Featured Application
Bioactive glass proposed in this study demonstrated its possibility as a drug delivery system based on its nanoporous structure and bioactivity for biomedical application.
Abstract
Bioactive glass (BG) was made by the sol–gel method and doped with boron (B) to increase its bioactivity. Microstructures of BG and B-doped BG were observed by scanning electron microscopy, and phase identification was performed using an X-ray diffraction diffractometer. The ion concentrations released after soaking in simulated body fluid (SBF) for 1, 4, and 7 days were measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, and the pH value of the SBF was measured after soaking samples to determine the variation in the environment. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis was performed to further verify the characteristics of mesoporous structures. High performance liquid chromatography was used to evaluate the drug delivery ability of teicoplanin. Results demonstrated that B-doped BG performed significantly better than BG in parameters assessed by the BET analysis. B-doped BG has nanopores and more rough structures, which is advantageous for drug delivery as there are more porous structures available for drug adsorption. Moreover, B-doped BG was shown to be effective for keeping pH values stable and releasing B ions during soaking in SBF. The cumulative release of teicoplanin from BG and B-doped BG reached 20.09% and 3.17% on the first day, respectively. The drug release gradually slowed, reaching 29.43% and 4.83% after 7 days, respectively. The results demonstrate that the proposed bioactive glass has potential as a drug delivery system.
1. Introduction
Bioactive ceramics are mainly composed of calcium, phosphate, silica, and oxygen. Regarding clinical use, they can chemically bond with surrounding soft tissue and hard tissue, such as bone. This type of inorganic material is widely employed in orthopedic and dental settings []. Various elements have been added to bioactive ceramics to enhance their bioactivity, such as silver (Ag) for antibacterial effects [], strontium (Sr) for bone growth [], and magnesium (Mg) for bone mineralization []. Boron (B) can influence bone growth and can act as a nutrition component to enhance bone strength under compression []. It improves bone health, stimulates wound healing, and has been demonstrated to increase bioactivity.
Bioactive glass (BG) is a biomaterial based on SiO2, Na2O, CaO, and P2O5 []. BG is rich in calcium and phosphorus, the main inorganic components of bones and teeth. Calcium phosphate can be absorbed into cells through endocytosis and dissolved in the lysosome, causing its membrane to rupture. The subsequent release of calcium ions into the cytoplasm will increase the intracellular calcium concentration and stimulate the release of exosomes []. Calcium phosphate can be made into nanorods and nanowires, and applied in intracellular protein delivery or used as a building block for the development of artificial bone []. Drugs can be added to the calcium and phosphorous apatite particles, resulting in many calcium and phosphorus ions and causing osmotic pressure changes. This induces the breakdown of lysosomes and leads to drug release into the cytoplasm. These inorganic materials act as long-acting drug carriers []. Mesoporous BG could be further developed as a drug delivery system for gentamicin and ampicillin. The combination of mesoporous BG with drugs could act as a multifunctional delivery platform to improve osteogenesis and antibacterial activity [].
B-doped BG has significant effects on the structural, physiochemical, and biological properties related to tissue regeneration []. Boron trioxide could be added to BG using the traditional melt and quench process []. The glass transition temperature and crystallization onset temperature of BG decreased as the amount of B increased, and B-doped BG was shown to have better hot working properties during scaffold processing without crystallization. []. Using sol–gel methods, porous mesopore B-doped BG scaffolds were prepared for dexamethasone delivery. B-doped BG improved the proliferation and bone-related gene expression of osteoblasts, and it also maintained the sustained release of dexamethasone over a long-term span. []. Mesoporous B-doped BG is a promising biomaterial with improved mechanical properties [].
Teicoplanin and vancomycin are the last lines of antibiotic defense for severe infections with Gram-positive bacteria. They have the strongest antibacterial effect, but teicoplanin has a lower renal toxicity and longer half-life. It is administered intramuscularly or intravenously once a day, so it is a valuable alternative to vancomycin []. Teicoplanin is suitable for the treatment of endocarditis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, septicemia, soft tissue infection, enteritis, and clostridial infection caused by staphylococcal infection []. BG was initially developed as a scaffold for bone repair materials, so BG can be mixed with teicoplanin to form a teicoplanin/BG composite to place in the repair region [].
In this study, BG was developed by the sol–gel method as a drug delivery system for teicoplanin. Various B concentrations were used to tune the physicochemical properties of BG. The feasibility of using BG and B-doped BG materials as drug delivery systems was evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of B-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass
BG was synthesized [] using tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), ethanol, and water under acid catalysis with various amounts of added calcium and phosphate ions. The detailed experimental steps were described in our previous study [,]. Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (Ca(NO3)2) and diammonium hydrogen phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4) were added with the atom ratio of Si:Ca:P = 60:34:6. The formula of BG was modified according to 58S bioglass with 60 mol% SiO2, 36 mol% CaO, and 4 mol% P2O5 []. Trimethyl borate (C3H9BO3) was added to the solution to produce boric acid for B doping. B-doped BG was made with an Si/B molar ratio of 10:1 for BG. The B-doped samples BG_B75, BG_B50, and BG_B25 were sequence reduced to 75%, 50%, and 25% of BG_B100, respectively. Calcium nitrate was used as the calcium source, and the nitrate was removed to form the mesoporous structure. Samples were placed in a muffle furnace that started at room temperature and rose to 500 °C after 2.5 h. Samples were sintered at 500 °C for 6 h. At the end of the sintering process, the furnace was turned off until room temperature was reached, and samples were taken out for washing with DI water twice. Finally, the samples were dried at 60 °C overnight to remove the residual water and then ground.
2.2. Characterization of B-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass
Microstructure observation was performed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, AURIGA, Zeiss, Germany). Dynamic light scattering (DLS, Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, England) was also used to analyze the diameter and polydispersity index (PDI) of BG particles. Crystal structures and phase identification were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker AXS Gmbh, Karlsruhe, Germany). XRD was conducted at 40 kV and 40 mA with Cu Kα = 1.54184 Å as the radiation source. XRD spectra were collected in a 2θ range from 10° to 50°, and the incremental step size was set at 0.02°.
2.3. In Vitro Ion Release Test
Simulated body fluid (SBF) was prepared in accordance with reference [] for the pH value variation test and ion release test. Samples were soaked in SBF for 0, 1, 4, and 7 days. The sample quantity was 250 mg per 50 mL of SBF []. After sample soaking, SBF was taken to measure the pH value and ion concentrations. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Thermo Scientific ELEMENT XR) was sensitive at the ppm level (µg/g) and measured the concentration of ions released, so the SBF with various amounts of sample soaking had to be diluted 100 times to meet the requirement for the measuring level of ICP-MS. SBF was purified by an 0.45 μm syringe filter before ICP-MS was performed.
2.4. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Analysis
A surface area and porosimetric analyzer (Micromeritics ASAP 2020) was used to measure the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and pore size distribution. The residual water inside samples was removed via pre-heating at a high temperature (110 °C). Samples were assessed at liquid nitrogen temperature after being gassed at 200 °C under the flow of N2 for 2 h. [].
2.5. Teicoplanin Release Test
The ratio of teicoplanin to BG powder was 0.1 g teicoplanin per 1 g BG powder. The teicoplanin was dissolved in 1 mL of PBS, and 3 mL of DI water was added into this solution. Then, BG powder was added into this teicoplanin solution. After mixing well, the BG suspension containing teicoplanin was dried at 60 °C. The BG powder containing teicoplanin was immersed in PBS at 38 °C for 0, 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 21, or 28 days. The ratio of BG powder containing teicoplanin to PBS was 0.2 g of powder per 1 mL of PBS. The solution was purified by an 0.45 μm syringe filter. The loading process was the same for BG and BG_B100. The teicoplanin concentration was measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, 1525 Binary HPLC, Waters, Milford, MA, USA), and experimental parameters were those used in a previous study []. The column was a Waters C18 (WAT 0544275), and it was used at 20 °C with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The mobile phase was methanol and acetonitrile (50:50), and the retention time was 2.83 min. The wavelength was 279 nm, the calibration curve of teicoplanin was plotted, and the representative linear equation had a correlation coefficient of 0.9979.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
In order to evaluate the variation in the pH value for various samples soaking for 7 days, the statistical differences were evaluated using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique. When evaluating the test results, a * p value of <0.05 was deemed to represent statistical significance, a ** p value of <0.01 represented a very statistically significant association, and a *** p value of <0.001 represented a highly statistically significant association.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of B-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass
Figure 1 shows the microstructures of BG and B-doped BG (BG_B100, BG_B75, BG_B50, and BG_B25). In Figure 2a, the BG particles obtained by the sol–gel synthesis process are shown to be small size powders with particles of less than 100 nm in size. In Figure 1b–e, the microstructures of B-doped BG are obviously different than those of BG. The microstructures of BG with less B doping are not like BG; they are coarser and more porous, as shown in Figure 1e. The nanoscaled pores are distributed on the surface, and more rough structures are shown in BG_B100. This is advantageous for drug delivery because BG_B100 has more porous structures for drug adsorption.
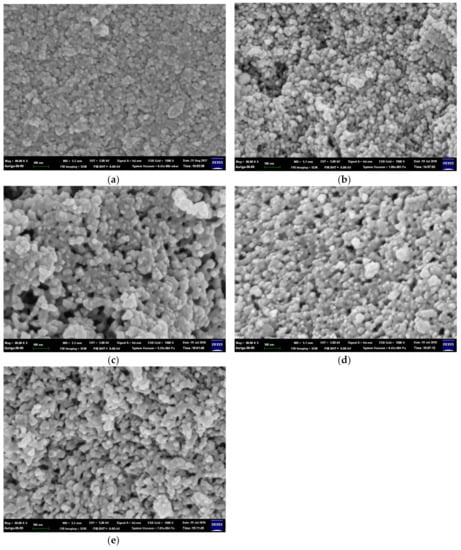
Figure 1.
Microstructures of (a) bioactive glass (BG), (b) BG_B25, (c) BG_B50, (d) BG _B75, and (e) BG_B100.
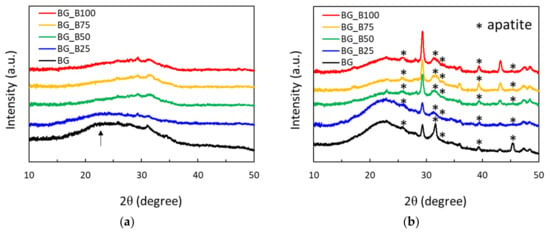
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction spectra of BG and B-doped BG soaking in simulated body fluid (SBF) for (a) 0 and (b) 7 days.
The average sizes of particles and PDI index values are shown in Table 1. The average sizes of particles measured by DLS were 436.23 ± 23.27, 347.60 ± 99.93, 556.60 ± 58.84, 431.57 ± 18.60, and 361.93 ± 17.15 for samples BG, BG_B25, BG_B50, BG_B75, and BG_B100, respectively. The PDI values of samples BG, BG_B25, BG_B50, BG_B75, and BG_B100 were 0.51 ± 0.01, 0.50 ± 0.03, 0.53 ± 0.02, 0.43 ± 0.04, and 0.42 ± 0.02, respectively. BG and B-doped BG samples contained nanoparticles with mesoporous microstructures. The particle size ranged from around 300 to 600 nm. The particle size range for drug deposition in various body organs via different dosage forms and routes of administration is as follows: transdermal (10–600 nm), intravenous/intramuscular (200–2000 nm), and ocular (100–3000 nm) [].

Table 1.
The average sizes and polydispersity index (PDI) index values of BG and B-doped BG.
Figure 2 shows the XRD spectra of BG and B-doped BG after immersion in SBF for 0 and 7 days. In Figure 2a, none of the samples show sharp diffraction peaks and BG has an obvious and wide SiO2 peak with a low intensity. The XRD pattern observed is similar to that shown in a previous study and is characterized by broad diffraction bands []. Amorphous nanosized bioglass has the ability to promote apatite deposition under physiological conditions []. In Figure 2b, the diffraction peaks could be characteristic of those found in nature, according to Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) File No. 9432. Crystalline diffraction peaks of apatite were mainly found at 25.9°, 31.8°, 32.9°, 39.8°, and 46.7° of 2θ and were correlated with Miller indices of (0 0 2), (2 1 1), (3 0 0), (1 3 0), and (2 2 2), respectively. Before soaking in SBF, BG was found to have amorphous SiO2. After soaking for 7 days, the apatite phase was found in all samples, and these BG based materials were demonstrated to be biomimetic in vitro.
3.2. In Vitro Ion Release Test of B-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass
Figure 3 shows the pH values and B ions released into SBF after BG and B-doped BG samples were soaked for 7 days. In order to determine the variation in SBF after sample soaking, the variation in the pH value is shown in Figure 3a. The initial pH values of SBF were kept at 7.49 ± 0.01. After the soaking period of 7 days, the basic components of all samples were dissolved in SBF and produced increases in the pH value, especially for BG. The pH value increment trend was similar to that observed in a previous study [], where the basic ions of BG were released in great amounts, causing the pH value to increase after soaking in SBF. On day 7, the pH values increased to 7.73 ± 0.03, 7.75 ± 0.04, 7.75 ± 0.08, 7.62 ± 0.02, and 8.02 ± 0.09 in samples BG_B100, BG_B75, BG_B50, BG_B25, and BG, respectively. This shows that the addition of borate can slow down the increment in the pH value. The difference in pH values between BG and BG_B100 on day 7 was very statistically significant with a p value of 0.001, which indicates that B doping was an effective way of keeping pH values stable during soaking in SBF. The pH value of BG_B25 on day 7 was lower than that of other B doped samples. The statistical differences among the four B-doped samples were determined using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique. The p value was 0.012, with values <0.05 being statistically significant. In order to determine why B25 had a lower pH than the other substrates, BG_B25 was further measured by BET. BG_B25 has a larger hysteresis loop of N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, which means that BG_B25 has a greater area available for apatite deposition. The basic ions from BG_B25 were used to form apatite, causing the pH value to decrease. In Figure 3b, the release of B ions also increased as the soaking period increased. There was a controlled release profile of B ions with various concentrations of B. On day 7, B ions were released in quantities of around 8.94, 4.41, 3.13, 2.16, and 0 ppm from samples BG_B100, BG_B75, BG_B50, BG_B25, and BG, respectively. This shows that the concentration of B ions released was altered by the addition of borate.
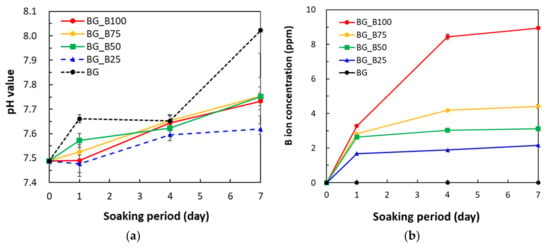
Figure 3.
(a) pH value and (b) boron ions released into SBF after BG and B-doped BG soaking for 7 days.
3.3. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Analysis
Figure 4a shows the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of samples. In Figure 4a, a hysteresis loop is presented for two samples and the mesopores of the samples are shown to induce capillary condensation to form a hysteresis loop. This indicates that the mesoporous structures exist in both BG and B-doped BG. Figure 4b shows the pore size distribution of samples. Figure 4b shows that BG mesopores have pore diameters of around 5–50 nm. According to International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature [], mesoporous materials have structure diameters ranging from 2 to 50 nm with some exclusive outstanding properties. B-doped BG (BG_B100) shows two pore size distributions: the first is from 5 to 30 nm and the second one is from 30 to 100 nm. This special pore size distribution characteristic is combined with mesoporous and macroporous (>50 nm) characteristics.
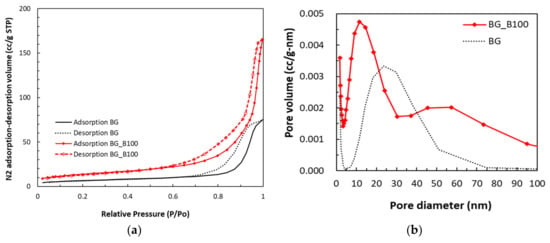
Figure 4.
(a) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution of BG and B-doped BG.
Parameters corresponding to the pore characteristics of BG and BG_B100 were measured, as shown in Table 2. BG had an average pore size of 19.43 nm, a BET surface area of 23.95 m2/g, and a total pore volume of 0.12 cm3/g. BG_B100 had an average pore size of 20.68 nm, a BET surface area of 49.42 m2/g, and a total pore volume of 0.26 cm3/g. Both samples showed good mesoporous character, and the corresponding parameters of BG_B100 were much better than those of BG. The characteristic hierarchical porous structure of BG_B100 is also shown in Figure 4b. The adsorption of proteins (such as albumin and fibronectin) or drugs can increase as the nanopore size increases [].

Table 2.
Average pore size Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and total pore volume of BG and B-doped BG.
3.4. Teicoplanin Release Test
Figure 5 shows the cumulative release of teicoplanin of BG and B-doped BG (BG_B100). Both BG and BG_B100 with two different antibiotic contents showed a similar pharmacokinetic pattern with early rapid release and later slow and sustained release. The cumulative release of teicoplanin from BG and BG_B100 reached 20.09% and 3.17% on the first day, respectively. The drug release gradually slowed, reaching 29.43% and 4.83% after 7 days, respectively. The release reached a stable plateau period until the end of the observation period. The antibiotic release time of the two groups of samples reached 28 days, and the total cumulative release rates were 32.90% and 6.36%, respectively.
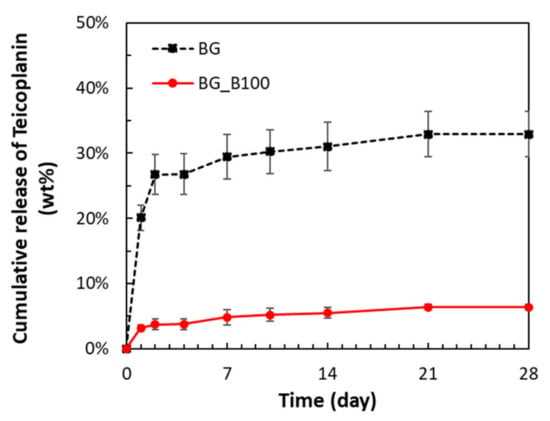
Figure 5.
Cumulative release of teicoplanin from BG and B-doped BG (BG_B100).
Teicoplanin is a water-soluble antibiotic. When PBS enters the drug carrier, it dissolves the drug in situ and has a high drug concentration. BG particles demonstrated the ability to deposit apatite, so the particle size increased. For example, the deposited layer upon Bioglass® powder increased in thickness to about 600 nm thick after 21 days of immersion in SBF []. In addition, from the first day to the 30th day of immersion in SBF, the porosity percent decreased from 8.5% to 0.7% []. Due to the apatite formation on the surface of BG, the drug is limited to that in the drug carrier. The difference in drug concentration between the inside and the outside of the drug carrier is used as the driving force to make the drug diffuse through the surface barrier layer to the outside of the carrier. Drug delivery consists of two processes: drug dissolution and drug diffusion. Because the drug dissolves quickly, the diffusion rate is slower, so the drug release process is controlled by the diffusion effect. BG_B100 has a special pore size distribution characteristic combined with mesoporous and microporous features and provides a greater surface area to form the apatite shell. It can slow drug diffusion and maintain the lower release rate of teicoplanin. A lower release rate of teicoplanin could maintain the antibacterial ability but not induce a reduction in the cell number in osteoblasts and chondrocytes []. The proposed material BG_B100 has potential to be used as a drug delivery system, especially for dentistry and bone tissue engineering applications.
4. Conclusions
The proposed B-doped BG was synthesized using the sol–gel method. Microstructures were observed using SEM and BET, and dual porous structures for drug adsorption were demonstrated. The drug delivery ability was evaluated using HPLC to measure the cumulative release of teicoplanin. The cumulative release of teicoplanin from BG and BG_B100 reached 20.09% and 3.17% on the first day, respectively. The drug release gradually slowed, reaching 29.43% and 4.83% after 7 days, respectively. The results show that the proposed BG materials have the potential to act as drug delivery systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and supervision was done by C.-L.H. and T.-M.L. Investigation was performed by W.F., B.-R.H., Y.-H.W., and G.-C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Taiwan (grant number MOST-108-2221-E-037-001-MY2) and the Kaohsiung Medical University Research Foundation (grant number KMU- KI109004).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Chang, J. Bioceramics to regulate stem cells and their microenvironment for tissue regeneration. Mater. Today 2019, 24, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, A.C.; Pereira, P.R.; Barbosa, A.M.; Torrado, E.; Alves, N.M. Optimization of silver-containing bioglass nanoparticles envisaging biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraei, S.B.A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Mahdavi, F.S.; Yus, J.; Ferrandez-Montero, A.; Sanchez-Herencia, A.J.; Gonzalez, Z.; Ferrari, B. Effect of SrR delivery in the biomarkers of bone regeneration during the in vitro degradation of HNT/GN coatings prepared by EPD. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.; Ruszler, P. Effects of dietary boron on poultry bone strength. Trans. ASAE 1995, 38, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Naasani, L.I.S.; Zanatelli, C.; Paim, T.C.; Azevedo, J.G.; de Lima, J.C.; da Cruz Fernandes, M.; Buchner, S.; Wink, M.R. Bioglass 45S5: Structural characterization of short range order and analysis of biocompatibility with adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyong, Y.-J.; Chang, K.-C.; Lin, F.-H. Calcium phosphate particles stimulate exosome secretion from phagocytes for the enhancement of drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Jana, N.R. Length-Controlled Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Nanorod and Nanowire and Application in Intracellular Protein Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8710–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyong, Y.-J.; Wang, M.-H.; Kuo, L.-W.; Su, C.-F.; Kuo, W.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; Lin, F.-H. Mesoporous hydroxyapatite as a carrier of olanzapine for long-acting antidepression treatment in rats with induced depression. J. Control. Release 2017, 255, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Multifunctional mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective delivery of therapeutic ions and drug/growth factors. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Buettner, T.; Pacheco, V.M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Boron-containing bioactive glasses in bone and soft tissue engineering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kolzow, J.; Chen, R.R.; Du, J. Effect of solution condition on hydroxyapatite formation in evaluating bioactivity of B2O3 containing 45S5 bioactive glasses. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.S.; Datta, S.; Adarsh, T.; Diwan, P.; Annapurna, K.; Kundu, B.; Biswas, K. Effect of boron oxide addition on structural, thermal, in vitro bioactivity and antibacterial properties of bioactive glasses in the base S53P4 composition. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2018, 498, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Miron, R.; Sculean, A.; Kaskel, S.; Doert, T.; Schulze, R.; Zhang, Y. Proliferation, differentiation and gene expression of osteoblasts in boron-containing associated with dexamethasone deliver from mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7068–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deilmann, L.; Winter, O.; Cerrutti, B.; Bradtmüller, H.; Herzig, C.; Limbeck, A.; Lahayne, O.; Hellmich, C.; Eckert, H.; Eder, D. Effect of boron incorporation on the bioactivity, structure, and mechanical properties of ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrubini, G.; Tengattini, S.; Colombo, R.; Bianchi, D.; Carlotti, F.; Orlandini, S.; Terreni, M.; Temporini, C.; Massolini, G. A new MS compatible HPLC-UV method for Teicoplanin drug substance and related impurities, part 1: Development and validation studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 162, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, K.; Oh, J.; Choi, R.; Woo, H.I.; Park, H.-D.; Kang, C.-I.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-Y. Therapeutic drug monitoring of teicoplanin using an LC–MS/MS method: Analysis of 421 measurements in a naturalistic clinical setting. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 167, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.-T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.-H.; Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E. Elution characteristics of teicoplanin-loaded biodegradable borate glass/chitosan composite. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Fang, W.; Chen, I.H.; Hung, T.-Y. Manufacture and biomimetic mineral deposition of nanoscale bioactive glasses with mesoporous structures using sol-gel methods. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17224–17229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-H.; Lian, M.-J.; Fang, W.; Huang, B.-R.; Liu, T.-H.; Chen, J.-A.; Huang, C.-L.; Lee, T.-M. In Vitro Properties for Bioceramics Composed of Silica and Titanium Oxide Composites. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Qiao, W.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Miao, S.; Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, A.; Qiu, D. Synthesis of nanosized 58S bioactive glass particles by a three-dimensional ordered macroporous carbon template. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernè, E.; Ferraris, S.; Cassinelli, C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Surface functionalization of Bioglass® with alkaline phosphatase. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 264, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilonga, A.; Kim, J.-K.; Sarawade, P.B.; Quang, D.V.; Shao, G.N.; Elineema, G.; Kim, H.T. BET study of silver-doped silica based on an inexpensive method. Mater. Lett. 2012, 80, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoni, M.H.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of a new and rapid HPLC for determination of lyophilized teicoplanin. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, A.; Balossier, G.; Kannan, S.; Michel, J.; Rebelo, A.H.S.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Development and in vitro characterization of sol–gel derived CaO–P2O5–SiO2–ZnO bioglass. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Veeresh, V.; Mallick, S.P.; Jain, Y.; Sinha, S.; Rastogi, A.; Srivastava, P. Design and evaluation of chitosan/chondroitin sulfate/nano-bioglass based composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Afshar, A. Double layer bioglass-silica coatings on 316L stainless steel by sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40 Pt A, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Huo, Q.-S. Synthetic Chemistry of the Inorganic Ordered Porous Materials. In Modern Inorganic Synthetic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 389–428. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Dong, L.; Cheng, K.; Weng, W. Effect of hierarchical pore structure on ALP expression of MC3T3-E1 cells on bioglass films. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 156, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallanes-Perdomo, M.; Meille, S.; Chenal, J.-M.; Pacard, E.; Chevalier, J. Bioactivity modulation of Bioglass® powder by thermal treatment. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoci, V., Jr.; Adams, C.S.; Hickok, N.J.; Shapiro, I.M.; Parvizi, J. Antibiotics for local delivery systems cause skeletal cell toxicity in vitro. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 462, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).