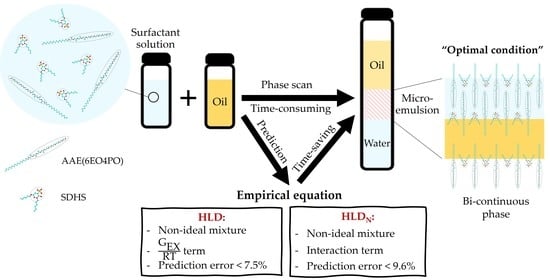
A Normalized HLD (HLDN) Tool for Optimal Salt-Concentration Prediction of Microemulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
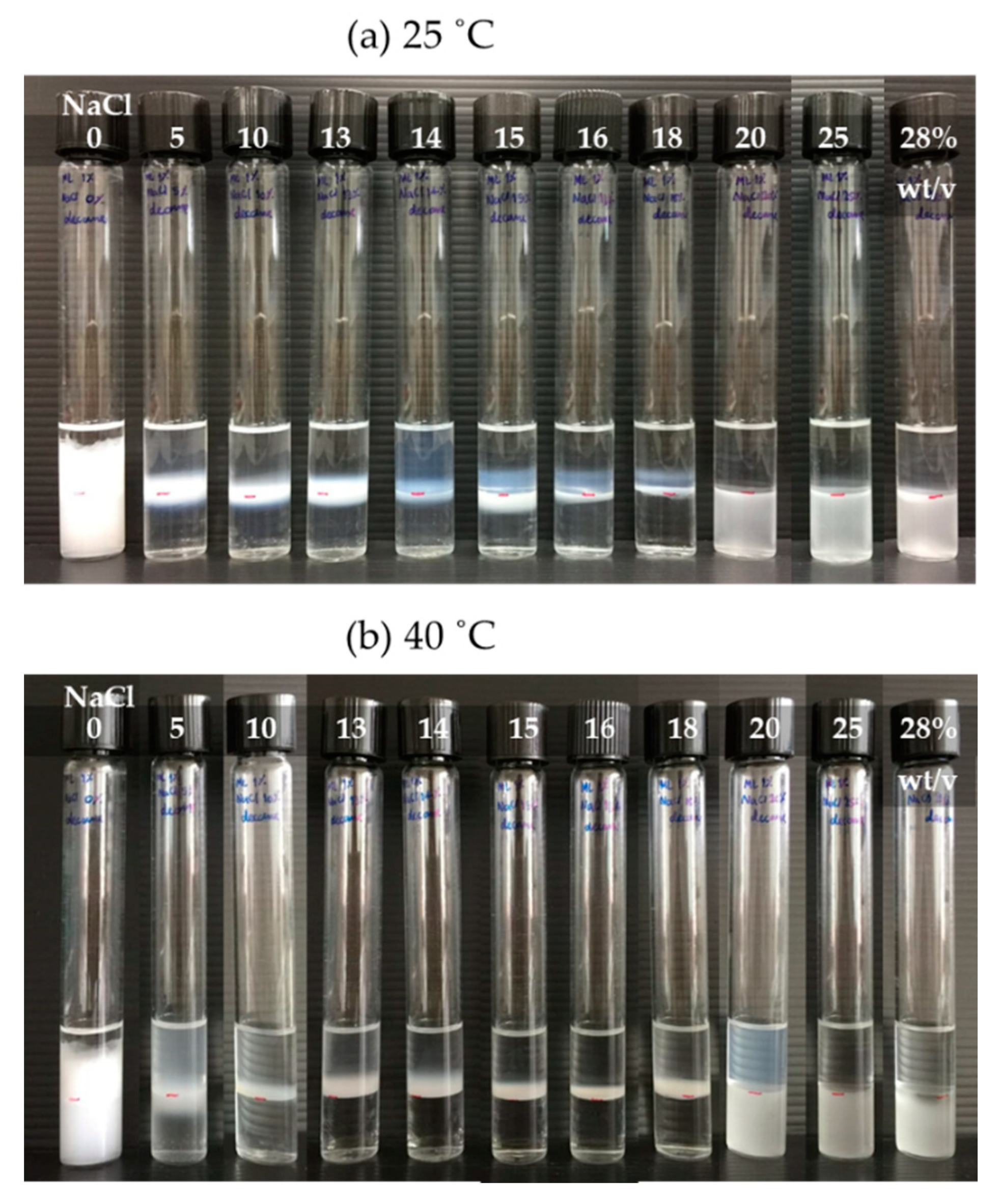
2.2. Microemulsion Phase Behaviors
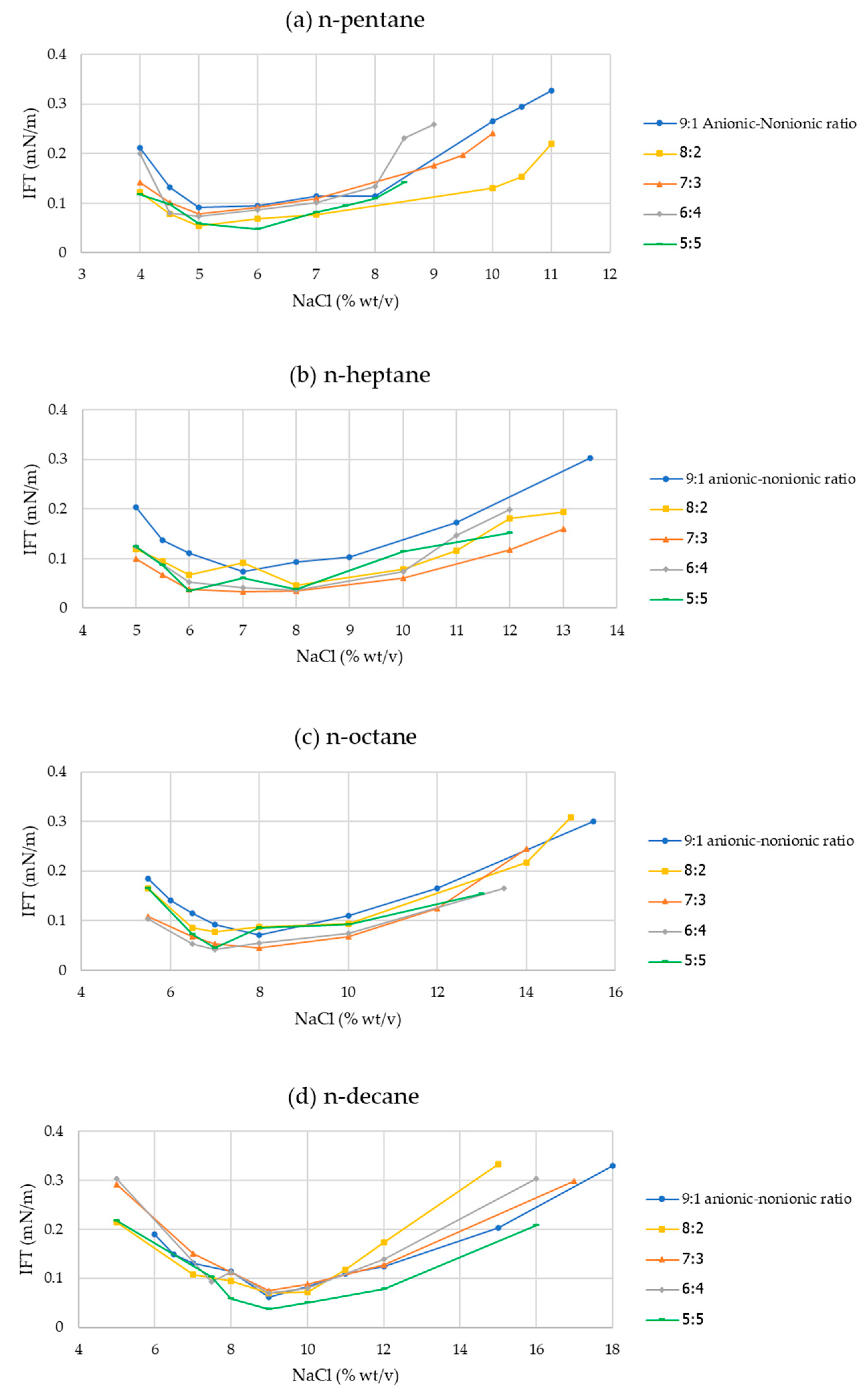
2.3. Interfacial Tension (IFT) Measurement
2.4. Empirical Models (HLD and HLDN)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Behavior of AAE(6EO4PO)
3.2. Phase Behavior of the SDHS-AAE(6EO4PO) Mixed System
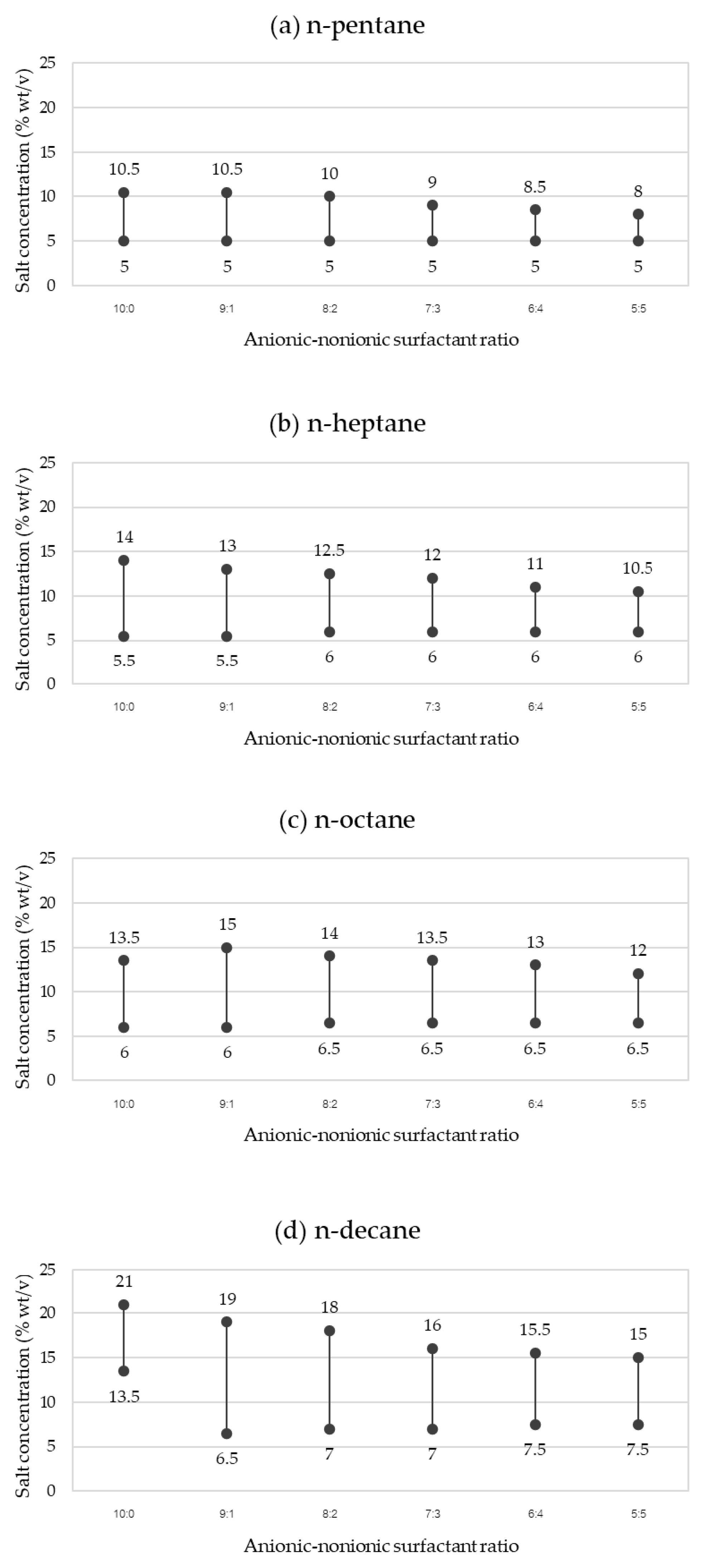
3.3. Interfacial Tension (IFT) and Optimal Salt Concentration of the SDHS-AAE(6EO4PO) Mixed System
3.4. HLD Equation of AAE(6EO4PO)
3.5. HLD Equation of the SDHS-AAE(6EO4PO) Systems
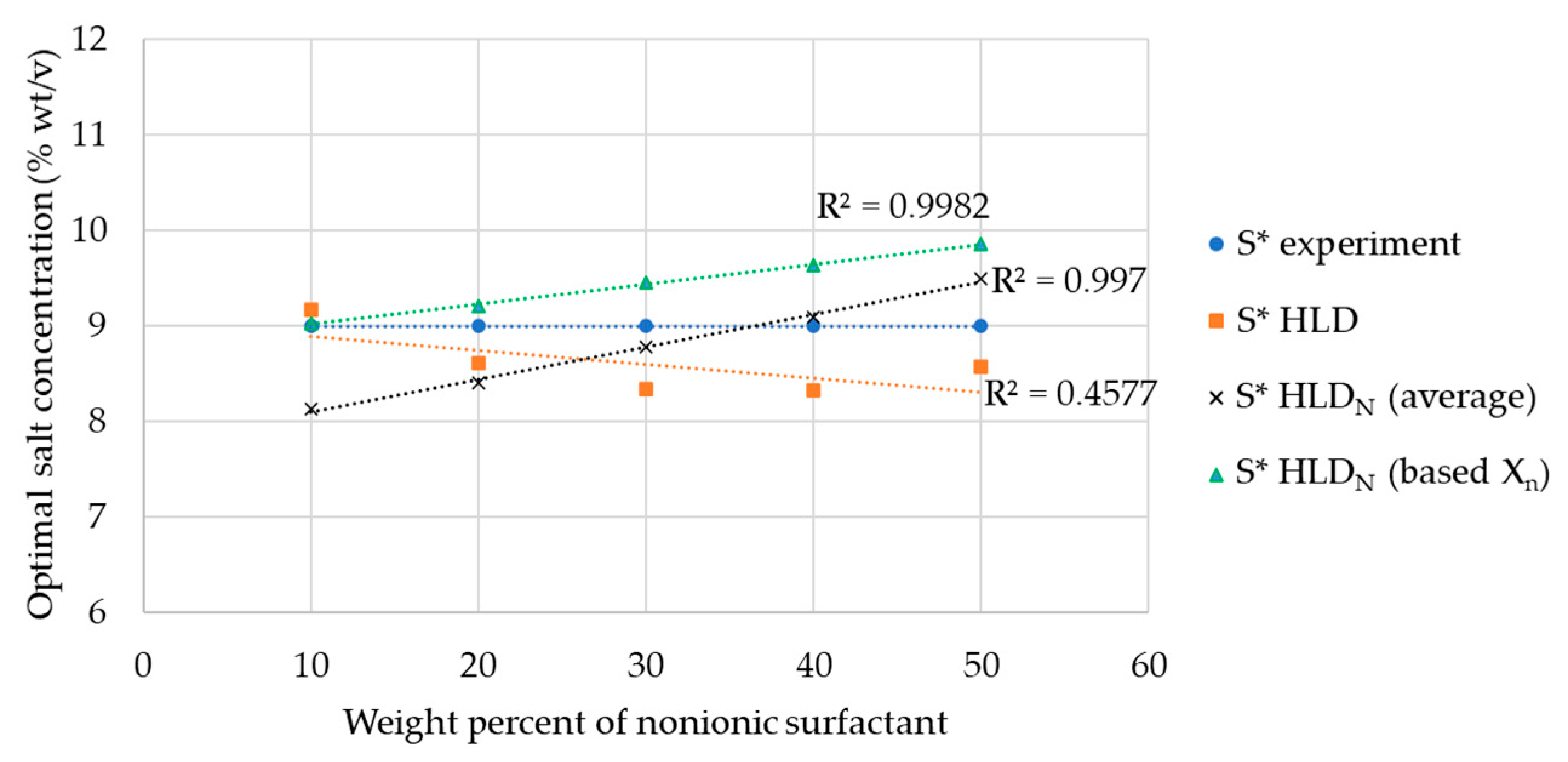
3.6. HLDN Equation of SDHS-AAE(6EO4PO) Systems
3.7. Prediction of Optimal Salt Concentration for Diesel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tadros, T. Encyclopedia of Colloid and Interface Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Agneta, M.; Zhaomin, L.; Chao, Z.; Gerald, G. Investigating synergism and antagonism of binary mixed surfactants for foam efficiency optimization in high salinity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Chang, H.W.; Cody, R.D. Synergism effect of mixed surfactant solutions in remediation of soil contaminated with PCE. Geosci. J. 2004, 8, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, D.A.; Knox, R.C.; Harwell, J.H.; Wu, B. Integrated design of surfactant enhanced DNAPL remediation: Efficient supersolubilization and gradient systems. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 45, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Yin, X. Effect of anionic-nonionic-mixed surfactant micelles on solubilization of PAHs. J. Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2013, 63, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z. Anionic–nonionic mixed-surfactant-enhanced remediation of PAH-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12769–12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Enhanced Soil Washing of Phenanthrene by Mixed Solutions of TX100 and SDBS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4274–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, W. Enhanced desorption and biodegradation of phenanthrene in soil–water systems with the presence of anionic–non-ionic mixed surfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhu, L. Enhanced soil flushing of phenanthrene by anionic-nonionic mixed surfactant. Water Res. 2008, 42, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.Q.; Zhang, M.J.; Fang, Y.; Jin, G.Y.; Chen, J. Extended surfactants: A well-designed spacer to improve interfacial performance through a gradual polarity transition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng Asp. 2014, 450, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñana-Perez, M.; Graciaa, A.; Lachaise, J.; Salager, J.L. Solubilization of polar oils with extended surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng Asp. 1995, 100, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.; Attaphong, C.; Sabatini, D.A. Effect of Extended Surfactant Structure on Interfacial Tension and Microemulsion Formation with Triglycerides. J. Am. Oil Chem Soc. 2011, 88, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, J.; Scorzza, C.; Vejar, F.; Vejar, A.M.; Antón, R.E.; Salager, J.L. Effect of Temperature and Other Variables on the Optimum Formulation of Anionic Extended Surfactant–Alkane–Brine Systems. J. Surfact Deterg. 2010, 13, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthayapanyanon, A.; Phan, T.T.; Heitmann, T.C.; Harwell, J.H.; Sabatini, D.A. Interfacial Properties of Extended-Surfactant-Based Microemulsions and Related Macroemulsions. J. Surfact Deterg. 2010, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, A.; Tiddy, G.J.T.; Solans, C.; Harrar, A.; Touraud, D.; Kunz, W. Effect of Salts on the Phase Behavior and the Stability of Nano-Emulsions with Rapeseed Oil and an Extended Surfactant. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8318–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Luo, D.; Peng, B. Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension Foam System for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, M.J.; Wang, H.; Shen, P.; Zhu, Y. Ultralow Interfacial Tension for Enhanced Oil Recovery at Very Low Surfactant Concentrations. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghraby, G.M.E.; Arafa, M.F.; Essa, E.A. Phase transition microemulsions as drug delivery systems. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery, 1st ed.; Inamuddin, A.M., Mohammad, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2018; pp. 787–803. [Google Scholar]
- Quintero, L.; Carnahan, N.F. Microemulsions for Cleaning Applications. Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning. In Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning, 1st ed.; Kohli, R., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; William Andrew: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 65–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wiącek, A.; Chibowski, E. Stability of oil/water (ethanol, lysozyme or lysine) emulsions. Colloids Surf. B 2000, 17, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Wiącek, A.; Holysz, L.; Terpilowski, K. Investigation of the electrokinetic properties of paraffin suspension. 2. In cationic and anionic surfactant solutions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7662–7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibowski, E.; Wiącek, A.E.; Holysz, L.; Terpilowski, K. investigation of the electrokinetic properties of paraffin suspension. 1. In inorganic electrolyte solutions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4347–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Mandal, A. Microemulsions: A novel approach to enhanced oil recovery: A review. J. Petrol. Explor Prod. Technol. 2015, 5, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, L.D.; Witthayapanyanon, A.; Harwell, J.H.; Sabatini, D.A. Environmentally Friendly Vegetable Oil Microemulsions Using Extended Surfactants and Linkers. J. Surfact Deterg. 2009, 12, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsor, P.A. Hydrotropy, solubilisation and related emulsification processes: Part I. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1948, 44, 376–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthayapanyanon, A.; Harwell, J.H.; Sabatini, D.A. Hydrophilic-lipophilic deviation (HLD) method for characterizing conventional and extended surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Morgan, J.C.; Schechter, R.S.; Wade, W.H.; Spe-Aime, M.; Vasquez, E. Optimum Formulation of Surfactant/Water/Oil Systems for Minimum Interfacial Tension or Phase Behavior. Soc. Pet. Eng. AIME J. 1979, 19, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Forgiarini, A.M.; Bullón, J. How to attain ultralow interfacial tension and three-phase behavior with surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: A review. Part 1. Optimum formulation for simple surfactant-oil-water ternary systems. J. Surfact Deterg. 2013, 16, 449–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Forgiarini, A.M.; Márquez, L.; Manchego, L.; Bullón, J. How to attain ultralow interfacial tension and three-phase behavior with surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: A review. Part 2. Performance improvement trends from Winsor’s premise to currenly proposed inter- and intra-molecular mixtures. J. Surfact Deterg. 2013, 16, 631–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szekeres, E.; Acosta, E.; Sabatini, D.A.; Harwell, H. Preferential solubilization of dodecanol from dodecanol-limonene binary oil mixture in sodium dihexyl sulfosuccinate microemulsions: Effect on optimum salinity and oil solubilization capacity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, W.H.; Morgan, J.C.; Schechter, R.S.; Spe-aime, M.; Jacobson, J.K.; Salager, J.L. Interfacial Tension and Phase Behavior of Surfactant Systems. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1978, 18, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrel, M.; Salager, J.L.; Schechter, R.S.; Wade, W.H. A Correlation for Phase Behavior of Nonionic Surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 75, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, W.; Testard, F.; Zemb, T. Correspondence between Curvature, Packing Parameter, and Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Deviation Scales around the Phase-Inversion Temperature. Langmuir 2009, 25, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardello, V.; Chailloux, N.; Poprawski, J.; Salager, J.L.; Aubry, J.M. HLD concept as a tool for the characterization of cosmetic hydrocarbon oils. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Morgan, C.; Poindexter, L.; Fernandez, J. Application of the Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Deviation Concept to Surfactant Characterization and Surfactant Selection for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Surfact Deterg. 2019, 22, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Antón, R.E. Physico-chemical characterization of a surfactant a quick and precise method. J. Dispers Sci. Technol. 1983, 4, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L. Formulation Concepts for the Emulsion Maker. In Pharmaceutical Emulsions and Suspensions; Nielloud, F., Marti-Mestres, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 19–72. [Google Scholar]
- Salager, J.L.; Márquez, L.; Pena, A.A.; Rondón, M. Current Phenomenological Know-How and Modeling of Emulsion Inversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Marquez, N.; Graciaa, A.; Lachaise, J. Partitioning of Ethoxylated Octylphenol Surfactants in Microemulsion-Oil-Water Systems: Influence of Temperature and Relation between Partitioning Coefficient and Physicochemical Formulation. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5534–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, E.J.; Yuan, J.S.; Bhakta, A.S. The characteristic curvature of ionic surfactants. J. Surfact Deterg. 2008, 11, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, E.J.; Bhakta, A.S. The HLD-NAC model for mixtures of ionic and nonionic surfactants. J. Surfact Deterg. 2009, 12, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; Lichtenthaler, R.N.; de Azevedo, E.G. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, E.J.; Kiran, S.K.; Hammond, C.E. The HLD-NAC Model for Extended Surfactant Microemulsions. J. Surfact Deterg. 2012, 15, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpornpong, N.; Charoensaeng, A.; Khaodhiar, S.; Sabatini, D.A. Formulation of microemulsion-based washing agent for oil recovery from spent bleaching earth-hydrophilic lipophilic deviation concept. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 541, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, M.; Hsu, T.P.; Lohateeraparp, P.; Roberts, B.L.; Shiau, B.J.; Harwell, J.H. Design of an optimal middle phase microemulsion for ultra high saline brine using hydrophilic lipophilic deviation (HLD) method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 488, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Johns, R.T. A new HLD-NAC based EOS approach to predict surfactant-oil-brine phase behavior for live oil at reservoir pressure and temperature. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–29 October 2014; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.K.; Acosta, E.J.; Moran, K. Evaluating the hydrophilic–lipophilic nature of asphaltenic oils and naphthenic amphiphiles using microemulsion models. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Sabatini, D.A. Characterization and Emulsification Properties of Rhamnolipid and Sophorolipid Biosurfactants and Their Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poprawski, J.; Catté, M.; Marquez, L.; Marti, M.J.; Salager, J.L.; Aubry, J.M. Application of hydrophilic–lipophilic deviation formulation concept to microemulsions containing pine oil and nonionic surfactant. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittithammavong, V.; Charoensaeng, A.; Khaodhiar, S. Effect of Ethylene Oxide (EO) Group in the Anionic-Nonionic Mixed Surfactant System on Microemulsion Phase Behavior. J. Surfact Deterg. 2020, 24, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.L.; Antón, R.E.; Bullón, J.; Forgiarini, A.; Marquez, R. How to use the normalized hydrophilic-lipophilic deviation (hldn) concept for the formulation of equilibrated and emulsified surfactant-oil-water systems for cosmetics and pharmaceutical products. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasol. Specialty product: Marlox RT64 Material Safety Data Sheet. Available online: http://www.sasoltechdata.com/td_productgroup.asp?VTI-GROUP=0&ProductGroup=Specialty+Products&btnSearch=Search (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Sasol Performance Chemicals. Low foaming nonionic Surfactants and Specialities. Sasol Performance Chemicals, Organics Division. Available online: https://sasoldcproducts.blob.core.windows.net/documents/Product%20Brochures/US_Surfactants%20Nonionic_Low%20foaming%20nonionic%20surfactants%20and%20specialities.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Acosta, E.J. The HLD-NAC equation of state for microemulsions formulated with nonionic alcohol ethoxylate and alkylphenol ethoxylate surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 320, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, S.Z.; Vasconcelos, F.T.; Myat, K.M.; Minchom, J.; Acosta, E. A simplified methodology to measure the characteristic curvature (Cc) of alkyl ethoxylate nonionic surfactants. J. Surfact Deterg. 2016, 19, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiącek, A.E.; Chibowski, E.; Wilk, K. Studies of oil-in-water emulsion stability in the presence of new dicephalic saccharide-derived surfactants. Colloids Surf. B 2002, 25, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiącek, A.; Chibowski, E. Zeta potential, effective diameter and multimodal size distribution in oil/water emulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 159, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiącek, A.E.; Adryanczyk, E. Interfacial properties of phosphatidylcholine-based dispersed systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongcumpou, C.; Acosta, E.J.; Quencer, L.B.; Joseph, A.F.; Scamehorn, J.F.; Sabatini, D.A.; Chavadej, S.; Yanumet, N. Microemulsion formation and detergency with oily soils: I. Phase behavior and interfacial tension. J. Surfact Deterg. 2003, 6, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, H.; Acosta, E.; Tran, S.; Sabatini, D.A.; Harwell, J.H. Supersolubilization in chlorinated hydrocarbon microemulsions: Solubilization enhancement by lipophilic and hydrophilic linkers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2704–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, Y.; Basily, I.K.; Mohamad, A.I.; Youssef, A.M. Polymeric Surfactants for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Part III-Interfacial Tension Features of Ethoxylated Alkylphenol-Formaldehyde Nonionic Surfactants. Br. Polym. J. 1989, 21, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundara, P.; Fu, E.; Xu, Q. Coadsorption of Anionic and Nonionic Surfactant Mixtures at the Alumina-Water Interface. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zana, R.; Kaler, E.W. Giant Micelles Properties and Applications: Surfactant Science Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, E.J.; Szekeres, E.; Harwell, J.H.; Grady, B.P.; Sabatini, D.A. Morphology of ionic microemulsions: Comparison of SANS studies and the net-average curvature (NAC) model. R. Soc. Chem. 2009, 5, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jamili, A.; Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Luo, H.; Shiau, B.J.B.; Delshad, M.; Harwell, J.H. Physics based HLD-NAC phase behavior model for surfactant/crude oil/brine systems. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 136, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

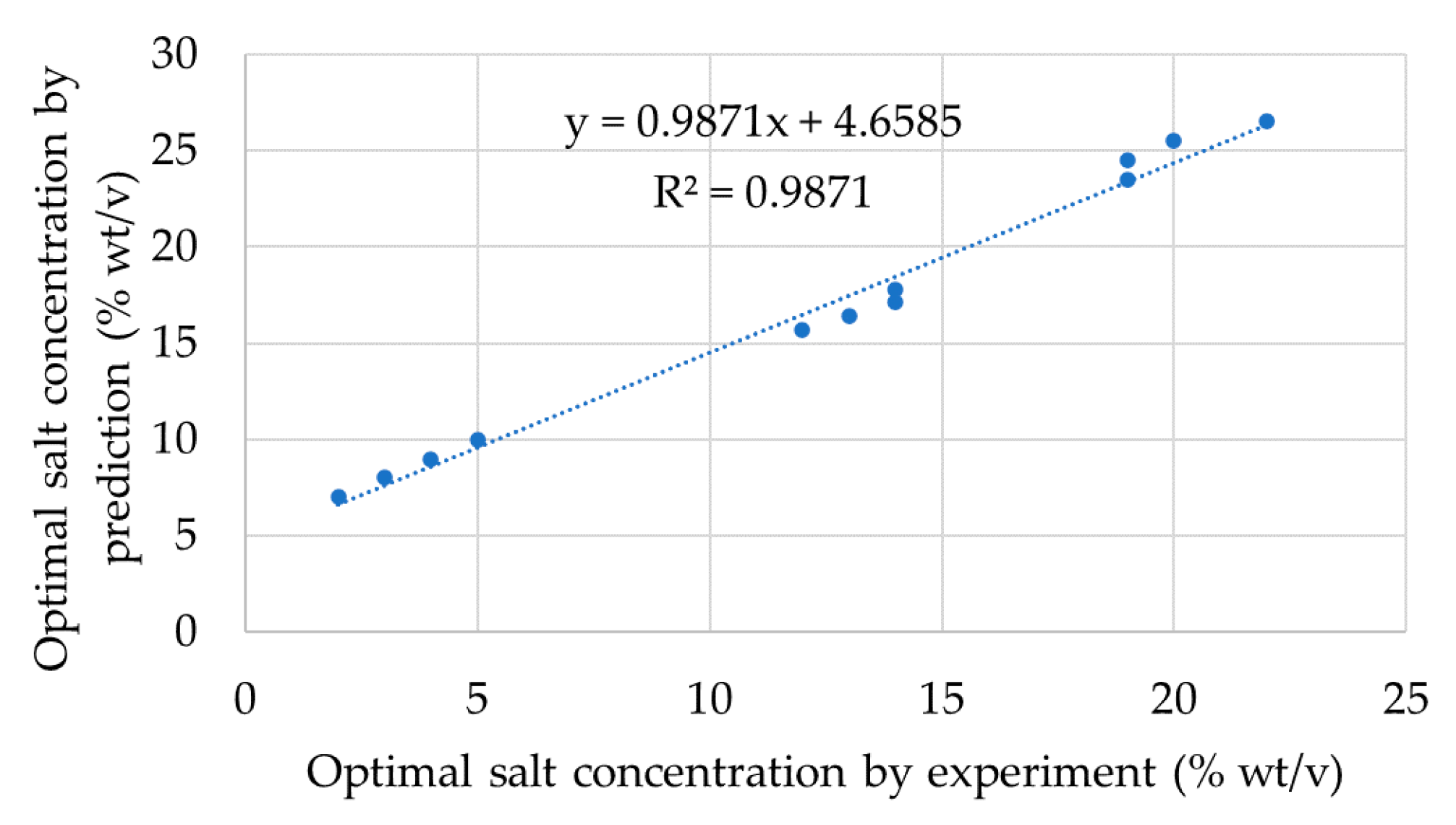
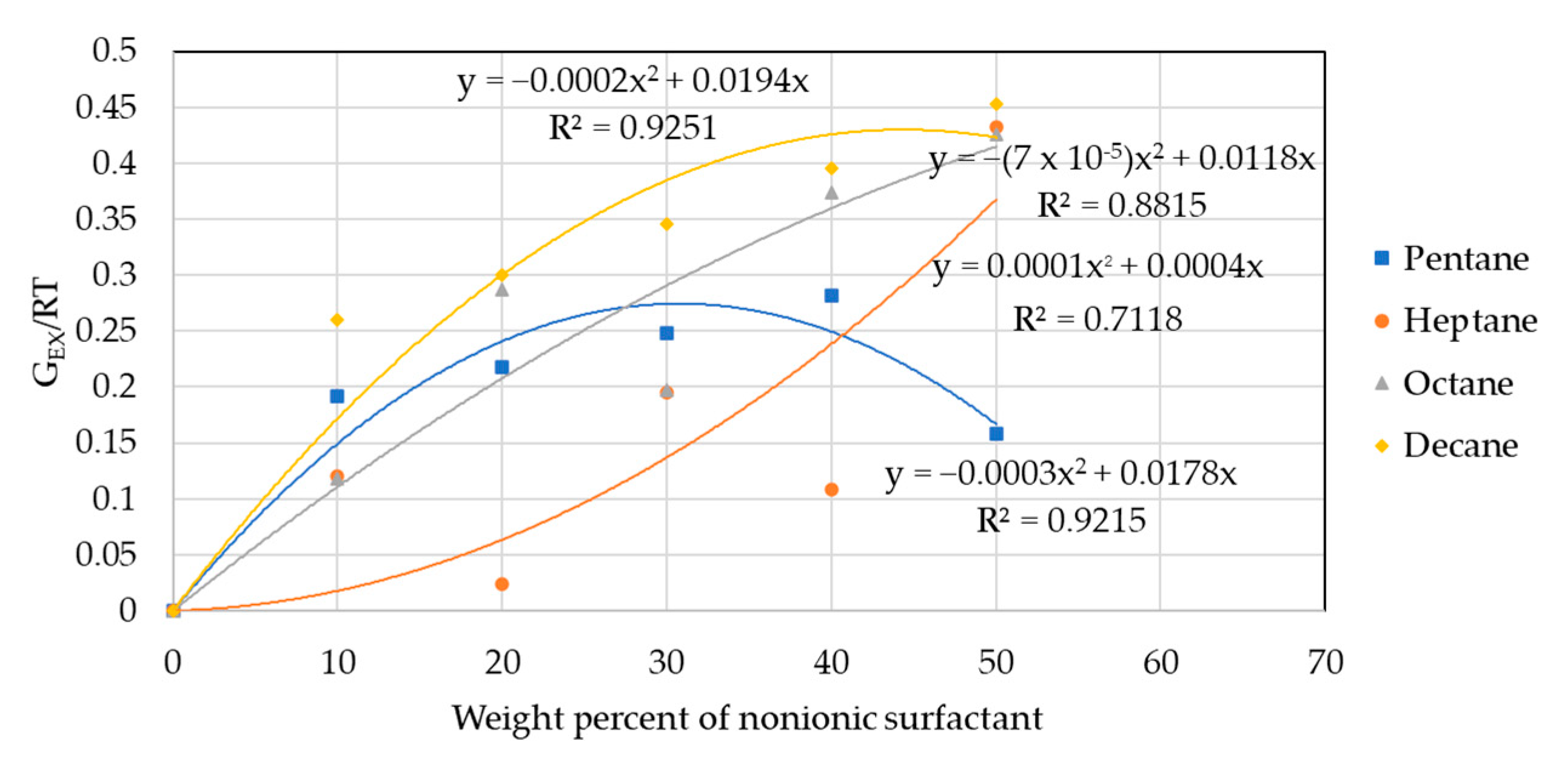
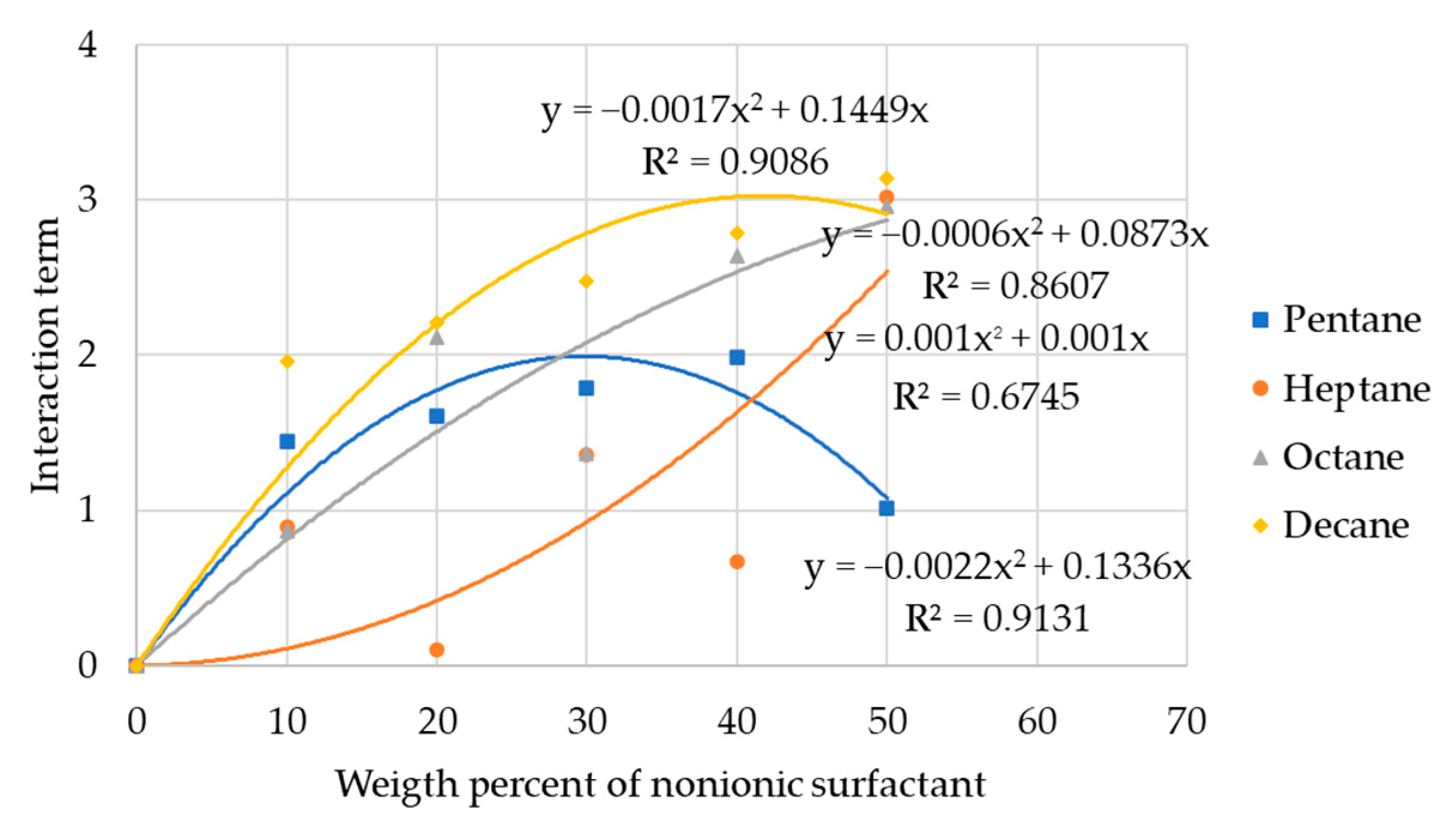
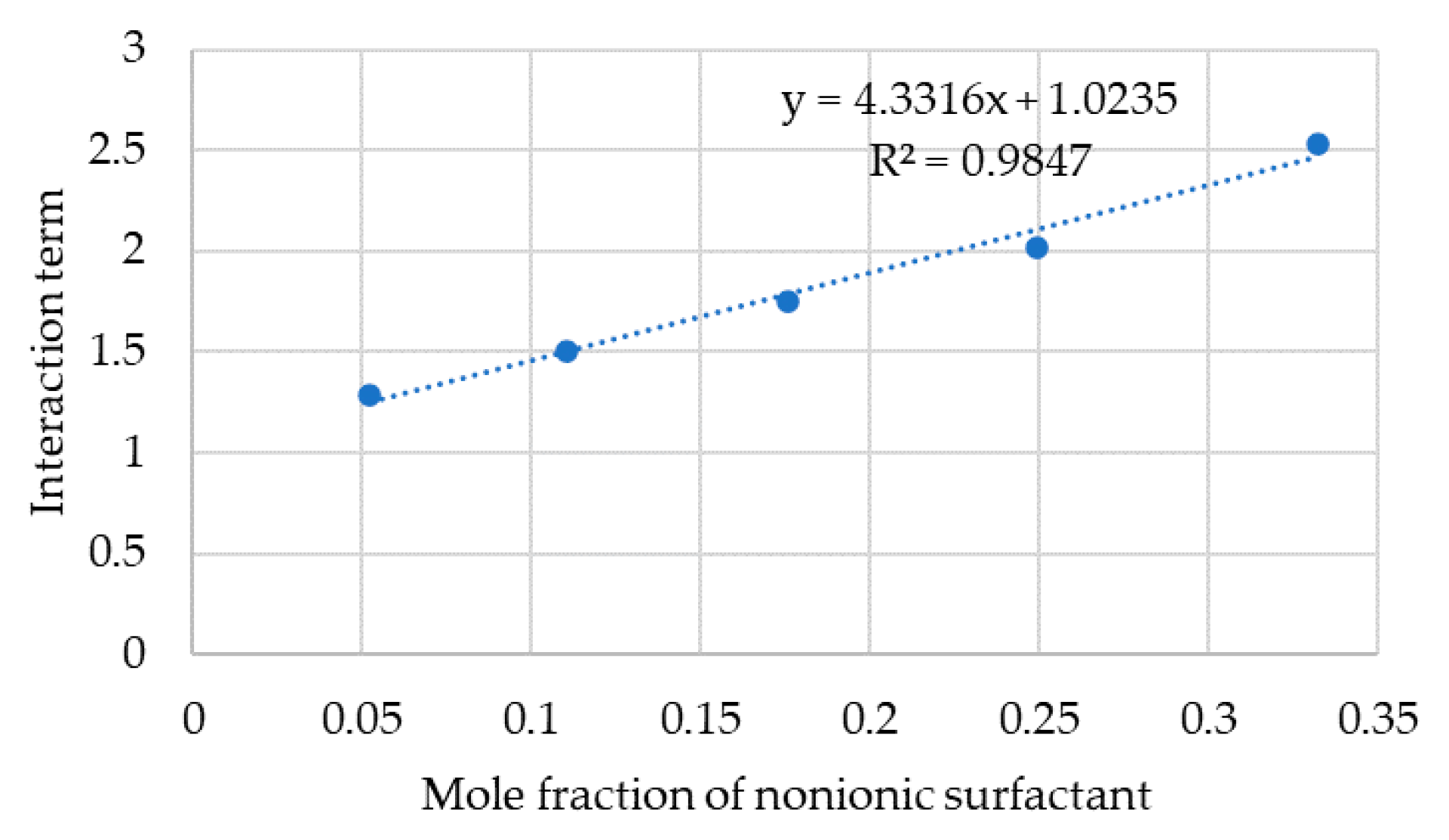
| Surfactant Name | Formula | MW (g/mol) | L (Å) | CMC (%wt/v) | HLB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium dihexyl sulfosuccinate (SDHS) | C16H29NaO7S | 388 1 | 10 3 | 0.25 | - |
| Alcohol, C16-18, 6-ethoxylated 4-propoxylated Alkyl polyglycol ether (AAE(6EO4PO)) | C17H35(PO)4(EO)6OH | 784 2 | 35.7 4 | 0.08 | 10 2 |
| Anionic–Nonionic Ratio | Oil | EACN | Optimal NaCl concentration (S*) (% wt/v) | IFT* (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:0 | n-pentane | 5 | 6 1 | 0.091 ± 0.009 1 |
| 9:1 | n-pentane | 5 | 5 | 0.091 ± 0.006 |
| 8:2 | n-pentane | 5 | 5 | 0.054 ± 0.001 |
| 7:3 | n-pentane | 5 | 5 | 0.078 ± 0.005 |
| 6:4 | n-pentane | 5 | 5 | 0.074 ± 0.005 |
| 5:5 | n-pentane | 5 | 6 | 0.047 ± 0.004 |
| 10:0 | n-heptane | 7 | 7 1 | 0.089 ± 0.000 1 |
| 9:1 | n-heptane | 7 | 7 | 0.073 ± 0.000 |
| 8:2 | n-heptane | 7 | 8 | 0.046 ± 0.004 |
| 7:3 | n-heptane | 7 | 7 | 0.033 ± 0.002 |
| 6:4 | n-heptane | 7 | 8 | 0.036 ± 0.003 |
| 5:5 | n-heptane | 7 | 6 | 0.034 ± 0.003 |
| 10:0 | n-octane | 8 | 8 1 | 0.138 ± 0.000 1 |
| 9:1 | n-octane | 8 | 8 | 0.071 ± 0.004 |
| 8:2 | n-octane | 8 | 7 | 0.077 ± 0.000 |
| 7:3 | n-octane | 8 | 8 | 0.046 ± 0.003 |
| 6:4 | n-octane | 8 | 7 | 0.042 ± 0.000 |
| 5:5 | n-octane | 8 | 7 | 0.046 ± 0.005 |
| 10:0 | n-decane | 10 | 14 1 | 0.274 ± 0.000 1 |
| 9:1 | n-decane | 10 | 9 | 0.063 ± 0.004 |
| 8:2 | n-decane | 10 | 9 | 0.070 ± 0.004 |
| 7:3 | n-decane | 10 | 9 | 0.075 ± 0.004 |
| 6:4 | n-decane | 10 | 9 | 0.071 ± 0.004 |
| 5:5 | n-decane | 10 | 9 | 0.037 ± 0.002 |
| 9:1 | diesel | 9.10 1 | 9 | 0.074 ± 0.000 |
| 8:2 | diesel | 9.10 | 9 | 0.077 ± 0.005 |
| 7:3 | diesel | 9.10 | 9 | 0.050 ± 0.000 |
| 6:4 | diesel | 9.10 | 9 | 0.029 ± 0.002 |
| 5:5 | diesel | 9.10 | 9 | 0.020 ± 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kittithammavong, V.; Charoensaeng, A.; Khaodhiar, S. A Normalized HLD (HLDN) Tool for Optimal Salt-Concentration Prediction of Microemulsions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199151
Kittithammavong V, Charoensaeng A, Khaodhiar S. A Normalized HLD (HLDN) Tool for Optimal Salt-Concentration Prediction of Microemulsions. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199151
Chicago/Turabian StyleKittithammavong, Virin, Ampira Charoensaeng, and Sutha Khaodhiar. 2021. "A Normalized HLD (HLDN) Tool for Optimal Salt-Concentration Prediction of Microemulsions" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199151
APA StyleKittithammavong, V., Charoensaeng, A., & Khaodhiar, S. (2021). A Normalized HLD (HLDN) Tool for Optimal Salt-Concentration Prediction of Microemulsions. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199151