A New Method to Evaluate Trueness and Precision of Digital and Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete Dental Arch
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
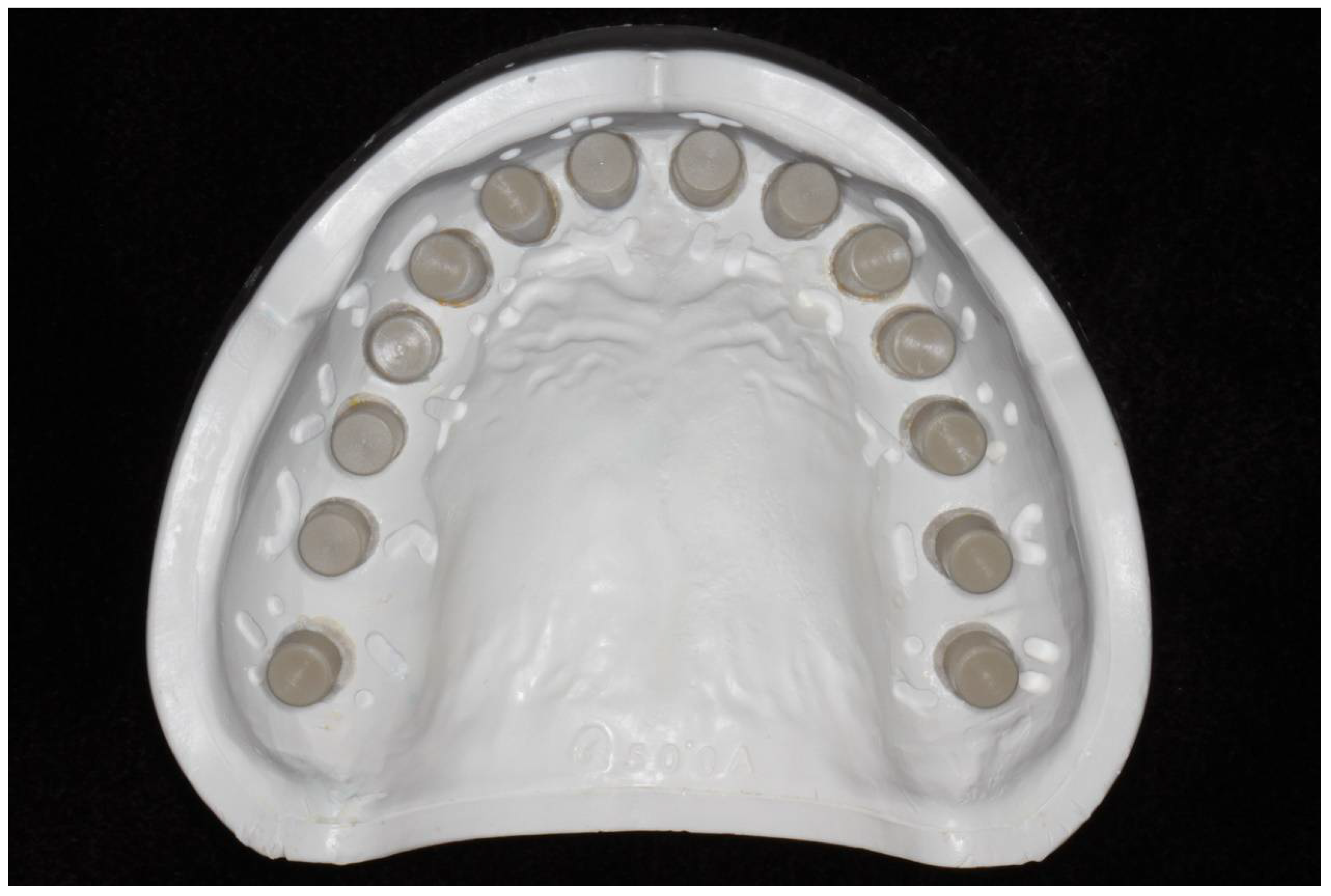
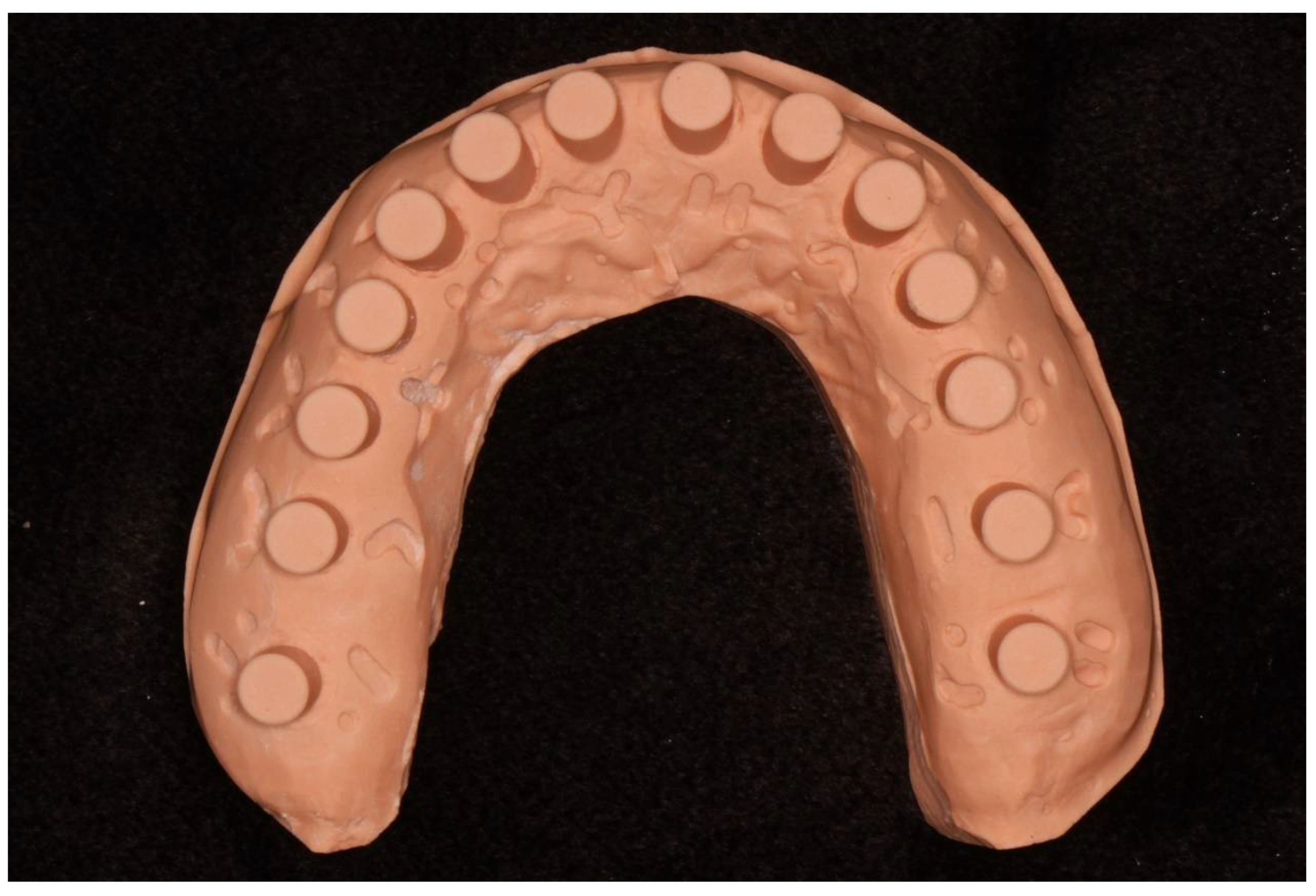
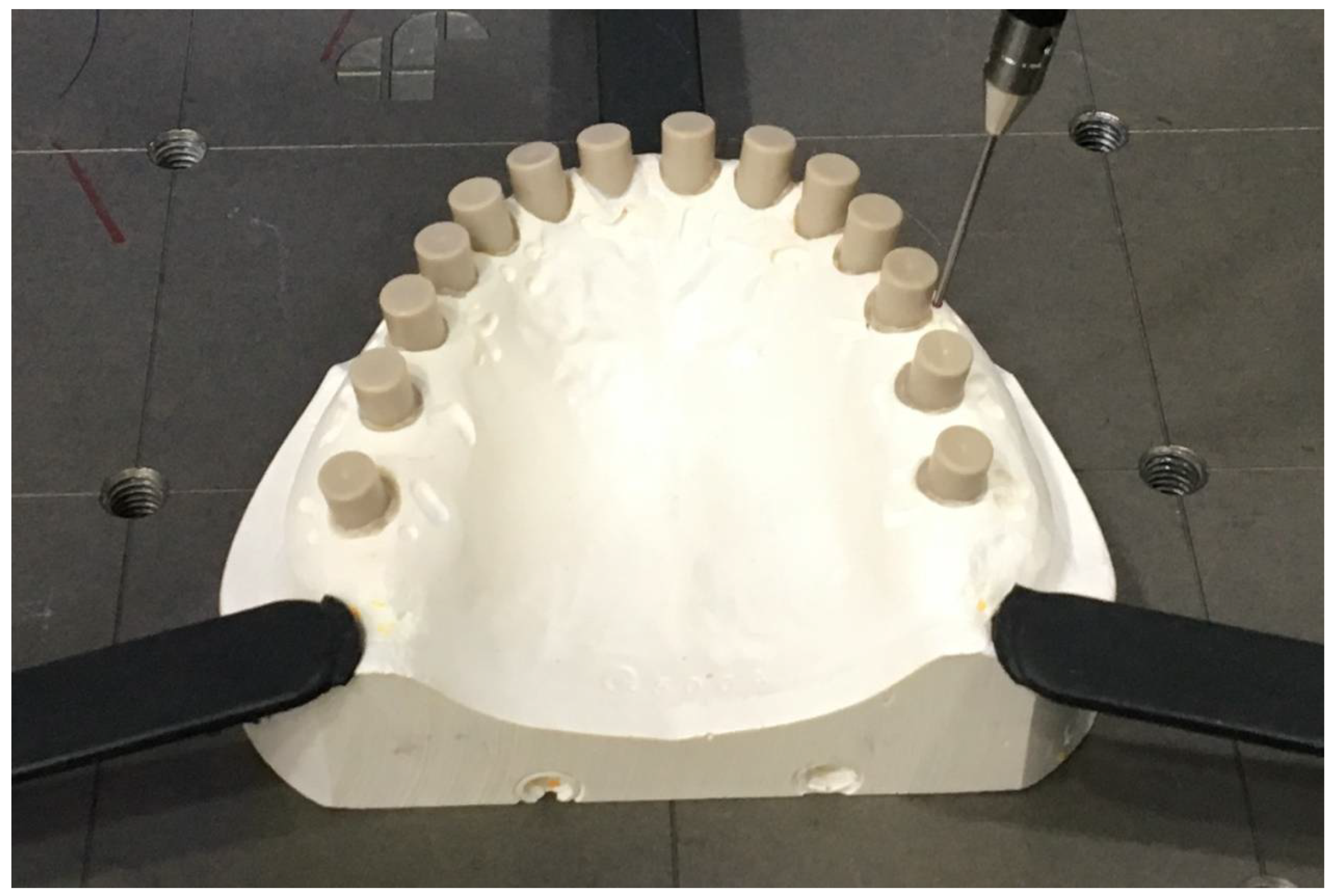
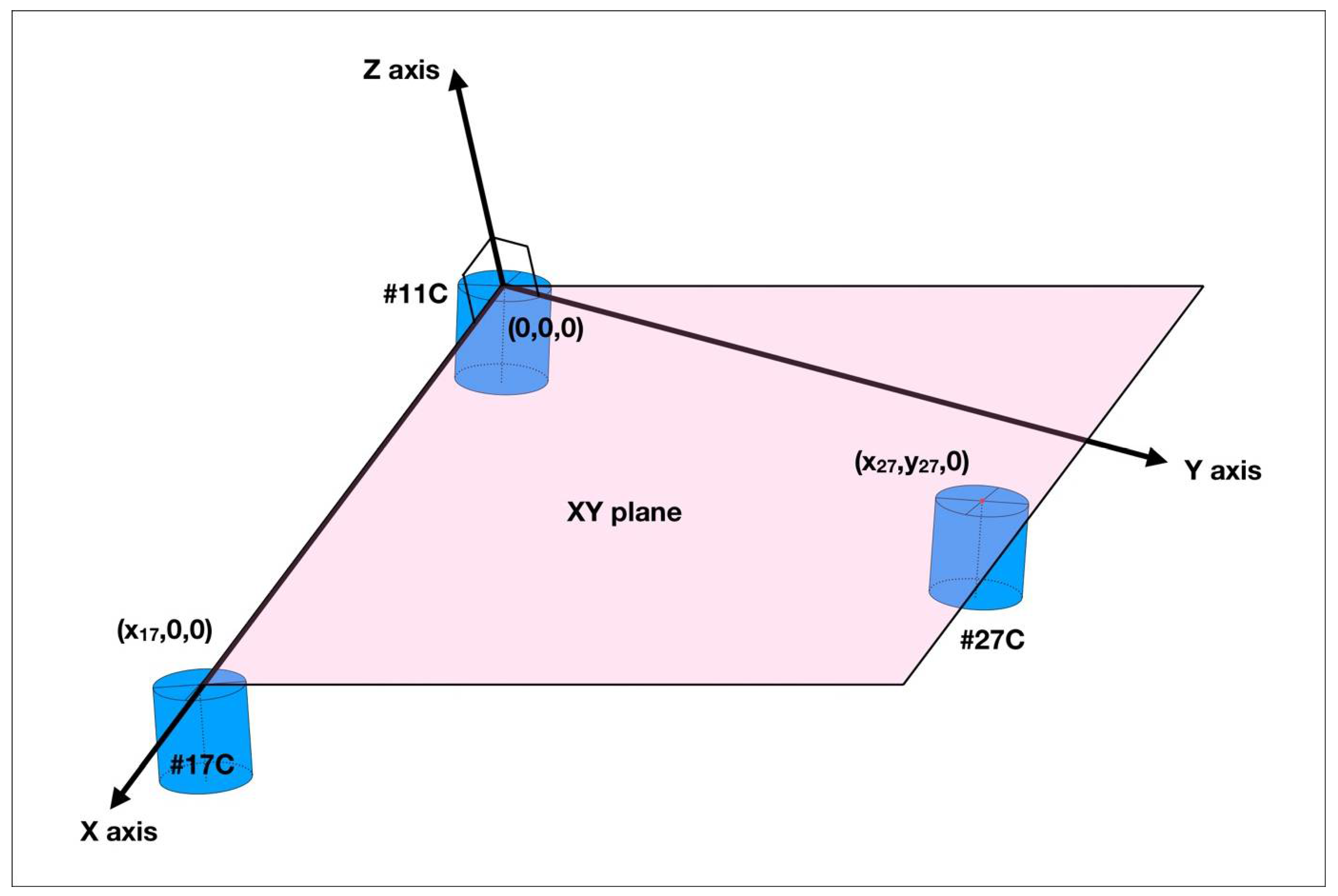
2.1. Fabrication of the Master Model, Definitive Casts, and Digital Models
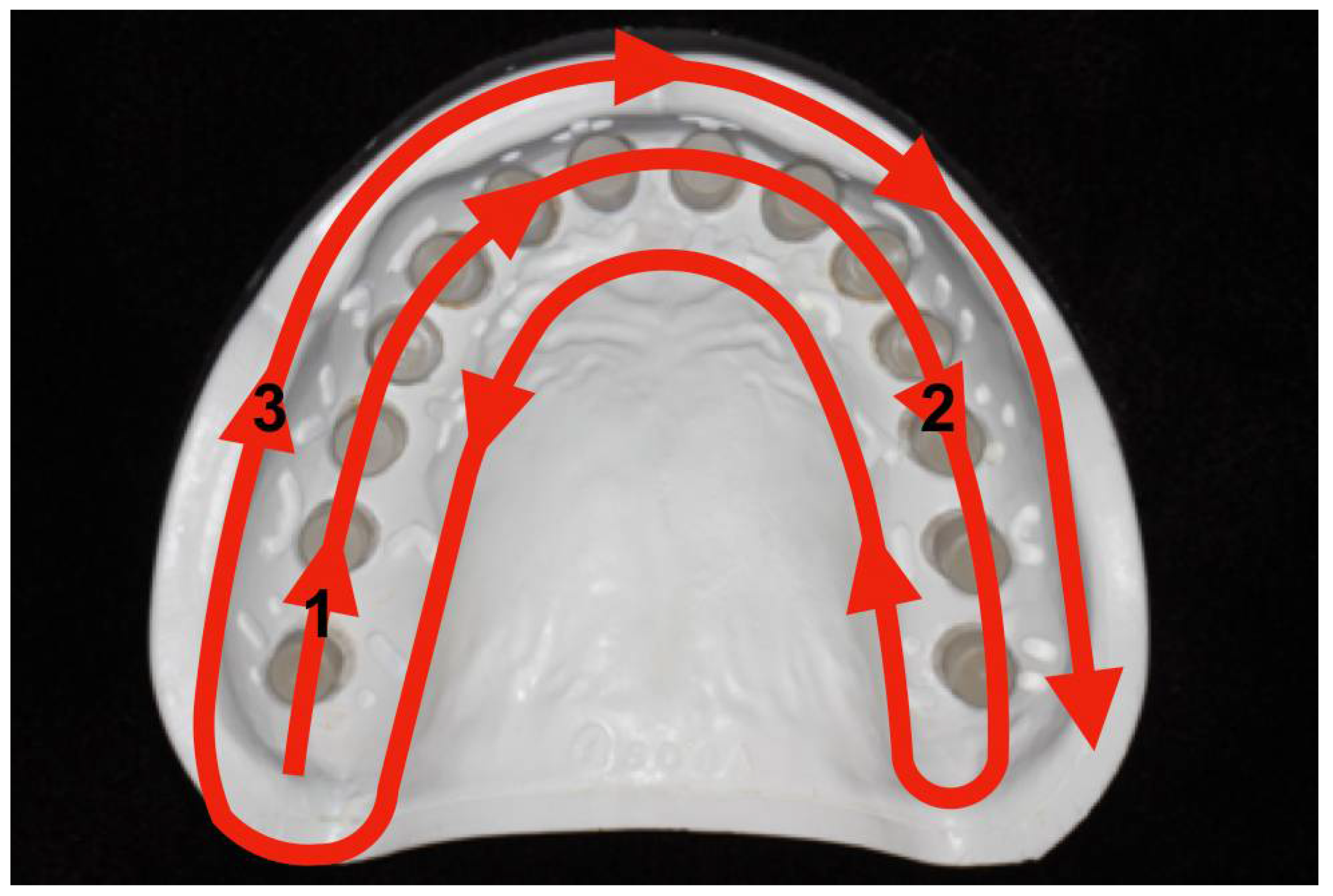
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
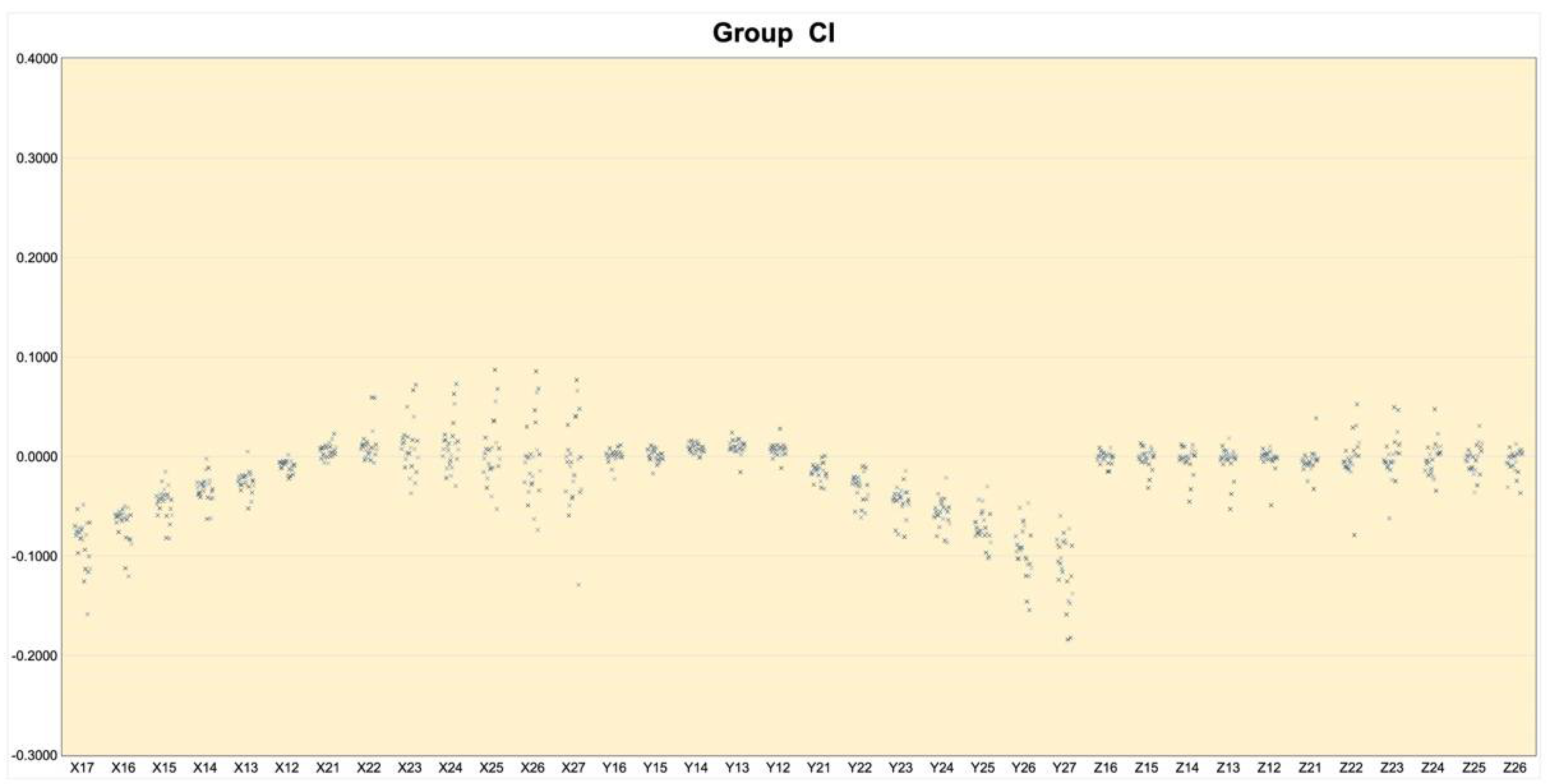
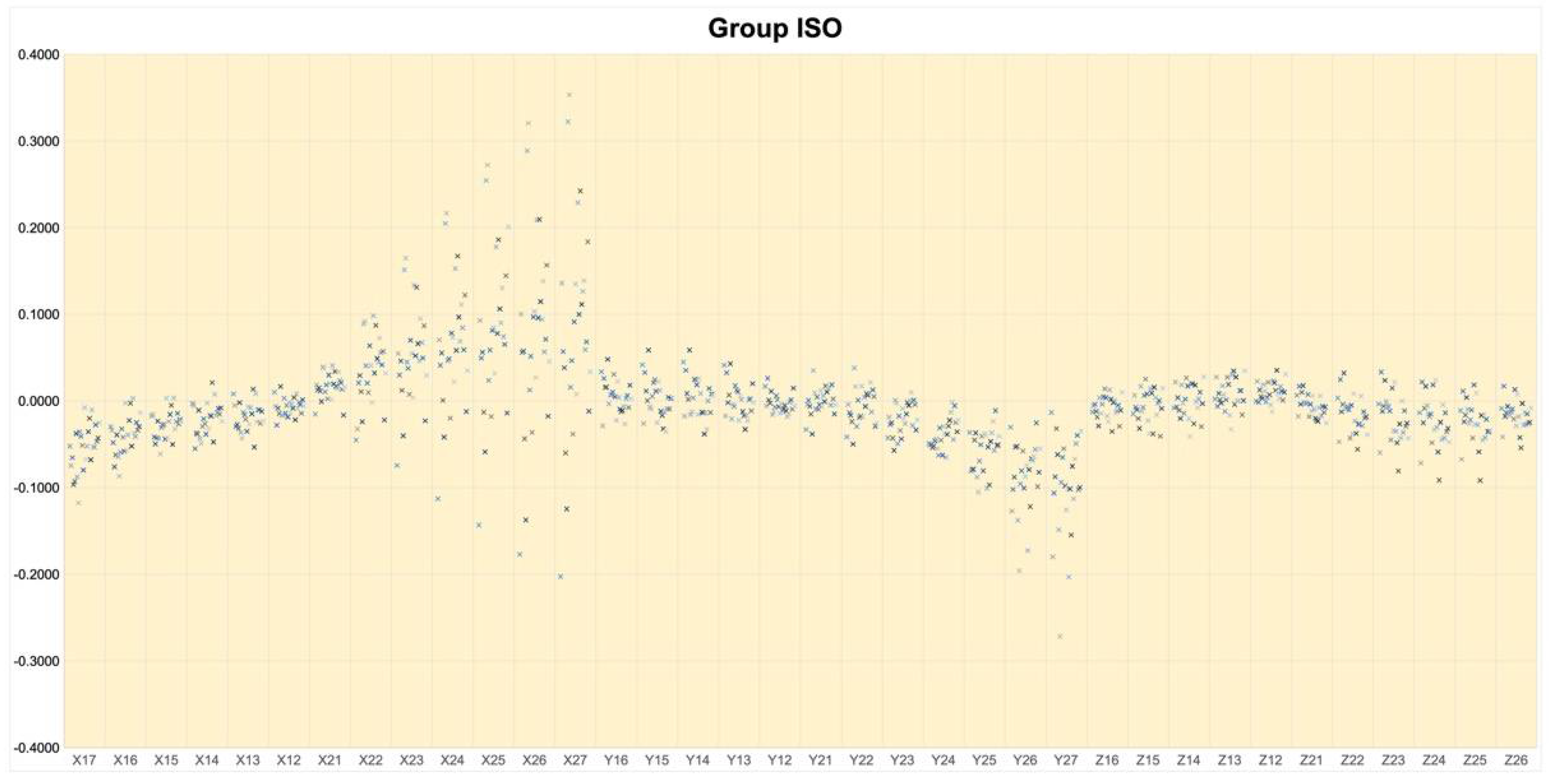
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The new method was reliable to evaluate the three-dimensional accuracy of complete-arch impressions.
- Conventional impressions showed a more accurate absolute trueness than intraoral digital scans in x, y, z coordinates, as well as the linear three-dimensional distance, ΔD.
- Conventional impression also showed more accurate precision than intraoral digital scans in the x, y, and z coordinates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perakis, N.; Belser, U.C.; Magne, P. Final impressions: A review of material properties and description of a current technique. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2004, 24, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, D.T.; Jagger, D.C.; Jagger, R.G.; Barbour, M.E. Two- and three-dimensional accuracy of dental impression materials: Effects of storage time and moisture contamination. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2010, 20, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soğanci, G.; Cinar, D.; Caglar, A.; Yagiz, A. 3D evaluation of the effect of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and stability of two elastomeric impression materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounis, K.S.; Dounis, G.; Ditmyer, M.M.; Ziebert, G.J. Accuracy of successive casts for full-arch fixed prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 23, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Sundaram, G.; Bartlett, D.; Sherriff, M. The use of a 3D laser scanner using superimpositional software to assess the accuracy of impression techniques. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robben, J.; Muallah, J.; Wesemann, C.; Nowak, R.; Mah, J.; Pospiech, P.; Bumann, A. Suitability and accuracy of CBCT model scan: An in vitro study. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2018, 20, 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Thongthammachat, S.; Moore, B.K.; Barco, M.T.; Hovijitra, S.; Brown, D.T.; Andres, C.J. Dimensional accuracy of dental casts: Influence of tray material, impression material, and time. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 11, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitti, R.P.; Da Silva, M.A.B.; Consani, R.L.X.; Sinhoreti, M.A.C. Dimensional Accuracy of Stone Casts Made from Silicone-Based Impression Materials and Three Impression Techniques. Braz. Dent. J. 2013, 24, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mann, K.; Davids, A.; Range, U.; Richter, G.; Boening, K.; Reitemeier, B. Experimental study on the use of spacer foils in two-step putty and wash impression procedures using silicone impression materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nicholls, J.I.; Han, C.-H.; Lee, K.-W. Displacement of implant components from impressions to definitive casts. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2006, 21, 745–755. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.-H.; Son, Y.-H.; Han, C.-H.; Kim, S. Accuracy of implant impressions without impression copings: A three-dimensional analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2011, 105, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M. The complete digital workflow in fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Brägger, U. Time-Efficiency Analysis Comparing Digital and Conventional Workflows for Implant Crowns: A Prospective Clinical Crossover Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuer, F.; Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D. Digital dentistry: An overview of recent developments for CAD/CAM generated restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2008, 204, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlholm, P.; Sipilä, K.; Vallittu, P.; Jakonen, M.; Kotiranta, U. Digital Versus Conventional Impressions in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkūnas, V.; Gečiauskaitė, A.; Jegelevičius, D.; Vaitiekūnas, M. Accuracy of digital implant impressions with intraoral scanners. A systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implant. 2017, 10 (Suppl. 1), 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chochlidakis, K.M.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Geminiani, A.; Chen, C.-J.; Feng, I.J.; Ercoli, C. Digital versus conventional impressions for fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.K.; Kim, S. Effect of number of pontics and impression technique on the accuracy of four-unit monolithic zirconia fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 860-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. In-vitro evaluation of the accuracy of conventional and digital methods of obtaining full-arch dental impressions. Quintessence Int. 2015, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Full arch scans: Conventional versus digital impressions--an in-vitro study. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2011, 14, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, S.B.M.; Emmanouilidi, A.; Stampf, S.; Strub, J.R.; Att, W. Accuracy of full-arch scans using intraoral scanners. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Weisbloom, M.; Petridis, H. Comparison of Accuracy Between a Conventional and Two Digital Intraoral Impression Techniques. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 31, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Uechi, J.; Konno, M.; Sasamoto, S.; Iijima, M.; Mizoguchi, I. Accuracy of digital models generated by conventional impression/plaster-model methods and intraoral scanning. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhr, F.; Schmidt, A.; Rehmann, P.; Wöstmann, B. A new method for assessing the accuracy of full arch impressions in patients. J. Dent. 2016, 55, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-S.; Sun, J. Comparison of repeatability between intraoral digital scanner and extraoral digital scanner: An in-vitro study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2015, 59, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, J.-F.; Edelhoff, D.; Schweiger, J.; Keul, C. A new method for the evaluation of the accuracy of full-arch digital impressions in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Accuracy of complete-arch dental impressions: A new method of measuring trueness and precision. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://applications.zeiss.com/C1257A26006EFF9E/0/DC5EC1E87A19912DC1257A3900659A80/$FILE/EN_60_020_0166II_ZEISS_Bridge-type-CMMs.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Available online: https://support.3dsystems.com/s/article/3D-Systems-Software-Certification?language=en_US (accessed on 2 May 2020).

| ICC (95% CI) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Master model | Δx | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 |
| Δy | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Δz | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Group CI | Δx | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 |
| Δy | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Δz | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Group IOS | Δx | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 |
| Δy | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Δz | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 | |
| Operators | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | <0.001 |
| Δx | Δy | Δz | ΔD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Group CI | Group IOS | p | Group CI | Group IOS | p | Group CI | Group IOS | p | Group CI | Group IOS | p |
| #17C | 0.086 ± 0.024 | 0.054±0.027 | <0.001 | 0.086±0.024 | 0.054±0.027 | <0.001 | ||||||
| #16C | 0.068 ± 0.018 | 0.039 ± 0.022 | <0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.005 | 0.015 ± 0.012 | <0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.004 | 0.012 ± 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.069 ± 0.018 | 0.048 ± 0.019 | <0.001 |
| #15C | 0.047 ± 0.016 | 0.028 ± 0.016 | <0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.004 | 0.018 ± 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.016 ± 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.048 ± 0.016 | 0.041 ± 0.019 | 0.111 |
| #14C | 0.032 ± 0.013 | 0.023 ± 0.015 | 0.033 | 0.008 ± 0.005 | 0.019 ± 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.011 | 0.015 ± 0.011 | 0.018 | 0.036 ± 0.013 | 0.038 ± 0.015 | 0.665 |
| #13C | 0.025 ± 0.010 | 0.020 ± 0.013 | 0.107 | 0.011 ± 0.005 | 0.015 ± 0.012 | 0.106 | 0.008 ± 0.013 | 0.014 ± 0.012 | 0.092 | 0.031 ± 0.013 | 0.034 ± 0.012 | 0.377 |
| #12C | 0.009 ± 0.006 | 0.010 ± 0.007 | 0.666 | 0.008 ± 0.005 | 0.009 ± 0.006 | 0.504 | 0.005 ± 0.010 | 0.012 ± 0.010 | 0.015 | 0.015 ± 0.011 | 0.021 ± 0.008 | 0.017 |
| #21C | 0.007 ± 0.006 | 0.019 ± 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.008 | 0.012 ± 0.010 | 0.247 | 0.008 ± 0.010 | 0.011 ± 0.007 | 0.241 | 0.021 ± 0.009 | 0.029 ± 0.010 | 0.012 |
| #22C | 0.013 ± 0.015 | 0.045 ± 0.027 | <0.001 | 0.031 ± 0.015 | 0.018 ± 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.014 ± 0.018 | 0.022 ± 0.015 | 0.089 | 0.040 ± 0.021 | 0.058 ± 0.023 | 0.006 |
| #23C | 0.020 ± 0.019 | 0.063 ± 0.043 | <0.001 | 0.045 ± 0.015 | 0.022 ± 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.016 | 0.026 ± 0.020 | 0.029 | 0.055 ± 0.023 | 0.079 ± 0.037 | 0.006 |
| #24C | 0.019 ± 0.019 | 0.080 ± 0.057 | <0.001 | 0.057 ± 0.015 | 0.039 ± 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.011 | 0.030 ± 0.021 | 0.001 | 0.064 ± 0.018 | 0.102 ± 0.050 | 0.001 |
| #25C | 0.023 ± 0.023 | 0.100 ± 0.072 | <0.001 | 0.071 ± 0.017 | 0.058 ± 0.025 | 0.036 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.029 ± 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.078 ± 0.022 | 0.126 ± 0.067 | 0.002 |
| #26C | 0.029 ± 0.026 | 0.109 ± 0.081 | <0.001 | 0.095 ± 0.026 | 0.087 ± 0.040 | 0.426 | 0.009 ± 0.010 | 0.019 ± 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.102 ± 0.030 | 0.147 ± 0.080 | 0.013 |
| #27C | 0.033 ± 0.029 | 0.117 ± 0.094 | <0.001 | 0.111 ± 0.033 | 0.099 ± 0.058 | 0.386 | 0.118 ± 0.038 | 0.160 ± 0.099 | 0.051 | |||
| Overall | 0.032 ± 0.029 | 0.055 ± 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.038 ± 0.038 | 0.035 ± 0.050 | 0.183 | 0.009 ± 0.012 | 0.019 ± 0.016 | <0.001 | 0.059 ± 0.037 | 0.072 ± 0.064 | 0.001 |
| Group CI | Group IOS | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δx | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Δy | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.024 |
| Δz | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | <0.001 |
| ΔD | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 0.006 |
| Δx | Δy | Δz | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Group CI | Group IOS | p | Group CI | Group IOS | p | Group CI | Group IOS | p |
| #17C | 0.026 ± 0.023 | 0.032 ± 0.023 | 0.004 | ||||||
| #16C | 0.018 ± 0.018 | 0.026 ± 0.019 | <0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.022 ± 0.016 | <0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.006 | 0.015 ± 0.010 | <0.001 |
| #15C | 0.017 ± 0.014 | 0.019 ± 0.014 | 0.15 | 0.007 ± 0.006 | 0.026 ± 0.019 | <0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.022 ± 0.015 | <0.001 |
| #14C | 0.014 ± 0.012 | 0.021 ± 0.015 | <0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.004 | 0.027 ± 0.020 | <0.001 | 0.014 ± 0.014 | 0.022 ± 0.015 | <0.001 |
| #13C | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.019 ± 0.013 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.016 | 0.020 ± 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.016 | 0.020 ± 0.014 | <0.001 |
| #12C | 0.006 ± 0.005 | 0.012 ± 0.009 | <0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.013 | 0.013 ± 0.009 | <0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.013 | 0.013 ± 0.009 | <0.001 |
| #21C | 0.008 ± 0.006 | 0.017 ± 0.013 | <0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.007 | 0.018 ± 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.013 | 0.014 ± 0.010 | 0.003 |
| #22C | 0.015 ± 0.017 | 0.045 ± 0.032 | <0.001 | 0.017 ± 0.013 | 0.024 ± 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.023 ± 0.023 | 0.025 ± 0.017 | 0.238 |
| #23C | 0.029 ± 0.023 | 0.063 ± 0.049 | <0.001 | 0.016 ± 0.015 | 0.021 ± 0.015 | <0.001 | 0.025 ± 0.022 | 0.032 ± 0.023 | <0.001 |
| #24C | 0.027 ± 0.022 | 0.083 ± 0.064 | <0.001 | 0.016 ± 0.013 | 0.020 ± 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.021 ± 0.018 | 0.033 ± 0.024 | <0.001 |
| #25C | 0.035 ± 0.028 | 0.106 ± 0.081 | <0.001 | 0.020 ± 0.015 | 0.029 ± 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.019 ± 0.015 | 0.028 ± 0.022 | <0.001 |
| #26C | 0.045 ± 0.034 | 0.126 ± 0.099 | <0.001 | 0.029 ± 0.022 | 0.044 ± 0.036 | <0.001 | 0.013 ± 0.011 | 0.018 ± 0.014 | <0.001 |
| #27C | 0.049 ± 0.039 | 0.143 ± 0.109 | <0.001 | 0.038 ± 0.029 | 0.064 ± 0.053 | <0.001 | |||
| Overall | 0.023 ± 0.025 | 0.054 ± 0.069 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.017 | 0.027 ± 0.027 | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.016 | 0.022 ± 0.018 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, K.; Kim, S. A New Method to Evaluate Trueness and Precision of Digital and Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete Dental Arch. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104612
Seo K, Kim S. A New Method to Evaluate Trueness and Precision of Digital and Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete Dental Arch. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104612
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, KweonSoo, and Sunjai Kim. 2021. "A New Method to Evaluate Trueness and Precision of Digital and Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete Dental Arch" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104612
APA StyleSeo, K., & Kim, S. (2021). A New Method to Evaluate Trueness and Precision of Digital and Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete Dental Arch. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104612






