Abstract
To establish complementary information for the diagnosis and evaluation of ocular surface diseases, we developed a multi-modal, non-invasive optical imaging platform by combining ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography (UHR-OCT) with a microvascular imaging system based on slit-lamp biomicroscopy. Our customized UHR-OCT module achieves an axial resolution of ≈2.9 μm in corneal tissue with a broadband light source and an A-line acquisition rate of 24 kHz with a line array CCD camera. The microvascular imaging module has a lateral resolution of 3.5 μm under maximum magnification of ≈187.5× with an imaging rate of 60 frames/s, which is sufficient to image the conjunctival vessel network and record the movement trajectory of clusters of red blood cells. By combining the imaging optical paths of different modules, our customized multi-modal anterior eye imaging platform is capable of performing real-time cross-sectional UHR-OCT imaging of the anterior eye, conjunctival vessel network imaging, high-resolution conjunctival blood flow videography, fluorescein staining and traditional slit-lamp imaging on a single device. With self-developed software, a conjunctival vessel network image and blood flow videography were further analyzed to acquire quantitative morphological and hemodynamics parameters, including vessel fractal dimensions, blood flow velocity and vessel diameters. The ability of our multi-modal anterior eye imager to provide both structural and functional information for ophthalmic clinical applications was demonstrated on a healthy human subject and a keratitis patient.
1. Introduction
The ocular surface is susceptible to infection, inflammation, trauma and other ocular surface diseases that strongly affect people’s health and quality of life [1,2,3]. Various clinical symptoms may exist for most of the ocular surface diseases. For example, mainly caused by the inflammation of the cornea, keratitis typically manifests as a defect of the corneal epithelium and even stromal infiltration, which could cause conjunctival vessel dilation, distortion and congestion, and even lead to abnormal blood vessel growth [4,5,6]. To establish complementary information for the diagnosis and treatment evaluation of ocular surface diseases, different imaging modalities are usually applied in ophthalmic clinics to provide multi-modal and multi-dimensional images [7,8].
Slit-lamp biomicroscopy (SLB) is the gold standard for routine ophthalmic examinations. By shining a thin sheet of light into the eye, an in vivo stereoscopic evaluation of the pathological changes of the cornea, conjunctiva and other anterior segment tissues can be performed by SLB [9]. However, the limited magnification and poor spatial resolution of traditional SLB make it difficult to visualize more detailed pathological structures and perform accurate biometric measurements [10,11,12]. Fluorescein stain could stain stroma while leaving the intact epithelium with a specific fluorescein dye, thereby demarcating the location and area of the epithelial loss in ocular surface diseases, on a relative macro scale as well [13]. Developed in the 1990s, optical coherence tomography (OCT) has revolutionized the field of ophthalmology and vision science with its non-contact, non-invasive and high-resolution nature and become one of the prominent diagnostic tools in offering cross-sectional tissue imaging [14,15,16]. Applications of OCT for in vivo human eye imaging have been widely demonstrated in the literature [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. With ever-improving techniques in broadband light sources, ultra-high resolution OCT (UHR-OCT) has achieved micron-scale axial resolution [21,22]. UHR-OCT imaging of the ocular surface can now resolve and even measure the thickness of tear film and the major structures, such as the individual corneal layers: the epithelium, the Bowman’s membrane, the Stroma, Descemet’s membrane and the endothelium [23,24,25,26], which helps clinicians be better in the diagnosis and management of ocular surface pathologies and diseases, including keratitis [23,26], keratoconus [27], ocular surface neoplasia [28], etc.
For ocular surface diseases, apart from the physiological structural changes, the microvascular system would also change when the eye is inflamed, as inflammatory mediators would induce a series of vascular changes, including vasodilation, increased permeability and increased blood flow [5,6], which correlates with the severity of the lesion. Techniques like OCT angiography [29,30] have been applied to image the vessels of the anterior segment, but they could only provide morphological information and lack of the function of providing quantitative functional parameters, such as the blood flow velocity. To measure the blood flow velocity in bulbar conjunctival vessels and also evaluate their network complexity, our team has developed functional slit-lamp biomicroscopy to achieve conjunctival vessel network imaging as well as high-resolution conjunctival blood flow videography [10,31]. With customized software, images and videos can be processed to achieve morphological parameters such as vessel diameter and complexity, as well as functional parameters of blood flow velocity. These methods have been demonstrated in clinical studies of healthy subjects [32,33] and ocular surface defects and inflammatory diseases [31,34,35], and proved to be a considerably easier and more cost-effective alternative to image and evaluate the bulbar conjunctival microvasculature system.
Nowadays, the development trends of ophthalmic imaging modalities are focused on improving the system resolution and providing functional imaging ability to achieve accurate early diagnosis and quantitative classification of ophthalmic diseases. While ophthalmic disease diagnoses and treatment evaluations are typically made based on separate information acquired with more than one technique, there is also a need for a multi-modal system that is capable of providing adequate and comprehensive information. Multi-modal systems will not only improve the examination efficiency by reducing patients’ moving from one examination system to the others, but also reduce the space and equipment investment. To date, researchers have developed a variety of multi-modal systems to combine the merits of each imaging modality for human eye imaging [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], among which, however, most are focused on posterior segment imaging [36,37,38,39,40]. Hybrid systems for anterior human eye imaging are relatively rare: few researches have demonstrated the integration of OCT system into SLB for both anterior and posterior segment imaging to improve the examination efficiency [41,42]; multi-modal systems combining OCT and corneal topography have been developed for anterior segment biometry measurements and applied to eyes with keratoconus [43,44]; a Scheimpflug camera combined with corneal topography has been used to measure pre/post-refractive surgery eyes [45]. All of these techniques offer only the structural information.
In this study, we developed a multi-modal non-invasive anterior eye imaging platform by combining our customized UHR-OCT and microvascular imaging system based on a functional slit-lamp biomicroscopy to provide both structural and functional information in ophthalmic clinical practice. The imaging platform was capable to perform: (1) real-time high-resolution OCT images of human cornea/conjunctiva with the UHR-OCT module; (2) conjunctival vessel network imaging and high-resolution conjunctival blood flow videography with the microvascular imaging module; (3) fluorescein staining and slit-lamp imaging with the SLB module. Customized software was also installed to achieve quantitative vessel parameters. Experiments were performed on a healthy human subject and a keratitis patient to demonstrate the feasibility of our multi-modal system.
2. Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
The schematic and photo of our multi-modal anterior eye imager are illustrated in Figure 1. The system combines three optical imaging modules that were installed on two moveable carts (Figure 1b). On the imaging cart, the microvascular imaging module is integrated into the SLB module in a common path optical design with the sample arm of our customized UHR-OCT module adapted on the top (Figure 1c). The reference arm and the spectrometer of the UHR-OCT module are placed on the processing cart together with a computer. Components on the two carts are connected with flexible communication cables and optical fibers to maintain the UHR-OCT stability when adjusting the imaging cart during patient examination.
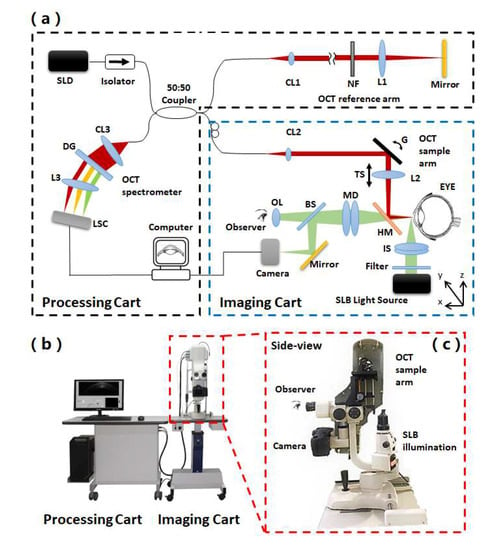
Figure 1.
Schematic and photo of the multi-modal anterior eye imager. (a) Schematic of the system, SLD: superluminescent diode, CL: collimator, NF: neutral-density filter, L: lens, G: galvano, TS: translational stage, DG: diffraction grating, LSC: line scanning camera, HM: hot mirror, IS: illumination shaper, BS: beam splitter, MD: magnification dial, OL: ocular lens. The UHR-OCT beam is depicted in red; the microvascular imaging module and SLB beam are depicted in green. Black dashed line-framed parts are installed on the processing cart, while blue dashed line-framed parts are installed on the imaging cart. (b) Photo of the system and (c) the side-view of the zoom-in area.
The commercialized SLB module (66VisionTech, YZ5, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China) has the basic slit-lamp examination function. By turning the control dial and adding/removing the diffuser on the SLB illumination shaper, the SLB illumination light sheet size is adjustable (width: 0–14 mm; length: 1–14 mm) to form the needed thin light sheet or diffused homogeneous illumination. It also offers the function of fluorescein stain imaging by using cobalt blue light of the SLB light source to generate blue excitation light with diffused homogeneous illumination. The microvascular imaging module uses the light source and optical system of the SLB module. Details of the microvascular imaging module development appeared in an earlier publication from our group [31]. In short, as shown in Figure 1a, a digital camera (Canon, EOS 60D, Beijing, China) is built into the SLB optics to acquire conjunctival microvascular network and videography. The camera is attached to the slit-lamp via an inherent camera port of SLB. A green filter (Thorlabs, FGV9, Newton, NJ, USA) is inserted into the illumination path to improve the image quality of the conjunctival vessel network and blood flow videography. The implementation of the camera on the SLB is simple and easy without any modifications or extra adapters. With the built-in optical magnifications of SLB to 25× (set by a magnification dial on the SLB) and the 7.5× magnification of the digital camera (set by Canon EOS 60D camera Movie Crop Function), the total imaging magnification can reach up to ≈187.5×. By imaging a USAF resolution target under the best magnification, as shown in Figure 2a,b, the element 2 of group 7 was readable, corresponding to a lateral resolution of 3.5 μm, which is sufficient to image the red blood cell (≈7 μm) in the conjunctival microvasculature. The vessel network imaging should be performed under a single-shot mode with the autofocus function of the camera. With a movie crop function that uses a center portion of pixels on the camera chip to perform high-magnification high-speed video recording at 60 frames per second (fps), the movement of red blood cell (RBC) clusters can be recorded for further processing to blood flow velocity. With the digital camera, digital images of the subject appearance and fluorescein stain can also be recorded and displayed on the computer screen in real-time.
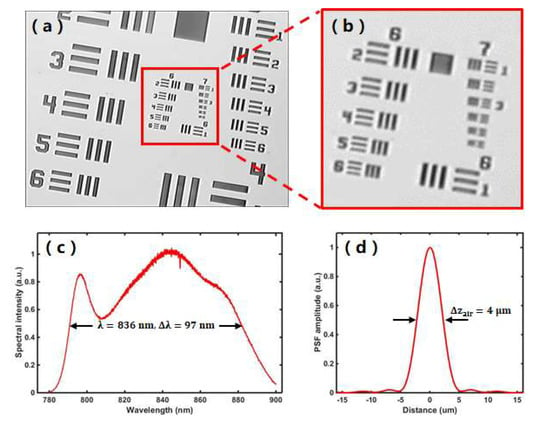
Figure 2.
System performance characterization. (a) Representative image of the microvascular imaging module imaging a USAF resolution target with the highest magnification of 187.5x. (b) Zoom-in area of the red box area in (a), showing that element 2 of group 7 was readable, corresponding to a lateral resolution of 3.5 μm. (c) Measured light source spectrum of the UHR-OCT system. (d) Measured axial point spread function (PSF) of the UHR-OCT system by imaging a mirror in air.
Our customized UHR-OCT module is a spectral domain OCT system. It uses a broadband superluminescent diode (SLD, Superlum, BLM2-D-840-B-10, Moscow, Russia) that is centered at a wavelength of 840 nm with 100 nm bandwidth. As shown in Figure 1a, after passing an isolator that is used to protect the light source from back reflections, the light from the source is split into the sample arm and the reference arm of the OCT interferometry by a 50:50 fiber coupler. In the sample arm, the OCT light is collimated with a fiber collimator (CL2, Thorlabs, PAF-X-11-B, Newton, NJ, USA), reflected on the galvanometric x-y scanners (G, Cambridge Technology, 6215H set, Bedford, MA, USA), and focused by a lens (L2, f = 100 mm, Edmund Optics, NT45-806, Barrington, NJ, USA) that is installed on a translational stage for focusing adjustment. To integrate the UHR-OCT sample arm to the SLB module, a 45-degree hot mirror (HM, Edmund Optics, NT64-471, Barrington, NJ, USA) is installed in front of the SLB imaging port and reflects the focused OCT beam to the human eye. The power of incident light on the human eye is adjusted to 750μW, below the maximum permissible exposure dictated by ANSI (American National Standard for Ophthalmics—Light Hazard Protection for Ophthalmic Instruments) [46]. The light going to the reference arm is collimated by a fiber collimator (CL1, Thorlabs, PAF-X-7-B, Newton, NJ, USA), passed through a neutral-density filter (NF, Thorlabs, NDC-25C-4M, Newton, NJ, USA) for reference signal control and focused on a mirror by a focusing lens (L1, f = 100 mm, Edmund optics, NT45-806, Barrington, NJ, USA). The optical pathlength of the reference arm is matched with the sample arm to the focal position. The light reflected from the eye in the sample arm and the mirror in the reference arm are collected, combined and sent to the self-built OCT spectrometer. The spectrometer is composed of a collimating lens (CL3, f = 50 mm, OZ Optics, HPUCO-23AF-830-S-50AC, Ottawa, Canada), a 1200 lines/mm volume holography transmission grating, an image enlargement lens (L3, f = 180mm, Schneider, PROJ.3.5/180, Bad Kreuznach, Germany) and a line array CCD camera (LSC, E2V, Aviiva SM2, San Jose, CA, USA). The spectrum of the interference signal is acquired with a maximum speed of 24,000 A-lines per second, transferred using the image acquisition board (National Instruments, PCIe-1428, Austin, TX, USA) and processed by our self-developed LabVIEW program running on a computer with Windows 10. Figure 2c shows the measured spectrum of the light source in our system. By imaging a mirror, the axial resolution of our UHR-OCT module was measured to be ≈4 μm in the air (Figure 2d), corresponding to ≈2.9 μm in corneal tissue with a refractive index of 1.38 [47]. The scanning range is adjustable up to 12 mm on the ocular surface of the human subject.
A head-rest is installed on the imaging cart table for its forehead and chin rests for the subjects during imaging, to minimize head movements. A fixation light is used as an external fixation target to guide the non-examined eye of the subject, thereby reducing eye movements during image acquisition and changing the imaging position for OCT and microvascular imaging. The entire optical parts on the imaging cart can be adjusted in three dimensions with the slide way of the SLB module and the table lift for imaging convenience.
2.2. Microvascular Imaging Algorithms
With the conjunctival vessel network images and blood flow video acquired by the microvascular imaging module, we further applied imaging algorithms to extract both the quantitative morphological and functional parameters. Details of the development of the customized software could refer to our former publications [31,32]. In brief, for conjunctival vessel network image, image quality is first improved by applying adaptive histogram equalization and further enhanced by subtracting the background image. The enhanced image is then converted into a binary image and a skeletonization algorithm is applied to get the vessel network skeleton. Qualitative analysis of the vessel skeleton image is finally demonstrated to calculate the fractal dimension complex degree and extract the fractal dimensions mono-fractal (Dbox) and multi-fractal (D0) values that can be used to evaluate vessel density and complexity. For conjunctival blood flow videography, based on space-time images on the bulbar conjunctiva, a motion correction algorithm is first applied to compensate the eye motion and get the registered images. After the enhancement and segmentation of vessel images, the average image from multiple frames is used for the vessel diameter measurement by calculating the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the vessel signal profile. By analyzing the movement of red blood cell clusters and the space between clusters, quantitative conjunctival hemodynamics parameters, including axial blood flow velocity (Va, mm/s), cross-sectional blood flow velocity (Vs, mm/s) and vessel diameter (D, μm) are obtained and the blood flow rate (Q, pl/s) is calculated by multiplying the cross-sectional blood flow velocity Vs with the cross-sectional area (A, μm2) (assuming a circular cross-section) [48].
3. Experiments and Results
To verify the performance of the multi-modal anterior eye imager, experiments were demonstrated on both a healthy subject and a keratitis patient. Before the experiments, informed consent was obtained for the subjects, and the experimental procedures adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. During the imaging procedures, the head of the subject was pressed on the head-rest. The subject was advised to look into the external target with the non-examined eye and avoid blinking within the recording periods. For each subject, a normal SLB examination was performed at first. UHR-OCT imaging and microvascular imaging were then performed sequentially on the central cornea/corneal lesion area and the bulbar conjunctiva area by changing the fixation target location. Fluorescein staining imaging of SLB was performed on the keratitis patient at last. With a well-trained operator and a cooperative subject, the total examination time would be around 15 min, including the imaging time and system adjusting time for all the imaging modes of SLB examination (5 min), UHR-OCT imaging (2 min), microvascular imaging (5 min) and fluorescein staining imaging (3 min).
In the experiments demonstrated in this paper, 20 UHR-OCT images were recorded at a scan rate of 24,000 A-scans/s, corresponding to 12 frames/s with 2048 A-scans to form a cross-sectional image with a scanning range of 6 mm, costing around 2 s. For microvascular imaging, a bulbar conjunctival vessel network image was taken for vessel fractal analysis under the single-shot mode of the camera by setting the SLB magnification set to 16×, corresponding to an imaging field of view of ≈18 × 12 mm2 with an image size of 5184 × 3456 pixels. Then, under the Movie Crop function of the camera, bulbar conjunctival blood flow video clips were taken for hemodynamic analysis at a speed of 60 frames/s. With the SLB magnification set to 25 × and 60D camera telephoto effect magnification of 7.5×, the imaging field of view is ≈1.15 × 0.86 mm2 with an image size of 640 × 480 pixels. For averaging purposes, five video clips on the temporal bulbar conjunctiva of one subject were needed to record from multiple locations for 1–2 s on each imaging location. Acquired images and video clips were then processed by our customized software to get the final results.
3.1. Healthy Subject
Figure 3 shows the experimental results acquired by our multi-modal anterior imager on the health subject. Figure 3b shows the UHR-OCT image of the healthy cornea. The best focus of the sample arm was set in the middle of the cornea, so the full cornea could be imaged with the highest sensitivity. In the zoom-in area of the UHR-OCT image (Figure 3c), major layer structures of the cornea, such as the epithelium layer (EP), Bowman’s layer (BL), stroma (ST) and endothelium layer (ED), are clearly seen. Figure 3d is the single-shot image of the conjunctival vessel network of the healthy subject. Figure 3e,f shows the segmented and skeletonized vessel network processed from Figure 3d with our customized software. The fractal dimensions of the microvascular network of the healthy subject were calculated to be: mono-fractal Dbox = 1.51 and multi-fractal D0 = 1.52. Figure 3g is a stilled conjunctival vessel image captured from one representative conjunctival blood flow video clip recorded on the healthy subject. From the zoom-in area shown in Figure 3h, clusters of red blood cells are visible. The registered video clip (Video s1) shows clearly, the movement trajectories of red blood cells, which were used by the software to calculate the hemodynamic results. The calculated quantitative results of the healthy subject are: mean vessel diameter D = 17.84 ± 1.52 μm, cross-sectional area = 251.40 ± 44.43μm2, axial blood flow velocity Va = 0.26 ± 0.07 mm/s, cross-sectional blood flow velocity Vs = 0.18 ± 0.05 mm/s and blood flow rate Q = 61.82 ± 22.29 pl/s.
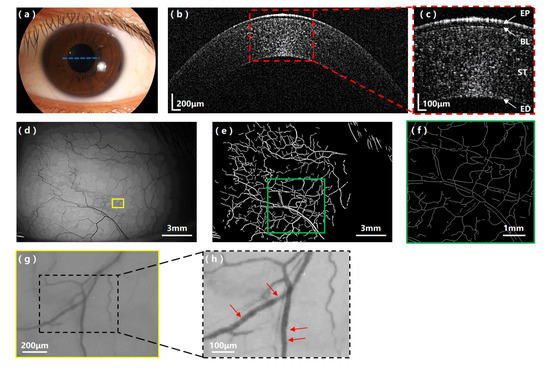
Figure 3.
Experimental results on the healthy subject with the multi-modal anterior eye imager. (a) Appearance image of the healthy subject’s eye; the blue dashed line indicates the UHR-OCT scanning position. (b) UHR-OCT image of the health cornea and (c) the zoom-in area showing clear corneal layer structures. EP: epithelium layer, BL: Bowman’s layer, ST: stroma, ED: endothelium layer. (d) The bulbar conjunctival vessel network image of the healthy subject; the yellow box indicates the location where the representative video clip (Video s1) was taken. (e) The segmented vessel network image and (f) the skeletonized vessel network image of the selected region (green box) in (e). (g) A representative conjunctival vessel image captured from the bulbar conjunctival blood flow video clip (Video s1). (h) Zoom-in area of (g) showing the resolved clusters of red blood cells (red arrows).
3.2. Keratitis Patient
Figure 4 shows the experimental results acquired by our multi-modal anterior imager on the keratitis patient. An inflamed lesion can be clearly observed on the appearance image (Figure 4a). As shown in the UHR-OCT image (Figure 4b,c), the inflamed corneal lesion presents as highly reflective structures in the central region close to the apex of the cornea; the defects of the cornea are clearly visible with violation of the epithelium and Bowman’s layer until the anterior stroma. Figure 4d–f shows the single-shot image of the conjunctival vessel network of the keratitis patient and the segmented and skeletonized vessel network processed with our customized software. The fractal dimensions of the microvascular network of the keratitis patient were calculated to be: mono-fractal Dbox = 1.59 and multi-fractal D0 = 1.76. Figure 4g,h is a stilled conjunctival vessel image captured from one representative conjunctival blood flow video clip of the keratitis patient (Video s2), and the zoom-in area shows resolved clusters of red blood cells. Processed by the software, the calculated quantitative hemodynamic results of the keratitis patient are: mean vessel diameter D = 23.12 ± 1.00 μm, cross-sectional area = 419.68 ± 37.00μm2, axial blood flow velocity Va = 0.27 ± 0.06 mm/s, cross-sectional blood flow velocity Vs = 0.18 ± 0.06 mm/s and blood flow rate Q = 119.3 ± 42.17 pl/s. Figure 4i is the fluorescein stain image of the keratitis patient highlighting the inflamed lesion location, size and boundary on the ocular surface.
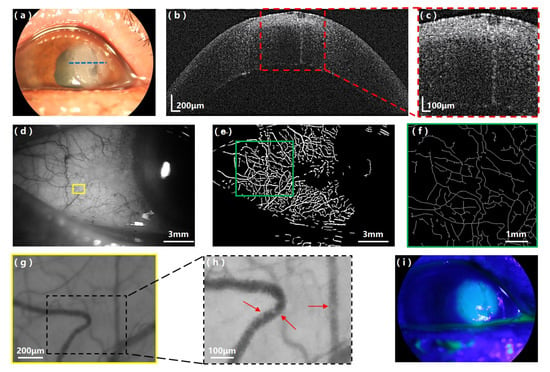
Figure 4.
Experimental results on the keratitis patient with the multi-modal anterior eye imager. (a) Appearance image of the keratitis patient’s eye; the blue dashed line indicates the UHR-OCT scanning position. (b) UHR-OCT image of the inflamed cornea and (c) the zoom-in area showing the highly reflective, inflamed lesion. (d) The bulbar conjunctival vessel network image of the keratitis patient; the yellow box indicates the location where the representative video clip (Video s2) was taken. (e) The segmented vessel network image and (f) the skeletonized vessel network image of the selected region (green box) in (e). (g) A representative conjunctival vessel image captured from the bulbar conjunctival blood flow video clip (Video s2). (h) Zoom-in area of (g) showing resolved clusters of red blood cells (red arrows). (i) Fluorescein stain image of the keratitis patient.
Table 1 shows the comparison of the obtained quantitative morphological and hemodynamic parameters from the healthy subject and keratitis patient. In general, the conjunctival vessel hemodynamics and fractal dimension values were in agreement with previous studies [31,32,33,34,35], which validates the performance of our system. The mono-fractal Dbox and multi-fractal D0 of the keratitis patient are both higher than the healthy subject, indicating an increase of both vessel density and complexity. Although the blood flow velocity shows no obvious difference between the keratitis and healthy subject, the mean vessel diameter of the keratitis patient is much larger compared with that of the healthy subject, resulting in a higher flow rate of the bulbar conjunctival vessels in the keratitis patient [5,6].

Table 1.
Comparison of the quantitative vessel parameters of the healthy and keratitis patient.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Here, we developed a non-invasive multi-modal imaging platform capable of doing both structural and functional imaging of the anterior eye by combining a customized UHR-OCT module and a microvascular imaging module on a traditional slit-lamp microscopy system for the first time. An axial resolution of ≈ 2.9 μm in corneal tissue was achieved by the UHR-OCT module for high-resolution corneal structure imaging. The microvascular imaging module had a lateral resolution of 3.5 μm with magnification up to ≈ 187.5×, resolving the conjunctival microvasculature and the moving clusters of red blood cells. With the multi-modal anterior eye imager, a high-resolution cross-sectional OCT image, a conjunctival vessel network image, conjunctival blood flow videography, a fluorescein staining image and a normal SLB image of in vivo human anterior eye could be achieved within 20 min by a well-trained examiner—much more efficient than the current examination scheme by different imaging modalities in ophthalmic clinics. We have successfully demonstrated the system’s feasibility by providing multi-modal information to show its potential for ophthalmic clinical application by imaging a healthy subject and a keratitis patient. With customized software, quantitative morphological and homodynamic vessel parameters were further obtained. Preliminary differences in the vessel density, complexity, vessel diameter and blood flow rate between the healthy subject and the keratitis patient were recognized which were consistent with clinical manifestations of vessel dilation, distortion and increased blood flow after inflammation [5,6].
Based on our literature searching, though various multi-modal ophthalmic imaging systems have been demonstrated for human eye imaging, only a few have been developed for the anterior segment. The integration of OCT with SLB conducted by both Stehouwer et al. [41] and Mueller et al. [42] can image both anterior and posterior segments more efficiently but only provides structural images. Other groups have applied the combinations of OCT [43,44] or a Scheimpflug camera [45] and corneal topography with a focus only on the anterior segment biometry measurements. Compared with current ophthalmic imaging modalities, our self-developed multi-modal anterior eye imager not only offers precise structural information with the UHR-OCT module, but also provides functional information of bulbar conjunctival vessels through the microvascular imaging module. With the multi-modal and multi-dimensional information, our system would potentially help ophthalmologists to achieve more comprehensive evaluations, and more accurate diagnoses and quantitative classifications of anterior eye diseases.
Future work on system improvement will be focused on increasing the UHR-OCT imaging speed to achieve three-dimensional imaging in real-time. As the morphological and hemodynamic parameters of the bulbar conjunctival vessels could potentially be used to access the status of ocular surface diseases, large scale clinical studies will need to be conducted to comprehensively characterize the relations between these quantitative parameters of human bulbar conjunctival microvasculature and differences of ocular diseases. What is more, while artificial intelligence has been recognized to be so promising in ophthalmic disease diagnosis with different ophthalmic images [49,50,51], our multi-modal system can potentially offer a technical basis for providing complementary images for multimodal artificial intelligence applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/7/2545/s1. Video s1: The registered bulbar conjunctival blood flow video clip taken at a frame rate of 60Hz with 640 × 480 pixels from the healthy subject. Video s2: The registered bulbar conjunctival blood flow video clip taken at a frame rate of 60Hz with 640 × 480 pixels from the keratitis patient.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.X., S.L. and J.Y.; methodology, P.X. and Z.D.; software, G.W.; data curation, Y.D. and Q.W.; writing—original draft preparation, P.X. and Z.D.; writing—review and editing, P.X., Z.D. and J.Y.; visualization, P.X.; supervision, J.Z., S.L. and J.Y.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0112400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81901788, 61975246, 61505267).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gipson, I.K. Age-related changes and diseases of the ocular surface and cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondino, B.J. Inflammatory diseases of the peripheral cornea. Ophthalmology 1988, 95, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xie, L.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Fu, S.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; et al. A multi-center, cross-sectional study on the burden of infectious keratitis in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, A.; Lietman, T.; Rose-Nussbaumer, J. Update on the management of infectious keratitis. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youlten, L.J.F. Inflammatory mediators and vascular events. In Inflammation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 571–587. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkhaleq, L.A.; Assi, M.A.; Abdullah, R.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Hezmee, M.N.M. The crucial roles of inflammatory mediators in inflammation: A review. Vet. World 2018, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oatts, J.T.; Keenan, J.D.; Mannis, T.; Lietman, T.M.; Rose-Nussbaumer, J. multimodal assessment of corneal thinning using optical coherence tomography, scheimpflug imaging, pachymetry and slit lamp examination. Cornea 2017, 36, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantopoulos, D.; Cruzat, A.; Hamrah, P. In vivo imaging of corneal inflammation: New tools for clinical practice and research. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 25, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, T.J.T.P. Intraocular light scatter, reflections, fluorescence and absorption: What we see in the slit lamp. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2018, 38, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, H.; Mao, X.; Ke, B.; Yan, W.; Liu, C.; Cintrón-Colón, H.R.; Perez, V.L.; Wang, J. Slit-lamp photography and videography with high magnifications. Eye Contact Lens 2015, 41, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzel, T.P.; Devarajan, K.; Lwin, N.C.; Yam, G.H.; Schmetterer, L.; Mehta, J.S.; Ang, M. Comparison of optical coherence tomography angiography to indocyanine green angiography and slit lamp photography for corneal vascularization in an animal model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, H.; Kennedy, A.; Comyn, O.; Spalton, D.J.; Nanavaty, M.A. Commercial slit lamp anterior segment photography versus digital compact camera mounted on a standard slit lamp with an adapter. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.; Ren, H.; Laurent, J. Corneal epithelial fluorescein staining. J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1995, 66, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhi, M.; Duker, J.S. Optical coherence tomography—current and future applications. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 24, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, W.; Liu, M.; Kumar, A.; Kamali, T.; Unterhuber, A.; Leitgeb, R.A. Optical coherence tomography today: Speed, contrast, and multimodality. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 071412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazlin, V.; Xiao, P.; Dalimier, E.; Grieve, K.; Irsch, K.; Sahel, J.A.; Fink, M.; Boccara, A.C. In vivo high resolution human corneal imaging using full-field optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Mazlin, V.; Grieve, K.; Sahel, J.A.; Fink, M.; Boccara, A.C. In vivo high-resolution human retinal imaging with wavefront-correctionless full-field OCT. Optica 2018, 5, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.; Baskaran, M.; Werkmeister, R.M.; Chua, J.; Schmidl, D.; Aranha Dos Santos, V.; Garhöfer, G.; Mehta, J.S.; Schmetterer, L. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 66, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanji, A.A.; Sayyad, F.E.; Galor, A.; Dubovy, S.; Karp, C.L. High-resolution optical coherence tomography as an adjunctive tool in the diagnosis of corneal and conjunctival pathology. Ocul. Surf. 2015, 13, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Lee, K.S.; Rolland, J.P.; Zavislan, J.M.; Aquavella, J.V.; Yoon, G. Micrometer axial resolution OCT for corneal imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 3037–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Hosseinaee, Z.; Han, L.; Kralj, O.; Sorbara, L.; Bizheva, K. 250 kHz, 1.5 µm resolution SD-OCT for in-vivo cellular imaging of the human cornea. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6569–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werkmeister, R.M.; Sapeta, S.; Schmidl, D.; Garhöfer, G.; Schmidinger, G.; Aranha Dos Santos, V.; Aschinger, G.C.; Baumgartner, I.; Pircher, N.; Schwarzhans, F.; et al. Ultrahigh-resolution OCT imaging of the human cornea. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werkmeister, R.M.; Alex, A.; Kaya, S.; Unterhuber, A.; Hofer, B.; Riedl, J.; Bronhagl, M.; Vietauer, M.; Schmidl, D.; Schmoll, T.; et al. Measurement of tear film thickness using ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5578–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Shen, M.; Li, M.; Zhu, D.; Wang, M.R.; Wang, J. Anterior segment biometry during accommodation imaged with ultralong scan depth optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, V.; Kagemann, L.; Wollstein, G.; Ishikawa, H.; Gabriele, M.L.; Wojtkowski, M.; Srinivasan, V.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Duker, J.S.; Dhaliwal, D.K.; et al. In Vivo Corneal High-Speed, Ultra–High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantalon, A.; Pfister, M.; Aranha dos Santos, V.; Sapeta, S.; Unterhuber, A.; Pircher, N.; Schmidinger, G.; Garhöfer, G.; Schmidl, D.; Schmetterer, L.; et al. Ultrahigh-resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography for analysis of corneal microarchitecture during wound healing. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e761–e771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shousha, M.A.; Karp, C.L.; Perez, V.L.; Hoffmann, R.; Ventura, R.; Chang, V.; Dubovy, S.R.; Wang, J. Diagnosis and management of conjunctival and corneal intraepithelial neoplasia using ultra high-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.; Romano, V.; Steger, B.; Vinciguerra, R.; Lawman, S.; Williams, B.; Hicks, N.; Czanner, G.; Zheng, Y.; Willoughby, C.E.; et al. Imaging of corneal neovascularization: Optical coherence tomography angiography and fluorescence angiography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.D.; Devarajan, K.; Chua, J.; Schmetterer, L.; Mehta, J.S.; Ang, M. Optical coherence tomography angiography for the anterior segment. Eye Vis. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhong, J.; DeBuc, D.C.; Tao, A.; Xu, Z.; Lam, B.L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J. Functional slit lamp biomicroscopy for imaging bulbar conjunctival microvasculature in contact lens wearers. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 92, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, H.; Yan, W.; Cintrón-Colón, H.R.; Perez, V.L.; DeBuc, D.C.; Feuer, W.J.; Wang, J. Vessel sampling and blood flow velocity distribution with vessel diameter for characterizing the human bulbar conjunctival microvasculature. Eye Contact Lens 2016, 42, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Tao, A.; Wu, S.; Yan, W.; Yuan, J.; Liu, C.; DeBuc, D.C.; Wang, J. Measurement variability of the bulbar conjunctival microvasculature in healthy subjects using functional slit lamp biomicroscopy (FSLB). Microvasc. Res. 2015, 101, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheung, A.T.W.; Hu, B.S.; Wong, S.A.; Chow, J.; Chan, M.S.; To, W.J.; Li, J.; Ramanujam, S.; Chen, P.C. Microvascular abnormalities in the bulbar conjunctiva of contact lens users. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 51, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Li, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; et al. Microvascular abnormalities in dry eye patients. Microvasc. Res. 2018, 118, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujat, M.; Ferguson, R.D.; Patel, A.H.; Iftimia, N.; Lue, N.; Hammer, D.X. High resolution multimodal clinical ophthalmic imaging system. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 11607–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, J.D.; El-Haddad, M.T.; Bozic, I.; Tye, L.A.; Majeau, L.; Godbout, N.; Rollins, A.M.; Boudoux, C.; Joos, K.M.; Patel, S.N.; et al. Simultaneous multimodal ophthalmic imaging using swept-source spectrally encoded scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wei, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuai, D.; Burke, J.M.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, H.F. Integrating photoacoustic ophthalmoscopy with scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, optical coherence tomography, and fluorescein angiography for a multimodal retinal imaging platform. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 061206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felberer, F.; Kroisamer, J.S.; Baumann, B.; Zotter, S.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Pircher, M. Adaptive optics SLO/OCT for 3D imaging of human photoreceptors in vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, R.J.; Zhang, P.; Zam, A.; Miller, E.B.; Goswami, M.; Wang, X.; Jonnal, R.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Flannery, J.G.; et al. Adaptive-optics SLO imaging combined with widefield OCT and SLO enables precise 3D localization of fluorescent cells in the mouse retina. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2191–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehouwer, M.; Verbraak, F.D.; de Vries, H.; Kok, P.H.; van Leeuwen, T.G. Fourier domain optical coherence tomography integrated into a slit lamp; a novel technique combining anterior and posterior segment OCT. Eye 2010, 24, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mueller, M.; Schulz-Wackerbarth, C.; Steven, P.; Lankenau, E.; Bonin, T.; Mueller, H.; Brueggemann, A.; Birngruber, R.; Grisanti, S.; Huettmann, G. Slit-lamp-adapted fourier-domain OCT for anterior and posterior segments: Preliminary results and comparison to time-domain OCT. Curr. Eye Res. 2010, 35, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiano-Lomoriello, D.; Bono, V.; Abicca, I.; Savini, G. Repeatability of anterior segment measurements by optical coherence tomography combined with Placido disk corneal topography in eyes with keratoconus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S.; Li, X.; Canedo, A.L.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Bykhovskaya, Y. Optical coherence tomography combined with videokeratography to differentiate mild keratoconus subtypes. J. Refract. Surg. 2014, 30, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, G.; Barboni, P.; Carbonelli, M.; Hoffer, K.J. Repeatability of automatic measurements by a new Scheimpflug camera combined with Placido topography. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American National Standards Institute. American National Standard for Ophthalmics—Light Hazard Protection for Ophthalmic Instruments, ANSI Z80.36-2016; American National Standards Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Atchison, D.; Smith, G. Optics of the Human Eye; Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, UK, 2000; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsiaris, A.G.; Tachmitzi, S.V.; Batis, N.; Kotoula, M.G.; Karabatsas, C.H.; Tsironi, E.; Chatzoulis, D.Z. Volume flow and wall shear stress quantification in the human conjunctival capillaries and post-capillary venules in vivo. Biorheology 2007, 44, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Hogarty, D.T.; Mackey, D.; Hewitt, A.W. Current state and future prospects of artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 47, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Pasquale, L.R.; Peng, L.; Campbell, J.P.; Lee, A.Y.; Raman, R.; Tan, G.S.W.; Schmetterer, L.; Keane, P.A.; Wong, T.Y. Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Sadeghipour, A.; Gerendas, B.S.; Waldstein, S.M.; Bogunović, H. Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 67, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).