Investigation of Dispersion, Interfacial Adhesion of Isotropic and Anisotropic Filler in Polymer Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
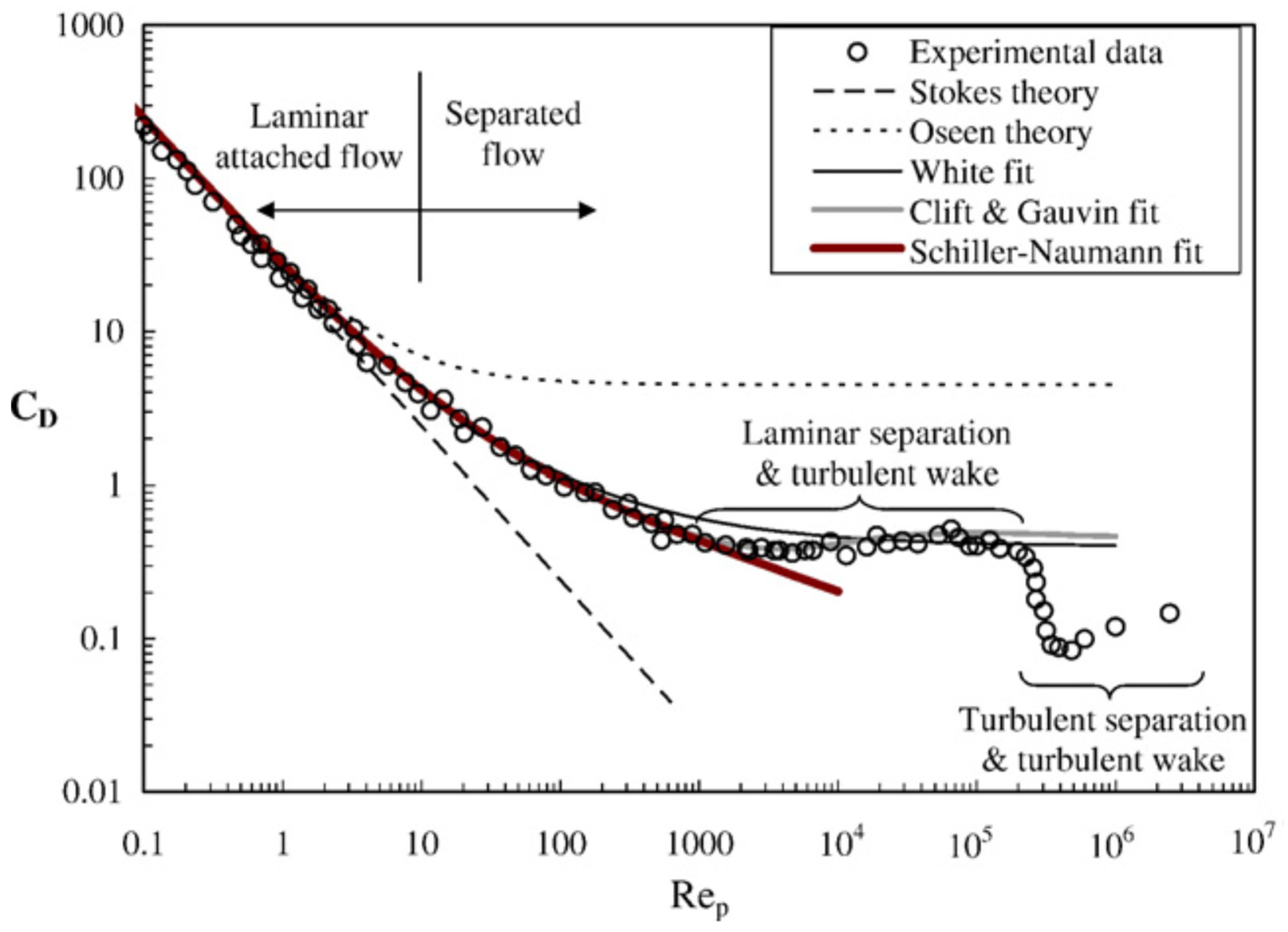
1.1. Movement of Spherical Particles within the Polymer Matrix
1.2. Movement of Non-Spherical Particles within Polymer Composite
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
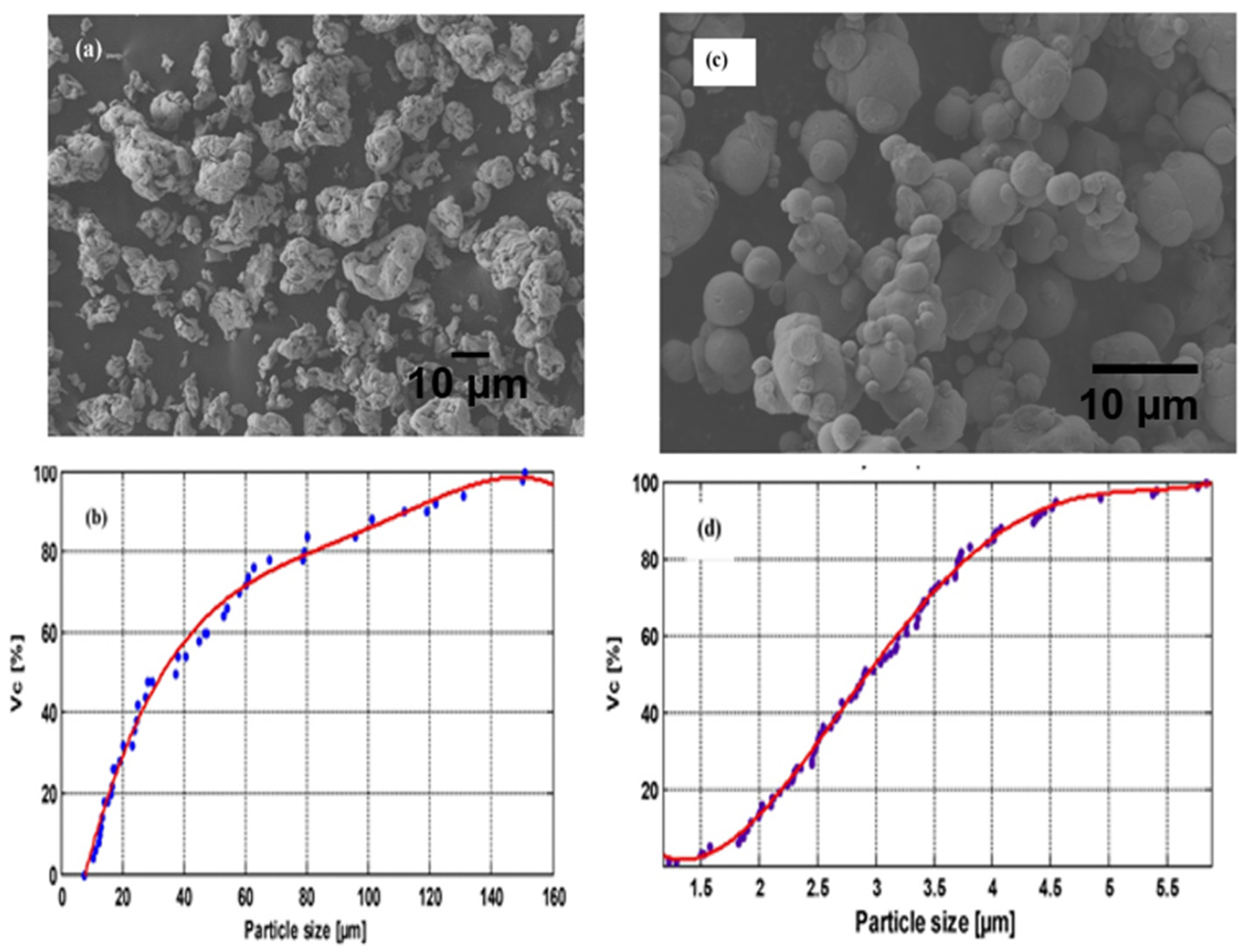
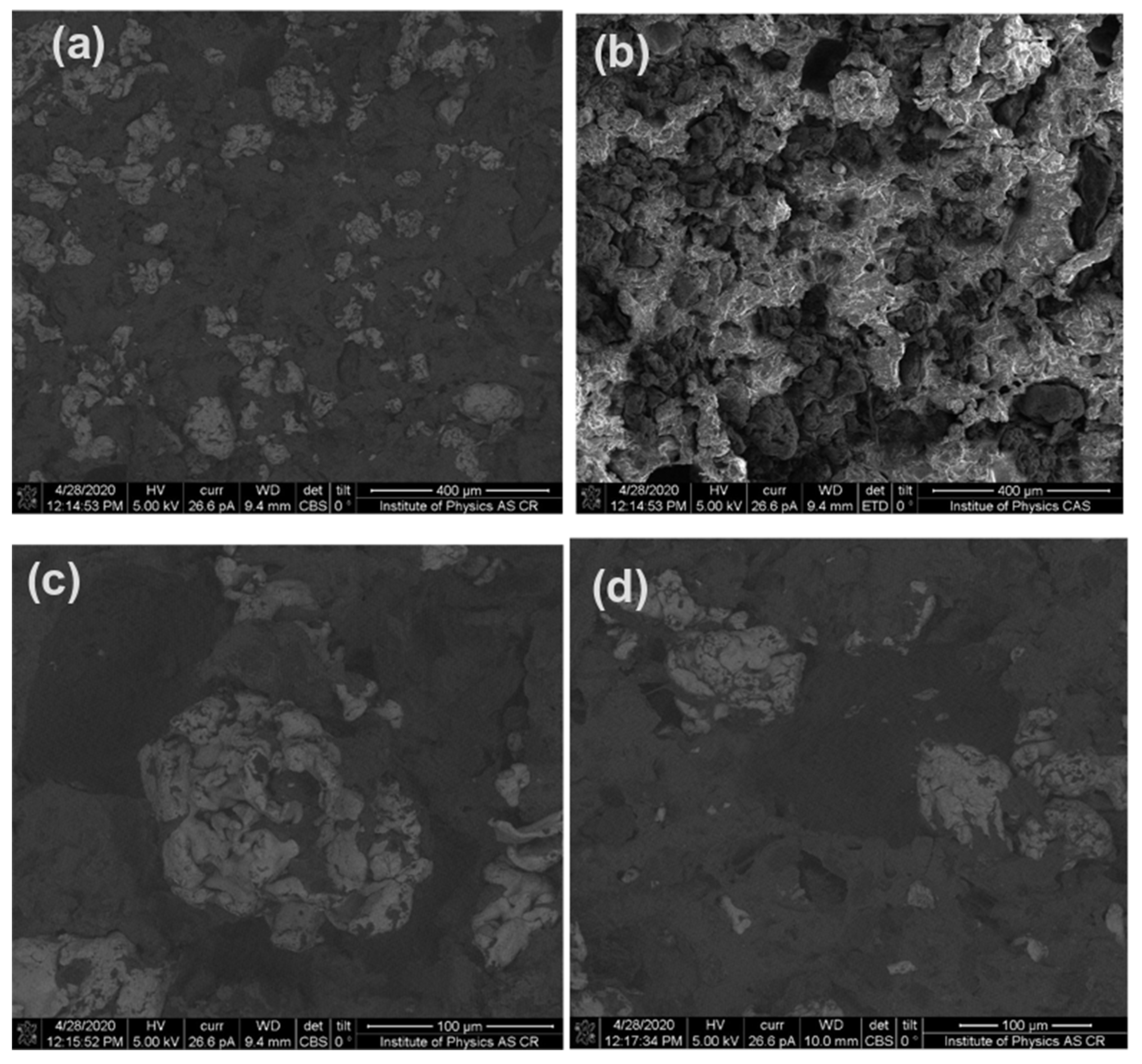
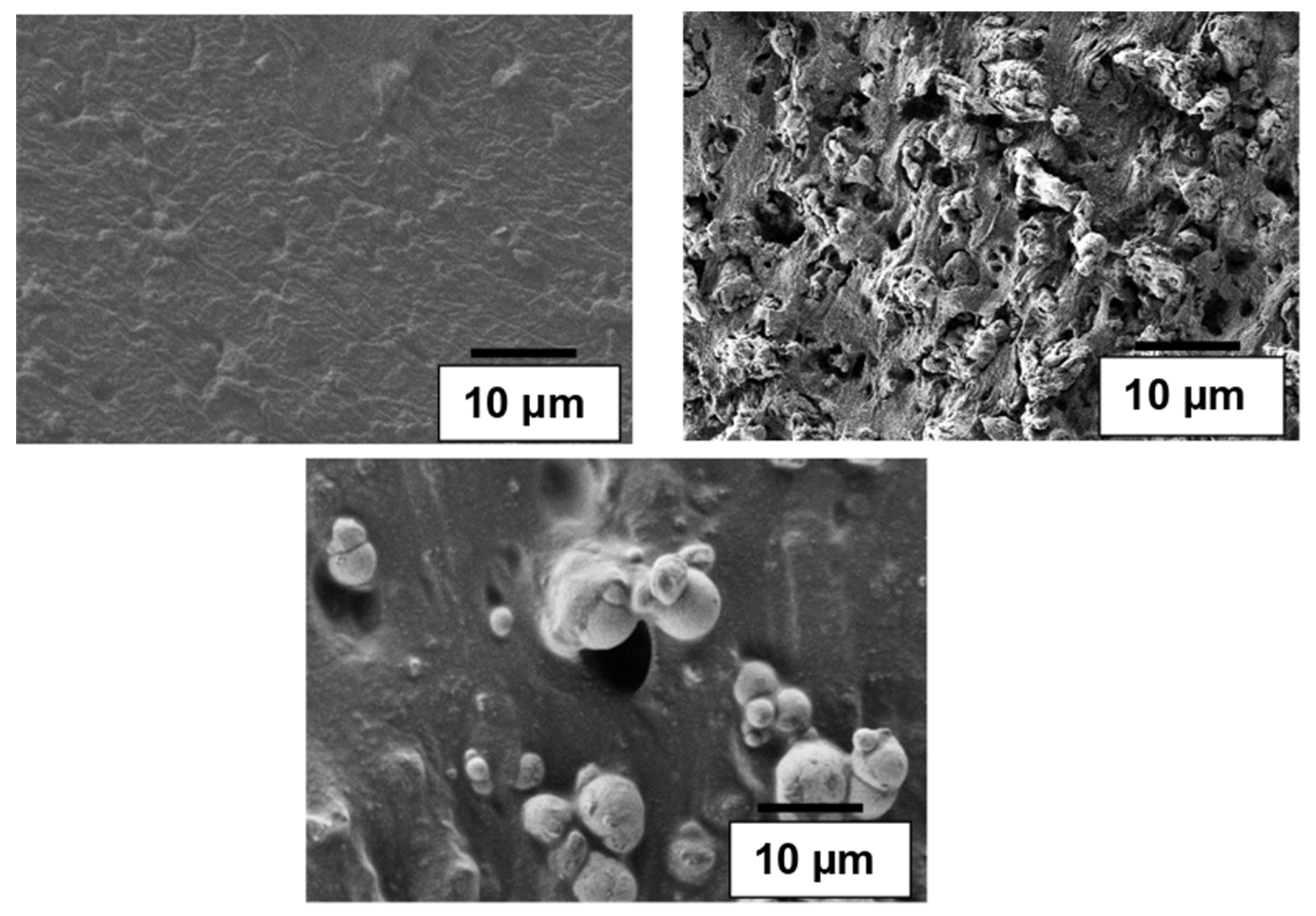
3.1. Surface Feature Analysis of the Filler within Polymer Matrix
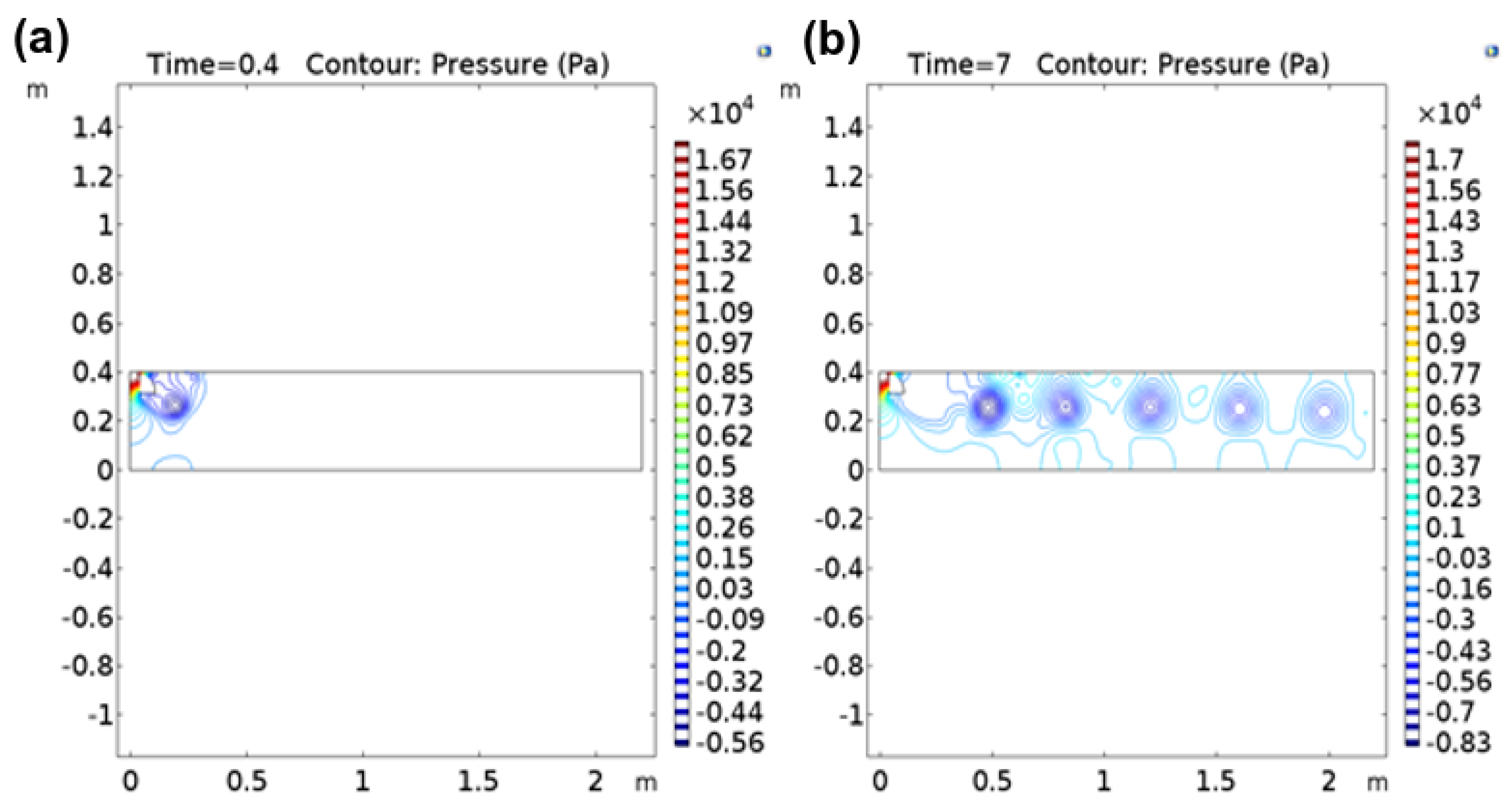
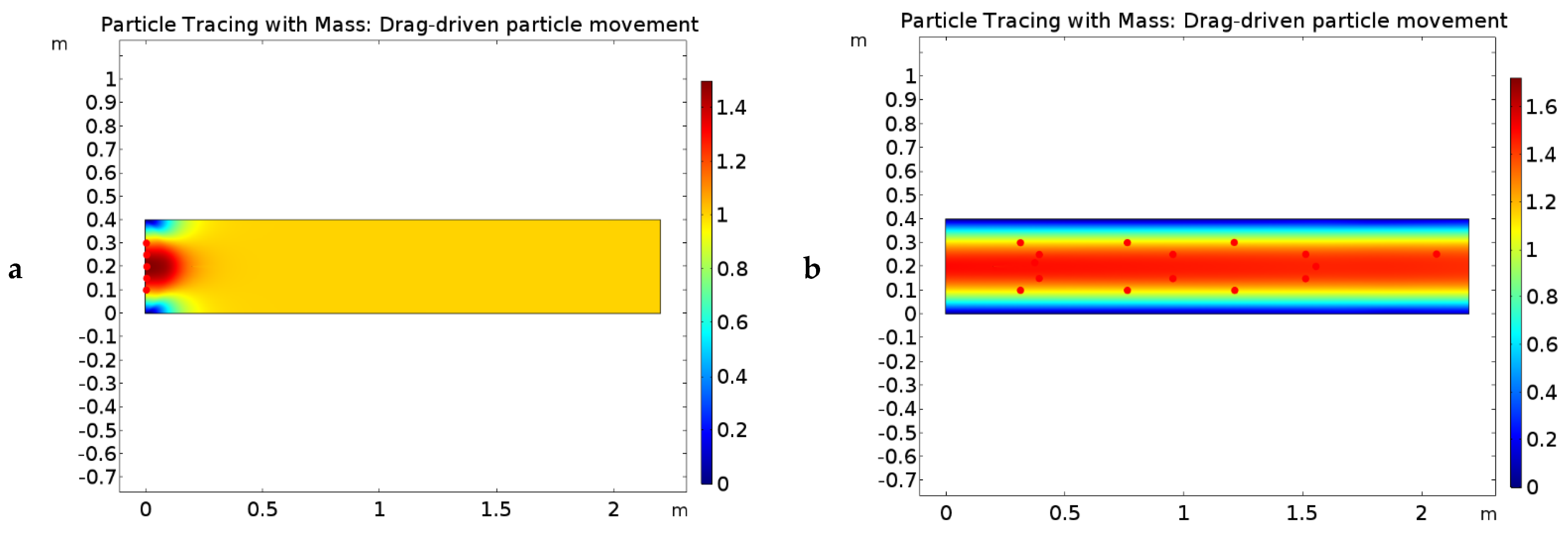
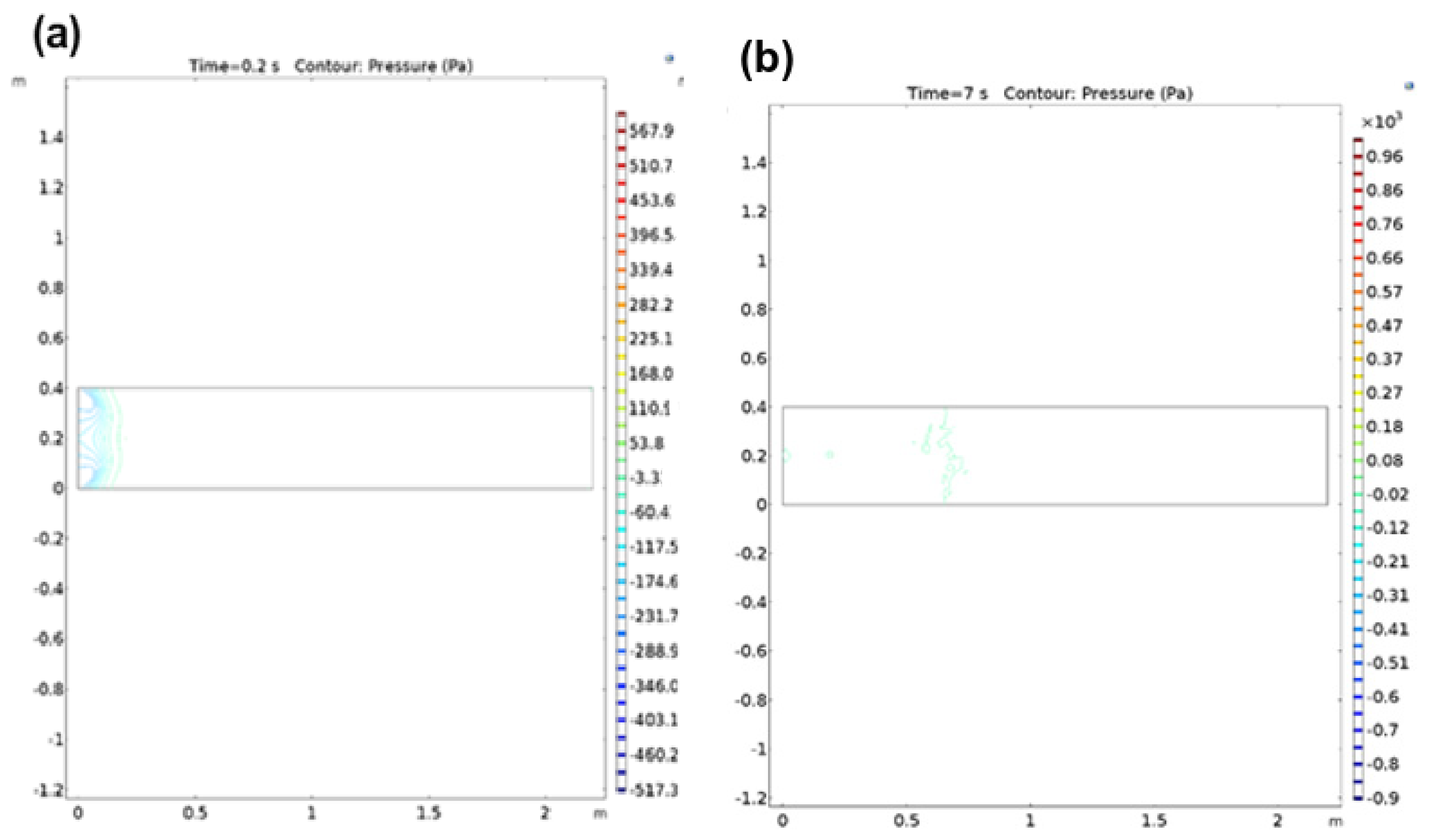
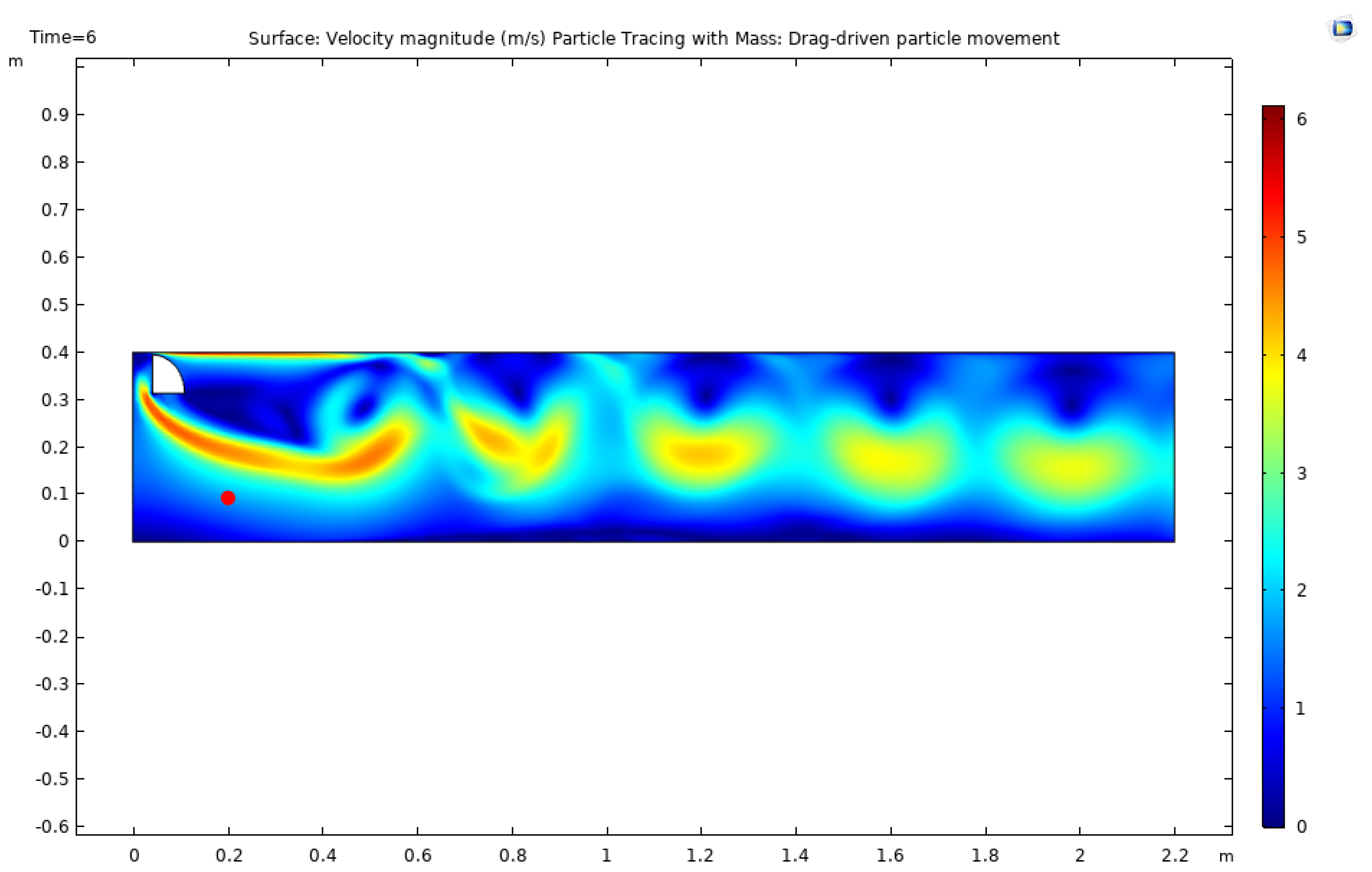
3.2. Simulation Studies on the Movement of Irregular and Regular Particles within Polymer Matrix
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Jones, F.R. A review of particulate reinforcement theories for polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 4933–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, J. Rubber–filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 627–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.R. The dynamic properties of carbon black loaded natural rubber vulcanizates. Part II. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1962, 6, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmann, A.; Ogden, R. A constitutive model for the Mullins effect with permanent set in particle-reinforced rubber. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2004, 41, 1855–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, J.; Fayolle, B.; Gilormini, P. A review on the Mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A.N.; Park, B. Failure processes in elastomers at or near a rigid spherical inclusion. J. Mater. Sci. 1984, 19, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M. Fluid Mechanics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Loth, E. Drag of non-spherical solid particles of regular and irregular shape. Powder Technol. 2008, 182, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallavalle, J.M. Micrometrics; Pitman Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, R.; Gauvin, W.H. Proc. CHEMECA ’70; Butterworth: Melbourne, Australia, 1970; Volume 1, pp. 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, L.; Naumann, A.Z. Über die grundlegenden Berechungen bei der Schwerkraftaufbereitung. Ver. Deut. Ing. 1933, 77, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaweera, K.O.L.F.; Mason, B.J. The behavior of freely falling cylinders, and cones in viscous fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 1965, 22, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringham, G.; Simons, D.; Guy, H. The behavior of large particles falling in quiescent liquids. Prof. Paper 1969, 562, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V.; Pruppacher, H.R. A Determination of the Terminal Velocity and Drag of Small Water Drops by Means of a Wind Tunnel. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, R.; Schemenauer, R.S. Free-fall behavior of planar snow crystals, conical graupel and small hail. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S. Effect of shape and size of filler particle on the aggregation and sedimentation behaviour of the polymer composite. Powder Technol. 2020, 366, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Škodová, M.; Blanco, I. Effects of Filler Distribution on Magnetorheological Silicon-Based Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Vlach, J.; Kolinova, M.; Kavan, P. Micro-Computed Tomography Characterization of Isotropic Filler Distribution in Magnetorheological Elastomeric Composites. In Advanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials; Ohji, T., Singh, M., Halbig, M., Moon, K., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, S.; Vlach, J.; Kavan, P. Improved mechanical properties of magneto rheological elastomeric composite with isotropic iron filler distribution. Ciênc. Tecnol. Mater. 2016, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Kolinova, M.; Blanco, I. The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H. Effects of Filler Size and Distribution on Viscous Behavior of Glass Composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Škodová, M.; Abate, L.; Blanco, I. Magneto-Rheological Elastomer Composites. A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Munstedt, H. Rheological behavior of concentrated mono-disperse suspensions as a function of preshear conditions and temperature: An experimental study. Rheol. Acta 2002, 41, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.O.; Ven, T.G.M.V.D. Shear-induced deformation and rupture of suspended solid/liquid clusters. Colloid Surf. 1985, 15, 131–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H. Rheological Model for Agglomerative Slurry of Mono-modal Silica Particles. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 1999, 25, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Usui, H.; Kishimoto, K.; Suzuki, H. Non-Newtonian viscosity of dense slurries prepared by spherical particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 2979–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H.; Li, L.; Kinoshita, S.; Suzuki, H. Viscosity Prediction of Dense Slurries Prepared by Non-Spherical Solid Particles. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn 2001, 34, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Jung, J.H.; Gil Kim, Y. Magnetic carbonyl iron/natural rubber composite elastomer and its magnetorheology. Compos. Struct. 2016, 136, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, A.; Sedaghati, R.; Rakheja, S. On the properties of magnetorheological elastomers in shear mode: Design, fabrication and characterization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 159, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokander, M.; Stenberg, B. Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkowska, A.; Awietjan, S.F.; Pietrzko, S.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers under shear deformation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.W. Current theories of adhesion and their relevance to adhesive technology. J. Phys. Colloq. 1993, 3, C7-1511–C7-1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Lee, D.-J. Iron particle and anisotropic effects on mechanical properties of magneto-sensitive elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapipi, N.M.; Mazlan, S.A.; Khairi, M.H.A.; Mohamad, N. The Damping Properties of Plate-Like Magnetorheological Elastomer. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 772, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Carlson, J.D.; Muñoz, B.C.; Bullions, T.A. The magnetoviscoelastic response of elastomer composites consisting of ferrous particles embedded in a polymer matrix. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.V.; Laherisheth, Z.; Shah, K. Rheological properties of soft magnetic flake shaped iron particle based magnetorheological fluid in dynamic mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilan, S.T.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ido, Y.; Hajalilou, A.; Jeyadevan, B.; Choi, S.-B.; Yunus, N.A. A comparison of field-dependent rheological properties between spherical and plate-like carbonyl iron particles-based magneto-rheological fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laherisheth, Z.; Upadhyay, R.V. Influence of particle shape on the magnetic and steady shear magnetorheological properties of nanoparticle based MR fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 054008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Phu, D.X.; Seong, M.-S.; Upadhyay, R.; Choi, S.-B. A low sedimentation magnetorheological fluid based on plate-like iron particles, and verification using a damper test. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 027001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
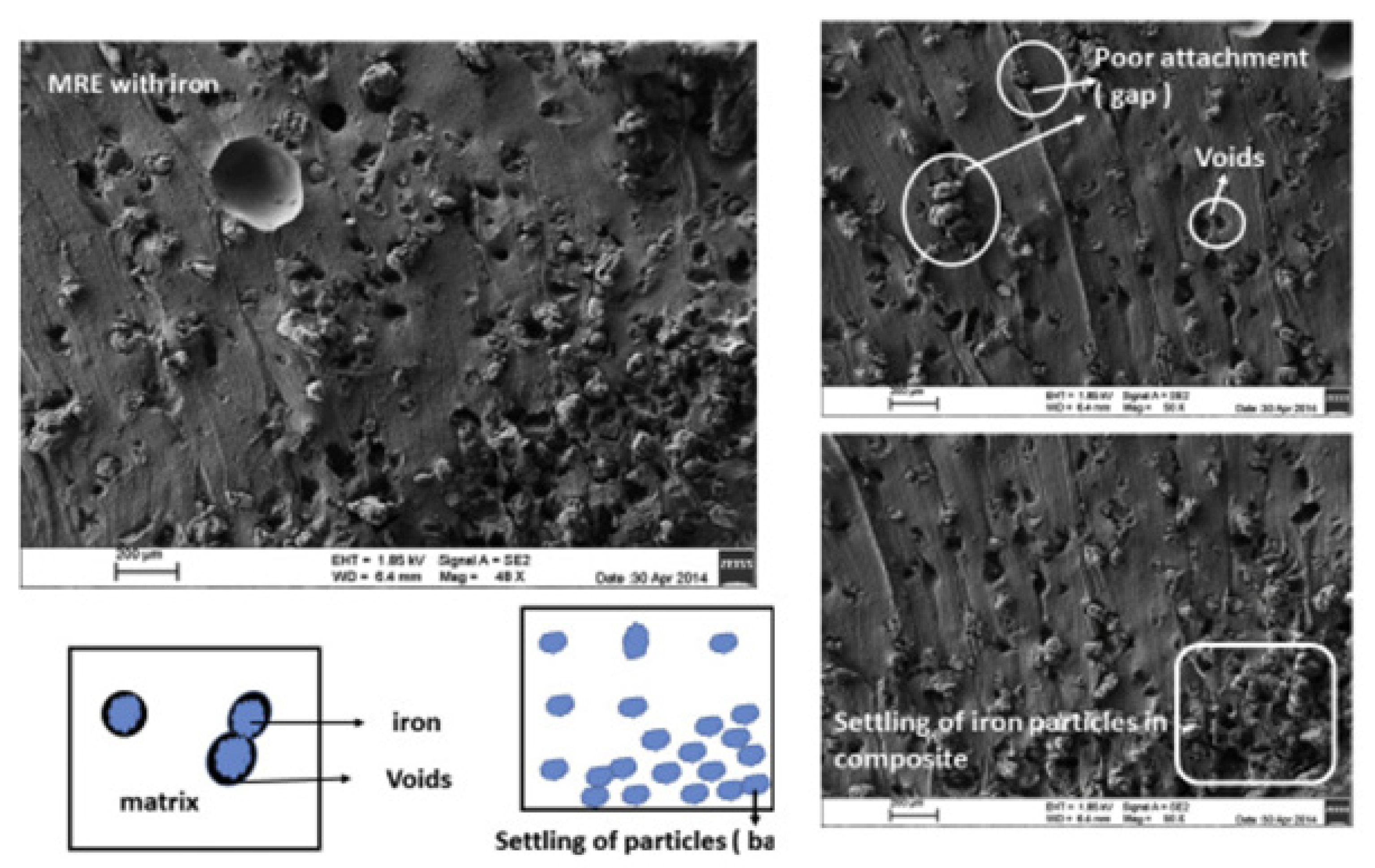






| Bond Type | Equilibrium Length (Å) | Energy KJ/Mole | Direction | Material Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Forces | 10−6–10−10 | - | no | Paper, cloth, leather or wood |
| Secondary, van der Waals | ||||
| Debye induction | 2–4 | ~20 | Yes | Liquid and solid surface |
| London dispersion | 4–8 | ~40 | No | |
| Hydrogen bonds | ~3 | ~60 | Yes | |
| Primary Forces | ||||
| Ionic | 2–4 | 600–1200 | No | Adhesive and substrate |
| Covalent | 0.8–3 | 60–800 | Yes | |
| Metallic | 2–6 | 100–350 | No | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samal, S.; Blanco, I. Investigation of Dispersion, Interfacial Adhesion of Isotropic and Anisotropic Filler in Polymer Composite. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188561
Samal S, Blanco I. Investigation of Dispersion, Interfacial Adhesion of Isotropic and Anisotropic Filler in Polymer Composite. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188561
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamal, Sneha, and Ignazio Blanco. 2021. "Investigation of Dispersion, Interfacial Adhesion of Isotropic and Anisotropic Filler in Polymer Composite" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188561
APA StyleSamal, S., & Blanco, I. (2021). Investigation of Dispersion, Interfacial Adhesion of Isotropic and Anisotropic Filler in Polymer Composite. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188561







