Spinel Iron Oxide by the Co-Precipitation Method: Effect of the Reaction Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morpho-Structural Properties
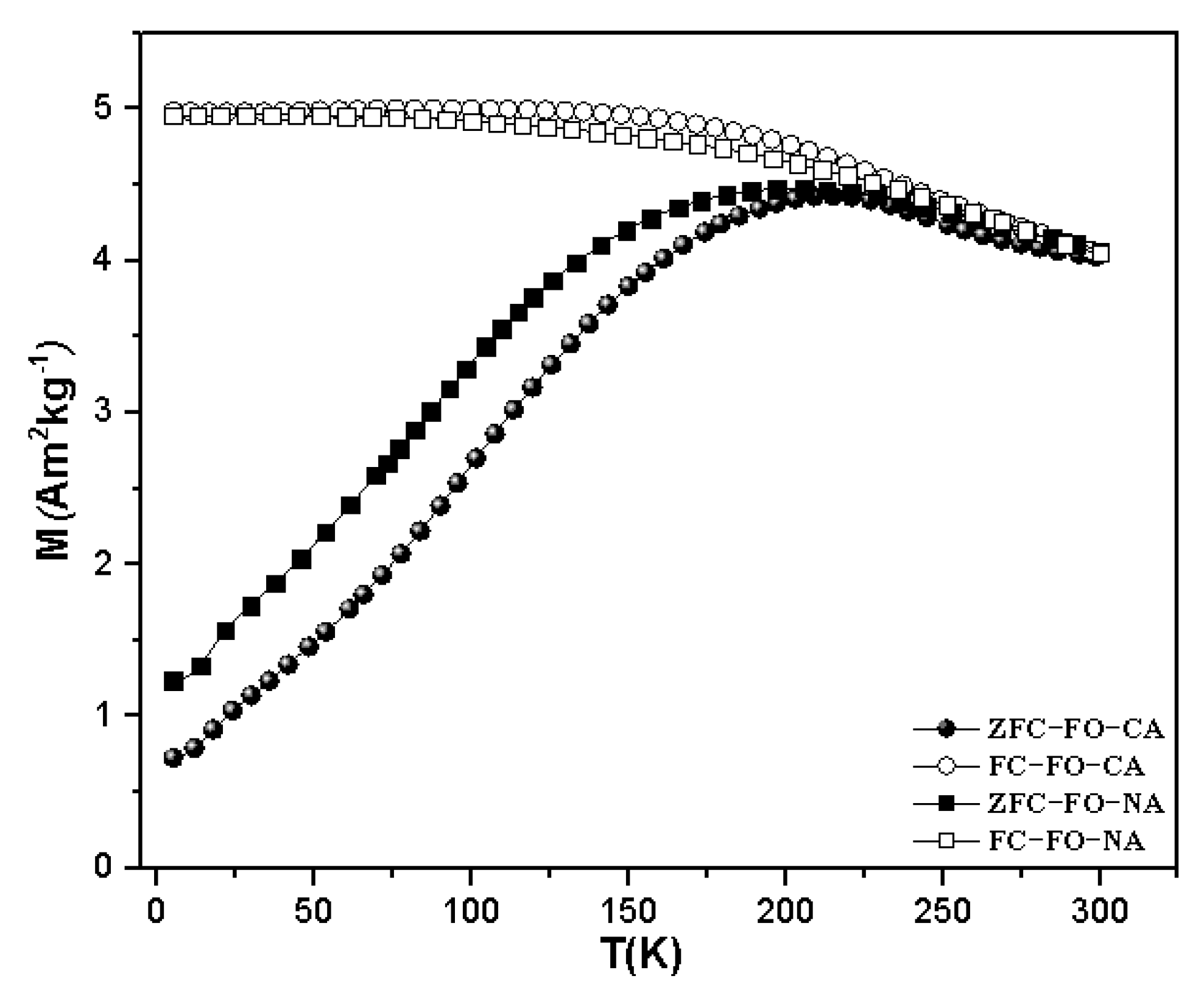
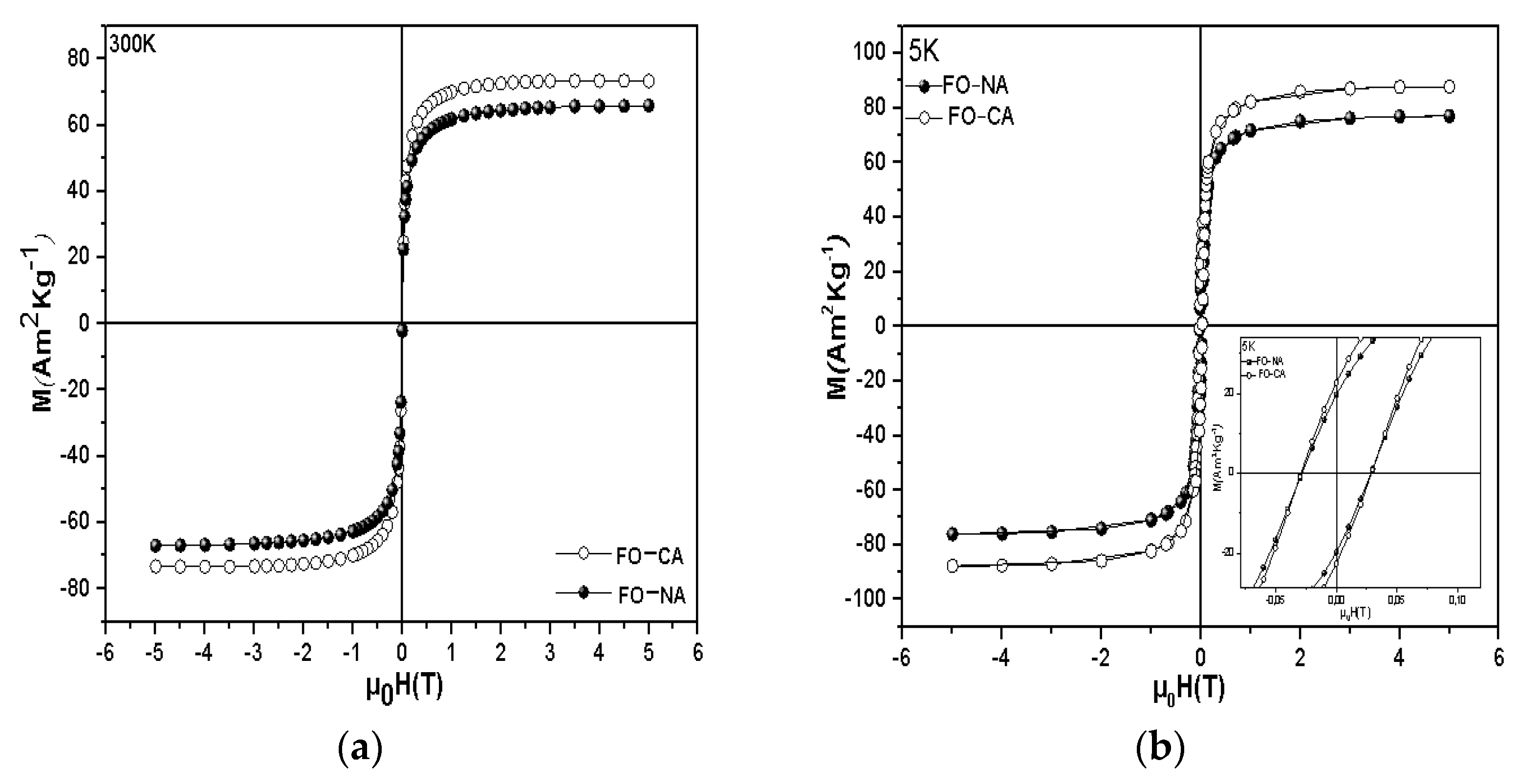
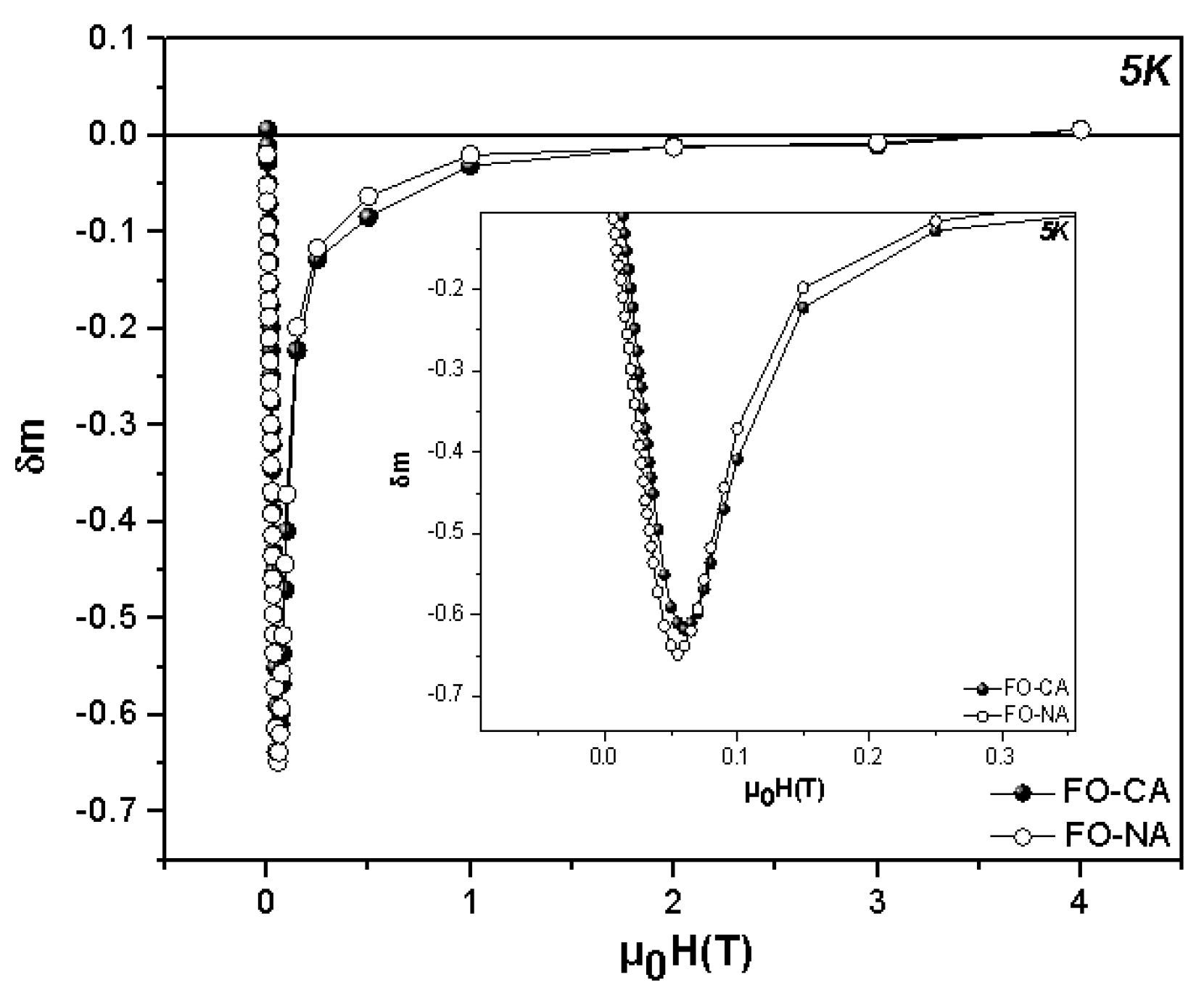
3.2. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuberger, T.; Schöpf, B.; Hofmann, H.; Hofmann, M.; Von Rechenberg, B. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Possibilities and Limitations of a New Drug Delivery System. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandhar, A.P.; Ferguson, R.M.; Krishnan, K.M. Monodispersed Magnetite Nanoparticles Optimized for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia: Implications in Biological Systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, A.; Cabras, V.; Marongiu, F.; Peddis, D.; Pilloni, M.; Ennas, G. New Opportunities in the Preparation of Nanocomposites from Biomedical Applications: Revised Mechanosynthesis of Magnetite-Silica Nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ran, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, M. Preparation of Biocompatible Magnetite Nanocrystals for in Vivo Magnetic Resonance Detection of Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2553–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazeau, F.; Lévy, M.; Wilhelm, C. Optimizing Magnetic Nanoparticle Design for Nanothermotherapy. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaría, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esakkimuthu, T.; Sivakumar, D.; Akila, S. Application of Nanoparticles in Wastewater Treatment. Pollut. Res. 2014, 33, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedanta, S.; Petracic, O.; Kleemann, W. Supermagnetism. In Handbook of Magnetic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 23, pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Concas, G.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Orrù, F.; Fiorani, D.; Laureti, S.; Rinaldi, D.; Piccaluga, G.; et al. Magnetic Properties of Small Magnetite Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 23378–23384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S. Synthesis and Applications of Nano-Structured Iron Oxides/Hydroxides—A Review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, Z.N.; Arshad, S.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel Technique and Their Characterization. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Jeevanandam, P. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Thermal Decomposition Approach. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 67, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, M.; Uhl, A.M.; Savliwala, S.; Savitzky, B.H.; Dhavalikar, R.; Garraud, N.; Arnold, D.P.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Andrew, J.S.; Rinaldi, C. Thermal Decomposition Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Diminished Magnetic Dead Layer by Controlled Addition of Oxygen. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.; Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S.; Civera, C.; Solans, C.; Kuttuva, G.R. Comparison and Functionalization Study of Microemulsion-Prepared Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8479–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massart, R. Preparation of Aqueous Magnetic Liquids in Alkaline and Acidic Media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetite Nanoparticles via the Chemical Co-Precipitation Method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Jeong, J.R.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.D. Synthesis and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Maghemite Nanoparticles Prepared by Coprecipitation Technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 282, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusigerski, V.; Illes, E.; Blanusa, J.; Gyergyek, S.; Boskovic, M.; Perovic, M.; Spasojevic, V. Magnetic Properties and Heating Efficacy of Magnesium Doped Magnetite Nanoparticles Obtained by Co-Precipitation Method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, H.C.; Schwaminger, S.P.; Schindler, M.; Wagner, F.E.; Berensmeier, S. Influencing Factors in the CO-Precipitation Process of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nano Particles: A Model Based Study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 377, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Fernandes, C.; Rocha, M.; Mendes, R.; Fernández-García, M.P.; Guedes, A.; Tavares, P.B.; Grenéche, J.M.; Araújo, J.P.; et al. Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M=Fe, Co, Mn) Nanoparticles: Tuning the Particle Size and Magnetic Properties through a Novel One-Step Coprecipitation Route. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Dey, S.K.; Majumder, S.; Poddar, A.; Dasgupta, P.; Banerjee, S.; Kumar, S. Superparamagnetic Behavior of Nanosized Co0.2Zn0.8Fe2O4 Synthesized by a Flow Rate Controlled Chemical Coprecipitation Method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2014, 448, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabadizadeh, A.; Salighe, Z.; Sarhaddi, R.; Lotfollahi, Z. Synthesis of ferrofluids based on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Influence of reaction time on structural, morphological and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 434, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talgatov, E.T.; Auyezkhanova, A.S.; Seitkalieva, K.S.; Tumabayev, N.Z.; Akhmetova, S.N.; Zharmagambetova, A.K. Co-Precipitation Synthesis of Mesoporous Maghemite for Catalysis Application. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragi, T.; Depi, B.L.; Butarbutar, S.; Permana, B. The Impact of Synthesis Temperature on Magnetite Nanoparticles Size Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1013, 012190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaz, S.; Kockar, H.; Tanrisever, T. Simple Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Magnetite Nanoparticles and Ion Effect on Magnetic Fluids. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Symp. 2009, 1, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Karaagac, O.; Kockar, H. A Simple Way to Obtain High Saturation Magnetization for Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized in Air Atmosphere: Optimization by Experimental Design. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 409, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klencsár, Z.; Ábrahám, A.; Szabó, L.; Szabó, E.G.; Stichleutner, S.; Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Tolnai, G. The Effect of Preparation Conditions on Magnetite Nanoparticles Obtained via Chemical Co-Precipitation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, E.; Aydogan, N. A Comparative Study: Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Air and N2 Atmosphere. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 510, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpert, E.; Stahel, W.A.; Abbt, M. Log-Normal Distributions across the Sciences: Keys and Clues. Bioscience 2001, 51, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cicco, A.; Aquilanti, G.; Minicucci, M.; Principi, E.; Novello, N.; Cognigni, A.; Olivi, L. Novel XAFS Capabilities at ELETTRA Synchrotron Light Source. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 190, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiesaro, I.; Battocchio, C.; Venditti, I.; Prosposito, P.; Burratti, L.; Centomo, P.; Meneghini, C. Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures Structural Characterization of 3d Metal Adsorbed AgNPs. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2020, 123, 114162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Athena, Artemis, Hephaestus: Data Analysis for X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Norton, M.G. Practical Aspects of X-Ray Diffraction. In X-Ray Diffraction; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronc, E.; Prené, P.; Jolivet, J.P.; Dormann, J.L.; Grenèche, J.M. Spin Canting in γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 1998, 112, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Noncollinear Spin Arrangement in Ultrafine Ferrimagnetic Crystallites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1971, 27, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menil, F. Systematic Trends of the 57Fe Mössbauer Isomer Shifts in (FeOn) and (FeFn) Polyhedra. Evidence of a New Correlation between the Isomer Shift and the Inductive Effect of the Competing Bond T-X (→ Fe) (Where X Is O or F and T Any Element with a Formal Posit. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1985, 46, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscas, G.; Singh, G.; Glomm, W.R.; Mathieu, R.; Kumar, P.A.; Concas, G.; Agostinelli, E.; Peddis, D. Tuning the Size and Shape of Oxide Nanoparticles by Controlling Oxygen Content in the Reaction Environment: Morphological Analysis by Aspect Maps. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, J.; Dey, A.; Bomans, P.H.; Le Coadou, C.; Fratzl, P.; Sommerdijk, N.A.; Faivre, D. Nucleation and Growth of Magnetite from Solution. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, J.P.; Cassaignon, S.; Chanéac, C.; Chiche, D.; Tronc, E. Design of Oxide Nanoparticles by Aqueous Chemistry. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 46, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrow, A.P.; Besenhard, M.O.; Hodzic, A.; Sergides, A.; Bogart, L.K.; Gavriilidis, A.; Thanh, N.T.K. Unravelling the Growth Mechanism of the Co-Precipitation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with the Aid of Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction in Solution. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6620–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besenhard, M.O.; LaGrow, A.P.; Hodzic, A.; Kriechbaum, M.; Panariello, L.; Bais, G.; Loizou, K.; Damilos, S.; Margarida Cruz, M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; et al. Co-Precipitation Synthesis of Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with NaOH: New Insights and Continuous Production via Flow Chemistry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudakar, C.; Subbanna, G.N.; Kutty, T.R.N. Effect of Anions on the Phase Stability of γ-FeOOH Nanoparticles and the Magnetic Properties of Gamma-Ferric Oxide Derived from Lepidocrocite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2003, 64, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bianco, L.; Fiorani, D.; Testa, A.M.; Bonetti, E.; Savini, L.; Signoretti, S. Magnetothermal Behavior of a Nanoscale Fe/Fe Oxide Granular System. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2002, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhout, G.W. van. Morphology of Synthetic Sub-Microscopic Crystals of α and γFeOOH and of γFe2O3 Prepared from FeOOH. Acta Crystallogr. 1960, 13, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.M.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.D. Formation Pathways of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coprecipitation Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6069–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedkov, I.; Merodiiska, T.; Slavov, L.; Vandenberghe, R.E.; Kusano, Y.; Takada, J. Surface Oxidation, Size and Shape of Nano-Sized Magnetite Obtained by Co-Precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 300, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirő -Kósa, I.; Csákberényi Nagy, D.; Pósfai, M. Size and Shape Control of Precipitated Magnetite Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Mineral. 2009, 21, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudennec, Y.; Lecerf, A. Topotactic Transformations of Goethite and Lepidocrocite into Hematite and Maghemite. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Matijević, E. Formation of Uniform Spherical Magnetite Particles by Crystallization from Ferrous Hydroxide Gels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 74, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demortière, A.; Panissod, P.; Pichon, B.P.; Pourroy, G.; Guillon, D.; Donnio, B.; Bégin-Colin, S. Size-Dependent Properties of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.F.; Mørup, S. Estimation of Blocking Temperatures from ZFC/FC Curves. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 203, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hilo, M. Nano-Particle Magnetism with a Dispersion of Particle Sizes. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantrell, R.W.; Popplewell, J.; Charles, S.W. The effect of a particle size distribution on the coercovity and remanence of a fine particle system. Physica B+C 1977, 86–88, 1421–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.M.; Zheng, Z.G. Effect of Temperature on Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Prepared by Coprecipitation Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 900, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, K.; Chantrell, R.W. Remanence Curves of Fine Particles Systems I: Experimental Studies. Magn. Prop. Fine Part. 1992, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
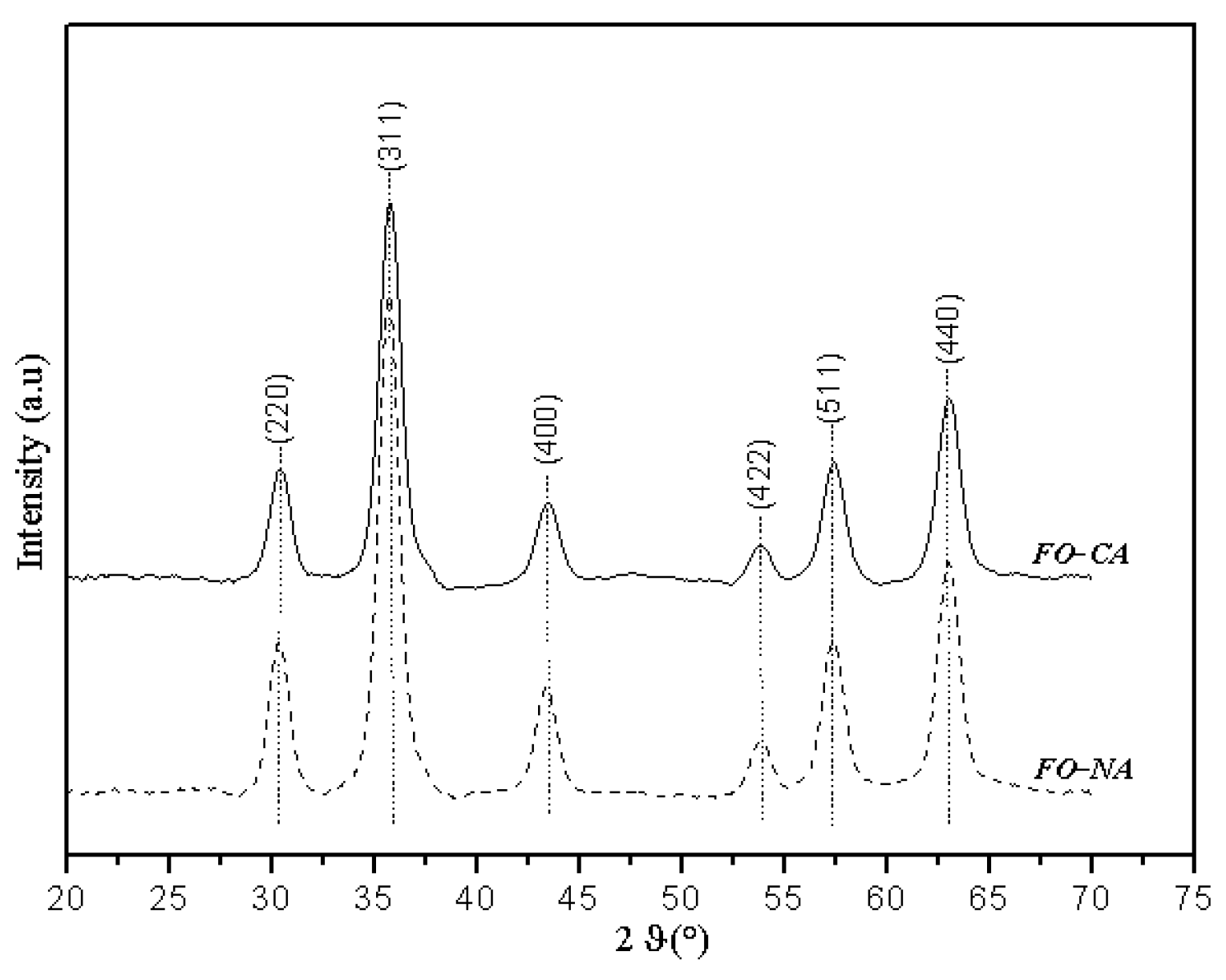


| Sample | DXRD (nm) | DTEM (nm) | Dm(nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FO_CA | 9.0(9) | 9.0(9) | 11(1) |
| FO_NA | 9.0(9) | 11(1) | 12(1) |
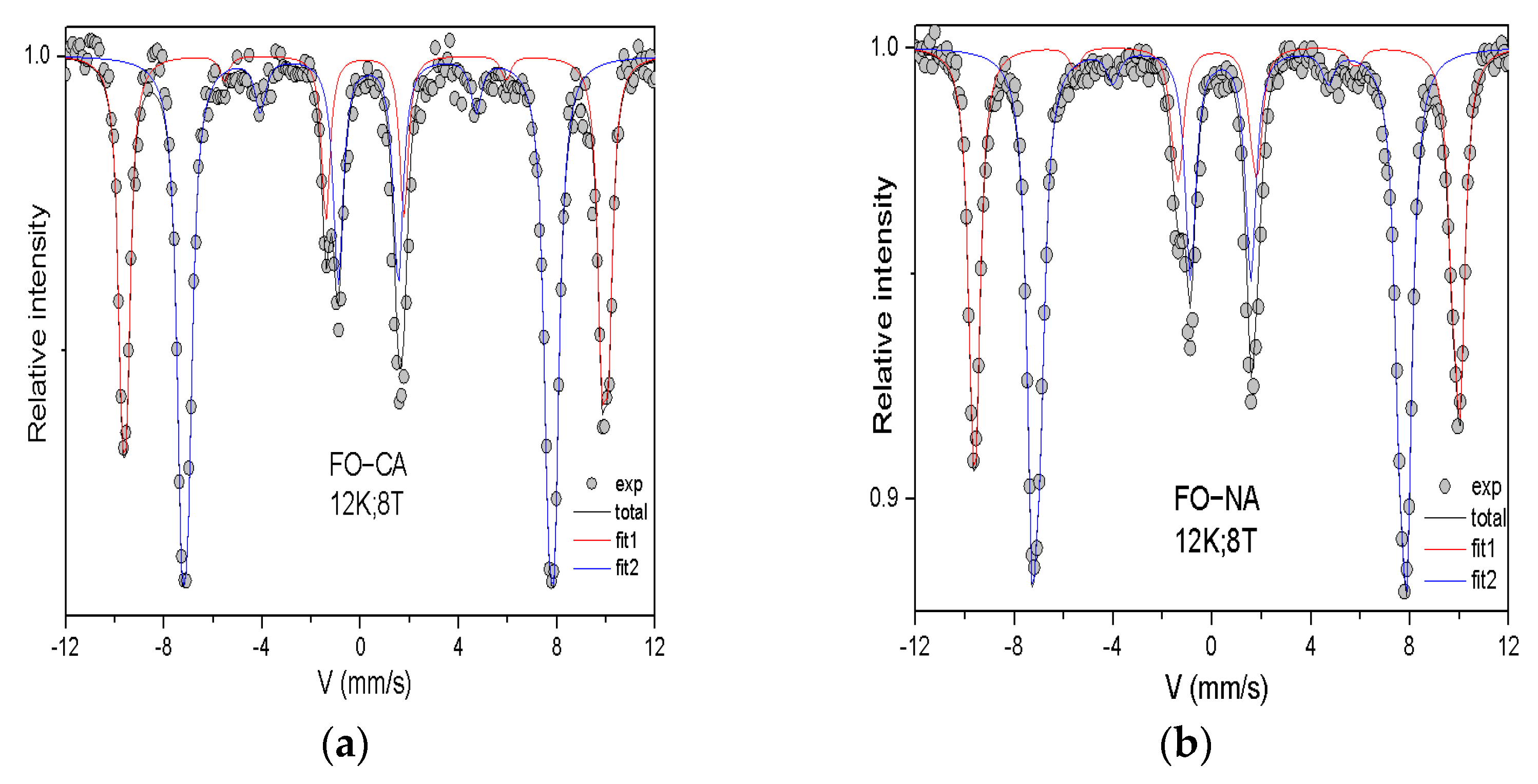
| Sample | Sites | (mm.S−1) | (mm.S−1) | (T) | (T) | (°) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO−CA | A | 0.36 | −0.01 | 60.5 | 52.8 | 16 | 38 |
| B | 0.50 | −0.00 | 46.2 | 53.8 | 20 | 62 | |
| FO−NA | A | 0.35 | −0.03 | 60.4 | 52.8 | 16 | 39 |
| B | 0.51 | −0.03 | 46.1 | 53.9 | 15 | 61 |
| Sample | Tmax(K) | TB-TRM (K) | Tirr(K) (3%) | TB.H.M (k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO−CA | 203(20) | 104(10) | 270(27) | 125(12) |
| FO−NA | 202(20) | 100(10) | 273(27) | 124(12) |
| Sample | Ms (Am2Kg−1) at 300K | Ms (Am2Kg−1) at 5 K | Mr/Ms at 5 K | Hc(mT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO−CA | 70.9(7) | 88(3) | 0.25 | 28.7(3) |
| FO−NA | 69.4(1) | 77(3) | 0.25 | 28.1(3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slimani, S.; Meneghini, C.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Talone, A.; Murillo, J.P.M.; Barucca, G.; Yaacoub, N.; Imperatori, P.; Illés, E.; Smari, M.; et al. Spinel Iron Oxide by the Co-Precipitation Method: Effect of the Reaction Atmosphere. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125433
Slimani S, Meneghini C, Abdolrahimi M, Talone A, Murillo JPM, Barucca G, Yaacoub N, Imperatori P, Illés E, Smari M, et al. Spinel Iron Oxide by the Co-Precipitation Method: Effect of the Reaction Atmosphere. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(12):5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlimani, Sawssen, Carlo Meneghini, Maryam Abdolrahimi, Alessandro Talone, Jean Pierre Miranda Murillo, Gianni Barucca, Nader Yaacoub, Patrizia Imperatori, Erzsébet Illés, Mourad Smari, and et al. 2021. "Spinel Iron Oxide by the Co-Precipitation Method: Effect of the Reaction Atmosphere" Applied Sciences 11, no. 12: 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125433
APA StyleSlimani, S., Meneghini, C., Abdolrahimi, M., Talone, A., Murillo, J. P. M., Barucca, G., Yaacoub, N., Imperatori, P., Illés, E., Smari, M., Dhahri, E., & Peddis, D. (2021). Spinel Iron Oxide by the Co-Precipitation Method: Effect of the Reaction Atmosphere. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125433











