Experimental Evaluation of Connectors Performance for Modular Double-Skinned Composite Tubular Wind Turbine Tower
Abstract
1. Introduction
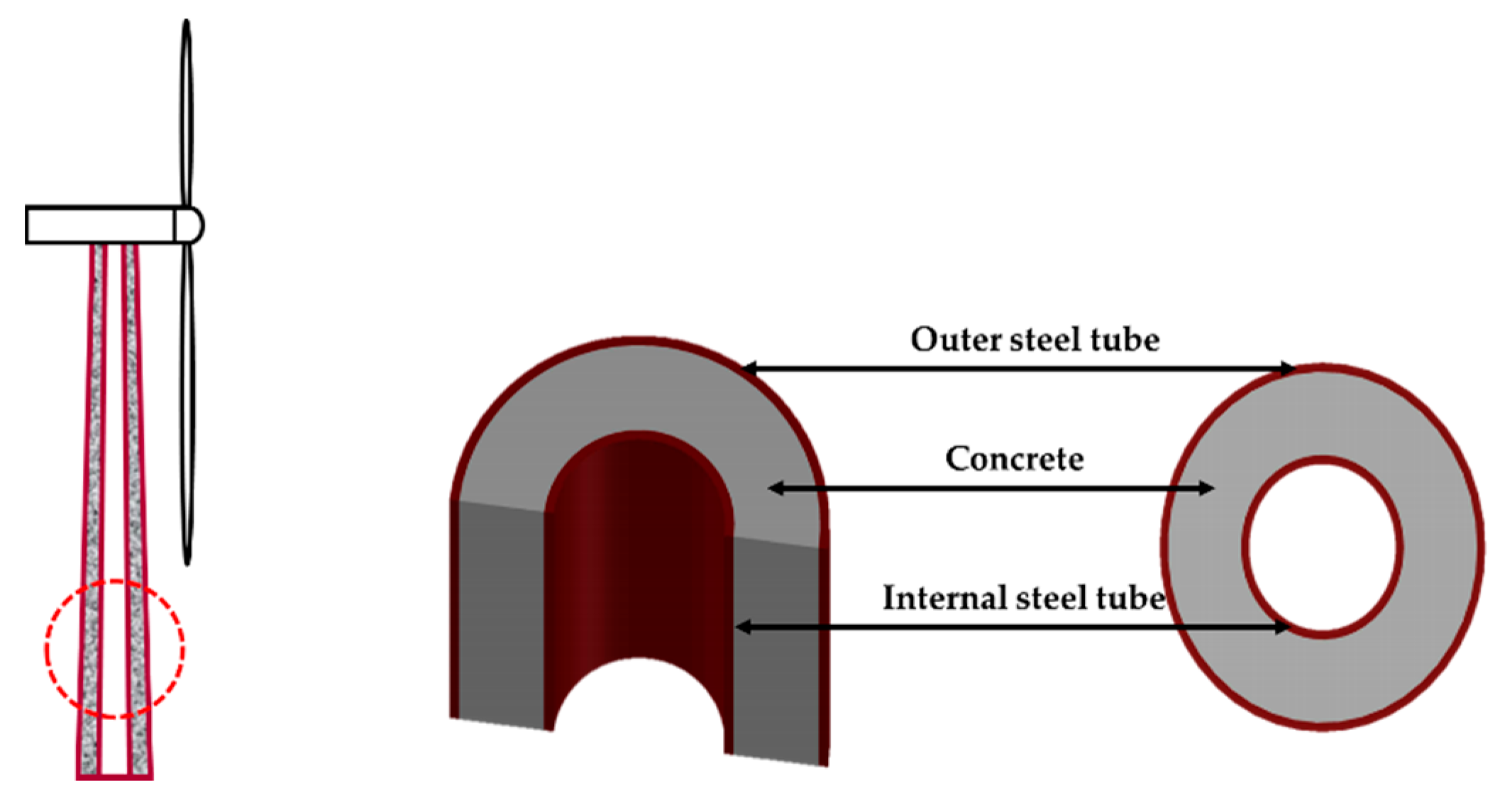
2. Design of DSCT Specimens
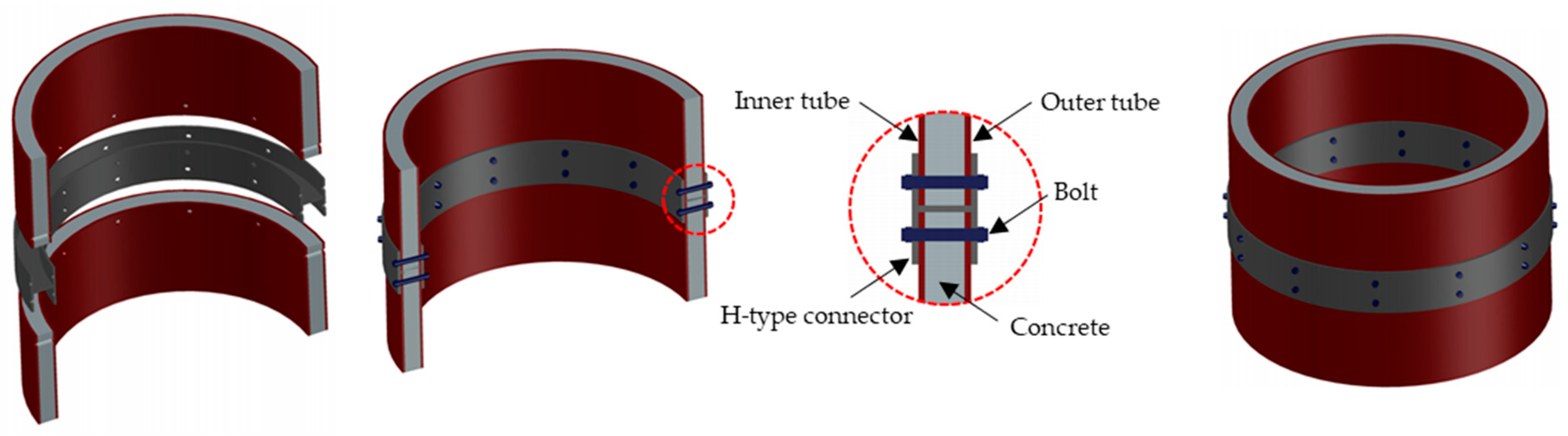
2.1. Types of Module Joints
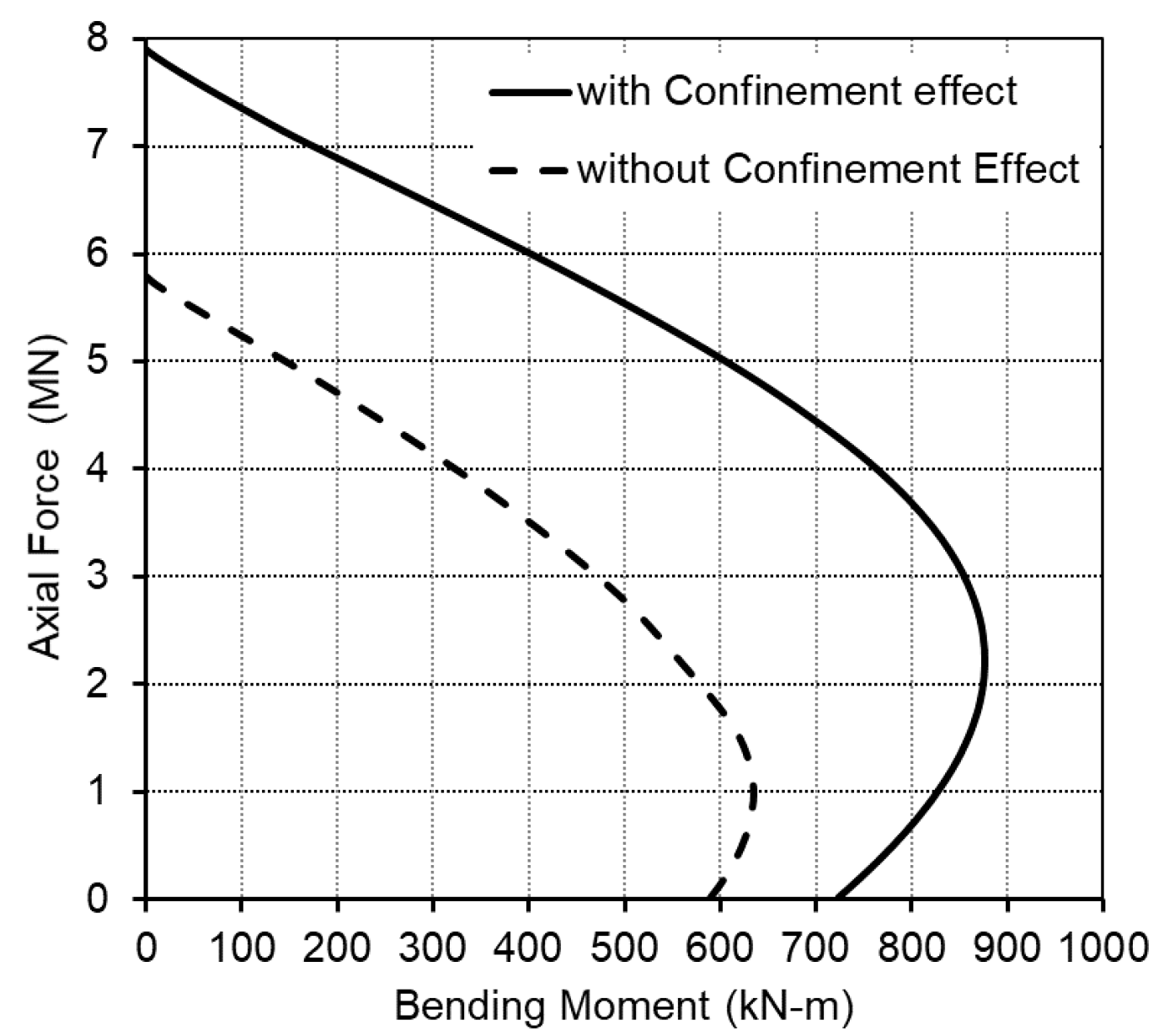
2.2. Section Design
| : inner diameter of confined concrete (=outer diameter of inner tube), | |
| : outer diameter of confined concrete (=inner diameter of outer tube) | |
| : yield strength of outer tube | |
| : thickness of outer tube | |
| : yield strength of inner tube | |
| : modulus of elasticity of inner tube. |
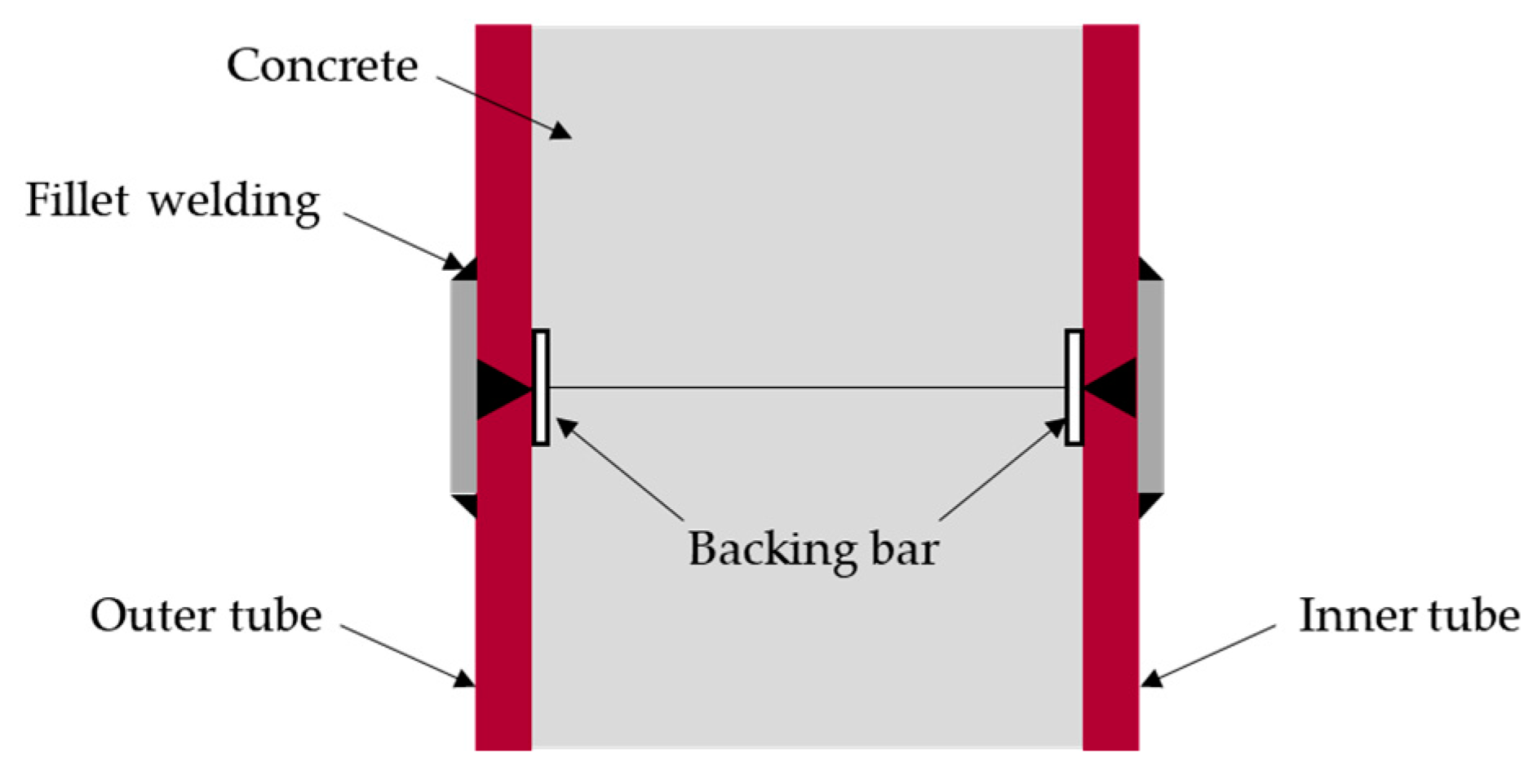
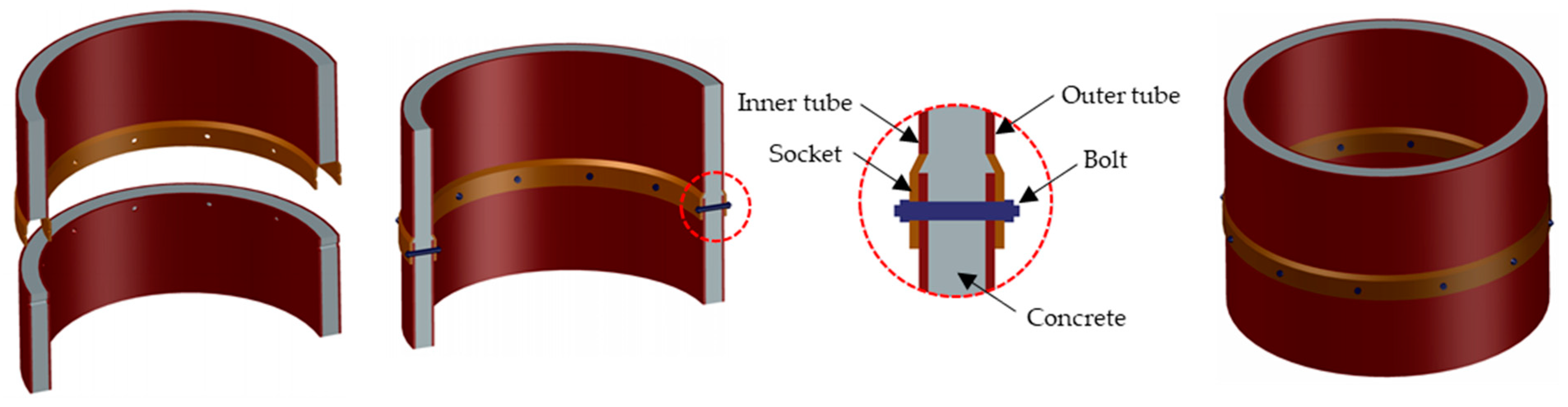
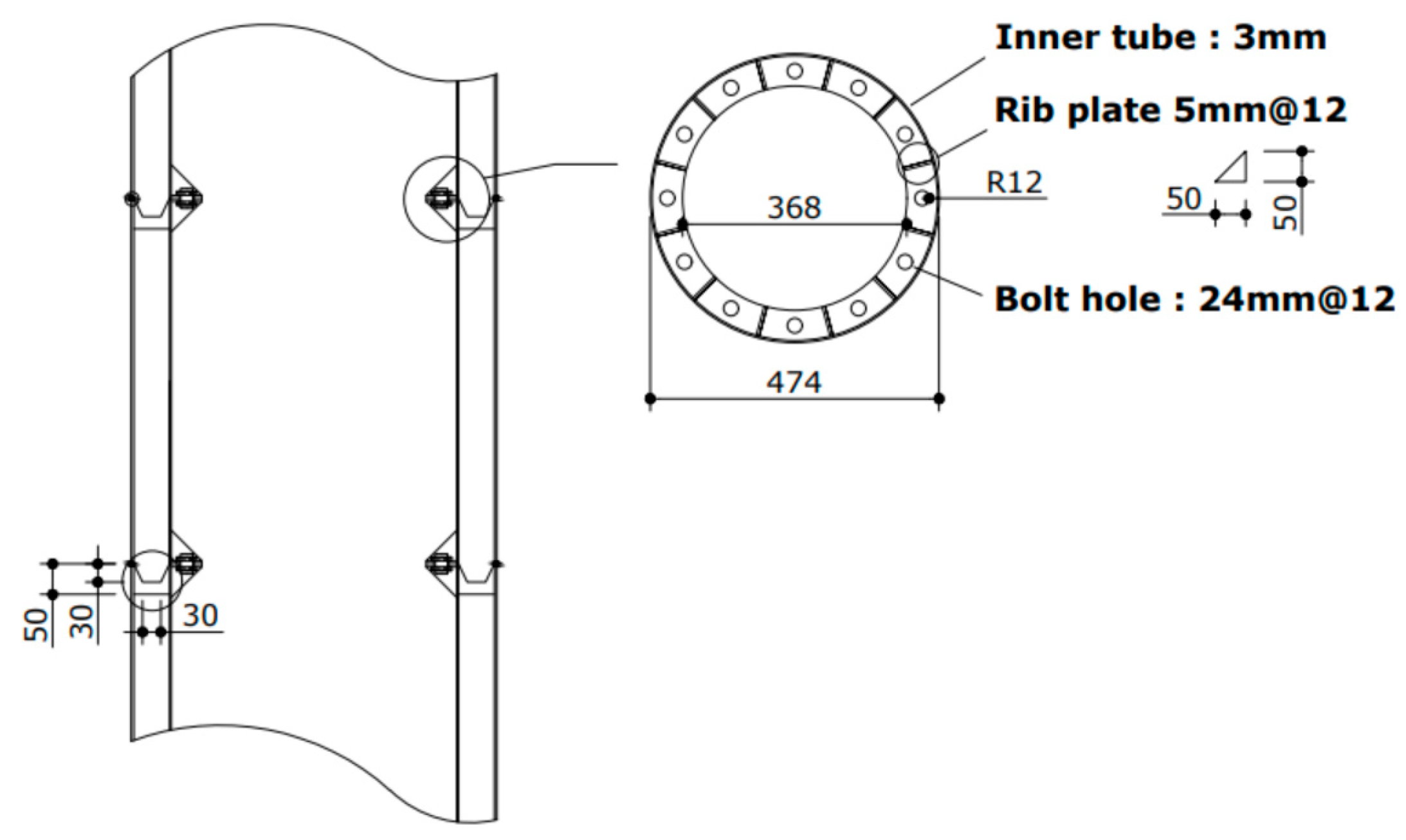
2.3. Design of Type-S Joint
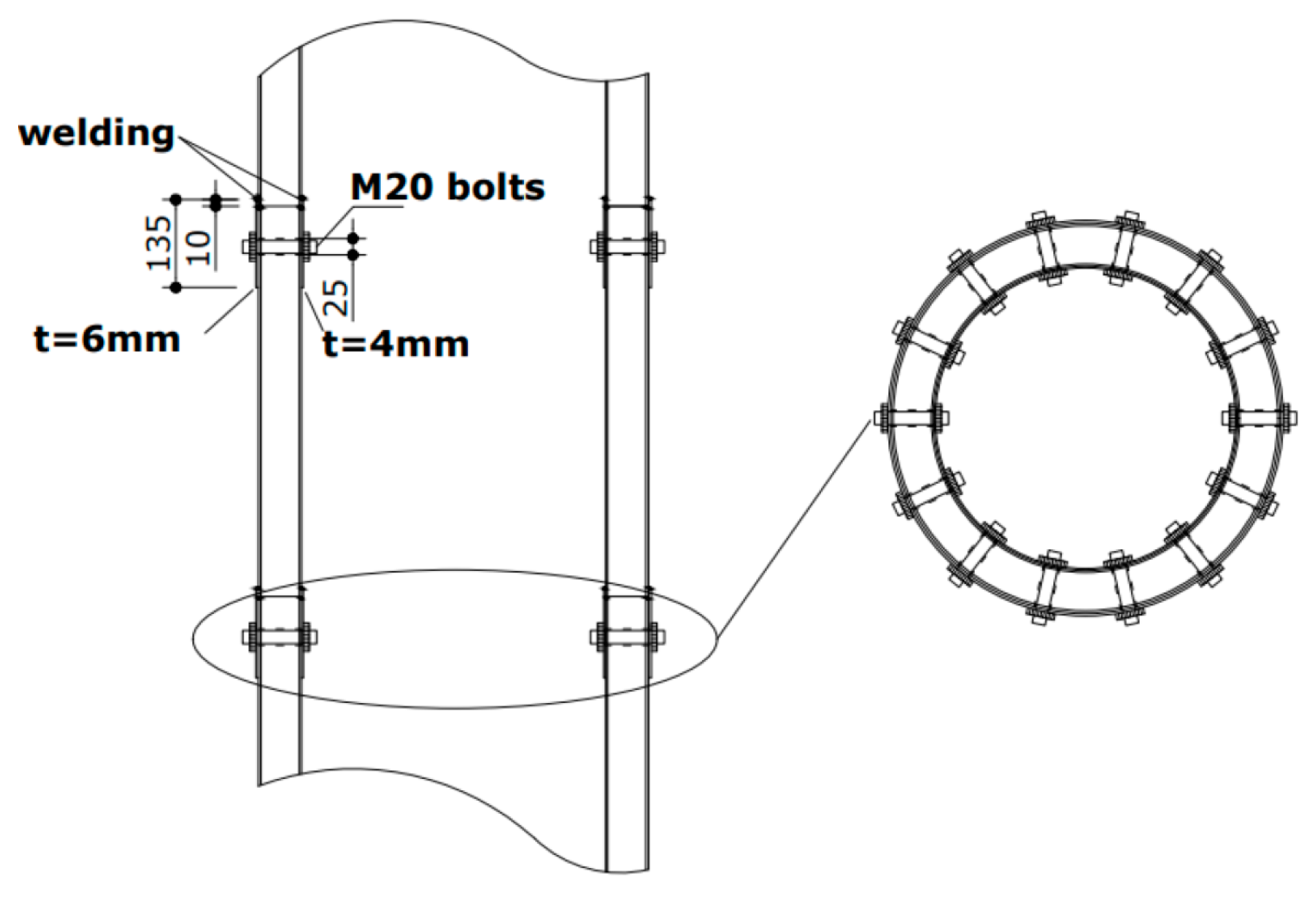
2.4. Design of Type-H Joint
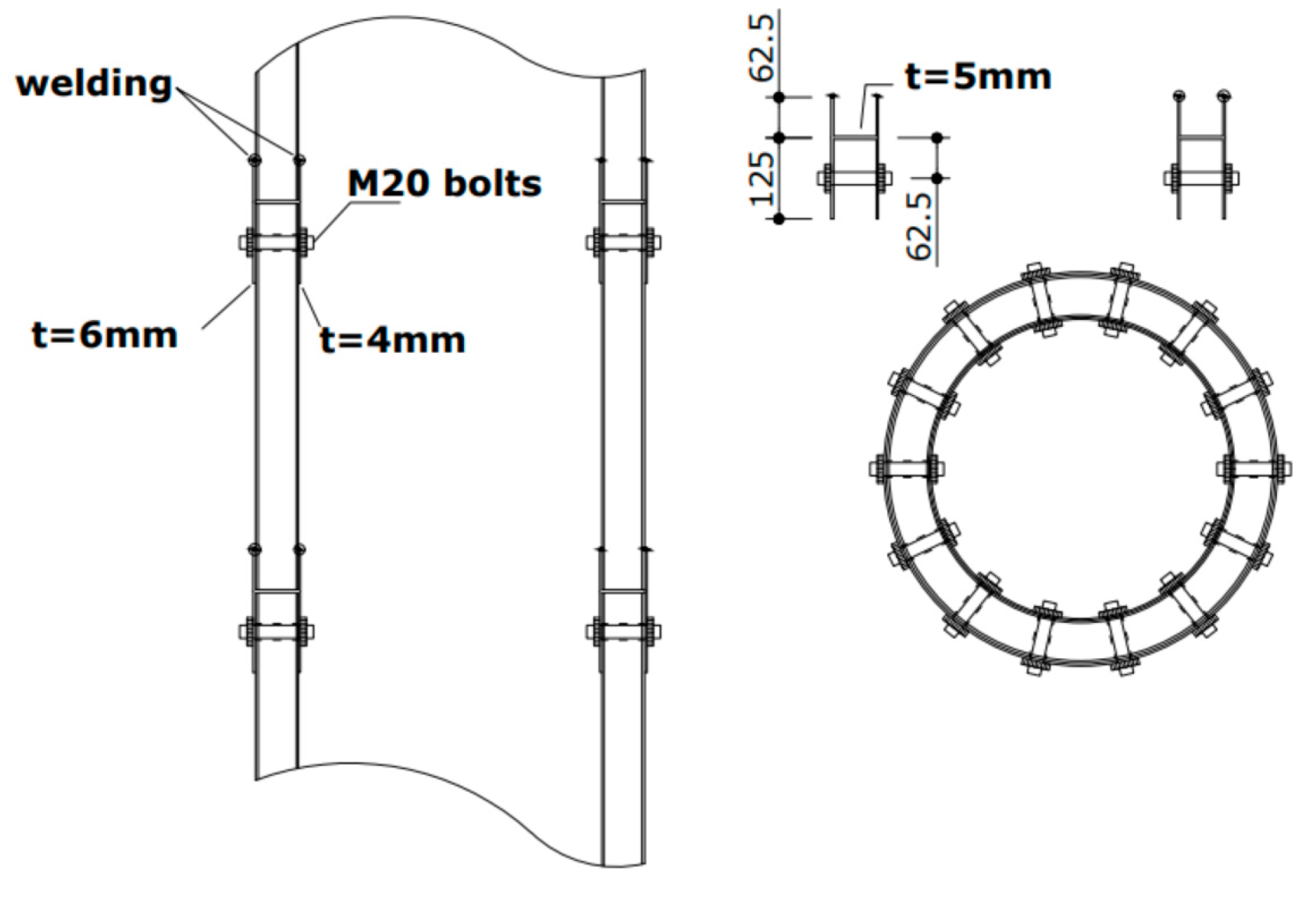
2.5. Design of Type-W Joint
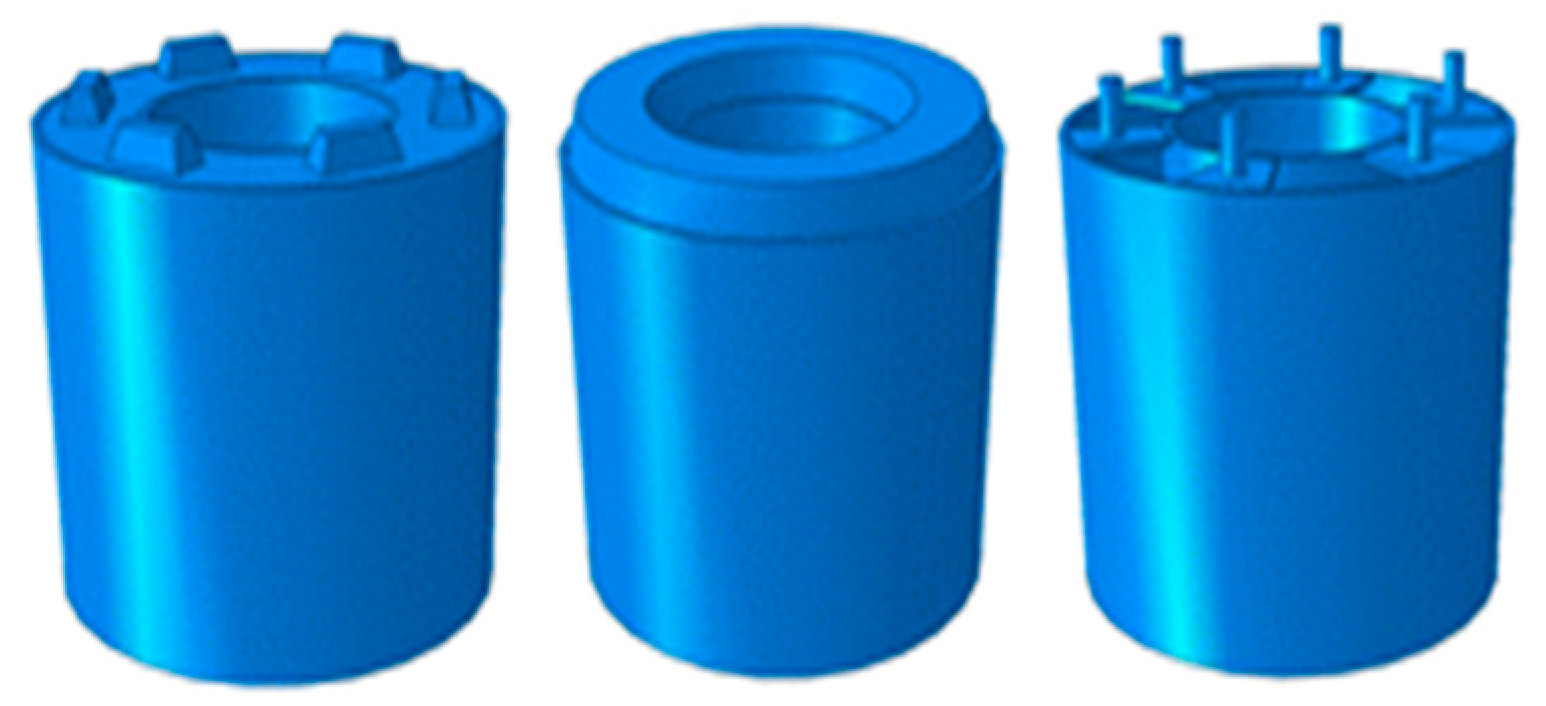
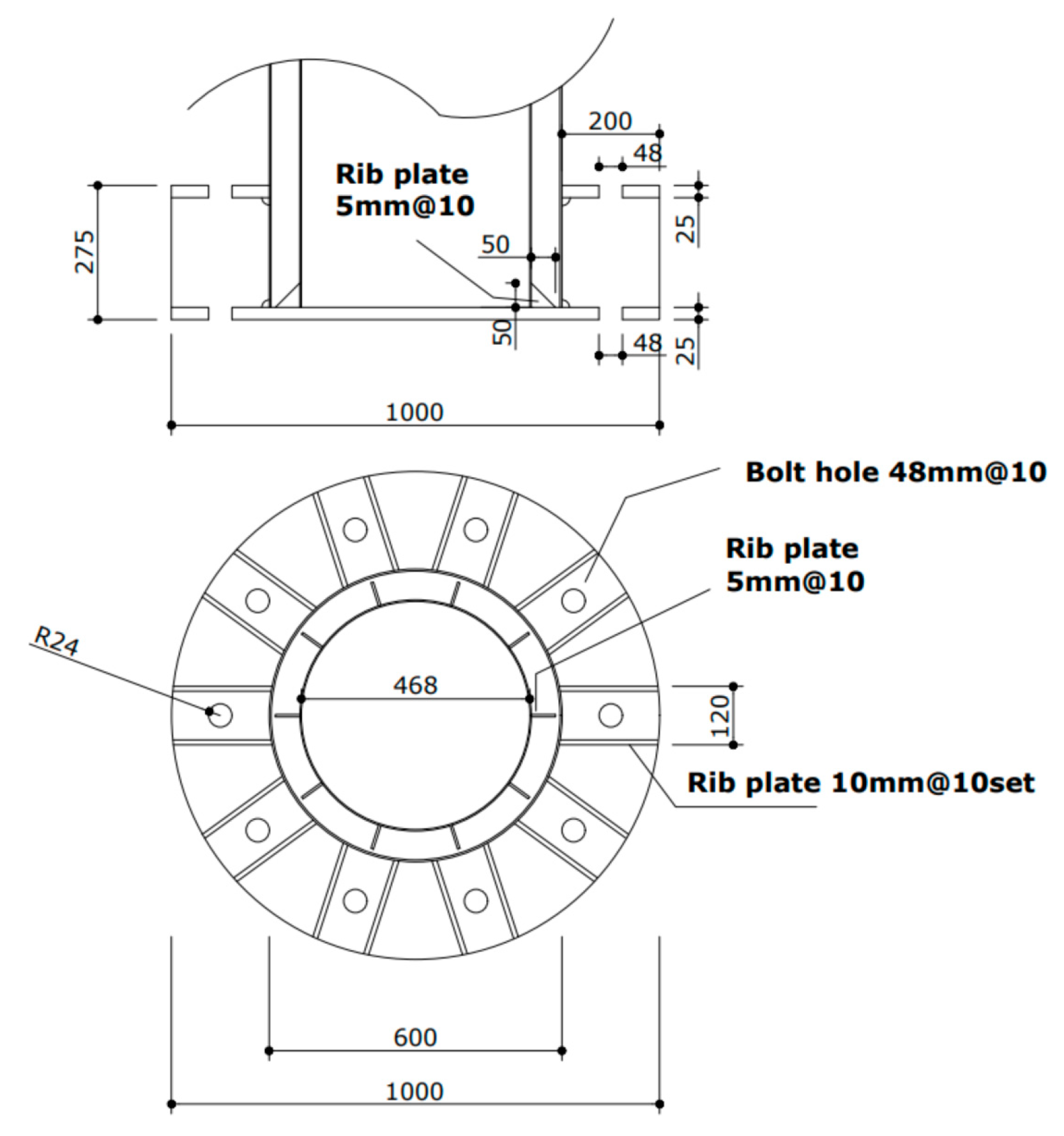
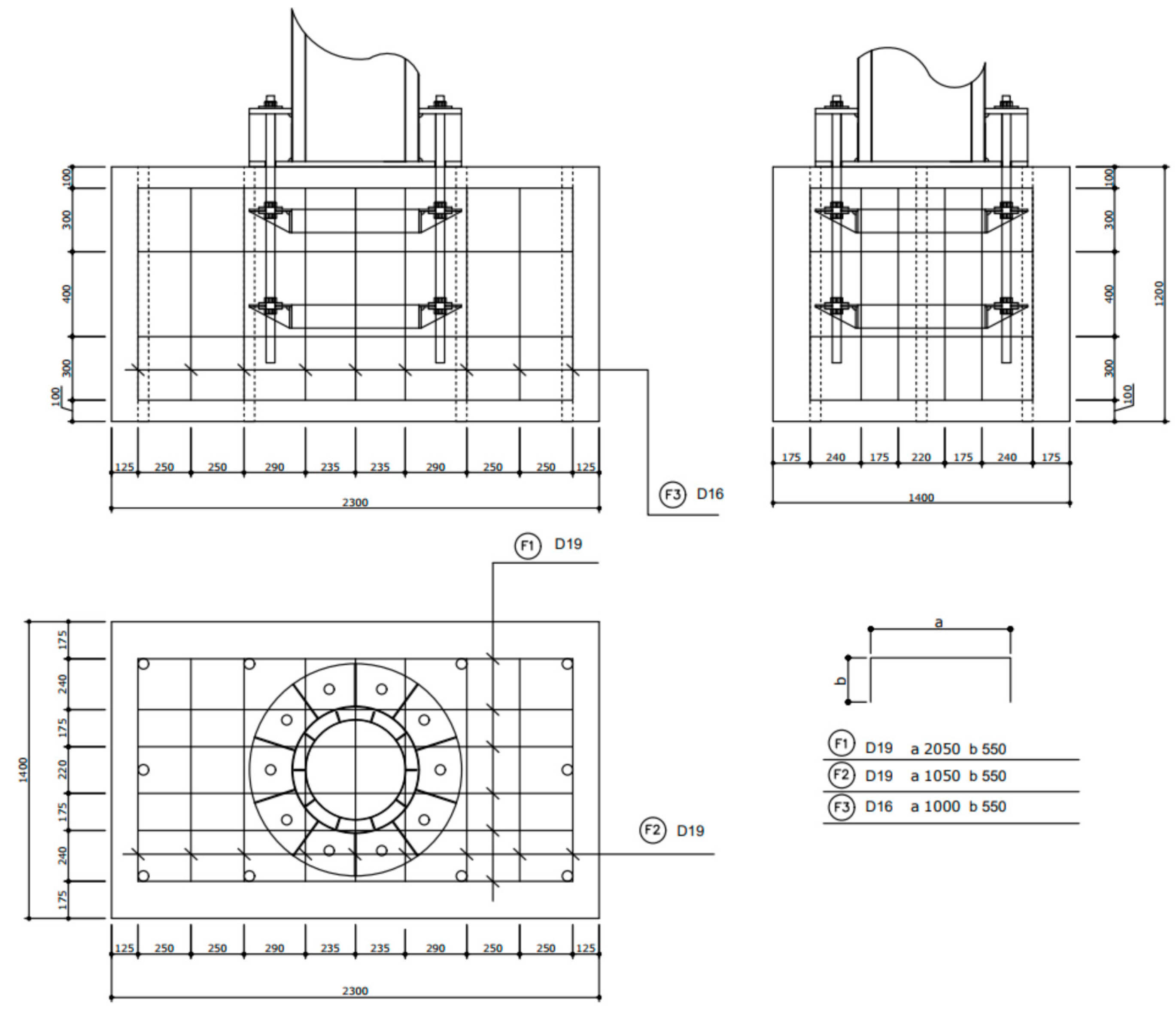
2.6. Design of Footing
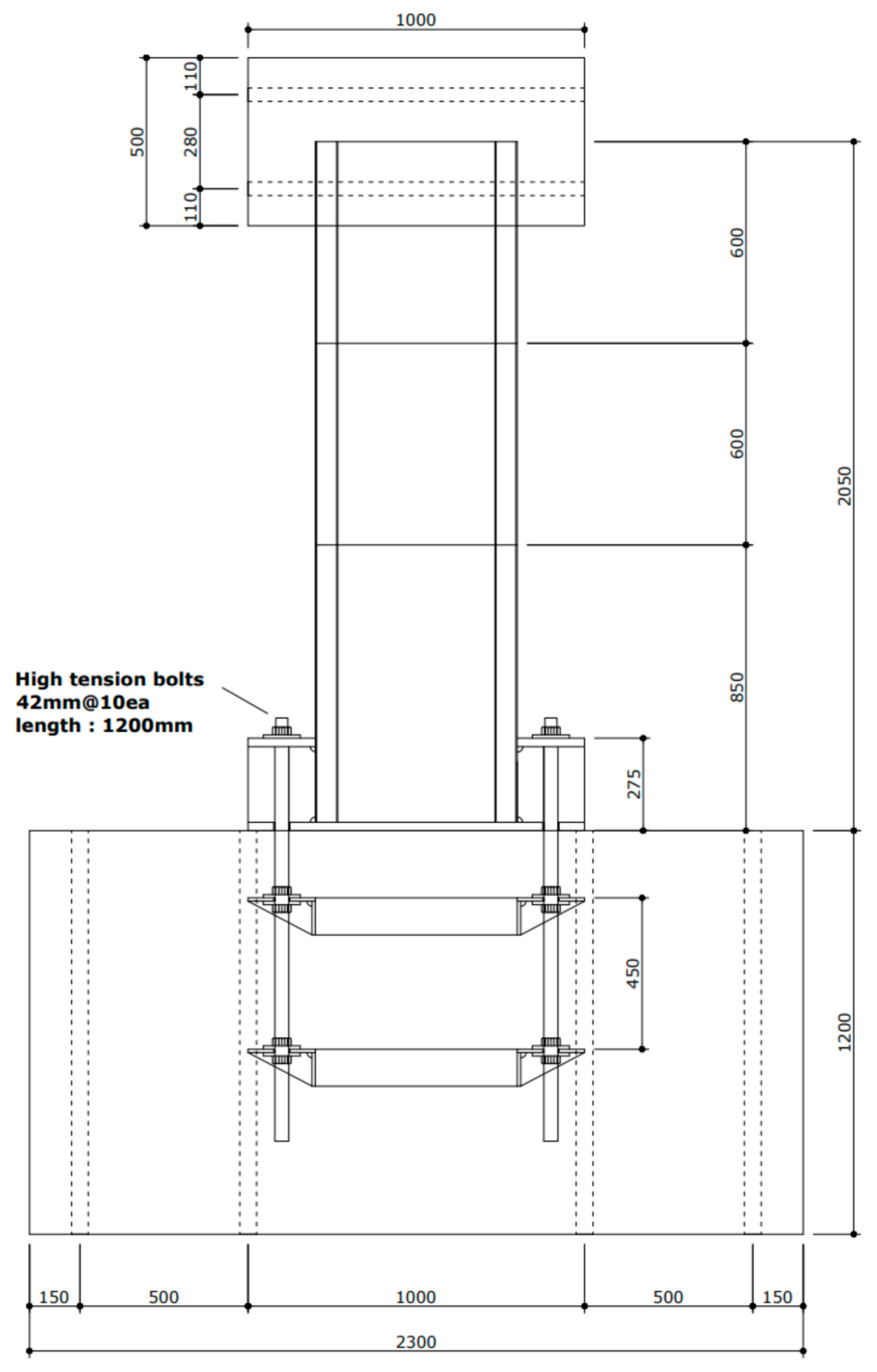
2.7. Design of Tower Specimens
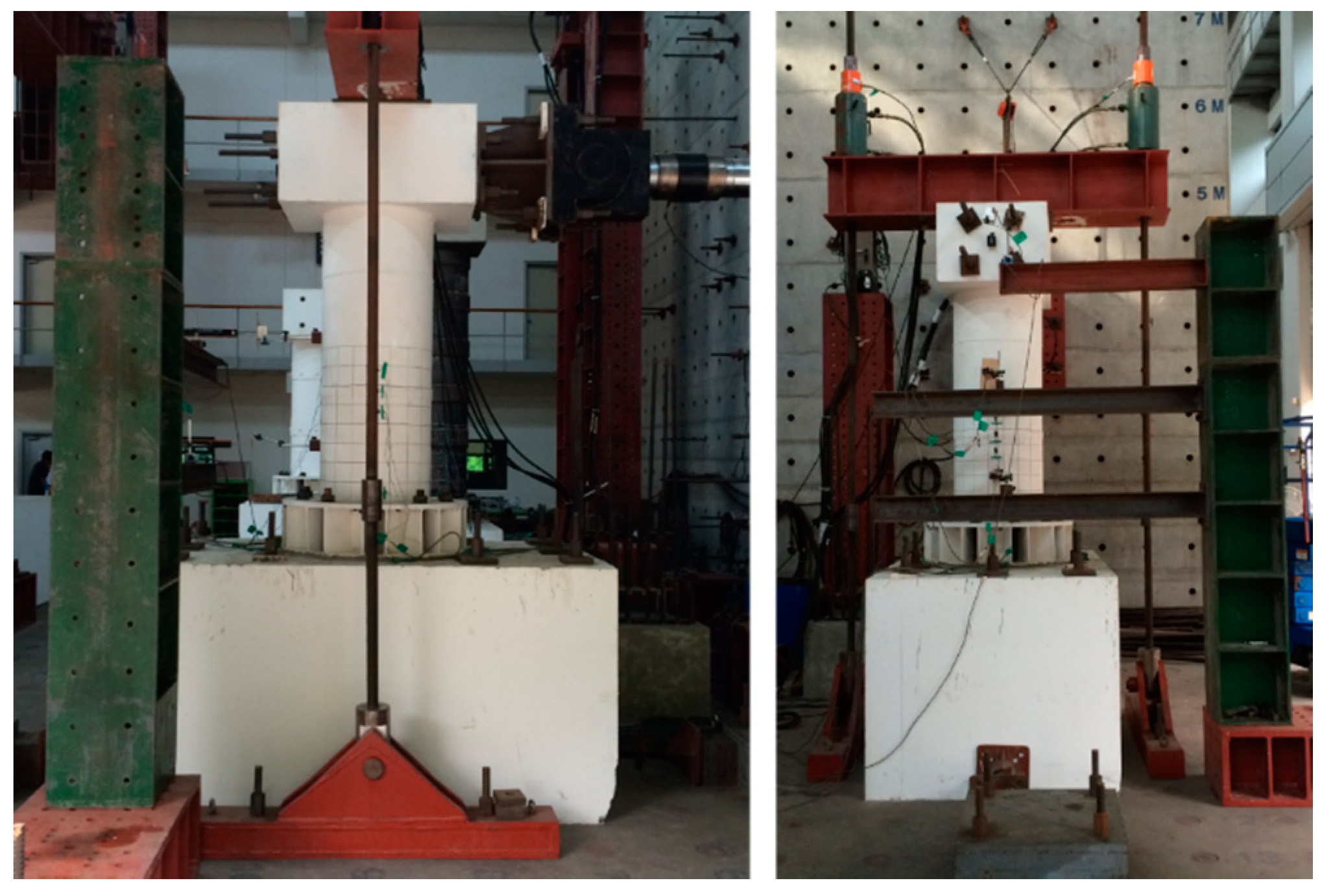
3. Experiments
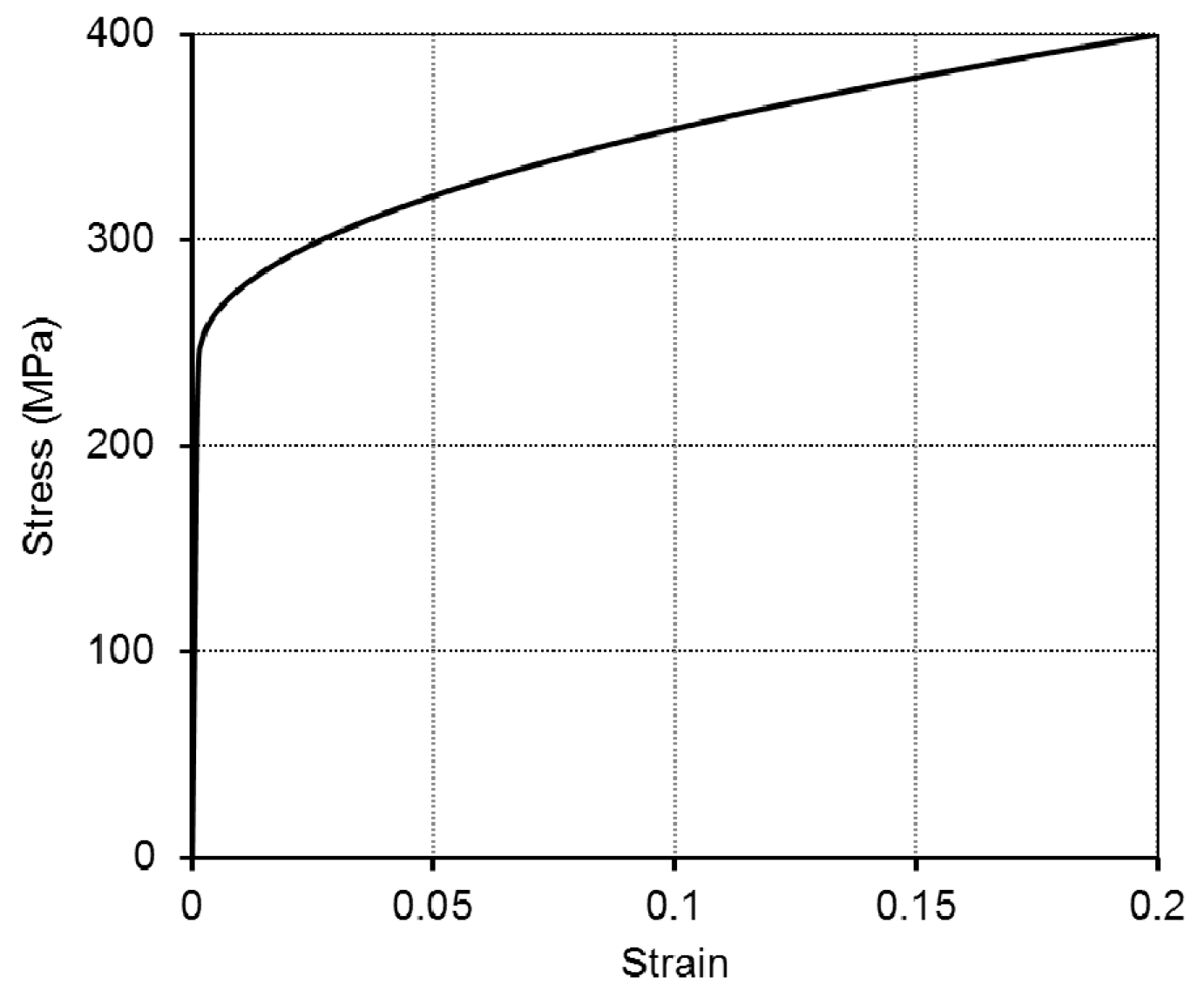
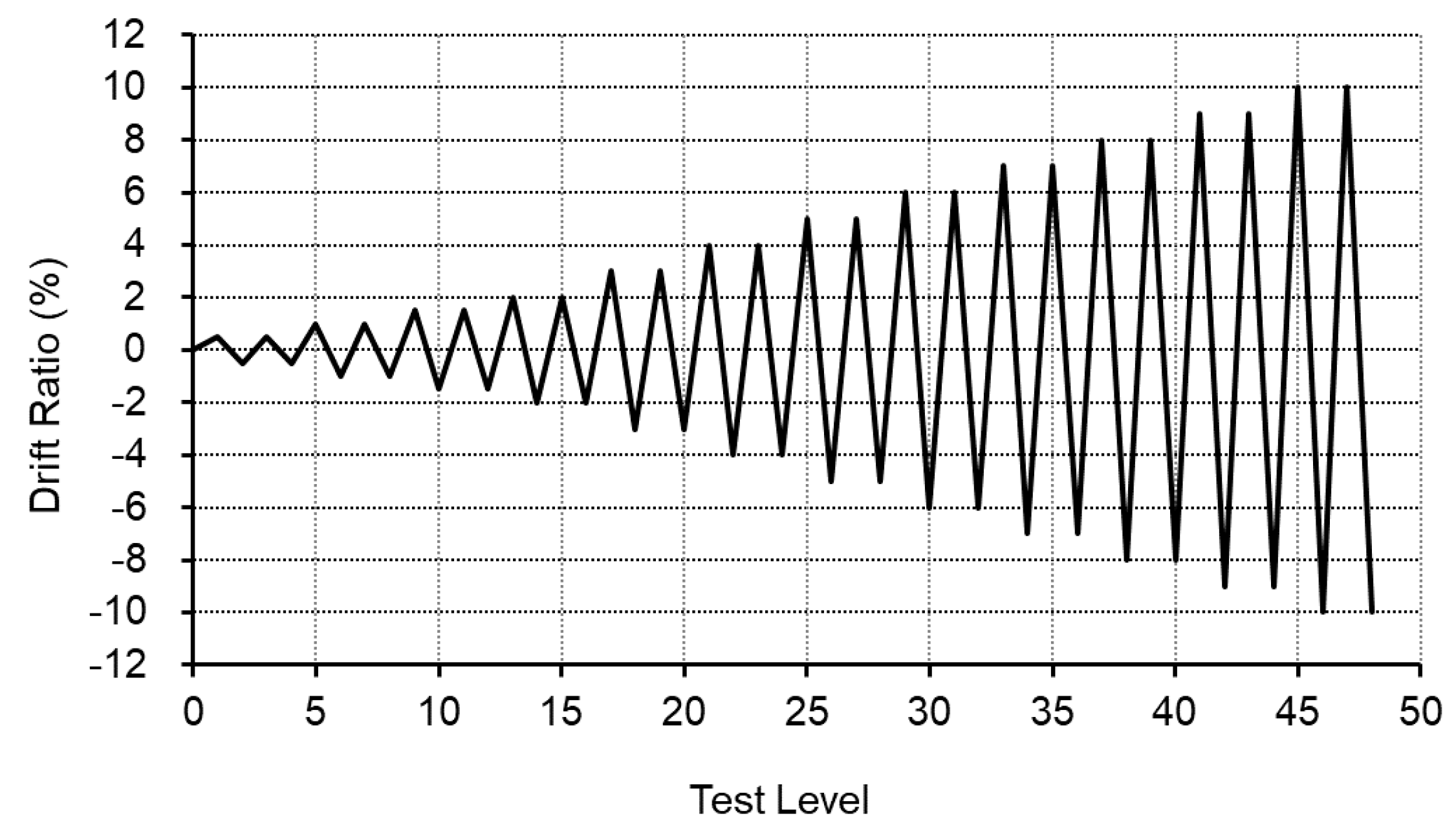
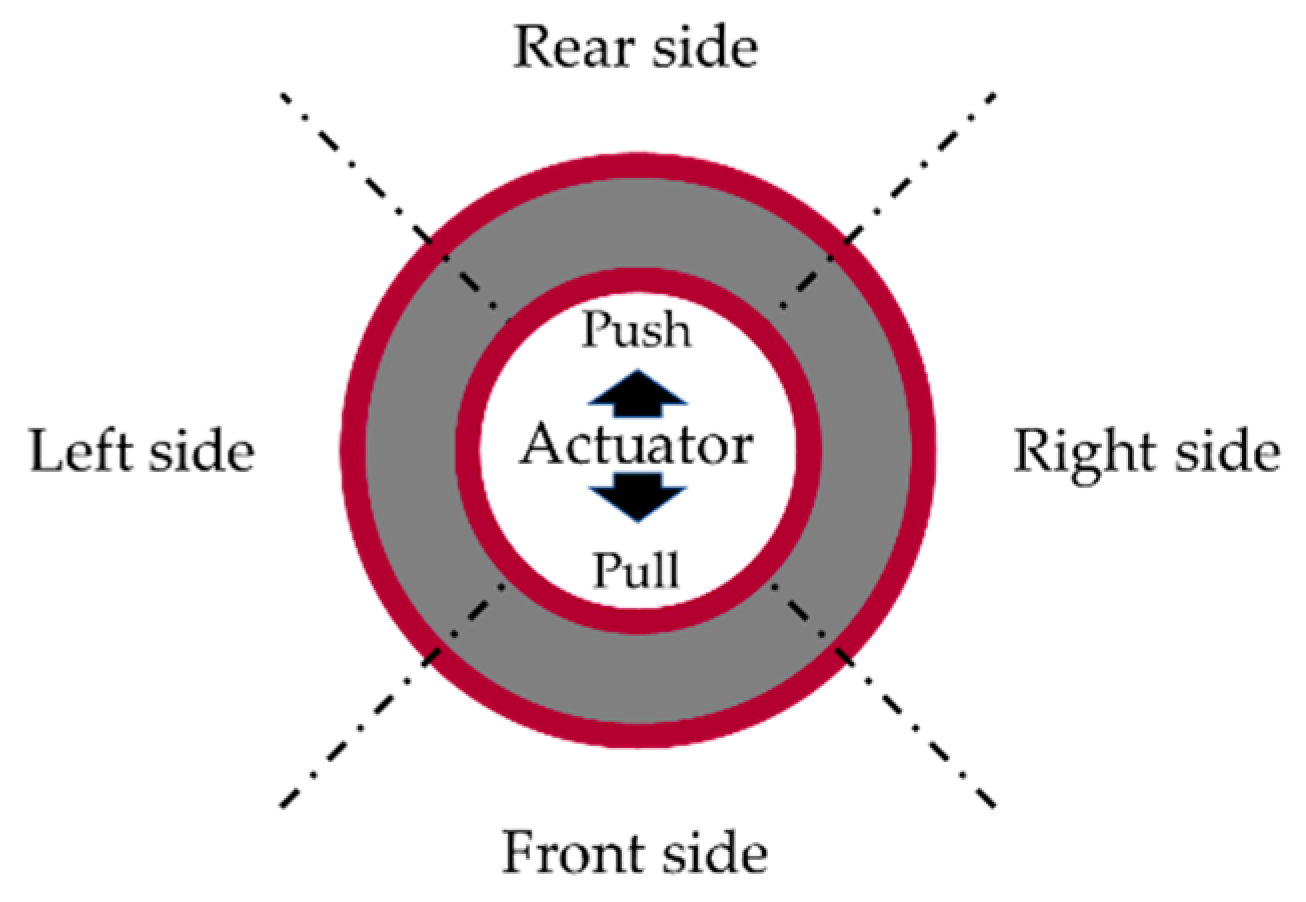
3.1. Experimental Program
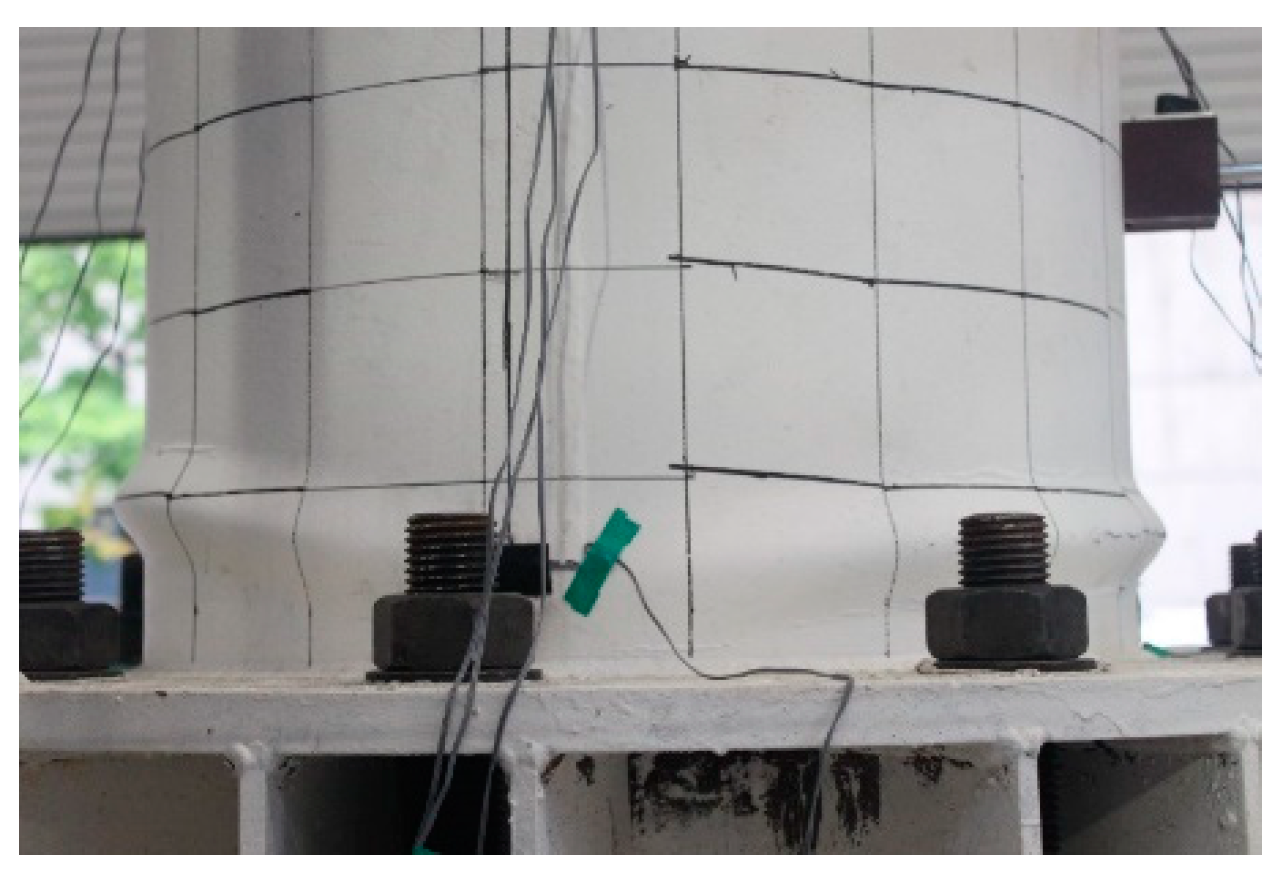
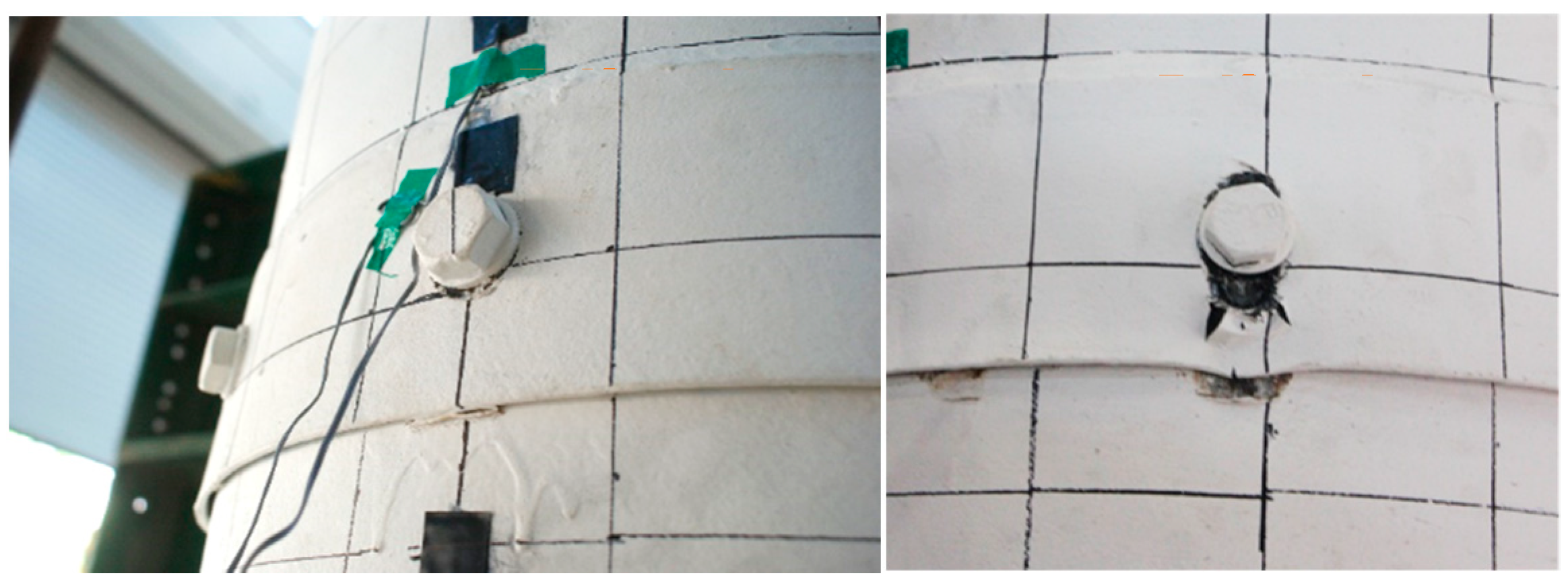
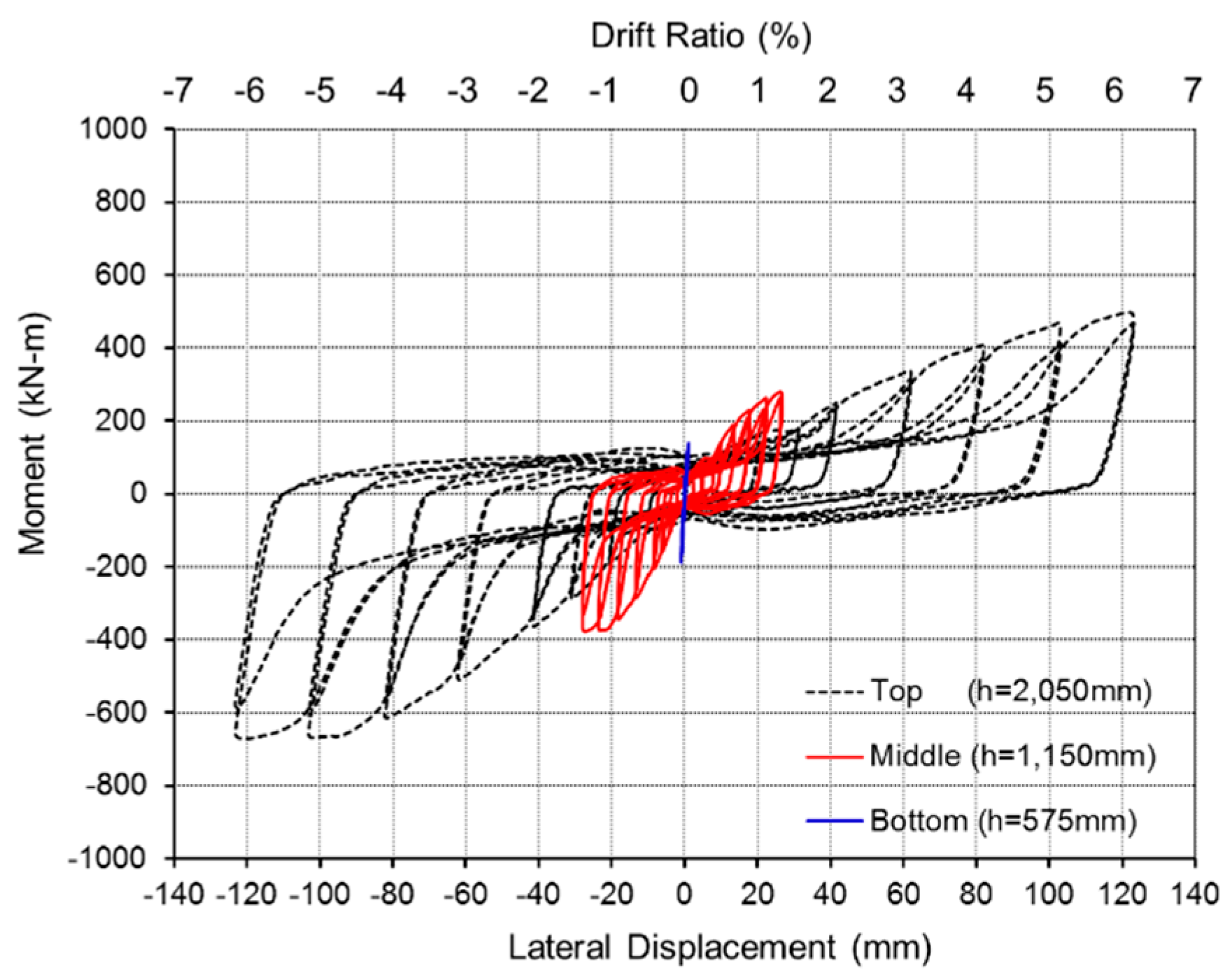
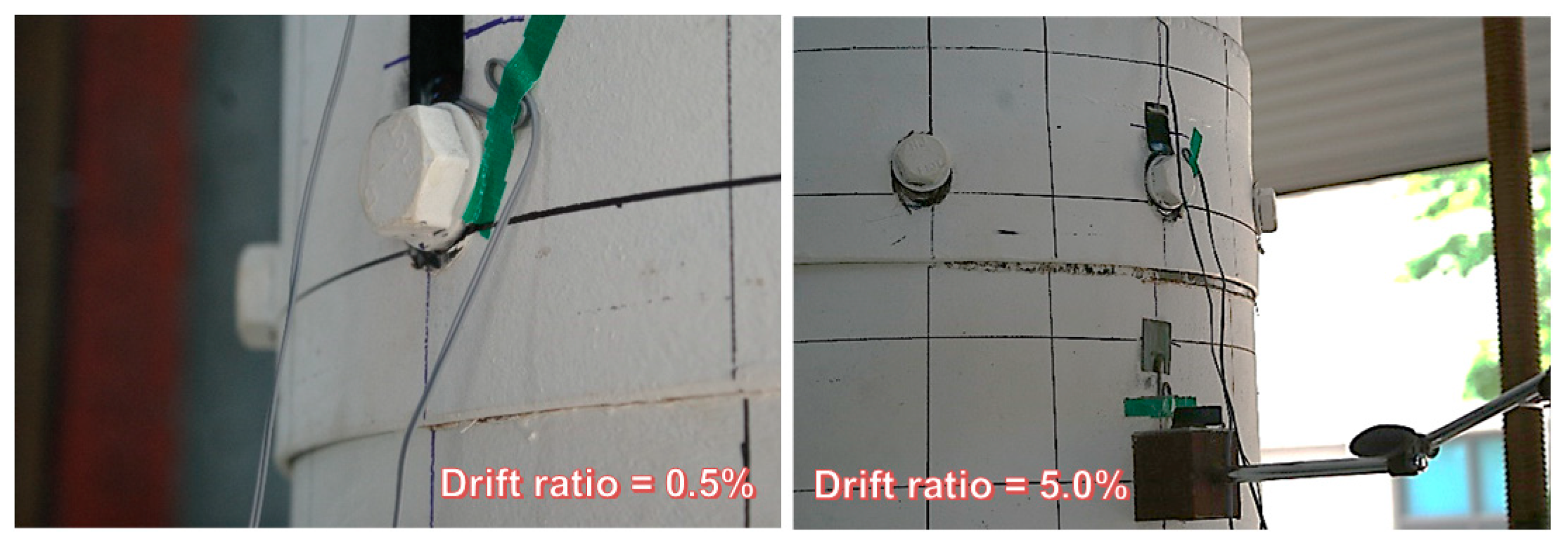
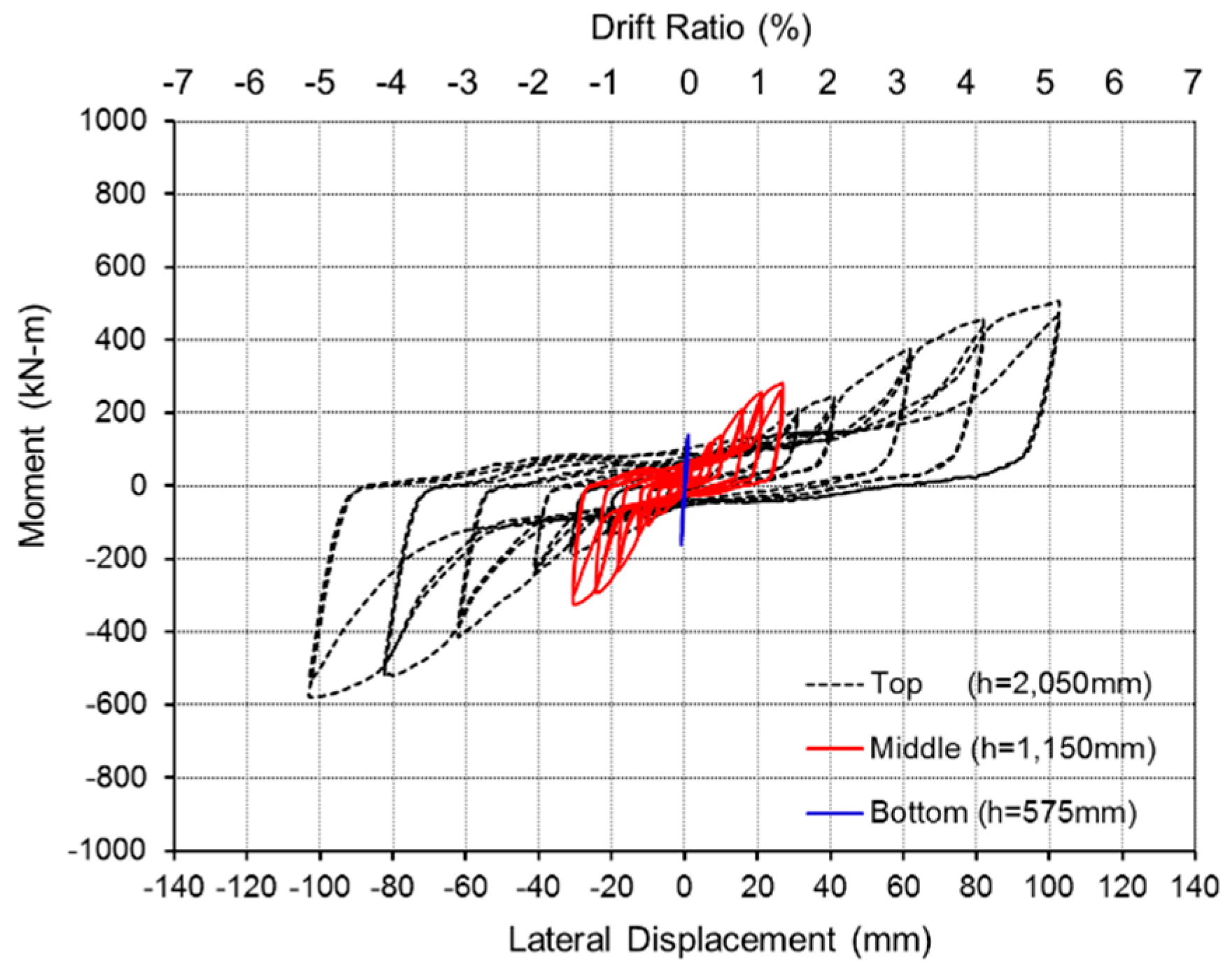
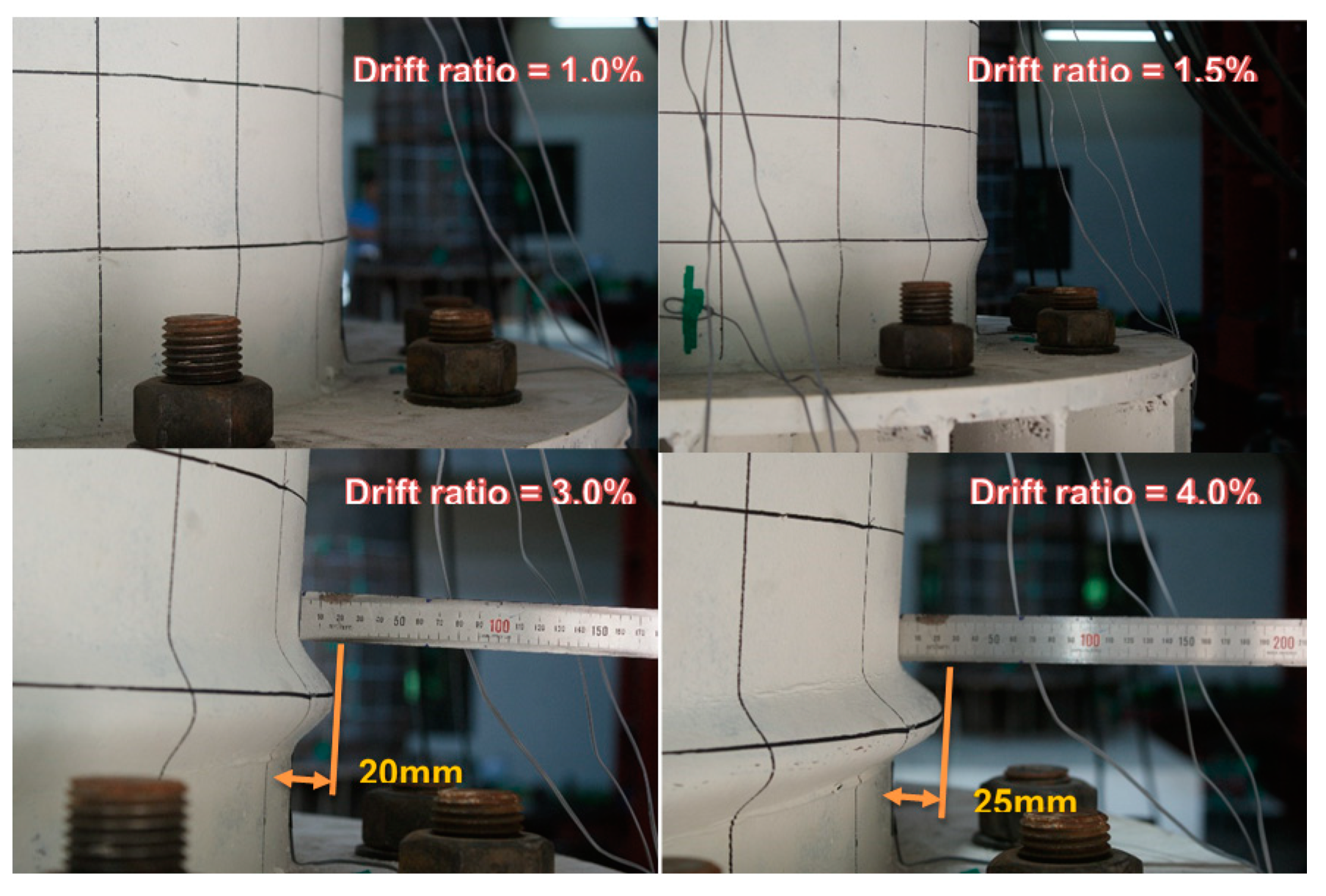
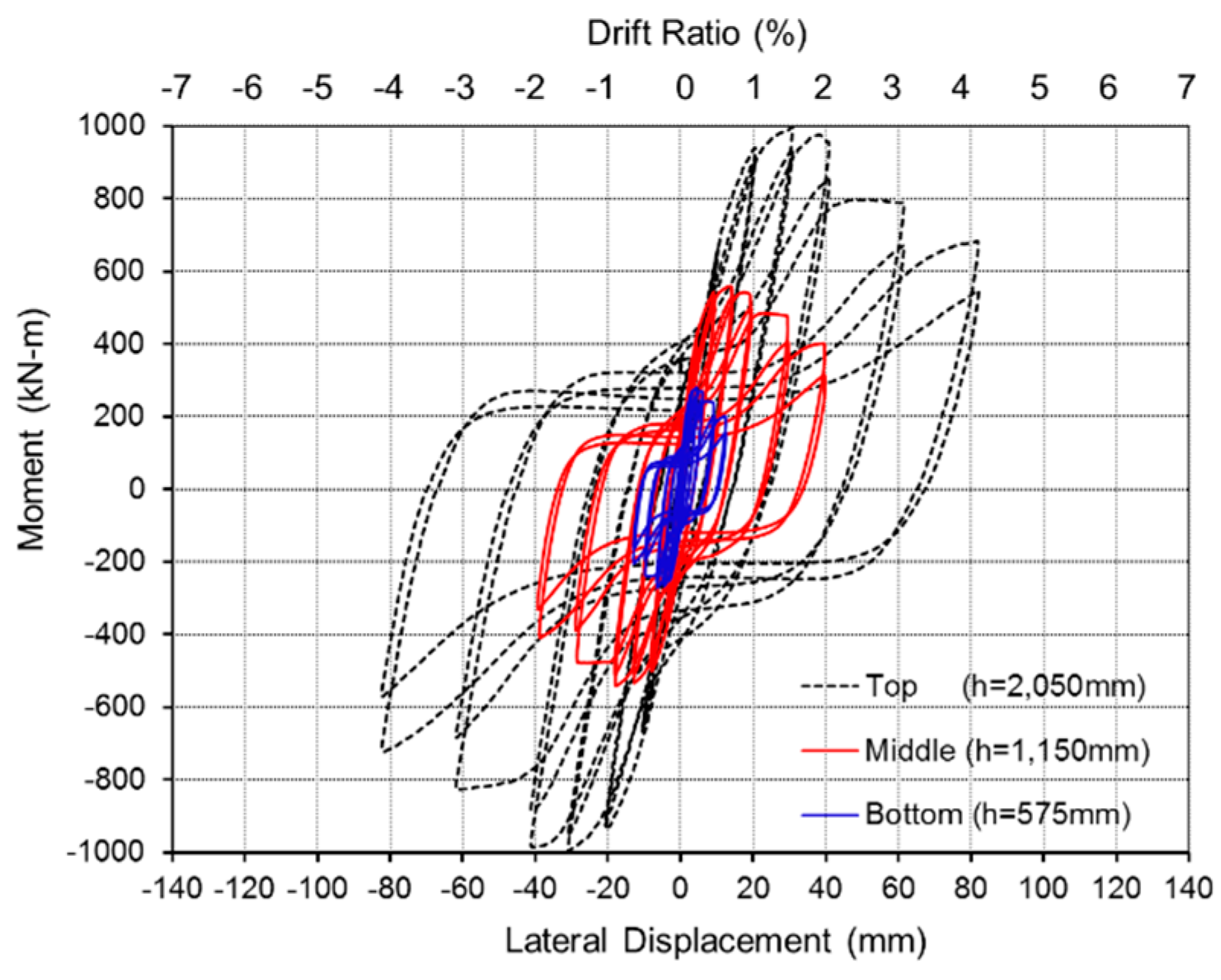
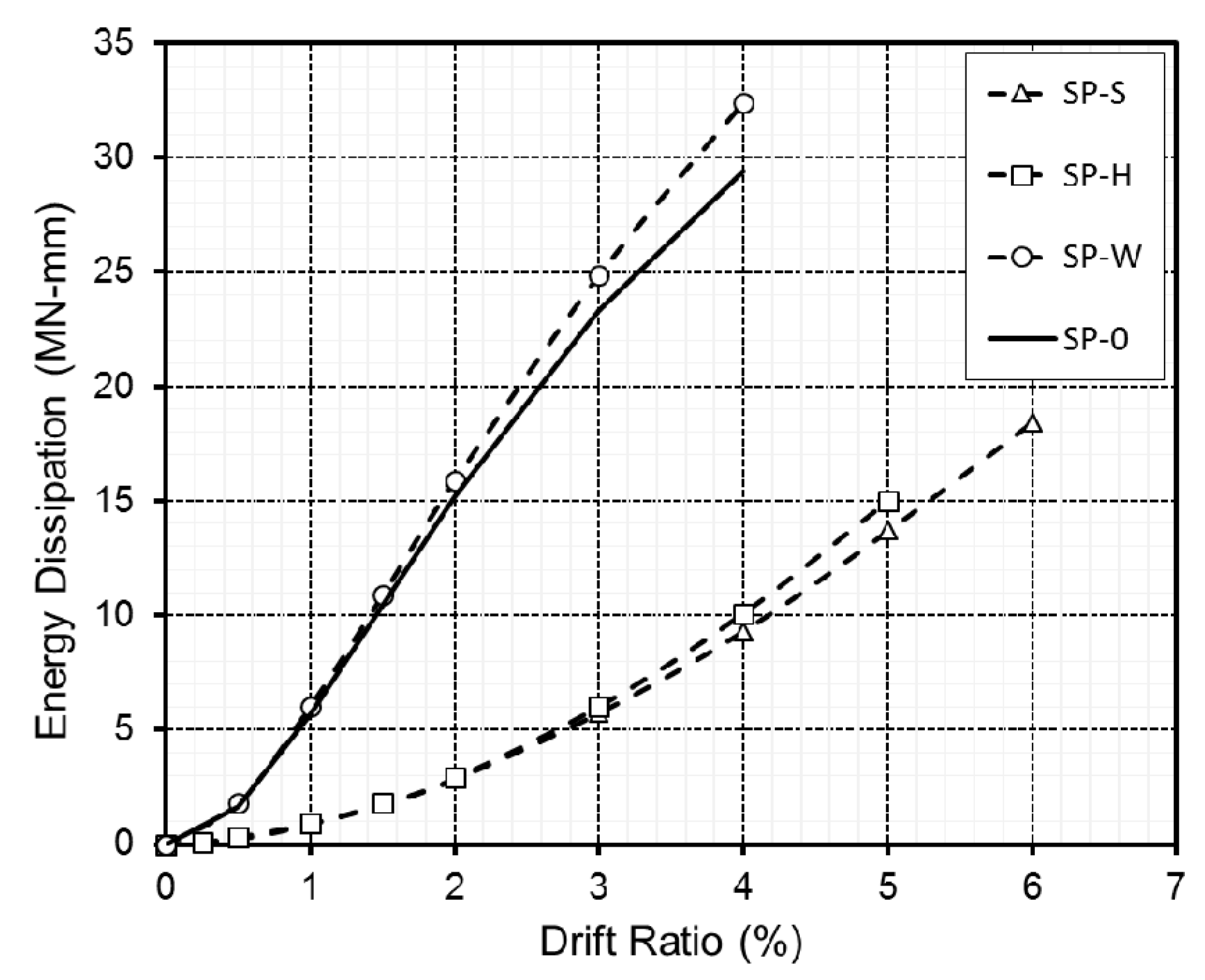
3.2. Test Result
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doagou-Rad, S.; Mishnaevsky, L., Jr.; Bech, J.I. Leading edge erosion of wind turbine blades: Multiaxial critical plane fatigue model of coating degradation under random liquid impacts. Wind Energy 2020, 23, 1752–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlanetto, A.; Gomes, H.M.; de Almeida, F.S. Design Optimization of Tapered Steel Wind Turbine Towers by QPSO Algorithm. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2020, 20, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CWIF. Summary of Wind Turbine Accident Data to 30 June 2020. Available online: http://www.caithnesswindfarms.co.uk/AccidentStatistics.htm (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Ma, Y.; Martínez-Vázquez, P.; Baniotopoulos, C. Wind turbine tower collapse cases: A historical overview. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Struct. Build 2019, 172, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INNEO. Precast Concrete Wind Towers. Available online: http://www.inneo.es/index.php/en/home.html (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Tindall. Innovative and Economical. Available online: https://tindallcorp.com/markets/power-energy/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Han, T.H.; Won, D.H.; Kim, S. Applicability of double-skinned composite tubular member for offshore wind turbine tower. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2013, 31, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, T.H.; Yi, J.; Yoon, G.; Won, D.H.; Yoo, S. Structural behavior analysis of DSCT wind power tower for 5 MW turbines considering large displacement effect. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2016, 15, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hong, H.; Han, T. Behavior of an Internally Confined Hollow Reinforced Concrete Column with a Polygonal Cross-Section. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hong, H.; Han, T.H. Section design and analysis of ICH RC tower supporting 5 MW wind turbine. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shakir-Khalil, H.; Illouli, S. Composite columns of concentric steel tubes. In Proceedings of the Conference on the Design and Construction of Non-Conventional Structures, London, UK, 8–10 December 1987; Volume 1, pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.H.; Stallings, J.M.; Kang, Y.J. Nonlinear concrete model for double-skinned composite tubular columns. Constr. Build Mater. 2010, 24, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.H.; Won, D.H.; Kim, S.; Kang, Y.J. Performance of a DSCT column under lateral loading: Analysis. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.H.; Han, T.H.; Lee, D.J.; Kang, Y.J. A Study of pier-segment joint for fabricated internally confined hollow CFT pier. J. Korean Soc. Steel Constr. 2010, 22, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.H.; Hong, H.; Kim, S. CoWiTA Manual 2018; Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology: Ansan, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mander, J.B.; Priestly, M.J.N.; Park, R. Seismic Design of Bridge Piers; Research Report No. 84-2; University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 1984; pp. 47–95. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.H.; Won, D.H.; Yi, G.; Kang, Y.J. Behavior of internally confined hollow RC columns. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2009, 21, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R. Ductility evaluation from laboratory and analytical testing. In Proceedings of the Ninth World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 2 August 1988; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]











| Material | Property | Value (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Modulus of elasticity | 205,000 |
| Yield strength | 245 | |
| Ultimate strength | 400 | |
| Concrete | Compressive strength | 24 |
| Specimen No. | Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30.70 |
| 2 | 28.23 |
| 3 | 29.58 |
| Average | 29.50 |
| Specimen | Maximum Load | Maximum Displacement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moment (kN-m) | Lateral Force (kN) | Comparison | Lateral Displ. (mm) | Comparison | |
| SP-0 | 996.83 | 486.26 | 100% | 82.195 | 100% |
| SP-S | 583.25 | 284.51 | 58.5% | 123.275 | 150% |
| SP-H | 541.04 | 263.92 | 54.3% | 102.885 | 125% |
| SP-W | 982.01 | 479.03 | 98.5% | 82.185 | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Hong, H.; Han, T.H. Experimental Evaluation of Connectors Performance for Modular Double-Skinned Composite Tubular Wind Turbine Tower. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135899
Kim S, Hong H, Han TH. Experimental Evaluation of Connectors Performance for Modular Double-Skinned Composite Tubular Wind Turbine Tower. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135899
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sungwon, Hyemin Hong, and Taek Hee Han. 2021. "Experimental Evaluation of Connectors Performance for Modular Double-Skinned Composite Tubular Wind Turbine Tower" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135899
APA StyleKim, S., Hong, H., & Han, T. H. (2021). Experimental Evaluation of Connectors Performance for Modular Double-Skinned Composite Tubular Wind Turbine Tower. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135899






