AIS Data Vulnerability Indicated by a Spoofing Case-Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
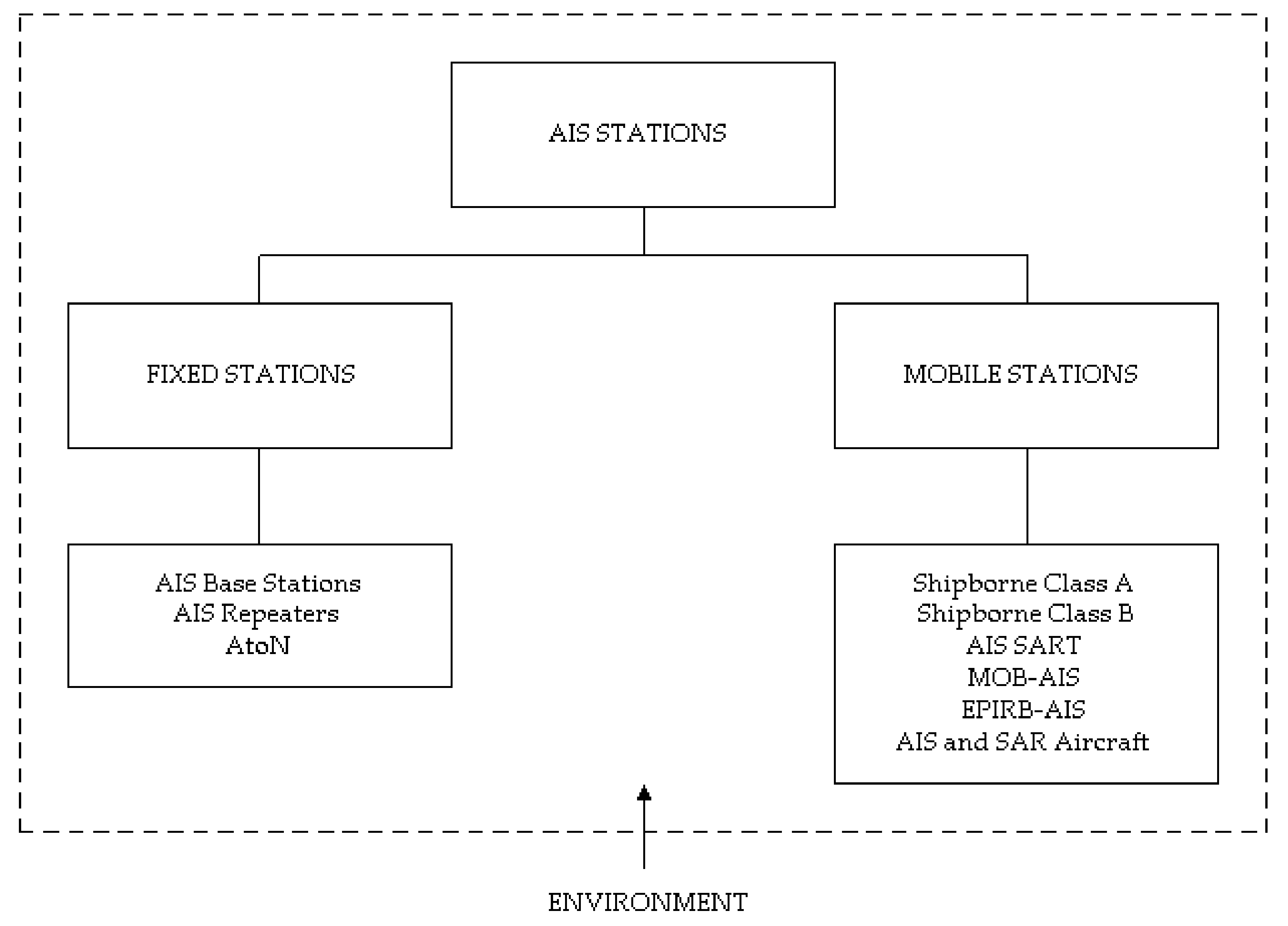
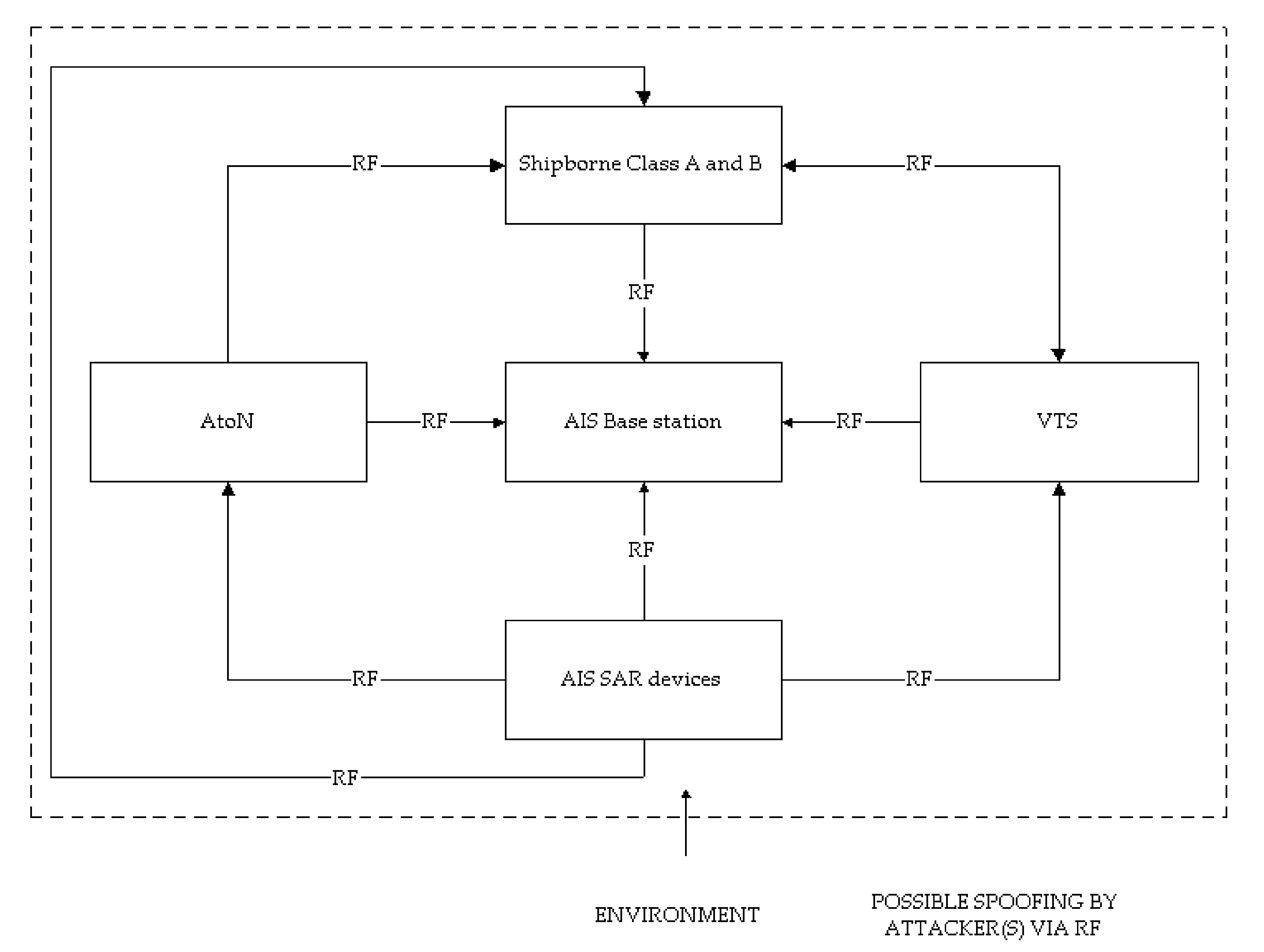
3.1. AIS Vulnerabilities
3.2. An Overview of AIS Spoofing Incidents in the Last Years
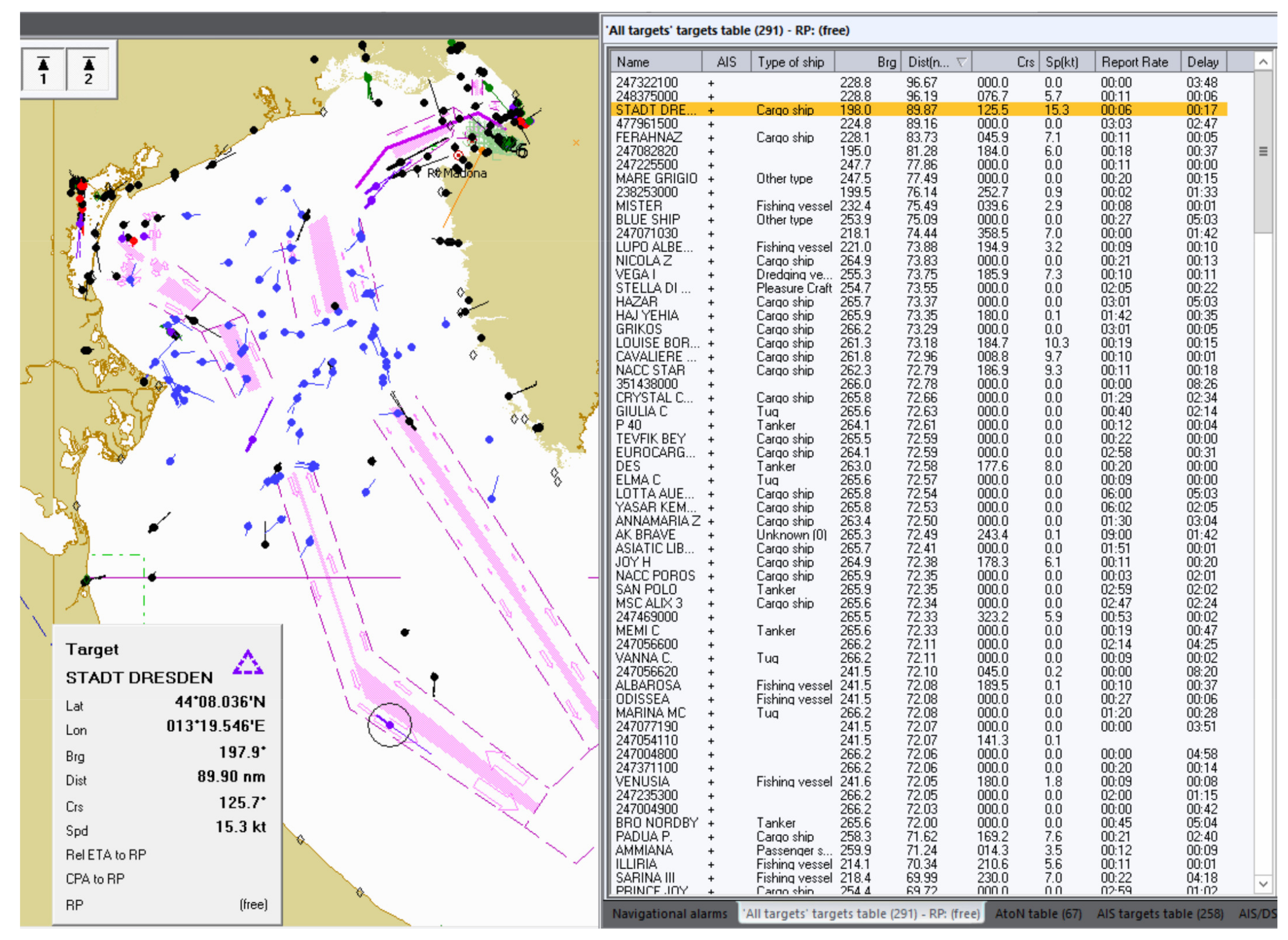
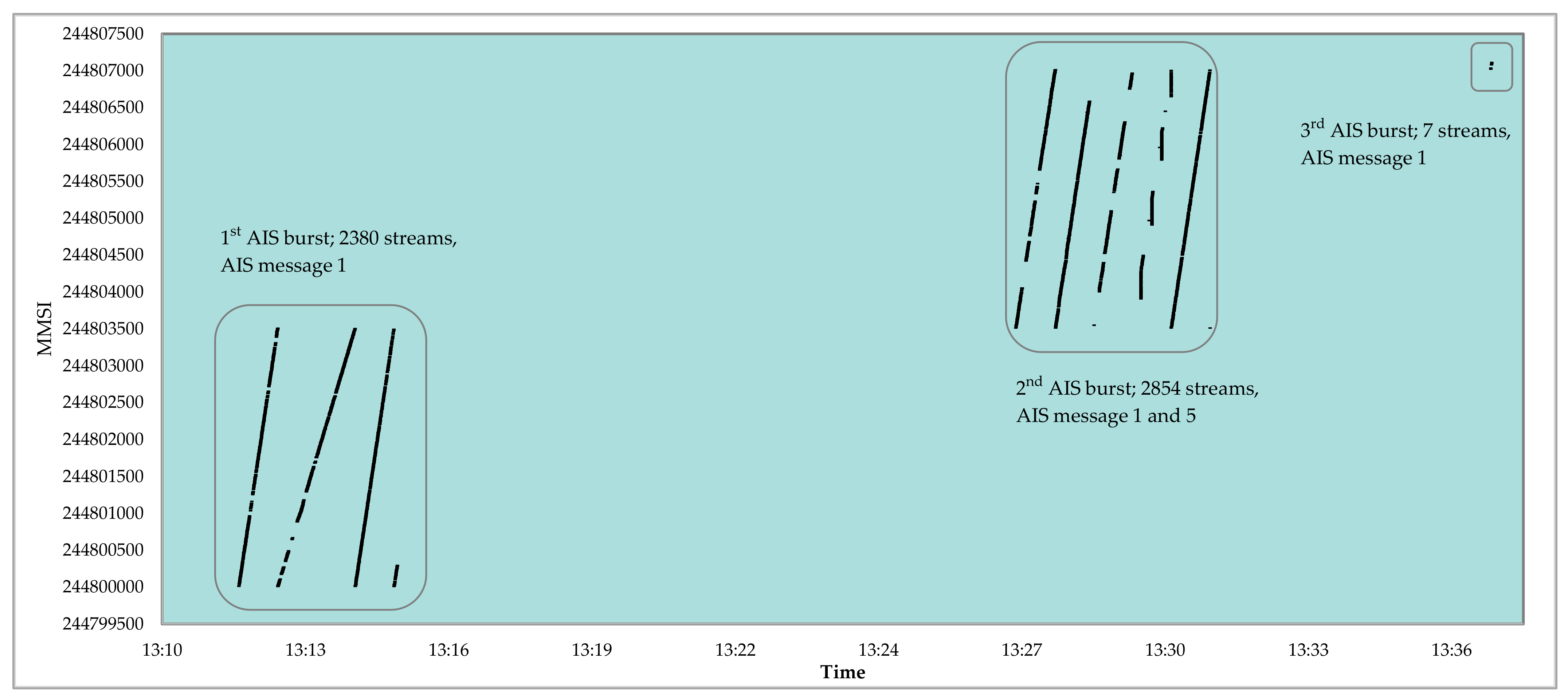
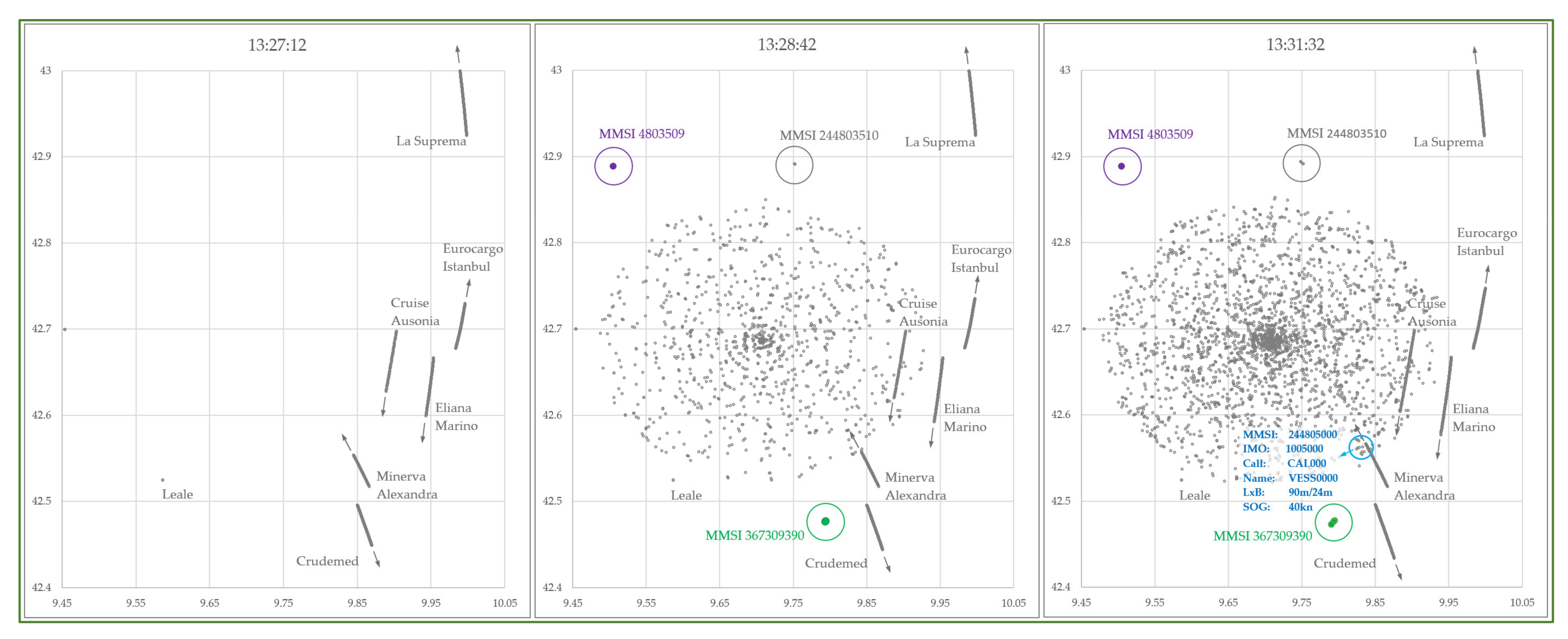
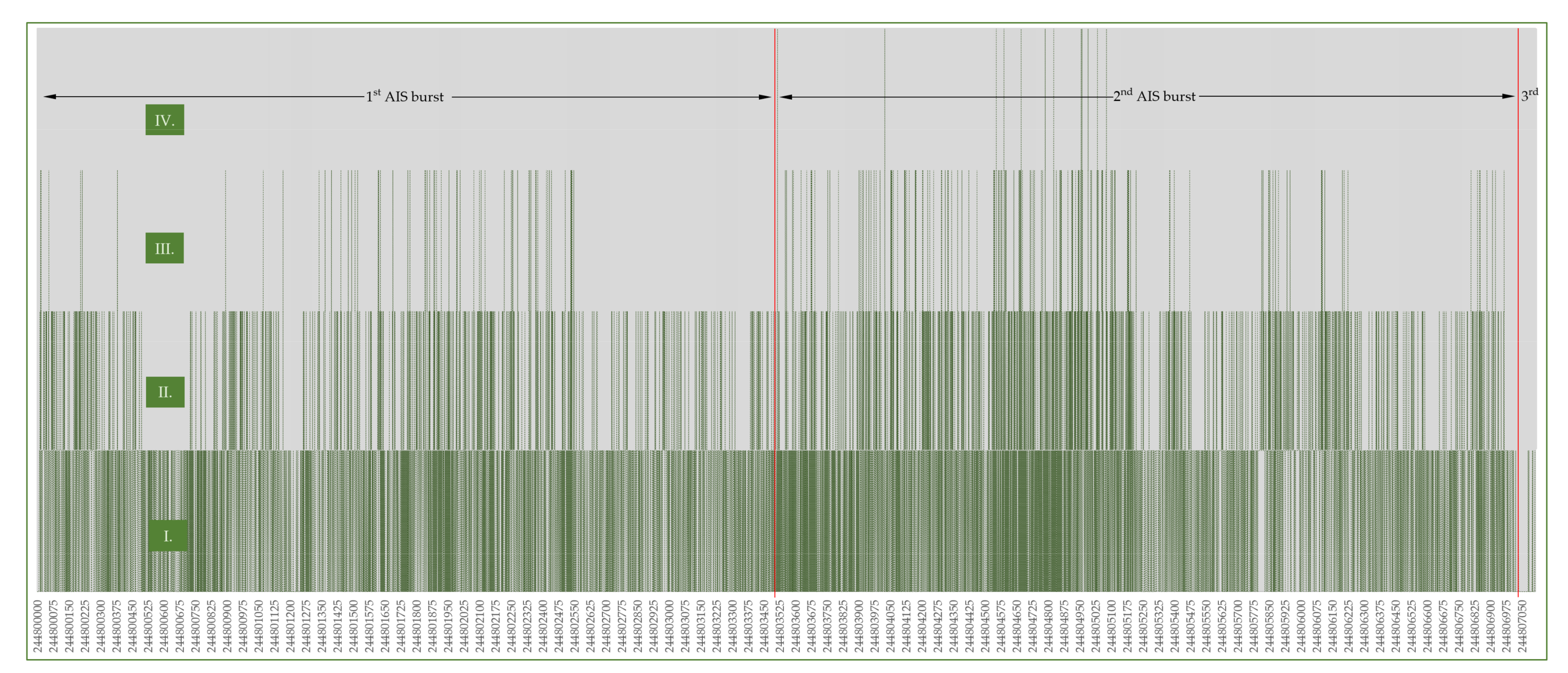
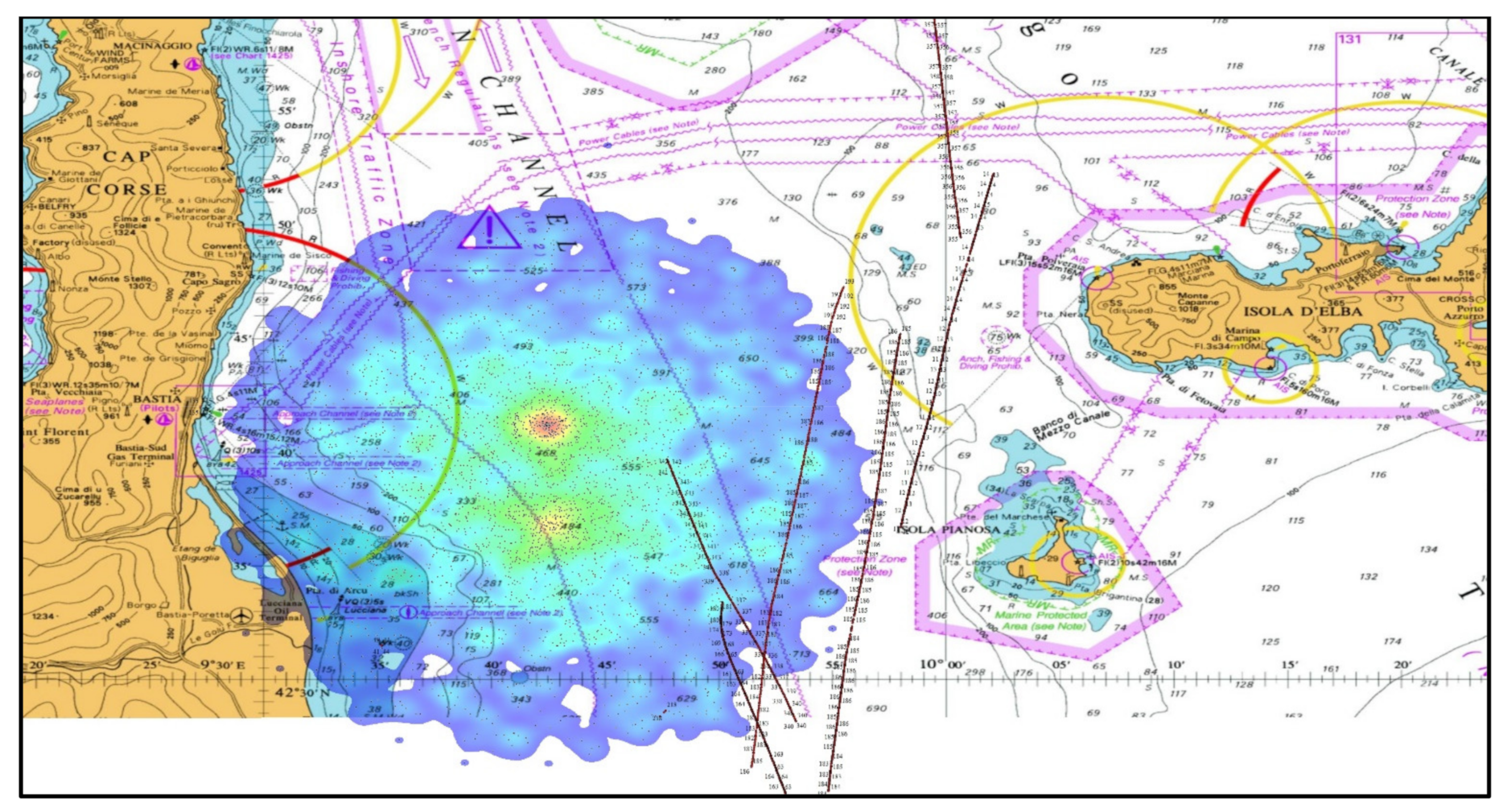
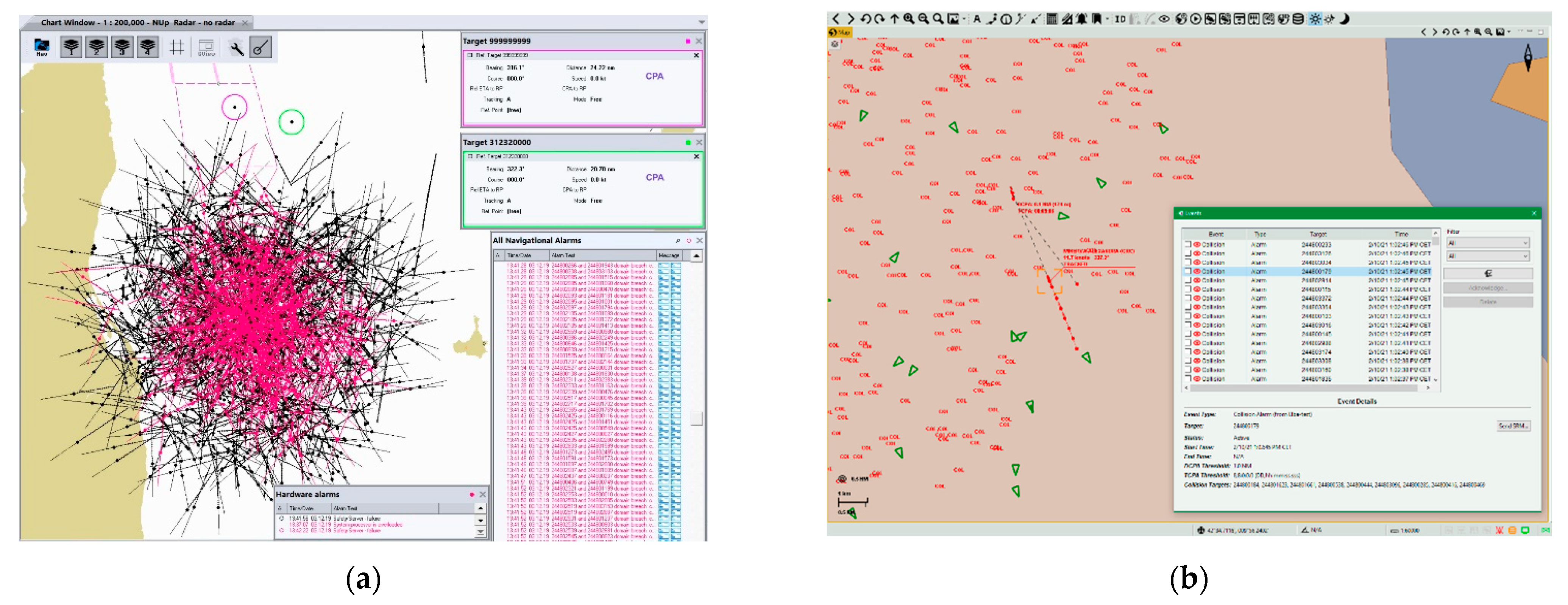
4. Case Study on Spoofing Large Amounts of AIS Fake Targets Nearby Elba Island and Its Impact on VDL
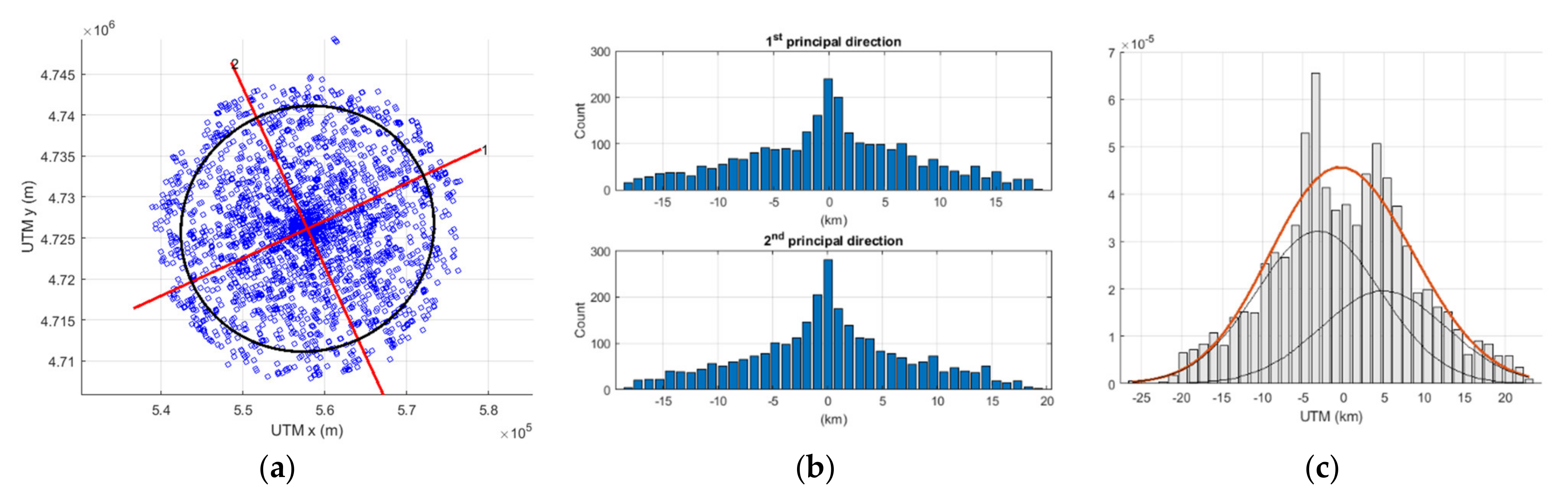
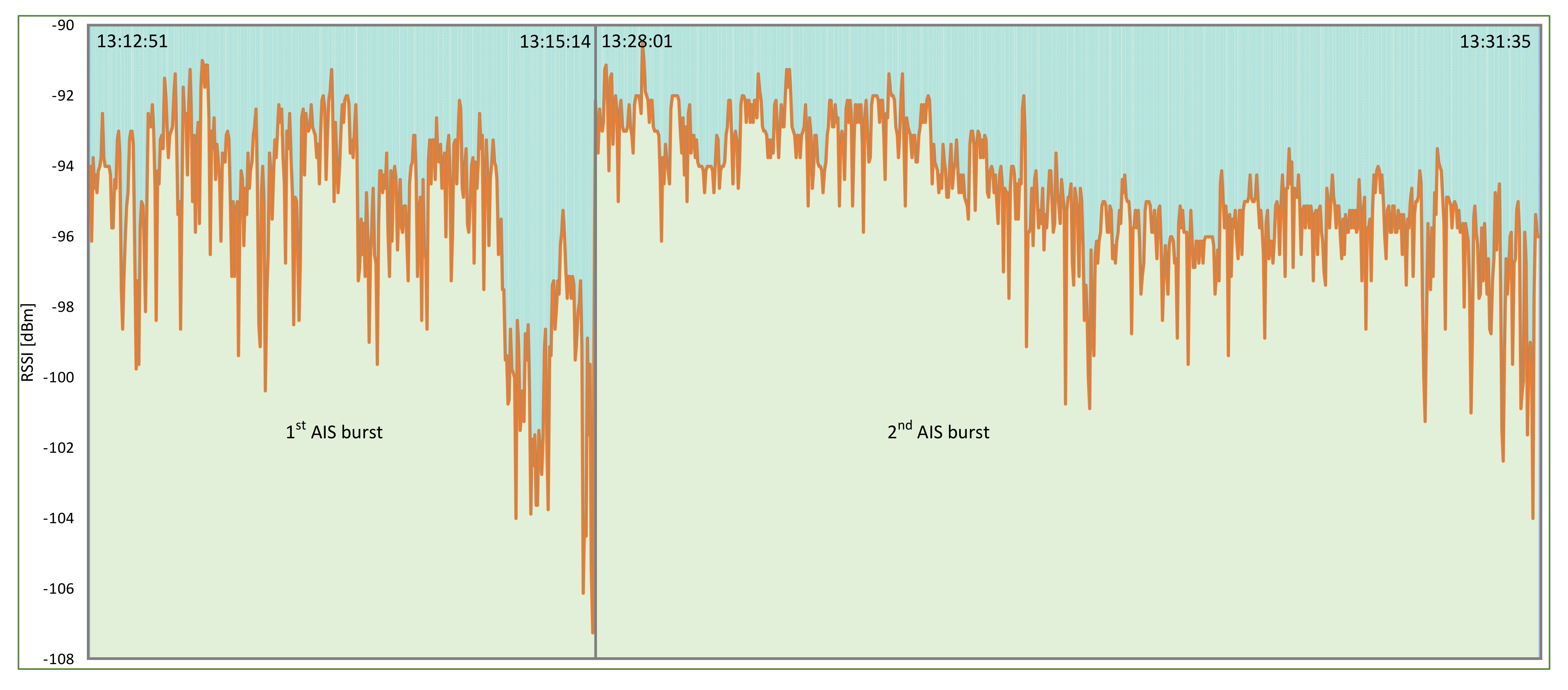
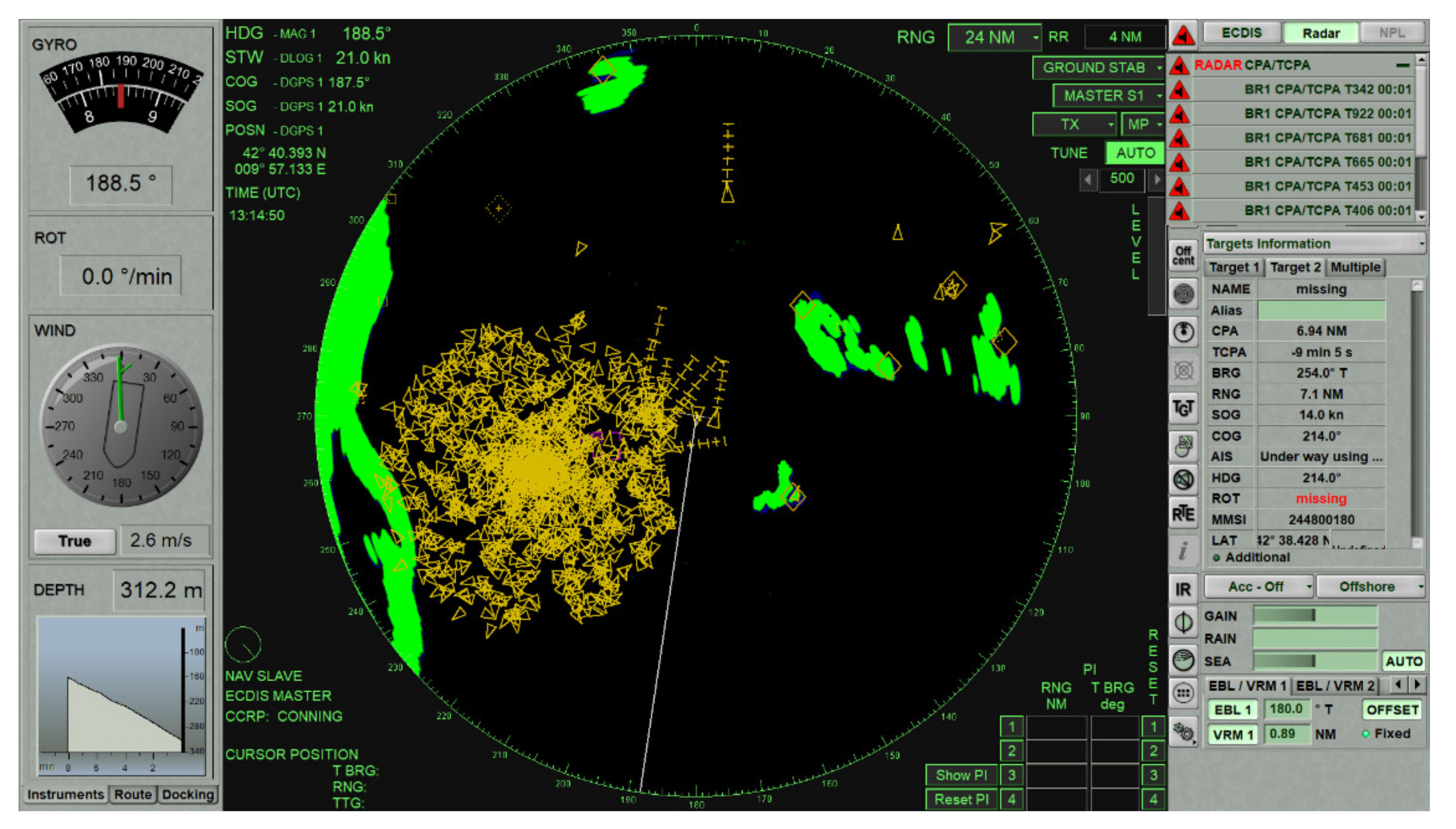
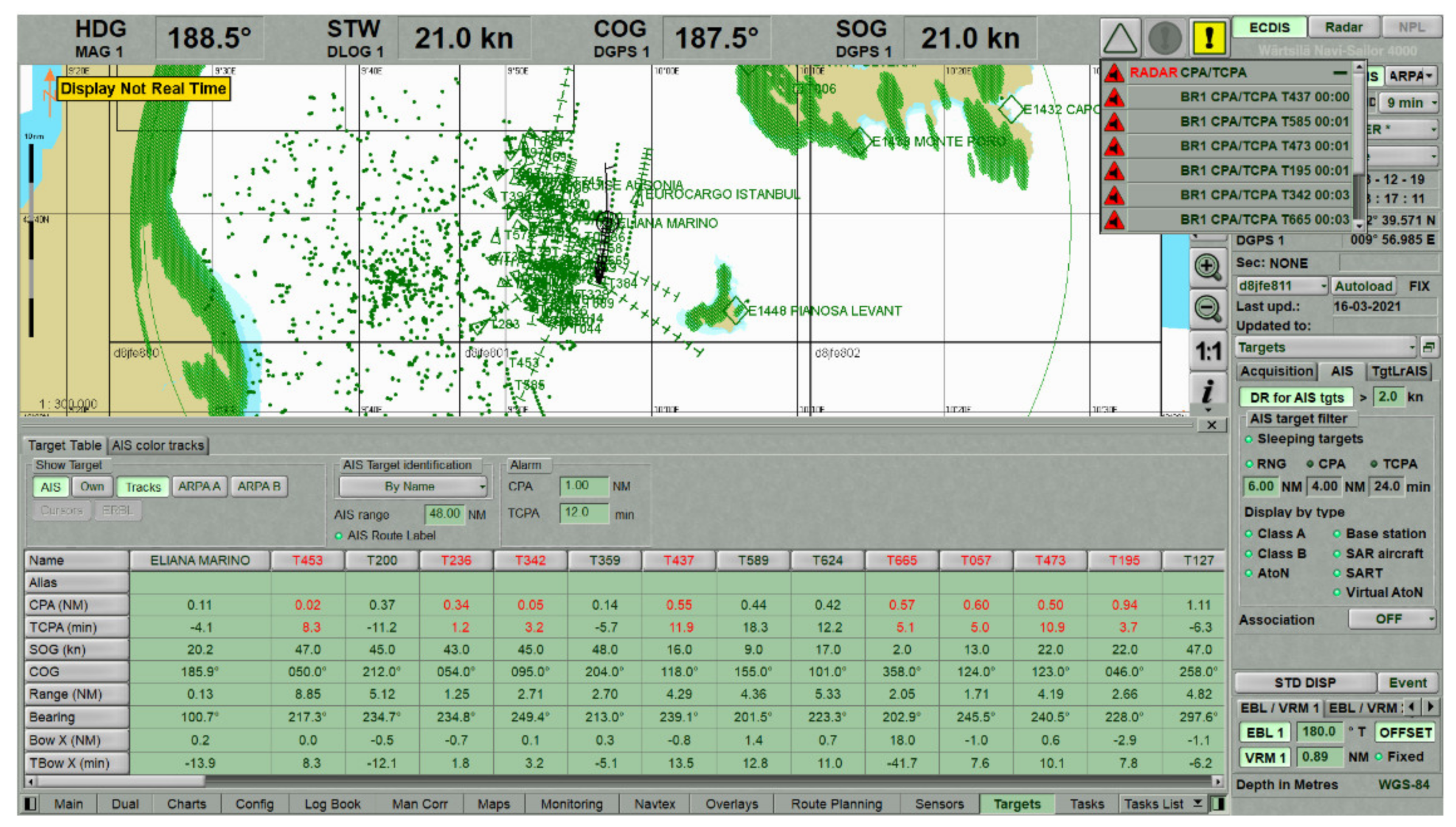
4.1. VDL Load and Spoofing Source Analysis
4.2. Potential Consequences of Spoofing Near ELBA Island
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Automatic Identification System |
| AIS BS | AIS base station |
| AIS SART | Automatic Identification System Search and Rescue Transmitter |
| ARPA | Automatic Radar Plotting Aid |
| AtoN | Aid to navigation |
| CPA | Closest Point of Approach |
| EBIOS | Expression des Besoins et Identification des Objectifs de Sécurité |
| ECDIS | Electronic Chart Display Information System |
| ECS | Electronic Chart Systems |
| EEZ | Exclusive Economic Zone |
| EMODnet | European Marine Observation and Data Network |
| EPIRB-AIS | Emergency Positioning Indicating Radio Beacon-AIS enabled |
| FATDMA | Fixed Access Time Division Multiple Access |
| GMSK | Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| GT | Gross tonnage |
| IALA | International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| ISM | International Safety Management |
| ITU | International Telecommunication Union |
| mIBC | Maritime certificate-less identity-based public key cryptography |
| MMSI | Maritime Mobile Service Identity |
| MOB-AIS | Man Over Board-AIS device |
| MSA | Maritime situational awareness |
| M/v | Motor vessel |
| NM | Nautical miles |
| NMEA | National Maritime Electronic Association |
| OOW | Officer of the watch |
| pAIS | Protected AIS |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| RSSI | Received signal strength indicator |
| S-AIS | Satellite-based AIS |
| SAR | Search and Rescue |
| SEG | SafeSeaNet Ecosystem Graphical Interface |
| SOTDMA | Self-organized time division multiple access |
| SOLAS | Safety Of Life At Sea |
| SWOT | Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats |
| TCPA | Time to Closest Point of Approach |
| TDM | Traffic Density Map |
| TESLA | Timed Efficient Stream Loss-tolerant Authentication |
| TOA | Time of arrival |
| V-AtoN | Virtual AtoN |
| VDL | VHF data link |
| VDES | VHF Data Exchange System |
| VHF | Very high frequency |
| VTS | Vessel Traffic System |
References
- IALA Guideline-An Overview of AIS, Edition 2.0. Available online: https://www.navcen.uscg.gov/pdf/IALA_Guideline_1082_An_Overview_of_AIS.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Weintrit, A. The Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS): An Operational Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 703–708. ISBN 978-0-414-48246-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bole, A.; Dineley, B.; Wall, A. Radar and ARPA Manual, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Butterworth–Hernemann: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 452–463. ISBN 0 7506 6434 7. [Google Scholar]
- Shipboard Automatic Identification System Displays, Meeting the Needs of Mariners; Special Report 273; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Available online: https://www.nap.edu/read/10708/chapter/1 (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- IMO. The International Convention for Safety of Life at Sea (Consolidated Edition 2020); IMO Publishing: London, UK, 2020; pp. 15/34–15/35. ISBN 9789280116908. [Google Scholar]
- Kjerstad, N. Electronic and Acoustic Navigation Systems; Norwegian Institute of Science and Technology: Alesund, Norway, 2016; pp. 2-143–2-157. ISBN 978-82-92186-57-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Satellite-based AIS and its Comparison with LRIT. TransNav 2014, 8, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, T.; Greidanus, H.; Delaney, C. Metrics and provider-based results for completeness and temporal resolution of satellite-based AIS services. Mar. Policy 2018, 93, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Tedeschi, P.; Sciancalepore, S.; Di Pietro, R. SecureAIS-Securing Pairwise Vessels Communications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Avignon, France, 29 June–1 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satellite Based AIS. Available online: https://www.kystverket.no/en/EN_Maritime-Services/Reporting-and-Information-Services/ais/Satellite-based-AIS/ (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Šakan, D.; Rudan, I.; Žuškin, S.; Brčić, D. Near Real-time S-AIS: Recent Developments and Implementation Possibilities for Global Maritime Stakeholders. Multidiscip. Sci. J. Marit. Res. 2018, 32, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, M.; Capata, A.; Bloisi, D.D. AIS Data Visualization for Maritime Spatial Planning (MSP). Int. J. e-Navig. Marit. Econ. 2016, 5, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. Resolution A.1106(29). In Revised Guidelines for the Onboard Operational Use of Shipborne Automatic Identification Systems (AIS); IMO Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Series, M. Technical Characteristics for An Automatic Identification System Using Time-Division Multiple Access in the VHF Maritime Mobile Band; Recommendation ITU: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 1371–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Sciancalepore, S.; Tedeschi, P.; Aziz, A.; Di Pietro, R. Auth-AIS: Secure, Flexible, and Backward-Compatible Authentication of Vessels AIS Broadcasts. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudossis, A.; Katsikas, S.K. Towards a secure automatic identification system (AIS). J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramin, A.; Masnawi, A.; Shaharudin, A. Prediction of Marine Traffic Density Using Different Time Series Model from AIS data of Port Klang and Straits of Malacca. Trans. Marit. Sci. 2020, 2, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, F.; Gibin, M.; Alessandrini, A.; Vespe, M.; Paulrud, A. Mapping fishing effort through AIS data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallotta, G.; Vespe, M.; Bryan, K. Vessel Pattern Knowledge Discovery from AIS Data: A Framework for Anomaly Detection and Route Prediction. Entropy 2013, 15, 2218–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkovic, M.; Twrdy, E.; Harsch, R.; Vidmar, P.; Gucma, M. Technological Advances and Efforts to Reduce Piracy. TransNav 2012, 6, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.S.; Mokashi, A.J.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, G.S. The Maturity of Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) and Its Implications for Innovation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, M.; Hilliard, R.C.; Rezaee, S.; Pelot, R. Past, present, and future of the satellite-based automatic identification system: Areas of applications (2004–2016). WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2018, 17, 311–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review* Introduction: The Need for an Evidence-Informed Approach. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, K.A. Systematic Reviews. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2015, 42, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traffic Density Mapping Service—Methodology. EMS—Ref. Ares (2019)4005069—24/06/2019. Available online: http://www.emsa.europa.eu/related-projects/tdms.html (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Balduzzi, M.; Wilhoit, K.; Pasta, A. A Security Evaluation of AIS. Trend Micro Res. Paper 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, G.C. Protected AIS: A Demonstration of Capability Scheme to Provide Authentication and Message Integrity. TransNav 2020, 14, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.; Iphar, C.; Napoli, A.; Gallen, R.; Bouju, A. DeAIS project: Detection of AIS Spoofing and Resulting Risks. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS’15, Genoa, Italy, 18–21 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Di Ciaccio, F.; Menegazzo, P.; Troisi, S. Optimization of the Maritime Signaling System in the Lagoon of Venice. Sensors 2019, 19, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IALA Guideline No. 1081-On Provision of Virtual Aids to Navigation, Edition 1.1. Available online: https://www.e-navigation.nl/sites/default/files/1081%20Virtual%20AtoN.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Madden, R. USCG Rolling Out AIS Aids to Navigation: Are They Safe AND Secure? Available online: https://gcaptain.com/uscg-ais-aton-navigation/ (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- IALA–Position on the Development of AtoN Service, Issue 1. Available online: https://www.iala-aism.org/content/uploads/2018/04/Position-on-the-development-of-AtoN-services-2017-12-15.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Iphar, C.; Napoli, A.; Ray, C.; Alincourt, E.; Brosset, D. Risk Analysis of falsified Automatic Identification System for the improvement of maritime traffic safety. In Proceedings of the ESREL 2016 Conference, Glasgow, UK, 25–29 September 2016; Lesley Walls, T.B., Matthew, R., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, Milton, UK; Abingdon, UK, 2016; pp. 606–613. [Google Scholar]
- Iphar, C.; Napoli, A.; Ray, C. An expert-based method for the risk assessment of anomalous maritime transportation data. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 104, 102337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NATO Science & Technology Organization, Centre for Maritime Research & Experimentation. Available online: https://www.cmre.nato.int/research/maritime-situational-awareness/ (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Goudossis, A.; Katsikas, S.K. Secure AIS with Identity-Based Authentication and Encryption. TransNav 2020, 14, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thousands of GMDSS Jamming and Spoofing Incidents Reported in 2020. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/thousands-gnss-jamming-spoofing-incidents-reported-2020-guy-buesnel/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Androjna, A.; Twrdy, E. Cyber Threats to Maritime Critical Infrastructure. In Cyber Terrorism and Extremism as Threat to Critical Infrastructure Protection; Čaleta, D., Powers, F.J., Eds.; Ministry of Defense, Republic of Slovenia, Institute for Corporative Security Studies, Joint Special Operations University: Ljubljana, Slovenia; Tampa, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Androjna, A.; Brcko, T.; Pavic, I.; Greidanus, H. Assessing Cyber Challenges of Maritime Navigation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seized UK Tanker Likely ‘Spoofed’ by Iran. Available online: https://lloydslist.maritimeintelligence.informa.com/LL1128820/Seized-UK-tanker-likely-spoofed-by-Iran (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Sinister Spoofing in Shanghai. Available online: https://insidegnss.com/sinister-spoofing-in-shanghai/#:~:text=Someone%20has%20updated%2019th%20century,experts%20have%20never%20seen%20before (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Patterns of GPS Spoofing at Chinese Ports. Available online: https://www.maritime-executive.com/editorials/patterns-of-gps-spoofing-at-chinese-ports (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- New GPS ‘Circle Spoofing’ Moves Ship Locations Thousands of Miles. Available online: https://www.gpsworld.com/new-gps-circle-spoofing-moves-ship-locations-thousands-of-miles/ (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Chinese Fishing Fleet Encroaches on the Galapagos Islands: HawkEye360 Monitors the Fleet for Suspicious Behavior and Potential Illegal Fishing. Available online: https://www.he360.com/insight/potential-illegal-fishing-seen-from-space/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- ITU-R, M. 2287-0. Automatic Identification System VHF Data Link Loading; ITU: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- John, P. Intelligent Maritime Navigation with the Automatic Identification System. Available online: https://ctrf.ca/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Intelligent-Maritime-Navigation.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- Series, M. Technical Characteristics for an Automatic Identification System Using Time Division Multiple Access in the VHF Maritime Mobile Frequency Band. Available online: http://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/R-REC-M.1371-5-201402-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- DHS Navihation Center. Automatic Identification System. Available online: https://www.navcen.uscg.gov/?pag (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- ICAO Doc 9861 AN/448. Manual on VHF Digital Link (VDL) Mode 4; ICAO: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella, F.; Vespe, M.; Alessandrini, A.; Tarchi, D.; Aulicino, G.; Vollero, A. A novel anomaly detection approach to identify intentional AIS on-off switching. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 78, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesnel, G. Threats to satellite navigation systems. Netw. Secur. 2015, 2015, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 7 Advantages of VDES, vs. AIS in Maritime Satellite Communications. Available online: https://info.alen.space/advantages-of-vdes-vs-ais-in-maritime-satellite-communications (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- IALA–VHF Data Exchange System (VDES)–Overview, Edition 2.0. Available online: https://www.iala-aism.org/product/vhd-data-exchange-system-vdes-overview-1117/ (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- AS, D. Cyber Security Resilience Management for Ships and Mobile offshore Units in Operation; DNVGL-RP-0496. DNV GL: Oslo, Norway, 2016. Available online: https://brandcentral.dnvgl.com/download/DownloadGateway.dll?h=BE1B38BB718539CC0AB58A5FF2EA7A83DE6D49BC96B8DB13C4CAAFA95E9ACCDA9F12593F5BB9D3D16F4B2EB2FF9780D9 (accessed on 8 March 2021).




| Number of Consecutive Slots | Maximum Binary Data Bytes |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 |
| 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 68 |
| 4 | 96 |
| 5 | 121 |
| AIS Class A Transponder-Ships Dynamic Conditions | Dual-Channel | Single-Channel |
|---|---|---|
| Ship at anchor or moored | 3 min | 6 min |
| SOG 0–14 knots | 10 s | 20 s |
| SOG 0–14 knots and changing | 3.3 s | 6.6 s |
| SOG 14–23 knots | 6 s | 12 s |
| SOG 14–23 knots and changing course | 2 s | 4 s |
| SOG > 23 knots | 2 s | 4 s |
| Ship static information | 6 min | 12 min |
| AIS Class B Transponder-Ships Dynamic Conditions | Dual-Channel | Single-Channel |
| SOG < 2 knots | 3 min | 6 min |
| SOG > 2 knots | 30 s | 1 min |
| SOG | ||
| Ship static information | 6 min | 12 min |
| Ais Anomalies | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Behaviour | Content of the Message | Lawfulness | Quality |
| Kinematic (position, move) data | Static data | Criminal issues | Unexpectedly changing data |
| Voyage data | Human data | Breach-level issues | Impossible data |
| Impossible with respect to others information | |||
| Missing data | |||
| Location and Date | Spoofing Incidents Description |
|---|---|
| The Southern Ocean, 2008–2018 | To disguise her illegal fishing operations, m/v Andrej Longov/Sea Breez 1/Ayda/STS-50 committed identity fraud by repeatedly falsifying her registry, producing multiple fake signals, and appearing in nearly 100 different locations simultaneously. |
| Gulf of Oman/Malaysia, September 2013 | M/v Ramtin was involved in “spoofing” by falsely transmitting her AIS identity during suspicious activities and deceiving authorities at Karachi port under the name of m/v Hamoda. |
| Ten global locations connected to one of the superpower states, 2016–2019 | 9883 suspected spoofing incidents. |
| The Black Sea, June 2017 | Vessel tracking systems placed many vessels near Novorossiysk Commercial Sea Port in the nonsensical location, on the Gelendzhik Airport. |
| The East China Sea, 28 October 2018 | M/v Yuk Tung was involved in “spoofing” by falsely transmitting its AIS identity in a suspicious ship-to-ship transfer and deceiving authorities under the name of m/v Hika, which was anchored in the Gulf of Guinea, more than 7000 m away. |
| Point Reyes in northern California, August 2018–June 2019 | Ships thousands of miles at sea mysteriously reported GPS positions in ring patterns off the coast of San Francisco. |
| Eastern Mediterranean and the Red Sea, 2018–2019 | Signal interference, loss of erratic AIS/GPS signals. |
| Strait of Hormuz, July 2019 | A British oil tanker, the Stena Impero, was seized by Iranian forces after the ship was spoofed into changing course into Iranian waters. |
| Ningbo (China)-Nampo (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea), July–November 2019 | The m/v Fu Xing 12 manipulated its identity by employing two AIS on board and using four different ship names to disguise its operations in delivering illegal coal and other resources. |
| Port of Shanghai, 2018–2019 | Fake signals caused ships to appear to be moving in ring patterns at short intervals. |
| Ponce De Leon Inlet, Florida, 2020 | Four visual AtoNs appeared on the map based on fake AIS messages. |
| Elba Island, 3 December 2019 | Deliberate spoofing of the vast number of artificial AIS targets temporarily affected the navigation of ships. |
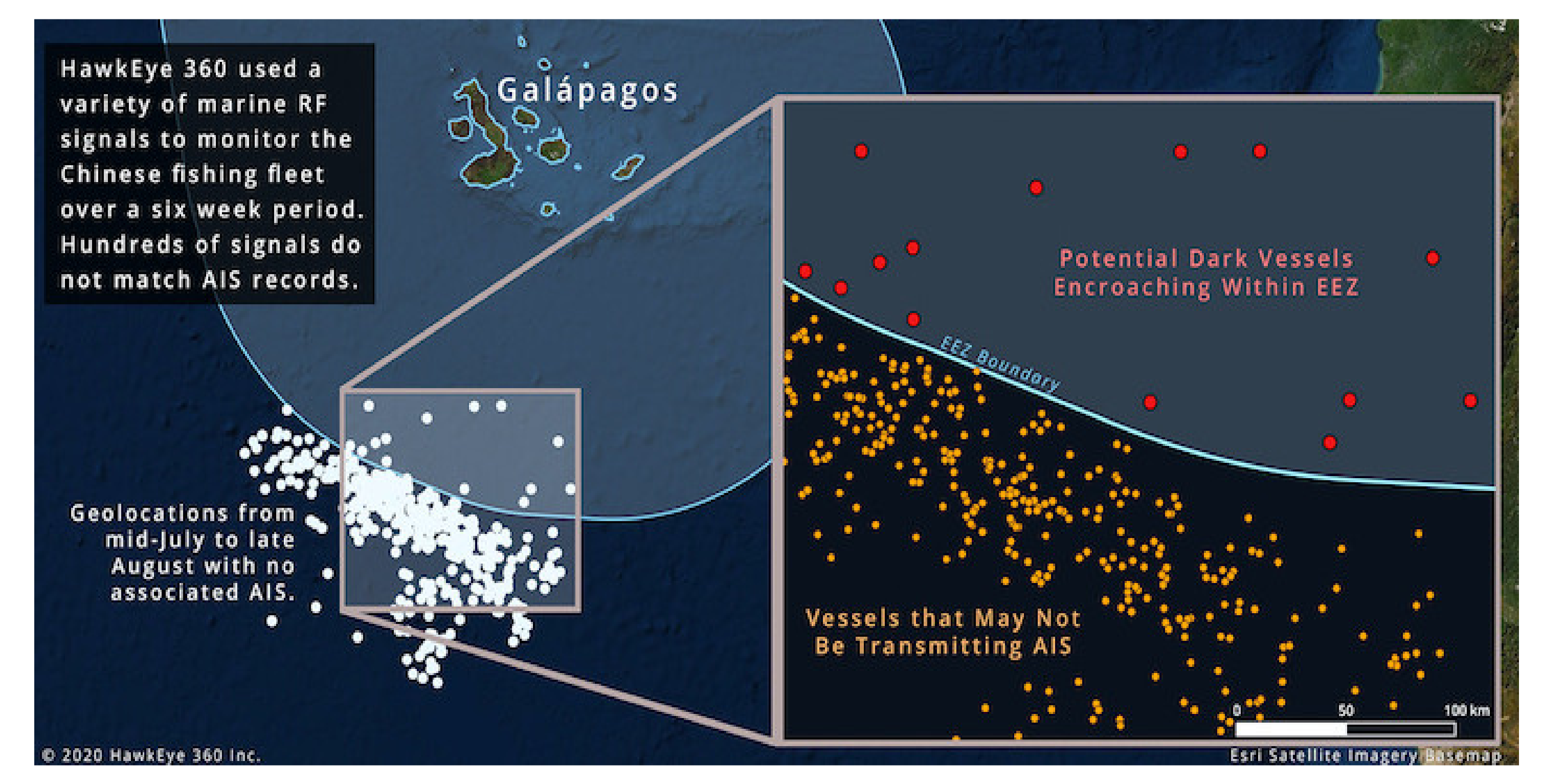
| Galapagos, July 2020 | One of the world’s largest fleets of fishing nations misreported its location (approximately 10,000 km from its observed location) to conceal illegal fishing activities in the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) around the Galápagos Islands. |
| Ship Name | Type | IMO N° | MMSI | Gross Tonnage | Year of Build | Registered Owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Suprema | Ro-Ro | 9214288 | 247083700 | 49,257 | 2003 | Grandi Navi Veloci Spa (Italy) |
| Blue Star (ex. Minerva Alexandra) | Crude Oil Tanker | 9198094 | 273218590 | 58,125 | 2000 | Marine Trans Shipping Llc (Russia) |
| Eliana Marino | Ro-Ro | 9226360 | 247370400 | 18,265 | 2000 | Moby Spa (Italy) |
| Mega Express Five | Ro-Ro | 9035101 | 247183200 | 28,338 | 1993 | Forship Spa (Italy) |
| Leale | Chemical/Oil Tanker | 9404637 | 247238700 | 4831 | 2008 | Elbana Di Navigazione Spa (Italy) |
| Crudemed | Crude Oil Tanker | 9832547 | 636018645 | 62,330 | 2018 | Sans Souci Shipping Co (Liberia) |
| Cruise Ausonia | Ro-Ro | 9227429 | 247378700 | 30,907 | 2002 | Grimaldi Euromed Spa (Italy) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Androjna, A.; Perkovič, M.; Pavic, I.; Mišković, J. AIS Data Vulnerability Indicated by a Spoofing Case-Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115015
Androjna A, Perkovič M, Pavic I, Mišković J. AIS Data Vulnerability Indicated by a Spoofing Case-Study. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrojna, Andrej, Marko Perkovič, Ivica Pavic, and Jakša Mišković. 2021. "AIS Data Vulnerability Indicated by a Spoofing Case-Study" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115015
APA StyleAndrojna, A., Perkovič, M., Pavic, I., & Mišković, J. (2021). AIS Data Vulnerability Indicated by a Spoofing Case-Study. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115015