Seismic Reflection Analysis of AETA Electromagnetic Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
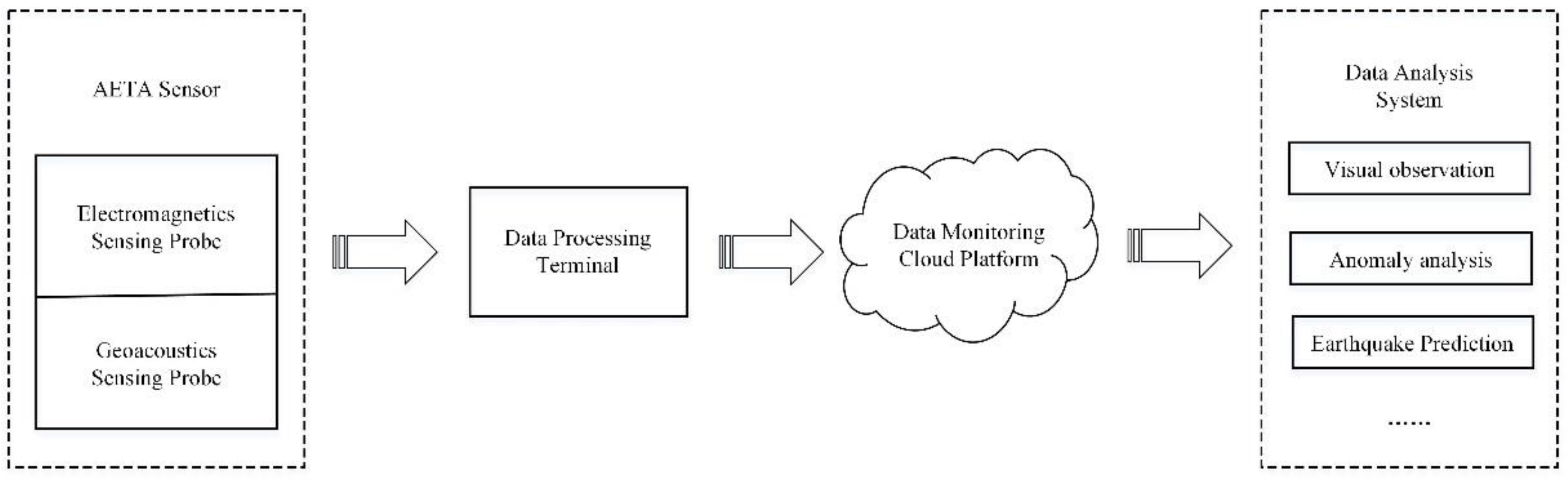
2. AETA System
3. Algorithm and Sample Extraction
3.1. Anomalies of Electromagnetic Signals before the Earthquake
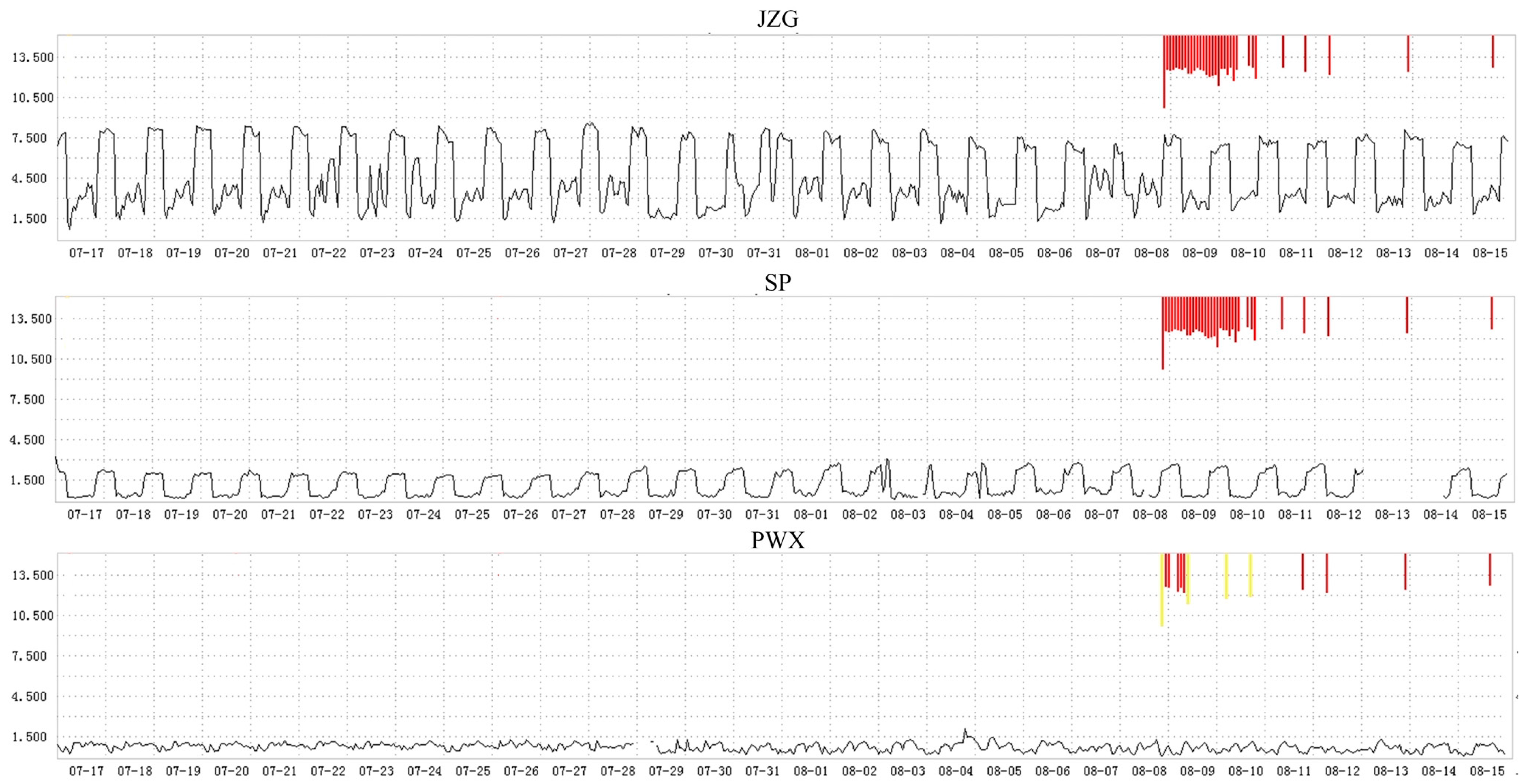
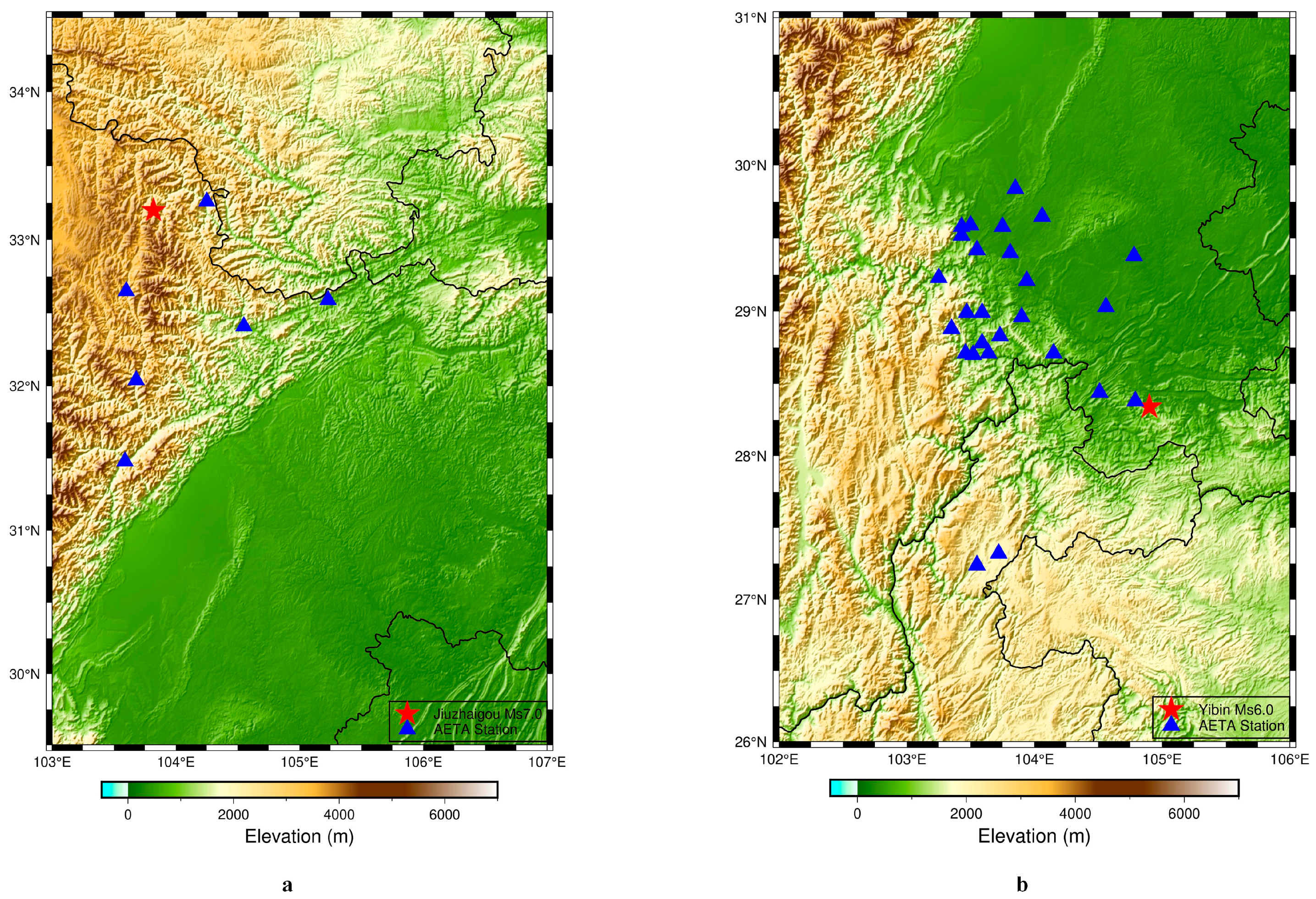
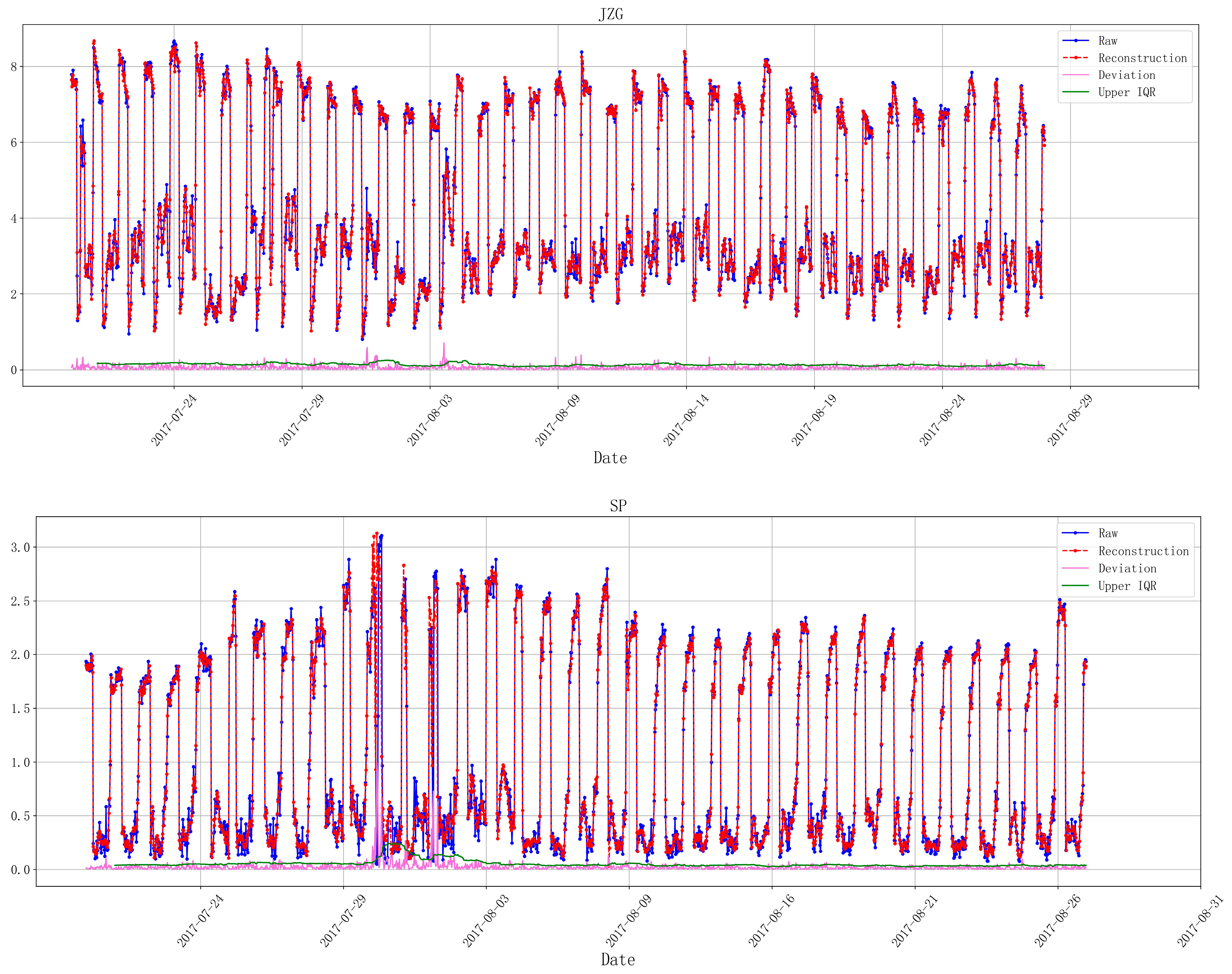
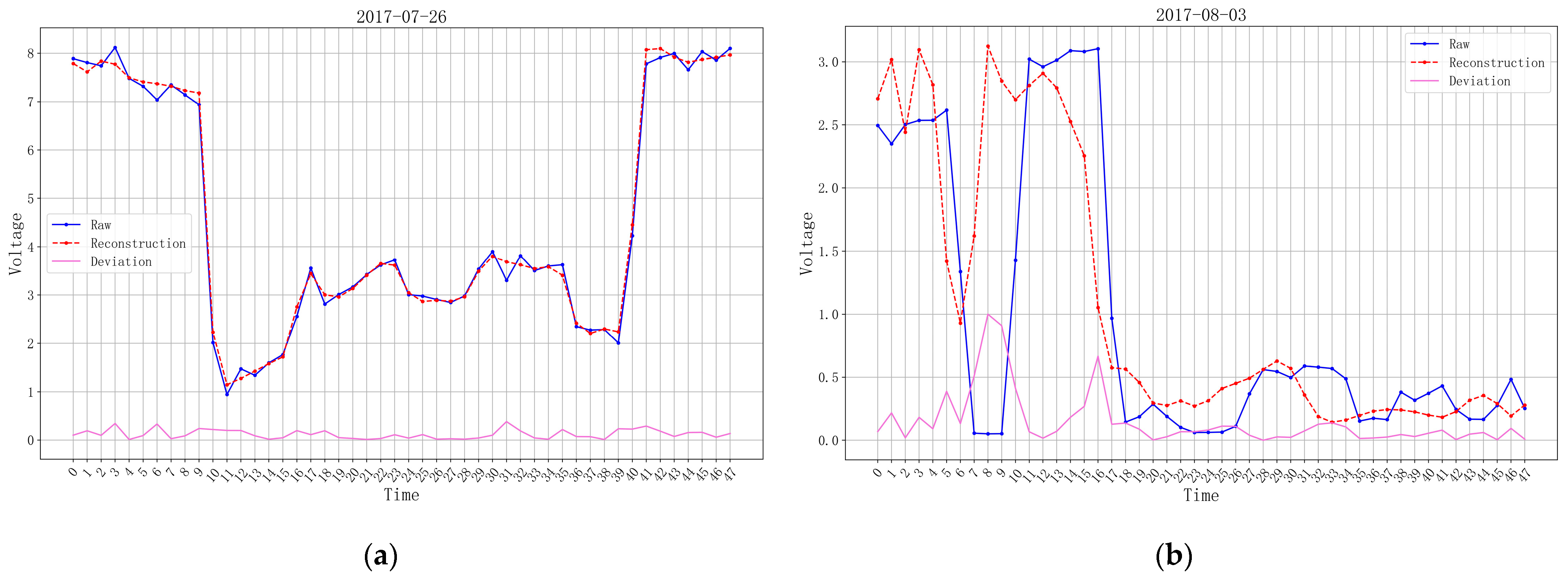
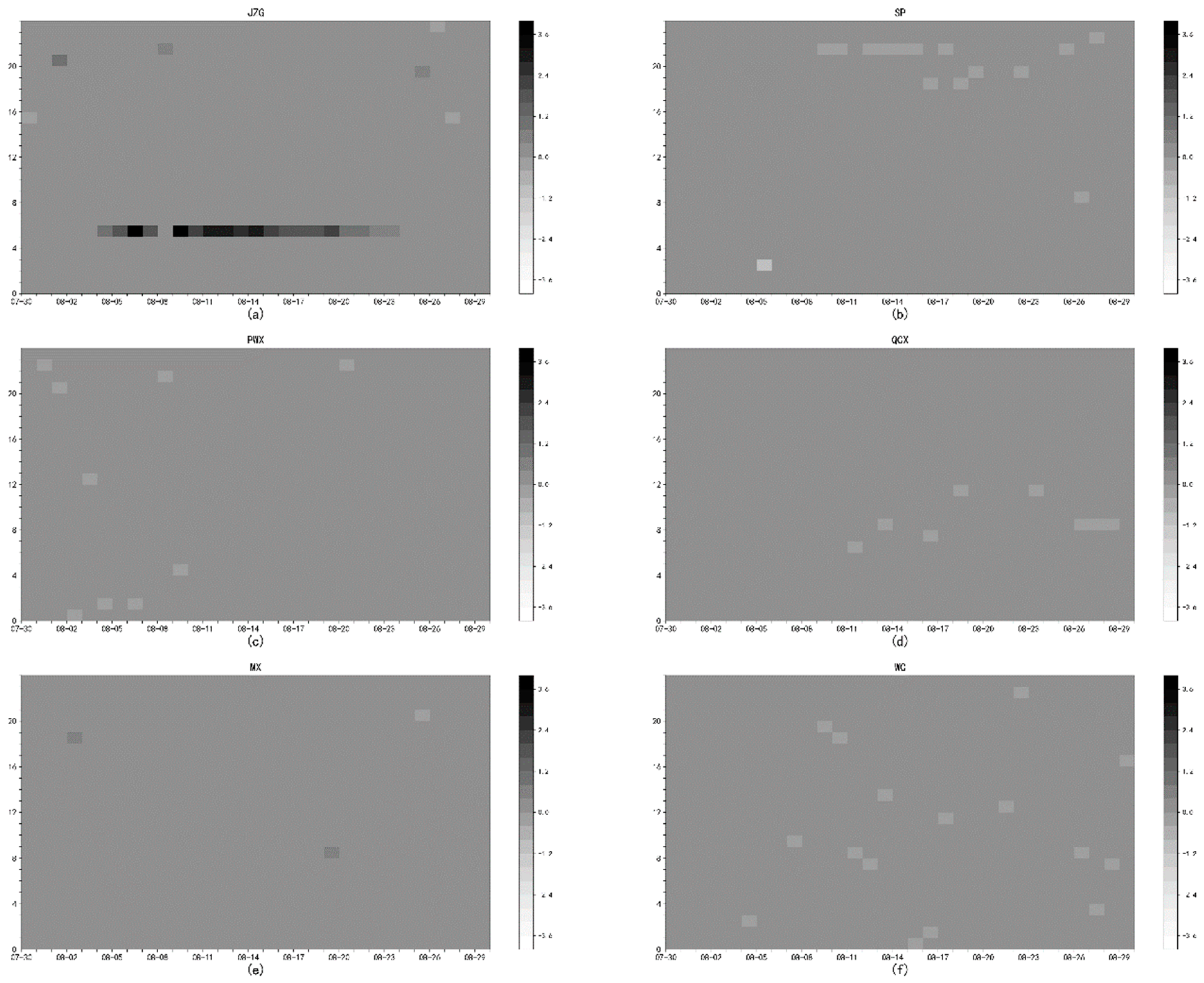
- On 8 August 2017, a magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred in Jiuzhaigou County, Aba Prefecture, Northern Sichuan Province. Figure 3 shows the changes of the electromagnetic disturbance signal of the AETA stations near the epicenter;
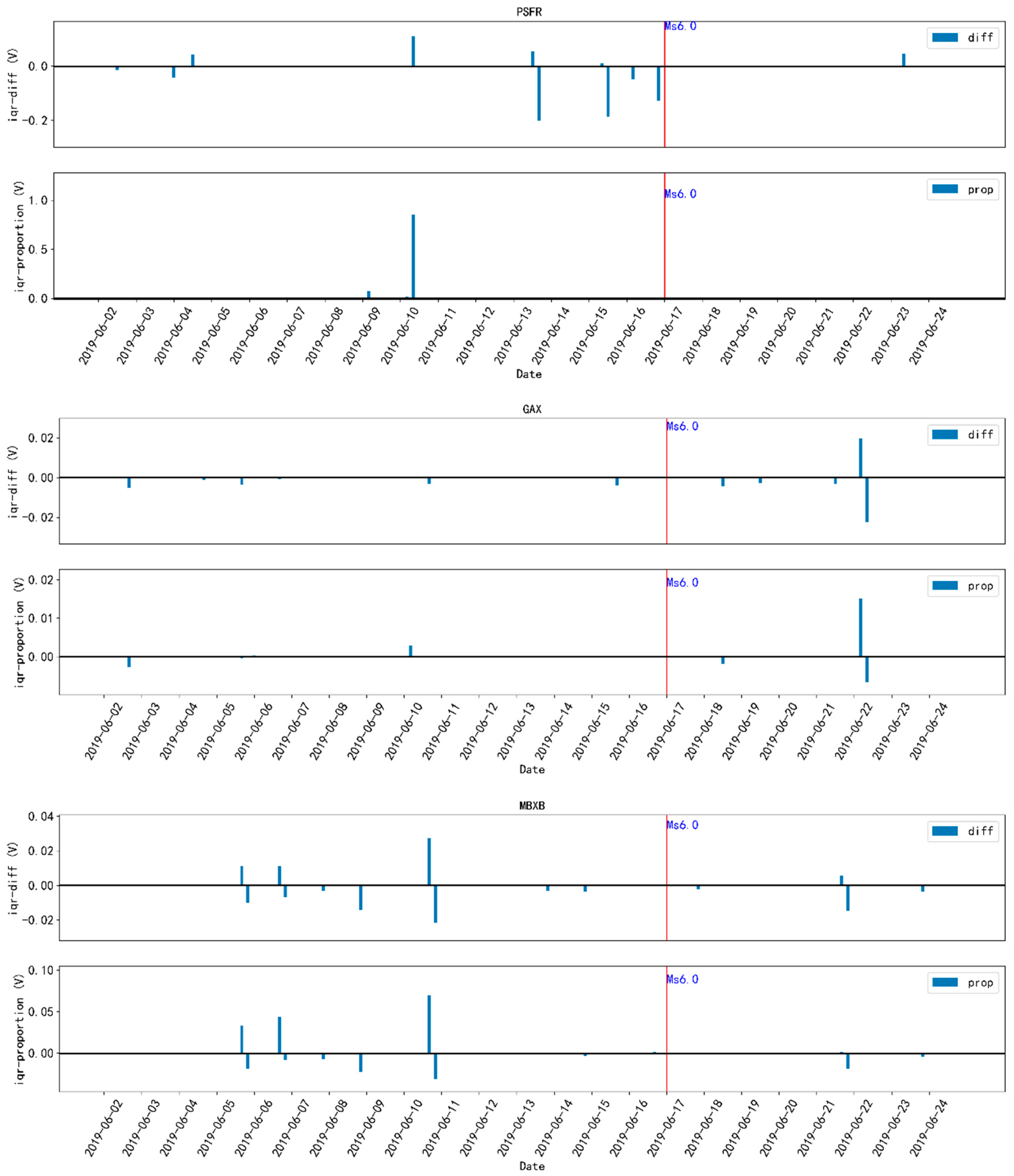
- On 17 June 2019, a magnitude 6.0 earthquake occurred in Changning County, Yibin City, Sichuan Province. Figure 4 shows the changes in electromagnetic disturbance signals of the AETA stations near the epicenter.
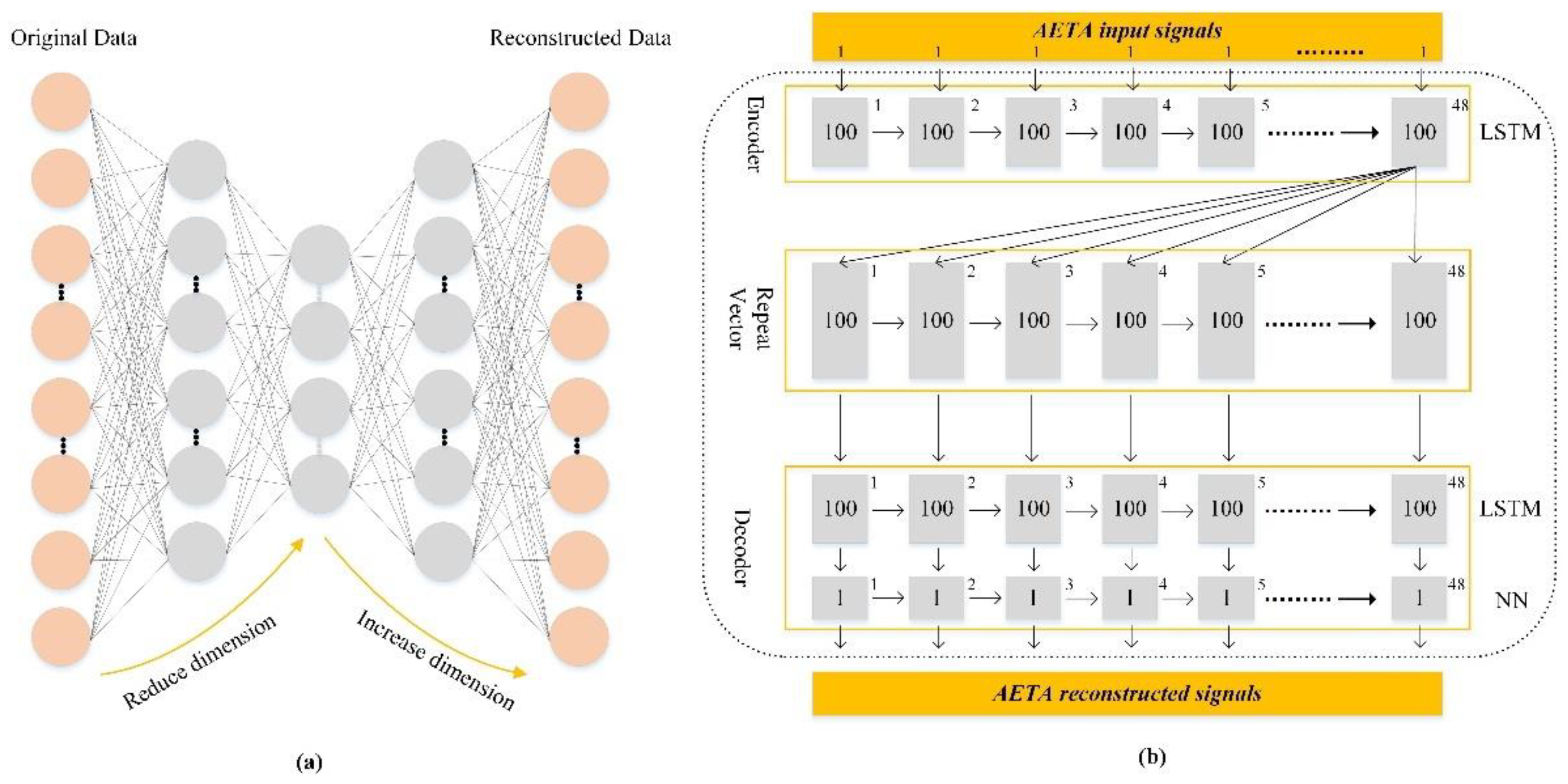
3.2. LAE and IQR Method
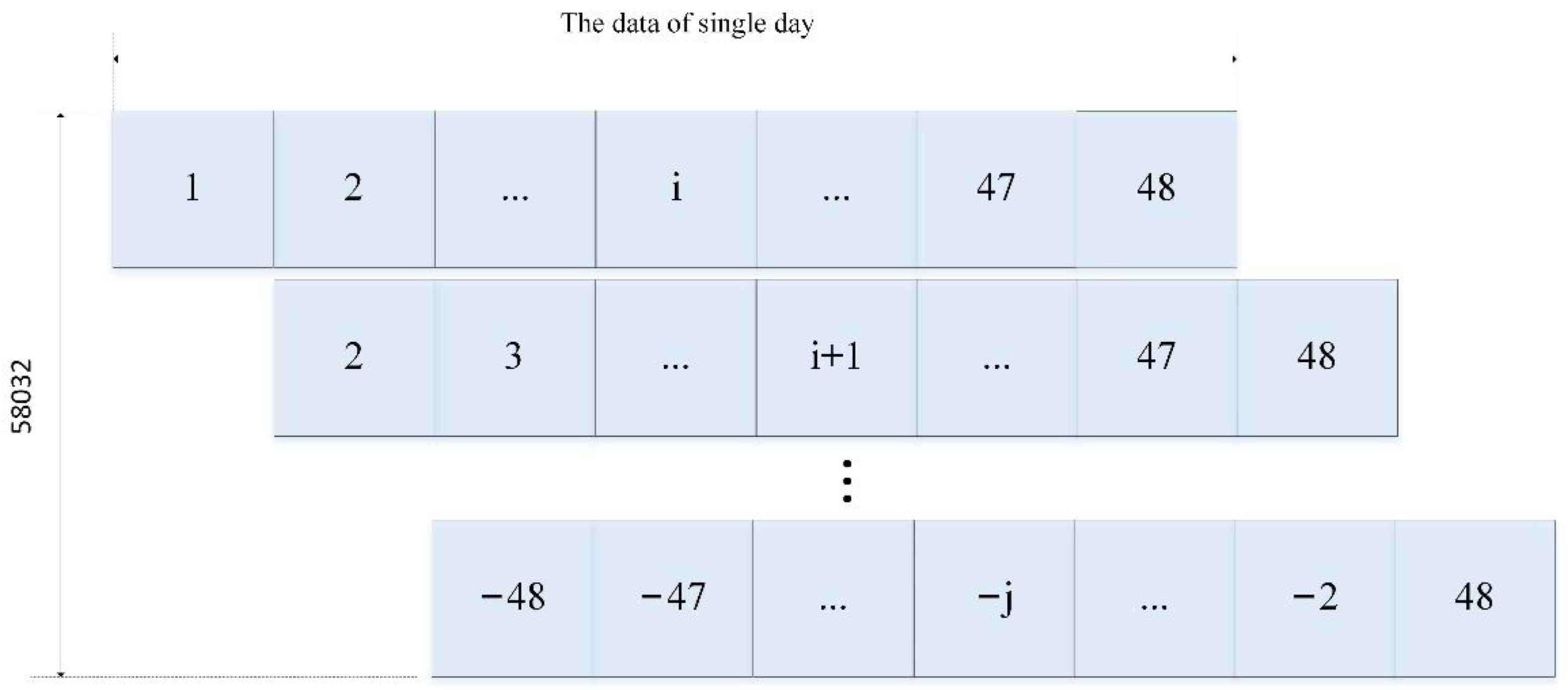
3.3. Sample Construction
4. Results
4.1. Seismic Case Analysis
4.1.1. Analysis of Jiuzhaigou M. 7.0 Earthquake
4.1.2. Analysis of Yibin M. 6.0 Earthquake
4.2. Comparison with Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyss, M.; Booth, D.C. The IASPEI procedure for the evaluation of earthquake precursors. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 131, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschvink, J.L. Earthquake prediction by animals: Evolution and sensory perception. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2000, 90, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulahci, F.; Cicek, S. Time-series analysis of water and soil radon anomalies to identify micro–macro-earthquakes. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5239–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Hattori, K.; Hirokawa, M.; Zhuang, J.; Yoshino, C. Statistical analysis of ULF seismomagnetic phenomena at Kakioka, Japan, during 2001–2010. J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys. 2014, 119, 4998–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, A.; Inyurt, S.; Yaprak, S. Pre-seismic ionospheric anomalies and spatio-temporal analyses of MODIS Land surface temperature and aerosols associated with Sep, 24 2013 Pakistan Earthquake. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 200, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzano, N.; Filizzola, C.; Hattori, K.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. Statistical correlation analysis between thermal infrared anomalies observed from MTSATs and large earthquakes occurred in Japan (2005–2015). J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Fox, G.C. TSEQPREDICTOR: Spatiotemporal Extreme Earthquakes Forecasting for Southern California. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.14336. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Mishra, S. LAC: LSTM AUTOENCODER with Community for Insider Threat Detection. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Big Data Research (ICBDR’20), Tokyo, Japan, 27–29 November 2020; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Daehyung, P.; Hoshi, Y.; Kemp, C.C. A Multimodal Anomaly Detector for Robot-Assisted Feeding Using an LSTM-Based Variational Autoencoder. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, S.; Yonghoon, J.; Kudo, K.; Takahashi, T.; Umeda, K. Anomaly Detection Based on Deep Learning Using Video for Prevention of Industrial Accidents. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.13734. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Tran, K.P.; Thomassey, S.; Hamad, M. Forecasting and Anomaly Detection approaches using LSTM and LSTM Autoencoder techniques with the applications in supply chain management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 102282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kim, Y. Deep Learning-Based Hybrid Intelligent Intrusion Detection System. CMC-Comput. Mat. Contin. 2021, 68, 671–687. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Arigi, A.M.; Kim, J. Development of a diagnostic algorithm for abnormal situations using long short-term memory and variational autoencoder. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2021, 153, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yong, S.; Xu, B.; Liang, Y.; Bai, Z.; An, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Xie, Z.; Lin, K.; et al. Research and Implementation of Multi-component Seismic Monitoring System AETA. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2018, 54, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, S.; Wang, X.; Pang, R.; Jin, X.; Zeng, J.; Han, C.; Xu, B. Development of Inductive Magnetic Sensor for Multi-component Seismic Monitoring System AETA. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2018, 54, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sepehr, M.; Sasan, M.; Nicholas, R.J. Unsupervised anomaly detection with LSTM autoencoders using statistical data-filtering. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2021, 108, 107443. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Wang, G.; Tu, K. Latent variable autoencoder. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 48514–48523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Chen, F. High-resolution SAR image classification via deep convolutional autoencoders. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2351–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, C. Hypergraph regularized autoencoder for image-based 3D human pose recovery. Signal Process. 2016, 124, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallak, A.; Fathi, M. Sensor and Component Fault Detection and Diagnosis for Hydraulic Machinery Integrating LSTM Autoencoder Detector and Diagnostic Classifiers. Sensors 2021, 21, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitish, S.; Elman, M.; Ruslan, S. Unsupervised Learning of Video Representations using LSTMs. In Proceedings of the ICML, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 843–852. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/srivastava15.html (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Bollini, P.; Chisci, L.; Farina, A.; Giannelli, M.; Timmoneri, L.; Zappa, G. QR versus IQR algorithms for adaptive signal processing: Performance evaluation for radar applications. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 1996, 143, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yuan, P.; Qin, C. Consider the IQR Law in the Detection of Outlier in Time Series Considering Skewness. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 35, 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, U.H.; Hong, S.H.; Shim, W.J.; Oh, J.R.; Chang, M. Spatio-temporal distribution and characteristics of PAHs in sediments from Masan Bay, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J. Two-dimensional ionospheric total electron content map (TEC) seismo-ionospheric anomalies through image processing using principal component analysis. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.; Panda, S.K.; Jamjareegulgarn, P. Singular spectrum analysis of GPS derived ionospheric TEC variations over Nepal during the low solar activity period. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 169, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Station | Installation | Location | Epicenter Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Epicenter | — | 33.20° N, 103.82° E | 0 |
| 1 | JZG | 10 June 2017 | 33.25° N, 104.24° E | 40 km |
| 2 | SP | 12 June 2017 | 32.65° N, 103.60° E | 64 km |
| 3 | PW | 8 June 2017 | 32.41° N, 104.55° E | 111 km |
| 4 | QC | 7 June 2017 | 32.59° N, 105.23° E | 147 km |
| 5 | MX | 13 June 2017 | 31.69° N, 103.85° E | 167 km |
| 6 | WC | 13 June 2017 | 31.48° N, 103.59° E | 192 km |
| No. | Station | Abnormal Points | Outliers over 0.7 | Total Points | Epicenter Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JZG | 16 | 0 | 1152 | 40 km |
| 2 | SP | 17 | 2 | 1152 | 64 km |
| 3 | PWX | 12 | 0 | 1152 | 111 km |
| 4 | QCX | 6 | 0 | 1152 | 147 km |
| 5 | MX | 45 | 1 | 1152 | 167 km |
| 6 | WC | 12 | 0 | 1152 | 192 km |
| No. | Station | Installation | Location | Epicenter Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Epicenter | 12 December 2017 | 28.34° N, 104.90° E | 0 |
| 1 | GOX | 13 January 2017 | 28.38° N, 104.79° E | 11 km |
| 2 | GAX | 13 March 2017 | 28.44° N, 104.51° E | 39 km |
| 3 | YBYX | 12 December 2017 | 29.03° N, 104.56° E | 83 km |
| 4 | PSFR | 12 December 2017 | 28.71° N, 104.15° E | 84 km |
| 5 | ZGDA | 21 August 2017 | 29.38° N, 104.78° E | 115 km |
| 6 | MC | 11 June 2017 | 28.96° N, 103.90° E | 119 km |
| 7 | MBXB | 11 October 2018 | 28.83° N, 103.73° E | 126 km |
| 8 | MBMZ | 12 October 2018 | 28.71° N, 103.64° E | 129 km |
| 9 | JWX | 8 June 2017 | 29.21° N, 103.94° E | 134 km |
| 10 | MBJS | 9 October 2018 | 28.78° N, 103.59° E | 137 km |
| 11 | YJX | 11 October 2018 | 28.70° N, 103.52° E | 140 km |
| 12 | MB | 16 October 2018 | 28.83° N, 103.54° E | 143 km |
| 13 | YFZ | 10 October 2018 | 28.71° N, 103.46° E | 146 km |
| 14 | MBRD | 12 October 2018 | 28.99° N, 103.59° E | 146 km |
| 15 | DZB | 21 August 2017 | 28.99° N, 103.47° E | 157 km |
| 16 | ZT | 21 August 2017 | 27.32° N, 103.72° E | 162 km |
| 17 | SKH | 1 August 2018 | 28.88° N, 103.35° E | 162 km |
| 18 | JY | 9 October 2018 | 29.65° N, 104.06° E | 166 km |
| 19 | LSS | 1 August 2018 | 29.58° N, 103.75° E | 177 km |
| 20 | LSSW | 9 October 2018 | 29.42° N, 103.55° E | 177 km |
| 21 | LD | 22 August 2017 | 27.24° N, 103.55° E | 180 km |
| 22 | EB | 11 April 2017 | 29.23° N, 103.25° E | 188 km |
| 23 | GQZ | 1 August 2018 | 29.52° N, 103.43° E | 194 km |
| 24 | EMS | 5 June 2017 | 29.59° N, 103.50° E | 194 km |
| 25 | QSX | 12 December 2017 | 29.84° N, 103.85° E | 195 km |
| 26 | HWZ | 1 August 2018 | 29.58° N, 103.43° E | 198 km |
| No. | Station | Abnormal Points | Outliers over 0.7 | Total Points | Epicenter Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GOX | 35 | 5 | 1152 | 11 km |
| 2 | GAX | 11 | 0 | 1152 | 39 km |
| 3 | YBYX | 12 | 0 | 1152 | 83 km |
| 4 | PSFR | 12 | 0 | 1152 | 84 km |
| 5 | ZGDA | 6 | 0 | 1152 | 115 km |
| 6 | MC | 15 | 1 | 1152 | 119 km |
| 7 | MBXB | 17 | 0 | 1152 | 126 km |
| 8 | MBMZ | 5 | 0 | 1152 | 129 km |
| 9 | JWX | 12 | 0 | 1152 | 134 km |
| 10 | MBJS | 9 | 0 | 1152 | 137 km |
| 11 | YJX | 9 | 2 | 1152 | 140 km |
| 12 | MB | 6 | 0 | 1152 | 143 km |
| 13 | YFZ | 16 | 0 | 1152 | 146 km |
| 14 | MBRD | 8 | 0 | 1152 | 146 km |
| 15 | DZB | 14 | 0 | 1152 | 157 km |
| 16 | ZT | 35 | 0 | 1152 | 162 km |
| 17 | SKH | 15 | 0 | 1152 | 162 km |
| 18 | JY | 4 | 0 | 1152 | 166 km |
| 19 | LSS | 11 | 0 | 1152 | 177 km |
| 20 | LSSW | 4 | 1 | 1152 | 177 km |
| 21 | LD | 20 | 0 | 1152 | 180 km |
| 22 | EB | 10 | 0 | 1152 | 188 km |
| 23 | GQZ | 2 | 0 | 1152 | 194 km |
| 24 | EMS | 16 | 3 | 1152 | 194 km |
| 25 | QSX | 8 | 0 | 1152 | 195 km |
| 26 | HWZ | 6 | 0 | 1152 | 198 km |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Z.; Yong, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Xie, J.; He, C. Seismic Reflection Analysis of AETA Electromagnetic Signals. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135869
Bao Z, Yong S, Wang X, Yang C, Xie J, He C. Seismic Reflection Analysis of AETA Electromagnetic Signals. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135869
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Zhenyu, Shanshan Yong, Xin’an Wang, Chao Yang, Jinhan Xie, and Chunjiu He. 2021. "Seismic Reflection Analysis of AETA Electromagnetic Signals" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135869
APA StyleBao, Z., Yong, S., Wang, X., Yang, C., Xie, J., & He, C. (2021). Seismic Reflection Analysis of AETA Electromagnetic Signals. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135869






