Transmission Phase Control of Annular Array Transducers for Efficient Second Harmonic Generation in the Presence of a Stress-Free Boundary
Abstract
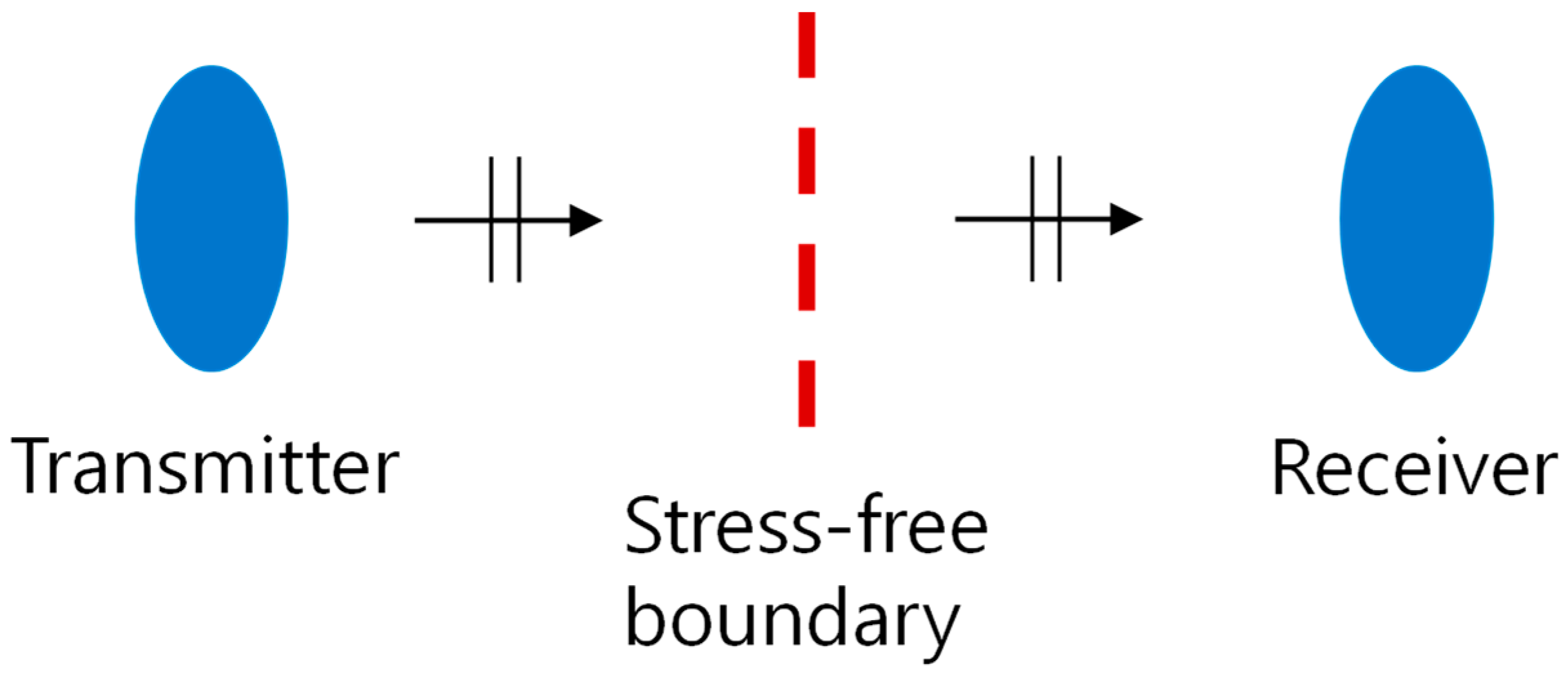
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
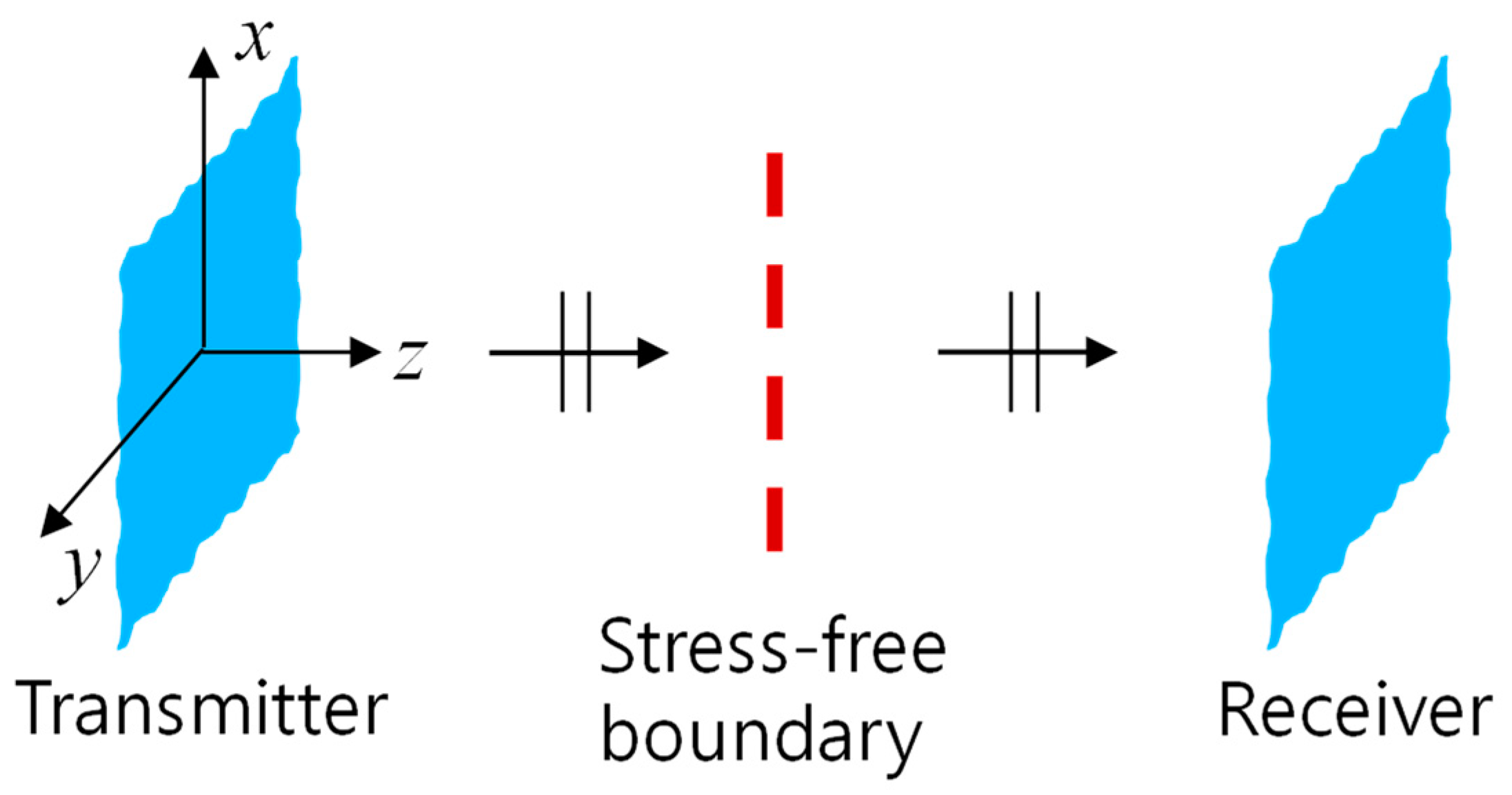
2.1. Pure Plane Wave
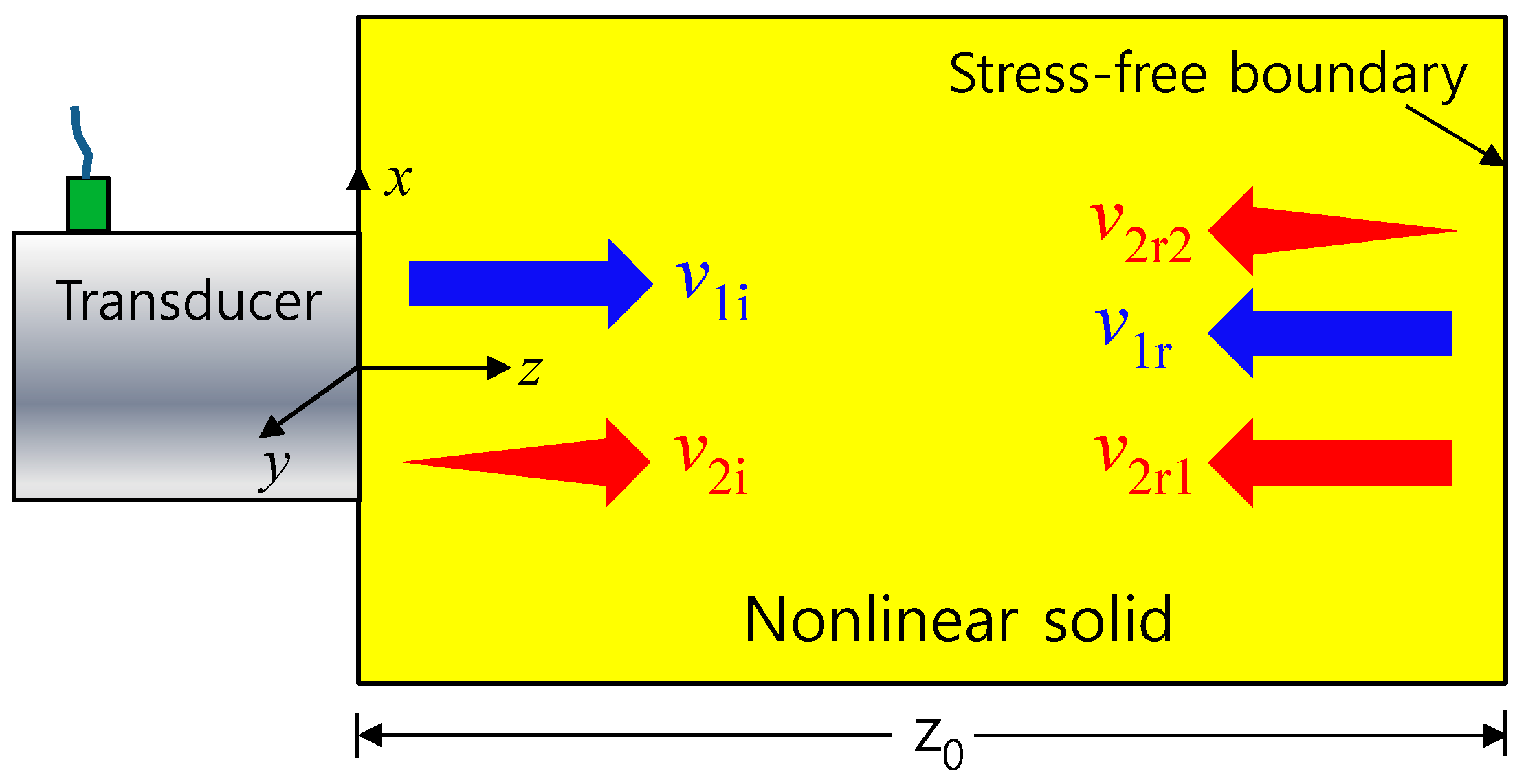
2.2. Single Element Transducer
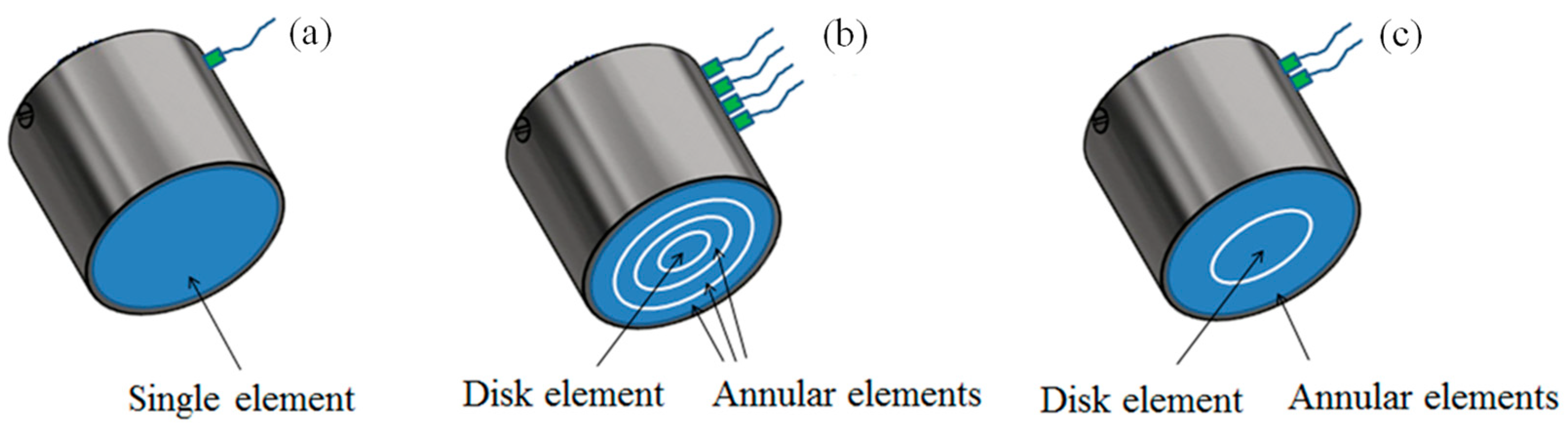
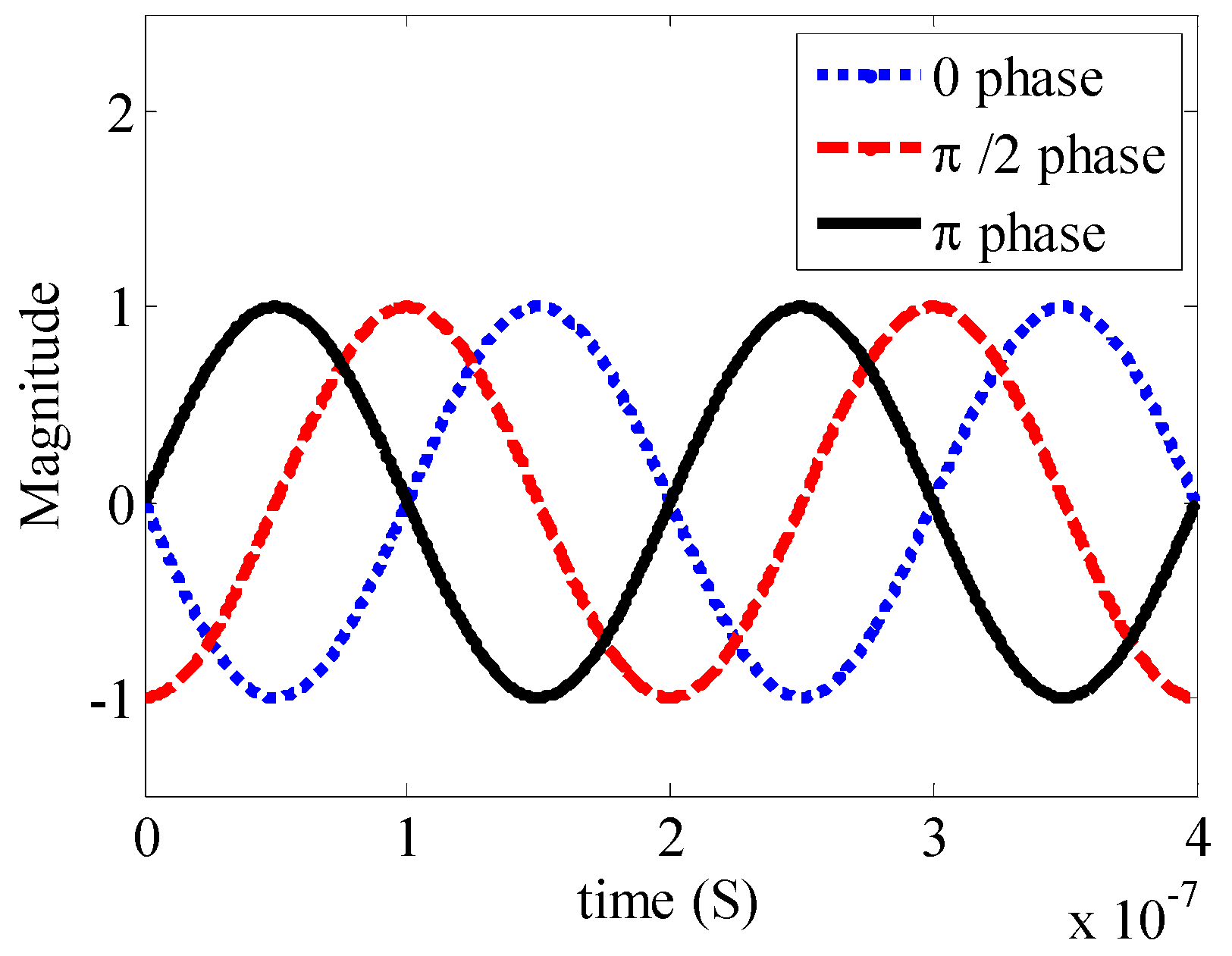
2.3. Annular Array Transducer with Phase-Shifted Radiation
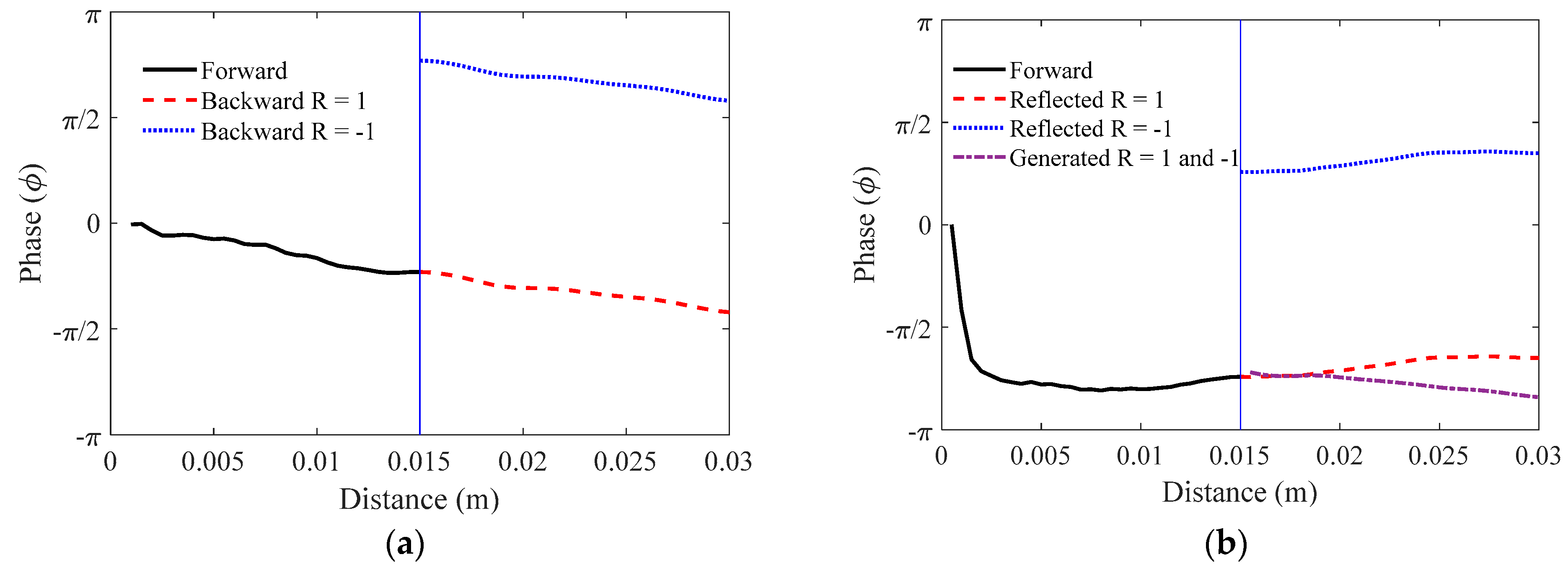
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
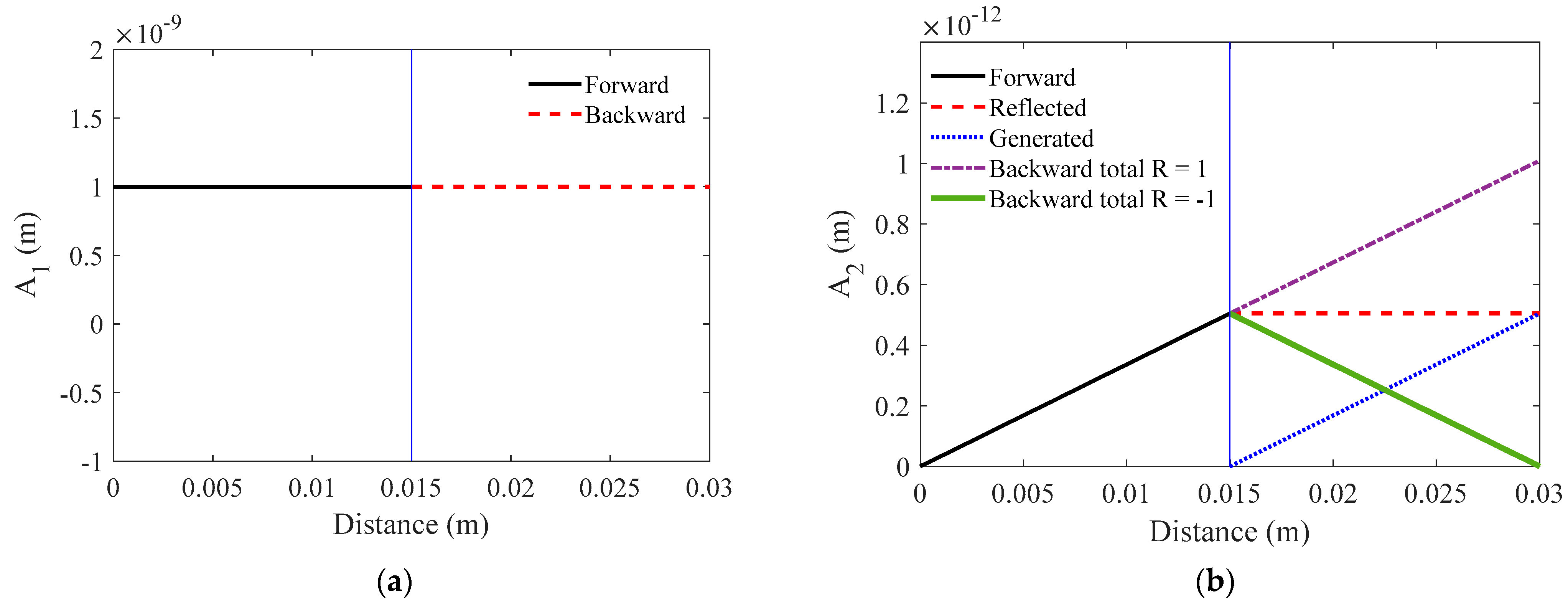
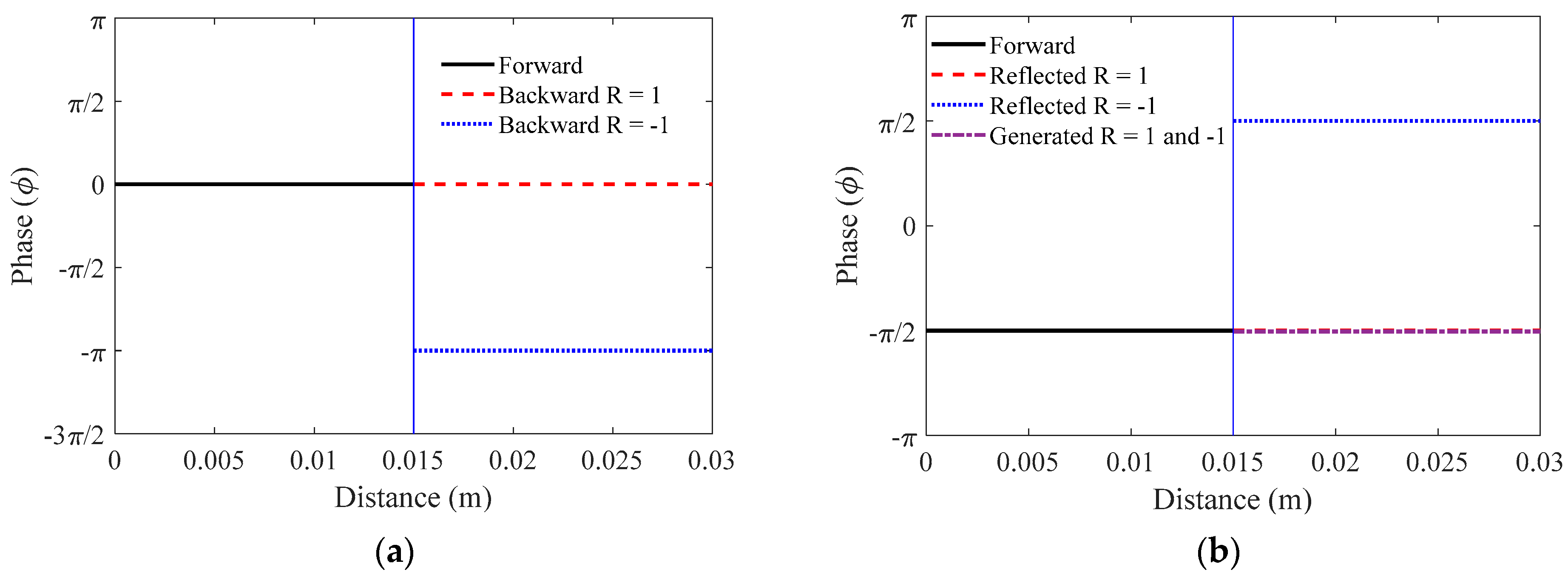
3.1. Pure Plane Wave
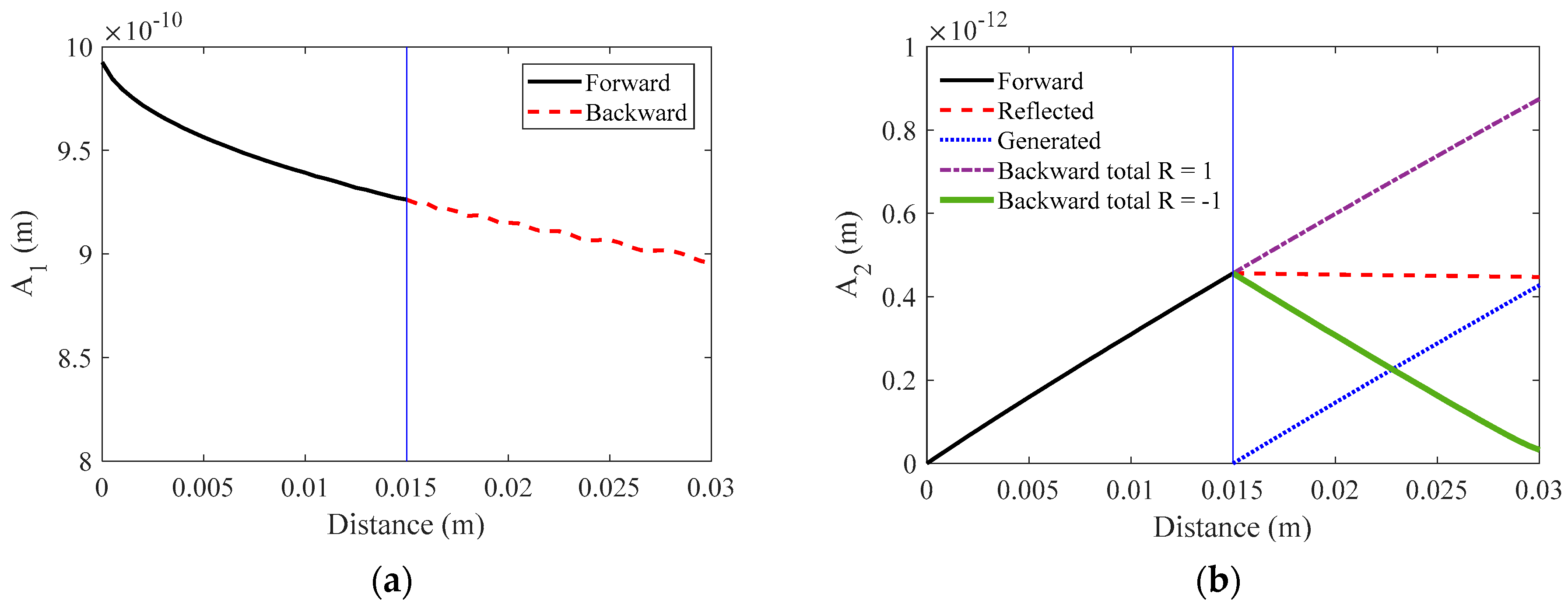
3.2. Single Element Transducer
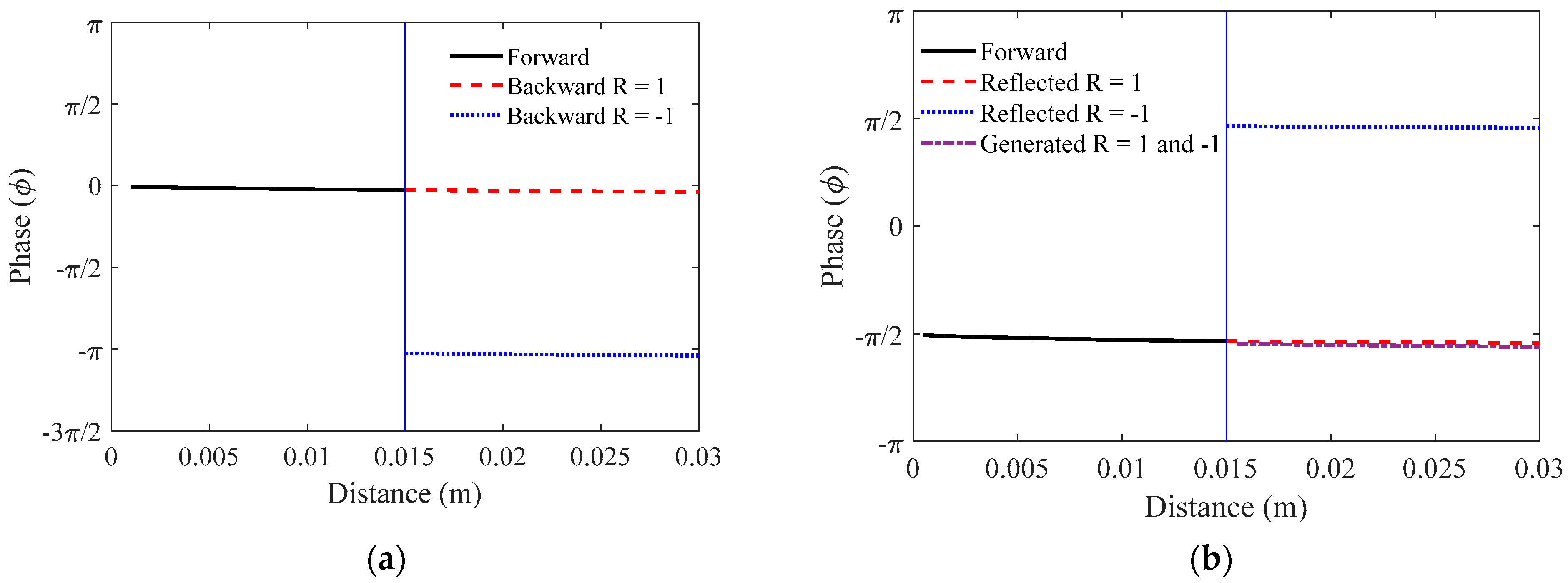
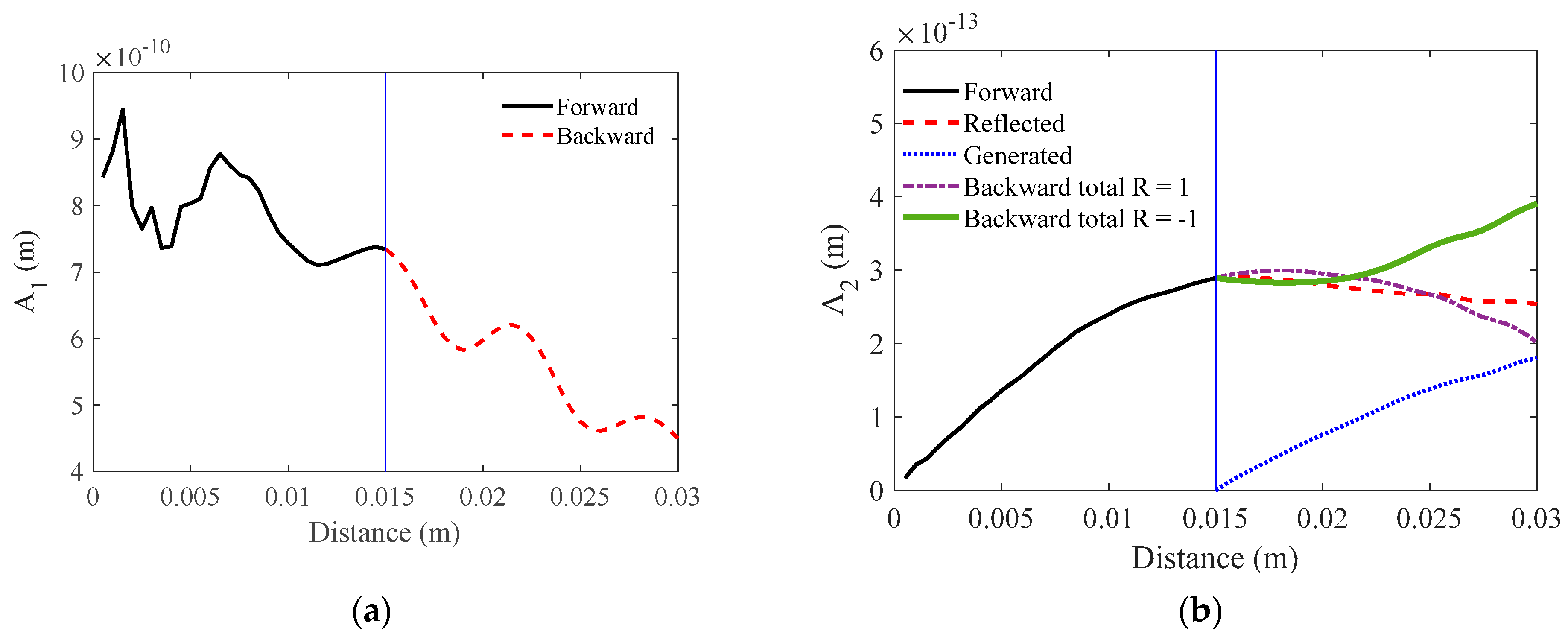
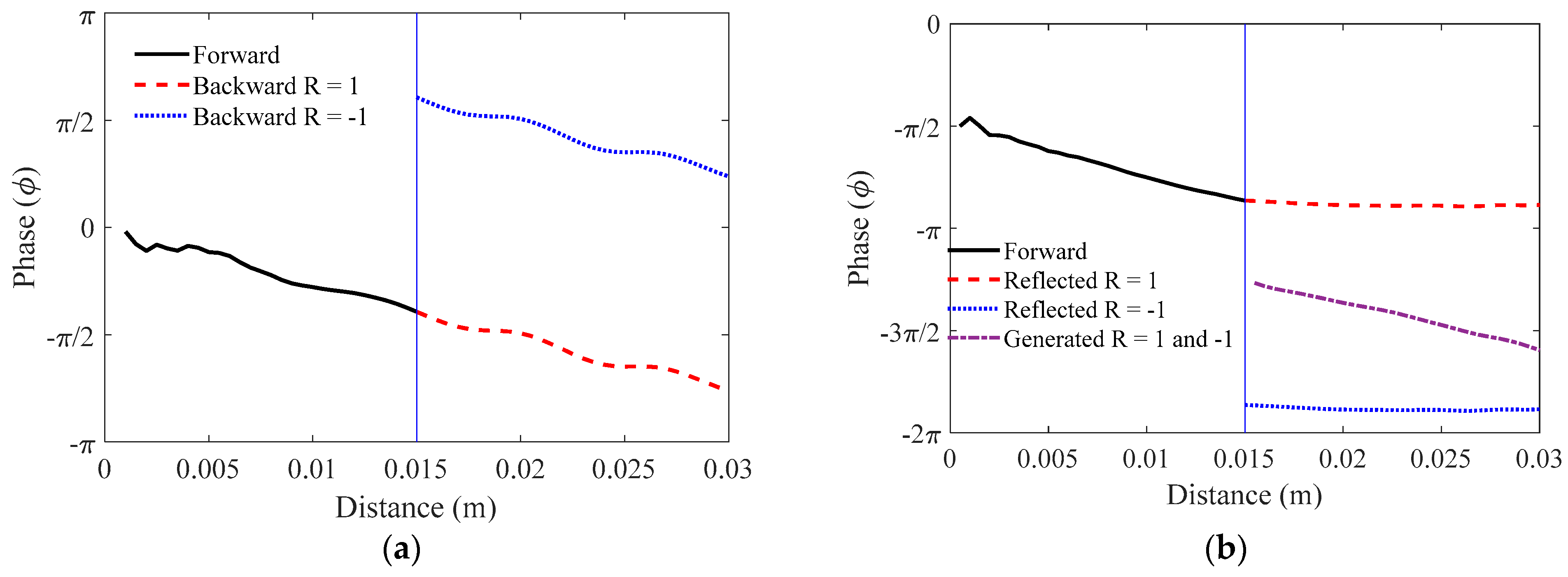
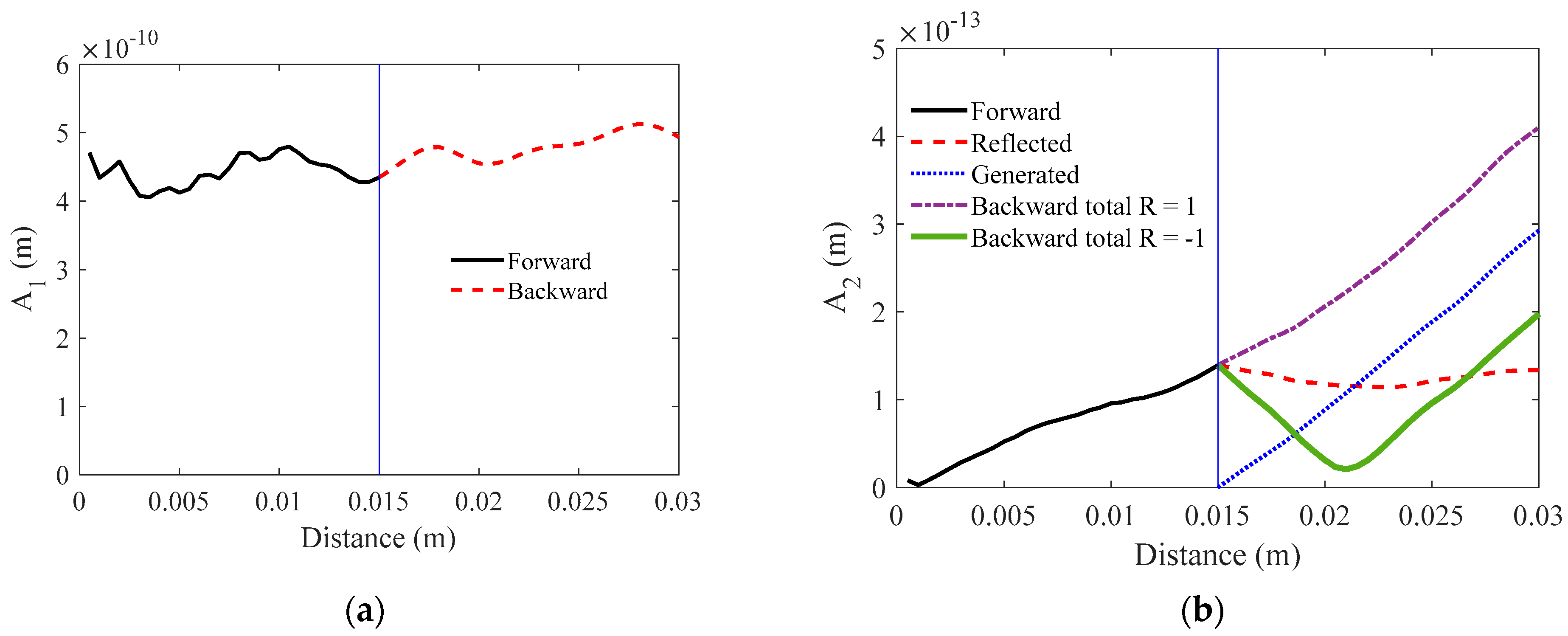
3.3. Annular Array Transducer with Phase-Shifted Radiation
- (1)
- Phase shift of π between adjacent elements.
- (2)
- Summary of phase−shifted simulation results.
4. Time Delay Focusing and Received Amplitudes
5. Comparison of Simulation Results and discussion
5.1. Fundamental and Second Harmonic Amplitudes
5.2. Uncorrected Nonlinear Parameter
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Plane or diffracted waves emitted by single−element transducers are difficult to use to generate second harmonic amplitudes or to measure the nonlinear properties of solids in the pulse-echo mode. This is because the two components of the second harmonic are out of phase with each other and cancel at the receiver position.
- (2)
- The transmission phase shift can be a useful tool in the pulse-echo SHG of relatively thin samples. Moreover, the design of four−element transducers can be optimized in terms of shape and size along with the amount of phase shift to obtain the maximum possible SHG. Array transducers with four elements offer distinct advantages over two elements, as they give more options when applying the phase shift or adjusting the focal length.
- (3)
- To measure the nonlinear parameter (β) of a specimen with much improved second harmonic amplitude, compared to a single element transducer, a four−element array transducer using a beam focused at the specimen boundary may be a good alternative.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Achenbach, J. Quantitative nondestructive evaluation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Park, I. Microstructural degradation assessment in pressure vessel steel by harmonic generation technique. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, A.; Rao, B.P.C.; Mahadevan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Raj, B. Microstructural characterization of M250 grade maraging steel using nonlinear ultrasonic technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 6719–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, D.C.; Balzar, D.; Purtscher, P.T. Nonlinear ultrasonic assessment of precipitation hardening in ASTM A710 steel. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, J.H.; Yost, W.T. Effect of precipitate coherency strains on acoustic harmonic generation. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Maev, R.G.; Solodov, I.Y. Nonlinear acoustic applications for material characterization: A review. Can. J. Phys. 1999, 77, 927–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulen, F.V.; Haumesser, L. Evaluation of B/A nonlinear parameter using an acoustic self-calibrated pulse-echo method. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 214106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, S.K.; Barnard, D.J. A calibration technique for ultrasonic immersion transducers and challenges in moving to-wards immersion based harmonic imaging. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2019, 38, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jeong, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Dual element transducer approach for second harmonic generation and material nonlinearity measurement of solids in the pulse echo method. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2020, 39, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Cho, S.; Shin, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Optimization and Validation of Dual Element Ultrasound Transducers for Improved Pulse-echo Measurements of Material Nonlinearity. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13596–13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, D.-G.; Jhang, K.-Y. A method to estimate the absolute ultrasonic nonlinearity parameter from relative measure-ments. Ultrasonics 2017, 77, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torello, D.; Thiele, S.; Matlack, K.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Qu, J.; Jacobs, L.J. Diffraction, attenuation, and source corrections for nonlinear Rayleigh wave ultrasonic measurements. Ultrasonics 2015, 56, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Jeong, H.; Hu, H. Modeling nonlinear Rayleigh wave fields generated by angle beam wedge transducers—A theoretical study. Wave Motion 2016, 67, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Jeong, H.; Xu, G. Characterization of Aging Treated 6061 Aluminum Alloy Using Nonlinear Rayleigh Wave. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2019, 38, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Su, Z.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, L.; Qing, X. Modeling nonlinearities of ultrasonic waves for fatigue damage characteriza-tion: Theory, simulation, and experimental validation. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Deng, M.; Xuan, F.-Z.; Liu, C.-J. Cumulative second-harmonic analysis of ultrasonic Lamb waves for ageing behavior study of modified-HP austenite steel. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, C.-J.; Deng, M.; Ma, C.; Xuan, F.-Z. Fatigue Damage Evaluation Using Nonlinear Lamb Waves with Quasi Phase-Velocity Matching at Low Frequency. Materials 2018, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christopher, T. Experimental investigation of finite amplitude distortion-based, second harmonic pulse echo ultrasonic imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1998, 45, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, I.R.S.; Averkiou, M.A.; Hamilton, M.F. Second-harmonic generation in a sound beam reflected and transmitted at a curved interface. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnalah, D.K.; Jakjoud, H.; Nadi, M. Pulse echo method for nonlinear ultrasound parameter measurement. Tech. Acoust. 2007, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Cho, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Acoustic nonlinearity parameter measurements in a pulse-echo setup with the stress-free reflection boundary. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, EL237–EL242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.O.; Tennison, M.A.; Buck, O. Reflections of harmonics generated by finite-amplitude waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1968, 44, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, F.A.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jacob, L.J.; Qu, J. The generation of second harmonic waves in an isotropic solid with quadratic non linearity under the presence of a stress free boundary. Wave Motion 2013, 50, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.R.; Croxford, A.J.; Neild, S.A. Pulse-echo Harmonic Generation Measurements for Non-destructive Evaluation. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2014, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Jeong, H. Characterizing Microstructural Evolution of TP304 Stainless Steel Using a Pulse-echo Nonlinear Method. Materials 2020, 13, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Li, X.-B. Second-harmonic generation in focused beam fields of phased-array transducers in a nonlinear solid with a stress-free boundary. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2019, 1, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Jeong, H.; Cho, S.; Hu, H. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the pulse-echo nonlinearity acoustic sound fields of focused transducers. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Improvement of pulse-echo harmonic generation from stress-free boundary through phase shift of a dual element transducer. Ultrasonics 2018, 87, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazard, C.; Fisher, R.; Mills, D.; Smith, L.; Tbomemus, K.; Wodnicki, R. Annular array beamforming for 2D arrays with reduced system channels. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Honoluludoi, HI, USA, 5–8 October 2003; pp. 1859–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaptsis, G.; Liaptsis, D.; Wright, B.; Charlton, P. Focal law calculations for annular phased array transducers. e-J. NDT 2015, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Jeong, H.; Park, I.K. Optimal Design of Annular Phased Array Transducers for Material Nonlinearity Determination in Pulse–Echo Ultrasonic Testing. Materials 2020, 13, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeele, K.V.D.; Breazeale, M.A. Theoretical model to describe dispersive nonlinear properties of lead zirconate–titanate ceramics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



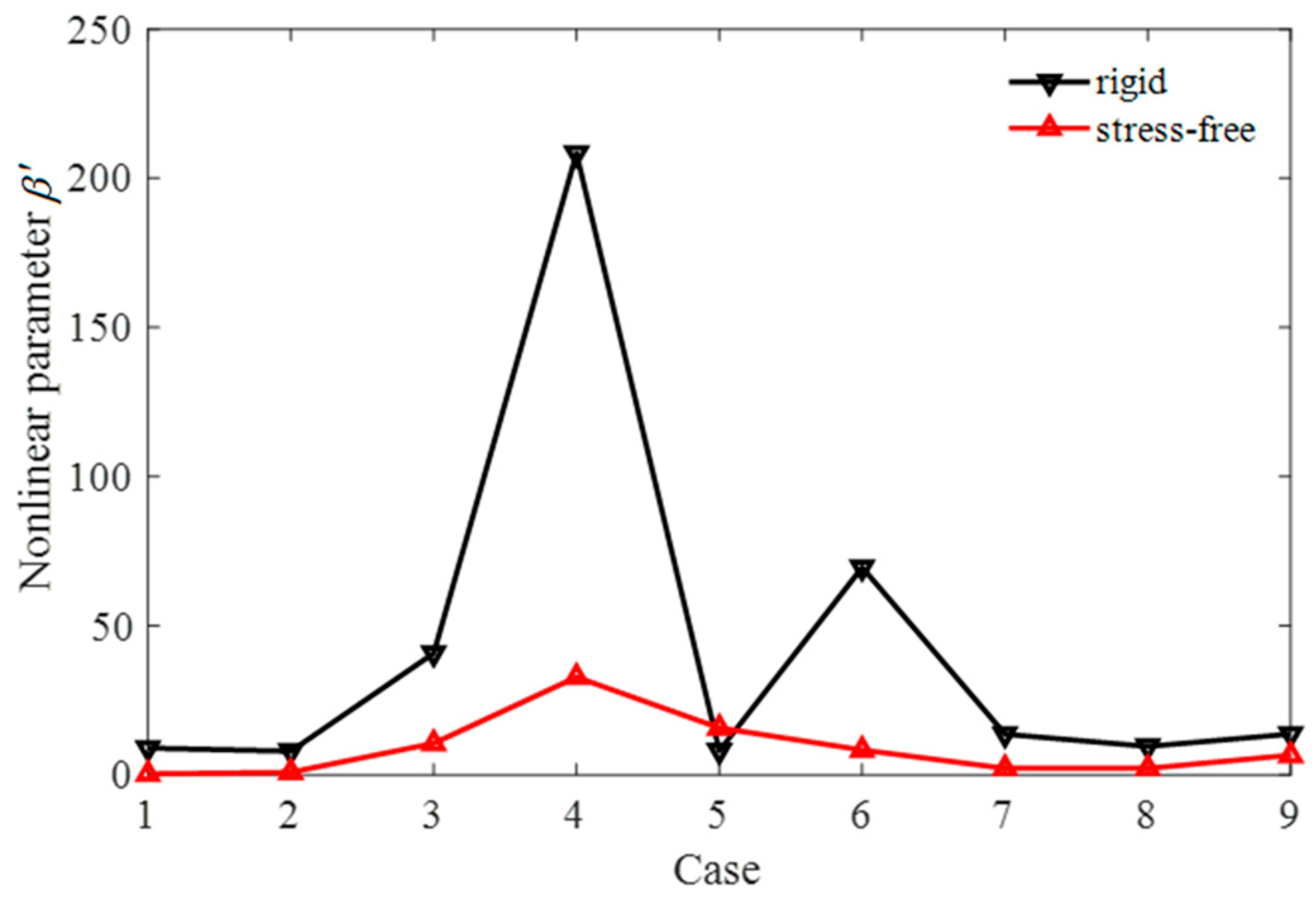
| Type | Case No. | Phase Shift | Fundamental (10−10 m) | Second Harmonic (10−13 m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk | Annular Elements | Rigid | Stress-Free | |||||
| Single element | 1 | - | - | - | - | 8.95 | 8.82 | 0.31 |
| Four element | 2 | 0 | π/4 | 2π/4 | 3π/4 | 3.78 | 1.39 | 0.16 |
| 3 | 0 | π/3 | 2π/3 | π | 1.62 | 1.31 | 0.34 | |
| 4 | 0 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 1.33 | 4.51 | 0.71 | |
| 5 | 0 | π | 2π | 3π | 4.51 | 2.02 | 3.92 | |
| Dual element | 6 | 0 | π/2 | - | - | 2.93 | 7.23 | 0.88 |
| 7 | 0 | 2π/3 | - | - | 5 | 4.18 | 0.67 | |
| 8 | 0 | π | - | - | 8.04 | 7.57 | 1.74 | |
| Focused | 9 | 0 | 1.16π | 3.10π | 5.78π | 4.94 | 4.09 | 1.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Shin, H. Transmission Phase Control of Annular Array Transducers for Efficient Second Harmonic Generation in the Presence of a Stress-Free Boundary. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114836
Jeong H, Shin H. Transmission Phase Control of Annular Array Transducers for Efficient Second Harmonic Generation in the Presence of a Stress-Free Boundary. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):4836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114836
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyunjo, and Hyojeong Shin. 2021. "Transmission Phase Control of Annular Array Transducers for Efficient Second Harmonic Generation in the Presence of a Stress-Free Boundary" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 4836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114836
APA StyleJeong, H., & Shin, H. (2021). Transmission Phase Control of Annular Array Transducers for Efficient Second Harmonic Generation in the Presence of a Stress-Free Boundary. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114836






