Experiment-Based Fatigue Behaviors and Damage Detection Study of Headed Shear Studs in Steel–Concrete Composite Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Study
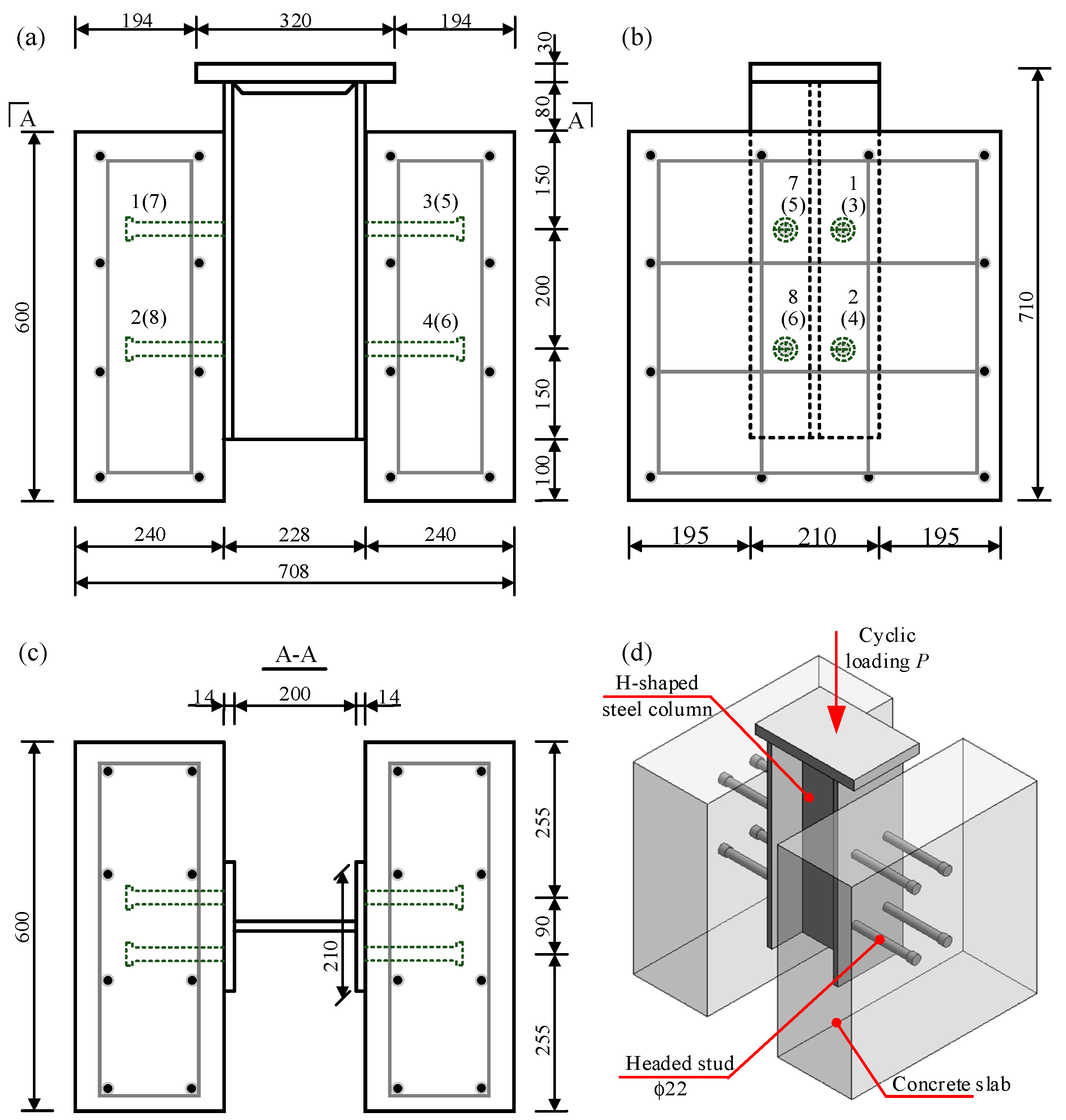
2.1. Test Specimens Details
2.2. Material Properties
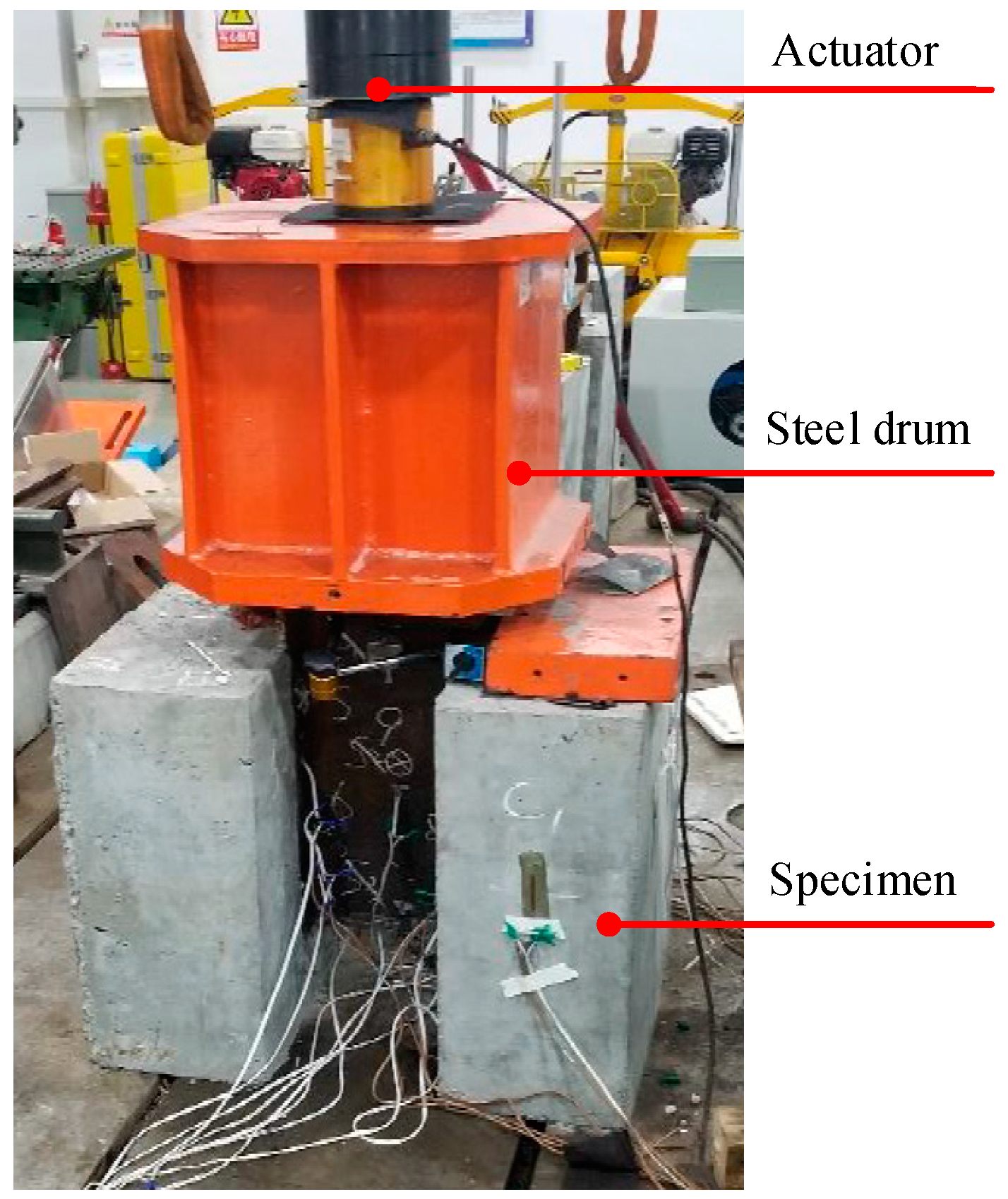
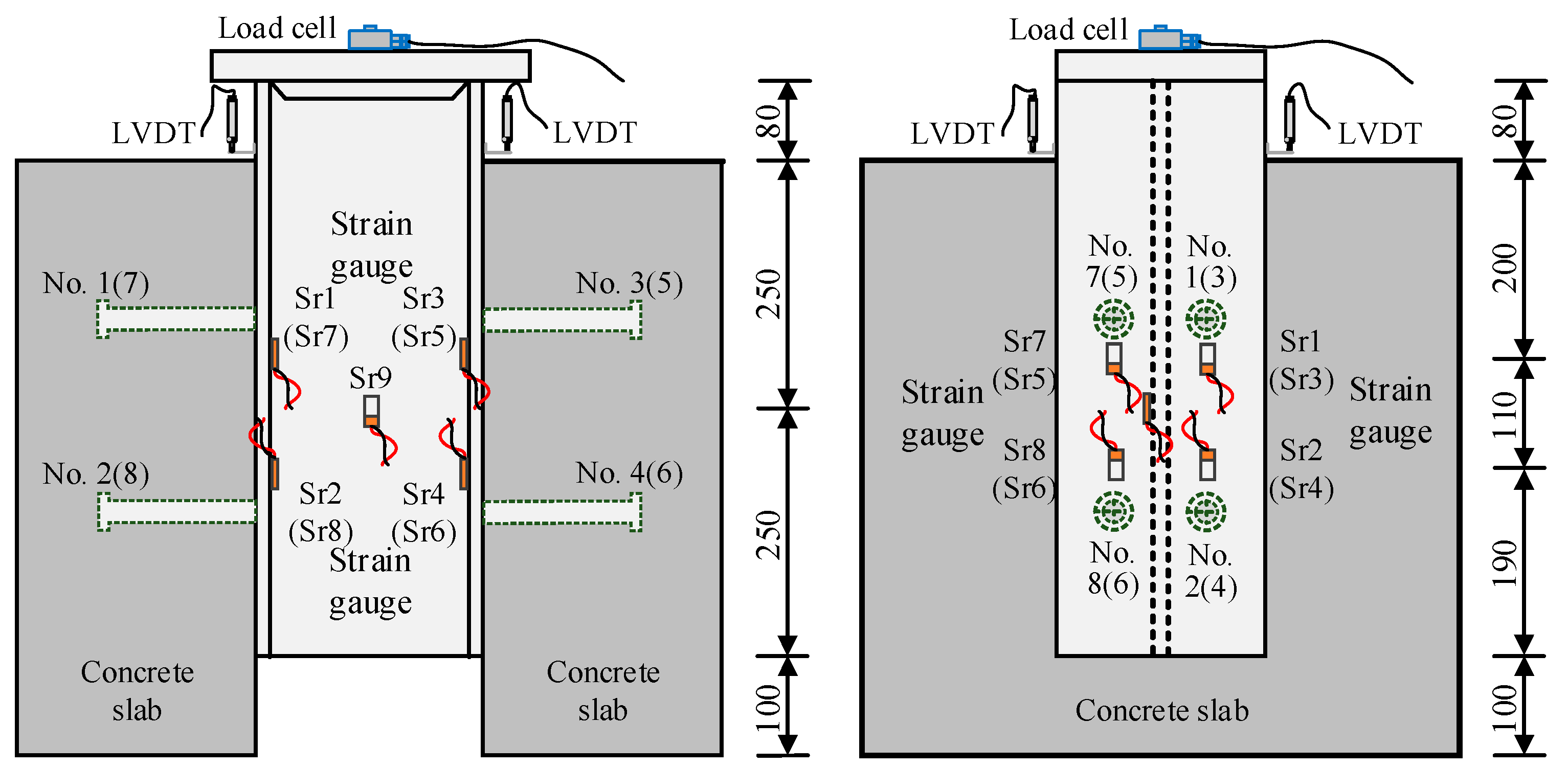
2.3. Test Instruments and Setup
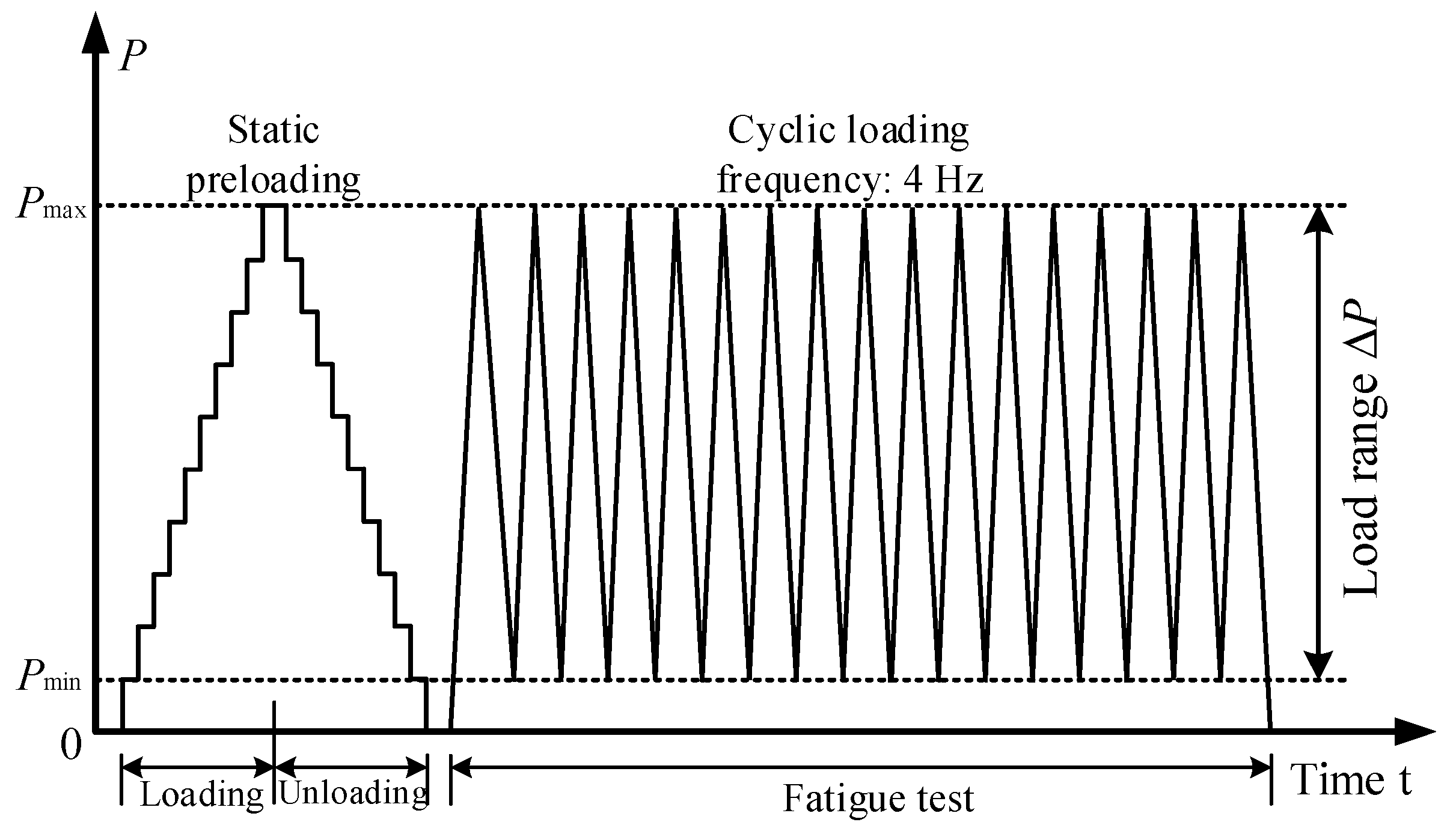
2.4. Fatigue Test Program
3. Fatigue Test Results
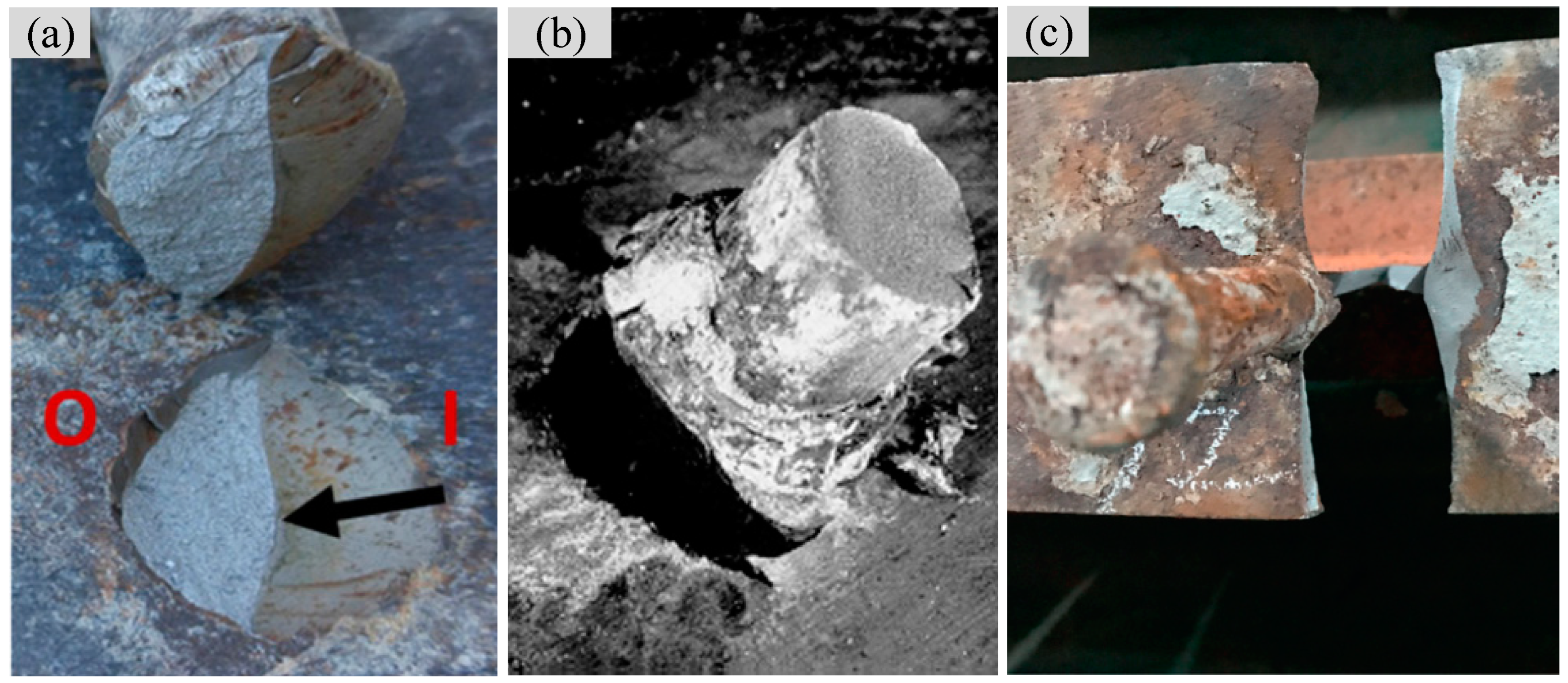
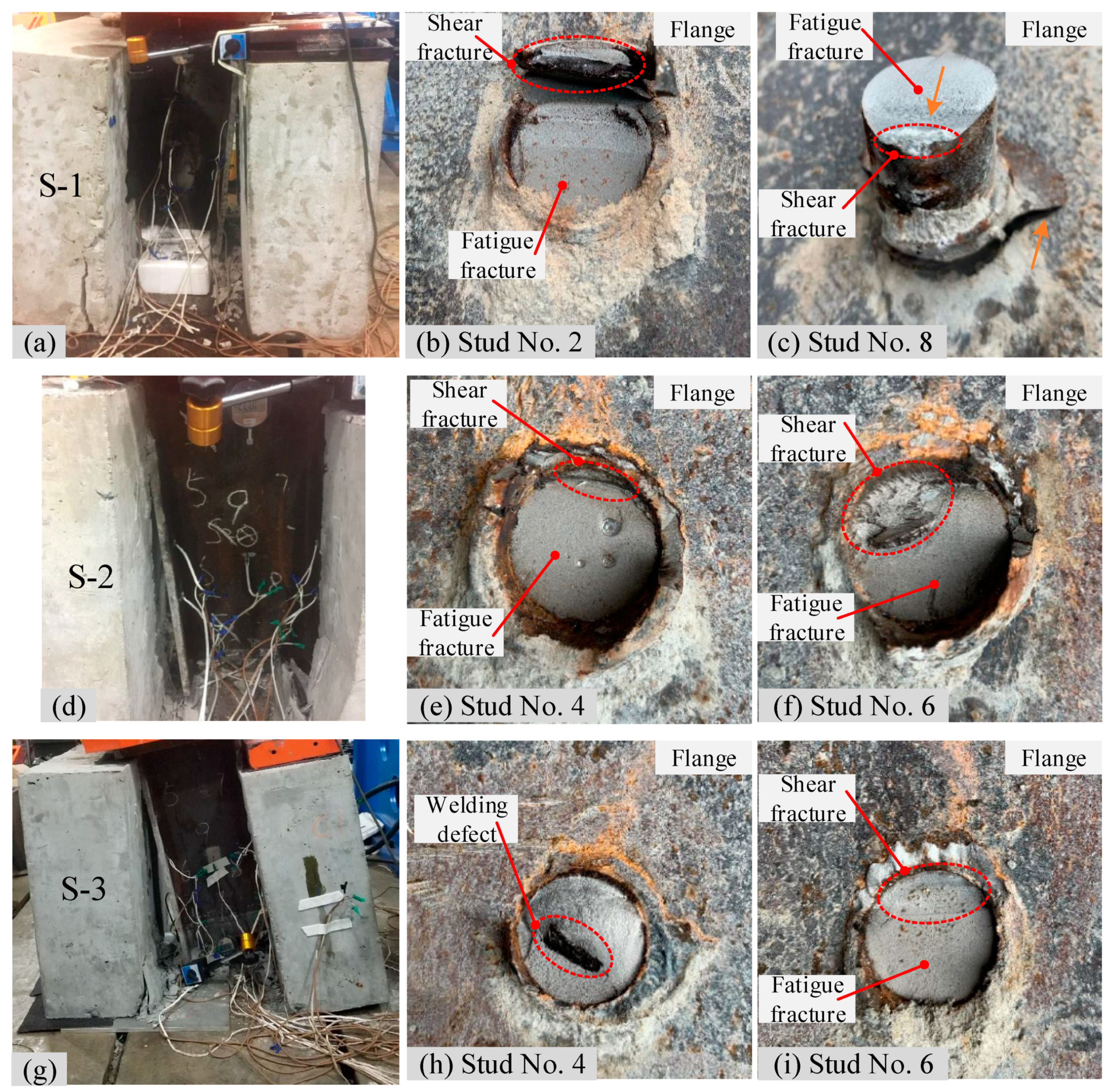
3.1. Fatigue Failure Mode
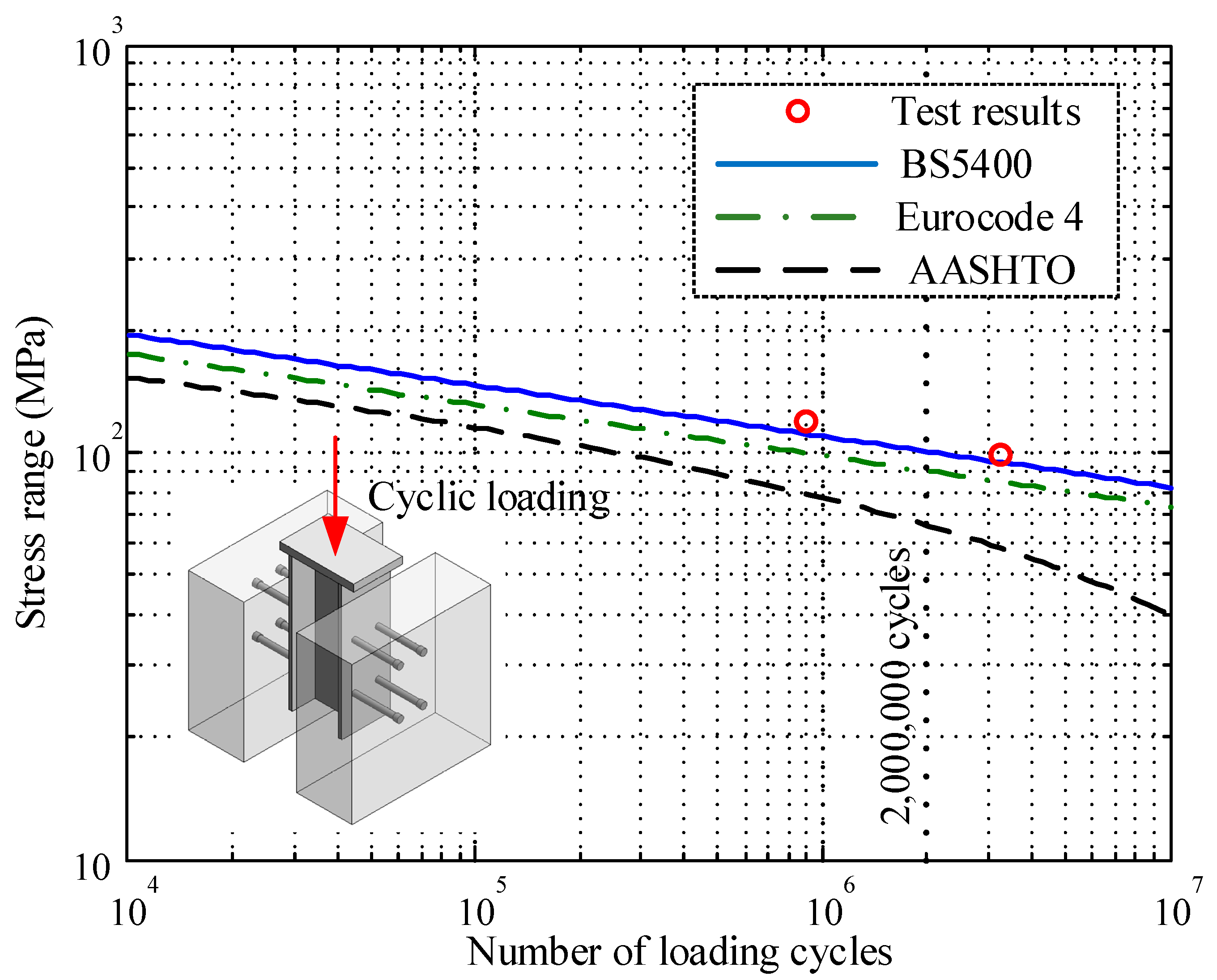
3.2. Fatigue Life Estimation
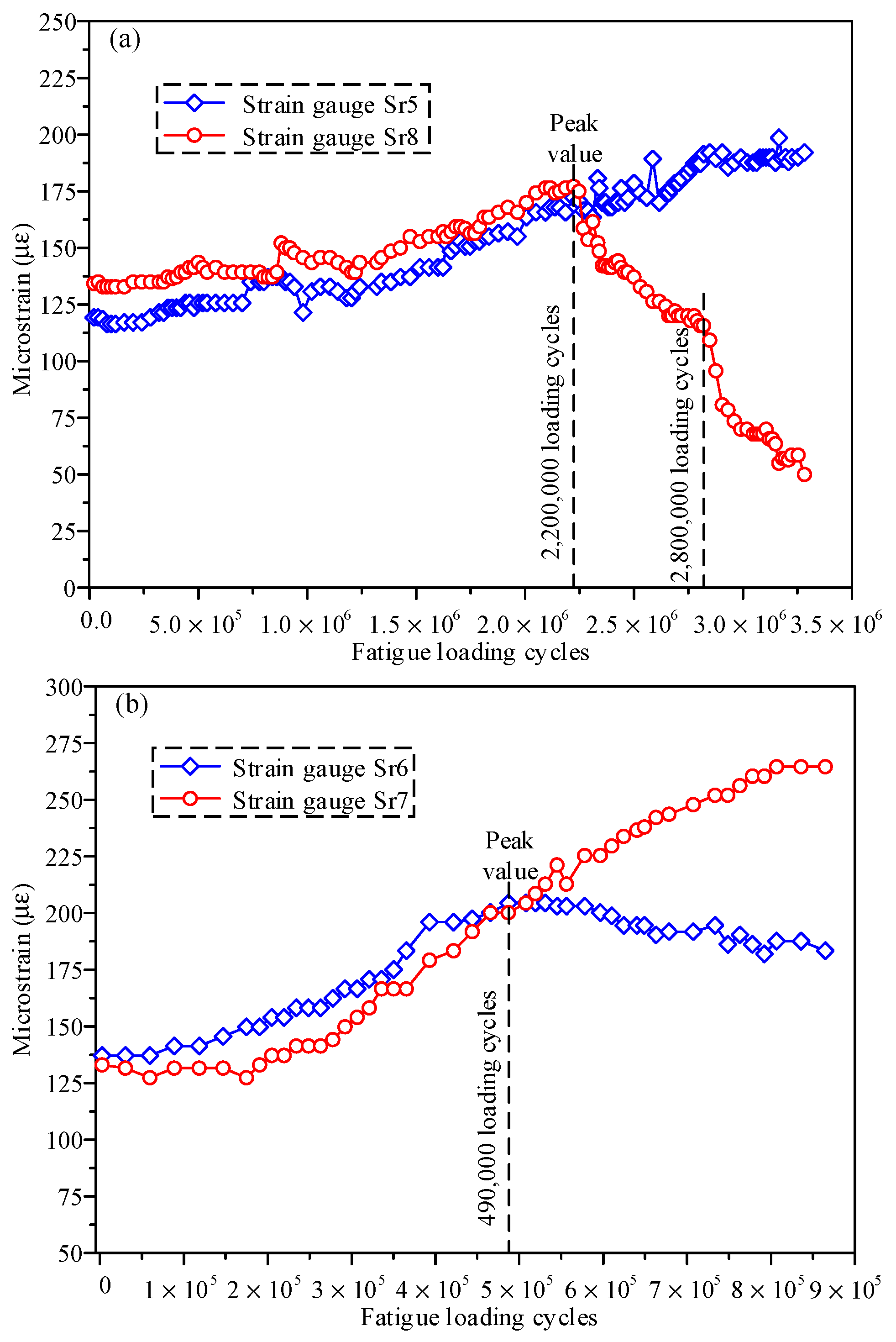
3.3. Strain Evolution under Cyclic Loading
4. Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing of Headed Shear Studs
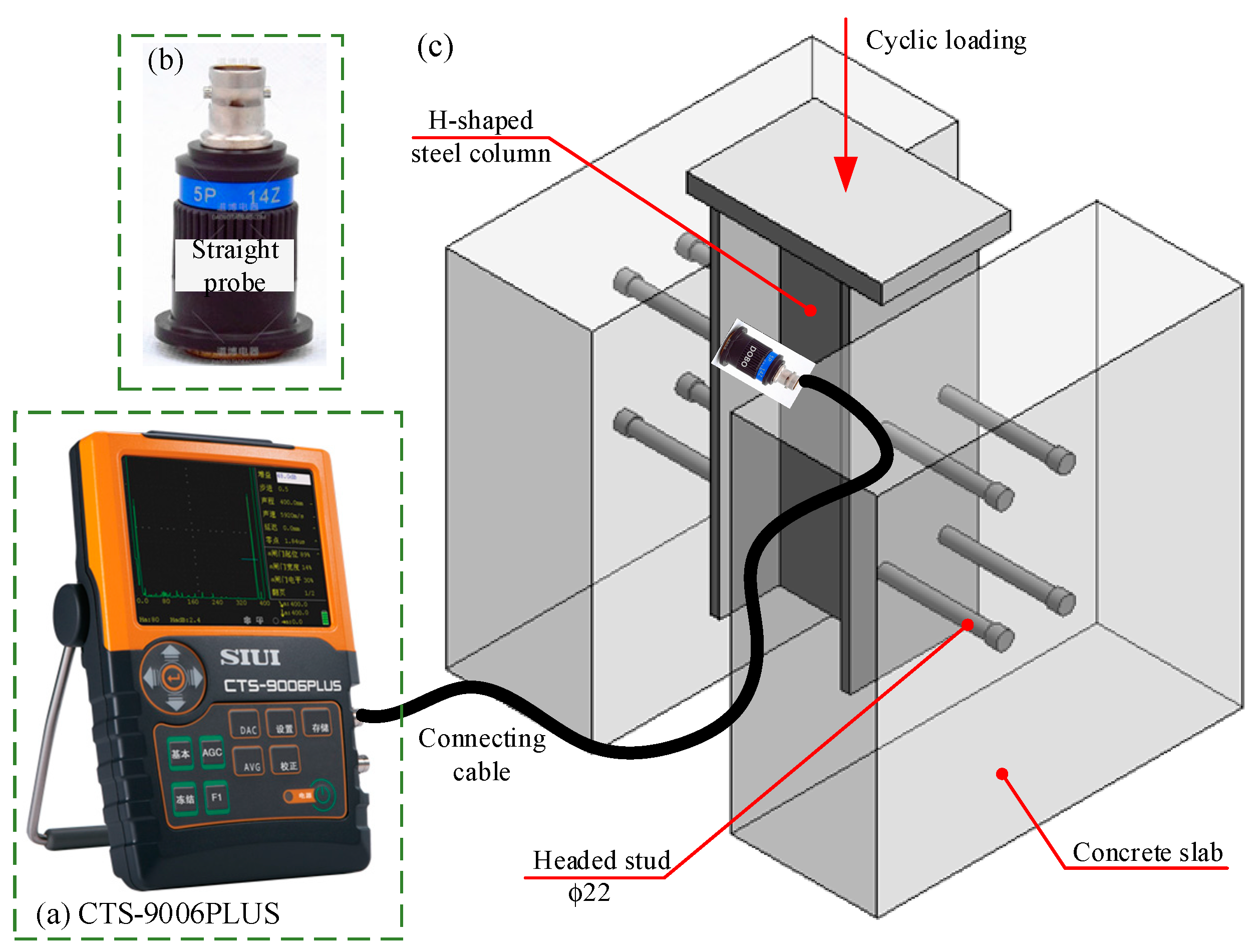
4.1. Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing Equipment and Distance–Amplitude Curve
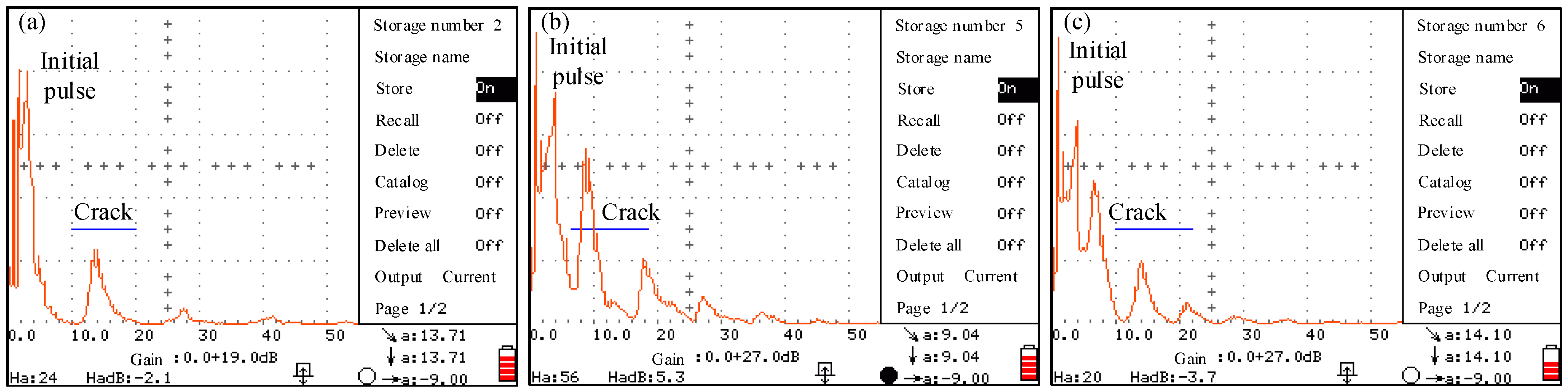
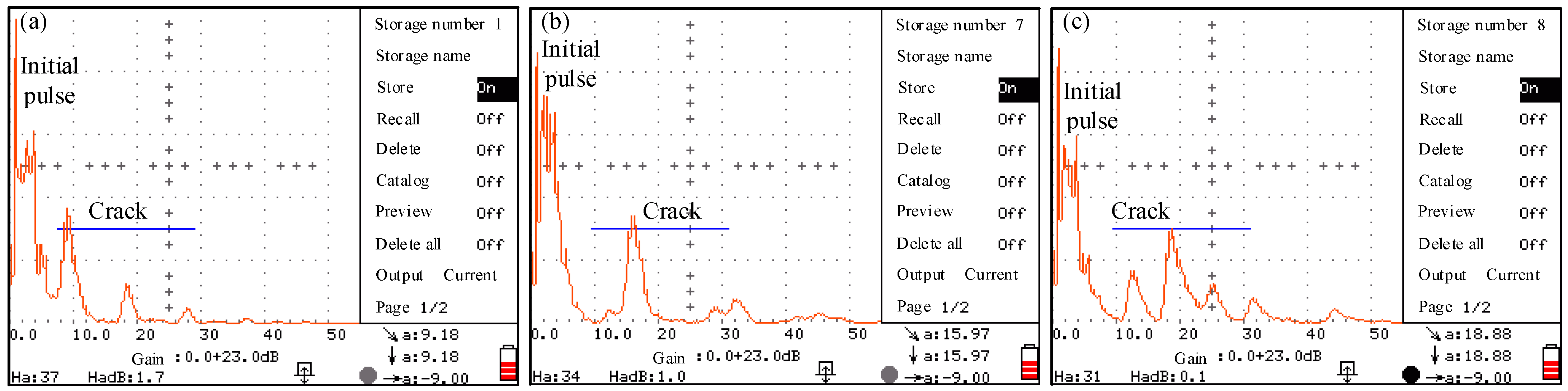
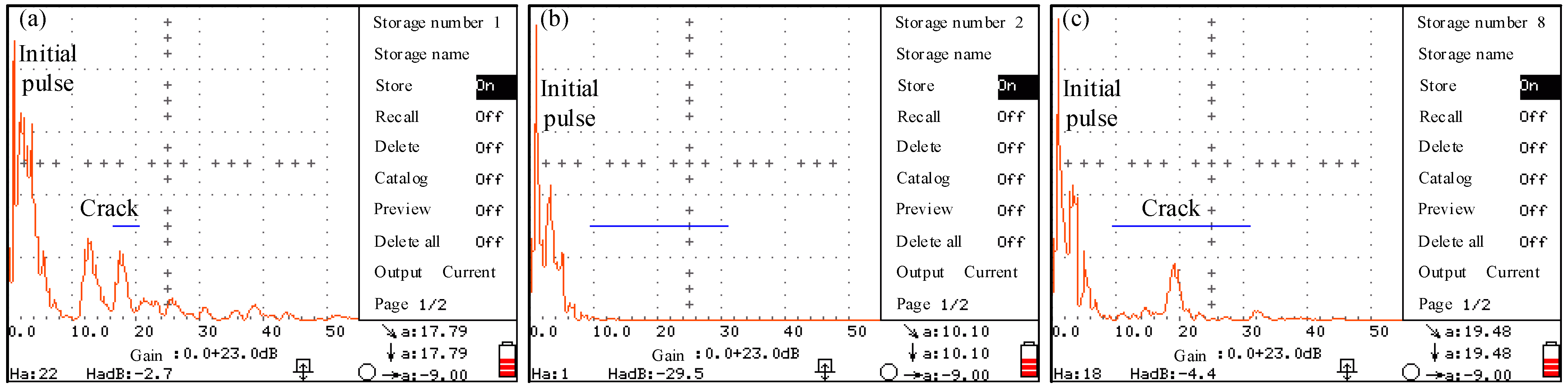
4.2. Crack Detection Results of Headed Shear Studs
5. Conclusions and Discussions
- (1)
- The root fracture was the main fatigue failure mode for headed shear studs under cyclic fatigue loading. Based on all the three current codes (i.e., AASHTO, Eurocode 4 and BS5400), the safe fatigue life estimation of headed shear studs can be guaranteed only with different safety redundancies.
- (2)
- The strain at the good shear stud gradually increased with the fatigue loading cycles until the failure of the specimen. The strain at the shear stud with fatigue damage showed a consistent increasing trend followed by decreasing behavior after reaching the peak value with the loading cycles. The strain measurements were helpful to estimate the fatigue damage to the embedded studs.
- (3)
- With the combination of a strain measurement, the ultrasonic non-destructive testing for fatigue crack detection of headed shear studs was feasible. The fatigue crack location of headed shear studs under cyclic loads can be measured.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xing, Y. Static behavior of stud shear connectors in elastic concrete–steel composite beams. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 113, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, C.; Lee, P.-G.; Yoon, T.-Y. Static behavior of large stud shear connectors. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjaarda, M.; Porter, T.; West, J.S.; Walbridge, S. Fatigue behavior of welded shear studs in precast composite beams. J. Bridg. Eng. 2017, 22, 04017089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slutter, R.G.; Fisher, J.W. Fatigue Strength of Shear Connectors; Highway Research Record No: New York, NY, USA, 1966; Volume 147, pp. 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hallam, M.W. The Behavior of Stud Shear Connectors under Repeated Loading; Research Rep. R281; School of Civil Engineering, University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Oehlers, D.; Coughlan, C. The shear stiffness of stud shear connections in composite beams. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1986, 6, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seracino, R.; Oehlers, D.J.; Yeo, M.F. Behaviour of stud shear connectors subjected to bi-directional cyclic loading. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2003, 6, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanswille, G.; Porsch, M.; Ustundag, C. Resistance of headed studs subjected to fatigue loading: Part I: Experimental study. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2007, 63, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanswille, G.; Porsch, M.; Ustundag, C. Resistance of headed studs subjected to fatigue loading Part II: Analytical study. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2007, 63, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovuoba, B.; Prinz, G.S. Fatigue capacity of headed shear studs in composite bridge girders. J. Bridg. Eng. 2016, 21, 04016094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, Y.; Matsuyi, S. Effects of Concrete Placing Direction on Static and Fatigue Strengths of Stud; Technology Reports of the Osaka University: Osaka, Japan, 1983; pp. 397–406.
- Badie, S.S.; Tadros, M.K.; Kakish, H.F.; Splittgerber, D.L.; Baishya, M.C. Large shear studs for composite action in steel bridge girders. J. Bridg. Eng. 2002, 7, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-G.; Shim, C.-S.; Chang, S.-P. Static and fatigue behavior of large stud shear connectors for steel–concrete composite bridges. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2005, 61, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, J.; Yoda, T.; Lebet, J.P. A study of the grouped arrangements of stud connectors on shear strength behavior. J. Struct. Mech. Earthq. Eng. 2006, 23, 75S–89S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, C.S.; Lee, P.G.; Kim, D.W.; Chung, C.H. Effects of group arrangement on the ultimate strength of stud shear connection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Composite Construction in Steel and Concrete IV; Leon, R.T., Perea, T., Rassati, C.A., Lange, J., Eds.; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Sugiura, K.; Su, Q.T. Fatigue behavior of the group stud shear connectors in steel-concrete composite bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 2018, 23, 04018055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, B.; Lam, C.; Tharmabala, B. Effect of shear stud clusters in composite girder bridge design. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 42, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlers, D.J.; Seracino, R.; Yeo, M.F. Fatigue behaviour of composite steel and concrete beams with stud shear connections. Prog. Struct. Eng. Mater. 2000, 2, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.-Q. Static and fatigue behavior of steel-concrete composite beams with corroded studs. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 156, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollgaard, J.G.; Slutter, R.G.; Fisher, J.W. Shear strength stud connect. lightweight normal-weight concrete. Aisc Eng. J. 1971, 8, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Y.; Tang, X.B. Research on the fatigue performance of lightweight aggregate concrete headed stud connectors. J. Railw. Eng. Soc. 2013, 176, 97–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Su, Q.; Masuya, H. Static and fatigue behavior of the stud shear connector in lightweight concrete. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2018, 18, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kwark, J.; Joh, C.; Yoo, S.-W.; Lee, K.-C. Headed stud shear connector for thin ultrahigh-performance concrete bridge deck. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 108, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Shao, X.; Deng, L.; Gan, Y. Static and fatigue behavior of short-headed studs embedded in a thin ultrahigh-performance concrete layer. J. Bridge Eng. 2017, 22, 04017005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewski, D.; Wille, K.; Zaghi, A.E. Push-out behavior of headed shear studs welded on thin plates and embedded in UHPC. Eng. Struct. 2018, 173, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, V.C. Influence of concrete material ductility on shear response of stud connections. ACI Mater. J. 2006, 103, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, Y.; Bu, Y. Static and fatigue push-out tests of short headed shear studs embedded in Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC). Eng. Struct. 2018, 182, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafipour, M.S.; Tatlari, S.; Azad, A.R.G.; Shahverdi, M.; Mohammadi, S. Fatigue behavior of headed stud shear connectors in steel-concrete composite bridge girders. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Research in Structural Engineering and Constructional Management, Tehran, Iran, 26–27 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Balkos, K.D.; Sjaarda, M.; West, J.S.; Walbridge, S. Static and fatigue tests of steel-precast composite beam specimens with through-bolt shear connectors. J. Bridg. Eng. 2019, 24, 04019036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Lobody, E.; Lam, D. Finite element analysis of steel-concrete composite girders. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2003, 6, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Bhowmick, A.K. A finite element based approach for fatigue life prediction of headed shear studs. Structures 2019, 19, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Sun, H.; Xie, Z.; Sun, J. Fatigue behaviour study of the shear stud using crack box technology and m integral method. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2019, 19, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovuoba, B.; Prinz, G. Investigation of residual fatigue life in shear studs of existing composite bridge girders following decades of traffic loading. Eng. Struct. 2018, 161, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; De Roeck, G. Damage detection of shear connectors in composite bridges. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Su, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y. Experimental and theoretical analysis of the correlation between cumulative plastic damage and SMFL of structural steel under low cycle fatigue. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 538, 168292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, R.; Saponaro, A. Real-time monitoring of fatigue damage by Electrical Resistance Change method. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 151, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, P.; Gołaszewski, J. Relationship of different properties from non-destructive testing of heavy concrete from magnetite and serpentinite. Materials 2021, 14, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENV 1994, Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures-Part 2: General Rules and Rules for Bridges; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for Design of Concrete Structures; GB 50010-2010; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Structural Steel for Bridge; GB/T 714-2015; Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- LRFD Bridge Design Specifications, 6th ed.; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Steel, Concrete and Composite Bridges-Part 10: Code of Practice for Fatigue; BS5400; British Standards Institute: London, UK, 1980.
- Krautkrämer, J.; Krautkrämer, H. Ultrasonic Testing of Materials; 4th Fully Revised Edition; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Matlack, K.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jacobs, L.; Qu, J. Review of second harmonic generation measurement techniques for material state determination in metals. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2014, 34, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Nondestructive Testing. Nondestructive Testing Handbook, 3rd ed.; Ultrasonic Testing: Columbus, OH, USA, 2007; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]

| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-shaped steel column | 345 | 490 | 2.05 × 105 |
| Headed shear studs | 240 | 400 | 2.05 × 105 |
| Reinforcement bars | 335 | 455 | 2.00 × 105 |
| Specimens | Minimum Load Pmin (kN) | Maximum Load Pmax (kN) | Load Range ΔP (kN) | Load Ratio R | Stress Range Δτ (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | 50 | 350 | 300 | 0.14 | 98.6 |
| S-2 | 40 | 400 | 360 | 0.10 | 118.4 |
| S-3 | 30 | 370 | 340 | 0.08 | 111.8 |
| Specimen | Stress Range Δτ (MPa) | Estimated Fatigue Lives | Actual Fatigue Lives | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AASHTO | Eurocode 4 | BS5400 | |||
| S-1 | 98.6 | 274,372 | 963,728 | 2,328,348 | 3,280,000 |
| S-2 | 118.4 | 81,598 | 222,923 | 538,579 | 890,000 |
| S-3 | 111.8 | 122,245 | 352,724 | 852,175 | 133,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, W.; Guo, X. Experiment-Based Fatigue Behaviors and Damage Detection Study of Headed Shear Studs in Steel–Concrete Composite Beams. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188297
Xu J, Sun H, Chen W, Guo X. Experiment-Based Fatigue Behaviors and Damage Detection Study of Headed Shear Studs in Steel–Concrete Composite Beams. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188297
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jun, Huahuai Sun, Weizhen Chen, and Xuan Guo. 2021. "Experiment-Based Fatigue Behaviors and Damage Detection Study of Headed Shear Studs in Steel–Concrete Composite Beams" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188297
APA StyleXu, J., Sun, H., Chen, W., & Guo, X. (2021). Experiment-Based Fatigue Behaviors and Damage Detection Study of Headed Shear Studs in Steel–Concrete Composite Beams. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188297






