Effect of Magnetic Field on the Forced Convective Heat Transfer of Water–Ethylene Glycol-Based Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticles and Nanofluids
2.2. Experimental Methods
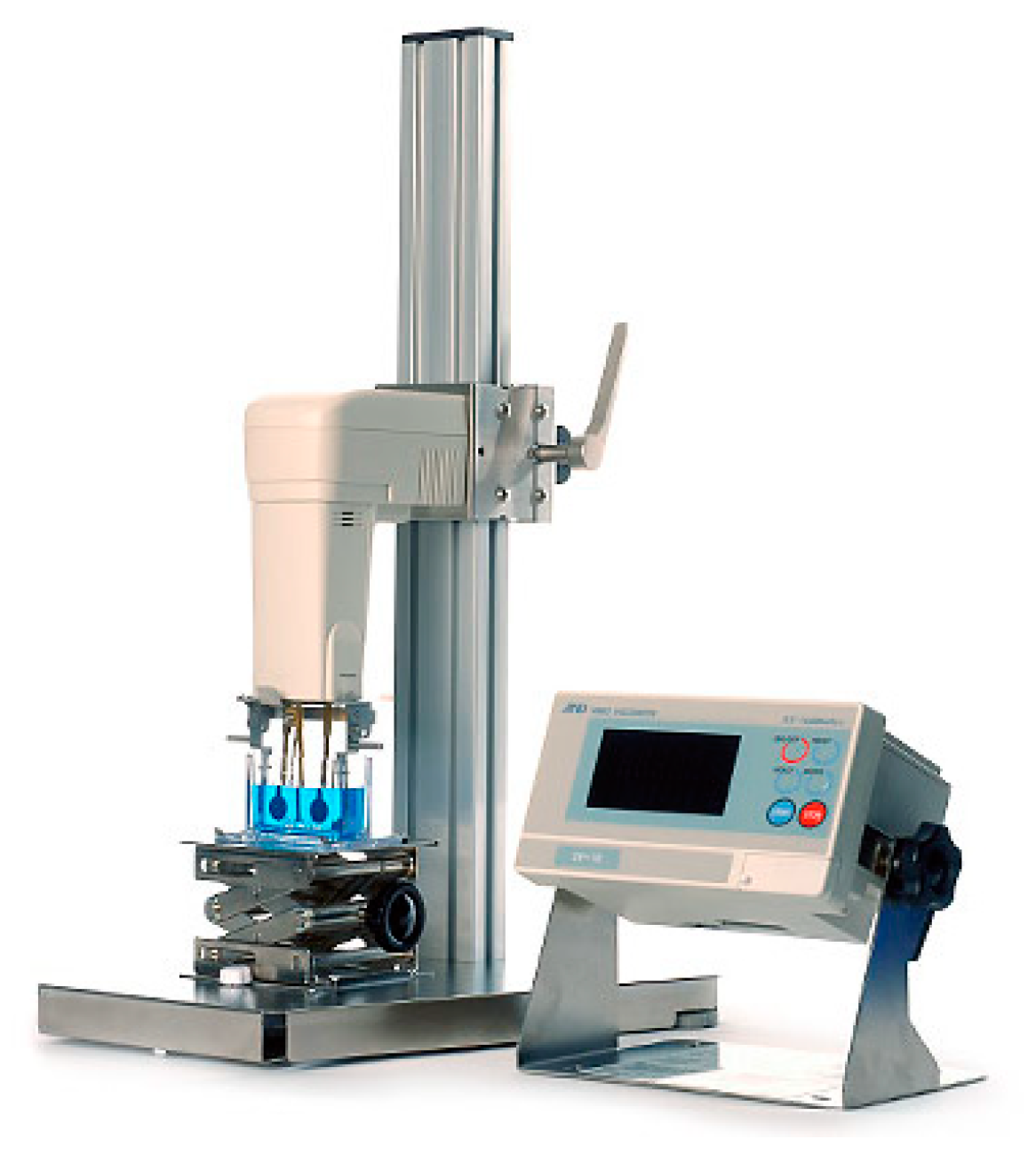
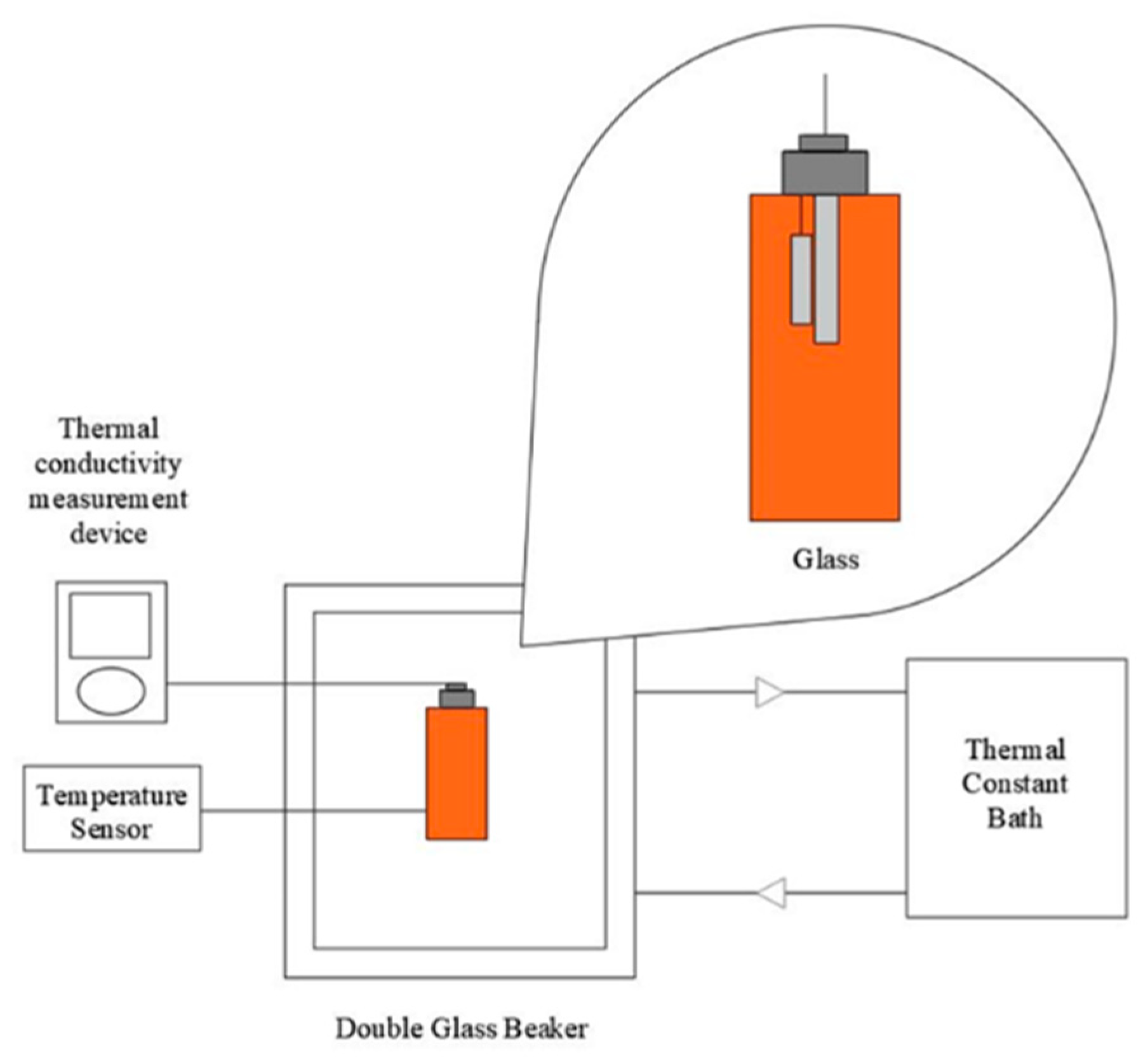
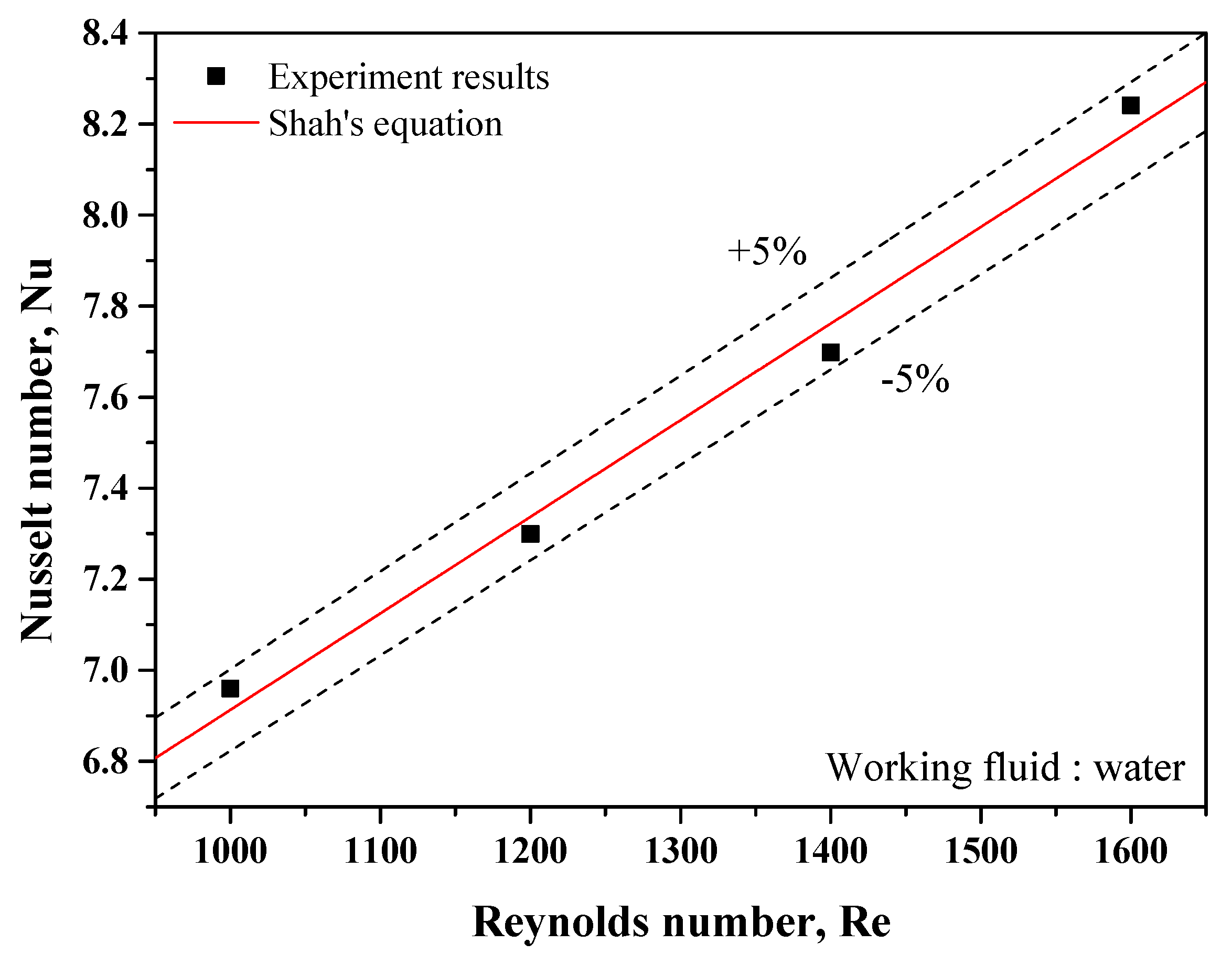
2.2.1. Thermal Conductivity Measurement
2.2.2. Viscosity Measurement
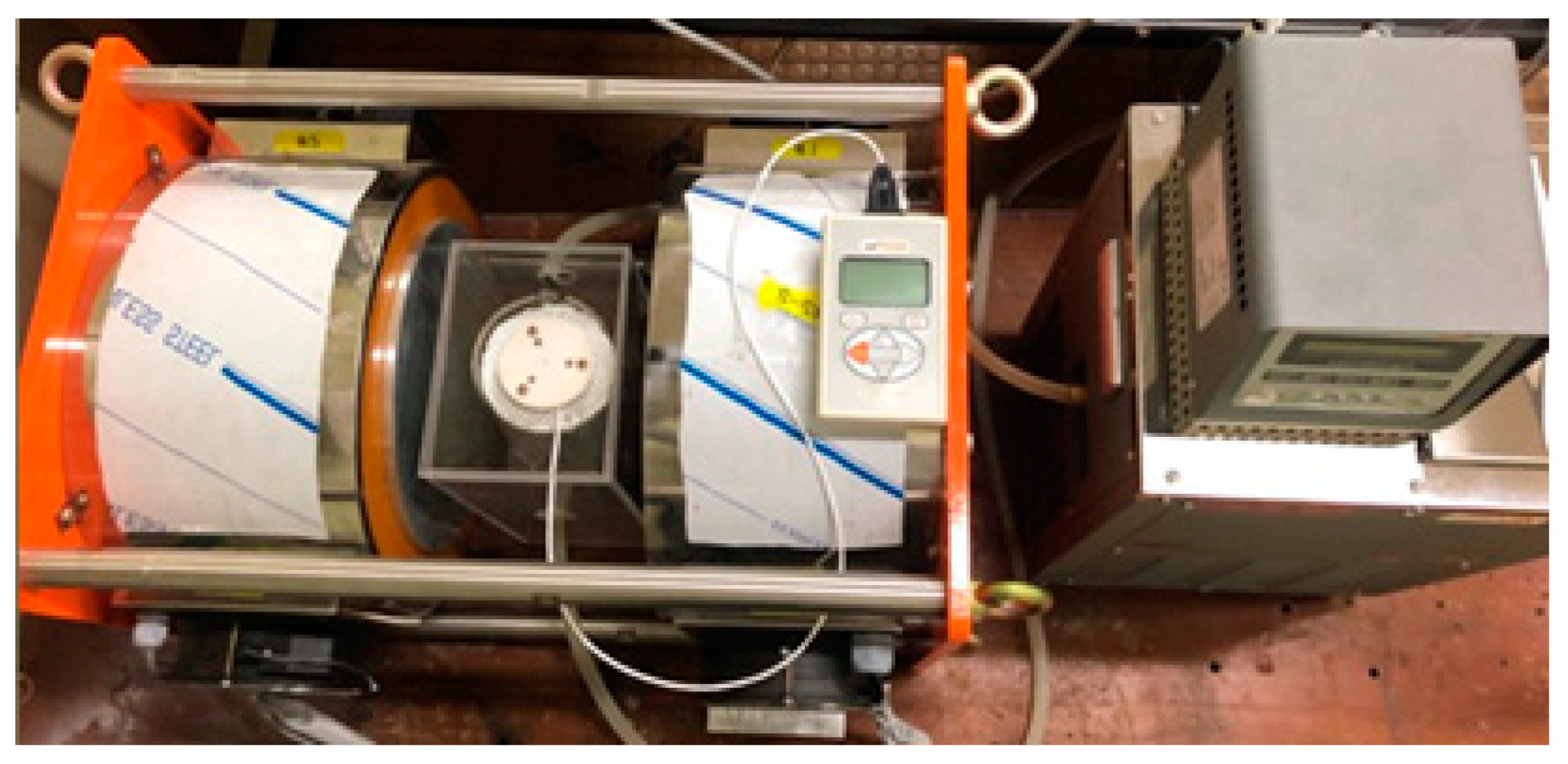
2.2.3. Measurement of Forced Convective Heat Transfer
2.3. Data Reduction
3. Results and Discussions
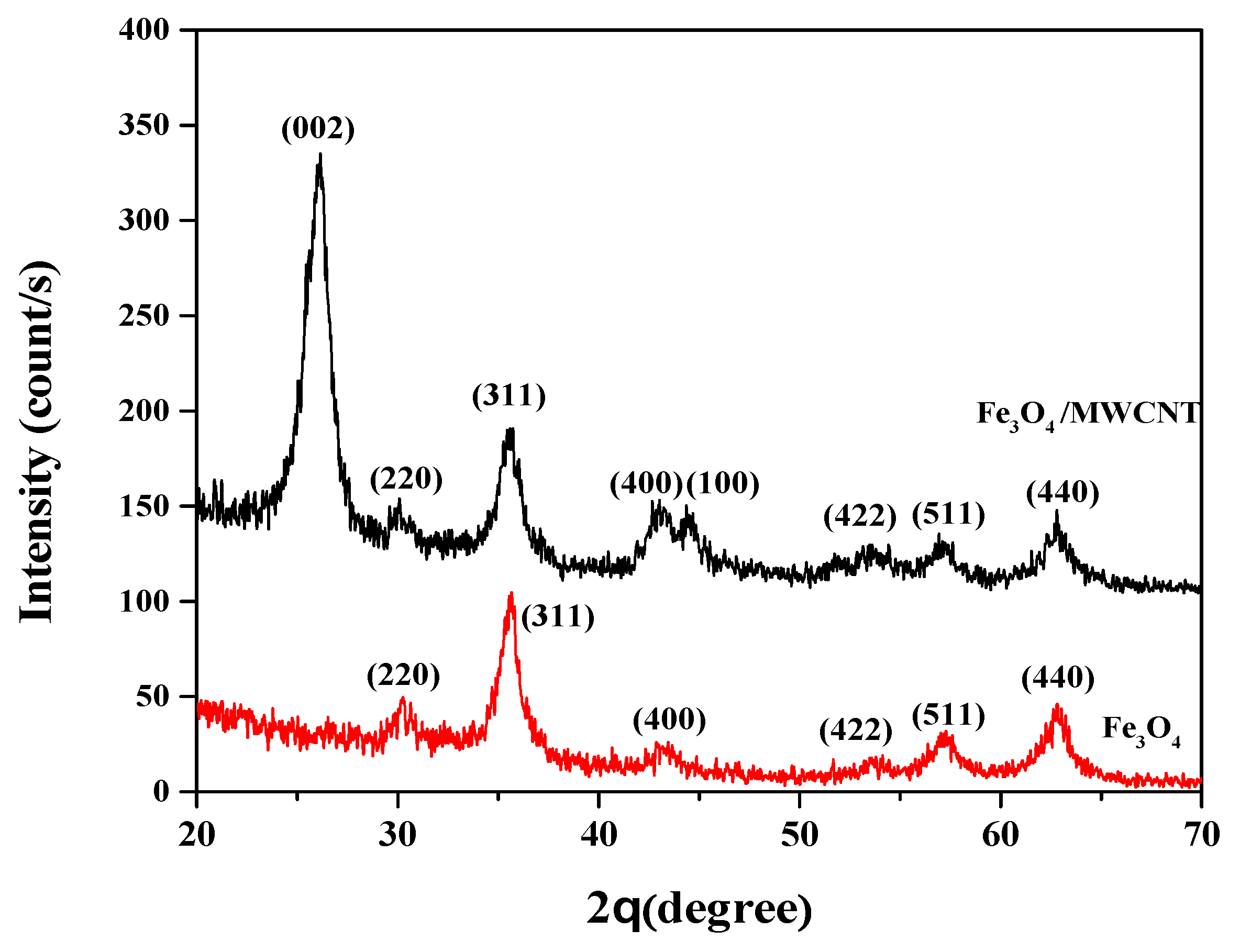
3.1. Characteristics of Nanoparticles
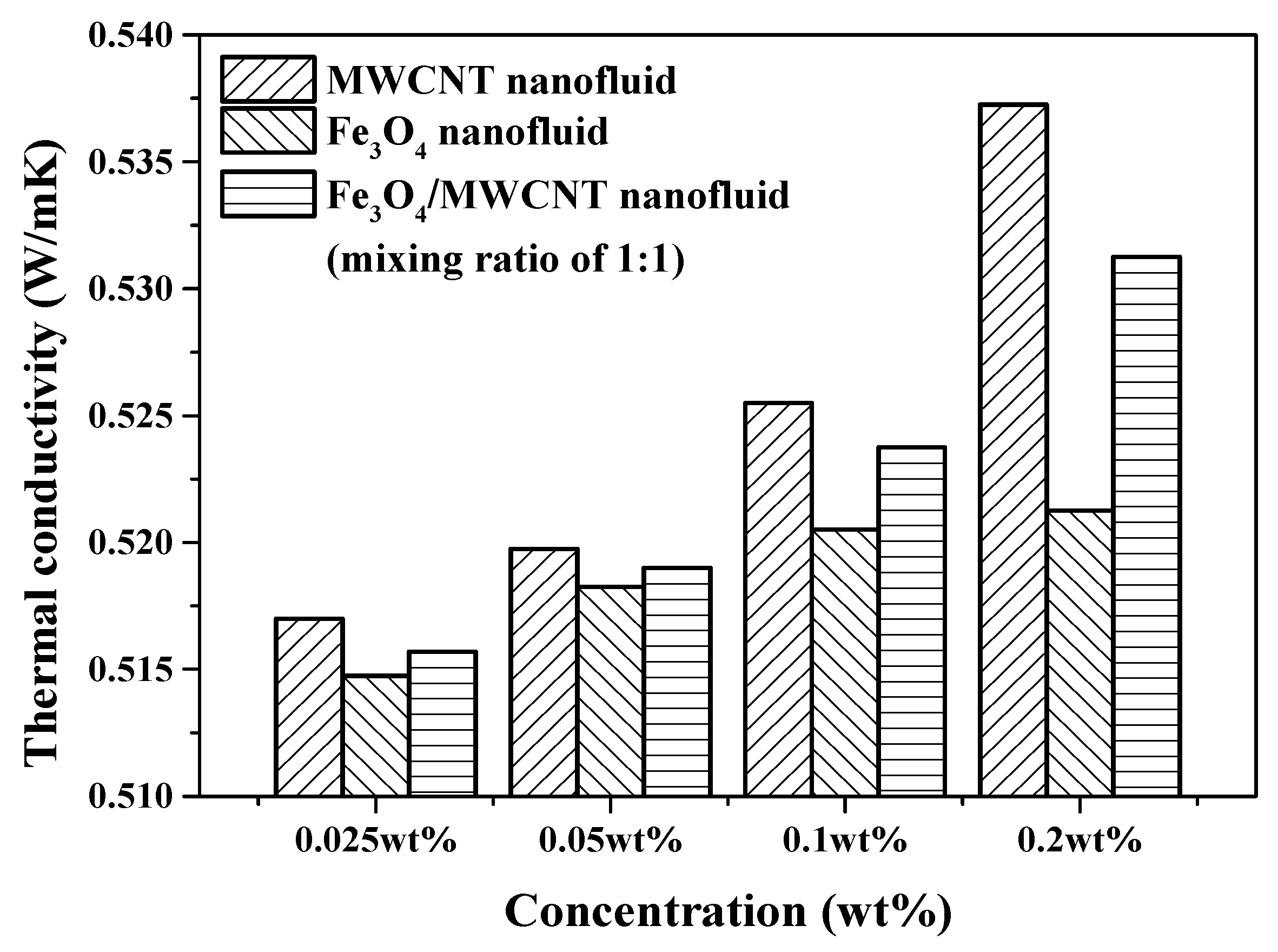
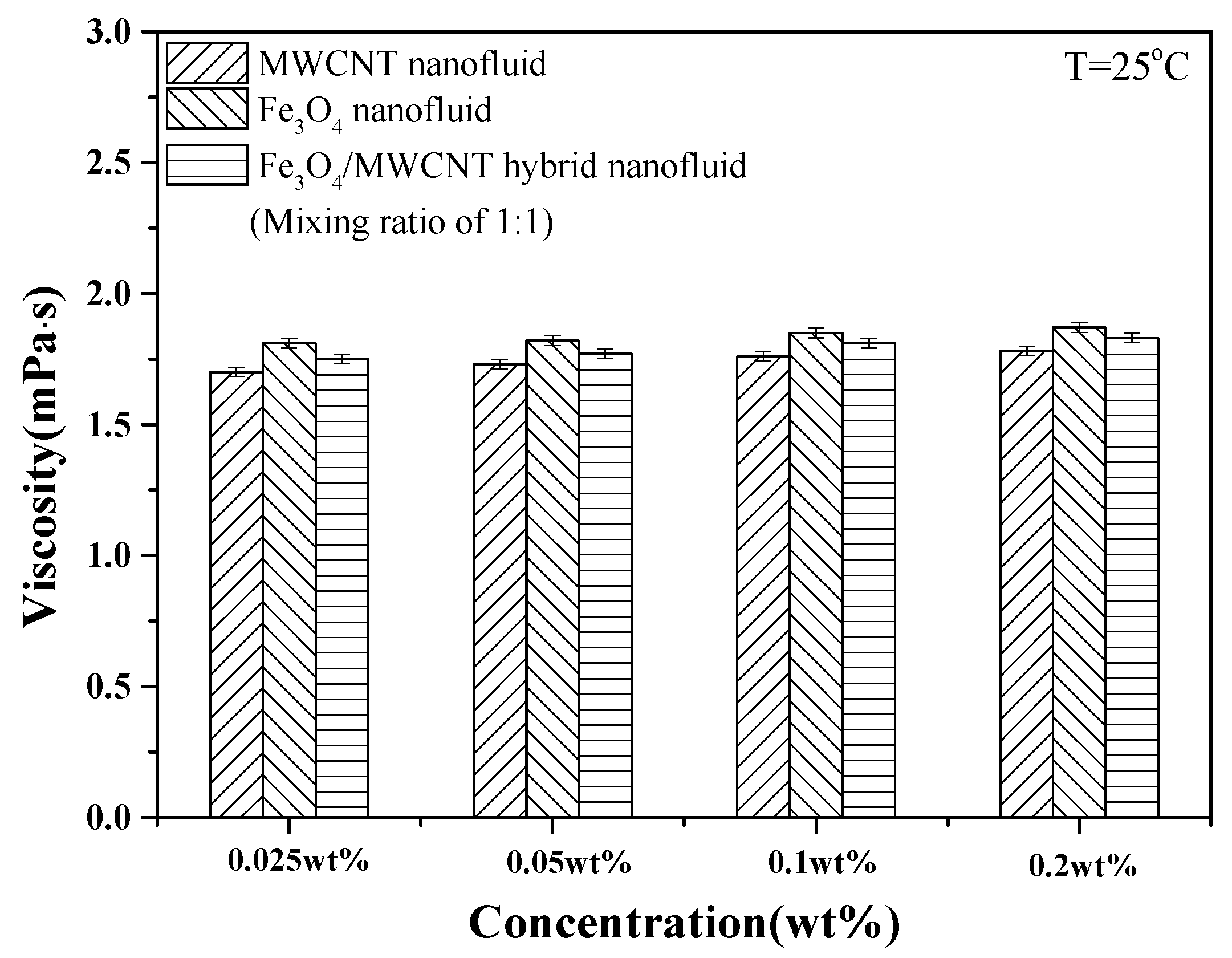
3.2. Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Hybrid Nanofluids
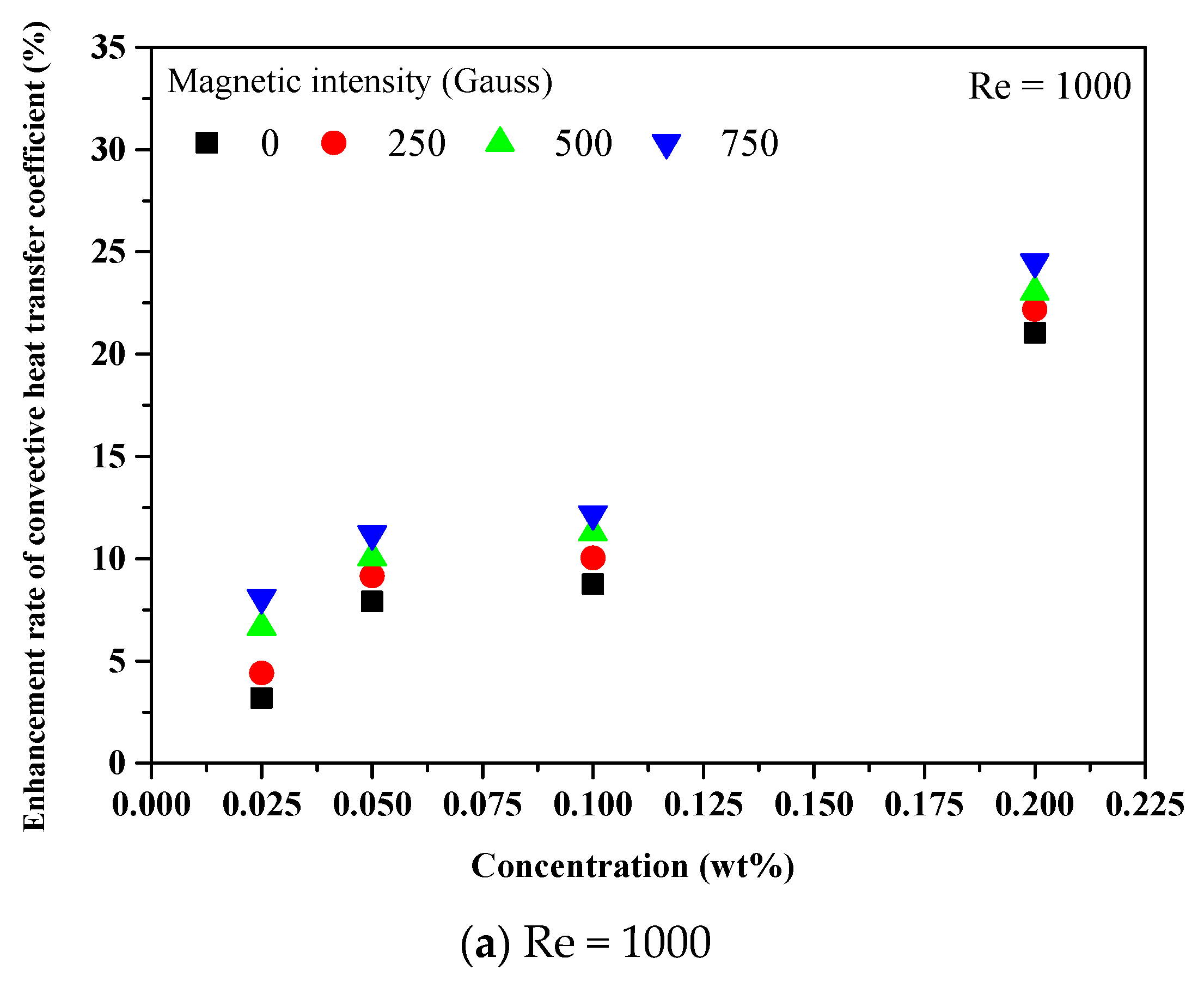
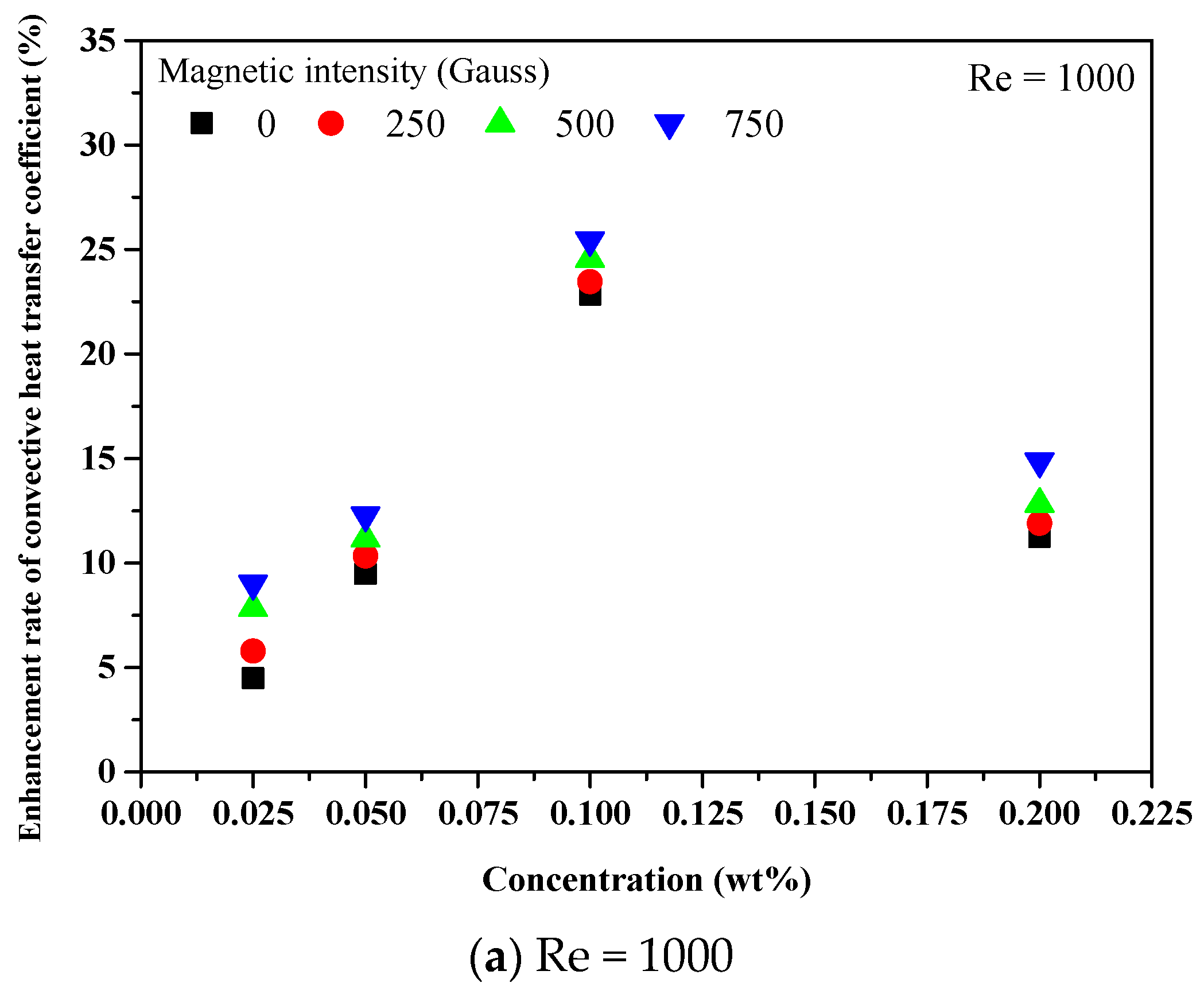
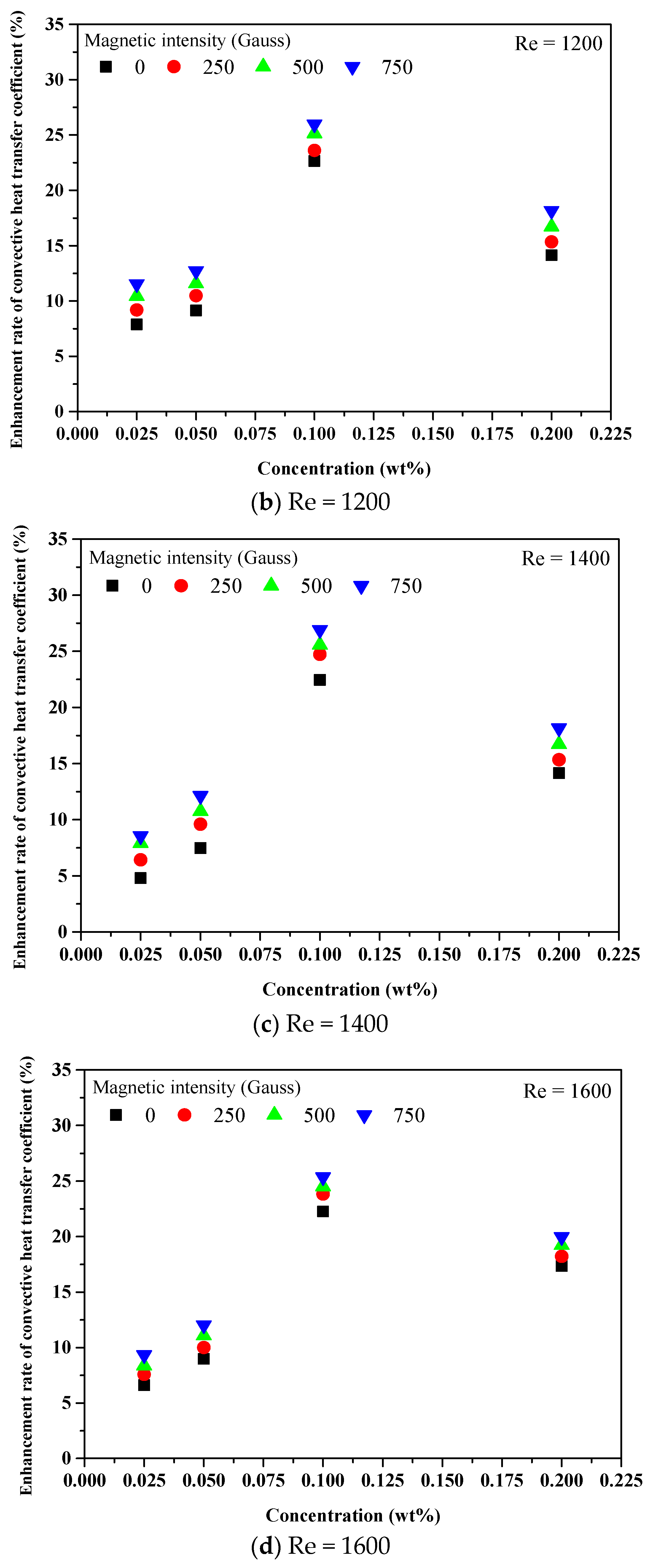
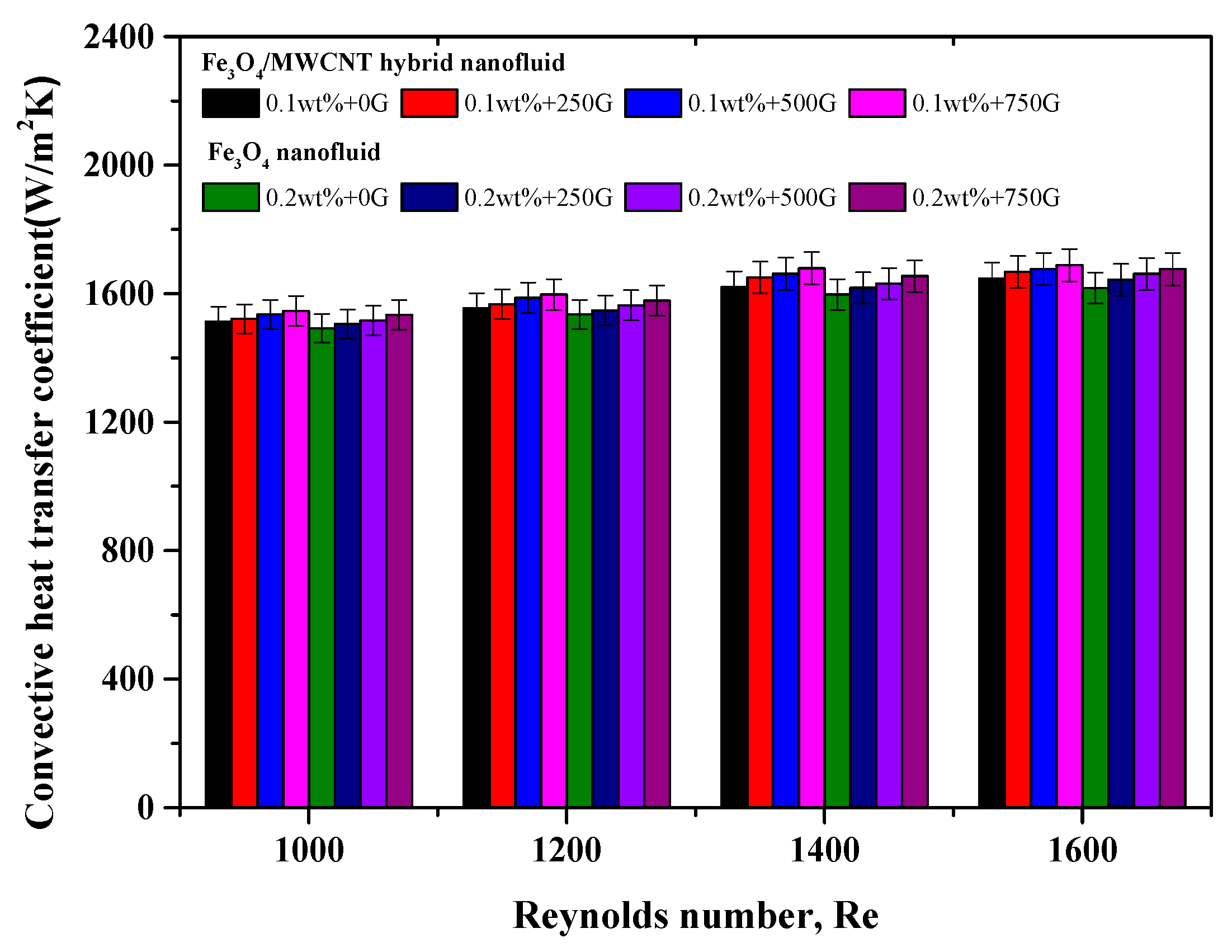
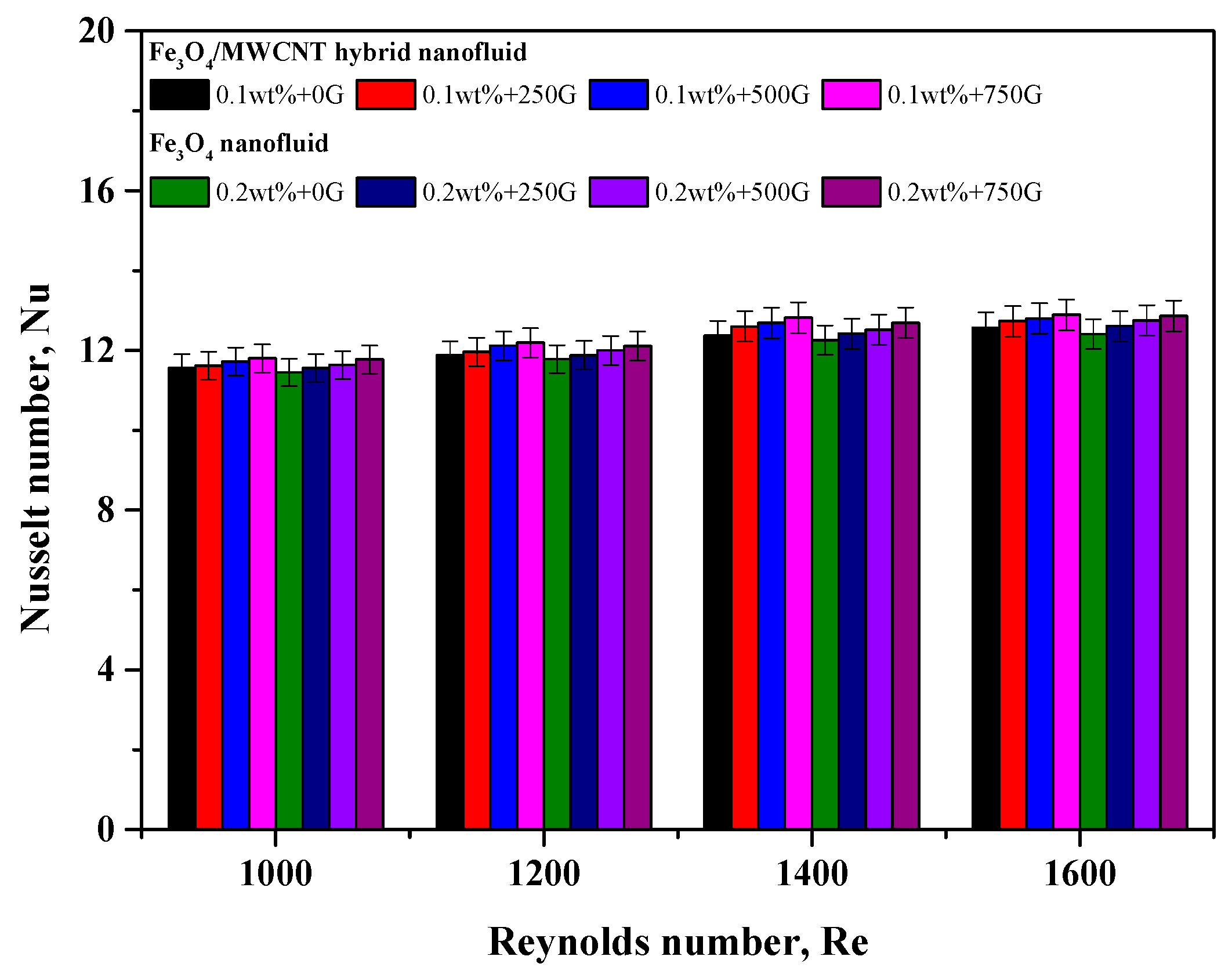
3.3. Convective Heat Transfer Performance of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids under a Magnetic Effect
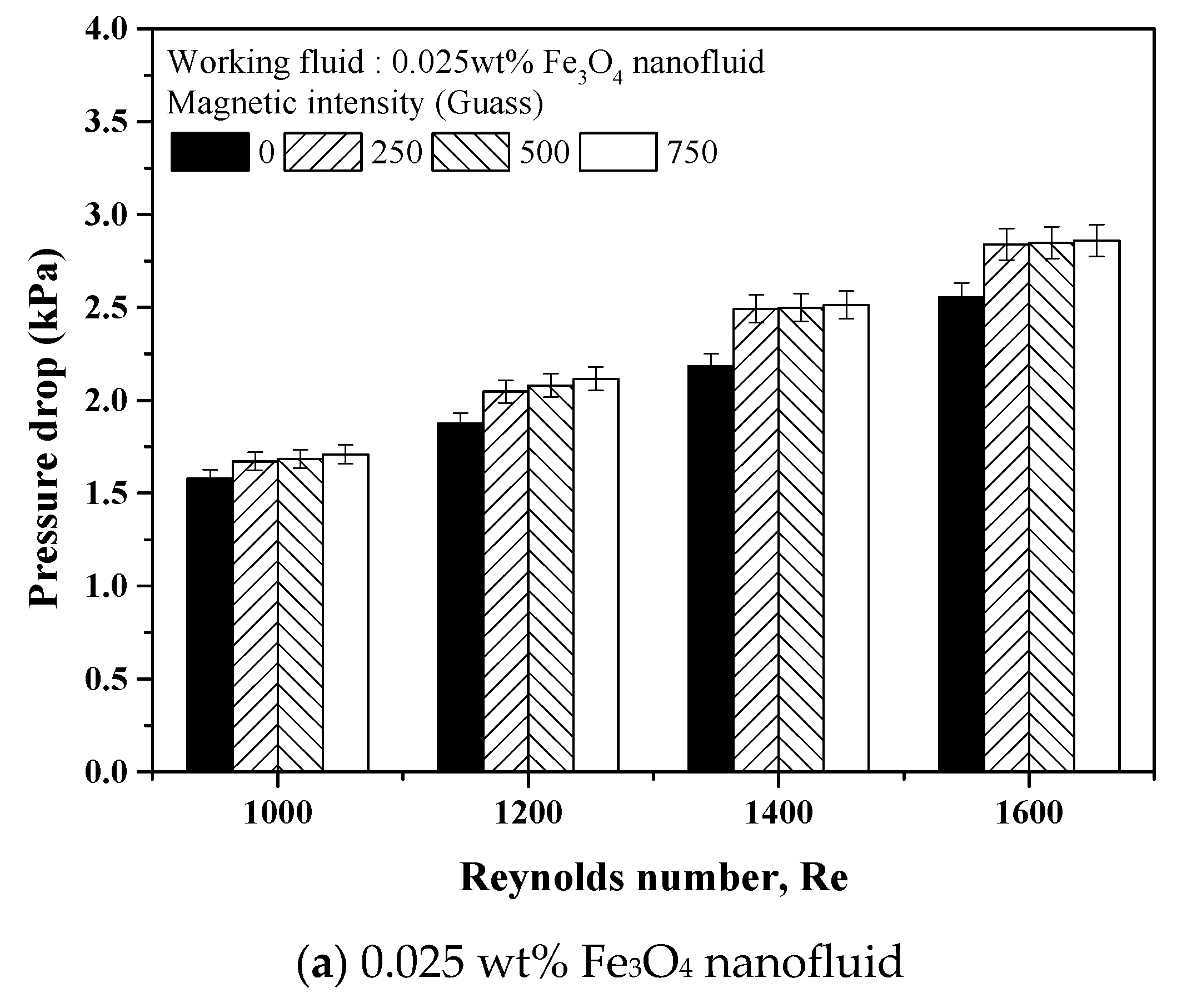
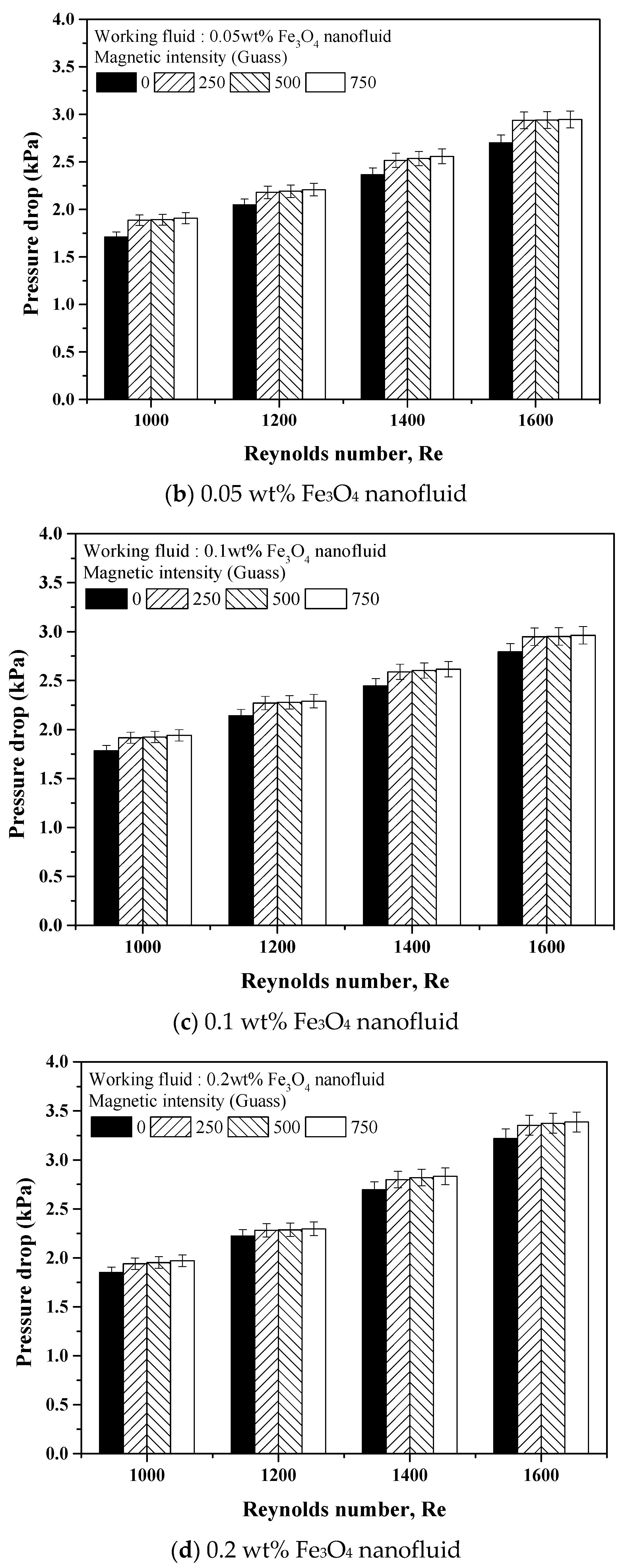
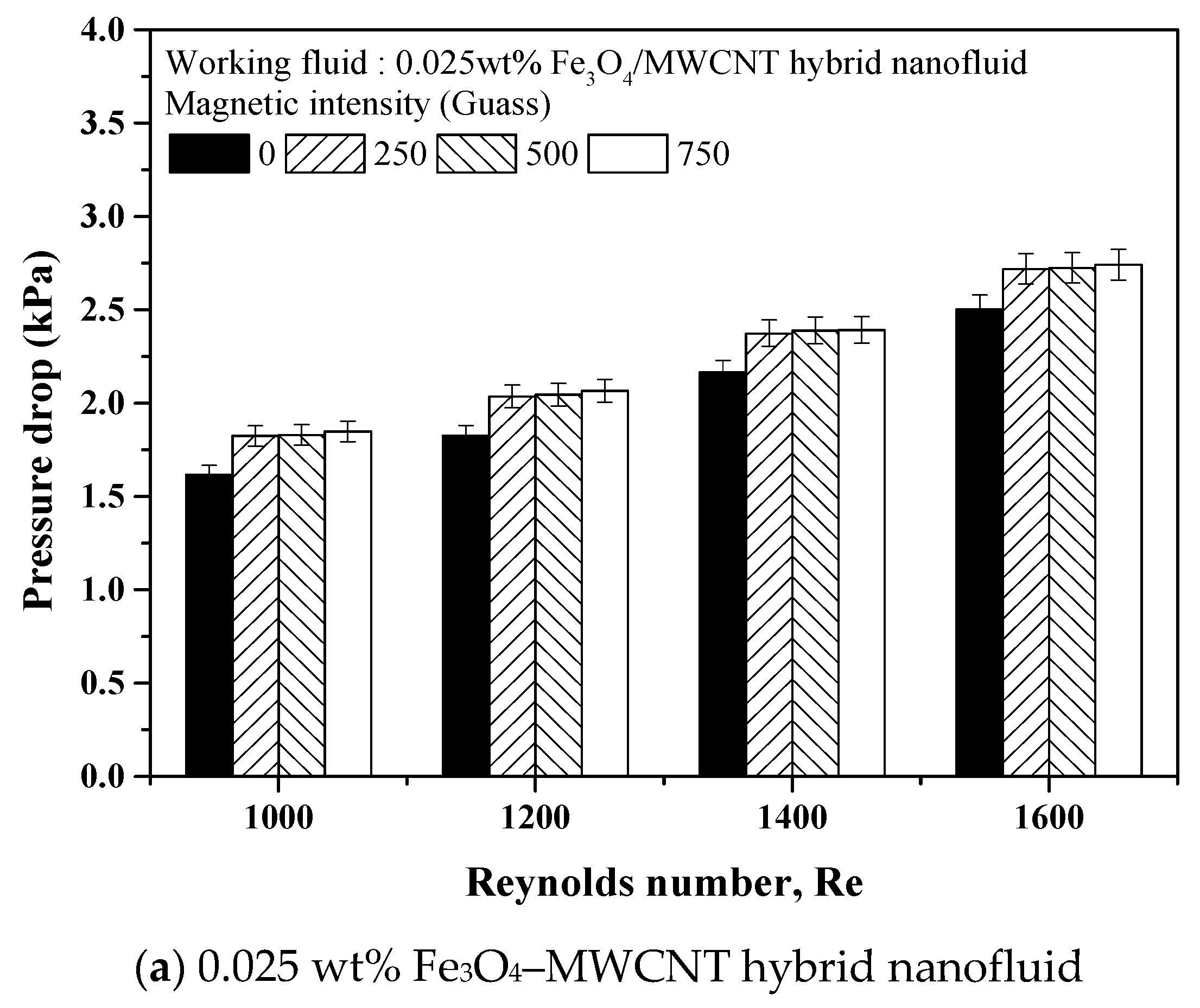
3.4. Pressure Drop of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Hybrid Nanofluids under a Magnetic Field
3.5. Comparison of Convective Heat Transfer Performance between Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; Argonne National Lab.: Du Page County, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jarahnejad, M.; Haghighi, E.B.; Saleemi, M.; Nikkam, N.; Khodabandeh, R.; Palm, B.; Toprak, M.S.; Muhammed, M. Experimental investigation on viscosity of water-based Al2O3 and TiO2 nanofluids. Rheol. Acta 2015, 54, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, H.W.; Azmi, W.H.; Usri, N.A.; Mamat, R.; Adam, N.M. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of Al2O3 nanofluids for different based ratio of water and ethylene glycol mixture. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 81, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashrafmansouri, S.-S.; Nasr, E.M.; Azimi, G.; Etesami, N. Experimental investigation of water self-diffusion coefficient and tracer diffusion coefficient of tert-butanol in water-based silica nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 86, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-T.; Lai, F.-H. Numerical study of flow and heat transfer characteristics of alumina-water nanofluids in a microchannel using the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; France, D.M.; Timofeeva, E.V.; Singh, D.; Routbort, J.L. Comparative review of turbulent heat transfer of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 5380–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Timofeeva, E.V.; Singh, D.; France, D.M.; Smith, R.K. Investigations of heat transfer of copper-in-Therminol 59 nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 64, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, H.; He, Y. Forced convective heat transfer of solar salt-based Al2O3 nanofluids using lattice Boltzmann method. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 8, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Aghakhani, S.; Pordanjani, A.H.; Afrand, M.; Cheraghian, G.; Oztop, H.F.; Shadloo, M.S. A review on the control parameters of natural convection in different shaped cavities with and without nanofluid. Processes 2020, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamand, S.M. Thermal Conductivity Calculations for Nanoparticles Embedded in a Base Fluid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I.M.; Rocha, C.; Souza, R.R.; Coutinho, G.; Pereira, J.E.; Moita, A.S.; Moreira, A.L.N.; Lima, R.; Miranda, J.M. Numerical Optimization of a Microchannel Geometry for Nanofluid Flow and Heat Dissipation Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, V.; Puupponen, S.; Saari, K.; Ala-Nissila, T.; Seppälä, A. Thermal properties and convective heat transfer of phase changing paraffin nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 117, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikkola, V.; Puupponen, S.; Granbohm, H.; Saari, K.; Ala-Nissila, T.; Seppälä, A. Influence of particle properties on convective heat transfer of nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 124, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ganji, D.D. Influence of electric field on Fe3O4-water nanofluid radiative and convective heat transfer in a permeable enclosure. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 250, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, S.; Puupponen, S.; Meriläinen, A.; Joneidi, A.; Seppälä, A.; Saari, K.; Ala-Nissila, T. Turbulent heat transfer characteristics in a circular tube and thermal properties of n-decane-in-water nanoemulsion fluids and micelles-in-water fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 81, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam Sundar, L.; Naik, M.T.; Sharma, K.V.; Singh, M.K.; Siva, R.T.C. Experimental investigation of forced convection heat transfer and friction factor in a tube with Fe3O4 magnetic nanofluid. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Saeed, T.; Chu, Y.-M.; Ali, H.M.; Cheraghian, G.; Kalbasi, R. Comprehensive study concerned graphene nano-sheets dispersed in ethylene glycol: Experimental study and theoretical prediction of thermal conductivity. Powder Technol. 2021, 386, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Yang, B.; Kim, S.H.; Zachariah, M.R. Application of hybrid sphere/carbon nanotube particles in nanofluids. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravifard, E.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Dadkhah, M.; Sodeifian, G. Synthesis and Characterization of TiO2-CNTs Nanocomposite and Investigation of Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity of a New Nanofluid. J. Nanostruct. 2012, 2, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, W.; Xie, H. Enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing Ag/MWNT composites. Powder Technol. 2012, 231, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, S.L.; Otero-Irurueta, G.; Singh, M.K.; Sousa, A.C.M. Heat transfer and friction factor of multi-walled carbon nanotubes–Fe3O4 nanocomposite nanofluids flow in a tube with/without longitudinal strip inserts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 100, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, Z.; Sunden, B. Effects of hybrid nanofluid mixture in plate heat exchangers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 72, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Torres, B.; Lopez-Salinas, J.L.; García-Cuéllar, A.J. Experimental Study of Forced Convective Heat Transfer in a Coiled Flow Inverter Using TiO2–Water Nanofluids. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, H. The influence of the magnetic field on the convective heat transfer characteristics of Fe3O4/water nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 126, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Experimental investigation on the convective heat transfer of Fe3O4/water nanofluids under constant magnetic field. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Gerdroodbary, M.B.; Ganji, D.D. Numerical investigation of forced convective heat transfer of Fe3O4-water nanofluid in the presence of external magnetic source. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 315, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ellahi, R.; Vafai, K. Study of Fe3O4-water nanofluid with convective heat transfer in the presence of magnetic source. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, E.; Ghazanfar, C.R.; Rounaghi, S.A. The influence of the alternating magnetic field on the convective heat transfer properties of Fe3O4-containing nanofluids through the Neel and Brownian mechanisms. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahiraei, M.; Hangi, M.; Rahbari, A. A two-phase simulation of convective heat transfer characteristics of water–Fe3O4 ferrofluid in a square channel under the effect of permanent magnet. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 147, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogonchi, A.S. Hashim Heat transfer by natural convection of Fe3O4-water nanofluid in an annulus between a wavy circular cylinder and a rhombus. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 130, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangar, Z.S.; Khodabandeh, R.; Safarzadeh, H.; Aminfar, H.; Trushkina, Y.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Ghanbarpour, M.; Salazar, A.G. Experimental investigation of the flow and heat transfer of magnetic nanofluid in a vertical tube in the presence of magnetic quadrupole field. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 91, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, F.; Ali, R.Y.; Nciri, R.; Ali, C. MHD Natural Convection of a Fe3O4–Water Nanofluid within an Inside Round Diagonal Corner Square Cavity with Existence of Magnetic Source. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, S.A.; Jalali, E.; Sarafraz, M.M.; Ali, A.O.; Karimipour, A.; Goodarzi, M.; Bach, Q.-V. Effects of magnetic field on micro cross jet injection of dispersed nanoparticles in a microchannel. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2020, 30, 2683–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshayeshi, H.R.; Goodarzi, M.; Safaei, M.R.; Dahari, M. Experimental study on the effect of inclination angle on heat transfer enhancement of a ferrofluid in a closed loop oscillating heat pipe under magnetic field. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 74, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshayeshi, H.R.; Goodarzi, M.; Dahari, M. Effect of magnetic field on the heat transfer rate of kerosene/Fe2O3 nanofluid in a copper oscillating heat pipe. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 68, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajatzadeh, P.A.; Aghakhani, S.; Karimipour, A.; Afrand, M.; Goodarzi, M. Investigation of free convection heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid flow inside a cavity affected by magnetic field and thermal radiation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 997–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, H. The effect of constant magnetic field on convective heat transfer of Fe3O4/water magnetic nanofluid in horizontal circular tubes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 171, 114920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrali, M.; Sadeghinezhad, E.; Akhiani, A.R.; Tahan, L.S.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Kherbeet, A.S.; Mehrali, M. Heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of hybrid graphene/Fe3O4 ferro-nanofluid flow under the influence of a magnetic field. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Saghafian, M.; Salimpour, M.R.; Shafii, M.B. Experimental investigation on laminar forced convective heat transfer of ferrofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes under constant and alternating magnetic fields. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 76, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, J.; Rahmani, R.; Shahsavar, A.; Afrand, M.; Wongwises, S.; Tran, M.D. Effect of magnetic field on laminar forced convective heat transfer of MWCNT–Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluid in a heated tube. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1809–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Libdeh, N.; Redouane, F.; Aissa, A.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Almuhtady, A.; Jamshed, W.; Al-Kouz, W. Hydrothermal and Entropy Investigation of Ag/MgO/H2O Hybrid Nanofluid Natural Convection in a Novel Shape of Porous Cavity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Karimipour, A.; Goodarzi, M. A novel comprehensive experimental study concerned synthesizes and prepare liquid paraffin-Fe3O4 mixture to develop models for both thermal conductivity & viscosity: A new approach of GMDH type of neural network. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 131, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, S.A.; D’Orazio, A.; Karimipour, A.; Goodarzi, M.; Bach, Q.-V. A novel sensitivity analysis model of EANN for F-MWCNTs-Fe3O4/EG nanofluid thermal conductivity: Outputs predicted analytically instead of numerically to more accuracy and less costs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 521, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; An, J.; Xi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Wang, L.; Sasmito, A.P. Thermal Conductivity and Stability of Novel Aqueous Graphene Oxide–Al2O3 Hybrid Nanofluids for Cold Energy Storage. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Ham, J.; Boldoo, T.; Cho, H. Magnetic effect on the enhancement of photo-thermal energy conversion efficiency of MWCNT/Fe3O4 hybrid nanofluid. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 215, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiyas, A.P.A.; Vinod, E.M.; Joseph, J.; Ganesan, R.; Pandey, R.K. Dependence of pH and surfactant effect in the synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and its properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhuja, A.; Suganthi, K.S.; Manikandan, S.; Rajan, K.S. Viscosity and thermal conductivity of dispersions of gum arabic capped MWCNT in water: Influence of MWCNT concentration and temperature. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilu, S.; Sharma, K.V.; Aklilu, T.B.; Azman, M.S.M.; Bhaskoro, P.T. Temperature Dependent Properties of Silicon Carbide Nanofluid in Binary Mixtures of Glycerol-Ethylene Glycol. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishna, V.K.P.V.; Kishore, P.S.; Durga, P.P.V. Enhancement of Heat Transfer Using Fe3O4/Water Nanofluid with Varying Cut-Radius Twisted Tape Inserts. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, L.S.; Singh, M.K.; Sousa, A.C.M. Enhanced heat transfer and friction factor of MWCNT-Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 52, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Cao, X.; Liu, G.H.; Hong, R.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, X.F.; Li, H.Z.; Xu, B.; Wei, D.G. Synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic fluid used for magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2953–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ma, K.; Wang, X.; Xiong, X.; Xu, W.; Jia, C. Fabrication and characterization of polymer composites surface coated Fe3O4/MWCNTs hybrid buckypaper as a novel microwave-absorbing structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Item | MWCNT | Fe3O4 |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | >95% | 99.9% |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 3000 | 80 |
| True density (kg/m3) | 1350 | 4950 |
| Specific heat (J/kg·K) | 650 | 670 |
| Parameter | Uncertainty (%) |
|---|---|
| T-Type thermocouple (K) | 0.75 |
| Power meter (V) | 3.0 |
| Pressure transmitter (PSID) | 0.2 |
| Mass flow meter (kg/s) | 1.0 |
| Magnetic strength meter (G) | 5.0 |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient (W/m2 K) | 0.3 |
| Nusselt number | 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, A.; Veerakumar, C.; Cho, H. Effect of Magnetic Field on the Forced Convective Heat Transfer of Water–Ethylene Glycol-Based Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104683
Lee A, Veerakumar C, Cho H. Effect of Magnetic Field on the Forced Convective Heat Transfer of Water–Ethylene Glycol-Based Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104683
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Areum, Chinnasamy Veerakumar, and Honghyun Cho. 2021. "Effect of Magnetic Field on the Forced Convective Heat Transfer of Water–Ethylene Glycol-Based Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104683
APA StyleLee, A., Veerakumar, C., & Cho, H. (2021). Effect of Magnetic Field on the Forced Convective Heat Transfer of Water–Ethylene Glycol-Based Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–MWCNT Nanofluids. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104683






