Closed Endotracheal Suctioning Impact on Ventilator-Related Parameters in Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Systems: A Bench Study
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparing the Lung Model and Closed Suction System
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Closed Suction on Respiratory Resistance in Both Respiratory Systems
3.2. Varied Effects of ETT and SC on PIP in Both Respiratory Systems
3.2.1. Varied Effects of Ventilation Area on △PIP/PIP% in Both Respiratory Systems
3.2.2. Analysis of the Impact Factors for △PIP
3.3. Varied Effects of ETT and SC on PEEP in Both Respiratory Systems
Analysis of the Impact Factors for △PEEP
3.4. Varied Effects of ETT and SC on Vexp in Both Types of Respiratory Systems
3.4.1. Varied Effects of ETTs and SCs on △Vexp/Vexp% in Both Types of Respiratory Systems
3.4.2. Analysis of the Factors Affecting △Vexp
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taheri, P.; Asgari, N.; Mohammadizadeh, M.; Golchin, M. The effect of open and closed endotracheal tube suctioning system on respiratory parameters of infants undergoing mechanical ventilation. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery Res. 2012, 17, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighat, S.; Yazdannik, A. The practice of intensive care nurses using the closed suctioning system: An observa-tional study. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery. Res. 2015, 20, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzi, M.; De Robertis, E.; Rispoli, F.; Piazza, O.; Tufano, R. A complication of a closed-tube endotracheal suction catheter. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 974–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, S.M.; Lellouche, F.; Pigeot, J.; Taille, S.; Deye, N.; Durrmeyer, X.; Richard, J.-C.; Mancebo, J.; Lemaire, F.; Brochard, L. Prevention of Endotracheal Suctioning-induced Alveolar Derecruitment in Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, M.; Villa, M.; Colombo, E.; Greco, G.; Nacoti, M.; Pesenti, A. Closed system endotracheal suctioning maintains lung volume during volume controlled mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhr, T.; Bonde, J.; Larsson, A. Lung recruitment manoeuvres are effective in regaining lung volume and oxygenation after open endotracheal suctioning in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2002, 7, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, S.; Odenstedt, H.; Olegård, C.; Sondergaard, S.; Lundin, S.; Stenqvist, O. Regional lung derecruitment after endotracheal suction during volume- or pressure-controlled ventilation: A study using electric impedance tomography. Intensiv. Care Med. 2006, 33, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolobow, T.; Moretti, M.P.; Fumagalli, R.; Mascheroni, D.; Prato, P.; Chen, V.; Joris, M. Severe impairment in lung function induced by high peak airway pressure during mechanical ventilation. An experimental study. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.; Kolsum, U.; Hitchen, P.; Gupta, V.; Singh, D. Clinical characteristics of copd patients with tidal expiratory flow limitation. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haake, R.; Schlichtig, R.; Ulstad, D.R.; Henschen, R.P. Barotrauma. Pathophysiology, risk factors, and prevention. Chest 1987, 91, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, A. Low-Tidal-Volume Ventilation in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, R.M.; Guntupalli, K.K. Review of ventilatory techniques to optimize mechanical ventilation in acute exac-erbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2007, 2, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xia, H.-F.; Shang, Y.; Yao, S.-L. Molecular Mechanisms of Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Athar, M. Mechanical ventilation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma. Ind. J. Anaesth. 2015, 59, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, G.N.; Nilsson, K.; Pourazar, J.; Hackett, T.-L.; Kazzam, E.; Blomberg, A.; Waldenström, A.; Warner, J.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; et al. Bronchoalveolar matrix metalloproteinase 9 relates to restrictive lung function impairment in systemic sclerosis. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koulouras, V.; Papathanakos, G.; Papathanasiou, A.; Nakos, G. Efficacy of prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: A pathophysiology-based review. World, J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 5, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, T.; Vasques, F.; Rapetti, F.; Maiolo, G.; Collino, F.; Romitti, F.; Camporota, L.; Cressoni, M.; Cadringher, P.; Quintel, M.; et al. Driving pressure and mechanical power: New targets for VILI prevention. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slutsky, A.S.; Ranieri, V.M. Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lionetti, V.; Recchia, F.A.; Ranieri, V.M. Overview of ventilator-induced lung injury mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2005, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Network, A.R.D.S.; Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A. Ventilation with Lower Tidal Volumes as Compared with Traditional Tidal Volumes for Acute Lung Injury and the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frengley, R.W.; Closey, D.N.; Sleigh, J.W.; Torrance, J.M. The effect of closed system suction on airway pressures when using the Servo 300 ventilator. Crit. Care Resusc. J. Austr. Acad. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 3, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Unal, S.; Ergenekon, E.; Kazanci, E.; Aktas, S.; Kulali, F.; Murat, I.; Turkyilmaz, C.; Atalay, Y. Effects of a closed system suction connector on airway resistance in ventilated neonates. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N. Closed suctioning system: Critical analysis for its use. Jpn. J. Nurs. Sci. 2010, 7, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.; Hillard, E.K. Further considerations on tracheal suction catheters. Br. J. Anaesth. 1963, 35, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magee, P.T. Gas flow between coaxial tubes: Impedance to gas flow in an endotracheal tube increases with a catheter within. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. H J. Eng. Med. 2012, 226, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russian, C.J.; Gonzales, J.F.; Henry, N.R. Suction Catheter Size: An Assessment and Comparison of 3 Different Calculation Methods. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrow, B. Closed-system suctioning: Why is the debate still open? Ind. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 61, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, L.N.; Baldwin, C.E.; Ward, E.C.; Cornwell, P.L.; O’Connor, S.N.; Cn, M.; Chapman, M.J. Tracheostomy Tube Type and Inner Cannula Selection Impact Pressure and Resistance to Air Flow. Respir. Care 2016, 61, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boussarsar, M.; Thierry, G.; Jaber, S.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Lemaire, F.; Brochard, L. Relationship between ventilatory settings and barotrauma in the acute respir-atory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuno, K.; Prato, P.; Kolobow, T. Acute lung injury from mechanical ventilation at moderately high airway pressures. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 69, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalini, G.; Tuzzo, D.; Rosano, A.; Testa, M.; Grazioli, M.; Pennestrì, V.; Amodeo, G.; Berruto, F.; Fiorillo, M.; Peratoner, A.; et al. Effect of external PEEP in patients under controlled mechanical ventilation with an auto-PEEP of 5 cm H2O or higher. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2016, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gass, R.; Merola, P.; Monteiro, M.B.; Cardoso, D.M.; Paiva, D.N.; Teixeira, P.J.; Knorst, M.M.; Berton, D.C. Effects of Expiratory Positive Airway Pressure on Exercise Tolerance, Dynamic Hyperinflation, and Dyspnea in COPD. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thille, A.W.; Rodriguez, P.; Cabello, B.; Lellouche, F.; Brochard, L. Patient-ventilator asynchrony during assisted mechanical ventilation. Intensiv. Care Med. 2006, 32, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasim, I.; Gulyas, M.; Almgren, B.; Högman, M. A recruitment breath manoeuvre directly after endotracheal suction improves lung function: An experimental study in pigs. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2009, 114, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuramoto, H.; Jesmin, S.; Shimojo, N.; Kamiyama, J.; Islam, M.; Khatun, T.; Kawano, S.; Mizutani, T. Effects of closed vs. open repeated endotracheal suctioning during mechanical ventilation on the pulmonary and circulatory levels of Endothelin-1 in a lavage induced surfactant depleted Rabbit ARDS model. Life Sci. 2013, 93, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.-S.; Park, H.-R. Endotracheal Colonization and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia in Mechanically Ventilated Patients according to Type of Endotracheal Suction System. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2011, 41, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavalcanti, A.B.; Suzumura, E.A.; Laranjeira, L.N.; de Moraes Paisani, D.; Petri Damiani, L.; Penna Guimaraes, P.; Renato Romano, E.; de Moraes Refenga, D.; Taniguchi, L.N.T.; Teixeira, C.; et al. Effect of lung recruitment and titrated positive end-expiratory pressure (peep) vs. low peep on mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Pogson, D.; Shirley, P.; Connolly, E.; Johnston, S. Closed system endotracheal suctioning maintains lung volume during volume controlled mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingay, D.G.; Copnell, B.; Grant, C.A.; Dargaville, P.A.; Dunster, K.R.; Schibler, A. The effect of endotracheal suction on regional tidal ventilation and end-expiratory lung volume. Intensiv. Care Med. 2010, 36, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, A.; Sharpe, N.; Caruana, L.R.; Spooner, A.J.; Fraser, F.F. Lung volume changes during cleaning of closed endotracheal suction cath-eters: A randomized crossover study using electrical impedance tomography. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corley, A.; Spooner, A.J.; Barnett, A.G.; Caruana, L.R.; Hammond, N.E.; Fraser, J.F. End-expiratory lung volume recovers more slowly after closed endotracheal suctioning than after open suctioning: A randomized crossover study. J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 742.e1–742.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glass, C.; Grap, M.; Sessler, C. Endotracheal tube narrowing after closed-system suctioning: Prevalence and risk factors. Am. J. Crit. Care 1999, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keszler, M. Volume-targeted ventilation. Early Hum. Dev. 2006, 82, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, L.P.; Bazik, J.R.; Powner, D.J. Compression volume during mechanical ventilation: Comparison of ventilators and tubing circuits. Crit. Care Med. 1985, 13, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

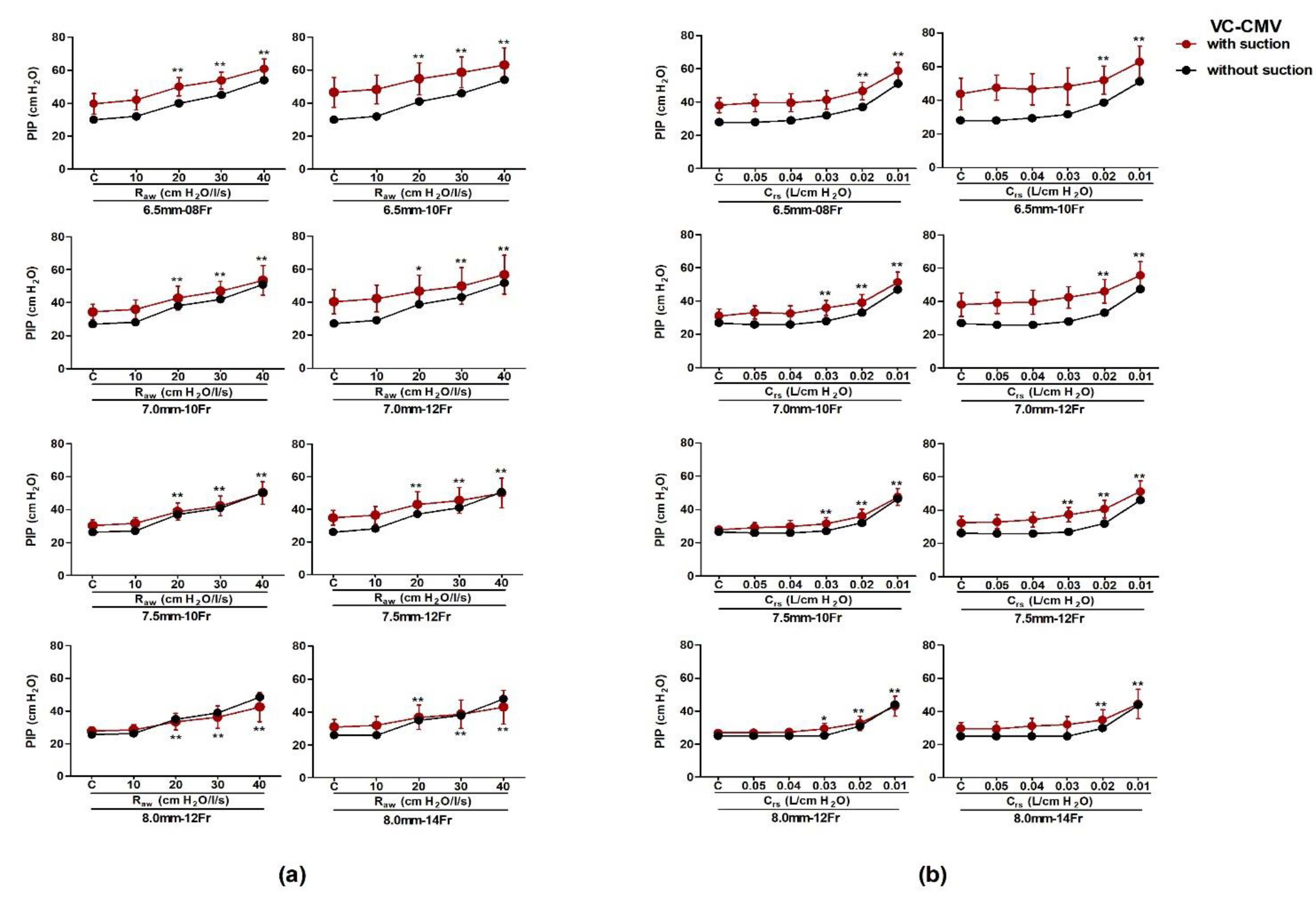




| (a) Obstructive Respiratory System | |||||||||||
| Variable | Raw(cm H2O·L−1·s) | VC-CMV | PC-CMV | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | p-Value | Post Hoc Test | Linear Trend Analysis | Mean | SD | p-Value | Post Hoc Test | Linear Trend Analysis | ||
| p-Value | p-Value | ||||||||||
| RINSP (cm H2O·L−1·s) | 5 | 13.38 | 8.12 | <0.01 | 40 > 30 > 20 > 10 > 5 | <0.01 | 14.86 | 5.47 | <0.01 | 40 > 30 > 20 > 10 > 5 | <0.01 |
| 10 | 15.58 | 8.51 | 15.87 | 5.12 | |||||||
| 20 | 23.74 | 9.75 | 19.82 | 5.30 | |||||||
| 30 | 27.83 | 10.8 | 21.19 | 5.46 | |||||||
| 40 | 35.92 | 12.34 | 24.23 | 5.96 | |||||||
| REXP (cm H2O·L−1·s) | 5 | 7.19 | 2.81 | <0.01 | 40 > 30 > 20 > 10 > 5 | < 0.01 | 9.14 | 4.11 | <0.01 | 40 > 30 > 20 > 10 > 5 | <0.01 |
| 10 | 7.90 | 2.81 | 9.82 | 3.88 | |||||||
| 20 | 10.56 | 2.86 | 12.70 | 4.27 | |||||||
| 30 | 11.59 | 2.90 | 13.54 | 4.48 | |||||||
| 40 | 13.87 | 3.12 | 15.99 | 5.02 | |||||||
| (b) Restrictive Respiratory System | |||||||||||
| Variable | Crs (L·cm H2O−1) | VC-CMV | PC-CMV | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | p-Value | Post Hoc Test | Linear Trend Analysis | Mean | SD | p-Value | Post Hoc Test | Linear Trend Analysis | ||
| p-Value | p-Value | ||||||||||
| RINSP (cm H2O·L−1·s) | 0.01 | 13.49 | 9.36 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 12.84 | 7.72 | < 0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| 0.02 | 13.26 | 8.75 | 14.01 | 6.86 | >0.01 | ||||||
| 0.03 | 10.37 | 7.26 | <0.01; <0.02 | 12.72 | 5.66 | <0.02 | |||||
| 0.04 | 11.32 | 7.67 | <0.01; <0.02; >0.03 | 13.40 | 5.39 | ||||||
| 0.05 | 11.06 | 7.70 | <0.01; <0.02 | 13.21 | 5.21 | <0.02 | |||||
| 0.08 | 9.07 | 5.99 | <0.01; <0.02; <0.03; <0.04; <0.05 | 12.51 | 5.00 | <0.02; <0.04; <0.05 | |||||
| REXP (cm H2O·L−1·s) | 0.01 | 11.58 | 6.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 9.09 | 3.67 | < 0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| 0.02 | 8.63 | 3.34 | <0.01 | 8.30 | 3.36 | <0.01 | |||||
| 0.03 | 6.95 | 2.80 | <0.01; <0.02 | 7.44 | 3.36 | <0.01; <0.02 | |||||
| 0.04 | 6.88 | 2.88 | <0.01; <0.02 | 8.10 | 3.62 | <0.01; <0.03 | |||||
| 0.05 | 6.52 | 2.85 | <0.01; <0.02; <0.03; <0.04 | 8.16 | 3.67 | <0.01; <0.03 | |||||
| 0.08 | 5.41 | 1.97 | <0.01; <0.02; <0.03; <0.04; <0.05 | 8.41 | 4.05 | <0.01; <0.03 | |||||
| (a) Obstructive Respiratory System Model | |||||||||
| △PIP (cm H2O) | △PEEP (cm H2O) | △Vexp (L) | |||||||
| B | SE | t | B | SE | t | B | SE | t | |
| Constant | 22.64 | 2.09 | 10.84 ** | −0.52 | 0.38 | −1.34 | 1.50 | 0.34 | 4.38 ** |
| ETT area (mm2) | −0.42 | 0.05 | −7.36 ** | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.19 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −3.48 ** |
| SC area (mm2) | 0.24 | 0.12 | 2.09 * | 0.07 | 0.02 | 3.40 * | 0.26 | 0.02 | 13.52 ** |
| Raw (cm H2O L−1 s) | −0.10 | 0.02 | −4.19 ** | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | −0.02 | 0.00 | −4.49 ** |
| Mode | −4.86 | 0.61 | −7.95 ** | −0.05 | 0.11 | −0.42 | 1.03 | 0.10 | 10.31 ** |
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.79 | ||||||
| p | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | ||||||
| (b) Restrictive Respiratory System Model | |||||||||
| △PIP (cm H2O) | △PEEP (cm H2O) | △Vexp (L) | |||||||
| B | SE | t | B | SE | t | B | SE | t | |
| Constant | 21.75 | 1.86 | 11.69 ** | −0.34 | 0.30 | −1.16 | −0.68 | 0.64 | −1.04 |
| ETT area (mm2) | −0.49 | 0.05 | −9.48 ** | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.42 | −0.05 | 0.02 | −2.56 * |
| SC area (mm2) | 0.47 | 0.11 | 4.47 ** | 0.06 | 0.17 | 3.84 ** | 0.32 | 0.04 | 8.63 ** |
| Crs (L cm H2O−1) | 22.98 | 11.99 | 1.92 | −5.19 | 1.96 | −2.65 ** | 39.15 | 4.15 | 9.42 ** |
| Mode | −7.35 | 0.54 | −13.52 ** | −0.09 | 0.09 | −1.07 | 1.42 | 0.19 | 7.52 ** |
| R2 | 0.72 | 0.23 | 0.68 | ||||||
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, F.; Chou, S.-S.P.; Yang, S.-H.; Lin, J.-C.; Jow, G.-M. Closed Endotracheal Suctioning Impact on Ventilator-Related Parameters in Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Systems: A Bench Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115266
Jung F, Chou S-SP, Yang S-H, Lin J-C, Jow G-M. Closed Endotracheal Suctioning Impact on Ventilator-Related Parameters in Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Systems: A Bench Study. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115266
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Fang, Shang-Shing P. Chou, Shih-Hsing Yang, Jau-Chen Lin, and Guey-Mei Jow. 2021. "Closed Endotracheal Suctioning Impact on Ventilator-Related Parameters in Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Systems: A Bench Study" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115266
APA StyleJung, F., Chou, S.-S. P., Yang, S.-H., Lin, J.-C., & Jow, G.-M. (2021). Closed Endotracheal Suctioning Impact on Ventilator-Related Parameters in Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Systems: A Bench Study. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115266






