Spatial Signal Analysis Based on Wave-Spectral Fractal Scaling: A Case of Urban Street Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Signals
2.1. Spatial Signals and Urban Density Models
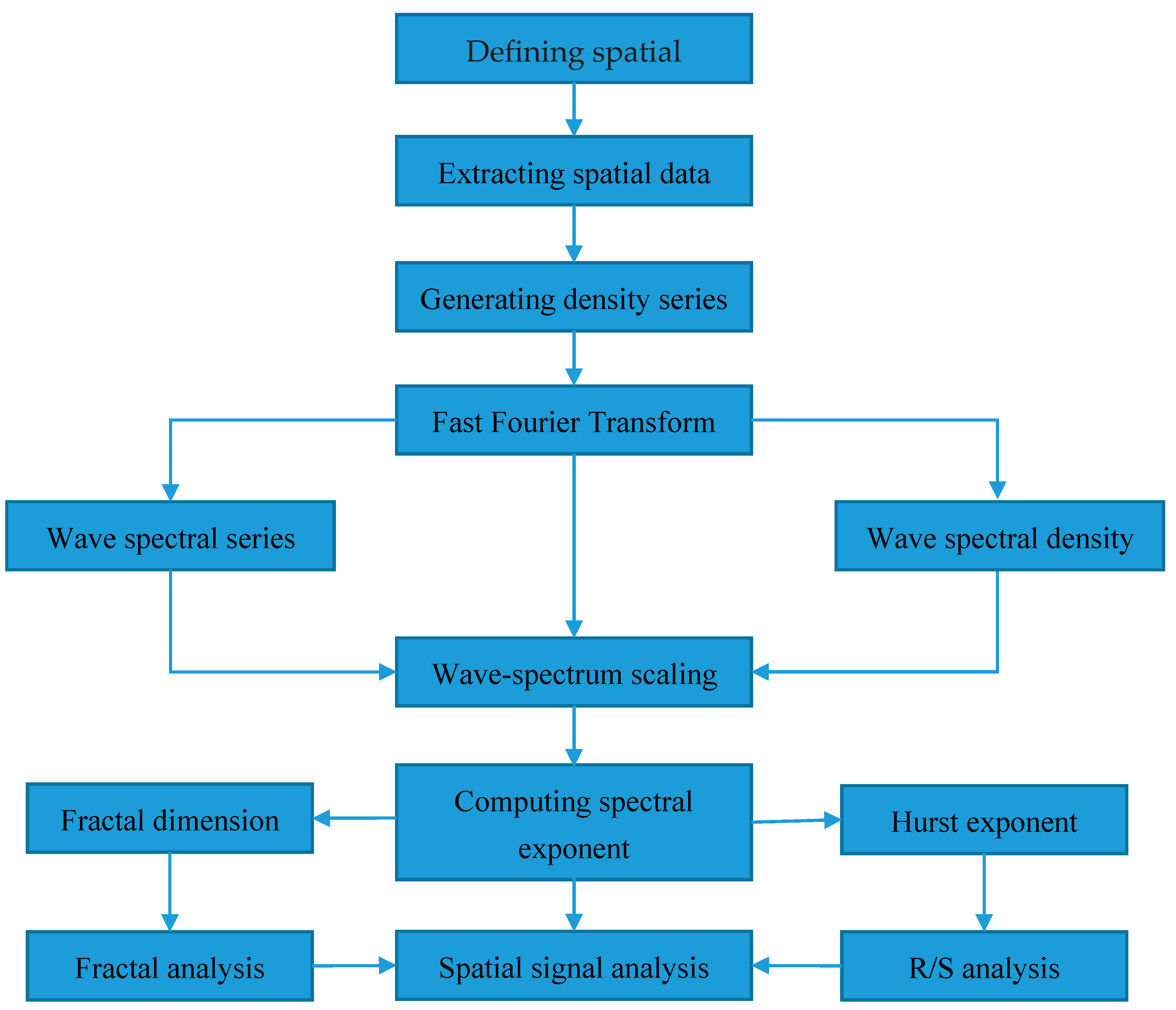
2.2. Fourier Transform and Spectral Scaling Analysis
2.3. Wave-Spectral Scaling Relation
3. Empirical Analysis
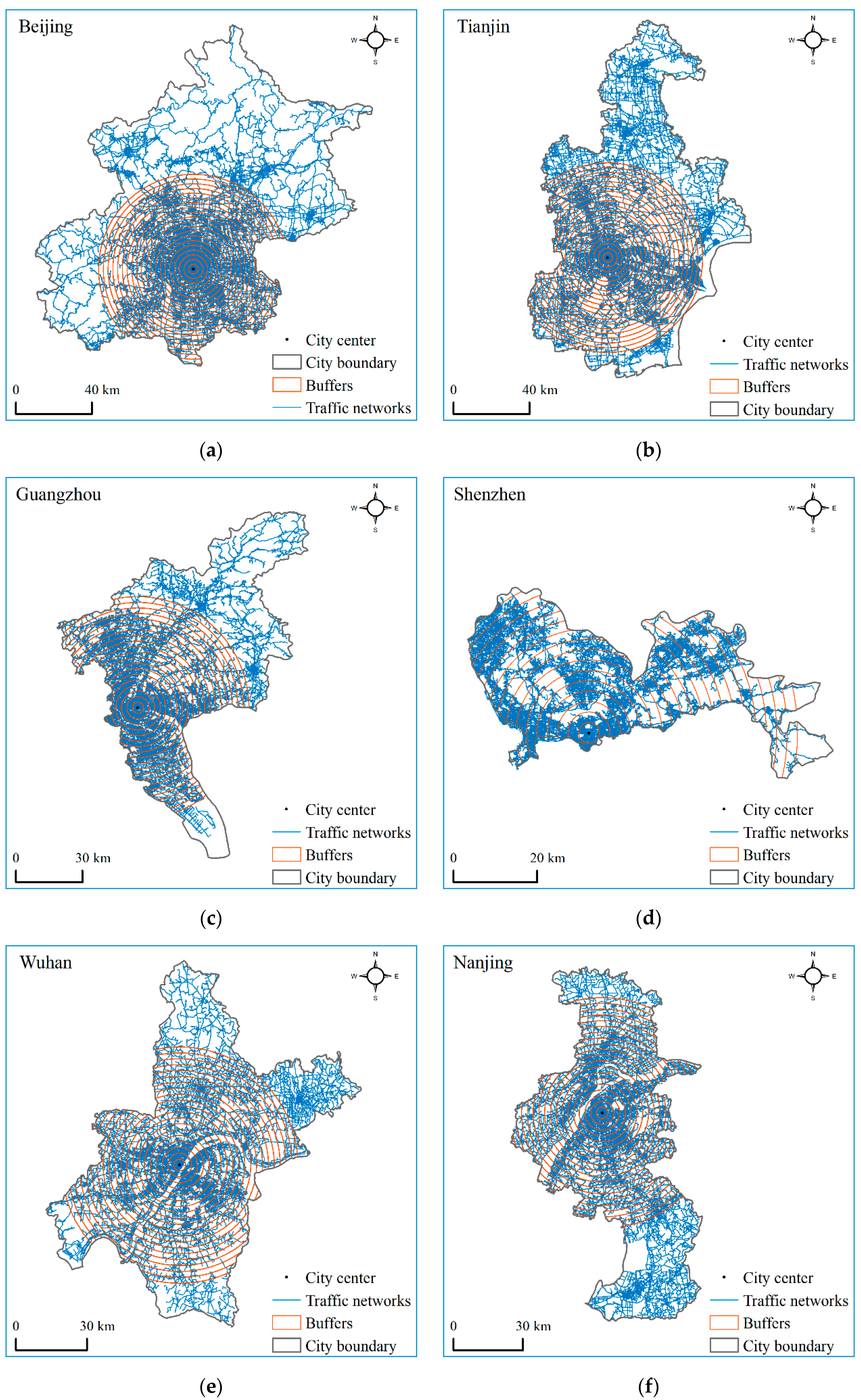
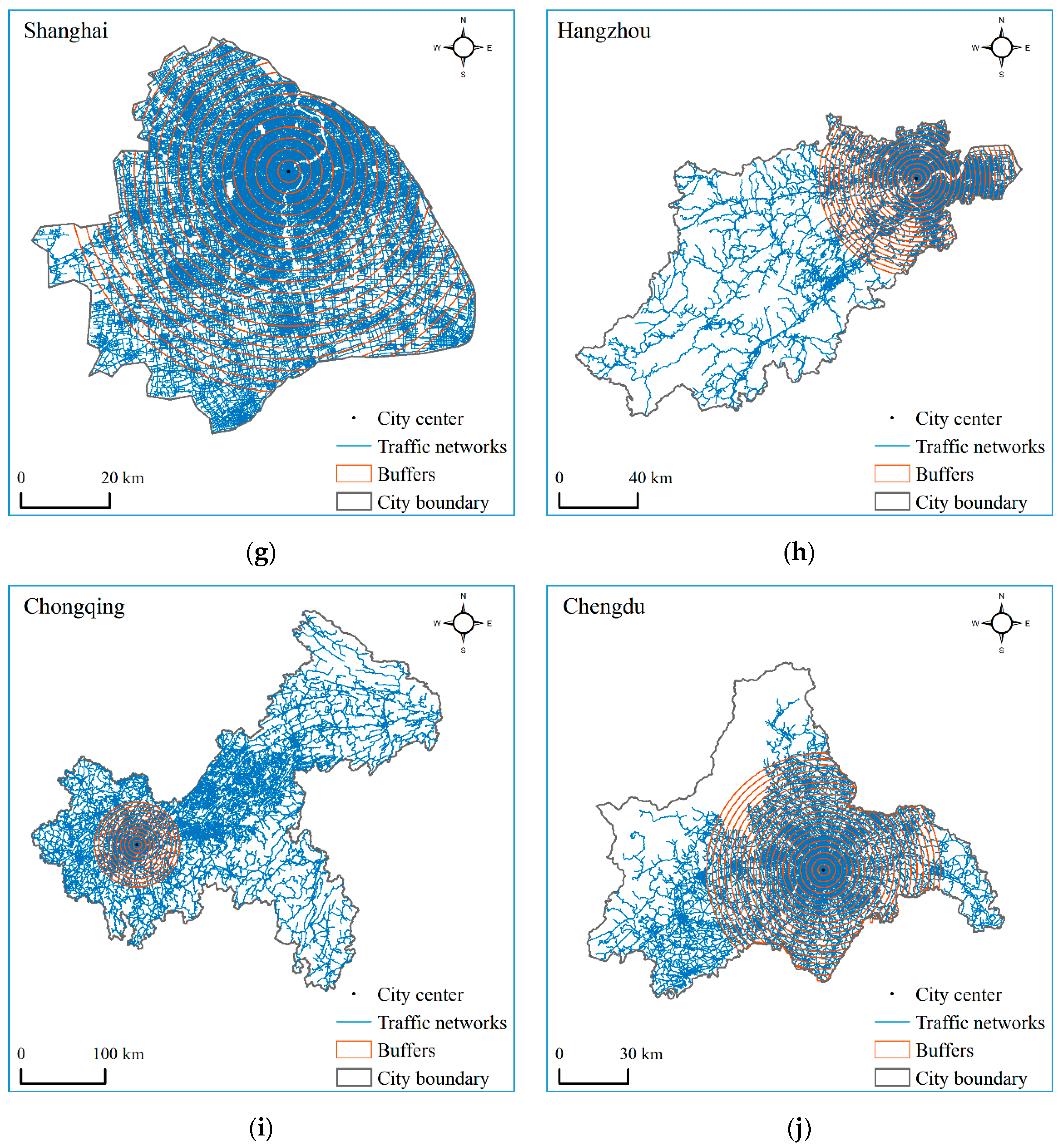
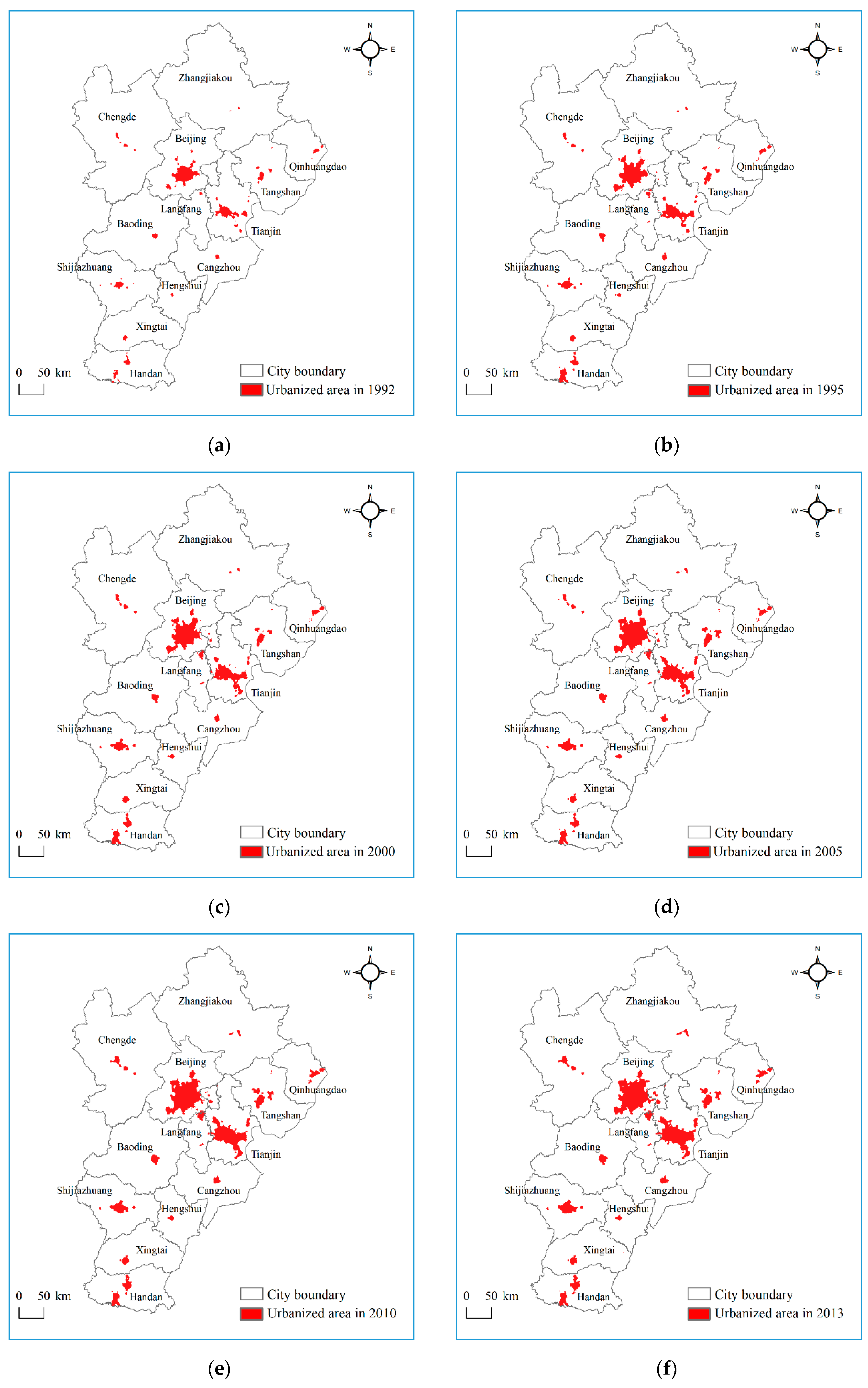
3.1. Data and Methods
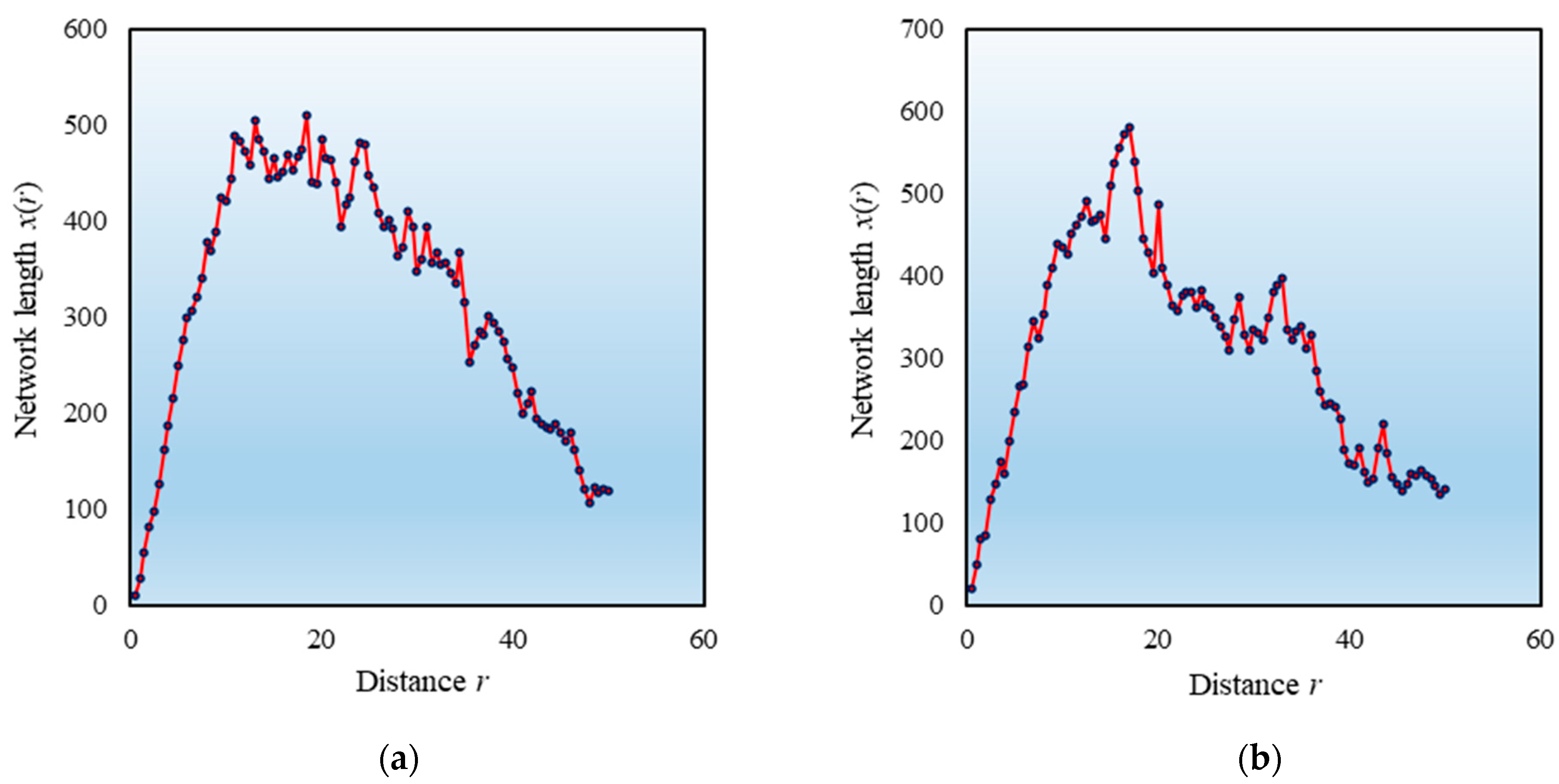
3.2. Results and Analysis
3.3. Cases of Power Spectral Scaling Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariglia, E. Entropy and fractal antennas. Entropy 2016, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, F. Chaos and Order: The Complex Structure of Living Systems; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. PNAS 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabko, B.Y. Noise-free coding of combinatorial sources, Hausdorff dimension and Kolmogorov complexity. Probl. Peredachi Inf. 1986, 22, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G.; Wang, J.-J.; Feng, J. Understanding the fractal dimensions of urban forms through spatial entropy. Entropy 2017, 19, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariglia, E. Primality, fractality, and image analysis. Entropy 2019, 21, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparavigna, A.C. Entropies and Fractal Dimensions. Philica. 2016. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01377975 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Zmeskal, O.; Dzik, P.; Vesely, M. Entropy of fractal systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G. Equivalence relation between normalized spatial entropy and fractal dimension. Phys. A 2020, 553, 124627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.N.; Shivakumara, P.; Jalab, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.W.; Pal, U.; Lu, T. A new fractal series expansion based enhancement model for license plate recognition. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2020, 89, 115958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, J. Fractals; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.-D.; Liu, S.K. An Introduction to Fractals and Fractal Dimension; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Takayasu, H. Fractals in the Physical Sciences; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Brockwell, P.J.; Davis, R.A. Time Series: Theory and Methods, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C. Urban population densities. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1951, 114, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.V.; Lewis, Z.V. On the Weierstrass-Mandelbrot fractal function. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1980, 370, 459–484. [Google Scholar]
- Smeed, R.J. Road development in urban area. J. Inst. High. Eng. 1963, 10, 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G. Exploring the fractal parameters of urban growth and form with wave-spectrum analysis. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2010, 2010, 974917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G. A wave-spectrum analysis of urban population density: Entropy, fractal, and spatial localization. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2008, 2008, 728420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P.A. Fractal Cities: A Geometry of Form and Function; Academic Press: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G. Fractal analytical approach of urban form based on spatial correlation function. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 49, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, X.J. Fractal dimensions derived from spatial allometric scaling of urban form. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 126, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankhauser, P. The fractal approach: A new tool for the spatial analysis of urban agglomerations. Popul. Engl. Sel. 1998, 10, 205–240. [Google Scholar]
- Frankhauser, P.; Sadler, R. Fractal analysis of agglomerations. In Natural Structures: Principles, Strategies, and Models in Architecture and Nature; Hilliges, M., Ed.; University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991; pp. 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.; Engelen, G. Cellular automata and fractal urban form: A cellular modeling approach to the evolution of urban land-use patterns. Environ. Plan. A 1993, 25, 1175–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, M.W., IV. Controlling the spatial coherence of an optical source using a spatial filter. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, L.-J.; Yang, J.; Xia, D.; Liu, W.-N. Short-term traffic flow prediction: From the perspective of traffic flow decomposition. Neurocomputing 2020, 413, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G. Fractal dimension analysis of urban morphology based on spatial correlation functions. In Mathematics of Urban Morphology; D’Acci, L., Ed.; Springer Nature: Birkhäuser, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 21–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, D. Explanation in Geography; Edward Arnold Ltd.: London, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G. Mathematical Methods for Geography; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G. The spatial meaning of Pareto’s scaling exponent of city-size distributions. Fractals 2014, 22, 1450001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.-F.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Wu, W. Multifractal and singularity analysis of weighted road networks. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2014, 28, 1450215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, D.; Montoya, S.; Sanabria, M.; Torres, F.; Serrano, D.; Acevedo, A. Fractal analysis of the influence of the distribution of road networks on the traffic. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1329, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, V.; Rodina, E. The fractal dimension of Tokyo’s streets. Fractals 2000, 8, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahitya, K.S.; Prasad, C.S.R.K. Modelling structural interdependent parameters of an urban road network using GIS. Spat. Inf. Res. 2020, 28, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério, D.; Lopes, A.M.; Machado, J.A.T. Entropy analysis of a railway network complexity. Entropy 2016, 18, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, S.; Luo, T. Fractal characteristics of urban surface transit and road networks: Case study of Strasbourg, France. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017692289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.-Q.; Chen, Y.-G. Fractal characterization of structural evolution of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei transportation network. Hum. Geogr. 2019, 34, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Guariglia, E. Harmonic Sierpinski gasket and applications. Entropy 2018, 20, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casti, J.L. Would-Be Worlds: How Simulation Is Changing the Frontiers of Science; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel, B.; Bokányi, E.; Di Clemente, R.; Kertész, J.; González, M.C. The role of geography in the complex diffusion of innovations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, P.L.; Marston, S.A. Places and Regions in Global Context: Human Geography, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.-Q.; Chen, Y.-G. Multi-scaling allometric analysis of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban system based on nighttime light data. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, H.E.; Black, R.P.; Simaika, Y.M. Long-Term Storage: An Experimental Study; Constable: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Su, H.-L.; Zhong, C.; Meng, Z.-Q.; Luo, H.-W.; Li, X.-C.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Lu, Y. Hyperspectral image classification using wavelet transform-based smooth ordering. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution Inf. Process. 2019, 17, 1950050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.-T. A framework of adaptive multiscale wavelet decomposition for signals on undirected graphs. IEEE Trans. Signal. Process. 2019, 67, 1696–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.T.; Zeng, Q.; Shao, Y.-M.; Wang, L.-M.; Ding, X.-X. Multi-scale demodulation for fault diagnosis based on a weighted-EMD de-noising technique and time–frequency envelope analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Data | Object | Parameter | Complexity | Geographical Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal signal | Time series data | Dynamic evolution | Hurst exponent | Time lag | Phase space |
| Spatial signal | Spatial data | Spatial distribution | Fractal dimension | Spatial dimension | Real space |
| Hierarchical signal | Cross-sectional data | Rank-size distribution | Zipf exponent | Interaction | Order space |
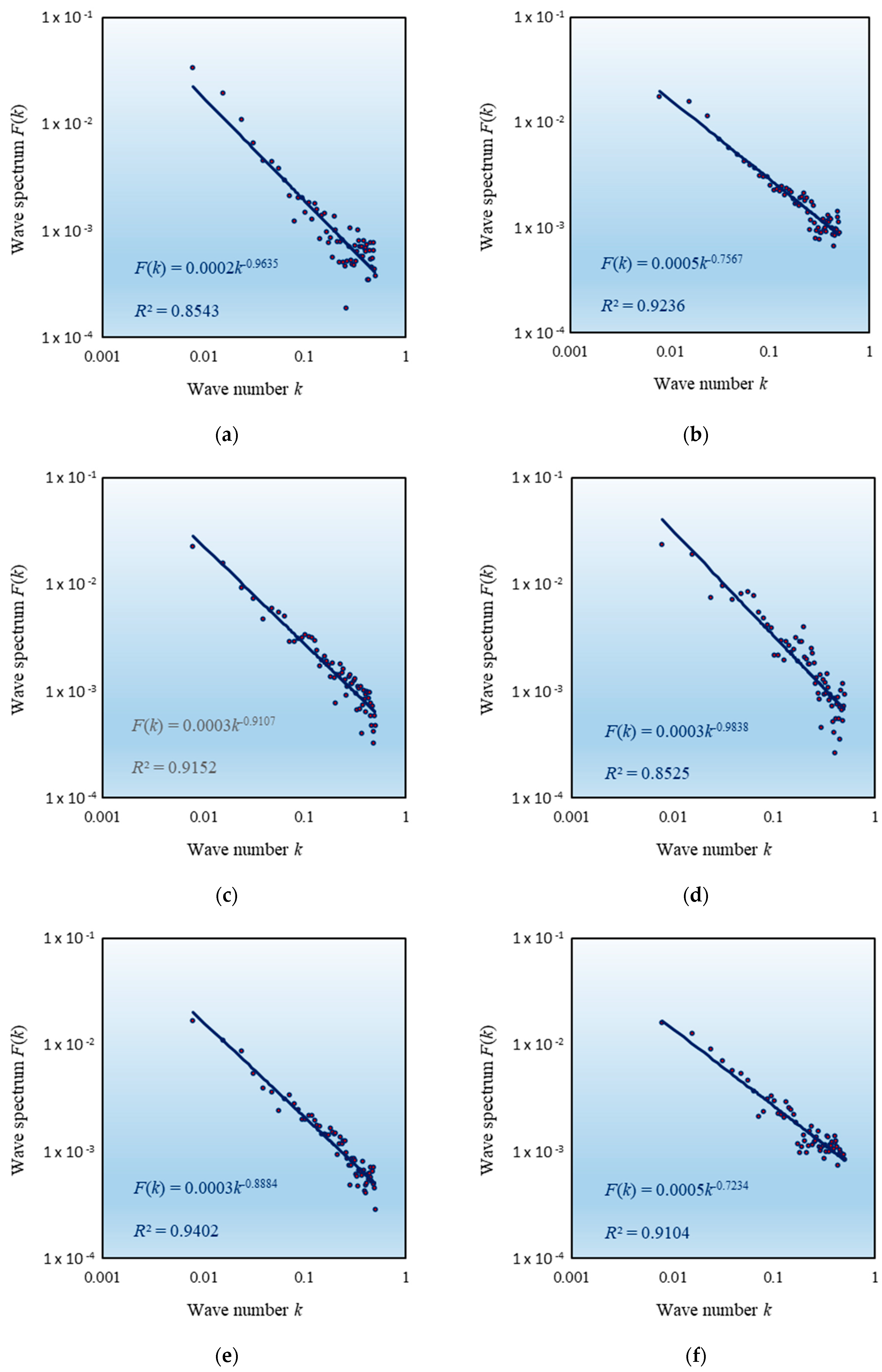
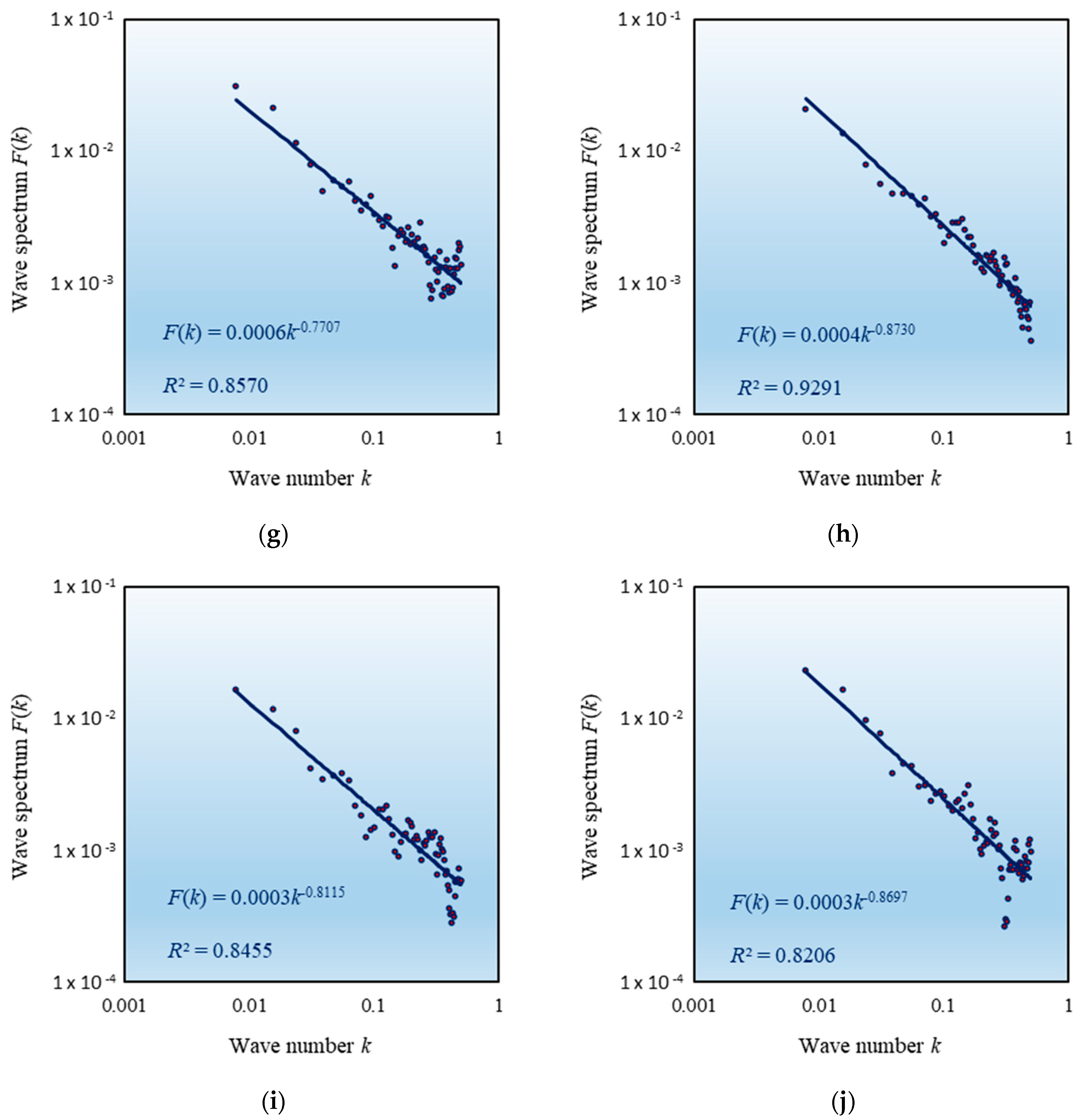
| Position | City | Coefficient F0 * | Spectral Exponent α | Goodness of Fit R2 | Fractal Dimension Df | Fractal Dimension Ds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | Beijing | 0.0002092 | 0.9635 | 0.8543 | 1.9635 | 1.5365 |
| Tianjin | 0.0005071 | 0.7567 | 0.9236 | 1.7567 | 1.7433 | |
| South | Guangzhou | 0.0003429 | 0.9107 | 0.9152 | 1.9107 | 1.5893 |
| Shenzhen | 0.0003437 | 0.9838 | 0.8525 | 1.9838 | 1.5162 | |
| Central | Wuhan | 0.0002729 | 0.8884 | 0.9402 | 1.8884 | 1.6116 |
| South-east | Nanjing | 0.0005069 | 0.7234 | 0.9104 | 1.7234 | 1.7766 |
| Shanghai | 0.0005876 | 0.7707 | 0.8570 | 1.7707 | 1.7293 | |
| Hangzhou | 0.0003653 | 0.8730 | 0.9291 | 1.8730 | 1.6270 | |
| South-west | Chongqing | 0.0003146 | 0.8115 | 0.8455 | 1.8115 | 1.6885 |
| Chengdu | 0.0003350 | 0.8697 | 0.8206 | 1.8697 | 1.6303 |
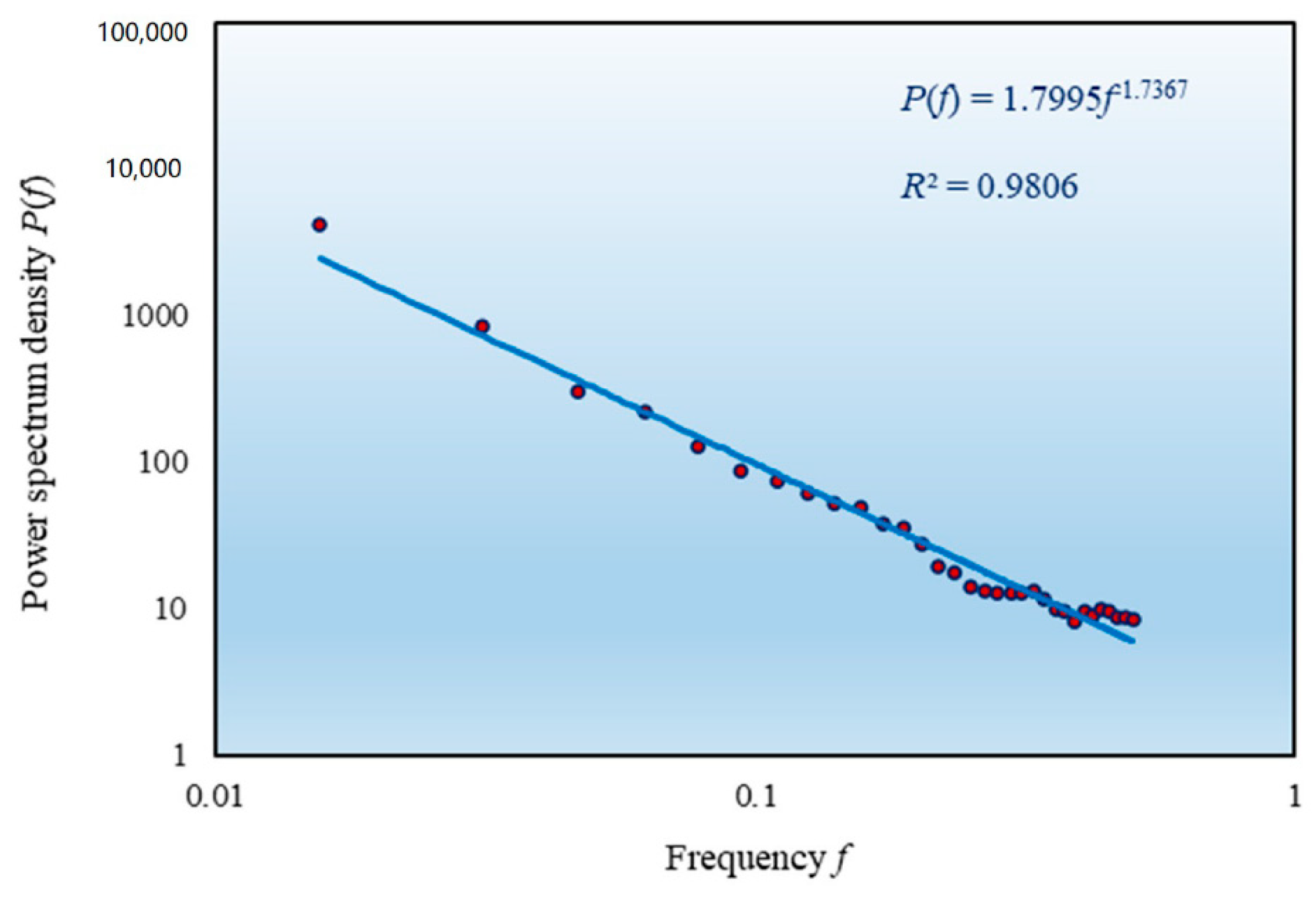
| City | Spectral Analysis | R/S Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | β | R2 | Ds | Df | Coefficient | H | R2 | |
| Baoding | 1532.2018 | 1.3649 | 0.5605 | 1.8176 | 1.6824 | 1.0111 | 0.5982 | 0.9373 |
| Beijing | 25,950.7422 | 1.8009 | 0.8385 | 1.5995 | 1.9005 | 0.9317 | 0.6642 | 0.9542 |
| Cangzhou | 1545.2501 | 1.3164 | 0.5322 | 1.8418 | 1.6582 | 0.9809 | 0.6280 | 0.9696 |
| Chengde | 194.4615 | 1.4499 | 0.7281 | 1.7750 | 1.7250 | 0.9598 | 0.6366 | 0.9152 |
| Handan | 1680.5985 | 1.4165 | 0.4976 | 1.7917 | 1.7083 | 1.2221 | 0.4628 | 0.7739 |
| Hengshui | 295.9529 | 1.2741 | 0.6029 | 1.8629 | 1.6371 | 0.9621 | 0.6091 | 0.9344 |
| Langfang | 2493.1480 | 1.4288 | 0.6164 | 1.7856 | 1.7144 | 1.0578 | 0.5842 | 0.9222 |
| Qinhuangdao | 447.7705 | 1.6063 | 0.7843 | 1.6968 | 1.8032 | 1.1647 | 0.5625 | 0.9301 |
| Shijiazhuang | 1866.2198 | 1.5853 | 0.6874 | 1.7074 | 1.7926 | 0.9727 | 0.6074 | 0.9366 |
| Tangshan | 3534.1318 | 1.5370 | 0.7094 | 1.7315 | 1.7685 | 1.0489 | 0.5620 | 0.9332 |
| Category | Type | Example | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-fractal signals | Stationary series | Random spatial processes | Conventional spatial statistics |
| Trend series with characteristic scale | Exponential distribution of urban population density | Conventional mathematical methods and wave-spectrum scaling | |
| Fractal signals | Self-similar series | Isotropic growing fractal networks | Wave-spectrum scaling based on correlation function |
| Self-affine series | Anisotropic growing fractal networks | Wave-spectrum scaling relation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Long, Y. Spatial Signal Analysis Based on Wave-Spectral Fractal Scaling: A Case of Urban Street Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010087
Chen Y, Long Y. Spatial Signal Analysis Based on Wave-Spectral Fractal Scaling: A Case of Urban Street Networks. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yanguang, and Yuqing Long. 2021. "Spatial Signal Analysis Based on Wave-Spectral Fractal Scaling: A Case of Urban Street Networks" Applied Sciences 11, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010087
APA StyleChen, Y., & Long, Y. (2021). Spatial Signal Analysis Based on Wave-Spectral Fractal Scaling: A Case of Urban Street Networks. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010087






