Modified GSC Method to Reduce the Distortion of the Enhanced Speech Signal Using Cross-Correlation and Sidelobe Neutralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
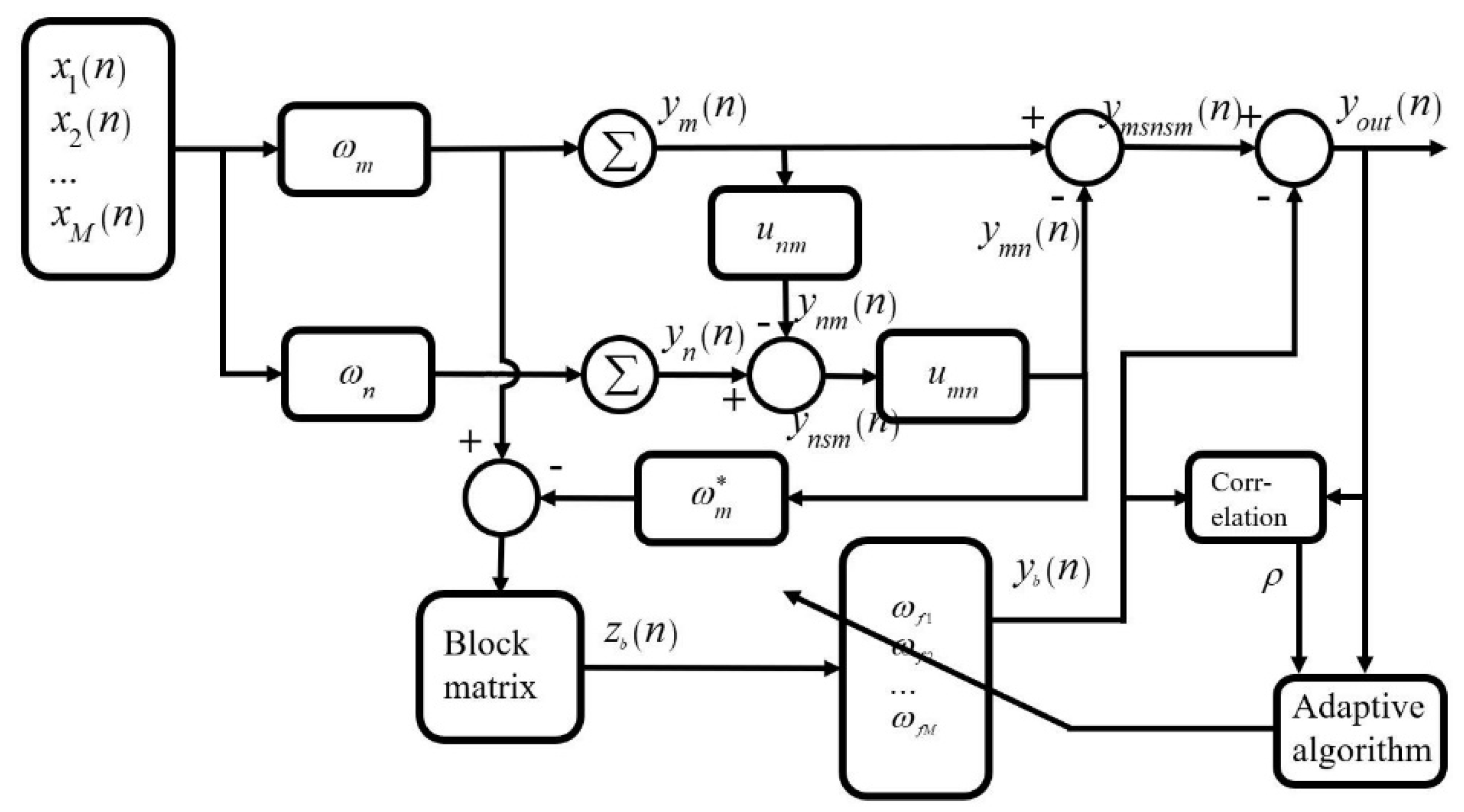
2. The Proposed Method
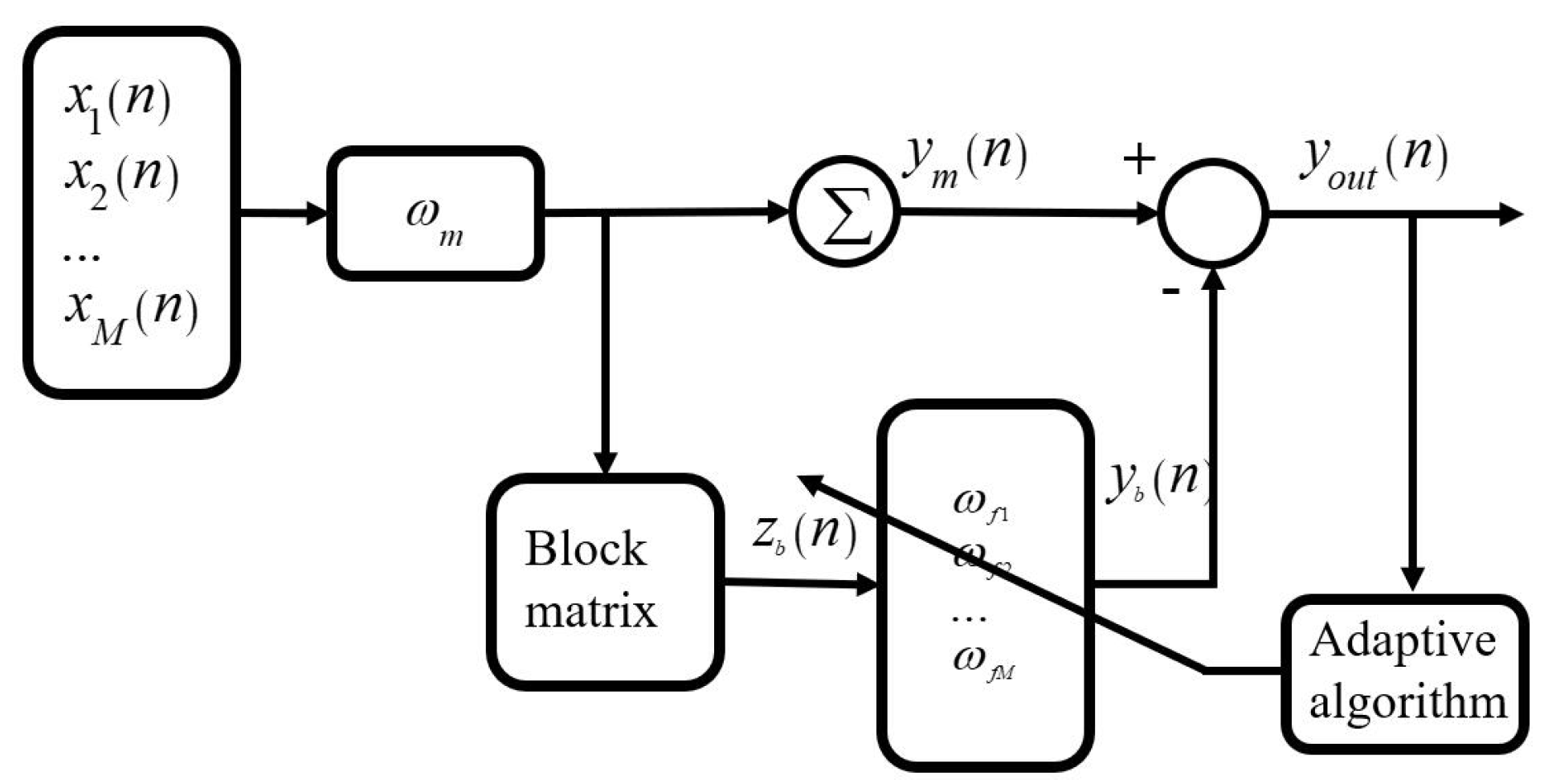
2.1. The Conventional GSC Method
0 1 −1 0 … 0 0
…
0 0 0 0 … 1 −1](M−1)*M
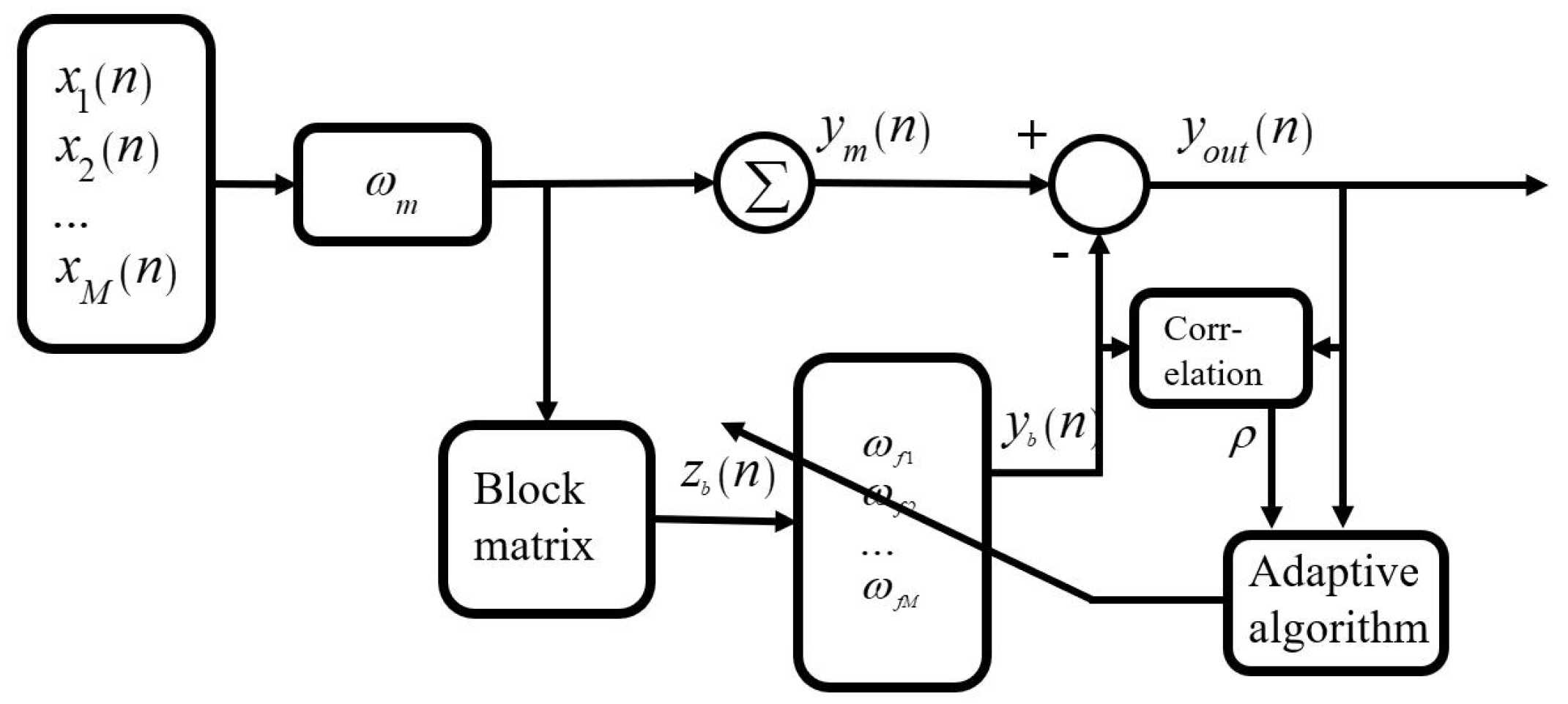
2.2. GSC Method with Cross-Correlation Coefficient
2.3. GSC Method with Sidelobe Neutralization
2.3.1. Beamforming Pattern
2.3.2. Beamforming Sidelobe Neutralization
2.3.3. The GSC Method with Sidelobe Neutralization
2.4. The Proposed GSC-SN-MCC Method
3. Experiment and Analysis
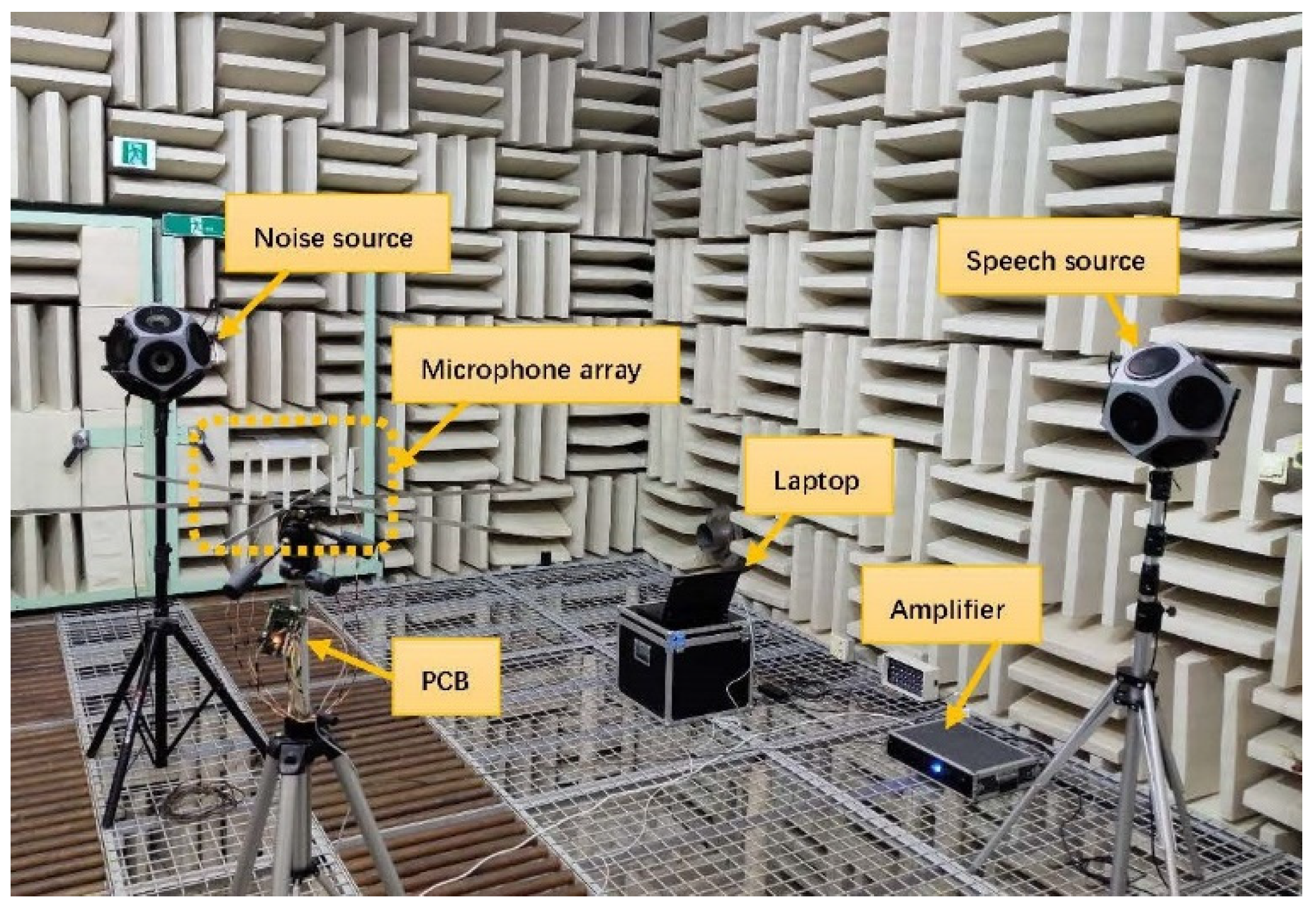
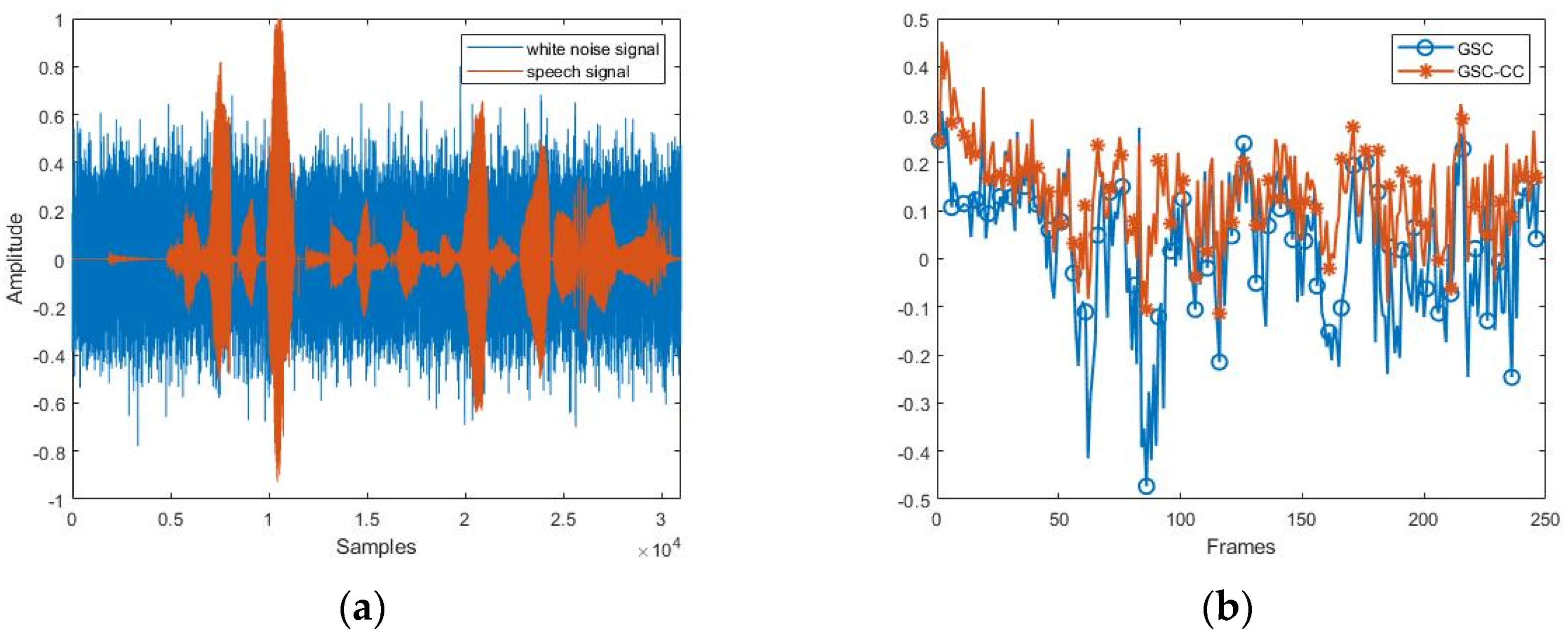
3.1. Experiment Implementation
3.2. Experiment Result Analysis
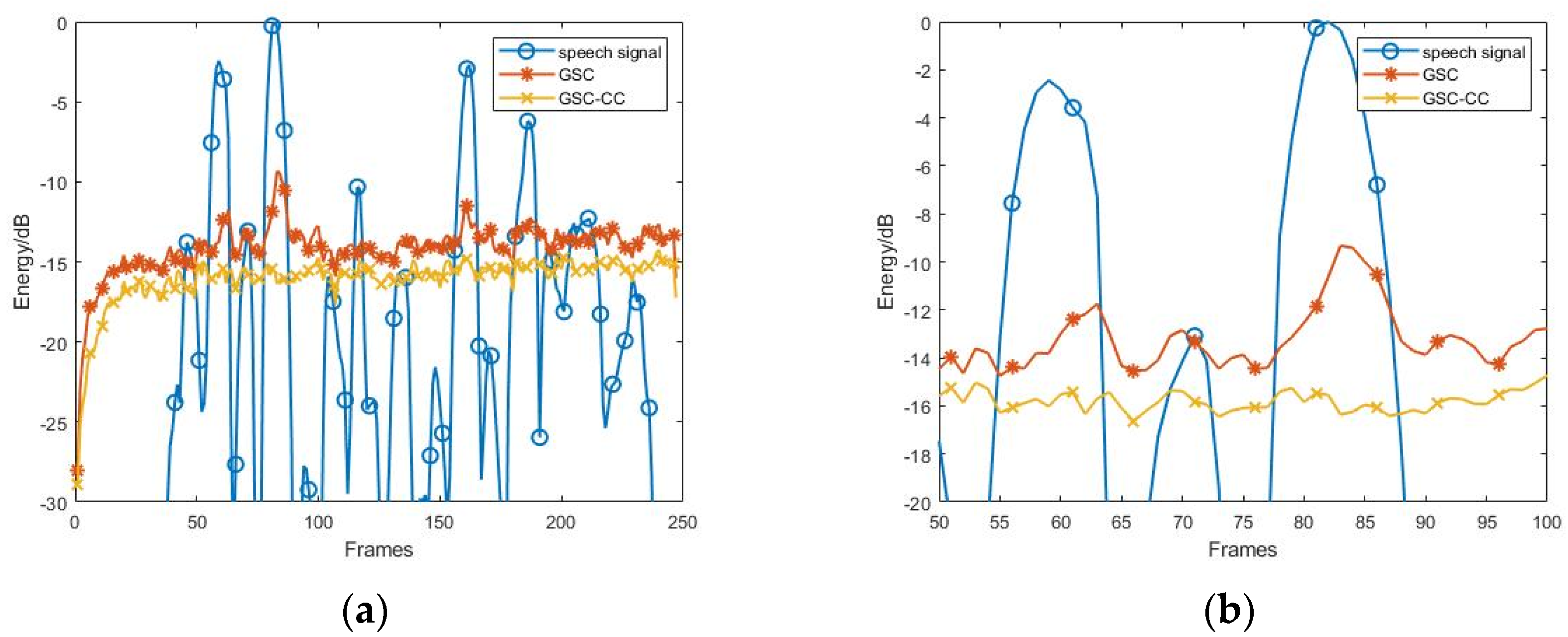
3.2.1. Effect of the Various SNR Conditions
3.2.2. Effect of the Inaccurate Estimated Noise Direction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flanagan, J.L.; Johnston, J.D.; Zahn, R.; Elko, G.W. Computer-steered microphone arrays for sound transduction in large rooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, O.L. An algorithm for linearly constrained adaptive array processing. Proc. IEEE 1972, 60, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.; Jim, C.W. An alternative approach to linearly constrained adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1982, 30, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshuyama, O.; Sugiyama, A.; Hirano, A. A robust adaptive beamformer for microphone arrays with a blocking matrix using constrained adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wu, W.R. A robust adaptive generalized sidelobe canceller with decision feedback. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 3822–3832. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.U.; Naveed, A.; Qureshi, I.M.; Zaman, F. Comparison of Adaptive Beamforming Algorithms Robust Against Directional of Arrival Mismatch. J. Space Technol. 2012, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gannot, S.; Burshtein, D.; Weinstein, E. Signal enhancement using beamforming and nonstationarity with applications to speech. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2001, 49, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reuven, G.; Gannot, S.; Cohen, L. Joint noise reduction and acoustic echo cancellation using the transfer-function generalized sidelobe canceller. Speech Commun. 2007, 49, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuven, G.; Gannot, S.; Cohen, I. Dual-Source Transfer-Function Generalized Sidelobe Canceller. IEEE Speech Audio Process. 2008, 16, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, G.; Spriet, A.; Moonen, M. Generalized sidelobe canceller based combined acoustic feedback- and noise cancellation. Signal Process. 2008, 88, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, A.; Warsitz, E.; Haeb-Umbach, R. Speech Enhancement With a GSC-Like Structure Employing Eigenvector-Based Transfer Function Ratios Estimation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glentis, G.O. Implementation of adaptive generalized sidelobe cancellers using efficient complex valued arithmetic. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2003, 13, 549–566. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.; Bernardi, G.; Waterschoot, T.V.; Moonen, M. Methods of Extending a Generalized Sidelobe Canceller With External Microphones. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, P.M. Optimal and Adaptive Signal Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Widrow, B.; Stearns, S.D. Adaptive Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Widrow, B.; Hoff, M.E. Adaptive Switching Circuits. IRE WESCON Conv. Rec. 1960, 4, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nagumo, J.I.; Noda, A. A learning method for system identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1967, AC-12, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.J.; Kailath, T. Adaptive algorithms with an automatic gain control feature. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1988, 35, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitlin, R.D.; Meadors, H.C.; Weinstein, S.B. The tap-leakage algorithm: An algorithm for the stable operation of a digitally implemented, fractionally spaced adaptive equalizer. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1982, 61, 1817–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannot, S.; Cohen, I. Speech enhancement based on the general transfer function GSC and postfiltering. IEEE Speech Audio Process. 2004, 12, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.; Berdugo, B. Microphone array post-filtering for non-stationary noise suppression. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 May 2002; pp. I-901–I-904. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, I. Analysis of two-channel generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) with post-filtering. IEEE Speech Audio Process. 2003, 11, 684–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, F.; Hayamizu, S. Speech enhancement using CSS-based array processing. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Munich, Germany, 21–24 April 1997; Volume 2, pp. 1191–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Doclo, S.; Moonen, M. SVD-based optimal filtering with applications to noise reduction in speech signals. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA’99), New Paltz, NY, USA, 17–20 October 1999; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Doclo, S.; Moonen, M. Multimicrophone noise reduction using recursive GSVD-based optimal filtering with ANC postprocessing stage. IEEE Speech Audio Process. 2005, 13, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Liu, R.W.; Soon, V.C.; Huang, Y.F. Indeterminacy and identifiability of blind identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1991, 38, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, A new concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Y.; Lee, C.M. Speech intelligibility improvement in noisy reverberant environments based on speech enhancement and inverse filtering. EURASIP J Audio Speech 2018, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, S.M. Adaptive active noise control systems: Algorithms and digital signal processing (DSP) implementations. In Digital Signal Processing Technology: A Critical Review; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1995; Volume 10279, pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active noise control: A tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 943–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitzer, J.; Simmer, K.U.; Kammeyer, K.D. Theoretical noise reduction limits of the generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP99 (Cat. No.99CH36258), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 15–19 March 1999; Volume 5, pp. 2965–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Zue, V.; Seneff, S.; Glass, J. Speech database development at MIT: TIMIT and beyond. Speech Commun. 1990, 9, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.; Steeneken, M.H.J. Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. NOISEX-92: A database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Commun. 1993, 12, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.F. Optimal Array Signal Processing: Modal Array Processing and Direction-of-Arrival Estimation; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]



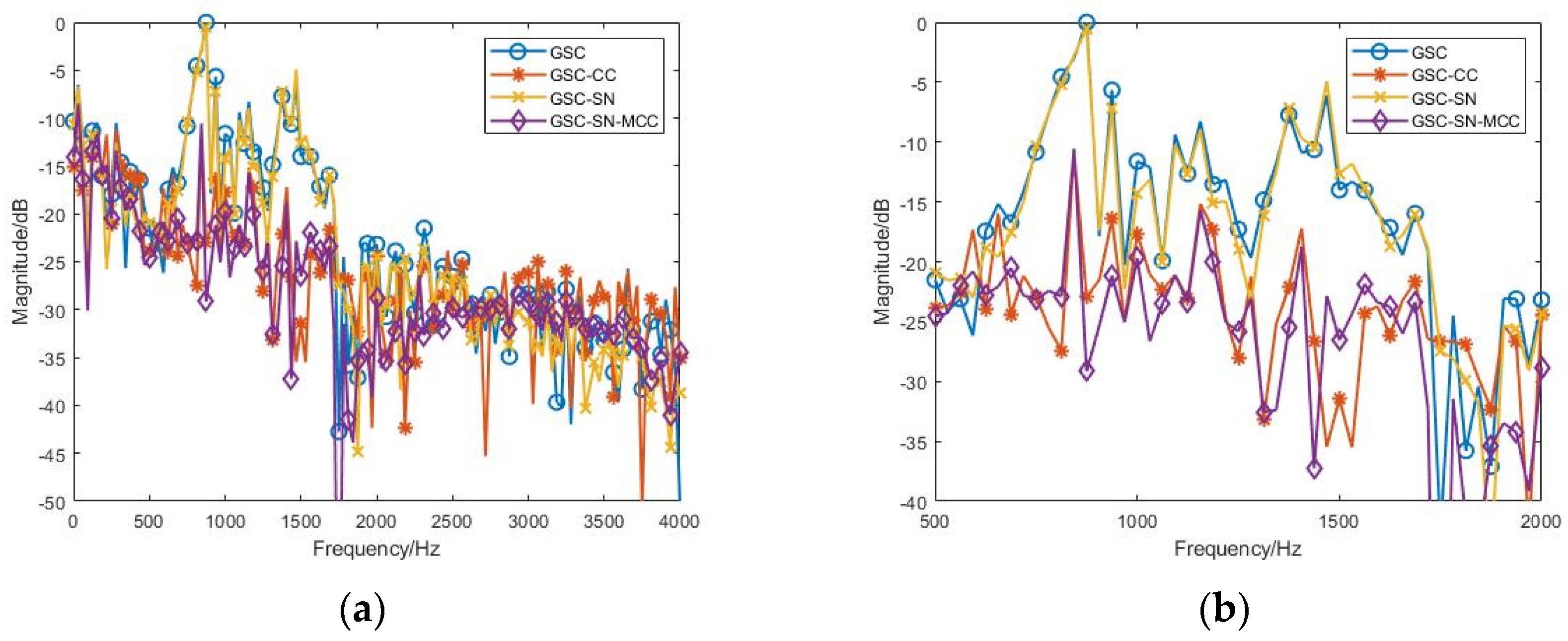

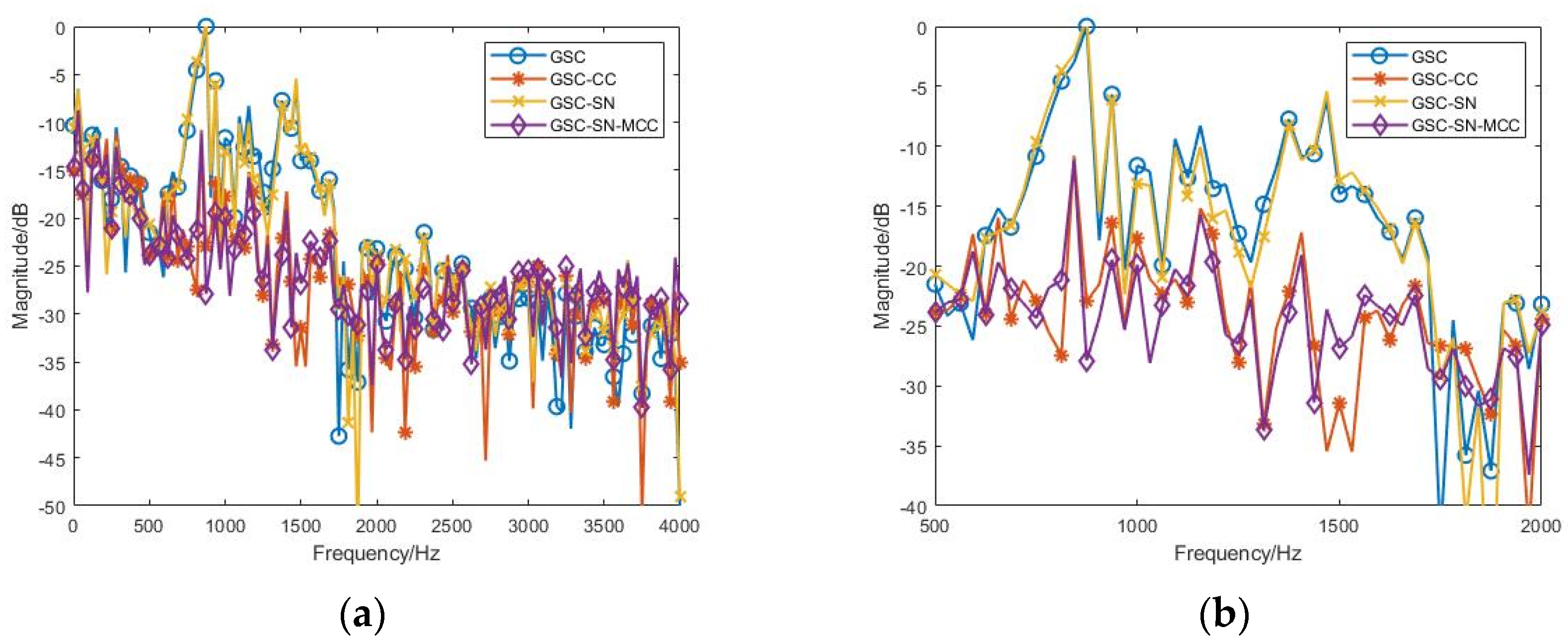
| SNR/dB | GSC | GSC-CC | GSC-SN | GSC-SN-MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 100% | 65.98% | 104.03% | 75.75% |
| 10 | 100% | 57.93% | 100.99% | 46.29% |
| 5 | 100% | 54.46% | 97.92% | 38.51% |
| 0 | 100% | 72.66% | 89.87% | 44.14% |
| −5 | 100% | 105.34% | 83.98% | 59.01% |
| −10 | 100% | 134.85% | 80.22% | 72.41% |
| −20 | 100% | 157.90% | 77.21% | 78.84% |
| SNR/dB | GSC | GSC-CC | GSC-SN | GSC-SN-MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 100% | 54.09% | 109.34% | 82.73% |
| 10 | 100% | 39.69% | 110.58% | 40.31% |
| 5 | 100% | 20.91% | 106.16% | 20.94% |
| 0 | 100% | 17.68% | 96.88% | 17.11% |
| −5 | 100% | 22.38% | 93.10% | 18.44% |
| −10 | 100% | 38.14% | 90.32% | 27.24% |
| −20 | 100% | 124.24% | 80.42% | 72.87% |
| Estimated Noise Direction/Degree | GSC | GSC-CC | GSC-SN | GSC-SN-MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −60 | 100% | 105.34% | 112.55% | 100.87% |
| −30 | 100% | 105.34% | 106.33% | 91.93% |
| 0 | 100% | 105.34% | 100% | 88.07% |
| 30 | 100% | 105.34% | 92.92% | 76.27% |
| 60 | 100% | 105.34% | 92.80% | 68.32% |
| 90 | 100% | 105.34% | 83.98% | 59.01% |
| 120 | 100% | 105.34% | 95.71% | 80.68% |
| 150 | 100% | 105.34% | 90.56% | 76.15% |
| 180 | 100% | 105.34% | 97.76% | 82.98% |
| −150 | 100% | 105.34% | 94.29% | 79.13% |
| −120 | 100% | 105.34% | 105.59% | 93.54% |
| −90 | 100% | 105.34% | 102.98% | 88.94% |
| Estimated Noise Direction/Degree | GSC | GSC-CC | GSC-SN | GSC-SN-MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −60 | 100% | 22.38% | 105.90% | 24.68% |
| −30 | 100% | 22.38% | 97.81% | 23.04% |
| 0 | 100% | 22.38% | 100% | 22.38% |
| 30 | 100% | 22.38% | 94.42% | 21.15% |
| 60 | 100% | 22.38% | 103.73% | 20.55% |
| 90 | 100% | 22.38% | 93.10% | 18.44% |
| 120 | 100% | 22.38% | 103.00% | 23.60% |
| 150 | 100% | 22.38% | 89.81% | 21.52% |
| 180 | 100% | 22.38% | 98.23% | 23.62% |
| −150 | 100% | 22.38% | 93.95% | 22.44% |
| −120 | 100% | 22.38% | 102.58% | 25.06% |
| −90 | 100% | 22.38% | 96.50% | 23.57% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, H.; Lee, C.-M. Modified GSC Method to Reduce the Distortion of the Enhanced Speech Signal Using Cross-Correlation and Sidelobe Neutralization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146288
Su H, Lee C-M. Modified GSC Method to Reduce the Distortion of the Enhanced Speech Signal Using Cross-Correlation and Sidelobe Neutralization. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(14):6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146288
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Hang, and Chang-Myung Lee. 2021. "Modified GSC Method to Reduce the Distortion of the Enhanced Speech Signal Using Cross-Correlation and Sidelobe Neutralization" Applied Sciences 11, no. 14: 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146288
APA StyleSu, H., & Lee, C.-M. (2021). Modified GSC Method to Reduce the Distortion of the Enhanced Speech Signal Using Cross-Correlation and Sidelobe Neutralization. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146288






