Abstract
As a universal quorum sensing (QS) signal, autoinducer-2 (AI-2) is utilized by both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria to coordinate several group behaviors, such as biofilm formation, virulence, and motility, when the bacterial cell density exceeds the thresholds. The determination of the AI-2 level is essential to understand the physiological and biochemical processes involved in bacterial communication. However, the current methods for AI-2 determination are complicated, time-consuming, and require costly equipment, such as a mass spectrometer (MS) or fluorescence detector (FLD). In this study, we present a new and easily applicable method for AI-2 determination. This method, based on the primary derivatization of AI-2 with 2,3-diaminonaphthalene (DAN), uses an affordable high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument with a UV detector. Under optimized conditions, our method showed a good linearity (r2 = 0.999) and demonstrated the effective detection of AI-2 levels in various environmental samples, as follows: 0.38 (±0.05) μM for E. coli K12, 0.48 (±0.05) μM for Aeromonas sp. YB-2, 0.32 (±0.06) μM for the Enterobacter sp. YB-3, and 0.28 (±0.16) μM for activated sludge.
1. Introduction
Bacteria can sense the presence of, and communicate with, neighbors by detecting chemical signals called autoinducers. This phenomenon, called quorum sensing (QS), enables bacteria to maintain their ecological niche and form an environment favorable for their survival. QS involves the regulation of gene expression, such as biofilm formation, dispersion, conjugation, virulence, symbiosis, motility, and morphology, in response to variations in bacterial cell density [1,2,3]. Three types of QS signaling molecules are known to be involved in bacterial communication—Gram-negative bacteria use N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs or HSLs), while Gram-positive bacteria use autoinducer peptides (AIPs) or oligopeptides. In addition, autoinducer-2 (AI-2) is used as a universal signal molecule by both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria [1,4]. Owing to its important implications in medical and environmental research, QS has been extensively studied for decades [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Accordingly, the development of methods to detect QS signals has been a key issue in the field of QS. Various methods, such as bioassay [11,12,13,14], high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [15,16], liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) [17,18], and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) [19], have been developed for the analysis of AHLs, demonstrating that the detection of these molecules is relatively easy. The detection of AI-2, however, has proven to be more complicated, as it can form various equilibrium structures through spontaneous cyclization in the aqueous phase (Figure S1) [20].
The current methods used to detect AI-2 can be classified into two categories (Table 1): (i) methods that require a derivative step (e.g., HPLC with fluorescence detector (HPLC-FLD) [21], LC–MS [22,23], GC–MS [24], etc.) and (ii) methods that do not require derivatization (e.g., AI-2 bioassay [25,26]).

Table 1.
Methods of AI-2 detection reported in the literature.
One example of the second type is the widely applied AI-2 bioassay method that uses the bioluminescent response of an AI-2 reporter strain (e.g., Vibrio harveyi BB strains) to measure the intensity of the AI-2 signal. Although the AI-2 bioassay has a relatively low detection limit, it requires a long preparation (>12 h) and measurement (5–7 h) time, in addition to sophisticated analytical skills. Moreover, the reproducibility of the method is relatively poor and depends on the AI-2 reporter strain and the state of the sample. Conversely, the first type of methods (HPLC-FLD, LC–MS, and GC–MS), which require a derivatization procedure for the fixation of the AI-2 signal structures, have the disadvantages that the additional derivative step is relatively less sensitive, and that advanced and costly detectors, such as a mass spectrometer (MS) or an FLD, are required. Nevertheless, these methods have the advantages of a short measuring time (<30 min), high reproducibility, and ease of application.
In view of the limitations of the current AI-2 determination methods, we developed a new method that uses a relatively accessible and low-cost HPLC-UV detector. Here, we demonstrate the validity of this new method for various environmental samples of pure and mixed bacterial cultures, such as E. coli K12 [9,27], Aeromonas sp. YB-2 [9], Enterobacter sp. YB-3 [9], and activated sludge.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The AI-2 precursor (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentandione (DPD; MW 132.115 g/mol) was purchased from Omm Scientific Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). DPD solutions with concentrations ranging from 0.3125 to 10.00 μM were used as the standards. 2,3-Diaminonaphthalene (DAN) was purchased from Alfa Aesar (Haverhill, MA, USA). The DAN solution was prepared by dissolving 0.2 mg DAN into 1.0 mL of 0.1 N HCl (Samchun, Korea). Acetonitrile (ACN) and formic acid (FA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). All of the solvents and other chemicals used were of analytical or HPLC grade.
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
The bacteria used in this study were E. coli K12 [9,27], Aeromonas sp. YB-2 [9], and Enterobacter sp. YB-3 [9], which were isolated from activated sludge in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) for wastewater treatment. The bacteria were cultured in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth (Difco, USA) at 30 °C and 200 rpm in a shaking laboratory incubator.
2.3. Procedures of Sample Preparation and Derivatization for AI-2 Detection
When E. coli K12, Aeromonas sp. YB-2, Enterobacter sp. YB-3, and activated sludge cultures reached an optical density of 2.0–3.5 at 600 nm, each culture broth was centrifuged at 8000× g for 10 min at 4 °C, and then filtered through a 0.2-μm syringe filter (PVDF, Pall, New York, NY, USA) to remove the cells and debris. Samples of the DPD standard and cell-free supernatant (600 μL each) were transferred to 1.5 mL Eppendorf Safe-Lock Tubes (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) containing an equal volume of DAN solution [21]. In the blank sample, an equal volume of deionized water was added instead. The two solutions were thoroughly mixed for 2 min and reacted for 40 min at 90 °C with linear shaking at 100 rpm in a water bath, were cooled in a refrigerator at 4 °C for 10 min, and then filtered through a 0.45 μm syringe filter (PVDF, Pall, USA) and immediately subjected to HPLC analysis. The data from triplicate measurements were averaged, and the standard deviations were calculated.
2.4. Chromatographic Procedures
Each 50 μL sample prepared in Section 2.3 was injected into an HPLC system equipped with a UV detector (Waters, USA) at a wavelength of 225 or 268 nm. The AI-2 in the injected samples was separated using a Phenomenex Luna 5 μm C18 reverse-phase column (150 × 2.0 mm). The mobile phase included 0.1% FA and pure ACN at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The sequence of gradient elution was as follows: time (t) = 0 min, 70% for FA, 30% for ACN; t = 4 min, 70% for FA, 30% for ACN; t = 12 min, 35% for FA, 65% for ACN; t = 20 min, 35% for FA, 65% for ACN; t = 24 min, 70% for FA, 30% for ACN; and t = 27 min, 70% for FA, and 30% for ACN.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal UV Wavelength for the Detection of the AI-2 Derivative
DPD was reacted with DAN to produce the AI-2 derivative (1-(3-methyl-benzo[g]quinoxaline-2-yl)-ethane-1,2-diol; Figure 1).
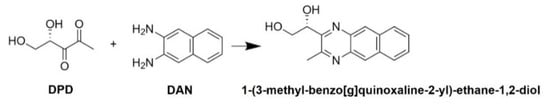
Figure 1.
Product of the reaction of (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentandione (DPD) with 2,3-diaminonaphthalene (DAN).
The reaction mixture was eluted using an HPLC with a UV detector at a wavelength of 225 nm (Figure 2a). The second peak, appearing at a retention time of 1.5 min, corresponded to DAN. The third peak at a retention time of approximately 3 min corresponded to the derivative of DPD and DAN. The structure of the derivative shown in Figure 2a was confirmed by mass spectrometry (Figure S2). The eluted sample corresponding to the derivative was further scanned using a UV spectrometer in the range of 200–380 nm. The derivative showed specific absorption peaks at 225, 268, and 365 nm (Figure 2b). As the peak at 268 nm gave the highest intensity, it was adopted for the subsequent analysis of the derivative.
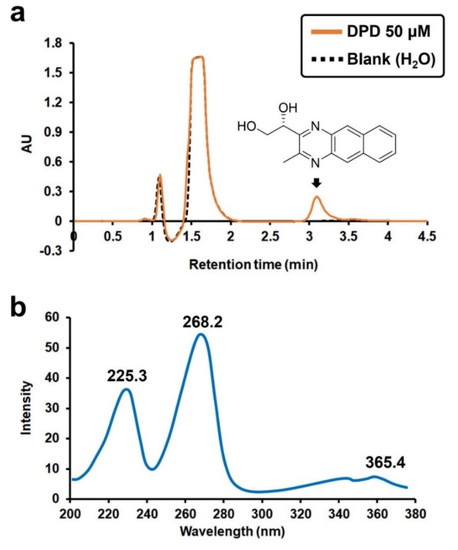
Figure 2.
(a) HPLC chromatogram of the reaction mixture of DPD and DAN with a UV detector at 225 nm, and (b) UV spectrum for the AI-2 derivative.
3.2. Validation of the Method for the Quantitative Analysis of DPD Concentration
As the goal of this study was to quantitatively determine the DPD concentrations in various environmental samples, the DPD concentrations were controlled in a wide range of 0.3125–10.00 μM, equivalent to 41.30–1322 ng/mL in the constant excess concentration of DAN for the reaction in Figure 1. Subsequently, each reaction mixture was analyzed by HPLC to monitor each peak of the AI-2 derivative corresponding to each DPD concentration. The chromatogram was obtained using a UV detector at 268 nm (Figure 3a).
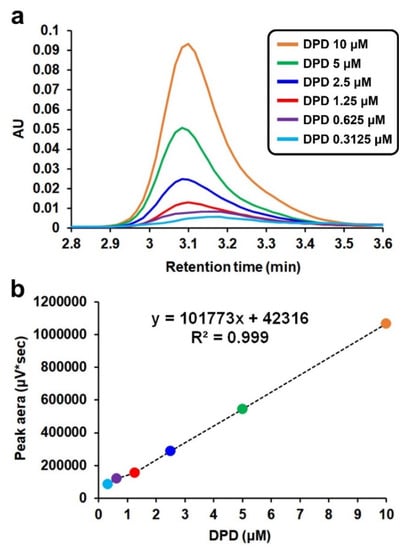
Figure 3.
(a) Chromatograms of the AI-2 derivative (1-(3-methyl-benzo[g]quinoxaline-2-yl)-ethane-1,2-diol), a reaction product of DPD and DAN, as a function of DPD concentration (HPLC with a UV detector at 268 nm). (b) Plot of peak area versus DPD concentration.
The plot of the peak area versus the DPD concentration showed good linearity (r2 = 0.999), proving that this analytical method is precise enough to be applied to the quantitative measurement of DPD (Figure 3b). The limit of detection (LOD) for the HPLC-UV method developed in this study was determined to be 0.25 μM (33 ng/mL), using the linear-regression model [28]. This value is higher than those of the other methods listed in Table 1; however, the cost of equipment for other methods is very high (LC–MS/MS, GC–MS) and their reproducibility is poor (AI-2 bioassay). Although the reported LOD for HPLC-FLD is lower, in practice, there was no significant difference between the two methods. In addition, there was no particular inconvenience when using HPLC-UV for the detection of trace amounts of DPD in environmental samples, such as activated sludge in wastewater, as long as such a sample is concentrated, for instance by liquid–liquid extraction. This is discussed further in the following section.
3.3. Measurement of the DPD Concentration in Various Environmental Samples
To test whether the method developed in this study can be used to measure DPD concentrations in environmental samples, we selected environmental samples presumed to contain DPD: cell cultures, such as E. coli K12, Aeromonas sp. YB-2, Enterobacter sp. YB-3, and activated sludge in MBRs.
As shown in Figure 4, the DPD concentrations were 0.38 (±0.05) μM for K12, 0.48 (±0.05) μM for YB-2, and 0.32 (±0.06) μM for YB-3, showing relatively narrow standard deviations and thus a good precision. After culturing the microorganisms (K12, YB-2, YB-3, and activated sludge) for approximately 12 h, considerable amounts of DPD were found to have accumulated in the supernatant. In particular, the DPD concentration was 0.28 (±0.16) μM for the activated sludge in this study. In previous reports, (i) the DPD concentrations determined by HPLC-FLD for E. coli MG1655 and V. harveyi BB120 were 3.7 µM (486.1 ng/mL) and 35.8 µM (4725.6) ng/mL, respectively [29], and (ii) the AI-2 levels in the activated sludge in MBR liquor determined by LC–MS ranged from 0.0038–0.014 µM (0.5–1.8 ng/mL) [23].
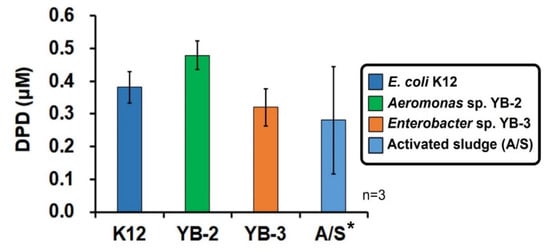
Figure 4.
Determination of the (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentandione (DPD) concentration secreted from various microorganisms. The error bars represent one standard deviation (n = 3, * n = 2).
4. Conclusions
We developed a new analytical method for AI-2 (DPD) detection using the preparation of the DPD derivative, followed by HPLC analysis using a UV detector. The advantage of this method is that it utilizes a UV detector, which is more affordable than the other available methods for AI-2 detection (e.g., MS and FLD). Although the proposed method achieved a rather high LOD level compared with that of the previous methods, it demonstrated that it could be effectively used to measure AI-2 in bacterial cultures or environmental samples. Therefore, we suggest that this low-cost and readily accessible method is suitable for the quantification of AI-2 in a variety of environmental, medical, and other samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11199116/s1, Figure S1: Equilibrium form of (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentandione (DPD) and its derivatives in water and in the presence of borate, Figure S2: Total ion current (TIC) chromatogram obtained with LTQ XL Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization (ESI) in a positive mode (Thermo Fisher Sci. Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
Author Contributions
Methodology and writing (original draft preparation), K.L.; conceptualization and editing, C.-H.L.; writing (review and editing), K.-H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1C1C1008369).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
ORCID, Kibaek Lee http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6877-1475, Kwang-Ho Choo http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4773-5886.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, D.G.; Parsek, M.R.; Pearson, J.P.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Greenberg, E.P. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 1998, 280, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bischofs, I.B.; Hug, J.A.; Liu, A.W.; Wolf, D.M.; Arkin, A.P. Complexity in bacterial cell–cell communication: Quorum signal integration and subpopulation signaling in the Bacillus subtilis phosphorelay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6459–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, C.S.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B. AI-2-mediated signalling in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Nahm, C.H.; Kwon, H.; Park, P.K.; Choo, K.H.; Koyuncu, I.; Drews, A. Stopping AI-2 chatter by means of an indigenous bacterium (Acinetobacter sp. DKY-1): A new anti-biofouling strategy in an MBR for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 6237–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, H.; Xiao, Y.; Hashmi, I.; Zhou, Y. The selective pressure of quorum quenching on microbial communities in membrane bioreactors. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Choo, K.-H. Quorum sensing and quenching in membrane bioreactors: Opportunities and challenges for biofouling control. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddela, N.R.; Sheng, B.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Villamar-Torres, R.; Meng, F. Roles of quorum sensing in biological wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.-R.; Oh, H.-S.; Park, P.-K.; Choo, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, C.-H. Fungal quorum quenching: A paradigm shift for energy savings in membrane bioreactor (MBR) for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10914–10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-S.; Lee, C.-H. Origin and evolution of quorum quenching technology for biofouling control in MBRs for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, C.; Winans, S.C. Conserved cis-acting promoter elements are required for density-dependent transcription of Agrobacterium tumefaciens conjugal transfer genes. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Beaber, J.W.; Moré, M.I.; Fuqua, C.; Eberhard, A.; Winans, S.C. Analogs of the autoinducer 3-oxooctanoyl-homoserine lactone strongly inhibit activity of the TraR protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5398–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raut, N.; Pasini, P.; Daunert, S. Deciphering bacterial universal language by detecting the quorum sensing signal, autoinducer-2, with a whole-cell sensing system. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9604–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teiber, J.F.; Draganov, D.I. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of N-acyl homoserine lactone hydrolysis by paraoxonases. In Quorum Sensing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-R.; Oh, H.-S.; Jo, S.-J.; Yeon, K.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Lim, D.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, J.-K. Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: Physical and biological effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.M.; Moore, J.D.; Blackwell, H.E.; Amador-Noguez, D. Identification of unanticipated and novel N-acyl L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) using a sensitive non-targeted LC-MS/MS method. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ng, T.C.A.; Xu, B.; Shi, X.; Ng, H.Y. Analysis of N-Acy-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) in wastewater treatment systems using SPE-LLE with LC-MS/MS. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, H.; Song, Y.; Bian, Y.; Wu, W.; Xiang, L.; Liu, G.; Jiang, X.; Wang, F. Determination of N-acyl homoserine lactones in soil using accelerated solvent extraction combined with solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.T.; Xavier, K.B.; Campagna, S.R.; Taga, M.E.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Salmonella typhimurium recognizes a chemically distinct form of the bacterial quorum-sensing signal AI-2. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-N.; Qiu, H.-B.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Li, W.-W.; Sheng, G.-P.; Li, X.-Y.; Yu, H.-Q. Determination of autoinducer-2 in biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection using pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1361, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, S.R.; Gooding, J.R.; May, A.L. Direct quantitation of the quorum sensing signal, autoinducer-2, in clinically relevant samples by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6374–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lee, K.; Yu, H.; Mameda, N.; Choo, K.-H. Photolytic quorum quenching: A new anti-biofouling strategy for membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, V.; Vilchez, R.; Sztajer, H.; Wagner-Döbler, I.; Schulz, S. Identification, Quantification, and Determination of the Absolute Configuration of the Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signal Autoinducer-2 by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Biol. Chem. 2009, 10, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, M.E.; Xavier, K.B. Methods for analysis of bacterial Autoinducer-2 production. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2011, 23, 1C.1.1–1C.1.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, R.; Lemme, A.; Thiel, V.; Schulz, S.; Sztajer, H.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Analysing traces of autoinducer-2 requires standardization of the Vibrio harveyi bioassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Attila, C.; Wang, L.; Wood, T.K.; Valdes, J.J.; Bentley, W.E. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli is signaled by AI-2/LsrR: Effects on small RNA and biofilm architecture. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6011–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanagi, M.M.; Ling, S.L.; Nasir, Z.; Hermawan, D.; Wan Ibrahim, W.A.; Naim, A.A. Comparison of signal-to-noise, blank determination, and linear regression methods for the estimation of detection and quantification limits for volatile organic compounds by gas chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Hara, S.; Nakamura, M. Determination of methylglyoxal in mouse blood by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1989, 221, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).