Efficient Removal of Azo Dye from Wastewater Using the Non-Toxic Potassium Ferrate Oxidation–Coagulation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Performance Evaluation of Dye Removal
2.4. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
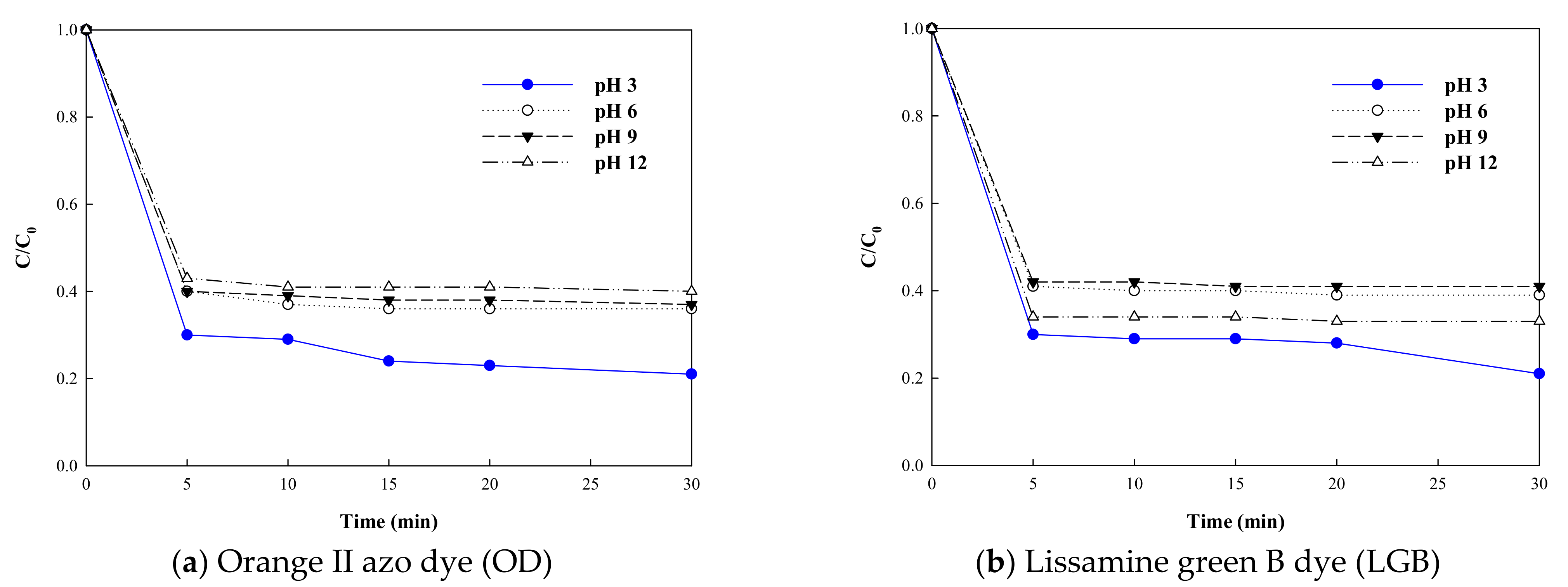
3.1. Effect of pH on Azo Dye Removal Efficiency by Potassium Ferrate (K2FeO4)
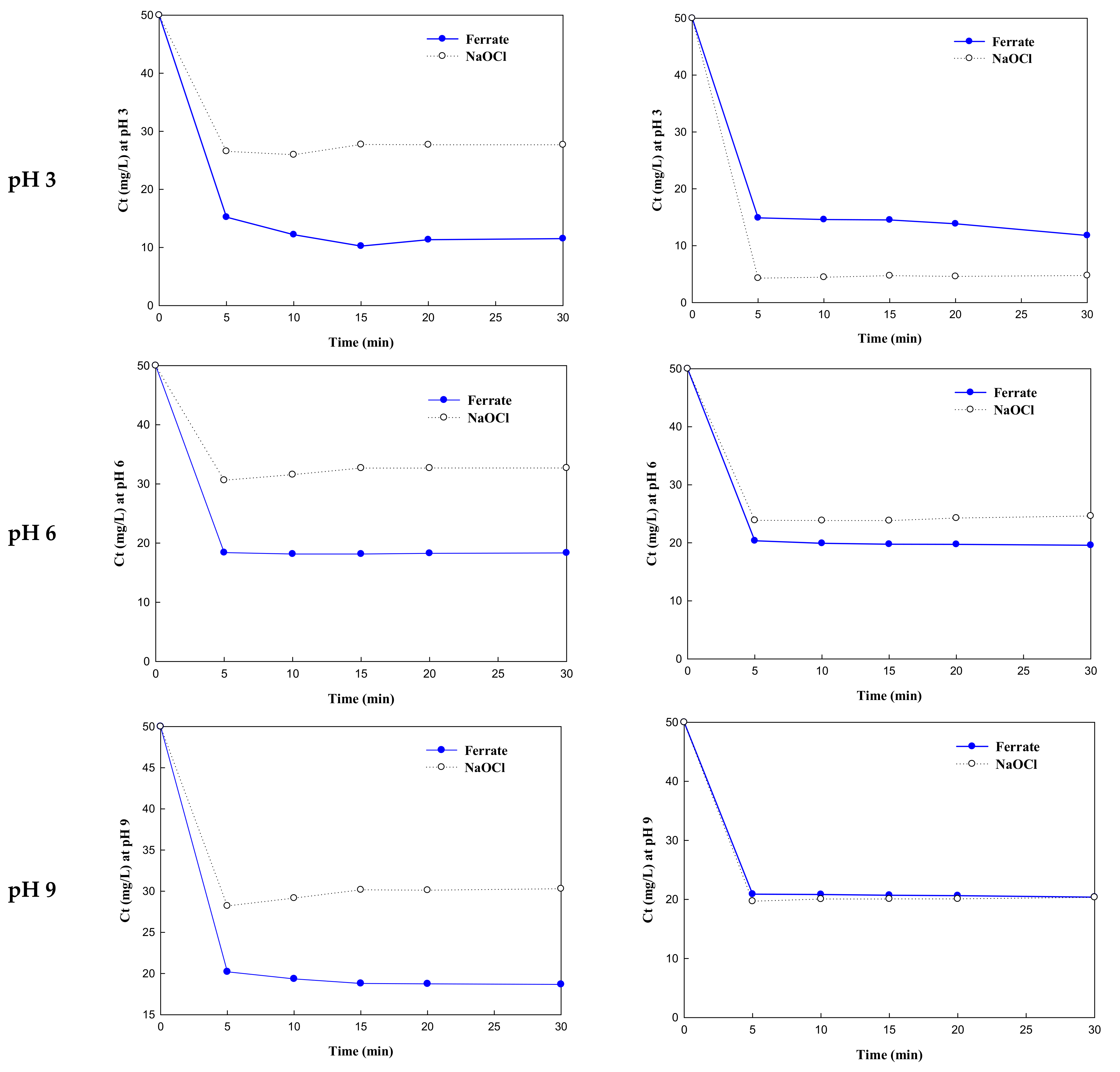
3.2. Dye Removal Rate by K2FeO4 and NaOCl
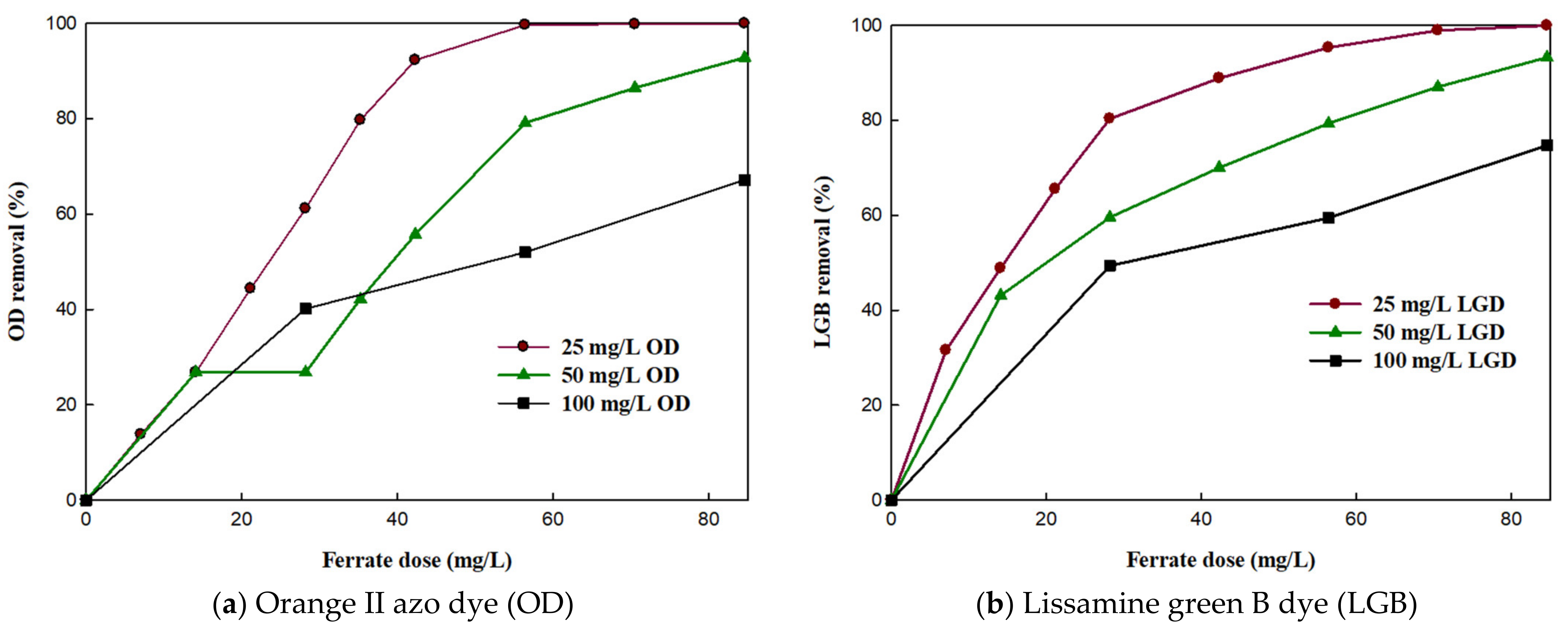
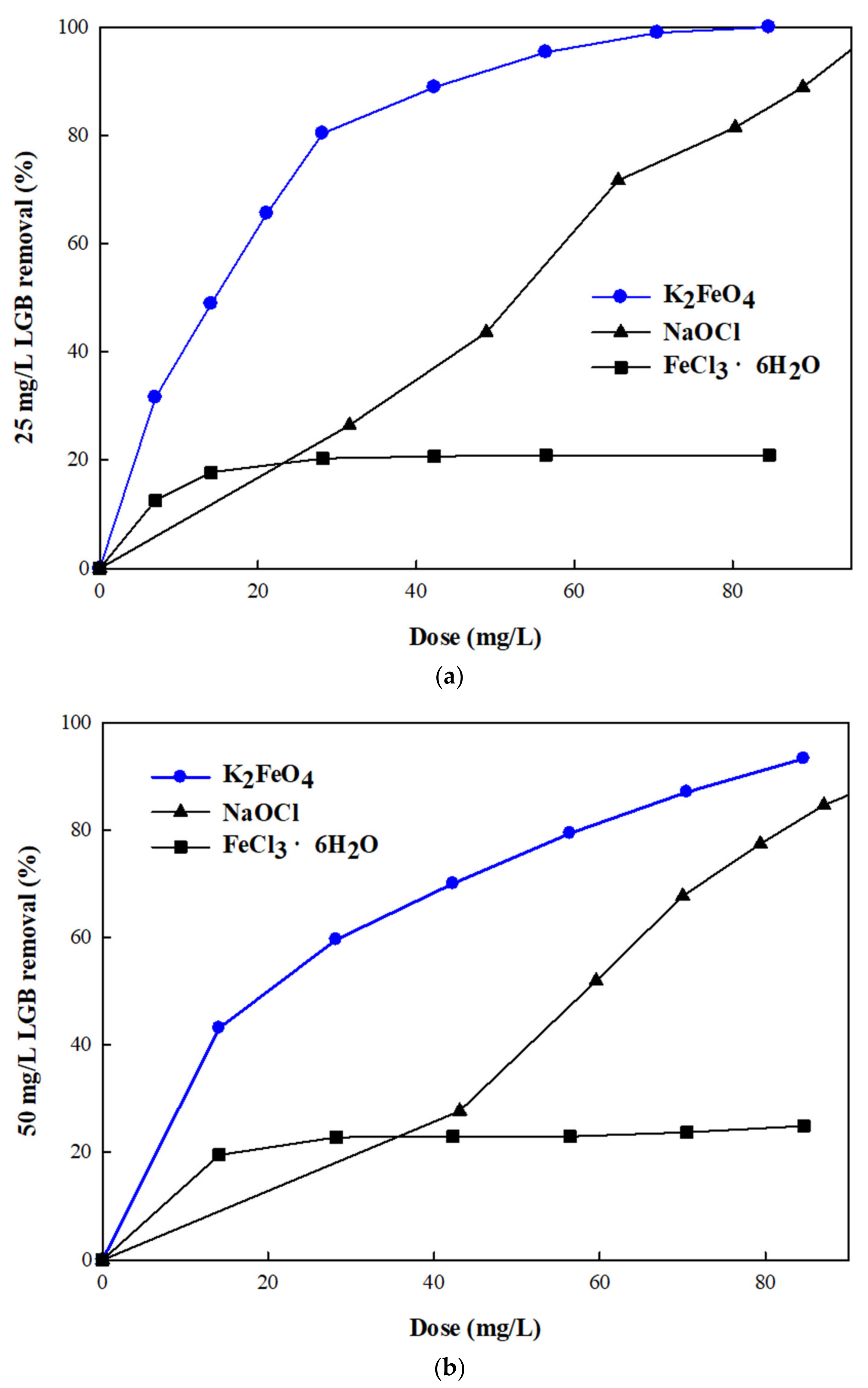
3.3. Effect of Potassium Ferrate (K2FeO4) Dose on Removal Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Guo, G.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Ding, K.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Azo dye decolorization by a halotolerant consortium under microaerophilic conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Juang, R.S. Treatment of waters and wastewaters containing sulfur dyes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geundi, M.S.; Ismail, H.M.; Attyia, K.M.E. Activated Clay as an Adsorbent for Cationic Dyestuffs. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 1995, 12, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Hybrid ozonation process for industrial wastewater treatment: Principles and applications: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiadh, L.; Barbucci, A.; Cerisola, G.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Panizza, M. Role of anode material on the electrochemical oxidation of methyl orange. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 3177–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alwani, M.A.M.; Ludin, N.A.; Mohamad, A.; Kadhum, A.H.; Mukhlus, A. Application of dyes extracted from Alternanthera dentata leaves and Musa acuminata bracts as natural sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 192, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S.A.; Rao, K.V.B. Aerobic biodegradation of Azo dye by Bacillus cohnii MTCC 3616, an obligately alkaliphilic bacterium and toxicity evaluation of metabolites by different bioassay systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7469–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dye. Pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Decolorization of dye wastewaters by biosorbents: A review. J Env. Manag. 2010, 91, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan-Yucel, U.G.; Gokcay, C.F. Effect of Initial Azo Dye Concentration and Biomass Acclimation on Sludge Digestion and Dye Co-treatment. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2010, 38, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.C.D.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Suanon, F.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.-P. Decolorization of azo dye methyl red by suspended and co-immobilized bacterial cells with mediators anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Teng, K.; Zhou, B.; Ma, M.; Shan, M.; Jiao, K.; Qian, X.; Fan, J. High flux and rejection of hierarchical composite membranes based on carbon nanotube network and ultrathin electrospun nanofibrous layer for dye removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, K.; Turgut, Z. Decolorization of direct dye in textile wastewater by ozonization in a semi-batch bubble column reactor. Desalination 2009, 242, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.J.; Yang, B.; Chen, J.H.; Sun, R. Treatment of wastewater containing azo dye reactive brilliant red X-3B using sequential ozonation and upflow biological aerated filter process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgacs, E.; Cserhati, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abba, A.; MiIno, M.; Arab, H.; Bestetti, M.; Franz, M. Decolorization and biodegradability of a real pharmaceutical wastewater treated by H2O2-assisted photoelectrocatalysis on TiO2 meshes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.D. Kinetics and Product Identification of Oxidation by Ferrate(VI) of Water and Aqueous Nitrogen Containing Solutes. In Ferrates; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 985, pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Oxidation of ethanethiol in aqueous alkaline solution by ferrate(VI): Kinetics, stoichiometry and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K. Potassium ferrate(VI): An environmentally friendly oxidant. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.Z.; Graham, N. A study of the preparation and reactivity of potassium ferrate. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoppe, M.L.; Schlemper, E.O.; Murmann, R.K. Structure of dipotassium ferrate(VI). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1982, 38, 2237–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.D.; Kelter, P.; Tabatabai, A.; Plichal, D.v.; Erickson, J.; Mclaughlin, C. Properties of Ferrate vi in Aqueous Solution an Alternate Oxidant in Wastewater Treatment. 1985. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Properties-of-ferrate-vi-in-aqueous-solution-an-in-Carr-Kelter/9fdac66c6273688ce15732940291d5540c8c89e8 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Karami, M.; Amin, M.; Nourmoradi, H.; Sadani, M.; Teimouri, F.; Bina, B. Degradation of reactive red 198 from aqueous solutions by advanced oxidation process: O3, O3/H2O2, and persulfate. Int. J. Environ. Health Eng. 2016, 5, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Arora, S. Removal of Synthetic Textile Dyes From Wastewaters: A Critical Review on Present Treatment Technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 807–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reaction Rate (ln(Ct)/t) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange II Azo Dye | Lissamine Green B Dye | |||
| Ferrate | NaOCl | Ferrate | NaOCl | |
| pH 3 | −1.1894 | −0.6330 | −1.2110 | −2.4569 |
| pH 6 | −0.9997 | −0.4907 | −0.8989 | −0.7396 |
| pH 9 | −0.9058 | −0.5722 | −0.8723 | −0.9314 |
| pH 12 | −0.8489 | −1.1426 | −1.0671 | −0.9036 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jargalsaikhan, M.; Lee, J.; Jang, A.; Jeong, S. Efficient Removal of Azo Dye from Wastewater Using the Non-Toxic Potassium Ferrate Oxidation–Coagulation Process. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156825
Jargalsaikhan M, Lee J, Jang A, Jeong S. Efficient Removal of Azo Dye from Wastewater Using the Non-Toxic Potassium Ferrate Oxidation–Coagulation Process. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(15):6825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156825
Chicago/Turabian StyleJargalsaikhan, Munkhtsooj, Jieun Lee, Am Jang, and Sanghyun Jeong. 2021. "Efficient Removal of Azo Dye from Wastewater Using the Non-Toxic Potassium Ferrate Oxidation–Coagulation Process" Applied Sciences 11, no. 15: 6825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156825
APA StyleJargalsaikhan, M., Lee, J., Jang, A., & Jeong, S. (2021). Efficient Removal of Azo Dye from Wastewater Using the Non-Toxic Potassium Ferrate Oxidation–Coagulation Process. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 6825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156825








