Abstract
Coagulation factor V (FV) is a liver-derived protein encoded by the F5 gene. Alternative splicing of F5 exon 13 produces a low-abundance splicing isoform, known as FV-short, which binds the anticoagulant protein tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPIα) with high affinity, stabilising it in the circulation and potently enhancing its anticoagulant activity. Accordingly, rare F5 gene mutations that up-regulate FV-short splicing are associated with bleeding. In this study we have explored the possibility of decreasing FV-short splicing by antisense-based splicing modulation. To this end, we have designed morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (MAOs) targeting the FV-short-specific donor and acceptor splice sites and tested their efficacy in a liver cell line (HepG2) that naturally expresses full-length FV and FV-short. Cells were treated with 0–20 µM MAO, and full-length FV and FV-short mRNA expression was analysed by RT-(q)PCR. Both MAOs, alone or in combination, decreased the FV-short/full-length FV mRNA ratio down to ~50% of its original value in a specific and dose-dependent manner. This pilot study provides proof-of-principle for the possibility to decrease FV-short expression by antisense-mediated splicing modulation. In turn, this may form the basis for novel therapeutic approaches to bleeding disorders caused by FV-short over-expression and/or elevated TFPIα (activity) levels.
1. Introduction
Eukaryotic protein-coding genes have a unique architecture characterised by alternating coding and non-coding regions, known as exons and introns, respectively. As a gene is transcribed by RNA polymerase II, the primary transcript undergoes splicing, a process in which introns are eliminated and exons are ligated together to form the mature mRNA. These reactions take place in the cell nucleus and are catalysed by a macromolecular ribonucleoprotein complex called spliceosome, which operates according to a splicing code embedded in the pre-mRNA itself. The beginning and end of each intron are marked by relatively conserved sequences, known as donor and acceptor splice sites. Moreover, additional exonic and intronic regulatory elements can promote (enhancers) or inhibit (silencers) splicing at nearby splice sites [1]. Depending on the strength of these signals and on the way they are decoded by the spliceosome, exonic sequence can be excluded from the mature mRNA and/or intronic sequence can be retained, generating different mRNAs from the same primary transcript (alternative splicing). In this way, most human genes can produce multiple isoforms of the same protein [2,3]. Due to the complexity of the splicing code, it is estimated that a substantial fraction of disease-causing genetic variants acts by deregulating splicing [4,5].
Physiological and pathological alternative splicing is amenable to specific modulation by various molecules [6,7,8]. In particular, antisense oligonucleotides designed to bind by base-pair-complementarity to specific splicing signals on a target pre-mRNA can prevent the recognition of these signals by the spliceosome [9]. Several studies support the ability of this technology to suppress unwanted splicing events (such as aberrant splicing induced by genetic mutations) in favour of alternative (correct or desirable) splicing events (see refs. [10,11,12,13] for some coagulation-related examples). In fact, several antisense oligonucleotides have entered clinical trials or have already been approved as therapeutic agents for various diseases [14,15].
Alternative splicing also contributes to the regulation of blood coagulation by generating variants of the same coagulation factor with different functional properties, as in the case of factor V (FV), encoded by the F5 gene [16]. FV is a liver-derived plasma protein with an A1-A2-B-A3-C1-C2 domain-structure. Its main isoform, referred to as (full-length) FV, is kept inactive by a tight electrostatic interaction between a basic and an acidic region within the large B domain [17]. Step-wise proteolysis of this domain activates FV into the essential cofactor (FVa) of factor Xa (FXa) in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, accelerating this reaction over a 1000-fold [18]. In the early stages of coagulation, the procoagulant activity of FV is regulated by the anticoagulant protein tissue factor pathway inhibitor α (TFPIα) [19]. In fact, the C-terminus of TFPIα contains a basic region that can bind to the free acidic region of partially activated forms of FV, thereby preventing their incorporation in the prothrombinase complex [20], as well as their full activation to FVa [21].
In 2013, a minor splicing variant of FV, normally accounting for <5% of plasma FV, was discovered [22]. This so-called FV-short isoform arises from the removal of an optional intron within exon 13 (Figure 1), resulting in the in-frame deletion of 702 amino acids of the B domain, including the basic region. TFPIα binds with high affinity to the unmatched acidic region of FV-short [22], thereby neutralising its constitutive prothrombinase activity [23]. In turn, FV-short stabilises TFPIα in the circulation [22,24] and potently enhances TFPIα-mediated inhibition of FXa in the presence of protein S [25], which binds to both TFPIα and FV-short and strengthens their interaction [26]. FV-short was originally identified in a family with FV-short over-expression due to a F5 gene mutation that enhances FV-short splicing, resulting in 10-fold increased TFPIα levels and a bleeding tendency (East Texas bleeding disorder) [22,27]. More recently, two other F5 gene mutations (F5-Amsterdam [28] and F5-Atlanta [29]) up-regulating FV-short splicing and plasma TFPIα levels have been reported in unrelated patients with similar histories of trauma-related bleeding.
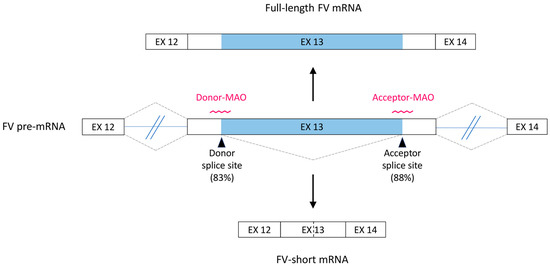
Figure 1.
Alternative splicing of the F5 gene. Schematic representation of the F5 pre-mRNA region spanning exons 12–14. The large exon 13 contains an internal optional intron (light blue), which is usually retained in the mature mRNA (default full-length FV transcript, top), but occasionally spliced out (alternative FV-short transcript, bottom). The consensus scores for the FV-short-specific donor and acceptor splice sites are reported in brackets and the morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (MAOs) designed to target these sites are shown. EX: exon.
As a possible therapeutic approach to these haemorrhagic disorders, we have explored the feasibility of decreasing FV-short expression by antisense-mediated F5 splicing modulation. To this end, we designed specific antisense oligonucleotides targeting FV-short splicing and tested them in vitro in a liver cell line (HepG2) that naturally expresses full-length FV and FV-short.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
The sequence of F5 exon 13 was analysed in silico for splicing signals using the Human Splicing Finder software [30]. Information on the occurrence of common genetic polymorphisms in the vicinity of the relevant splice sites was retrieved from the Ensembl database (www.ensembl.org, accessed on 10 September 2021).
2.2. Antisense Oligonucleotides
Morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (MAOs) are nucleic acid analogues in which DNA bases are bound to a non-charged backbone (morpholine rings linked by phosphorodiamidate bonds) [31]. MAOs targeting the FV-short-specific donor splice site (5′-CAAGGTTATTGACAGTGAACTTACT-3′, Donor-MAO) and acceptor splice site (5′-AGGTCTGGATAAGGAAAAGACTCAT-3′, Acceptor-MAO) were designed. Specificity for the intended target sites was verified by BLAST analysis against the human transcriptome. Another MAO with an irrelevant sequence (5′-CCTCTTACCTCAGTTACAATTTATA-3′) was used as a negative control. All MAOs were purchased from GeneTools (Philomath, OR, USA).
2.3. Characterisation of the F5 Gene in HepG2 Cells
2.3.1. Cell Model
HepG2 (ATCC database, accession number HB-8065™) is a well-established human liver cell line derived from a 15-year-old Caucasian male patient with hepatoblastoma [32,33].
2.3.2. DNA Isolation
Genomic DNA from HepG2 cells was isolated using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and quantified with a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific Nanodrop Products, Wilmington, DE, USA).
2.3.3. Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA)
The F5 gene copy number in HepG2 cells was determined by MLPA analysis [34] using the SALSA MLPA Probemix P469 F5 (MRC Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). This kit contains 26 F5-specific probes covering all F5 exons except exon 2, as well as 9 reference probes recognising other autosomic loci. Genomic DNA isolated from HepG2 cells was standardized to 20 ng/µL and the MLPA reaction was performed following the manufacturer’s protocol. FAM-labelled MLPA amplification products were mixed with GeneScanTM 600 LIZ® dye Size Standard and Hi-DiTM formamide (Life Technologies, Bleiswijk, The Netherlands), denatured and separated by capillary electrophoresis on an ABI 3730 DNA Analyzer (Life Technologies), as previously described [35]. The results were analysed using Coffalyser.Net (MRC Holland).
2.3.4. Amplification and Sequencing of F5 exon 13
F5 exon 13 was amplified and sequenced using primer sets that collectively cover the whole exon 13 in 7 overlapping amplicons (primers and amplification conditions available on request).
2.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
HepG2 cells were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with low glucose (Biowest, Nuaillé, France), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin and 2 mM L-glutamine. Cells were maintained in an incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Prior to each treatment experiment, the cells were seeded in 6-well plates at ~70% confluency.
Cells seeded in 6-well plates were treated with different MAO concentrations (0–20 μM) for 48 h in serum-free OptiMEM (Gibco™). MAOs were delivered using Endo-Porter reagent (GeneTools) at a concentration of 6 μM. Three biological replicates of each treatment were performed.
2.5. F5 Transcript Analysis
2.5.1. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
Total RNA was isolated from HepG2 cells using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and quantified with a NanoDrop 2000. Total RNA from primary human hepatocytes, which was used as control in some experiments, was purchased from 3H Biomedical AB (Uppsala, Sweden).
RNA (2 µg) was reverse-transcribed with MultiScribeTM Reverse Transcriptase (Applied Biosystems) using a F5-specific primer (5′-ATTCCGAGATGCTCTTCATAC-3′) located in exon 14.
2.5.2. F5 mRNA Analysis by PCR and Gel Electrophoresis
Due to the extreme differences in size and relative abundance of the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts, the development of a PCR-based protocol for the simultaneous amplification and quantification of both transcripts required extensive optimisation (see Results section). The full-length FV and FV-short transcripts were initially amplified using a common forward primer located in exon 12 (5′-ATGCGTGGAGAATCTGTGAC-3′) and transcript-specific reverse primers in exon 13. The reverse primer for the full-length FV transcript (5′-TCTGCAAGGTTATTGACAGTG-3′) was located in the portion of exon 13 that is spliced out in FV-short (443-bp amplicon), whereas, the FV-short-specific reverse primer (5′-CATCTGACCAAGGTTAATATTAC-3′) was designed on the junction site created by the alternative splicing event (429-bp amplicon). Since the primers for the full-length FV transcript turned out to co-amplify an unexpected alternatively spliced transcript (see Results section), a second set of primers spanning exons 13–14 was designed and used in all subsequent experiments. Forward primers specific for full-length FV (5′-TATCACCTCCTCCAGACCTTG-3′, located in the portion of exon 13 that is spliced out in FV-short) and FV-short (5′-TTCTTCCCCAAGTAATATTAACCTTG-3′, located across the junction created by the FV-short splicing event), were combined with a common reverse primer in exon 14 (5′-TTCTGGAATATCATCAGAGTCTTCA-3′), yielding PCR products of 473 bp and 397 bp, respectively.
To avoid competition for PCR reagents between full-length FV and FV-short mRNA, the two transcripts were amplified in separate PCR reactions run in parallel using the same amplification conditions (denaturation: 30 s at 92 °C; annealing: 20 s at 59 °C; extension: 25 s at 72 °C; repeated for 32 cycles) on a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Veenendaal, The Netherlands). PCR products were analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis (2% agarose) and their identity was confirmed by Sanger sequencing.
2.5.3. Quantification of Alternatively Spliced F5 Transcripts by qPCR
The alternatively spliced F5 transcripts (full-length FV and FV-short) were quantified by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) with SYBR-Green detection using a LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR instrument (Roche Applied Science). Separate amplification reactions for the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts were carried out using the second set of primers (spanning exons 13–14) described above. Each qPCR reaction was performed in a total volume of 10 μL including 5 μL LightCycler® 480 SYBR Green I Master mix (Roche), 0.5 μM of each primer and 10 ng of cDNA. The qPCR conditions were as follows: Initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 45 cycles of 20 s of denaturation at 95 °C, 15 s of annealing at 60 °C, and 15 s of extension at 72 °C. The specificity of the amplified products was verified by melting curve analysis (65–95 °C) and by agarose gel electrophoresis. qPCR data were analysed using LC480 Conversion (Roche) and LinRegPCR [36] software. Data analysis was carried out by relative quantification using the modified ΔΔCt method, described by Ruijter et al. [36], which takes amplification efficiency into account. All qPCR reactions were carried out in duplicate.
2.5.4. Statistical Analysis
The effects of increasing MAO concentrations on the FV-short/full-length FV mRNA ratio were evaluated with the Jonckheere-Terpstra trend test using the IBM SPSS statistical package. The significance level (α) was set at 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatics Analysis and Antisense Strategy
In silico analysis of the F5 exon 13 sequence showed that the donor and acceptor splice sites, defining the FV-short specific intron, have relatively high consensus scores of 83% and 88%, respectively (Figure 1). Two MAOs masking these splice sites were designed (Figure 1) and predicted to have no other targets in the human transcriptome. Interrogation of the Ensembl database revealed no common genetic variants in the vicinity of the FV-short splice sites that could potentially weaken the interaction of the MAOs with the target F5 pre-mRNA.
3.2. Characterisation of the F5 Gene in HepG2 Cells
Since the HepG2 cell line is known to have multiple chromosomal aberrations [33], we performed a preliminary characterisation of the F5 gene in these cells (Figure 2), in order to ensure the suitability of this model for the intended splicing modulation experiments.
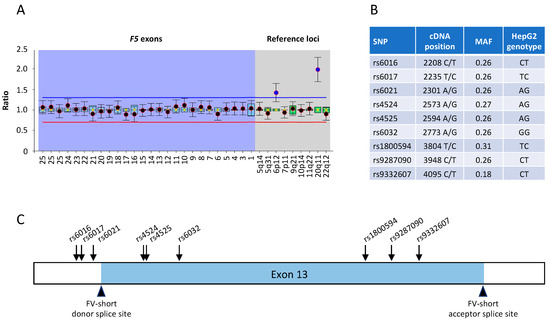
Figure 2.
Characterisation of the F5 gene in HepG2 cells. (A) MLPA analysis of the F5 gene in HepG2 cells. The normalised copy number is plotted for individual F5 exons (purple background) and for reference genes located on different chromosomes (grey background). A ratio of ~1 indicates a normal copy number (n = 2), whereas ratios above the blue line or below the red line indicate copy numbers >2 or <2, respectively. (B) Common SNPs identified in F5 exon 13 in the genomic DNA of HepG2 cells; MAF: minor allele frequency. (C) Positions of the identified F5 exon 13 SNPs relative to the FV-short-specific donor and acceptor splice sites.
The number of copies of the F5 gene in HepG2 cells was assessed by MLPA analysis and found to be normal (Figure 2A). Two reference probes yielded ratios of 1.5 and 2 in this analysis, indicating the presence of 3 and 4 copies of the corresponding control loci on chromosomes 6 and 20, respectively (Figure 2A). This is consistent with reported copy number changes in the HepG2 genome [33] and unlikely to interfere with the F5 gene analysis, as the copy numbers of the F5 gene exons are normalised against the average copy number of all 9 reference probes.
Sequencing of the whole F5 exon 13 from genomic DNA of HepG2 cells identified several well-known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (Figure 2B), but no novel sequence variations. Importantly, none of the identified variants was located at or close to the FV-short-specific donor or acceptor splice sites (Figure 2C). Accordingly, preliminary experiments indicated that HepG2 cells express both full-length FV and FV-short mRNA, with a vast predominance of the full-length transcript, as in normal hepatocytes.
3.3. Optimisation of Full-Length FV and FV-Short Transcript Amplification and Identification of a New Alternatively Spliced F5 Transcript
In view of determining the effect of MAO treatment on the alternative splicing of F5, we developed and optimised an RT-(q)PCR protocol for the simultaneous detection and quantification of the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts, taking into account the extreme differences in the size (~2.1 kb) and relative abundance (>100-fold) of the two transcripts. To this end, we used a F5-specific primer (instead of random hexamers) for the reverse-transcription of total RNA, which greatly improved the detection of the low-abundance FV-short transcript. Moreover, to eliminate the bias associated with the higher amplification efficiency of the much shorter FV-short amplicon, we employed transcript-specific primers generating PCR products of similar lengths. Finally, to prevent competition for the PCR reagents between templates of vastly different abundance, we amplified the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts in separate PCR reactions, which were run in parallel using the same thermal cycles.
Our original PCR design comprised a common forward primer in exon 12 and transcript-specific primers in exon 13 (red primers in Figure 3A). This set-up worked well for FV-short, but the primer pair for the full-length FV transcript yielded not only the expected product of 443 bp, but also a lesser lower-molecular weight band, which appeared specific, as it could not be eliminated by manipulating the amplification conditions (Figure 3B).
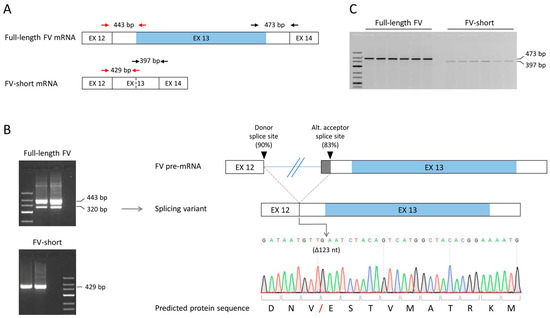
Figure 3.
Amplification of FV transcripts and identification of a new alternatively spliced transcript. (A) Schematic representation of the region spanning F5 exons 12–14 in the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts. The positions of the primers used to amplify these transcripts (first primer set in red, second primer set in black) are shown and amplicon sizes are indicated. EX: exon. (B) Left: Typical PCR products obtained after amplification of HepG2 cDNA using the first (red) set of primers (note: since the unexpected 320-bp band was more prominent in qPCR than in normal PCR experiments, the figure shows a gel loaded with qPCR products). Right: Schematic representation and sequencing chromatogram of the new splicing variant lacking the first 123 nucleotides (nt.) of exon 13. The red forward slash in the protein sequence marks the position of the predicted 41-amino acid deletion. (C) Typical PCR products obtained after amplification of HepG2 cDNA using the second (black) set of primers.
Purification and sequencing of the unexpected PCR product revealed a novel splicing event between the donor splice site of F5 intron 12 and an alternative acceptor splice site located 123 bp into exon 13 (Figure 3B), leading to the in-frame deletion of the first 123 nucleotides of exon 13. Upon translation, this would predict the loss of 41 amino acids (residues 659–699) between the A2 and B domains of the protein. This alternative splicing event may occur physiologically, as it was also observed in RNA isolated from human primary hepatocytes (data not shown). In silico analysis indicated that the alternative acceptor splice site in exon 13 has a consensus sequence of 83% (vs. 88% for the canonical acceptor splice site at the end of intron 12).
To avoid co-amplification of this additional F5 splicing variant, we switched to a new PCR design based on transcript-specific forward primers in exon 13 and a common reverse primer in exon 14 (black primers in Figure 3A). This revised PCR set-up yielded unique and specific products for both the full-length FV and the FV-short transcript (Figure 3C) and was adopted in all subsequent qualitative and quantitative analyses.
3.4. F5 Splicing Modulation in HepG2 Cells
In order to reduce the relative expression of FV-short, HepG2 cells were treated with increasing concentrations (0–20 µM) of MAOs targeting the FV-short-specific donor splice site (Donor-MAO) or acceptor splice site (Acceptor-MAO). After 48 h of treatment, total RNA was isolated and full-length FV and FV-short mRNA expression was analysed by RT-PCR and gel electrophoresis (Figure 4). Both MAOs caused a dose-dependent decrease of FV-short expression without affecting full-length FV expression. Similar results were obtained with a 1:1 mix of Donor-MAO and Acceptor-MAO (MAO-mix, i.e., 50% Donor-MAO and 50% of Acceptor-MAO to obtain an overall concentration of 5 µM, 10 µM and 20 µM), whereas treatment with a Control-MAO up to a concentration of 20 µM did not affect FV-short or full-length FV expression.
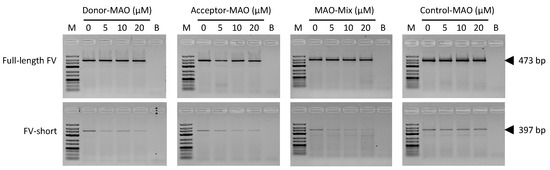
Figure 4.
Qualitative analysis of the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts in untreated and treated HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were treated for 48 h with increasing concentrations (0–20 µM) of a morpholino antisense oligonucleotide (MAO) targeting the FV-short-specific donor splice site (Donor-MAO), a MAO targeting the FV-short-specific acceptor splice site (Acceptor-MAO), a 1:1 mix of Donor-MAO and Acceptor-MAO, (MAO-mix), or a control MAO with an irrelevant sequence. Total RNA was isolated and reverse transcribed into cDNA. Amplicons corresponding to the full-length FV (top) and FV-short transcripts (bottom) were amplified in separate PCR reactions and PCR products were analysed by gel electrophoresis. M: molecular weight marker, B: blank. Sequencing chromatograms of the full-length FV and FV-short amplicons are shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
The effects of the MAOs on the FV-short/full-length FV transcript ratio were quantified using real-time qPCR analysis (Figure 5). Untreated HepG2 cells typically expressed 2–3 orders of magnitude more full-length FV than FV-short mRNA. Treatment with the Donor-MAO dose-dependently decreased the FV-short/full-length FV transcript ratio to ~50% of its original value in untreated cells (Figure 5A, p-for-trend = 0.008). The Acceptor-MAO was somewhat less effective, reducing the FV-short/full-length FV transcript ratio by ~40% at the maximal dose of 20 µM (Figure 5B, p-for-trend = 0.063). The MAO-mix showed an intermediate effect (Figure 5C, p-for-trend = 0.010), while the Control-MAO did not decrease the FV-short/full-length FV transcript ratio (Figure 5D, p-for-trend = n.s.). Increasing the concentration of Donor-MAO or Acceptor-MAO to 50 µM did not result in any further decrease of the FV-short/full-length FV ratio (not shown).

Figure 5.
Quantitative analysis of full-length FV and FV-short transcripts in untreated and treated HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were treated with 0–20 µM morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (MAOs) for 48 h. Total RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and the full-length FV and FV-short transcripts were quantified by real-time qPCR analysis. The FV-short/full-length FV mRNA ratio, normalised to the FV-short/full-length FV ratio of untreated cells, was plotted as a function of the concentration of (A) a MAO targeting the FV-short-specific donor splice site (Donor-MAO), (B) a MAO targeting the FV-short-specific acceptor splice site (Acceptor-MAO), (C) a 1:1 mix of Donor-MAO and Acceptor-MAO (MAO-mix), and (D) a control MAO with an irrelevant sequence. Results are reported as mean ± S.E.M. of three biological replicates (two for the Control-MAO). The numbers in the top right corner of each graph represent the p-for-trend (Jonckheere-Terpstra trend test) of the respective titrations. Note the different y-axis scale for Control-MAO.
4. Discussion
F5 gene mutations that up-regulate FV-short splicing are associated with a bleeding tendency, such as in the recently characterised East Texas [22], Amsterdam [28] and Atlanta [29] bleeding disorders. This is due to the major increase in the level and anticoagulant activity of plasma TFPIα that accompanies FV-short over-expression [22]. Currently, there is no specific treatment for these bleeding disorders and their clinical management remains challenging. Affected patients have been treated with plasma and/or prothrombin complex concentrates [22,28], but therapies specifically targeting TFPIα (such as those used as bypassing agents for haemophilia) might be more appropriate. Although several aptamers, antibodies and peptides against TFPIα are already in various stages of development as therapeutic agents [37], in this study we propose an alternative strategy based on the use of antisense oligonucleotides to down-regulate FV-short splicing. The rationale for this approach is that elevated FV-short is the primary abnormality in the East Texas and allied bleeding disorders, and that FV-short is both the carrier of TFPIα in plasma [22] and a potent cofactor for its activity [25]. Therefore, down-regulating FV-short might be even more effective than antagonising TFPIα directly. Moreover, the liver, which is the main site of FV biosynthesis, is considered an optimal target for splicing modulation therapies [38], and MAOs generally show high bioavailability and low toxicity profiles in in vivo studies [39].
In order to decrease FV-short splicing, we have targeted the donor and acceptor splice sites that define the FV-short-specific intron. This was a somewhat necessary choice, because enhancers and silencers potentially regulating FV-short splicing are presently unknown and, due to their rather degenerate consensus sequences, cannot be easily predicted in silico. However, splicing regulatory elements are likely to play an important role in the physiological control of FV-short splicing, as suggested by (a) the very low in vivo expression of FV-short despite the relatively high consensus scores (>80%) of the FV-short-specific donor and acceptor splice sites; and (b) the massive up-regulation of FV-short splicing associated with the F5-Atlanta deletion [29], which presumably acts by eliminating one or more splicing silencers or by bringing a splicing enhancer closer to the FV-short donor splice site [40]. Therefore, future elucidation of these additional splicing signals may suggest novel and better targets for antisense-mediated FV-short splicing modulation.
The ability of our MAOs to decrease FV-short splicing was tested in vitro in HepG2 cells, which express both full-length FV and FV-short mRNA in proportions similar to normal hepatocytes. Both MAOs, alone or in combination, dose-dependently decreased the FV-short/full-length FV ratio down to ~50% of its original value in the absence of treatment. Some scattering in the qPCR data might be attributed to the very low concentration of the FV-short mRNA already before treatment, and the consequent extremely narrow dynamic range following treatment. The effects of the two MAOs were specific, but (contrary to our expectation) not synergistic. To produce an appreciable change in the overall splicing pattern, MAOs need to access a substantial fraction of cells and to end up in the nucleus. Although MAO transfection efficiency was unfortunately not evaluated in our study, previous work from our laboratory suggests that the Endo-Porter reagent is able to effectively deliver MAOs to HepG2 cells, as judged by the high efficiency of splicing correction achieved upon treatment with a mutation-specific MAO [11]. Moreover, the analysis of the F5 gene in HepG2 cells excluded F5 gene amplification, as well as the presence of sequence variations that could interfere with the annealing of the MAOs to their intended target sites on the F5 pre-mRNA. Therefore, we speculate that the inability of our MAOs to reduce FV-short expression below 50% (even at a concentration of 50 µM) may be related to the complexity of alternative splicing regulation [41], which involves many other mechanisms (epigenetics, transcription rate, pre-mRNA secondary structures, etc.) and regulatory elements (splicing enhancers and silencers, trans-acting splicing factors) than just the donor and acceptor splice sites.
Since the FV-short concentration in conditioned media was too low for detection by Western blot analysis and no other assay is currently available to measure FV-short, we could unfortunately not verify whether the observed reduction in FV-short mRNA upon MAO treatment also translates in a decrease in FV-short protein expression. This is a major limitation of our study. Moreover, it should be emphasised that, unlike the East Texas [22], Amsterdam [28] and Atlanta [29] patients, the HepG2 cell model employed in our study has a normal F5 exon 13 sequence and a very low basal expression of FV-short. Therefore, it remains to be established whether an antisense-mediated approach using mutation-specific MAOs would be able to correct FV-short over-expression in models of these diseases, such as patients’ induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived hepatocytes. On the other hand, it is worth noting that FV-short levels show major inter-individual differences even in the absence of F5 gene mutations, and that high levels and/or activity of TFPIα contribute to the haemorrhagic tendency in various coagulopathies, from haemophilia [42] to bleeding arising from unknown causes [43,44]. Therefore, antisense-mediated strategies aimed at decreasing FV-short splicing might be more widely applicable than just to the East Texas and allied disorders.
As a by-product of this study, the carefully optimised (q)PCR-based protocol for the detection and quantification of the FV-short transcript may find application in the analysis of this splicing variant in total RNA samples from primary hepatocytes and other cell types under various (pathological) conditions. Since the F5 gene is robustly transcribed in blood cells, FV-short transcript levels determined in whole blood RNA might serve as a surrogate marker for protein levels until a FV-short ELISA becomes available.
Finally, we have serendipitously identified a new F5 splicing event between exons 12 and 13, which eliminates the first 123 nucleotides of exon 13, predicting the in-frame deletion of amino acids 659–699 between the A2 and B domains of FV. Whether the low-abundance alternatively spliced transcript containing this deletion is also translated into protein is currently unknown. Interestingly, this alternative splicing event is yet different from the one recently reported as an incidental finding in the F5-Atlanta paper [29], further underscoring the variety and complexity of the splicing pattern of this region of the F5 gene.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this pilot study provides in vitro proof-of-principle for the possibility to specifically down-regulate FV-short mRNA expression using MAOs targeting the donor and acceptor splice sites of the FV-short-specific intron. Additional work is needed to validate these findings at the protein level and to extend them to more relevant models of FV-short over-expression. Considering the dual function of FV-short as a carrier and cofactor of TFPIα, antisense-based down-regulation of FV-short splicing may eventually create opportunities for novel therapeutic avenues for various bleeding disorders caused by elevated TFPIα (activity) levels.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11209621/s1, Figure S1: Supplementary Figure S1 Sequencing chromatogram of the 473-bp band corresponding to the full-length FV transcript shown in Figure 4 of the manuscript and Sequencing chromatogram of the 397-bp band corresponding to the FV-short transcript shown in Figure 4 of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, E.C.; methodology, A.M.T. and E.C.; investigation, A.M.T.; formal analysis, A.M.T. and E.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.T.; writing—review and editing, E.C. and T.M.H.; visualisation, A.M.T. and E.C.; supervision, E.C. and T.M.H.; funding acquisition, T.M.H. and E.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was initiated under the auspices of the Dutch Thrombosis Foundation (TSN grant 2014-1) and further developed with financial support of the Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht (CARIM).
Conflicts of Interest
T.M.H. is co-founder and shareholder of Coagulation Profile BV. The other authors have no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, Z.; Burge, C.B. Splicing regulation: From a parts list of regulatory elements to an integrated splicing code. RNA 2008, 14, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblihtt, A.R.; Schor, I.E.; Allo, M.; Dujardin, G.; Petrillo, E.; Munoz, M.J. Alternative splicing: A pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen, T.W.; Graveley, B.R. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature 2010, 463, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.I.; van de Geijn, B.; Raj, A.; Knowles, D.A.; Petti, A.A.; Golan, D.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. RNA splicing is a primary link between genetic variation and disease. Science 2016, 352, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, J.; Baralle, D. Splicing in the Diagnosis of Rare Disease: Advances and Challenges. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 689892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.M.; Wood, M.J. Genetic therapies for RNA mis-splicing diseases. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, A.J.; Gamarra, J.R.; Giudice, J. More than a messenger: Alternative splicing as a therapeutic target. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, D.; Branchini, A. Molecular Mechanisms and Determinants of Innovative Correction Approaches in Coagulation Factor Deficiencies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havens, M.A.; Hastings, M.L. Splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6549–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.L.; Homer, V.M.; George, P.M.; Brennan, S.O. A deep intronic mutation in FGB creates a consensus exonic splicing enhancer motif that results in afibrinogenemia caused by aberrant mRNA splicing, which can be corrected in vitro with antisense oligonucleotide treatment. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, F.; Radu, C.; Baralle, M.; Spiezia, L.; Hackeng, T.M.; Simioni, P.; Castoldi, E. Antisense-based RNA therapy of factor V deficiency: In vitro and ex vivo rescue of a F5 deep-intronic splicing mutation. Blood 2013, 122, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nuzzo, F.; Bulato, C.; Nielsen, B.I.; Lee, K.; Wielders, S.J.; Simioni, P.; Key, N.S.; Castoldi, E. Characterization of an apparently synonymous F5 mutation causing aberrant splicing and factor V deficiency. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, D.; Barbon, E.; Scalet, D.; Cavallari, N.; Perrone, D.; Zanibellato, S.; Bernardi, F.; Pinotti, M. Regulation of a strong F9 cryptic 5′ss by intrinsic elements and by combination of tailored U1snRNAs with antisense oligonucleotides. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4809–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.A. Treating Disease at the RNA Level with Oligonucleotides. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooke, S.T.; Liang, X.H.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, R.M. Antisense technology: A review. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlbäck, B. Pro- and anticoagulant properties of factor V in pathogenesis of thrombosis and bleeding disorders. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.H.A.; Camire, R.M. A Bipartite Autoinhibitory Region within the B-domain Suppresses Function in Factor V. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26342–26351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosing, J.; Tans, G.; Govers-Riemslag, J.W.; Zwaal, R.F.; Hemker, H.C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.P.; Ellery, P.E.R.; Maroney, S.A.; Mast, A.E. Biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood 2014, 123, 2934–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.P.; Bunce, M.W.; Maroney, S.A.; Tracy, P.B.; Camire, R.M.; Mast, A.E. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-alpha inhibits prothrombinase during the initiation of blood coagulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17838–17843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, P.; Rosing, J.; Wielders, S.J.; Hackeng, T.M.; Castoldi, E. The C-terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-alpha inhibits factor V activation by protecting the Arg1545 cleavage site. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.M.; Tran, S.; Livaja, R.; Bensend, T.A.; Milewicz, D.M.; Dahlbäck, B. Coagulation factor V(A2440G) causes east Texas bleeding disorder via TFPIα. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrillo, T.; Ayombil, F.; Van’t Veer, C.; Camire, R.M. Regulation of factor V and factor V-short by TFPIalpha: Relationship between B-domain proteolysis and binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckers, C.; Simioni, P.; Spiezia, L.; Radu, C.; Gavasso, S.; Rosing, J.; Castoldi, E. Low plasma levels of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with congenital factor V deficiency. Blood 2008, 112, 3615–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlbäck, B.; Guo, L.J.; Livaja-Koshiar, R.; Tran, S. Factor V-short and protein S as synergistic tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPIalpha) cofactors. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlbäck, B.; Tran, S. The preAR2 region (1458–1492) in Factor V-Short is crucial for the synergistic TFPIalpha-cofactor activity with protein S and the assembly of a trimolecular Factor Xa-inhibitory complex comprising FV-Short, protein S and TFPIalpha. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.Q.; Hasham, S.; Phillips, M.D.; Wolf, D.; Wan, Y.; Thiagarajan, P.; Milewicz, D.M. Characterization of a novel autosomal dominant bleeding disorder in a large kindred from east Texas. Blood 2001, 97, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.L.; Bakhtiari, K.; Peter, J.; Marquart, J.A.; Meijers, J.C.; Middeldorp, S. A novel mutation in the F5 gene (factor V Amsterdam) associated with bleeding independent of factor V procoagulant function. Blood 2015, 125, 1822–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimowski, K.L.; Petrillo, T.; Ho, M.D.; Wechsler, J.; Shields, J.E.; Denning, G.; Jhita, N.; Rivera, A.A.; Escobar, M.A.; Kempton, C.L.; et al. F5-Atlanta: A novel mutation in F5 associated with enhanced East Texas splicing and FV-short productio. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, F.O.; Hamroun, D.; Lalande, M.; Collod-Beroud, G.; Claustres, M.; Beroud, C. Human Splicing Finder: An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerton, J.; Weller, D. Morpholino antisense oligomers: Design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997, 7, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Terrada, D.; Cheung, S.W.; Finegold, M.J.; Knowles, B.B. Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1512–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Ho, S.S.; Greer, S.U.; Spies, N.; Bell, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Arthur, J.G.; Byeon, S.; Pattni, R.; et al. Haplotype-resolved and integrated genome analysis of the cancer cell line HepG2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3846–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, J.P.; McElgunn, C.J.; Waaijer, R.; Zwijnenburg, D.; Diepvens, F.; Pals, G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, F.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Straniero, L.; Pavlova, A.; Duga, S.; Castoldi, E. Identification of a novel large deletion in a patient with severe factor V deficiency using an in-house F5 MLPA assay. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ramakers, C.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Karlen, Y.; Bakker, O.; van den Hoff, M.J.; Moorman, A.F. Amplification efficiency: Linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdary, P. Anti-tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) therapy: A novel approach to the treatment of haemophilia. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 111, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, A.; Vaishnaw, A.; Fitzgerald, K. Liver as a target for oligonucleotide therapeutics. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amantana, A.; Iversen, P.L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of phosphorodiamidate morpholino antisense oligomers. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, E. F5-Atlanta: Factor V-short strikes again. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1638–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenasa, H.; Hertel, K.J. Combinatorial regulation of alternative splicing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelle, P.; Montmartin, A.; Damien, P.; Piot, M.; Cournil, M.; Lienhart, A.; Genre-Volot, F.; Chambost, H.; Morin, C.; Tardy-Poncet, B. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor is the main determinant of thrombin generation in haemophilic patients. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, S.; White, D.; Langdown, J.; Downes, K.; Thomas, W. Investigation of patients with unclassified bleeding disorder and abnormal thrombin generation for physiological coagulation inhibitors reveals multiple abnormalities and a subset of patients with increased tissue factor pathway inhibitor activity. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehic, D.; Tolios, A.; Hofer, S.; Ay, C.; Haslacher, H.; Rejto, J.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Downes, K.; Haimel, M.; Pabinger, I.; et al. Elevated levels of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with mild to moderate bleeding tendency. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).