Model-Free Tracking Control with Prescribed Performance for a Shape Memory Alloy-Based Robotic Hand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A novel model free control method combined with DLT and PPC is investigated for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems to guarantee the tracking error in a preassigned boundary;
- The condition, which cannot satisfy the continuity assumption, is considered to improve the applicability in the proposed method;
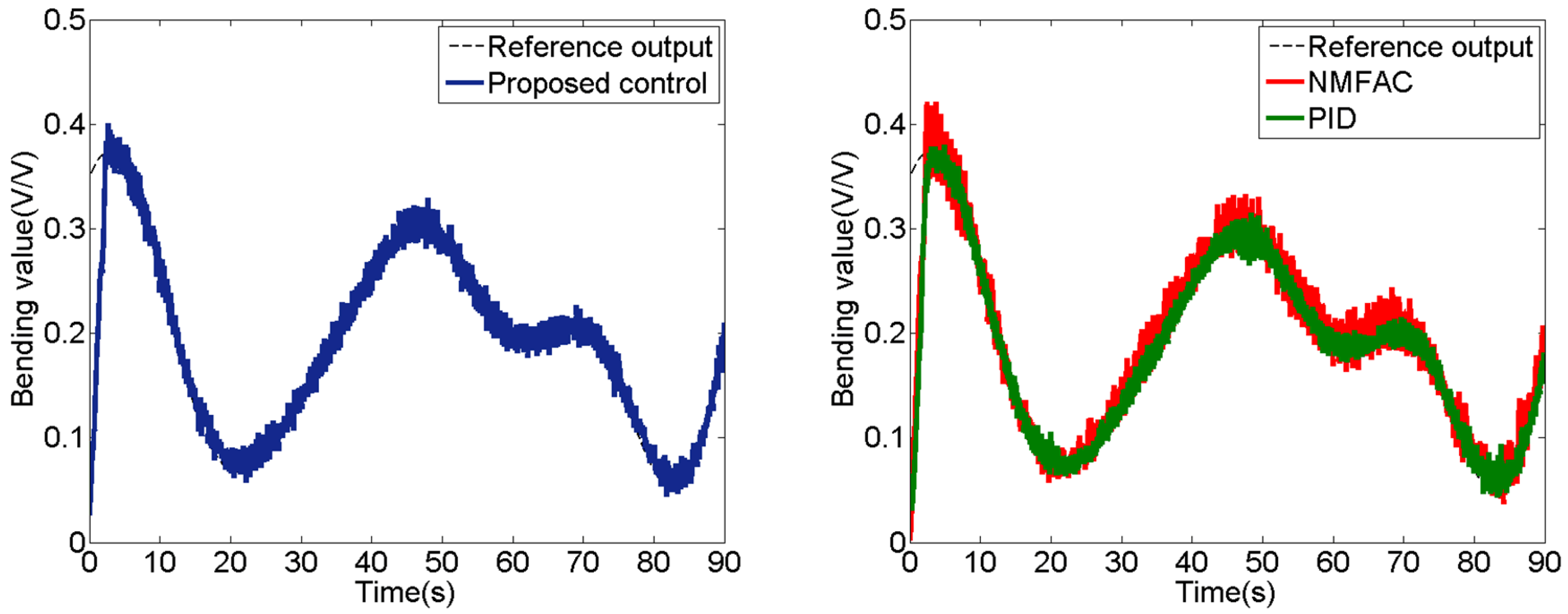
- Experiments are implemented on an SMA-based robotic hand to testify that the proposed control method has a remarkable performance compared with PID and new model free adaptive control (NMFAC).
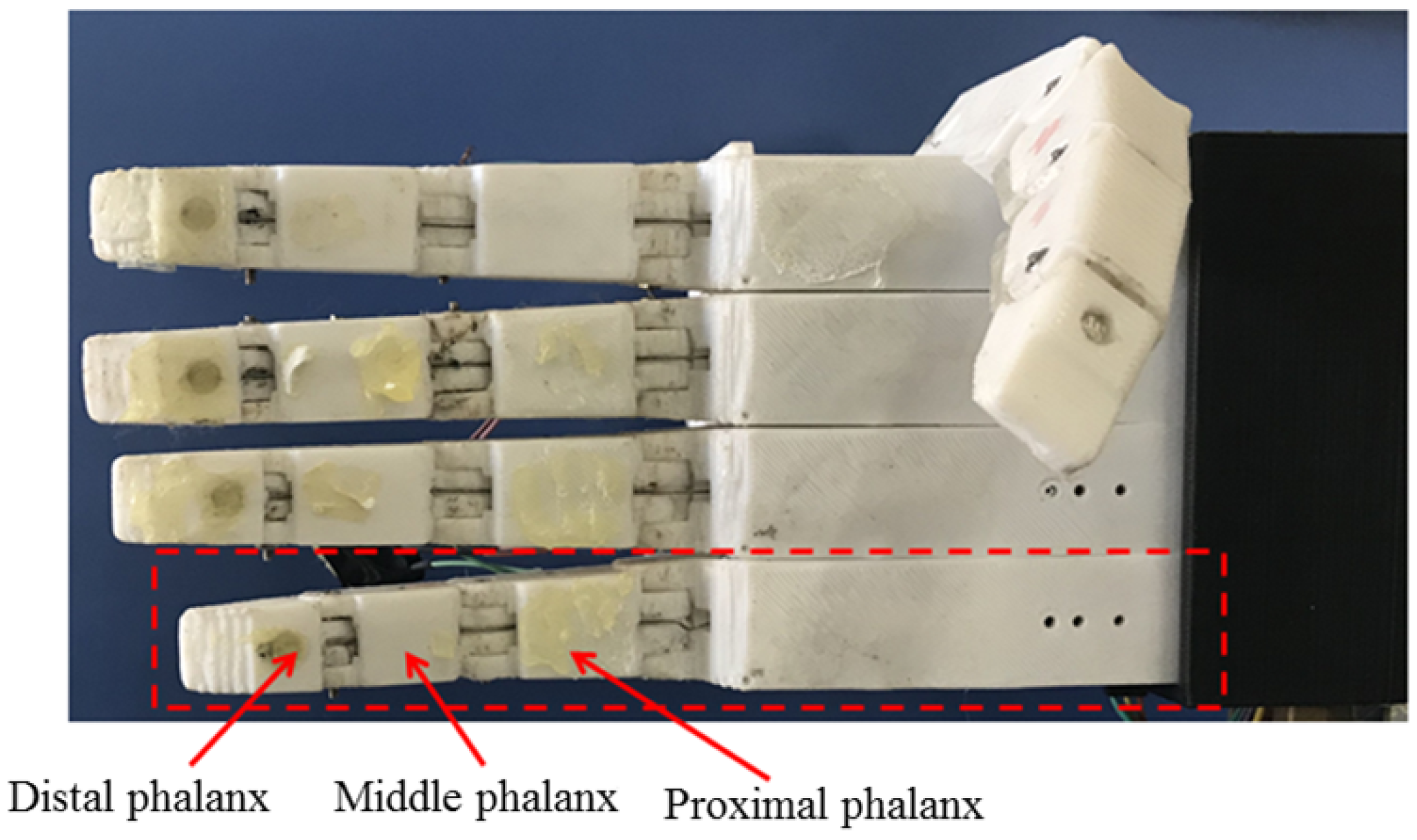
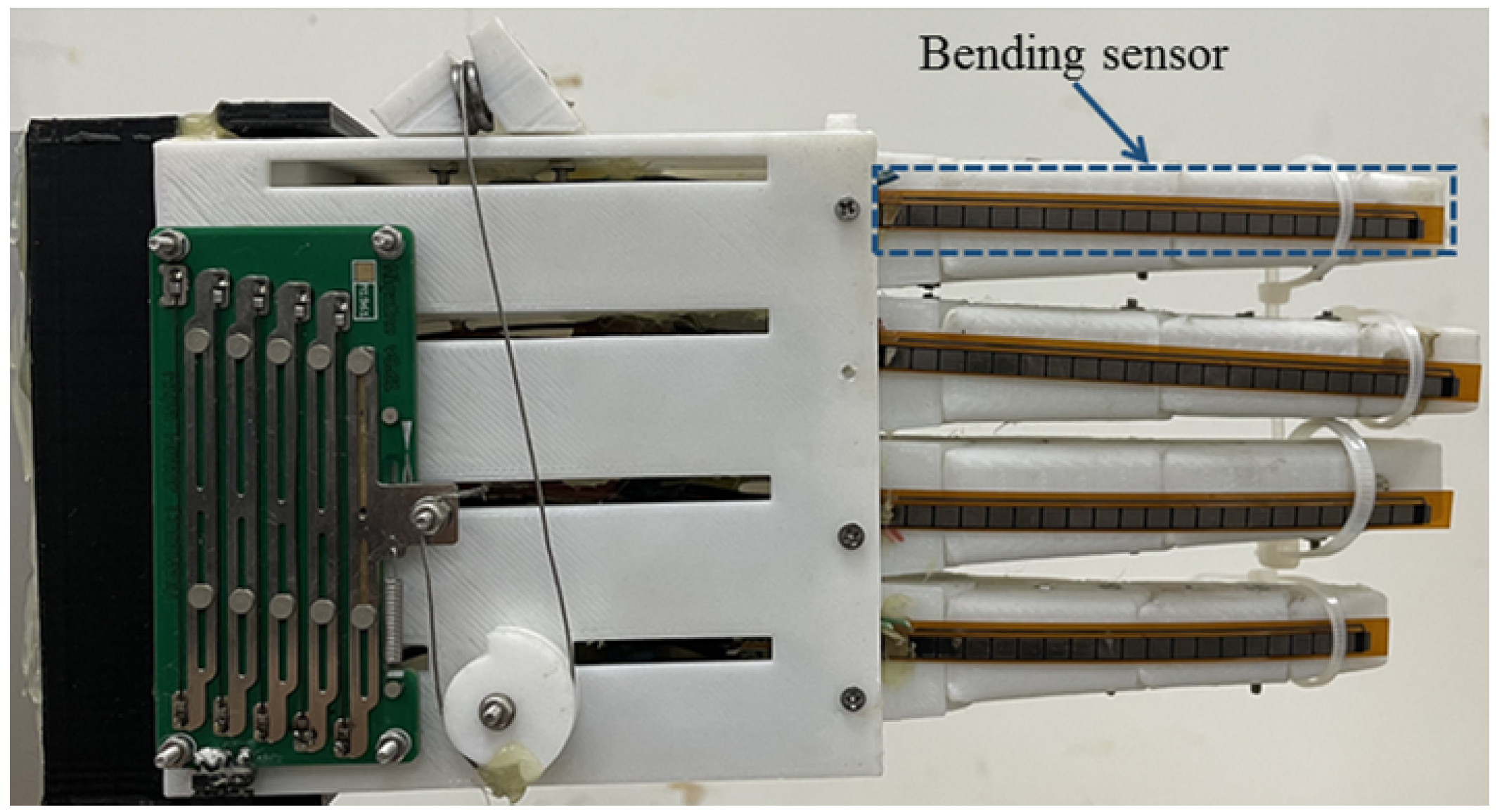
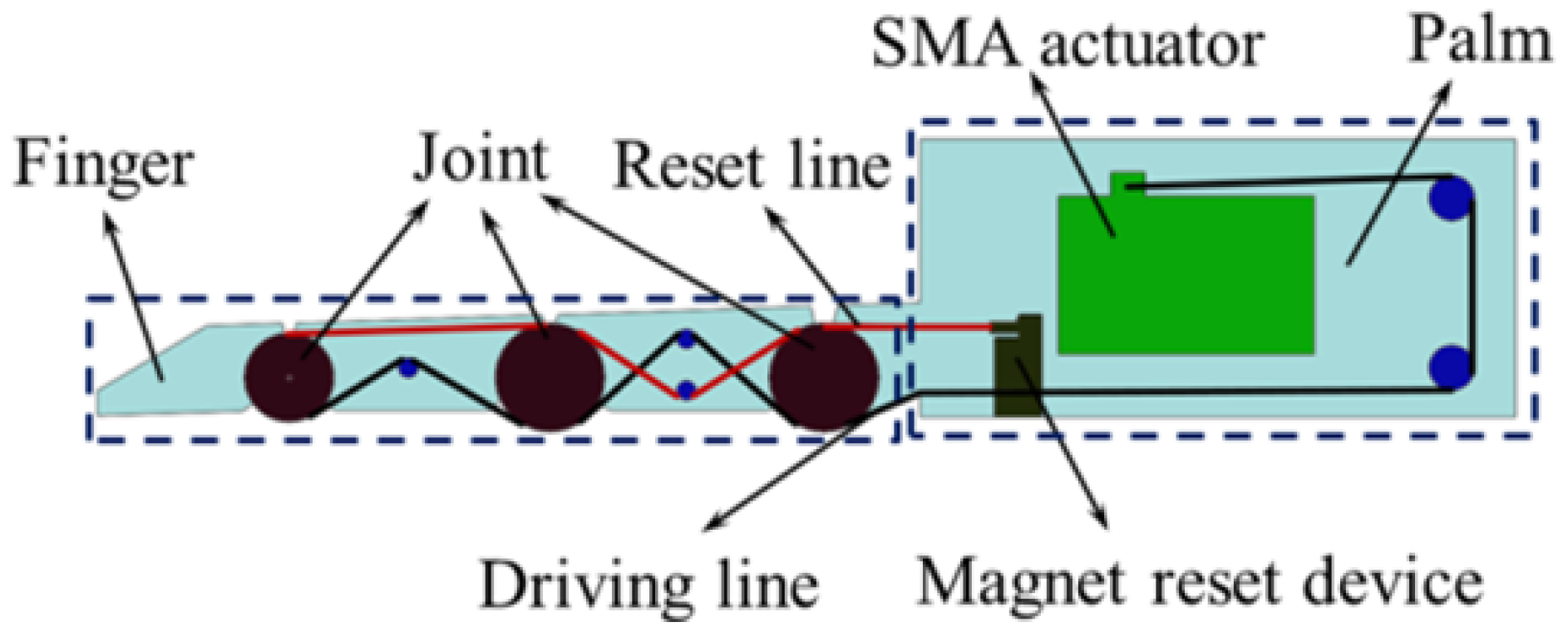
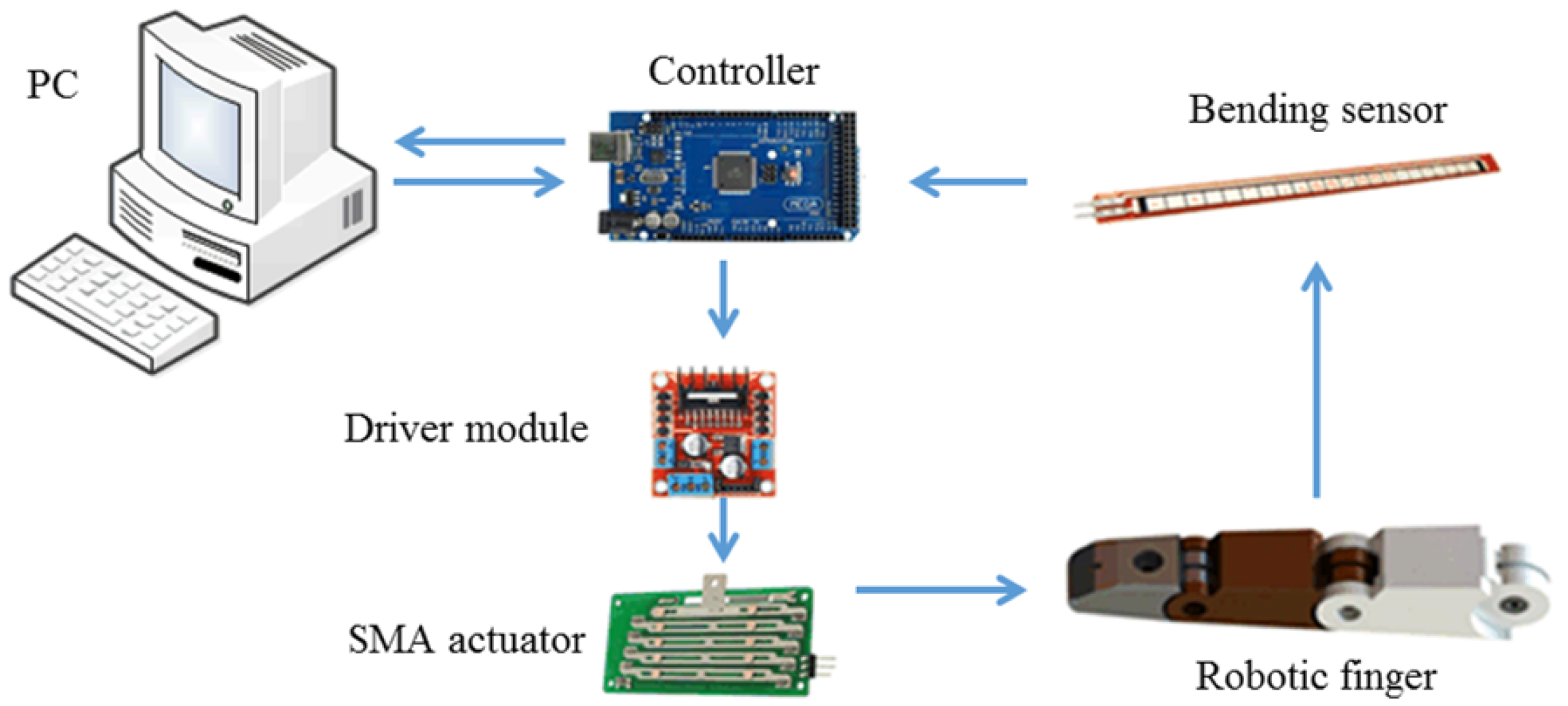
2. SMA-Based Robotic Hand
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. System Model
3.2. Prescribed Performance Control
- , for all .
- .
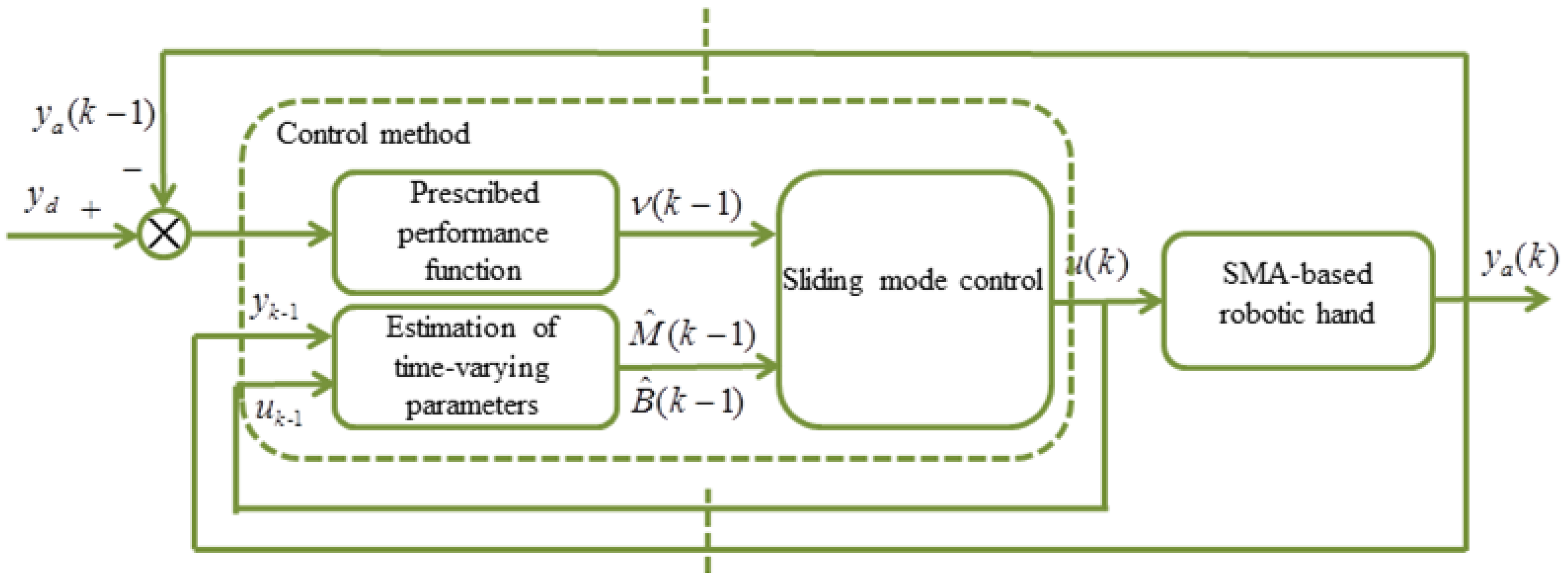
4. Control Method Design
4.1. Disturbance Estimation
4.2. Controller Design
4.3. Stability Analysis
- If , based on (27), will monotonically decrease until it falls into .
- If , based on (27), can increase until it arrives to .
5. Experiment Studies
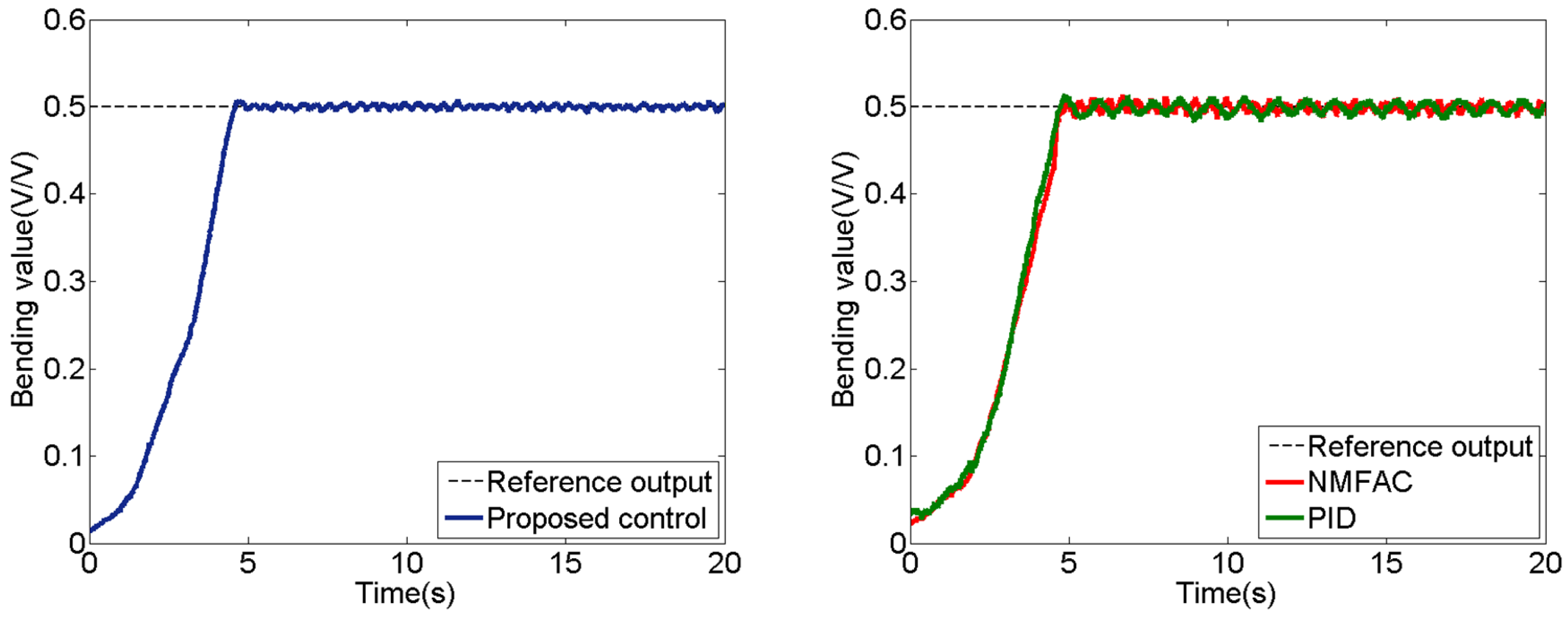
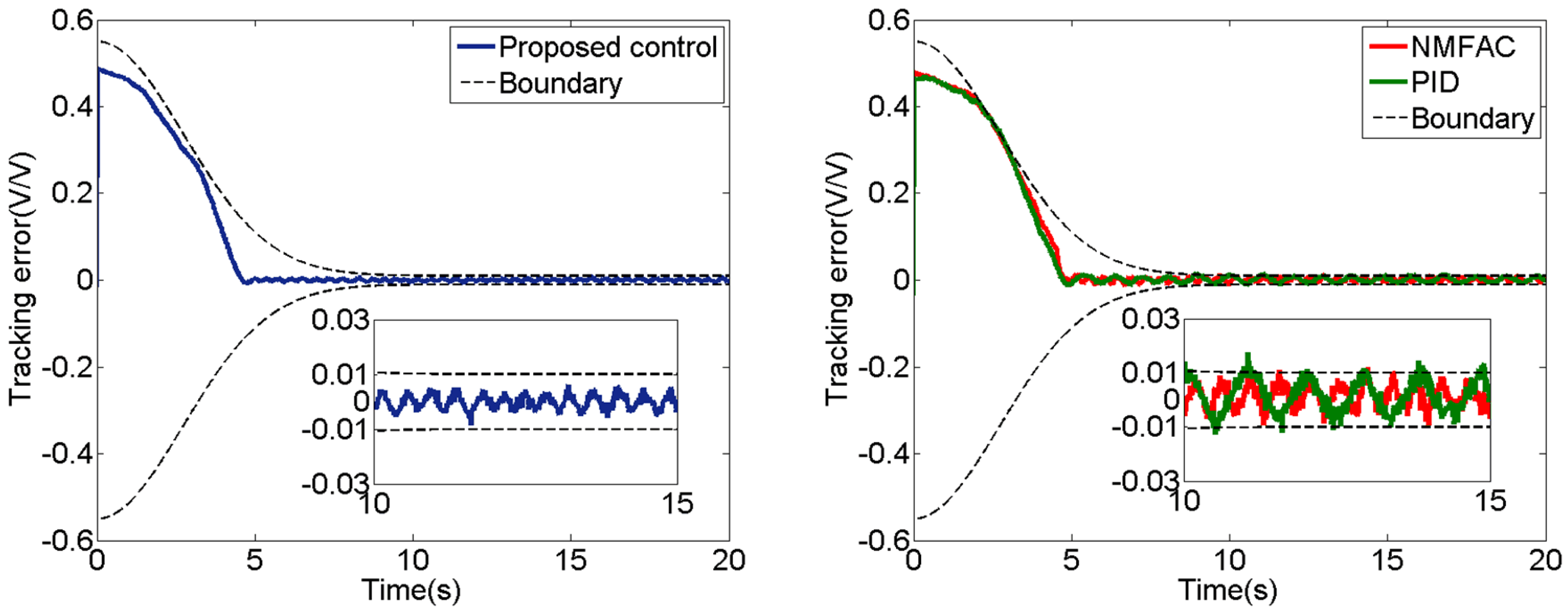
5.1. Experiment of Step Signal
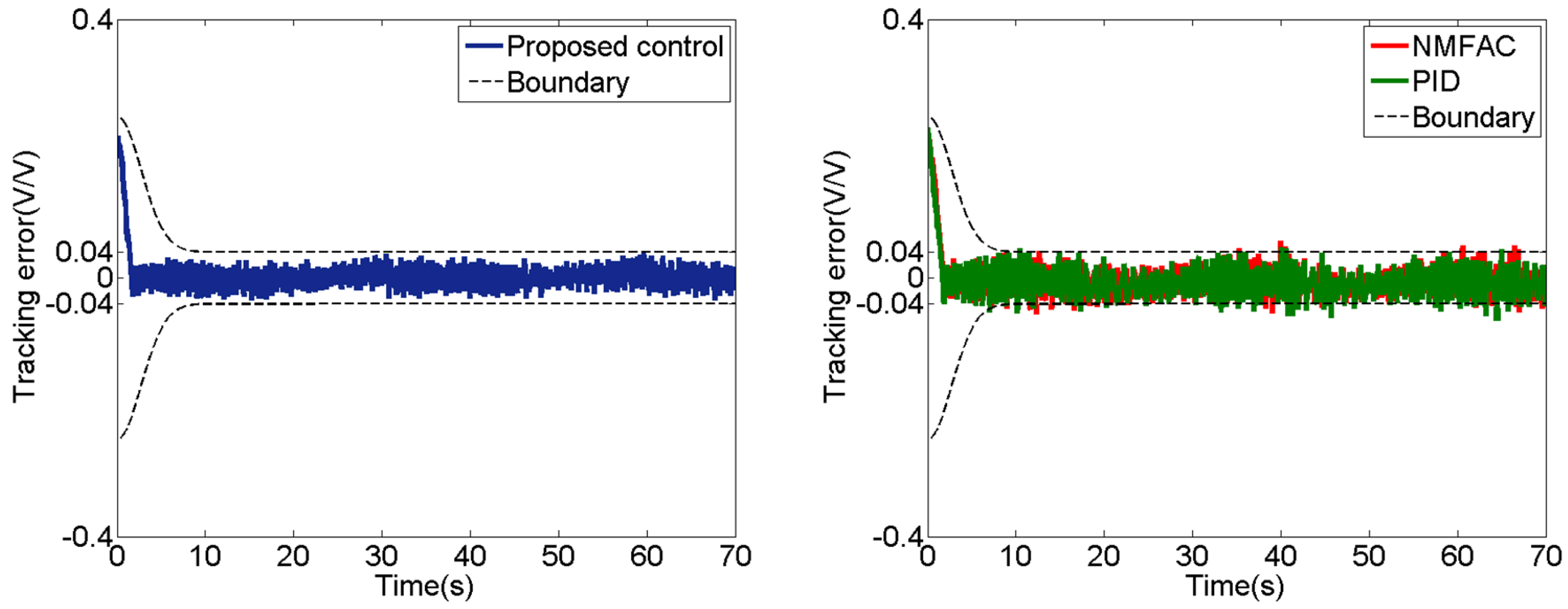
5.2. Experiment of Sinusoidal Signal
5.3. Experiment of Sinusoidal Signal with Time Variation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abondance, S.; Teeple, C.B.; Wood, R.J. A Dexterous Soft Robotic Hand for Delicate In-Hand Manipulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5502–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Selvaggio, M.; Ferrentino, P.; Moccia, R.; Pirozzi, S.; Bracale, U.; Ficuciello, F. The MUSHA Hand II:A Multifunctional Hand for Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Agrawal, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. A Bioinspired Soft Swallowing Gripper for Universal Adaptable Grasping. Soft Robot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J.; Yue, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y. A novel design of a parallel gripper actuated by a large-stroke shape memory alloy actuator. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 159, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, C. Controlling bending deformation of a shape memory alloy-based soft planar gripper to grip deformable objects. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 193, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Hou, Y.; Dou, W. A soft pneumatic dexterous gripper with convertible grasping modes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 153, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, X.; Wu, H.; Sun, M.; Bao, G.; Wu, H.; Jiang, S. Pneumatically Actuated Soft Gripper with Bistable Structures. Soft Robot. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Rosset, S.; Schubert, B.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Versatile soft grippers with intrinsic electroadhesion based on multifunctional polymer actuators. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shian, S.; Bertoldi, K.; Clarke, D.R. Dielectric elastomer based “grippers” for soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6814–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Wang, W.; Han, M.W.; Kim, T.J.; Ahn, S.H. An overview of shape memory alloy-coupled actuators and robots. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Okamoto, S.; Matsubara, S. Development of multi-fingered prosthetic hand using shape memory alloy type artificial muscle. Comput. Technol. Appl. 2012, 3, 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Bundhoo, V.; Haslam, E.; Birch, B.; Park, E.J. A shape memory alloy-based tendon-driven actuation system for biomimetic artificial fingers, part I: Design and evaluation. Robotica 2009, 27, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeno, T.; Hino, T. Miniature five-fingered robot hand driven by shape memory alloy actuators. In Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference, Robotics and Applications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–25 August 2006; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Simone, F.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. Metal muscles and nerves—A self-sensing SMA-actuated hand concept. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ahn, S.H. Shape memory alloy-based soft gripper with variable stiffness for compliant and effective grasping. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Hao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. A novel design of shape-memory alloy-based soft robotic gripper with variable stiffness. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420907813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayender, J.; Patel, R.V.; Nikumb, S.; Ostojic, M. Modeling and Control of Shape Memory Alloy Actuators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2008, 16, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Ghorbel, F. Differential hysteresis modeling of a shape memory alloy wire actuator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2005, 10, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, J.H.; Buckner, G.D. Indirect Intelligent Sliding Mode Control of Antagonistic Shape Memory Alloy Actuators Using Hysteretic Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannen, J.C.; Crews, J.H.; Buckner, G.D. Indirect intelligent sliding mode control of a shape memory alloy actuated flexible beam using hysteretic recurrent neural networks. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 085015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Jin, M.; Ahn, K.K. Precise tracking control of shape memory alloy actuator systems using hyperbolic tangential sliding mode control with time delay estimation. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kha, N.B.; Ahn, K.K. Position control of shape memory alloy actuators by using self tuning fuzzy PID controller. In Proceedings of the 2006 1ST IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Singapore, 24–26 May 2006; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nakshatharan, S.S.; Dhanalakshmi, K.; Ruth, D.J.S. Fuzzy based sliding surface for shape memory alloy wire actuated classical super-articulated control system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 32, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, R. Tactile feedback control for a gripper driven by SMA springs. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 032134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikdel, N.; Nikdel, P.; Badamchizadeh, M.A.; Hassanzadeh, I. Using neural network model predictive control for controlling shape memory alloy-based manipulator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, S.K.; Dhanalakshmi, K. Control of shape memory alloy actuated gripper using Sliding Mode Control. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA), Hyderabad, India, 28–30 August 2013; pp. 1247–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.F.; da Silva, S.A.; dos Santos, A.J.; Ries, A.; Souto, C.R.; de Araújo, C.J. Fuzzy control of a robotic finger actuated by shape memory alloy wires. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2018, 140, 064502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayari, A.; Talari, M.; Kheirikhah, M.M. Fuzzy PID controller design for artificial finger based SMA actuators. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE 2011), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 727–732. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Bae, J.; Moon, I. Lightweight prosthetic hand with five fingers using SMA actuator. In Proceedings of the 2011 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 26–29 October 2011; pp. 1797–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Simone, F.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Design and fabrication of a three-finger prosthetic hand using SMA muscle wires. In Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication 2015; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9429, p. 94290T. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianesis, K.; Tzes, A. Development and control of a multifunctional prosthetic hand with shape memory alloy actuators. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2015, 78, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Li, F.; Yang, C. A New Data-Driven Model-Free Adaptive Control for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126224–126233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, C.P.; Rovithakis, G.A. Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, G.H. Prescribed Performance Model-Free Adaptive Integral Sliding Mode Control for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 2222–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. Discrete-Time Quasi-Sliding-Mode Control With Prescribed Performance Function and its Application to Piezo-Actuated Positioning Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, D.; Jiang, B.; Pan, T. Prescribed performance based model-free adaptive sliding mode constrained control for a class of nonlinear systems. Inf. Sci. 2021, 544, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, J.T.; Maggiore, M.; Ordonez, R.; Passino, K.M. Stable Adaptive Control and Estimation for Nonlinear Systems: Neural and Fuzzy Approximator Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]


| Control Method | RMSTE (V/V) | Response Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 0.0046 | 4.9 |
| NMFAC | 0.0061 | 5.2 |
| Proposed control | 0.0025 | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, W. Model-Free Tracking Control with Prescribed Performance for a Shape Memory Alloy-Based Robotic Hand. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199040
Hao L, Xiao J, Li W. Model-Free Tracking Control with Prescribed Performance for a Shape Memory Alloy-Based Robotic Hand. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):9040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Lina, Jichun Xiao, and Wenlong Li. 2021. "Model-Free Tracking Control with Prescribed Performance for a Shape Memory Alloy-Based Robotic Hand" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 9040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199040
APA StyleHao, L., Xiao, J., & Li, W. (2021). Model-Free Tracking Control with Prescribed Performance for a Shape Memory Alloy-Based Robotic Hand. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 9040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199040






