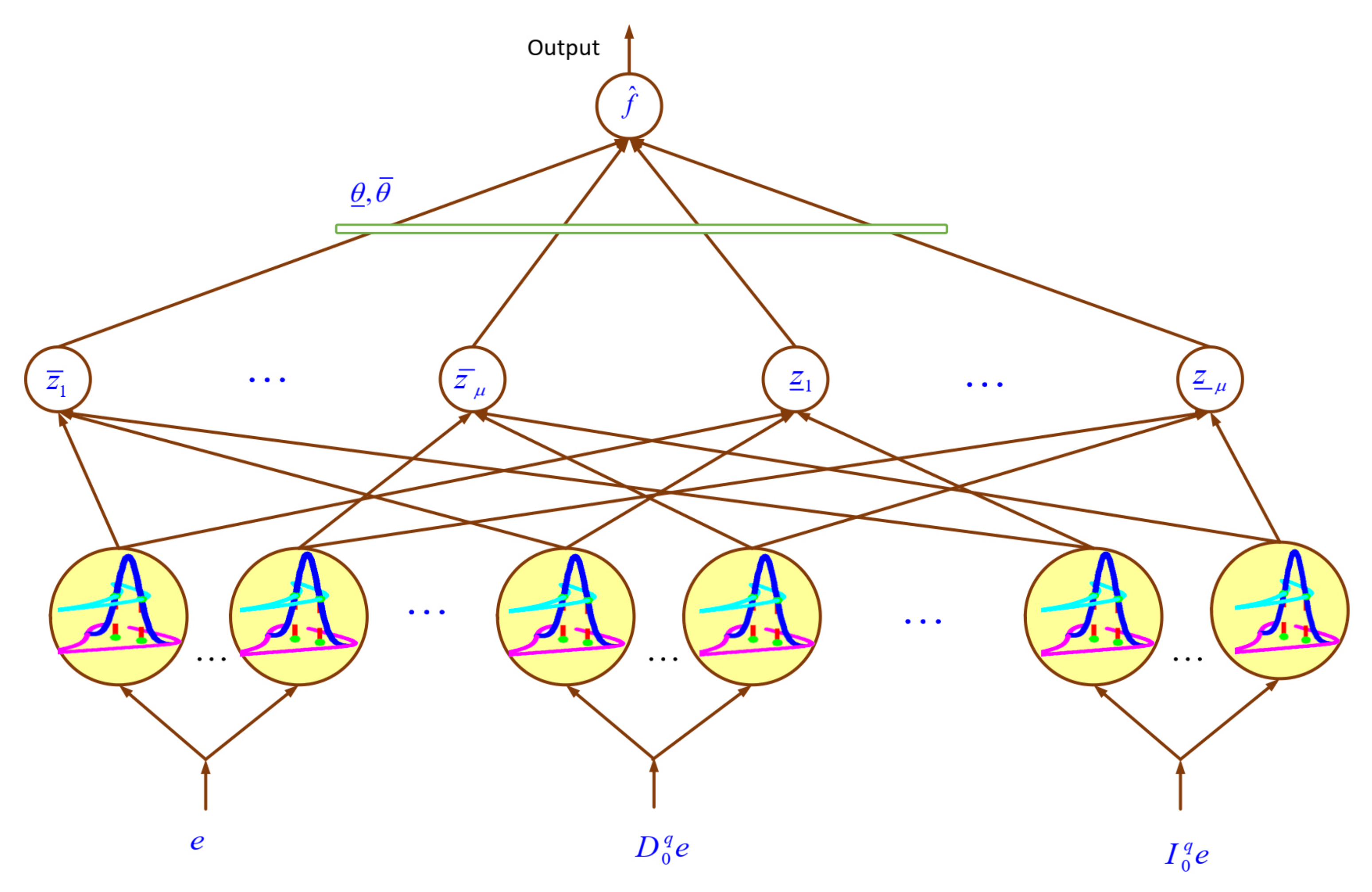
3. Identification by Fuzzy System
- (1)
- The inputs of GT2-FLS are control signal and system output at previous sample times.
- (2)
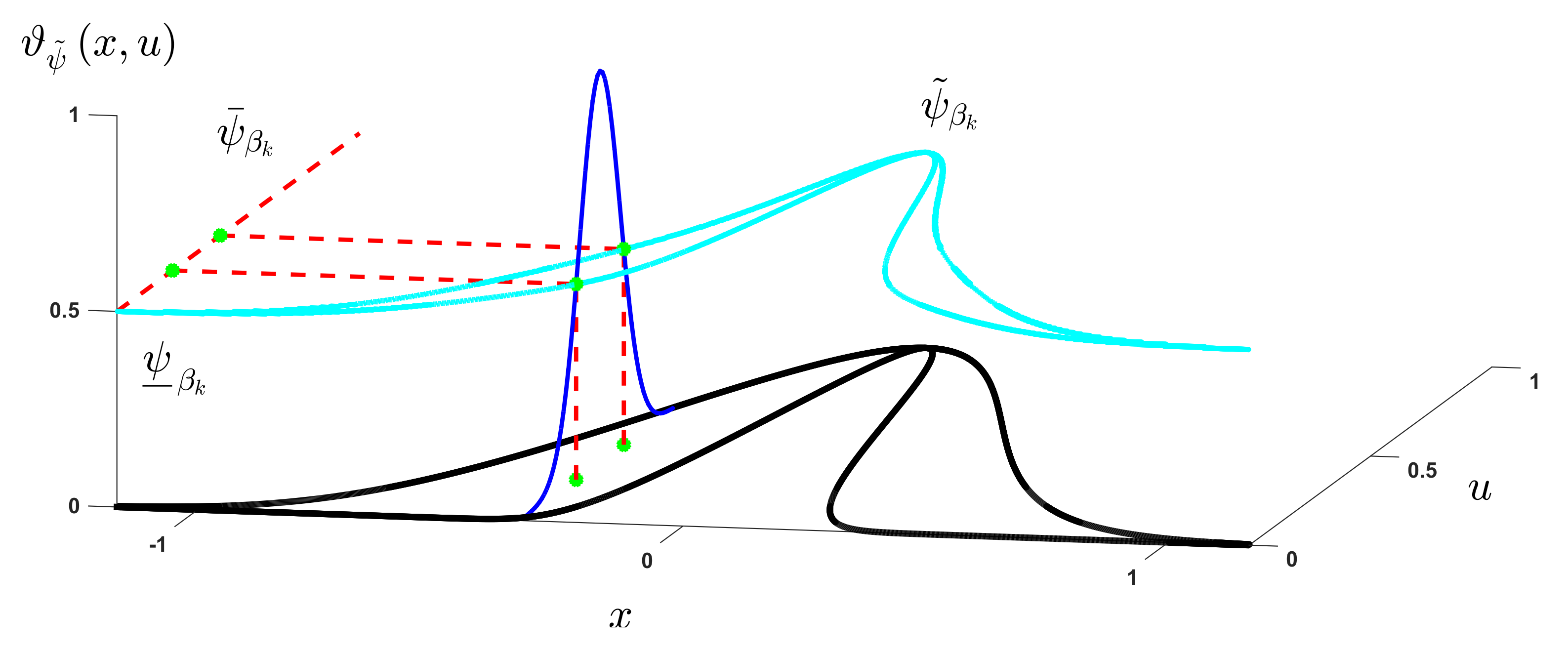
- The suggested membership function (MF) is shown in Figure 3. For slice level, we have:where,where denotes the MF for input, represents the center of MF, is the small constant and and are the standard divisions.
- (3)
- The rule firings are written as:where, and are rules number.
- (4)
- The output is written as:where, and are rule parameters.The rule parameters are leaned by the following adaptation law:where, is a constant and e represents the tracking error.
4. Predictive Control
GPC Controller
5. Obtain PID Parameters with Predictive Control
6. Observer Controller
7. Temperature Control of CSTR Units
7.1. Control Performance
7.2. CSTR Temperature Control
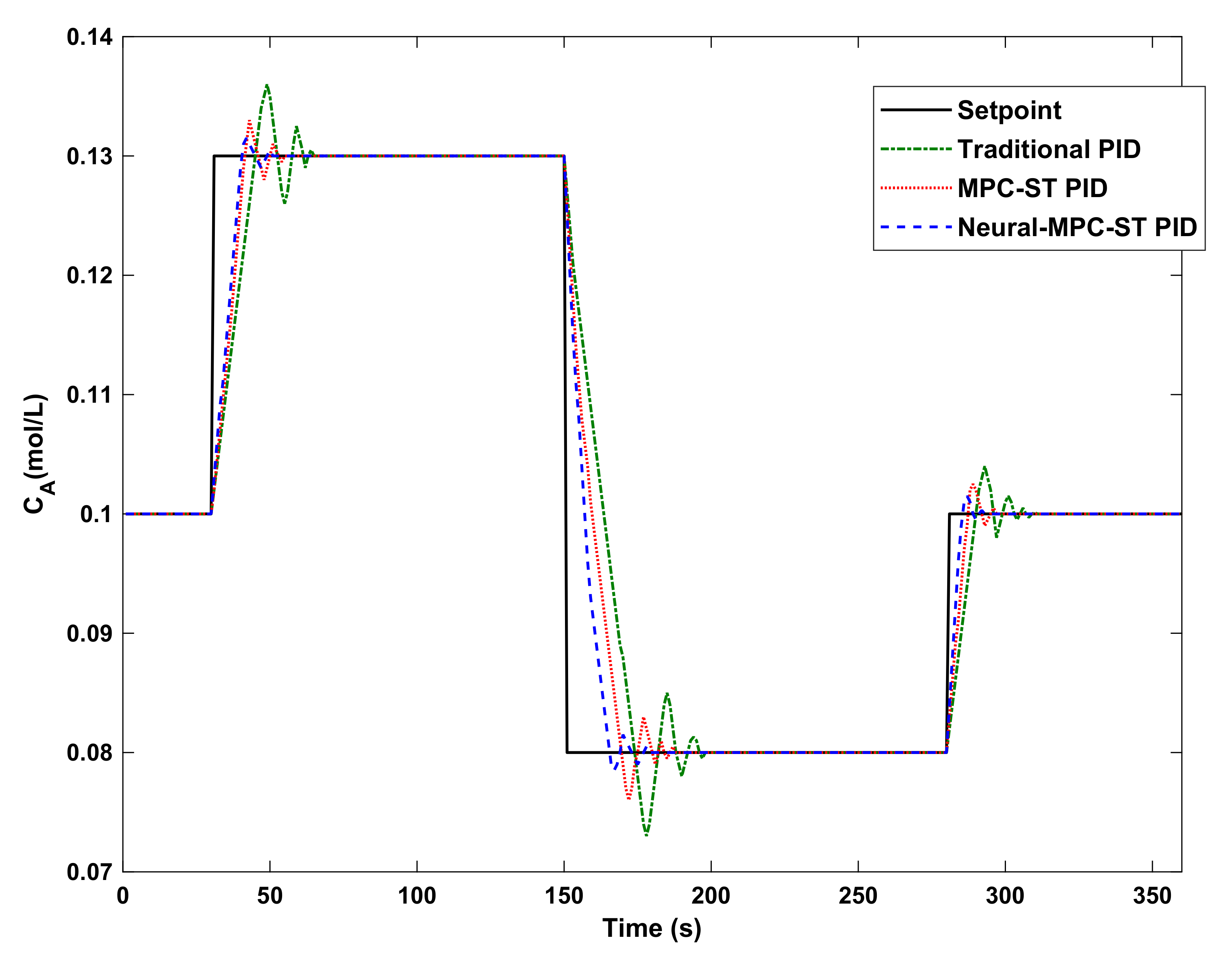
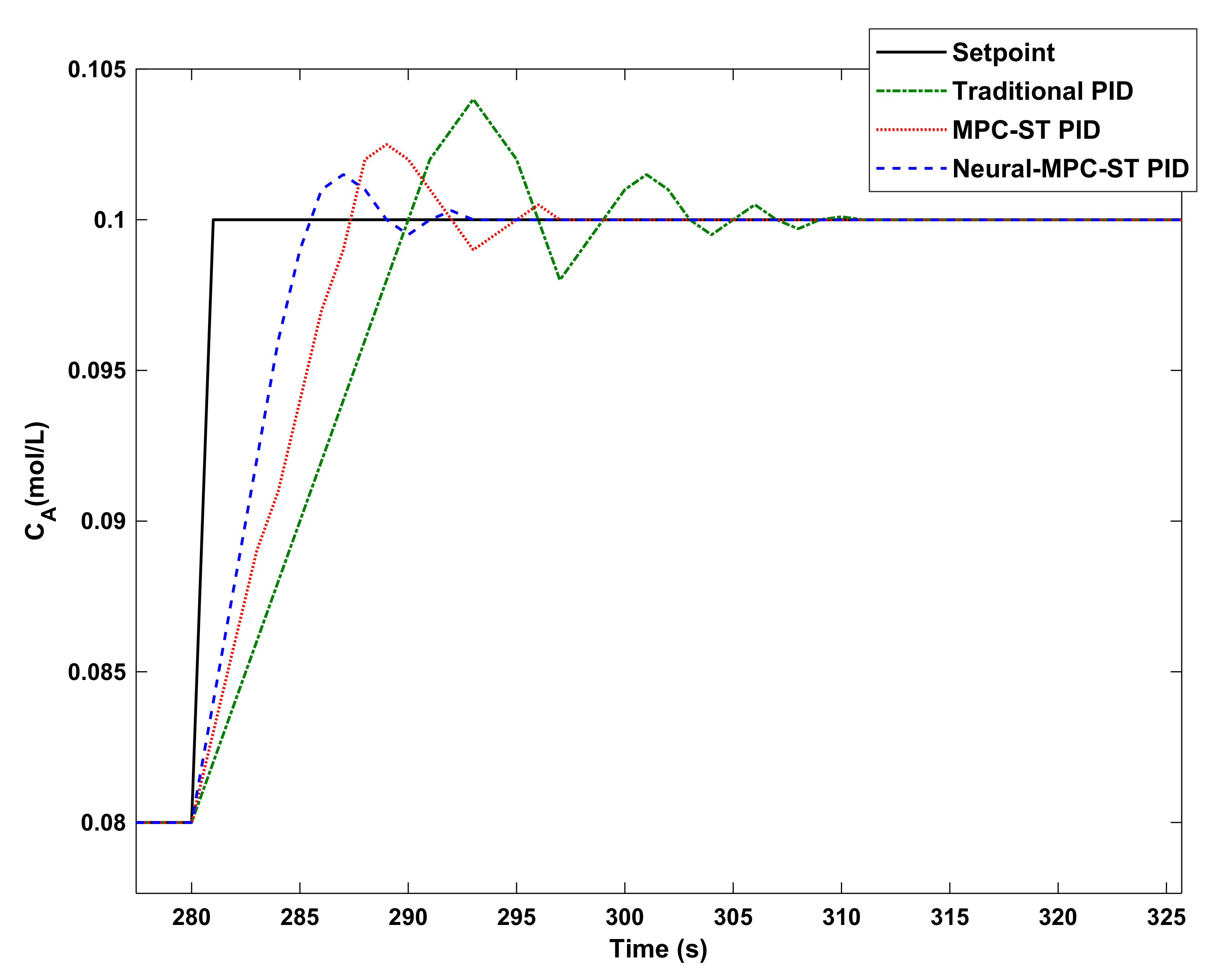
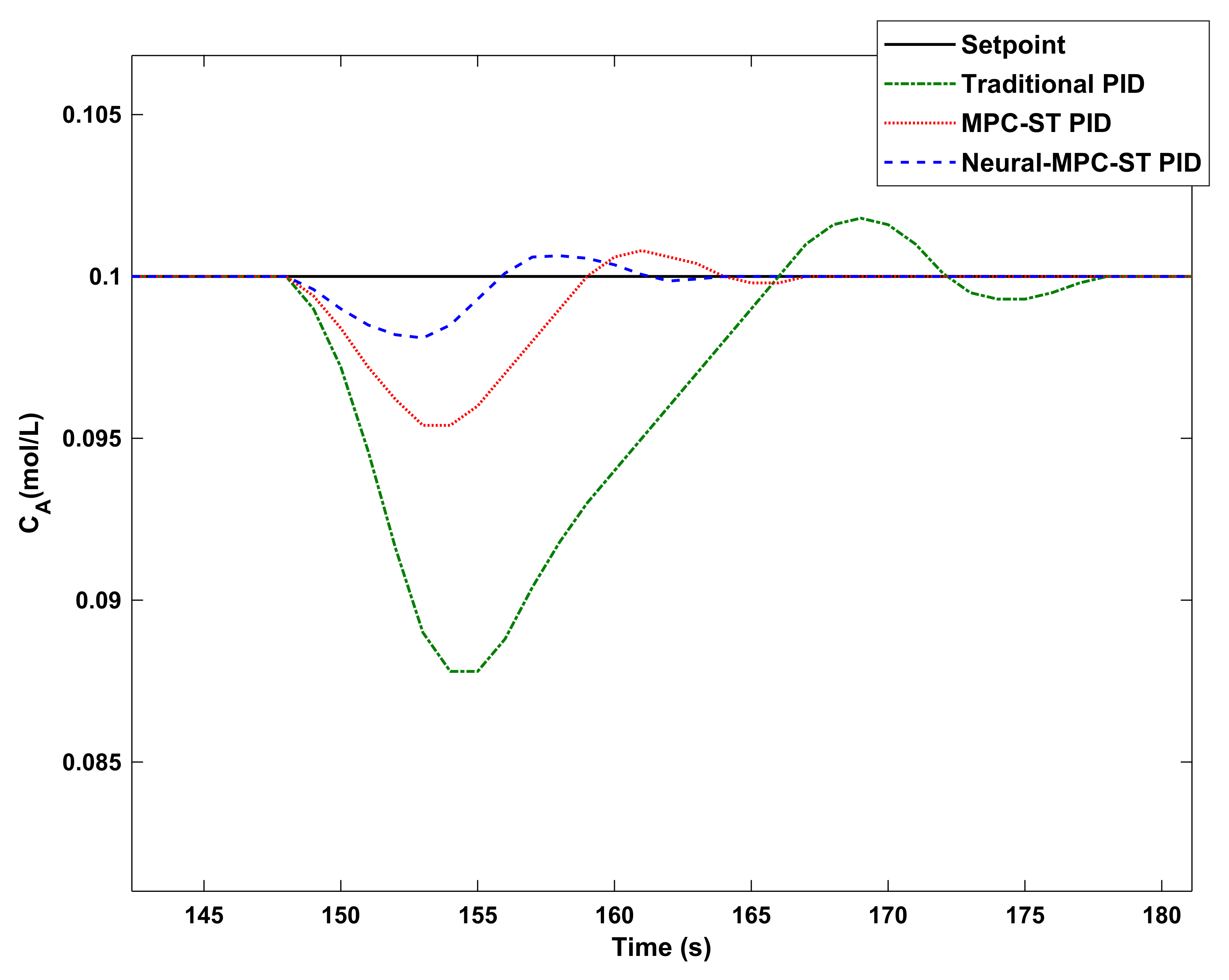
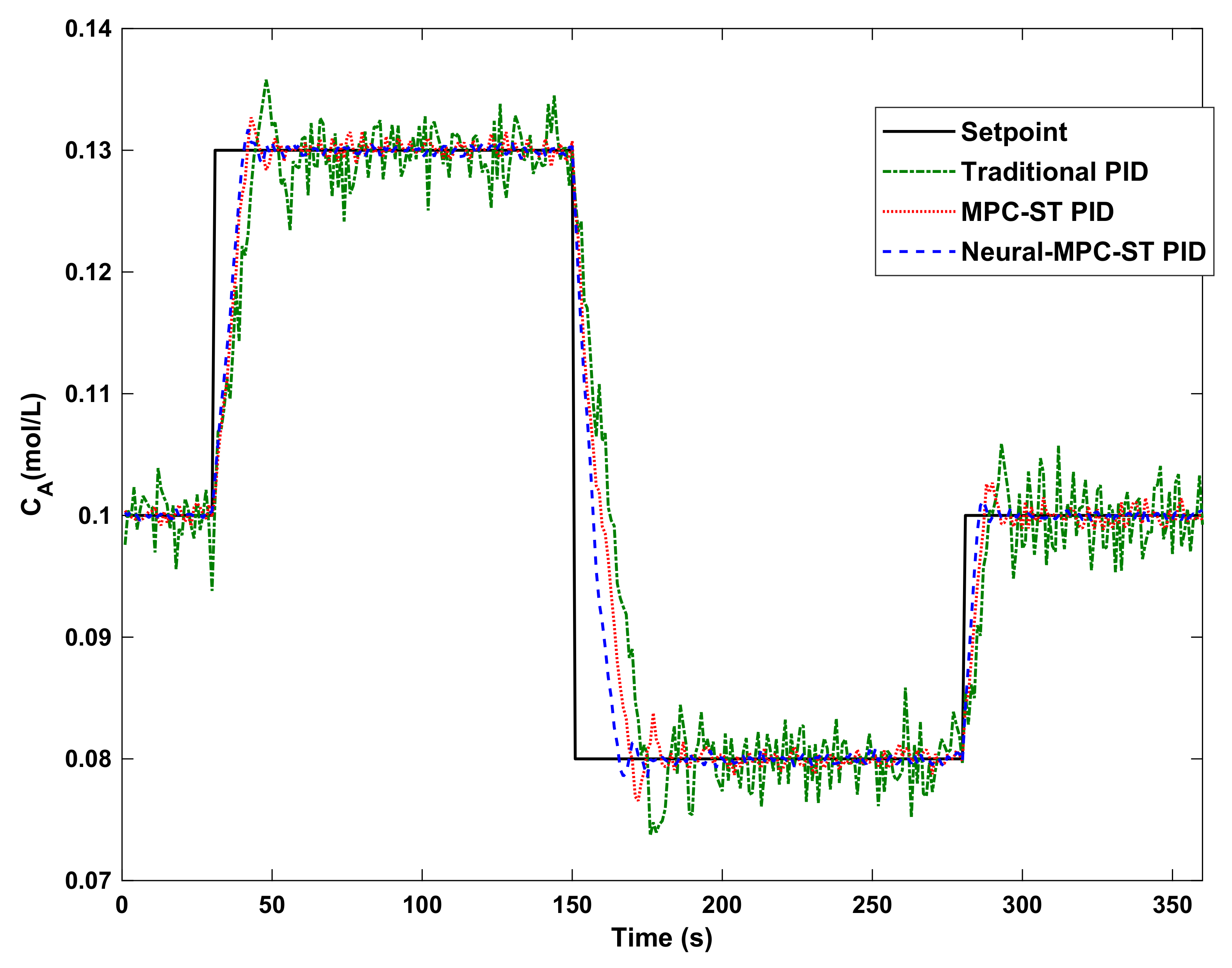
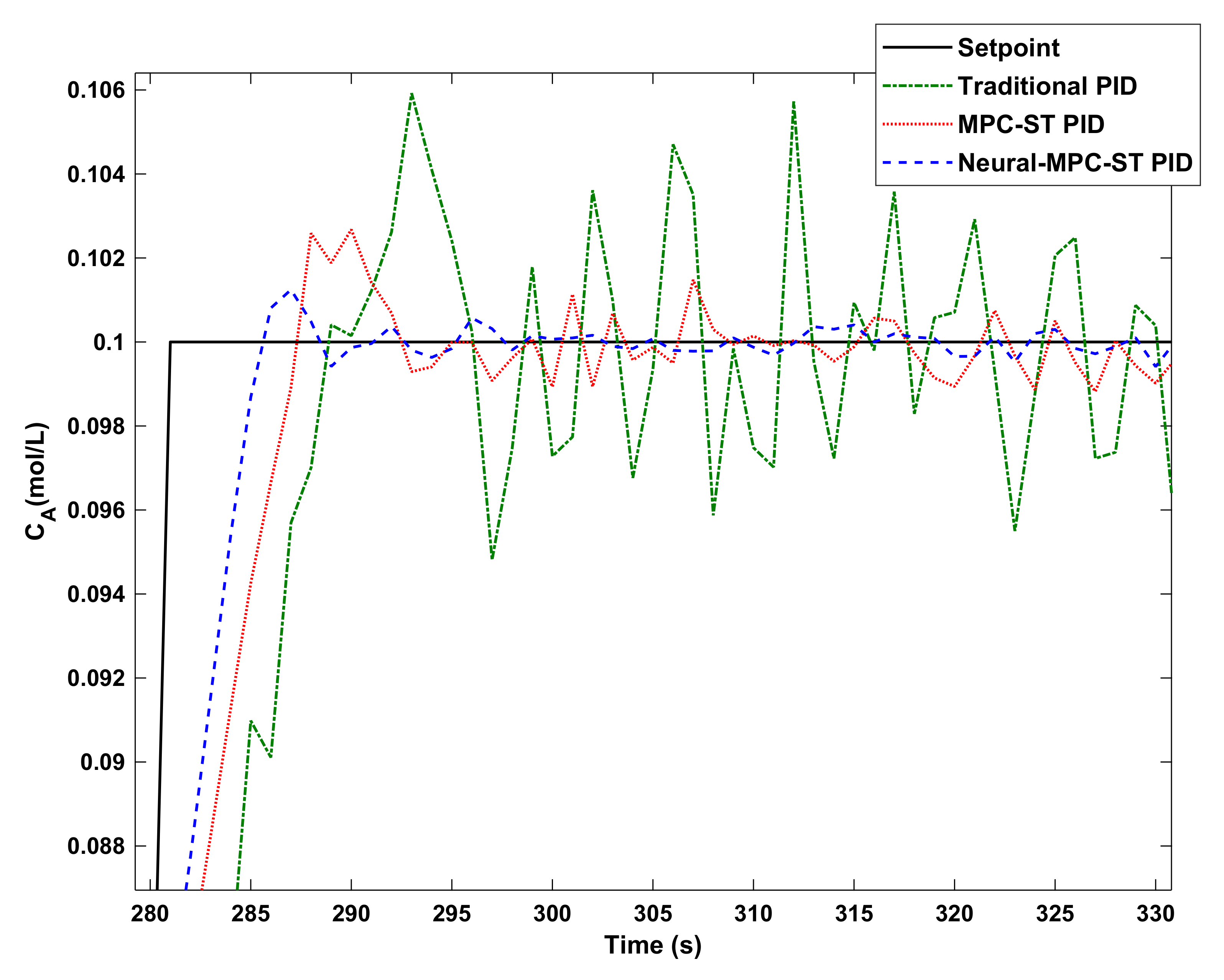
8. Simulation Results
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chavero-Navarrete, E.; Trejo-Perea, M.; Jáuregui-Correa, J.C.; Carrillo-Serrano, R.V.; Ronquillo-Lomeli, G.; Ríos-Moreno, J.G. Pitch Angle Optimization for Small Wind Turbines Based on a Hierarchical Fuzzy-PID Controller and Anticipated Wind Speed Measurement. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jang, D.W. Optimization of Neural Network-Based Self-Tuning PID Controllers for Second Order Mechanical Systems. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.W.; Lee, S.; Park, J.W.; Baek, D.C. Failure detection technique under random fatigue loading by machine learning and dual sensing on symmetric structure. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 114, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavero-Navarrete, E.; Trejo-Perea, M.; Jáuregui-Correa, J.C.; Carrillo-Serrano, R.V.; Ronquillo-Lomeli, G.; Ríos-Moreno, J.G. Hierarchical pitch control for small wind turbines based on fuzzy logic and anticipated wind speed measurement. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, A.; Turabieh, H.; Thaher, T.; Too, J.; Mafarja, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Surani, S.R. Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea from ECG Signals Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Classifiers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, A.P.; Deb, D.; Ozana, S. Kalman Filter and Variants for Estimation in 2DOF Serial Flexible Link and Joint Using Fractional Order PID Controller. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Islam, M.; Rashid, M.; Mounis, S.; Ahsan, M.M.; Ahad, M.T.; Siddique, Z.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mahmud, M. Investigation of 2DOF PID Controller for Physio-Therapeutic Application for Elbow Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, S.; Bekdaş, G.; Nigdeli, S.M.; Kim, S.; Geem, Z.W. Performance of optimum tuned PID controller with different feedback strategies on active-controlled structures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Yin, J. A Biased Proportional-Integral-Derivative-Incorporated Latent Factor Analysis Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Yu, M.; Xu, Y.; Ma, C.; Lai, H.; Chen, F.; Lin, H. An Improved PID Controller for the Compliant Constant-Force Actuator Based on BP Neural Network and Smith Predictor. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, W.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. Design of an IMCPID Optimized Neural Network for Stepless Flow Control of Reciprocating Mechinery. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, J.P.; da Fonseca Neto, J.V.; Rêgo, P.H.M. A Neuro-Fuzzy Model for Online Optimal Tuning of PID Controllers in Industrial System Applications to the Mining Sector. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 28, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, S.; Hamdani, S.S.Z.; Khan, H.U.; ur Rehman, M.; Khan, H. Artificial neural network based self-tuned PID controller for flight control of quadcopter. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET), Lahore, Pakistan, 21–22 February 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Alvarado, R.; García-Valdovinos, L.G.; Salgado-Jiménez, T.; Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Fonseca-Navarro, F. Neural network-based self-tuning PID control for underwater vehicles. Sensors 2016, 16, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Wang, J.; Jegatheesan, V.; Shi, G. Dissolved oxygen control in activated sludge process using a neural network-based adaptive PID algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Fan, Y. A PID Tuning Strategy Based on a Variable Weight Beetle Antennae Search Algorithm for Hydraulic Systems. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9579453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Ullah, M.A. Optimal PID tuning for controlling the temperature of electric furnace by genetic algorithm. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirsat, M.P.; Sarwadnya, R.V. Swarm-based optimizers for PID tuning of bioreactor. In Smart Sensors Measurements and Instrumentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, N.; Hanif, A.; Ali, M.U.; Zafar, A. Chaotic-based particle swarm optimization algorithm for optimal PID tuning in automatic voltage regulator systems. Electr. Eng. Electromech. 2021, 1, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, V.; Gomez, N.; Rodas, J.; Paiva, E.; Saad, M.; Gregor, R. Pareto optimal pid tuning for Px4-Based unmanned aerial vehicles by using a multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Aerospace 2020, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V. Comparative Analysis of PID Tuning Techniques for Blood Glucose Level of Diabetic Patient. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 2948–2953. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Cao, X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, C. Event-triggered asynchronous sliding mode control of CSTR based on Markov model. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 4687–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, O.; Mahyuddin, M.N.; Jerbi, H. An advanced PID based control technique with adaptive parameter scheduling for a nonlinear CSTR plant. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158085–158094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrov, D.; Nadzinski, G.; Deskovski, S.; Stankovski, M. Quadratic Model-Based Dynamically Updated PID Control of CSTR System with Varying Parameters. Algorithms 2021, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Nisi, K. A deep analysis on optimization techniques for appropriate PID tuning to incline efficient artificial pancreas. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 7587–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Pan, Z. Design of a predictive RBF compensation fuzzy PID controller for 3D laser scanning system. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Farzaneh, H. Adaptive cruise control for eco-driving based on model predictive control algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Yu, C.C.; Tsai, C.T. Adaptive ORFWNN-based predictive PID control. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 1544–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. Generalized predictive PID control for main steam temperature based on improved PSO algorithm. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Informat. 2017, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterle, F.; Rampazzo, M.; Beghi, A. Control of second order processes with dead time: The predictive PID solutions. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, Z.; Fu, B.; He, L.; Li, C. Research on the predictive optimal PID plus second order derivative method for AGC of power system with high penetration of photovoltaic and wind power. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 14, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X.; Li, C. Adaptive condition predictive-fuzzy PID optimal control of start-up process for pumped storage unit at low head area. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 177, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
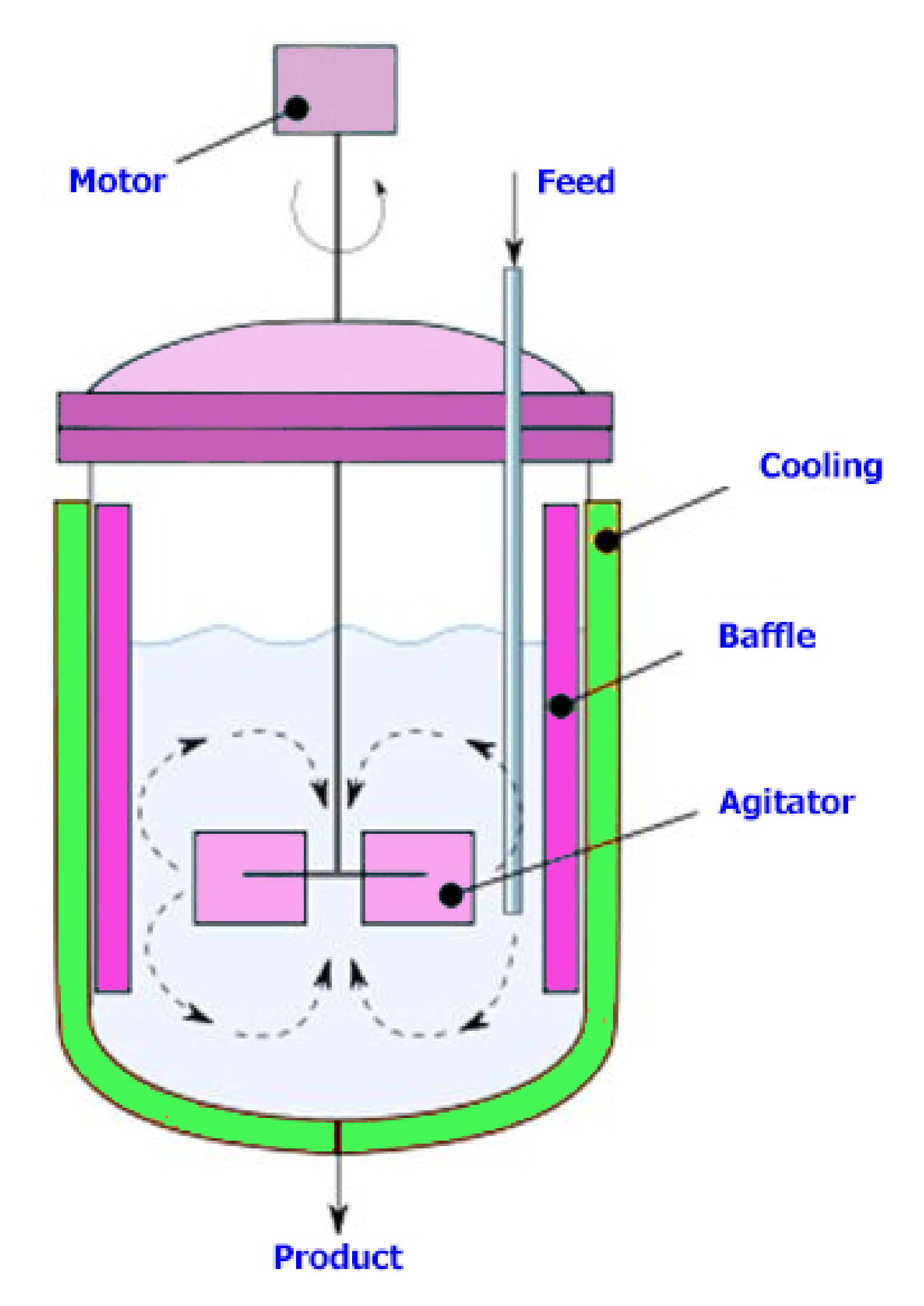


| CA | Concentration of the substance A inside the reactor |
| T | Temperature inside the reactor |
| Q | feed fluid flow, 0.2 m3/min |
| V | reactor volume, 2 m3 |
| TF | feed temperature, 30 °C |
| P | Medium density of material, 1000 kg/m3 |
| k0 | constant reaction speed, 3.5 × 106 L/min |
| Ea | activation energy, 49.88 Kj/mol |
| UA | heat transfer coefficient, 252 kj/min°C |
| R | gases constant, 8.134 × 10−3 kj/mol°C |
| Vj | jacket volume, 0.4 m3 |
| Hr | heat of reaction, 500 kj/mol |
| TjF | inlet fluid temperature to the jacket, 10 °C |
| CAF | Concentration of substance A in feed, 100 mol/m3 |
| φc(t) | Deactivation coefficient, 1 |
| φh(t) | Fouling coefficient, 1 |
| hA | Heat transfer term, 7 × 105 cal/(min · k) |
| T | Reactor temperature, 438.7763 K |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tavoosi, J.; Shirkhani, M.; Abdali, A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Nazari, M.; Mobayen, S.; Asad, J.H.; Bartoszewicz, A. A New General Type-2 Fuzzy Predictive Scheme for PID Tuning. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110392
Tavoosi J, Shirkhani M, Abdali A, Mohammadzadeh A, Nazari M, Mobayen S, Asad JH, Bartoszewicz A. A New General Type-2 Fuzzy Predictive Scheme for PID Tuning. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):10392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110392
Chicago/Turabian StyleTavoosi, Jafar, Mohammadamin Shirkhani, Ali Abdali, Ardashir Mohammadzadeh, Mostafa Nazari, Saleh Mobayen, Jihad H. Asad, and Andrzej Bartoszewicz. 2021. "A New General Type-2 Fuzzy Predictive Scheme for PID Tuning" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 10392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110392
APA StyleTavoosi, J., Shirkhani, M., Abdali, A., Mohammadzadeh, A., Nazari, M., Mobayen, S., Asad, J. H., & Bartoszewicz, A. (2021). A New General Type-2 Fuzzy Predictive Scheme for PID Tuning. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 10392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110392











