Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Kampo Medicine, BO
2.3. KOA Induction by Destabilization of the Medial Meniscus (DMM)
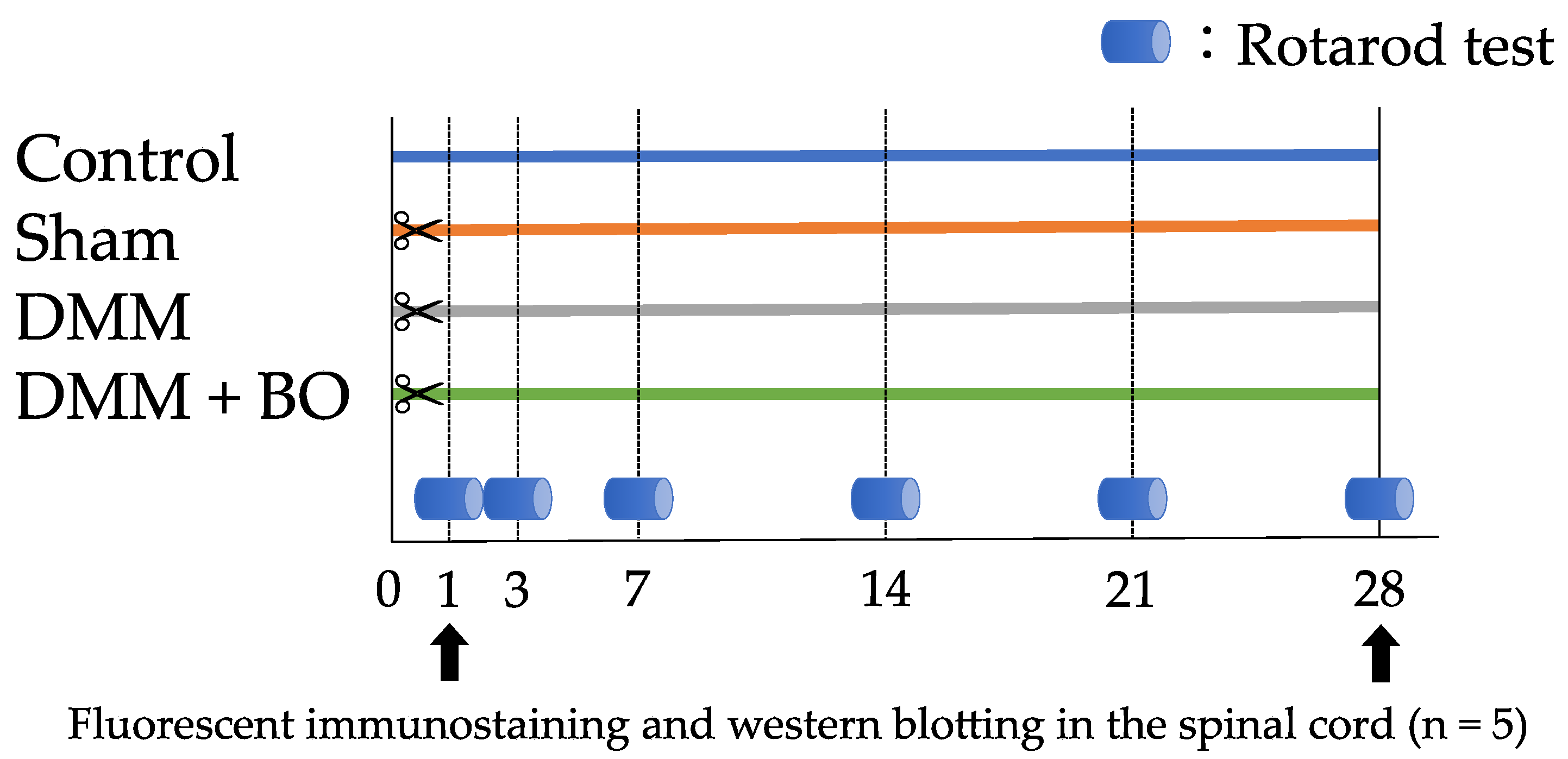
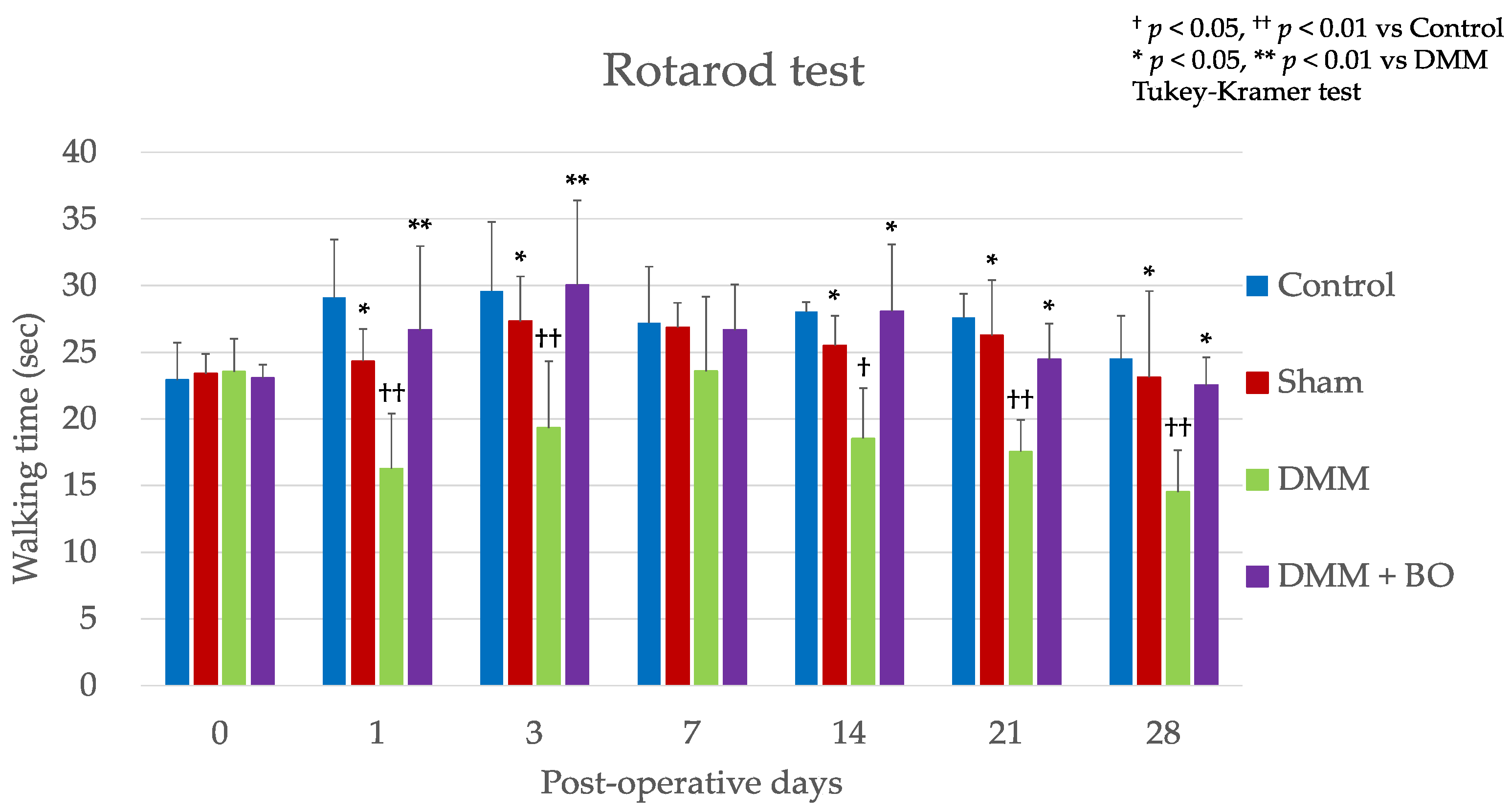
2.4. Rotarod Test
2.5. Experiment 1: Investigation of the Analgesic Effect of BO
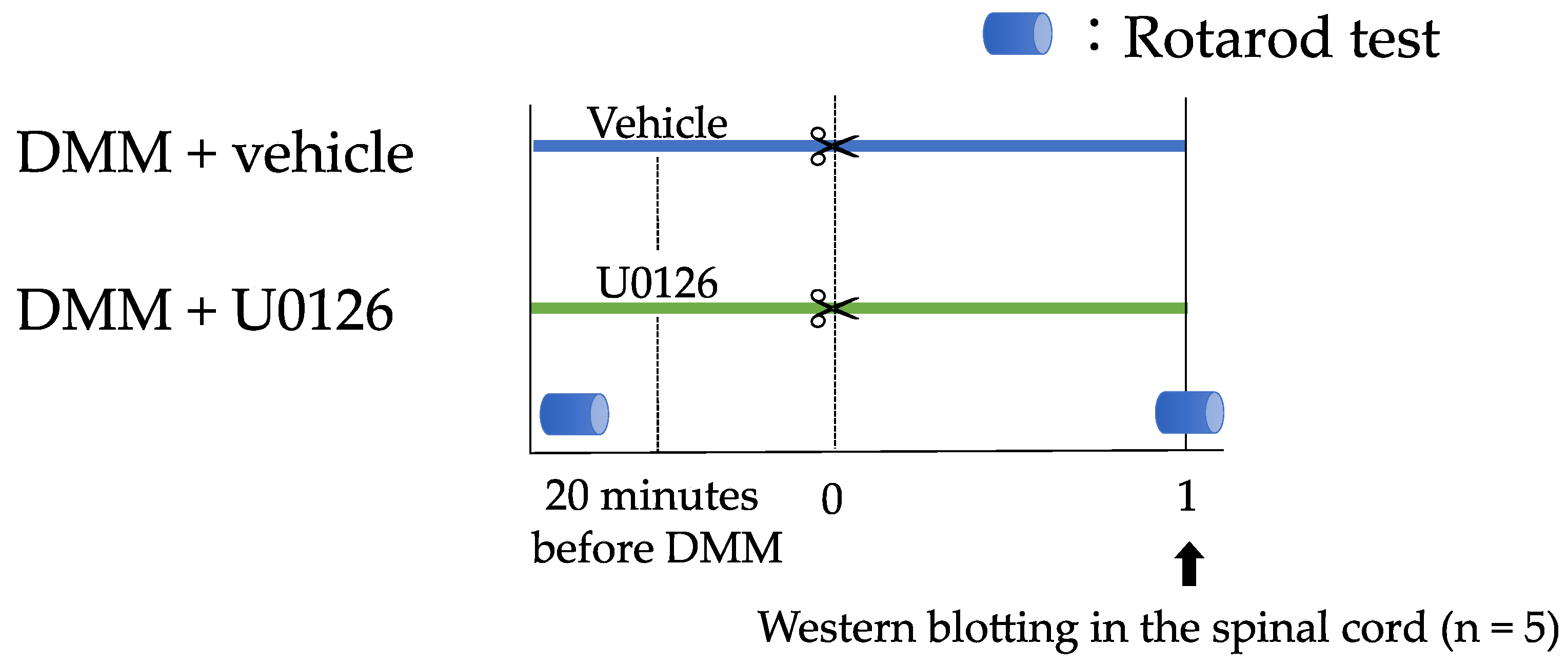
2.6. Experiment 2: Contribution of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation to Pain-Related Locomotive Dysfunction with DMM Surgery
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1: Analgesic Effect of BO
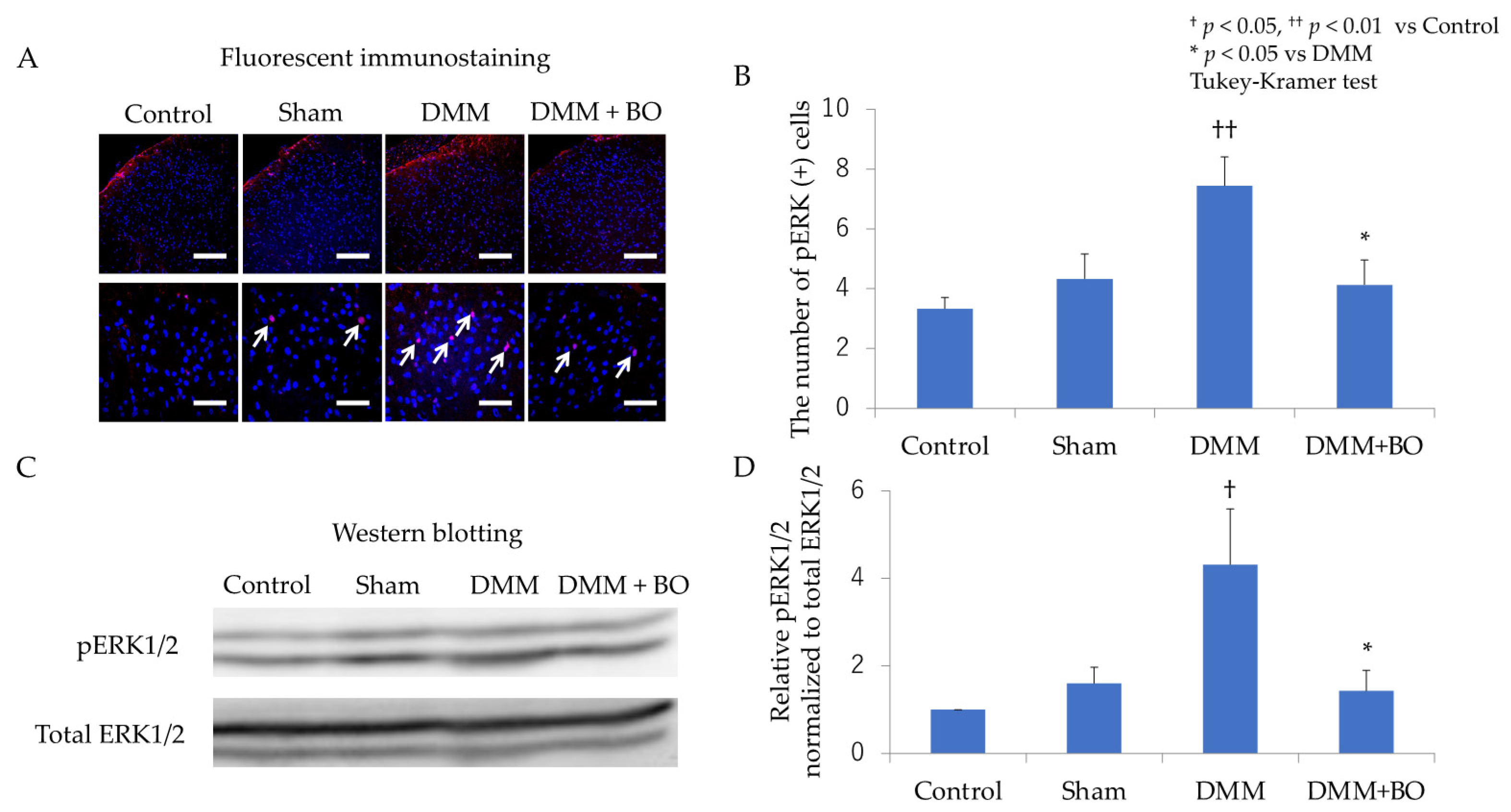
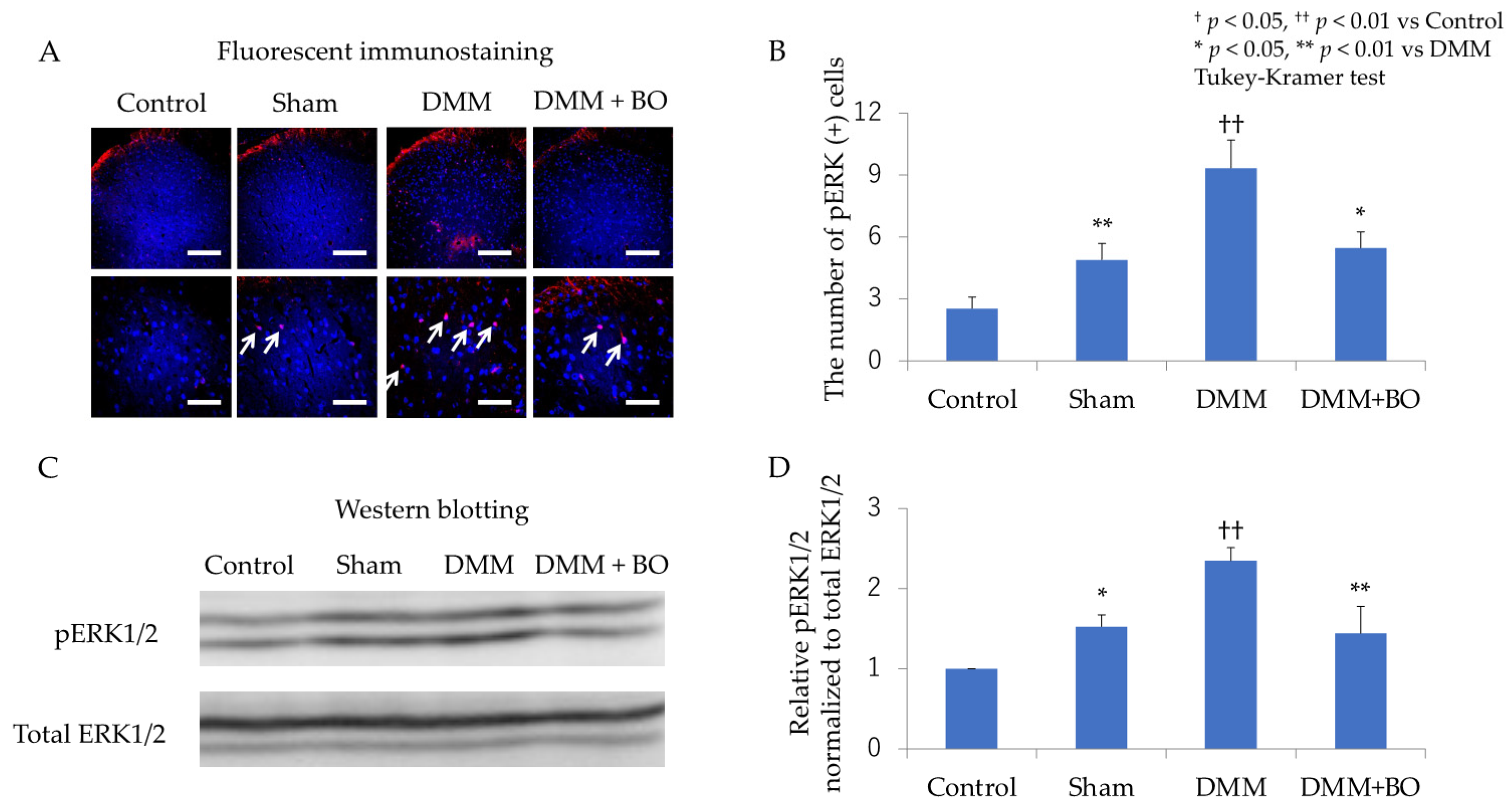
3.2. Suppressive Effect of BO on ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord in the Acute Phase after DMM Surgery
3.3. Suppressive Effect of BO on ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord in the Chronic Phase after DMM Surgery
3.4. Experiment 2: Contribution of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation to Pain-Related Locomotive Dysfunction with DMM Surgery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kloppenburg, M.; Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis years. 2019: Epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jordan, J.M. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina, E.R.; Kwoh, C.K. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Literature update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Johnston, R.C.; Saltzman, C.L.; Marsh, J.L.; Buckwalter, J.A. Posttraumatic osteoarthritis: A first estimate of incidence, prevalence, and burden of disease. J. Orthop. Trauma 2006, 20, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Paul, I.L.; Rose, R.M. Role of mechanical factors in pathogenesis of primary osteoarthritis. Lancet 1972, 1, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.C.; Hunter, D.J. Emerging drugs for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2015, 20, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijimatsu, R.; Kunugiza, Y.; Taniyama, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Tomita, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Expression and pathological effects of periostin in human osteoarthritis cartilage. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, L.C.; Ritvo, S.E.; Ferguson, M.K.; Clarke, H.; Seltzer, Z.; Katz, J. Pain catastrophizing as a risk factor for chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Osani, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Arden, N.K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Kraus, V.B.; Lohmander, L.S.; Abbott, J.H.; Bhandari, M.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotin, Y.; Clutterbuck, A.L.; Allaway, D.; Lodwig, E.M.; Harris, P.; Mathy-Hartert, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Mobasheri, A. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.; Bartels, E.M.; Altman, R.D.; Astrup, A.; Bliddal, H. Does the hip powder of Rosa canina (rosehip) reduce pain in osteoarthritis patients? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.C.; Makino, I.; Ikemoto, T.; Saisu, H.; Terajima, Y.; Owari, K. Kampo for the treatment of pain in Japan: A review. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majima, T.; Inoue, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Onodera, T.; Takahashi, D.; Minami, A. Effect of the Japanese herbal medicine, Boiogito, on the osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Ther. Technol. 2012, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Tamai, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Iizuka, S.; Tsuchiya, N.; Makino, B.; Hattori, T.; Kase, Y.; Isohama, Y. Boiogito, a Kampo medicine, improves hydrarthrosis in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaga, M.; Niimi, J.; Hamaguchi, A.; Asano, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Ohta, Y.; Yudoh, K.; Inoue, H. Protective effect of boiogito extract with glucosamine HCL against adjuvant–induced arthritis in rats. Tradit. Kampo Med. 2018, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oike, J.; Okumo, T.; Ikemoto, H.; Kunieda, Y.; Nakai, S.; Takemura, H.; Takagi, H.; Kanzaki, K.; Sunagawa, M. Preventive effect of the Japanese traditional herbal medicine Boiogito on posttraumatic osteoarthritis in rats. Medicines 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, H.G. Mechanisms of chronic pain in osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.A.; Nie, H.; Laursen, M.B.; Laursen, B.S.; Madeleine, P.; Simonsen, O.H.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Sensitization in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. Pain 2010, 149, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Ji, R.R. c-Fos and pERK, which is a better marker for neuronal activation and central sensitization after noxious stimulation and tissue injury? Open Pain J. 2009, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.D.; Fu, D.; Xu, J.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dai, R.P. Activation of spinal ERK1/2 contributes to mechanical allodynia in a rat model of postoperative pain. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Regulatory Science Society of Japan, Japanese Pharmacopoeia, 17th ed.English Version; Yakuji Nippo: Tokyo, Japan, 2016.
- Ozeki, N.; Muneta, T.; Kawabata, K.; Koga, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Saito, R.; Udo, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Ohara, T.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Centralization of extruded medial meniscus delays cartilage degeneration in rats. J. Orthop. Sci. 2017, 22, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, R.; Muriuki, M.; Gilbertson, L.; Harner, C.D. Biomechanical consequences of a tear of the posterior root of the medial meniscus: Similar to total meniscectomy. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Hara, K.; Haranishi, Y.; Sata, T. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecal administration of taurine in rat models of neuropathic pain. Can. J. Anaesth. 2011, 58, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmon, K.J.; Vyas, M.; Woodley, E.; Thompson, P.; Walia, J.S. Battery of behavioral tests assessing general locomotion, muscular strength, and coordination in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e55491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Akase, T.; Kosugi, M.; Aburada, M. Preventive effect of boiogito on metabolic disorders in the TSOD mouse, a model of spontaneous obese type II diabetes mellitus. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2011, 2011, 931073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, Y.J. Crosstalk between Cdk5/p35 and ERK1/2 signaling mediates spinal astrocyte activity via the PPARγ pathway in a rat model of chronic constriction injury. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, H.; Aoyama, T.; Ito, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nagai, M.; Tajino, J.; Zhang, X.; Kuroki, H. Effects of short-term gentle treadmill walking on subchondral bone in a rat model of instability-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Li, T.T.; Zhao, J.; Mao-Ying, Q.L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, S.; Li, Q.; Mi, W.L.; Wu, G.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in spinal astrocytes and microglia contributes to cancer-induced bone pain in rats. Neuroscience 2012, 217, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Shen, J.; Qiu, J.; Yin, X.; Yin, H.; Jiang, S. Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 84, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.T.; Wang, B.; Jia, Y.N.; Liu, N.; Ma, P.S.; Gong, S.S.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.X.; Yu, J.Q. Neuroprotective effect of liquiritin against neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Paz, M.-D.S.; Garcia-Gimenez, M.D.; Quilez, A.M.; De la Puerta, R.; Fernandez-Arche, A. Ginger rhizome enhances the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of paracetamol in an experimental mouse model of fibromyalgia. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Takayama, Y.; Sunagawa, M. The calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A is Inhibitied by liquiritigenin. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, Y.; Hitomi, S.; Omiya, Y.; Ujihara, I.; Kokabu, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Ono, K. Isoliquiritigenin, an active ingredient of Glycyrrhiza, elicits antinociceptive effects via inhibition of Nav channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, Z.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Isoliquiritigenin is a novel NMDA receptor antagonist in Kampo medicine yokukansan. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Z.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Glycyrrhizin and its metabolite 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid in glycyrrhiza, a constituent herb of yokukansan, ameliorate thiamine deficiency-induced dysfunction of glutamate transport in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 626, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunieda, Y.; Okumo, T.; Ikemoto, H.; Adachi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Kimura, T.; Yusa, K.; Kanzaki, K.; Sunagawa, M. Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
Kunieda Y, Okumo T, Ikemoto H, Adachi N, Tanaka M, Kimura T, Yusa K, Kanzaki K, Sunagawa M. Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunieda, Yusuke, Takayuki Okumo, Hideshi Ikemoto, Naoki Adachi, Midori Tanaka, Taro Kimura, Kanako Yusa, Koji Kanzaki, and Masataka Sunagawa. 2021. "Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
APA StyleKunieda, Y., Okumo, T., Ikemoto, H., Adachi, N., Tanaka, M., Kimura, T., Yusa, K., Kanzaki, K., & Sunagawa, M. (2021). Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421






