Characterization of a Novel Family IV Esterase Containing a Predicted CzcO Domain and a Family V Esterase with Broad Substrate Specificity from an Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenomic Library
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Two Esterase-Positive Clones from the Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenome Library
2.3. Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree
2.4. Enzyme Assays
2.5. Preparation of Crude Enzymes
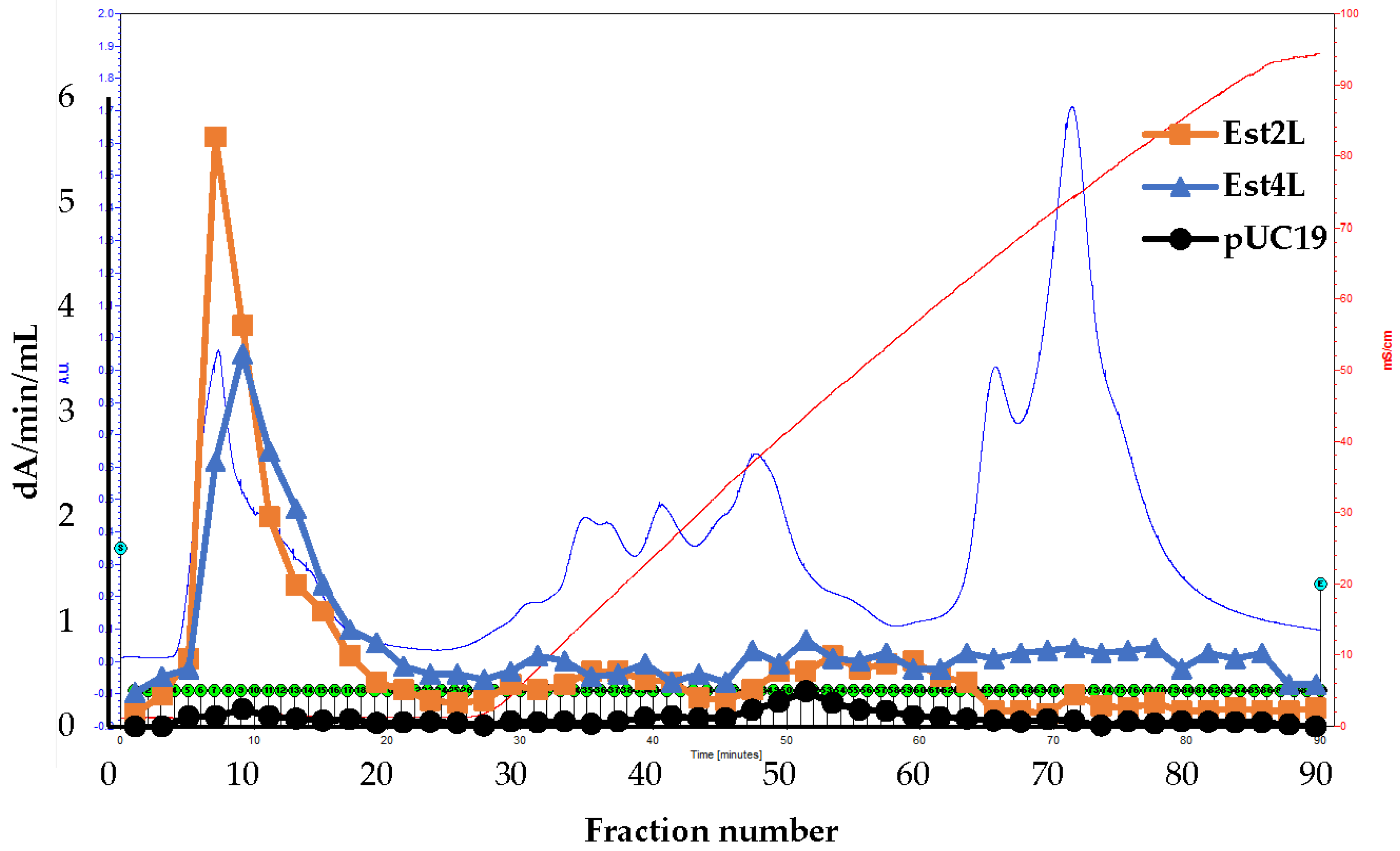
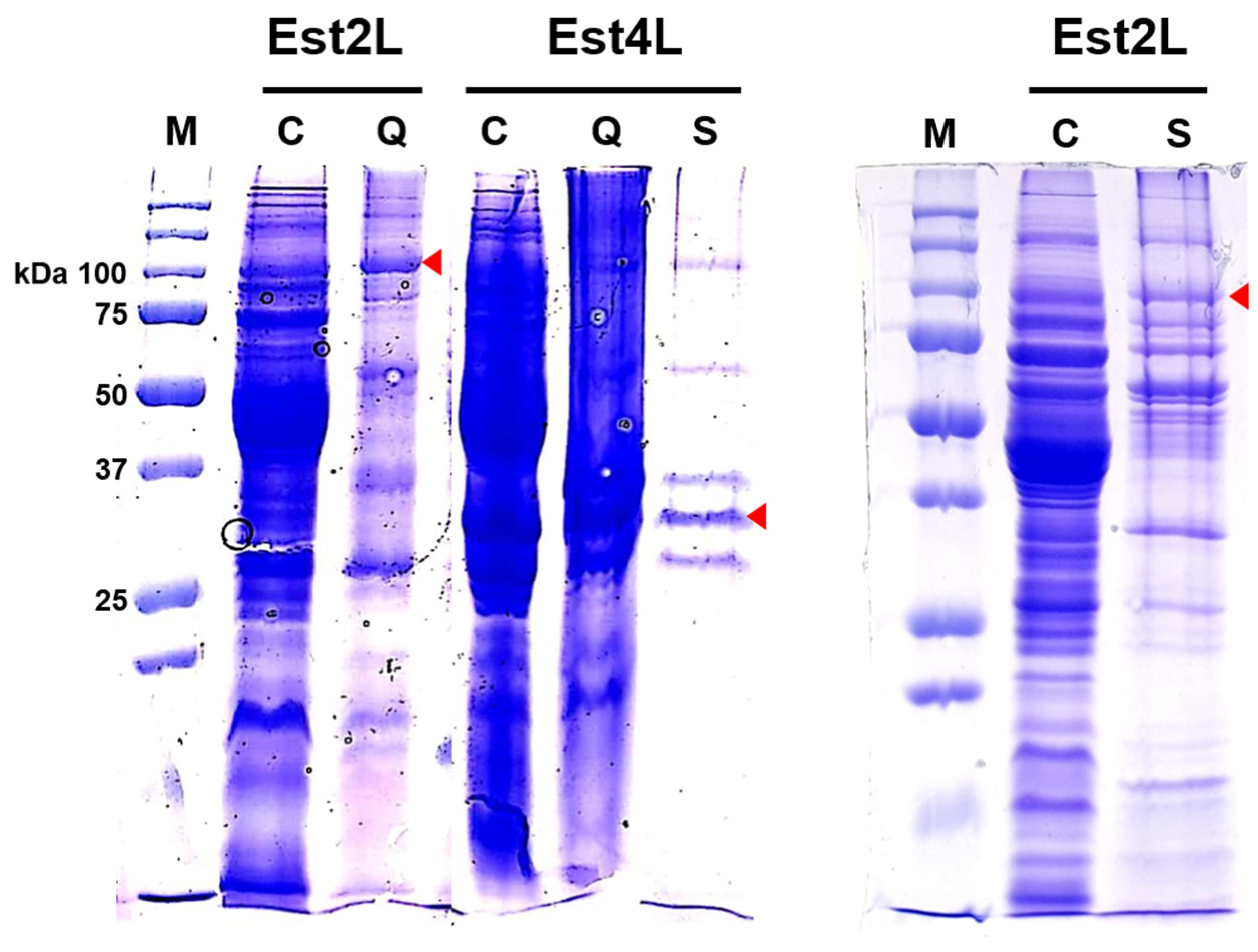
2.6. Isolation of the Enzymes
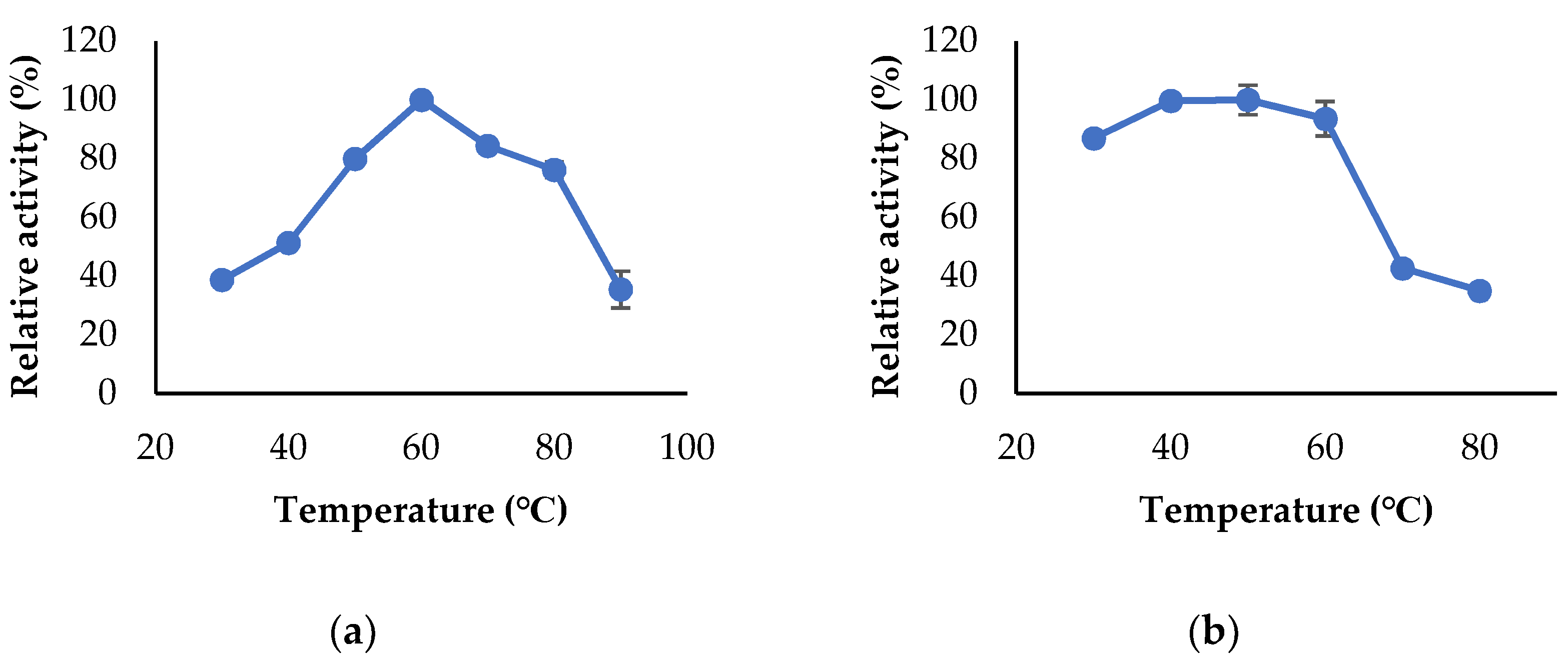
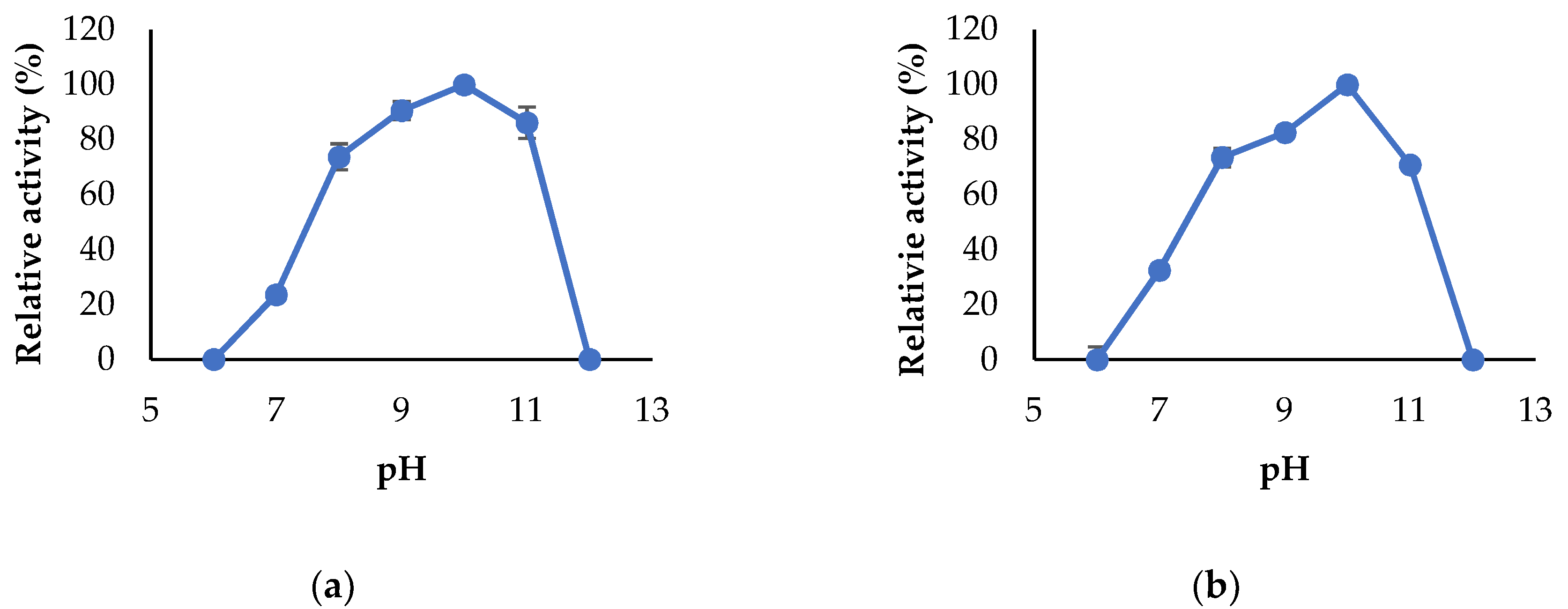
2.7. Characterization of the Enzymes
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analyses and Multiple Alignments of Est2L and Est4L
3.2. Isolation of Est2L and Est4L
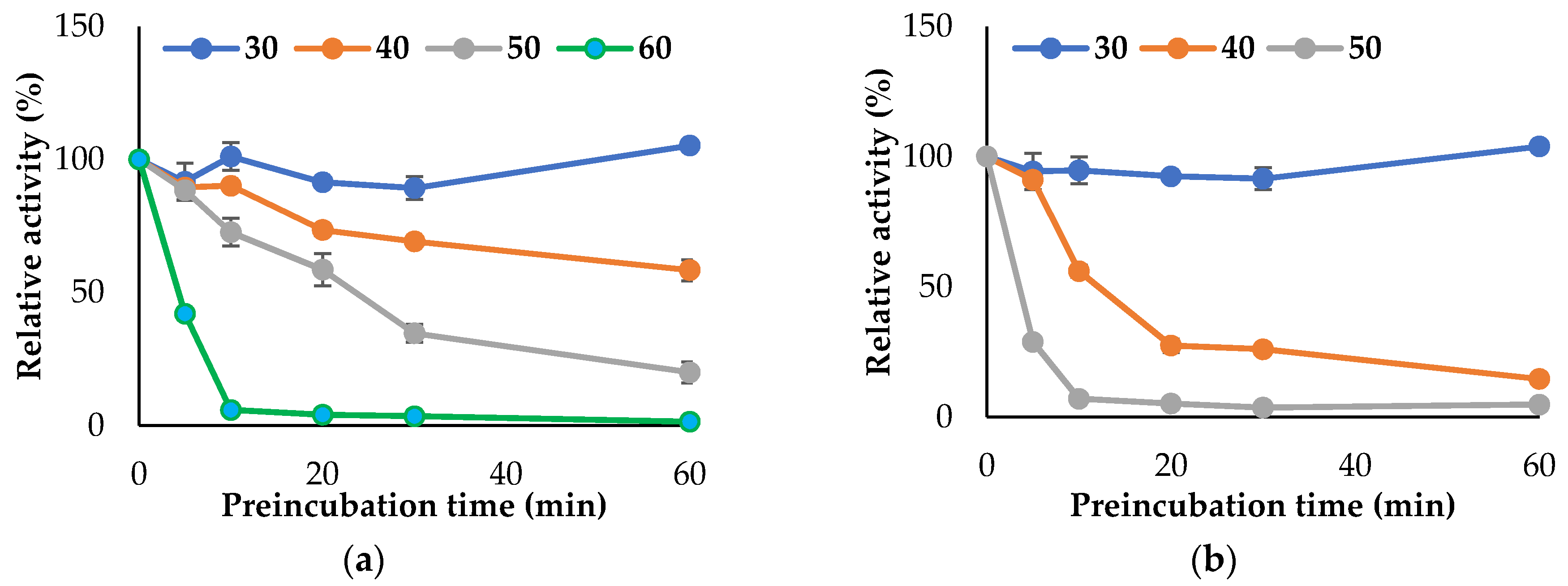
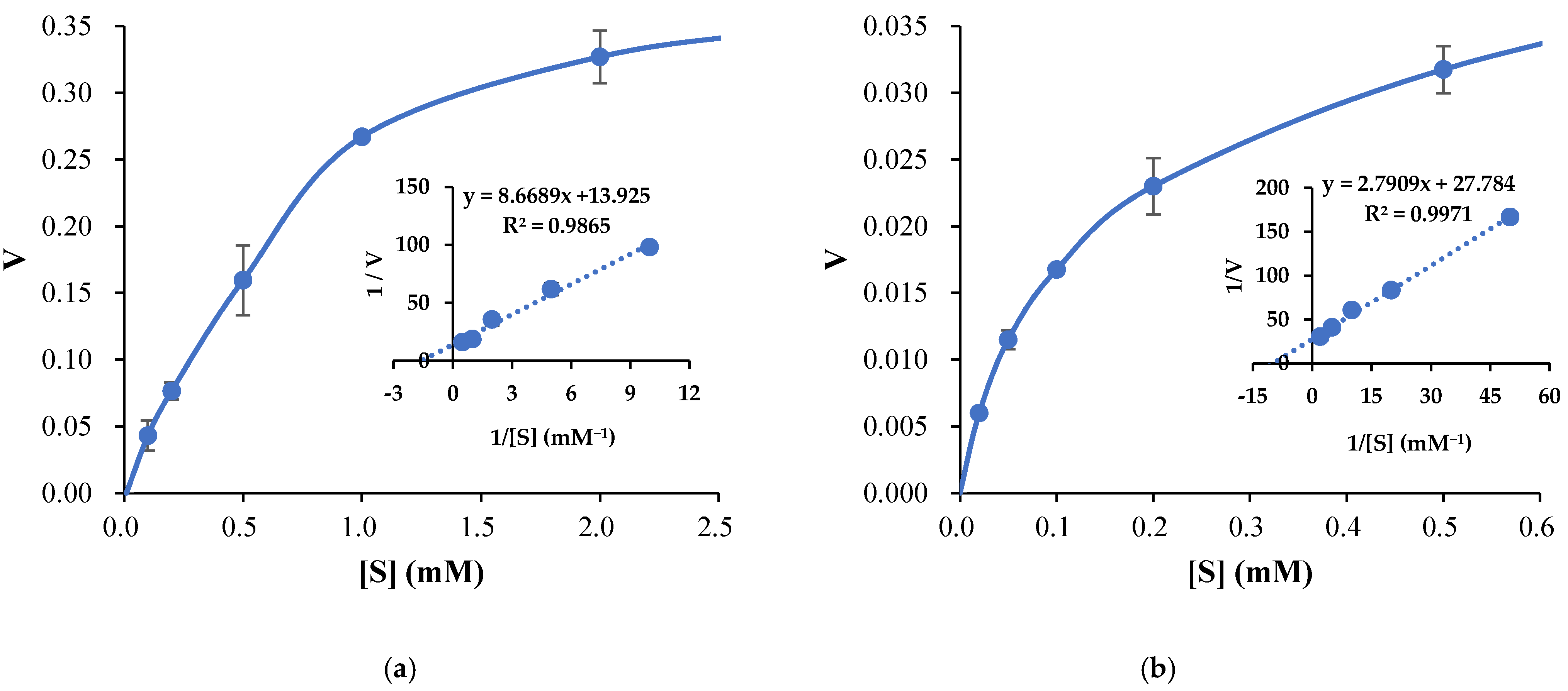
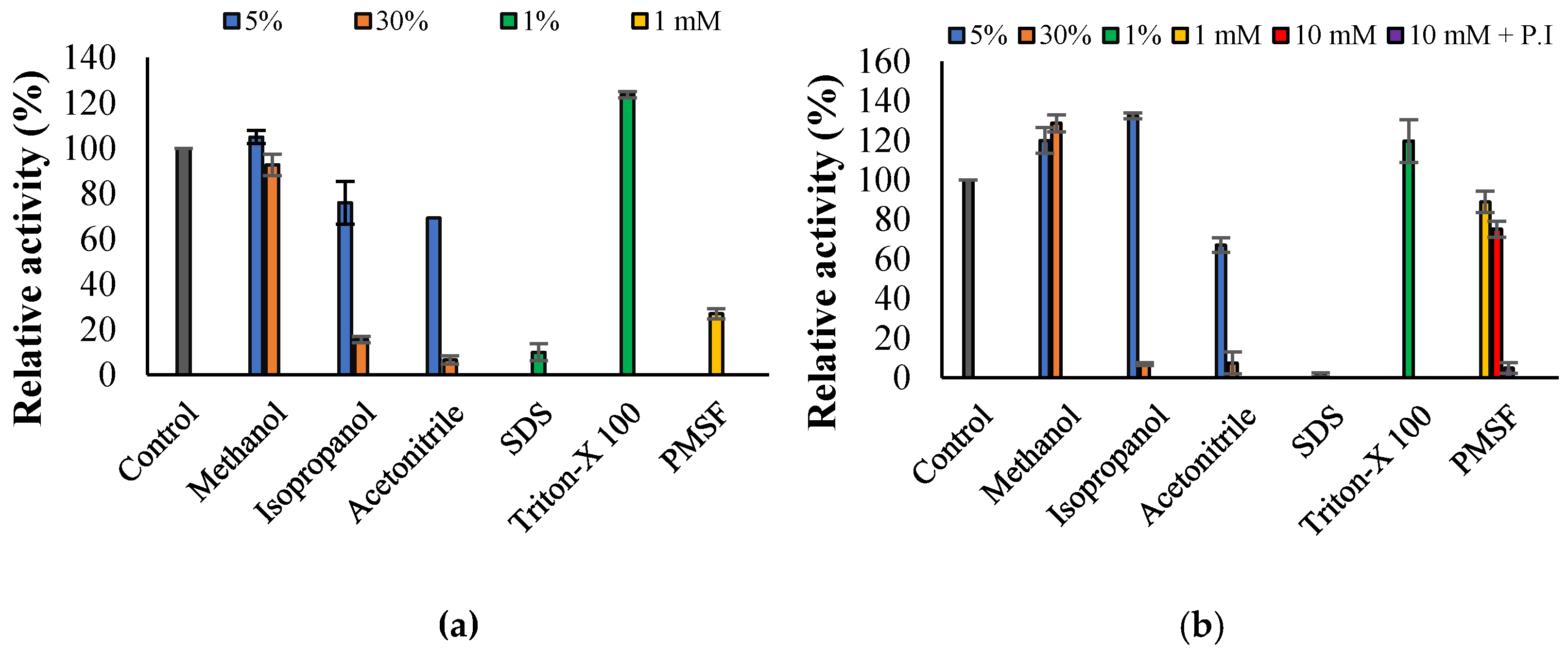
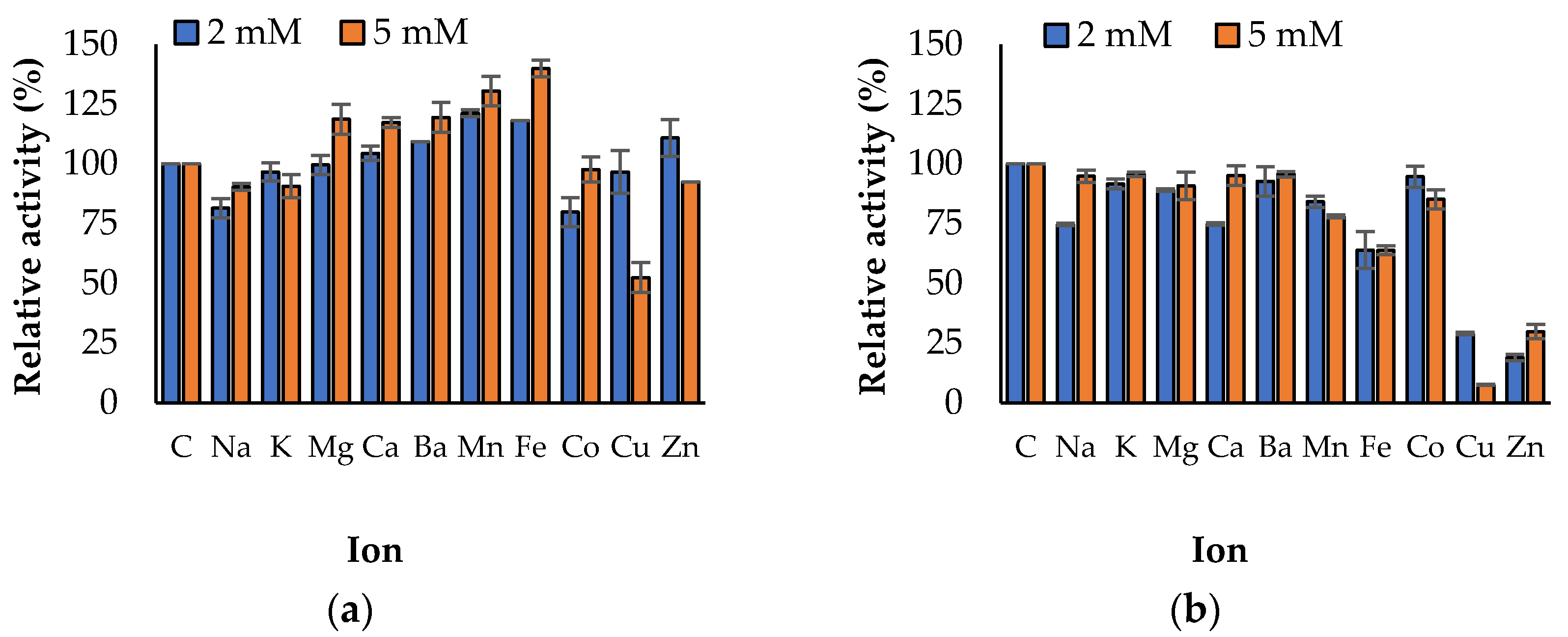
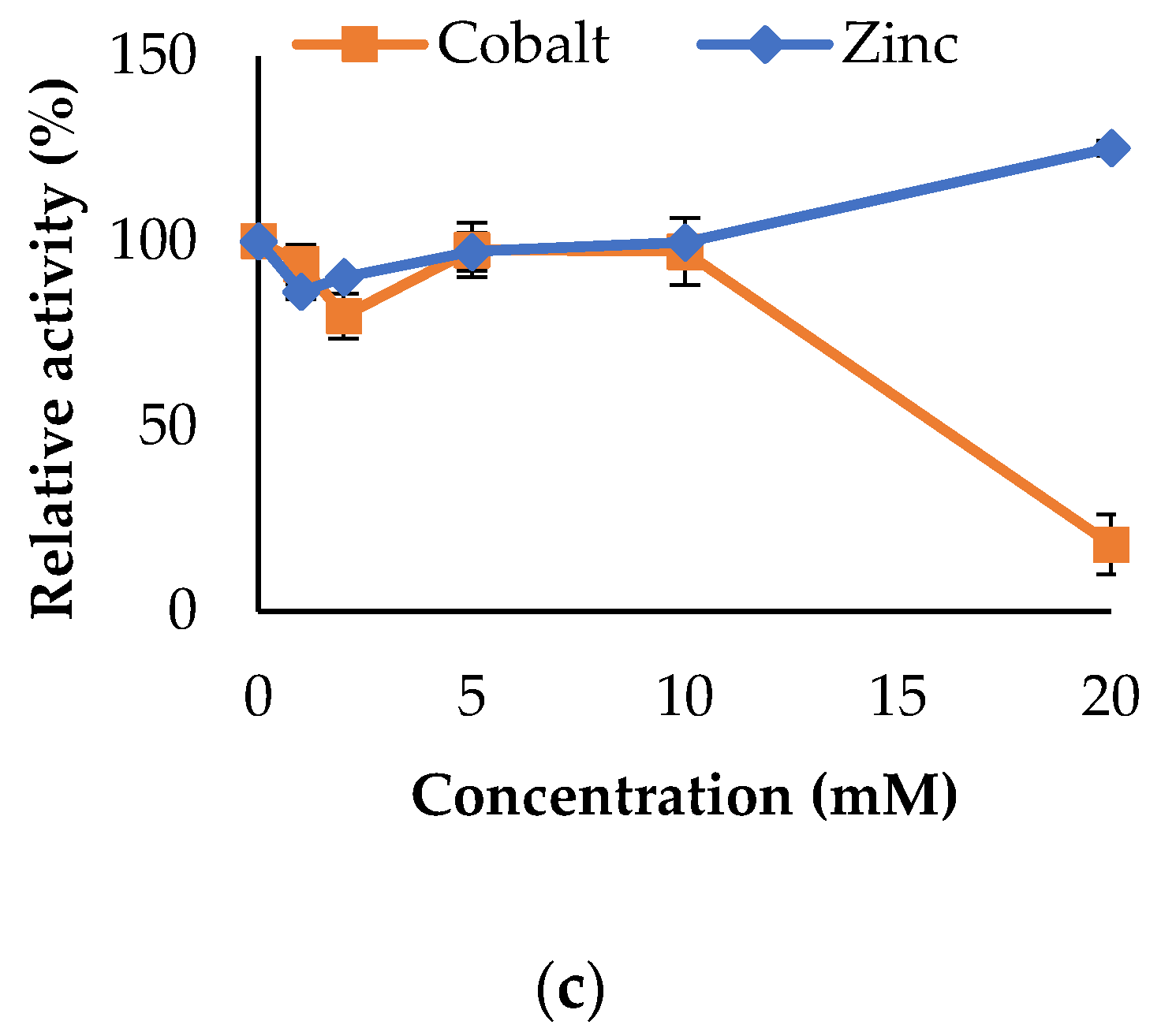
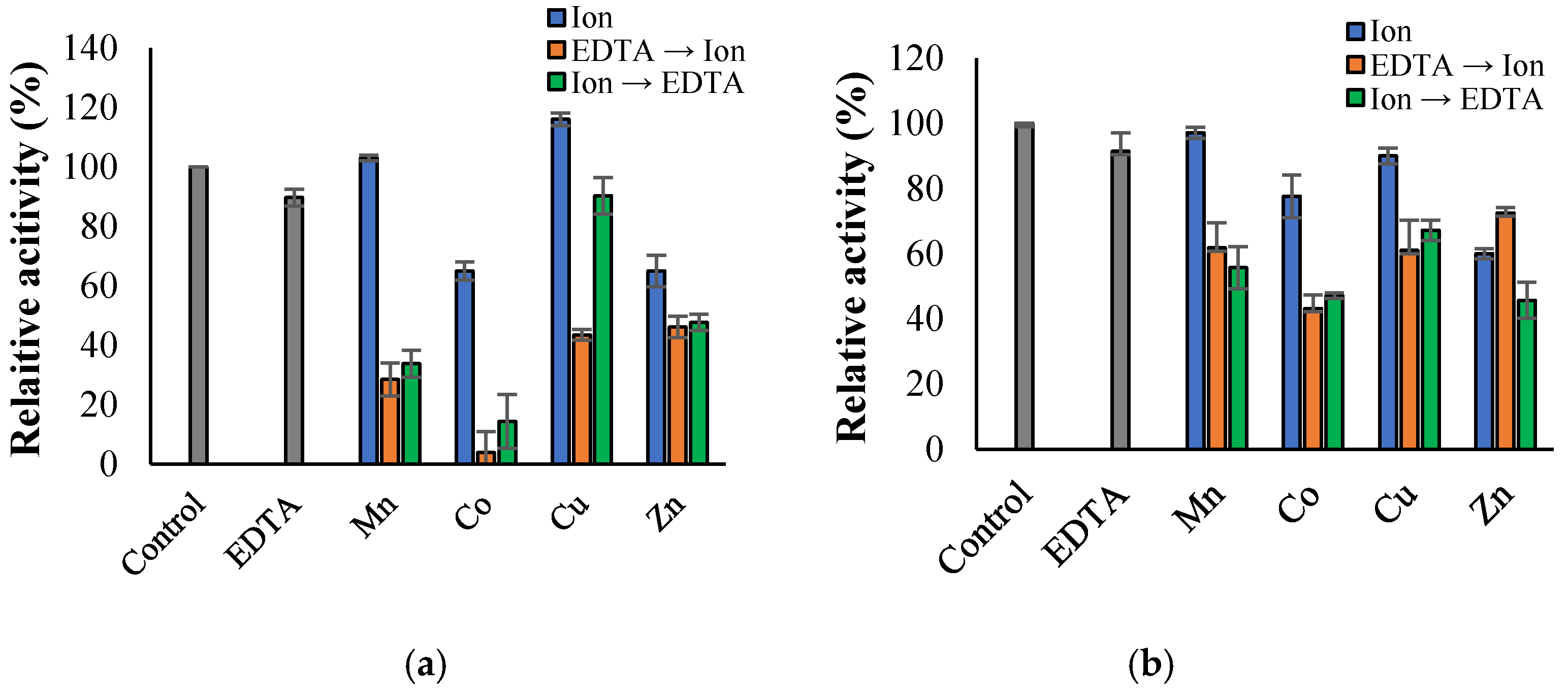
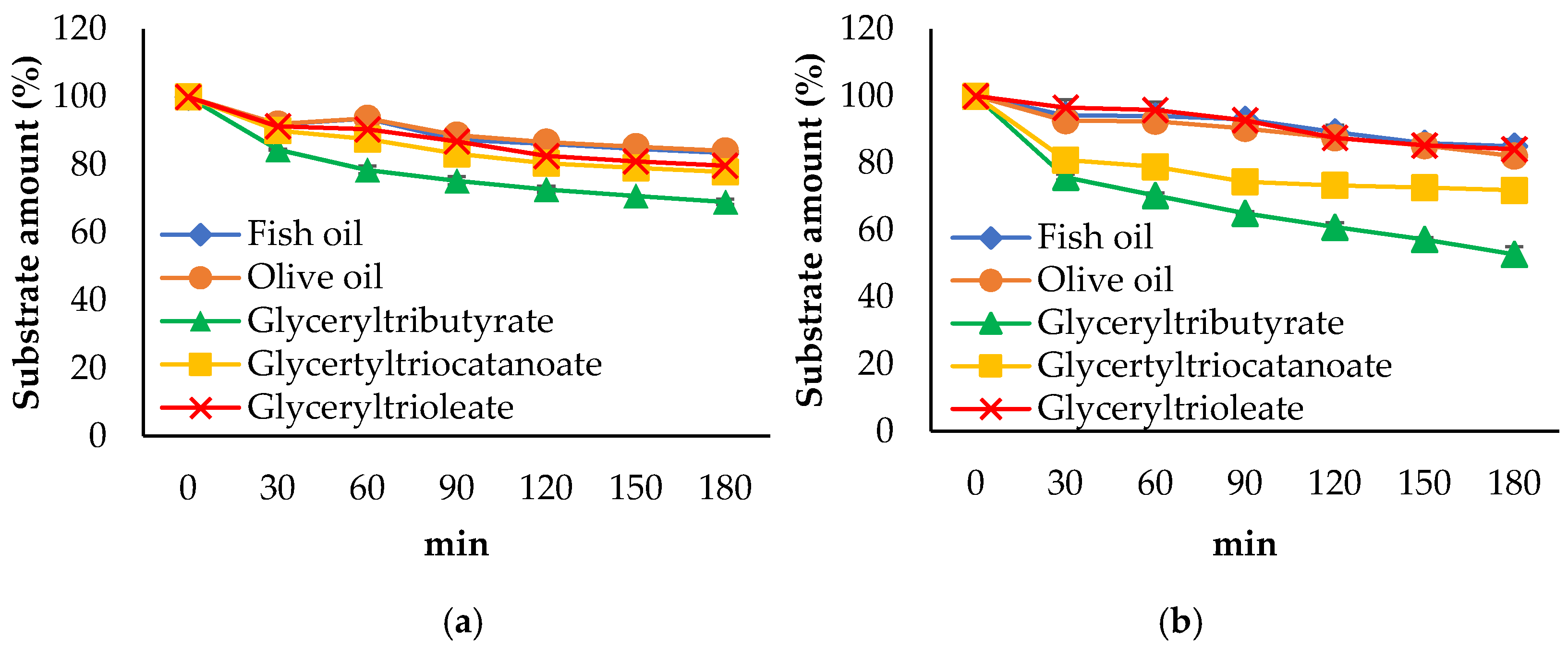
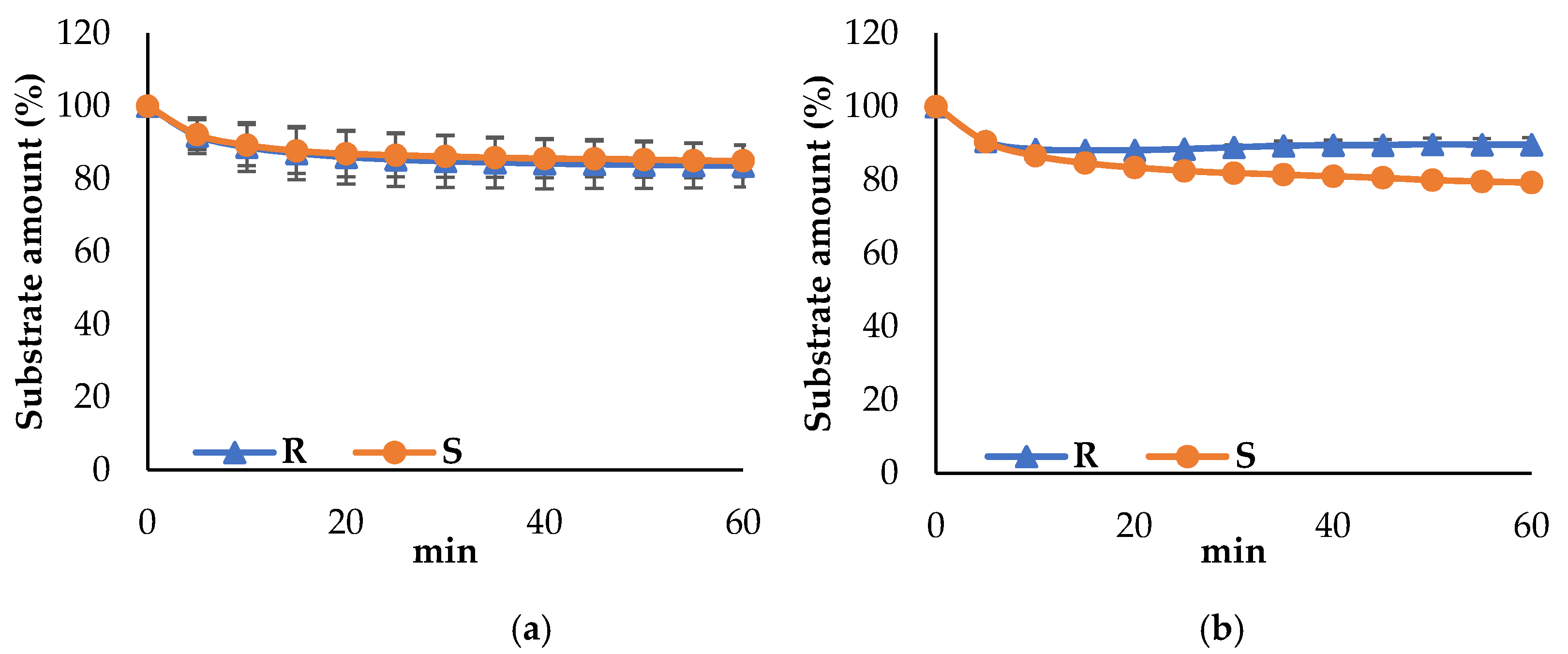
3.3. Propeties of Est2L and Est4L
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arpigny, J.L.; Jaeger, K.E. Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: Classification and properties. Biochem. J. 1999, 343, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudiukaite, R.; Gricajeva, A. Microbial lipolytic fusion enzymes: Current state and future perspectives. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, P.; Tan, Y.; Kinsella, G.K.; Henehan, G.T.; Ryan, B.J. Solvent stable microbial lipases: Current understanding and biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, E.M.; Johnson, R.J. Microbial esterases and ester prodrugs: An unlikely marriage for combating antibiotic resistance. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Gupta, N.; Rathi, P. Bacterial lipases: An overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Azeem, F.; Hussain, S.; Rasul, I.; Siddique, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Afzal, M.; Kouser, A.; Nadeem, H. Bacterial lipases: A review on purification and characterization. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 132, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapouli, M.; Foukis, A.; Stergiou, P.Y.; Koukouritaki, M.; Magklaras, P.; Gkini, O.A.; Papamichael, E.M.; Afendra, A.S.; Hatziloukas, E. Molecular, biochemical and kinetic analysis of a novel, thermostable lipase (LipSm) from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Psi-1, the first member of a new bacterial lipase family (XVIII). J. Biol. Res. Thessalon. 2018, 25, 4, reprinted in J. Biol. Res. Thessalon. 2018, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J.; et al. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handelsman, J.; Rondon, M.R.; Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J.; Goodman, R.M. Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R245–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogram, A.; Sayler, G.S.; Barkay, T. The extraction and purification of microbial DNA from sediments. J. Microbiol. Methods 1987, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.R.; August, P.R.; Bettermann, A.D.; Brady, S.F.; Grossman, T.H.; Liles, M.R.; Loiacono, K.A.; Lynch, B.A.; MacNeil, I.A.; Minor, C.; et al. Cloning the soil metagenome: A strategy for accessing the genetic and functional diversity of uncultured microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.M.; Alnoch, R.C.; Souza, E.M.; Mitchell, D.A.; Krieger, N. Metagenomics: Is it a powerful tool to obtain lipases for application in biocatalysis? Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zou, D.; Ding, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Khan, U.; Sun, S.; et al. Characterization of XtjR8: A novel esterase with phthalate-hydrolyzing activity from a metagenomic library of lotus pond sludge. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuncu, H.E.; Balci, N.; Tuter, M.; Karaguler, N.G. Recombinant production and characterization of a novel esterase from a hypersaline lake, Acıgöl, by metagenomic approach. Extremophiles 2019, 23, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.J.; Hissa, D.C.; Silva, G.O.; Antunes, A.S.L.M.; Nogueira, V.L.R.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Melo, V.M.M. A novel bacterial carboxylesterase identified in a metagenome derived-clone from Brazilian mangrove sediments. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3919–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.L.; Zhong, X.L.; Lin, Z.W.; Dong, B.X.; Li, G. Expression and characterization of an esterase belonging to a new family via isolation from a metagenomic library of paper mill sludge. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 1, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.L.; Tian, Y.Z.; Jia, M.L.; Liu, Y.D.; Cheng, D.; Li, G. Characterization and purification via nucleic acid aptamers of a novel esterase from the metagenome of paper mill wastewater sediments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 15, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Nan, F.; Jiang, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, B.; Li, S.; Xin, Z. Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of a novel feruloyl esterase from a soil metagenomic library with phthalate-degrading activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.M.; Martini, V.P.; Iulek, J.; Alnoch, R.C.; Moure, V.R.; Müller-Santos, M.; Souza, E.M.; Mitchell, D.A.; Krieger, N. Biochemical characterization and application of a new lipase and its cognate foldase obtained from a metagenomic library derived from fat-contaminated soil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 15, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Qiao, B.; Li, S.; Xin, Z. A novel VIII carboxylesterase with high hydrolytic activity against ampicillin from a soil metagenomic library. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.; Dutta, A.; Chowdhury, P.P.; Chakraborty, J.; Dutta, T.K. Characterization of a novel family VIII esterase EstM2 from soil metagenome capable of hydrolyzing estrogenic phthalates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 24, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Shao, Y.; Xin, Z. Identification and characterization of a novel phthalate-degrading hydrolase from a soil metagenomic library. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 1, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Singh, I.; Kumar, P.; Rasool, S.; Verma, V. A hydrolase with esterase activity expressed from a fosmid gene bank prepared from DNA of a North West Himalayan glacier frozen soil sample. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.W.S.; Chan, V.J.; Liao, H. Metagenomic discovery of feruloyl esterases from rumen microflora. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8449–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Dukunde, A.; Daniel, R. Biochemical profiles of two thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant esterases derived from a compost metagenome. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3421–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Kang, C.H.; Won, S.M.; Oh, K.H.; Yoon, J.H. Characterization of a novel moderately thermophilic solvent-tolerant esterase isolated from a compost metagenome library. Front Microbiol. 2020, 24, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasmaei, K.M.; Sundh, J. Identification of novel putative bacterial feruloyl esterases from anaerobic ecosystems by use of whole-genome shotgun metagenomics and genome binning. Front Microbiol. 2019, 20, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, Y.S.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, H.W.; Kahng, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, H. Characterization of novel family IV esterase and family I.3 lipase from an oil-polluted mud flat metagenome. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 7, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.; Grosse, C.; Reissmann, J.; Pribyl, T.; Nies, D.H. CzcD is a heavy metal ion transporter involved in regulation of heavy metal resistance in Ralstonia sp. strain CH34. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6876–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guffanti, A.A.; Wei, Y.; Rood, S.V.; Krulwich, T.A. An antiport mechanism for a member of the cation diffusion facilitator family: Divalent cations efflux in exchange for K+ and H+. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.K.; Lee, H.W.; Yoo, W.; Kim, T.D.; Kim, H. Characterization of an alkaline family I.4 lipase from Bacillus sp. W130-35 isolated from a tidal mud flat with broad substrate specificity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 2024–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.P.; Kang, M.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, J.M.; Baek, S.C.; Leem, H.H.; Park, D.; Cho, M.L.; Kim, H. Potent inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by sargachromanol I from Sargassum siliquastrum and by selected natural compounds. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Ryu, B.H.; Ju, H.; Jang, E.J.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, T.D. Crystallographic analysis and biochemical applications of a novel penicillin-binding protein/β-lactamase homologue from a metagenomic library. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krintel, C.; Klint, C.; Lindvall, H.; Mörgelin, M.; Holm, C. Quarternary structure and enzymological properties of the different hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) isoforms. PLoS ONE 2010, 17, e11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.D. Bacterial hormone-sensitive lipases (bHSLs): Emerging enzymes for biotechnological applications. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 28, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.J.; Sanders, M.A.; Juhlmann, B.E.; Hertzel, A.V.; Bernlohr, D.A. Mapping of the hormone-sensitive lipase binding site on the adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (AFABP). Identification of the charge quartet on the AFABP/aP2 helix-turn-helix domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 28, 33536–33543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandrich, L.; Merone, L.; Pezzullo, M.; Cipolla, L.; Nicotra, F.; Rossi, M.; Manco, G. Role of the N terminus in enzyme activity, stability and specificity in thermophilic esterases belonging to the HSL family. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 21, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D.H. CzcR and CzcD, gene products affecting regulation of resistance to cobalt, zinc, and cadmium (czc system) in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 8102–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zha, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, Y. N-terminal transmembrane domain of lipase LipA from Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5: A must for its efficient folding into an active conformation. Biochimie 2014, 105, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudary, R.A.; Venkatachalam, R.; Katzer, M.; Elleuche, S.; Antranikian, G. A cold-adapted esterase of a novel marine isolate, Pseudoalteromonas arctica: Gene cloning, enzyme purification and characterization. Extremophiles 2010, 14, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.V.; Horsfall, L.E.; Wardrope, C.; Togneri, P.D.; Marles-Wright, J.; Rosser, S.J. Characterisation of a new family of carboxyl esterases with an OsmC domain. PLoS ONE 2016, 16, e0166128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjan, R.; Yadav, M.K.; Suneja, G.; Sharma, R. Discovery of a diverse set of esterases from hot spring microbial mat and sea sediment metagenomes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Priyadarshi, A.; Kwon, S.T.; Koo, B.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Hwang, K.Y. Structural and functional analysis of a novel hormone-sensitive lipase from a metagenome library. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2009, 74, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, R.; Esteban-Torres, M.; Acebrón, I.; de Las Rivas, B.; Muñoz, R.; Alvarez, Y.; Mancheño, J.M. Structure, biochemical characterization and analysis of the pleomorphism of carboxylesterase Cest-2923 from Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 6658–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virk, A.P.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. A new esterase, belonging to hormone-sensitive lipase family, cloned from Rheinheimera sp. isolated from industrial effluent. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, M.R.; Mercaldi, G.F.; Maester, T.C.; Balan, A.; Lemos, E.G. Est16, a new esterase isolated from a metagenomic library of a microbial consortium specializing in diesel oil degradation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Purification and properties of a novel quizalofop-p-ethyl-hydrolyzing esterase involved in quizalofop-p-ethyl degradation by Pseudomonas sp. J-2. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Yu, D.; Yin, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X. Biochemical characterization of an enantioselective esterase from Brevundimonas sp. LY-2. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Y.Y.; Rong, Z.; Jian, S.L.; Xu, C.D.; Li, J.; Xu, X.W. A Novel halotolerant thermoalkaliphilic esterase from marine bacterium Erythrobacter seohaensis SW-135. Front Microbiol. 2017, 22, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, J.S.; Rhee, J.K.; Kim, N.D.; Yoon, J.; Kim, D.U.; Koh, E.; Oh, J.W.; Cho, H.S. Crystal structure of hyperthermophilic esterase EstE1 and the relationship between its dimerization and thermostability properties. BMC Struct. Biol. 2007, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Xie, B.B.; Shi, M.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, P.Y. Identification and characterization of a novel salt-tolerant esterase from the deep-Sea sediment of the south china sea. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Xie, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. Fervidobacterium changbaicum Lip1: Identification, cloning, and characterization of the thermophilic lipase as a new member of bacterial lipase family V. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Huo, Y.Y.; Ji, R.; Kuang, S.; Ji, C.; Xu, X.W.; Li, J. Structural insights of a hormone sensitive lipase homologue Est22. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.J.; Jeong, H.B.; Kim, H.K. Characterization of novel salt-tolerant esterase isolated from the marine bacterium Alteromonas sp. 39-G1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, Y.; Ezaki, S.; Atomi, H.; Imanaka, T. Extremely stable and versatile carboxylesterase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3925–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; Galdiero, S.; Manco, G.; Lang, D.; Rossi, M.; Pedone, C. A snapshot of a transition state analogue of a novel thermophilic esterase belonging to the subfamily of mammalian hormone-sensitive lipase. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 303, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, G.J.; Fernández-Álvaro, E.; Bogdanović, X.; Bartsch, S.; Sczodrok, J.; Singh, R.K.; Böttcher, D.; Atomi, H.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Hinrichs, W. The crystal structure of an esterase from the hyperthermophilic microorganism Pyrobaculum calidifontis VA1 explains its enantioselectivity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotrim, C.A.; Jarrott, R.J.; Martin, J.L.; Drew, D. A structural overview of the zinc transporters in the cation diffusion facilitator family. Acta Cryst. 2019, D75, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

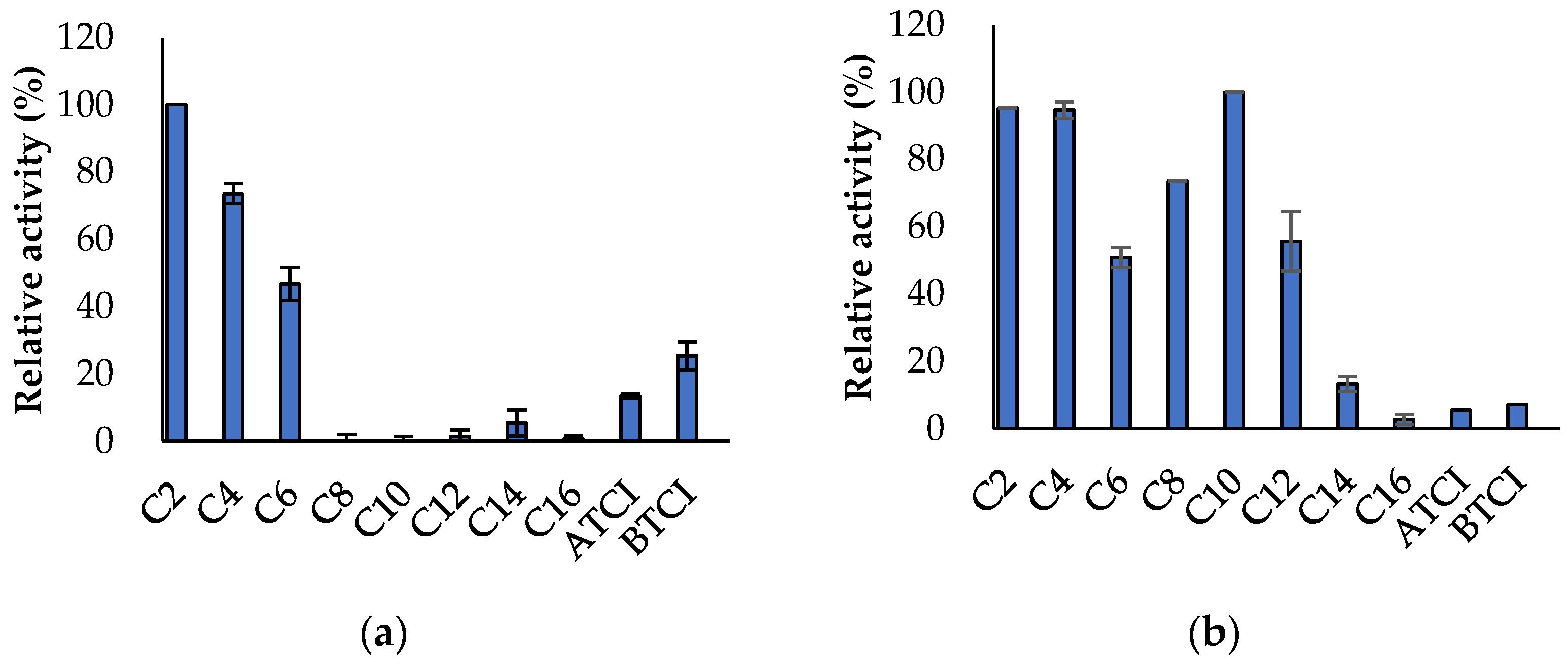
| Enzyme | Preparation | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification (Fold) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Est2L | Crude extract | 0.043 | 1.00 | 100 |
| HiTrap-Q | 0.11 | 2.56 | 22.6 | |
| Crude extract | 0.041 | 1.00 | 100 | |
| Sephacryl S-200 | 0.22 | 5.36 | 9.45 | |
| Est4L | Crude extract | 0.037 | 1.00 | 100 |
| HiTrap-Q | 0.063 | 1.70 | 12.5 | |
| Sephacryl S-200 | 0.027 | 0.73 | 2.25 |
| Protein | Fraction Volume (mL) | Molecular Mass (kDa) | log Mw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Est2L | 37.5 | 183.2 ± 23.6 | 2.26 |
| Est4L | 43.6 | 125.4 ± 8.65 | 2.10 |
| IgG | 39 | 166 | 2.22 |
| BSA | 54 | 66.4 | 1.82 |
| Protein | Accession | Source | Homology (%) | AA | MW (kDa) | Native Form | Opt Temp. (°C) | Opt. pH | pNP Esters | Solvent Stability (%) | Metal Ion | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | MeOH | ACN | Activating | Inhibiting | |||||||||||
| Family IV | |||||||||||||||
| Est2L * | MT989338 | Uncultured bacterium | 100 | 839 | 92.5 | Di | 60 | 10.0 | C2 | 15.7 a | 92.7 a | 6.67 a | Mg2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ | Cu2+ | This study |
| Est3K | AKG92633 | Uncultured bacterium | 19.90 | 299 | 32.4 | 50 | 9 | C4 | 87.5 a | 86.9 a | 47.7 a | Cu2+ | [29] | ||
| EstE7 | ABI18352 | Uncultured bacterium | 27.93 | 322 | 34.6 | Di | 40 | 5 | C4 | [47] | |||||
| Cest-2923 | CCC79999 | Lactobacillus plantarum | 9.75 | 282 | 31.2 | Di, Tetra | 30 | 7 | C2 | [48] | |||||
| REst1 | FJ645062 | Rheinheimera sp. | 15.56 | 342 | 37.2 | Mono, Tri | 50 | 8 | C4 | 0 a | Cd2+ | Mg2+, Hg2+ | [49] | ||
| E69 | AUD08548 | Erythrobacter seohaensis | 18.18 | 274 | 29.5 | 10.5 | 6 | C4 | 0 b | 28.8 b | 35.0 b | [53] | |||
| EstE1 | AAW62260 | Uncultured archaeon | 19.85 | 311 | 33.7 | Di | 95 | 6 | C6 | [54] | |||||
| Est22 | AFB82695 | Uncultured bacterium | 16.51 | 365 | 39 | Di | 40 | 7.5 | C2 | 40 b | 120 b | 0 b | Zn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ | [57] | |
| EstA1 ** | PHS53692.1 | Alteromonas sp. | 18.97 | 379 | 41.2 | 45 | 8 | C2 | 102 b | 100 b | 68 b | [58] | |||
| PestE | BAC06606 | Pyrobaculum calidifontis | 20.49 | 313 | 34.4 | Di | 90 | 7 | C6 | 110 c | 109 c | 117 c | [59,61] | ||
| EST2 | QGT40748 | Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius | 20.34 | 311 | 34.4 | Mono | 70 | 7.1 | C6 | [60] | |||||
| Family V | |||||||||||||||
| Est4L | MT989339 | Uncultured bacterium | 100 | 267 | 30.1 | Tetra | 50 | 10.0 | C10 | 6.94 a | 128.6 a | 7.47 a | Cu2+, Zn2+ | This study | |
| Est16 | ADM63076 | Uncultured bacterium | 21.28 | 302 | 31.9 | Mono | 55 | 9.0 | C4 | Mg2+, Mn2+ | Zn2+ | [50] | |||
| QpeH | ANT80587 | Pseudomonas sp. J-5 | 17.67 | 309 | 38.5 | Mono | 30 | 8.0 | Ca2+, Li2+, Cd2+ | Mg2+ | [51] | ||||
| LacH | AGS18892 | Brevundimonas sp. LY-2 | 12.46 | 306 | 32.4 | Di | 40 | 7.0 | C2 | Fe2+, Cd2+ | Zn2+, Hg2+ | [52] | |||
| H8 | ARH02619 | Uncultured bacterium | 17.33 | 305 | 32.8 | 35 | 10.8 | C6 | 4.4 d | 52.6 d | 2.7 d | Cu2+, Zn2+ | [55] | ||
| FCLip1 | ABL95965 | Fervidobacterium changbaicum | 10.64 | 315 | 35.9 | 78 | 7.8 | C10 | 123.4 d | Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ | [56] | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.E.; Jeong, G.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, H. Characterization of a Novel Family IV Esterase Containing a Predicted CzcO Domain and a Family V Esterase with Broad Substrate Specificity from an Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenomic Library. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135905
Park JE, Jeong GS, Lee HW, Kim SK, Kim J, Kim H. Characterization of a Novel Family IV Esterase Containing a Predicted CzcO Domain and a Family V Esterase with Broad Substrate Specificity from an Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenomic Library. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135905
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jong Eun, Geum Seok Jeong, Hyun Woo Lee, Sung Kyum Kim, Jungho Kim, and Hoon Kim. 2021. "Characterization of a Novel Family IV Esterase Containing a Predicted CzcO Domain and a Family V Esterase with Broad Substrate Specificity from an Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenomic Library" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135905
APA StylePark, J. E., Jeong, G. S., Lee, H. W., Kim, S. K., Kim, J., & Kim, H. (2021). Characterization of a Novel Family IV Esterase Containing a Predicted CzcO Domain and a Family V Esterase with Broad Substrate Specificity from an Oil-Polluted Mud Flat Metagenomic Library. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135905







