Developmental Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption of Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride and Humidifier Disinfectant in Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Chemicals
2.2. Fish Maintenance and Exposures
2.3. Hormone Measurement
2.4. Quantification of Gene Transcription
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
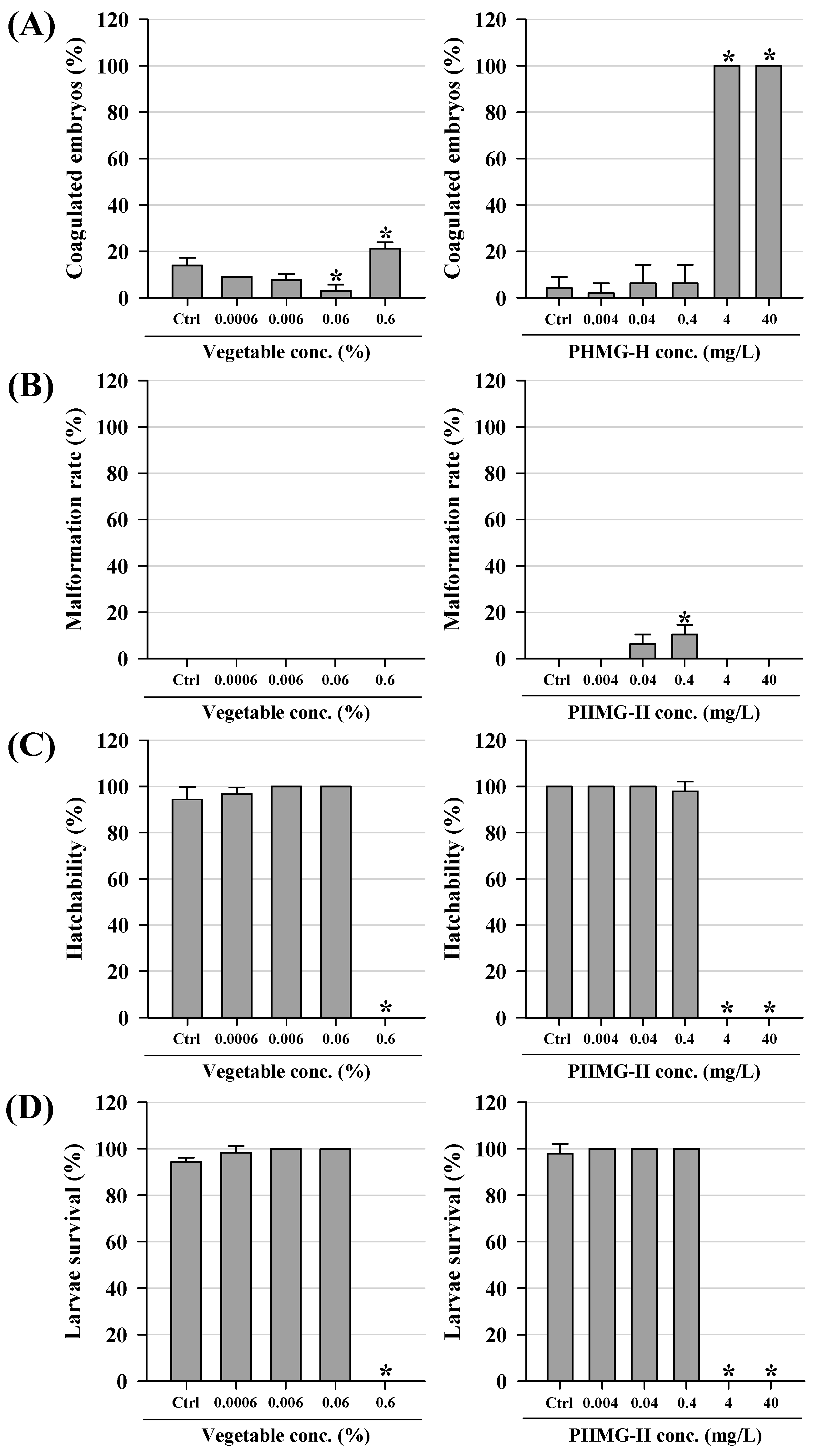
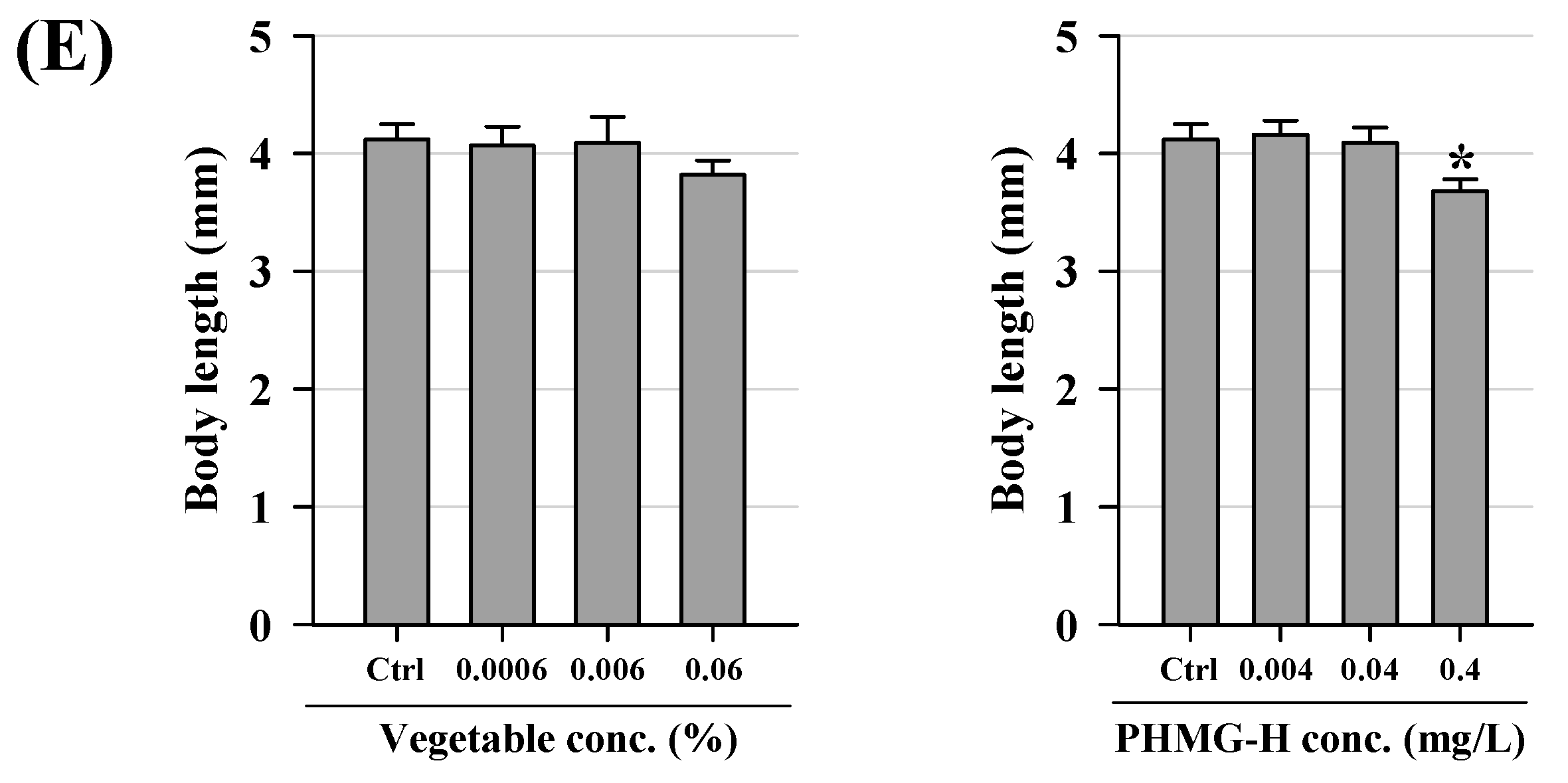
3.1. Acute Lethality and Developmental Effects of Zebrafish Embryo/Larvae
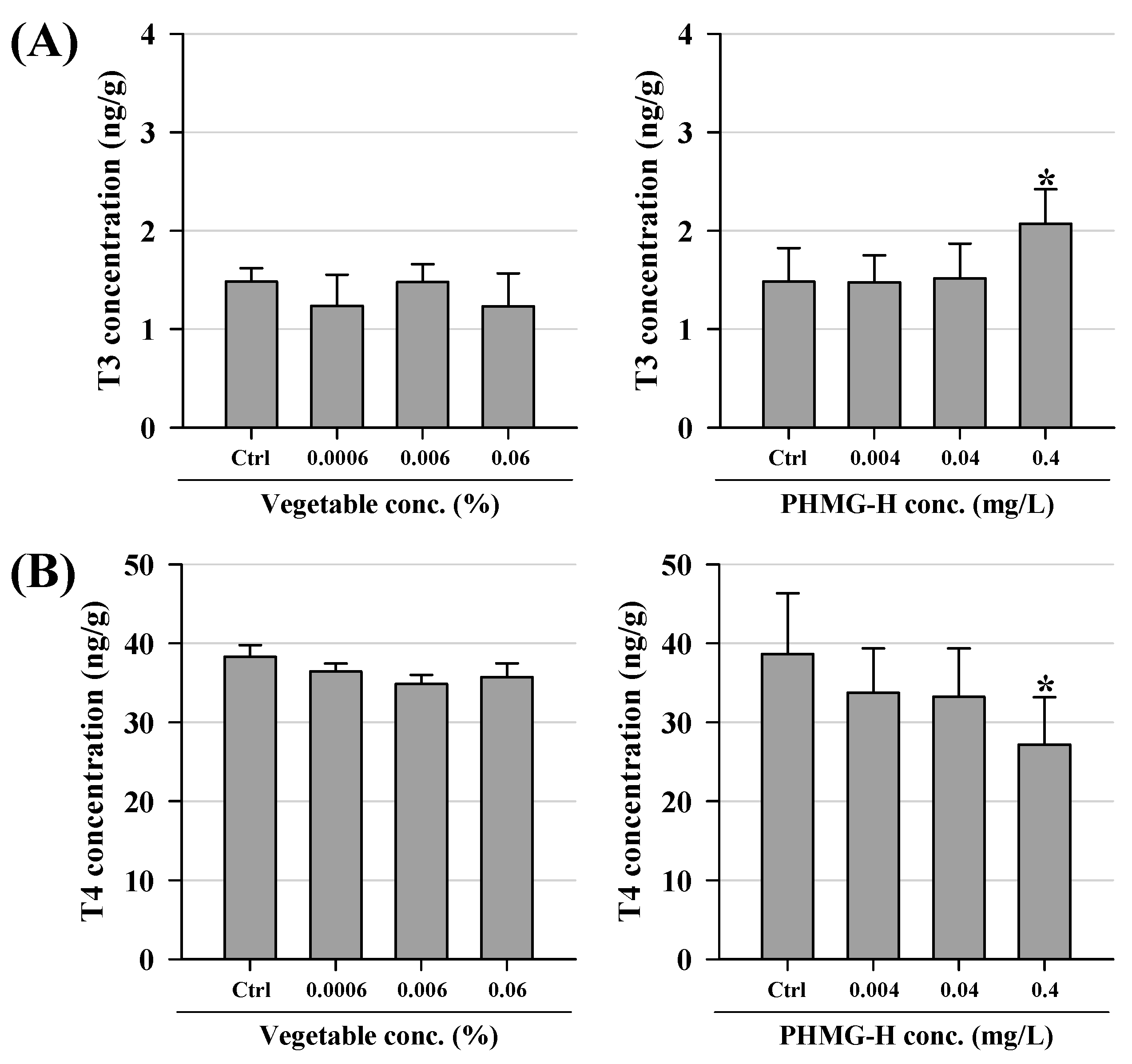
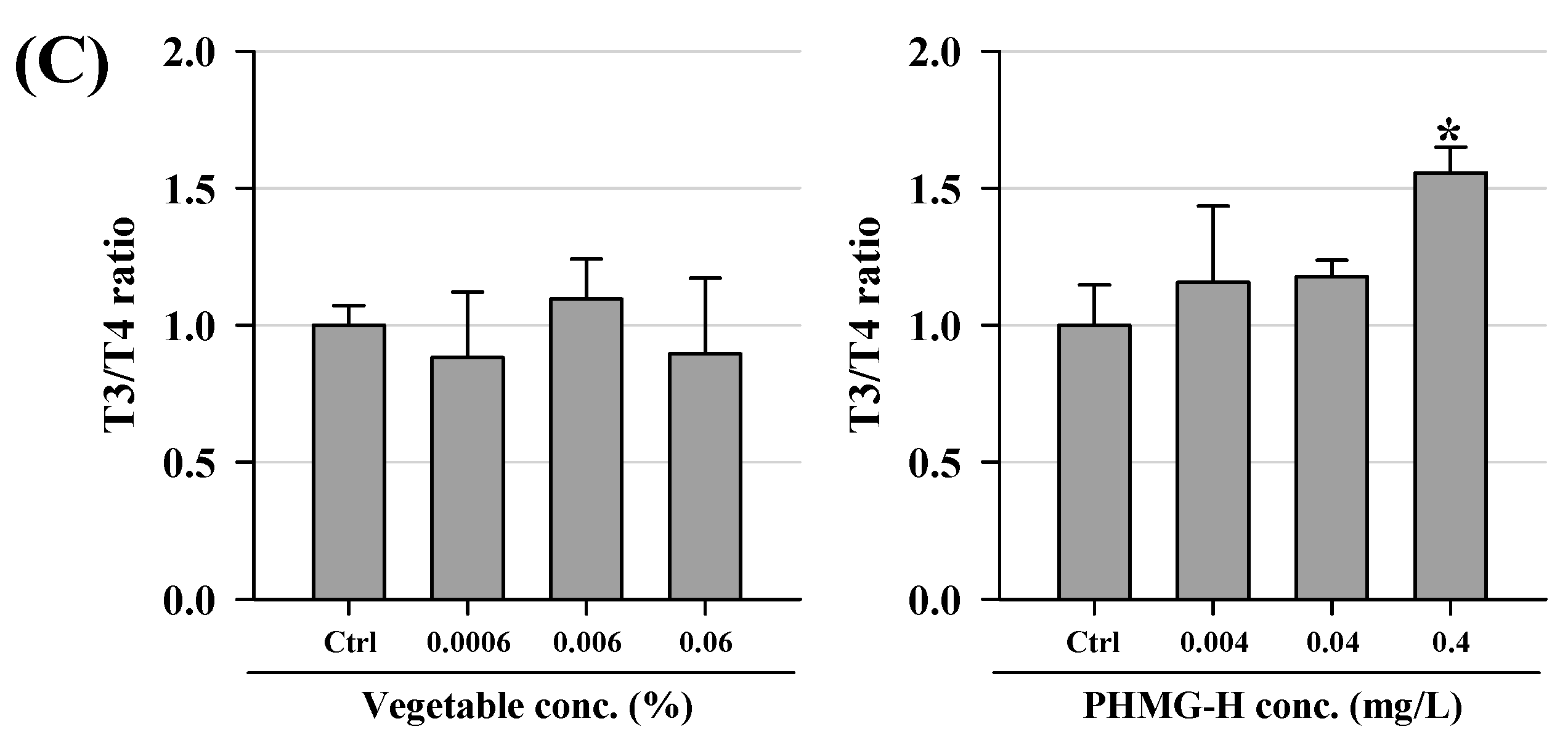
3.2. Hormonal Changes in T3 and T4
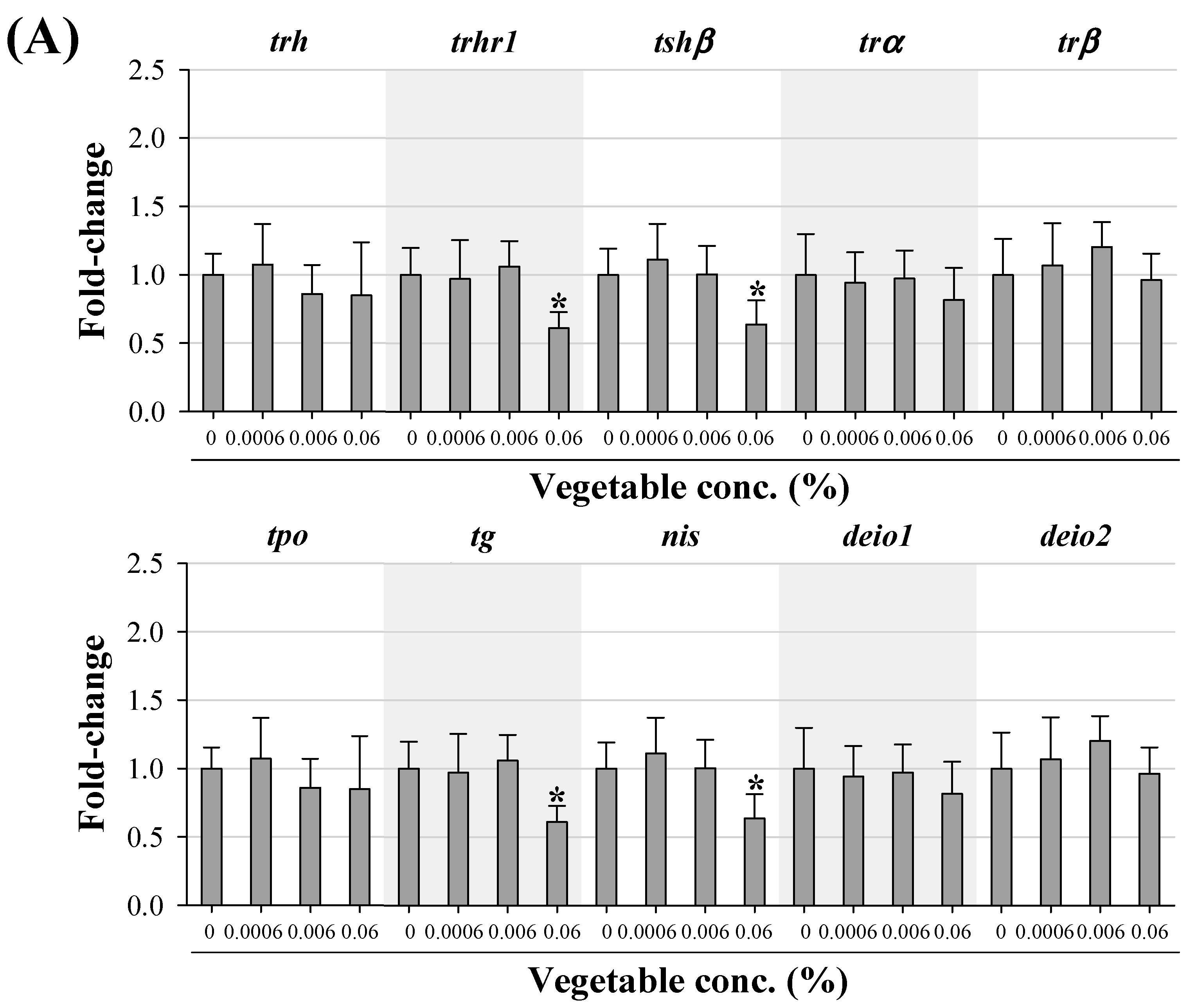
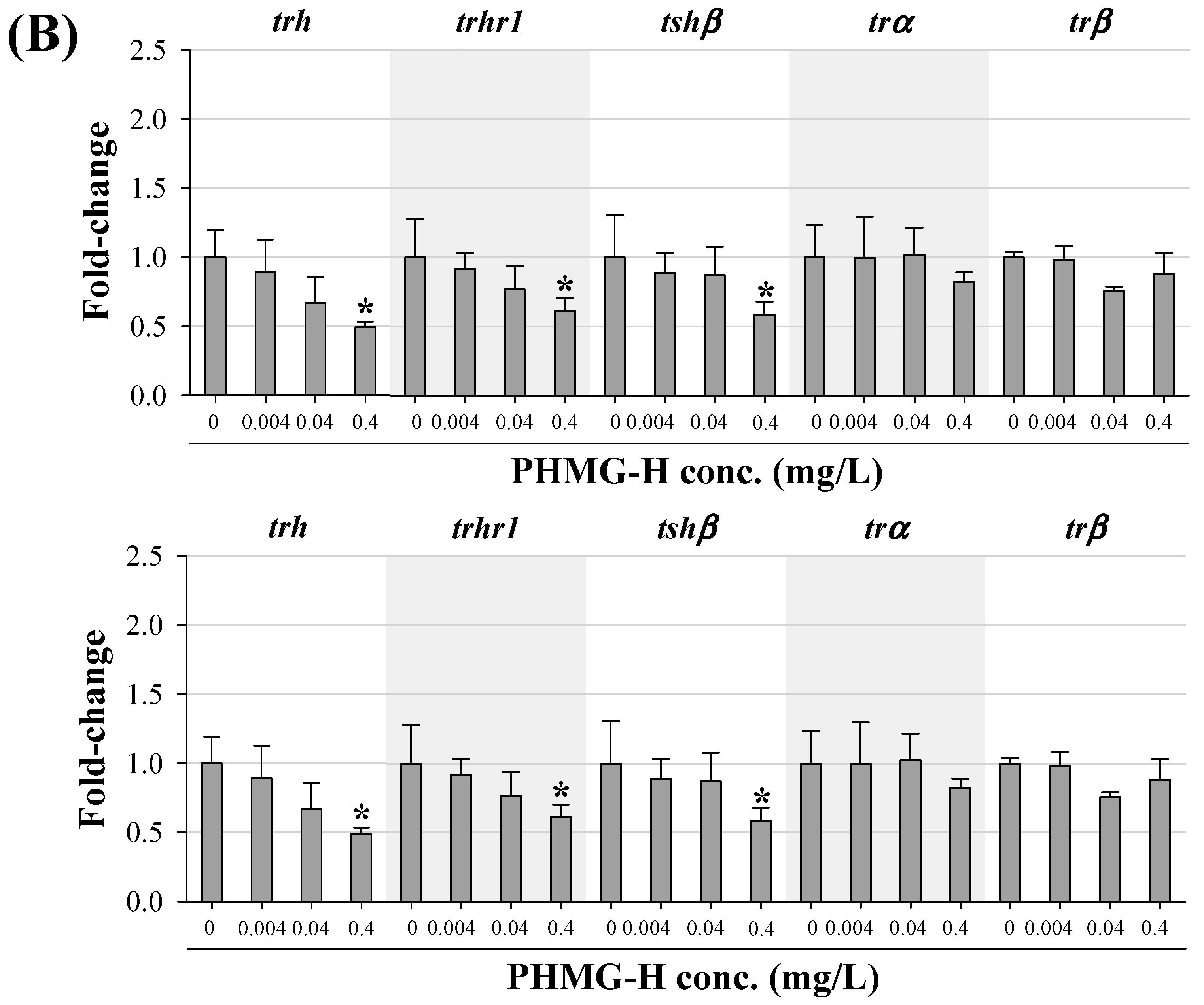
3.3. Transcriptional Changes in Genes Related to HPT Axis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asiedu-Gyekye, I.J.; Mahmood, S.A.; Awortwe, C.; Nyarko, A.K. A preliminary safety evaluation of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride. Int. J. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathurin, Y.K.; Koffi-Nevry, R.; Guehi, S.T.; Tano, K.; Oule, M.K. Antimicrobial activities of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride–based disinfectant against fungi isolated from cocoa beans and reference strains of bacteria. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitt, A.; Sofrata, A.; Silzen, V.; Sugars, R.V.; Gustafsson, A.; Gudkova, E.I.; Kazeko, L.A.; Ramberg, P.; Buhlin, K. Antimicrobial activity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in comparison to chlorhexidine using the quantitative suspension method. Ann. Clin. Microb. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.; Park, C.W.; Song, J.A.; Shin, D.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, K.H. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate aerosol particles induce pulmonary inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Hong, S.B. Humidifier disinfectant-associated lung injury: Six years after the tragic event. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2017, 80, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.S.; Hong, S.B.; Huh, J.W.; Do, K.H.; Jang, S.J.; Lim, C.M.; Chae, E.J.; Lee, H.; Jung, M.; et al. A cluster of lung injury cases associated with home humidifier use: An epidemiological investigation. Thorax 2014, 69, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, J.; Lee, E.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Kwon, G.Y.; Park, J.H.; Gwack, J.; et al. Inhalation toxicity of humidifier disinfectants as a risk factor of children’s interstitial lung disease in Korea: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 64430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, D.; Koh, Y.; Park, D.U.; Cheong, H.K.; Do, K.H.; Lim, C.M.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Leem, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; et al. Nationwide study of humidifier disinfectant lung injury in South Korea, 1994–2011. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.U.; Ryu, S.H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, Y.Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Lee, E.; Hong, S.B.; Do, K.H.; Cho, J.L.; et al. Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Kim, C.Y.; Ryu, B.; Kim, U.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, B.H.; Moon, J.; Jung, C.R.; Park, J.H. Respiratory toxicity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate exposure in zebrafish. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jung, K.J.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, K.; Kim, B. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces cytotoxicity through disruption of membrane integrity. Toxicology 2019, 414, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Ji, K. Exposure to humidifier disinfectants induces developmental effects and disrupts thyroid endocrine systems in zebrafish larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, Y.N.; Brusin, K.M.; Zobnin, Y.V.; Shchupak, A.Y.; Vishnevetskiy, M.K.; Sentsov, V.G.; Novikova, O.V.; Alekseenko, S.A.; Lebed’ko, O.A.; Puchkov, Y.B. Acute cholestatic liver injury caused by polyhexamethyleneguanidine hydrochloride admixed to ethyl alcohol. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Seo, D.S. Toxicity of humidifier disinfectant polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride by two-week whole body-inhalation exposure in rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 33, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Seo, D.S.; Lee, M.J.; Cha, H.G. Immunohistochemical characterization of oxidative stress in the lungs of rats exposed to the humidifier disinfectant polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 32, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.N.; Zerin, T.; Podder, B.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Cytotoxicity and gene expression profiling of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride in human alveolar A549 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poštulková, E.; Kopp, R. Guanicid and phmg toxicity tests on aquatic organisms. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2016, 64, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, D.; Ryu, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.I.; Hong, S.J. Early-life exposure to humidifier disinfectant determines the prognosis of lung function in children. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Nam, M.W.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, H.C.; Mun, E.C.; Park, S.Y. Mental health impact on a humidifier disinfectant disaster victim: A case report. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 32, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deal, C.K.; Volkoff, H. The role of the thyroid axis in fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 596585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Jia, Y.F.; Chen, N.; Bian, W.P.; Li, Q.K.; Ma, Y.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Pei, D.S. Zebrafish as a model system to study toxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.U.; Ryu, S.H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Roh, H.S.; Cha, W.S.; Park, D. Estimation of humidifier disinfectant amounts inhaled into the respiratory system. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2016, 42, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, D.U.; Lee, S.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Zoh, K.E. Comprehensive review on humidifier disinfectant (HD) products, focusing on the number of products and their disinfectant type. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2020, 46, 481–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.T.; Colicino, E.G.; DiPaola, E.J.; Al-Hasnawi, H.J.; Whipps, C.M. Evaluating the effectiveness of common disinfectants at preventing the propagation of Mycobacterium spp. isolated from zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 178, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council on Animal Care (CCAC). CCAC Guidelines: Zebrafish and Other Small, Warm-Water Laboratory Fish; CCAC Publishing: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2020; ISBN 978-0-919087-84-2. Available online: https://ccac.ca/Documents/Standards/Guidelines/CCAC_Guidelines-Zebrafish_and_other_small_warm-water_laboratory_fish.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.U.; Park, J.; Yang, K.W.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Oh, H.B. Properties of polyhexamethylene guanidine (PHMG) associated with fatal lung injury in Korea. Molecules 2020, 25, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.U.; Friesen, M.C.; Roh, H.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Koh, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Estimating retrospective exposure of household humidifier disinfectants. Indor Air 2015, 25, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Suh, S. Health risks of chemicals in consumer products: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Hwang, G.W.; Naganuma, A.; Chung, K.H. Adverse health effects of humidifier disinfectants in Korea: Lung toxicity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, K.M.; Miller, G.W.; Chen, X.; Yaghoobi, B.; Puschner, B.; Lein, P.J. Effects of thyroid hormone disruption on the ontogenetic expression of thyroid hormone signaling genes in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 272, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, T.W.K.; Khezri, A.; Lewandowska-Sabat, A.M.; Henry, T.; Ropstad, E. Endocrine disruptors affect larval zebrafish behavior: Testing potential mechanisms and comparisons of behavioral sensitivity to alternative biomarkers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 193, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.H.; Zhou, E.X.; Yang, Z.L. Waterborne exposure to BPS causes thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0176927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, F.; Diao, X. Thyroid disruption in zebrafish larvae by short-term exposure to bisphenol AF. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13069–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shkil, F.; Siomava, N.; Voronezhskaya, E.; Diogo, R. Effects of hyperthyroidism in the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles of zebrafish, with notes on evolutionary developmental pathology (Evo-Devo-Path). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Gui, W.; Zhu, G. Thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae following exposure to hexaconazole and tebuconazole. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 138, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Xie, P.; Zhang, X. Changes in plasma thyroid hormones and cortisol levels in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) exposed to the extracted microcystins. Chemosphere 2008, 74, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geyten, S.; Byamungu, N.; Reyns, G.E.; Kuhn, E.R.; Darras, V.M. Iodothyronine deiodinases and the control of plasma and tissue thyroid hormone levels in hyperthyroid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Endocrinol. 2005, 184, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Shi, X.J.; Liu, C.S.; Yu, K.; Zhou, B.S. Exposure to DE-71 alters thyroid hormone levels and gene transcription in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis of zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, A.; Valverde, R.C. Thyroid hormone deiodination in fish. Thyroid 2005, 15, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, R.; Maquet, E.; Zoenen, M.; Dadhich, R.; Costagliola, S. TSH receptor function is required for normal thyroid differentiation in zebrafish. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1579–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stinckens, E.; Vergauwen, L.; Blackwell, B.R.; Ankley, G.T.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Knapen, D. Effect of thyroperoxidase and deiodinase inhibition on anterior swim bladder inflation in the zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6213–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Accession No. | Primer | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | NM_131031 | Forward | TGCTGTTTTCCCCTCCATTG |
| Reverse | TCCCATGCCAACCATCACT | ||
| rpl8 | NM_200713 | Forward | TTGTTGGTGTTGTTGCTGGT |
| Reverse | GGATGCTCAACAGGGTTCAT | ||
| trh | NM_001012365 | Forward | GCTCTCTCCGTCGGTCTGTT |
| Reverse | GCGAGATCCGTGCTGATGA | ||
| trhr1 | NM_001114688 | Forward | CAGTGCCATCAACCCTCTGA |
| Reverse | GGCAGCGCGGAACTTCT | ||
| tshβ | NM_181494 | Forward | GCAAAACCCACAGTGATGAATG |
| Reverse | TGCACAGGTTTGGAGCATCTC | ||
| tra | NM_131396 | Forward | GCCGCTTCCTGCACATG |
| Reverse | AGCGGCGGGAACAGTTC | ||
| trβ | NM_131340 | Forward | TGGCATGGCTAAGACTTGGT |
| Reverse | TCAGCTTCCGCTTGGCTAA | ||
| tpo | EU267076 | Forward | GTTCGGTCTGCCAGGACACT |
| Reverse | TCCAAGCGCTTCAGCAGAGT | ||
| tg | XM_689200 | Forward | GTCTCTTGAGTGTTCGAATGACAAG |
| Reverse | AAAGGCGGGCCATTAAGG | ||
| nis | NM_001089391 | Forward | AATCAAGCCACAGGCCTGAA |
| Reverse | AATGTGCAGATGAGCCCAGTT | ||
| deio1 | BC076008 | Forward | AACTTGGAGGAGAGGCTTGCT |
| Reverse | AGGGCATGGAGGGTCTTCTT | ||
| deio2 | NM_212789 | Forward | CGCGAAATGGGCTTGCT |
| Reverse | CCAGGCAAAATCTGCAAAGTTA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, H.; Ji, K. Developmental Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption of Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride and Humidifier Disinfectant in Zebrafish Larvae. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114884
Park S, Kim H, Ji K. Developmental Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption of Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride and Humidifier Disinfectant in Zebrafish Larvae. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114884
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Suhyun, Hyojin Kim, and Kyunghee Ji. 2021. "Developmental Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption of Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride and Humidifier Disinfectant in Zebrafish Larvae" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114884
APA StylePark, S., Kim, H., & Ji, K. (2021). Developmental Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption of Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride and Humidifier Disinfectant in Zebrafish Larvae. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114884







