Smart Helmet and Insole Sensors for Near Fall Incidence Recognition during Descent of Stairs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
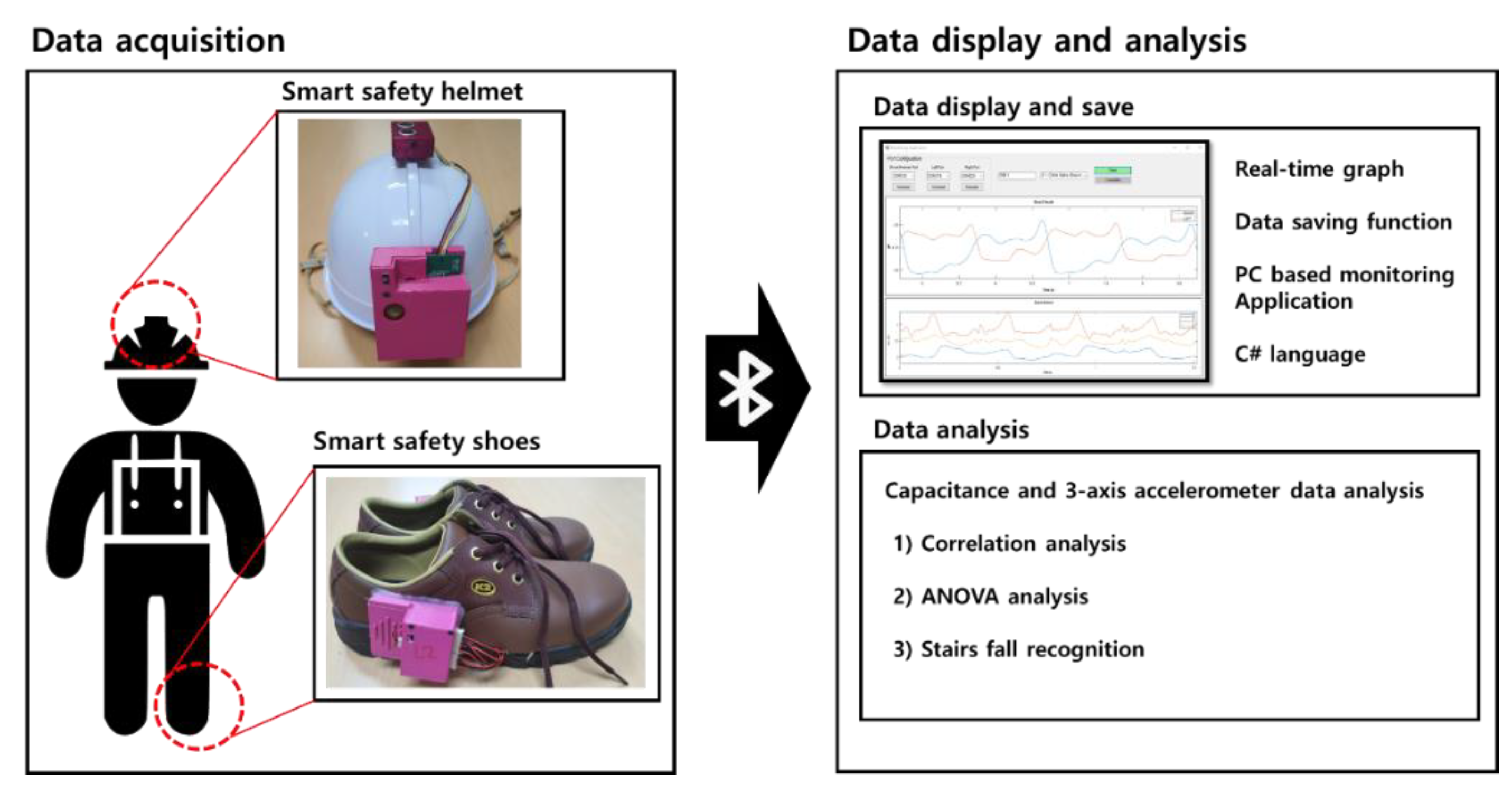
2.1. Development of Smart Helmet and Smart Shoes
2.1.1. System Architecture
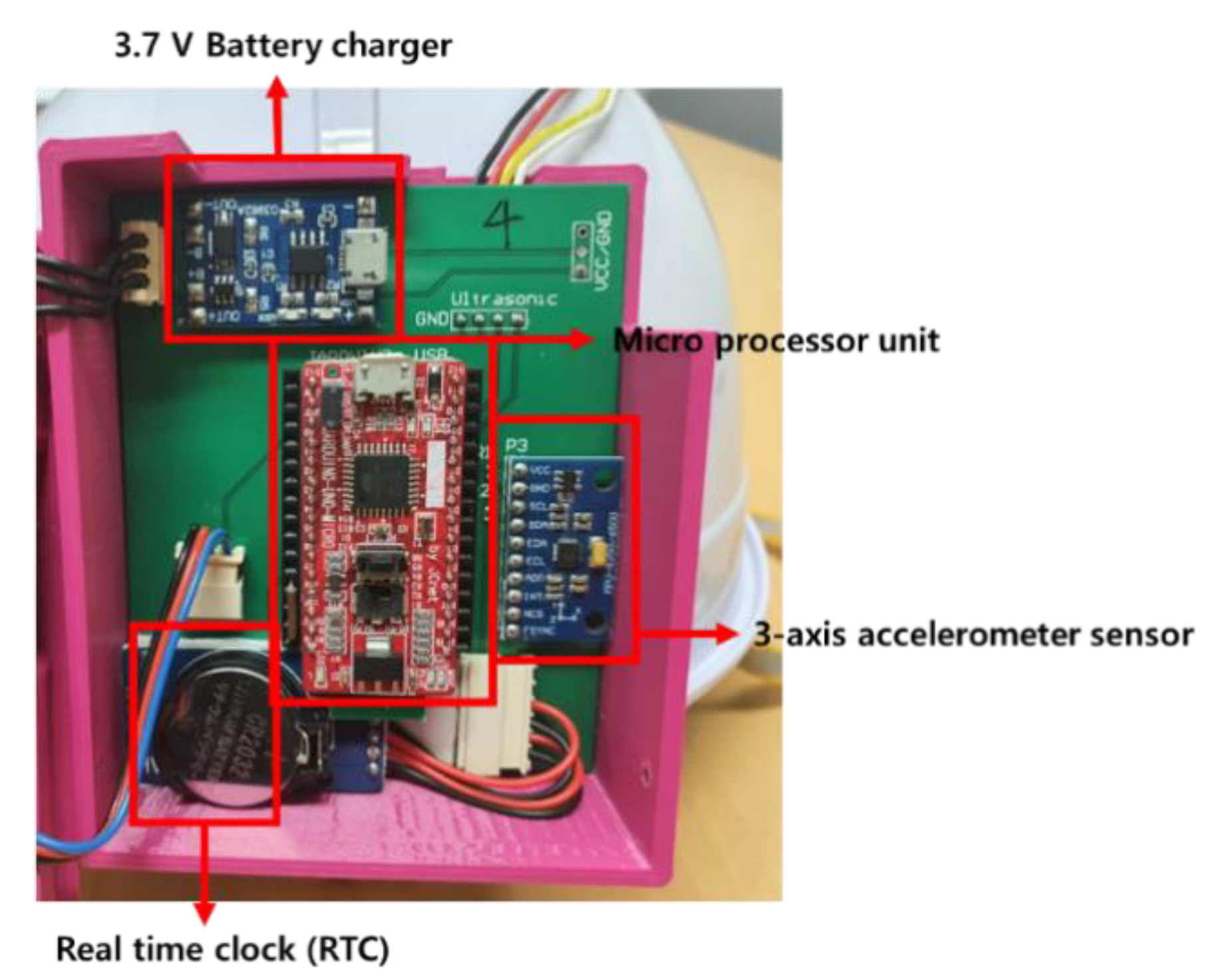
2.1.2. Development of Smart Helmet
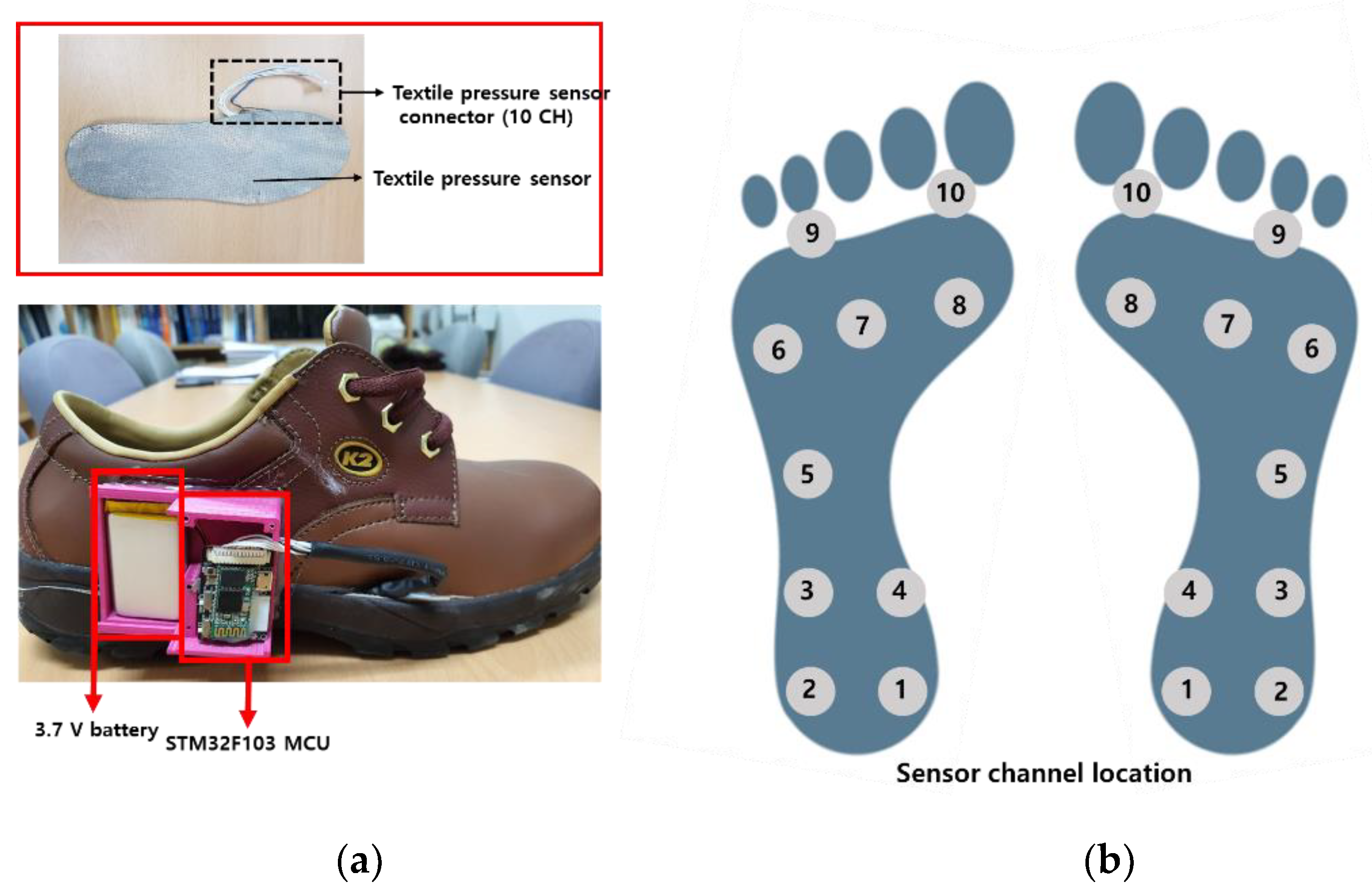
2.1.3. Development of Smart Shoes
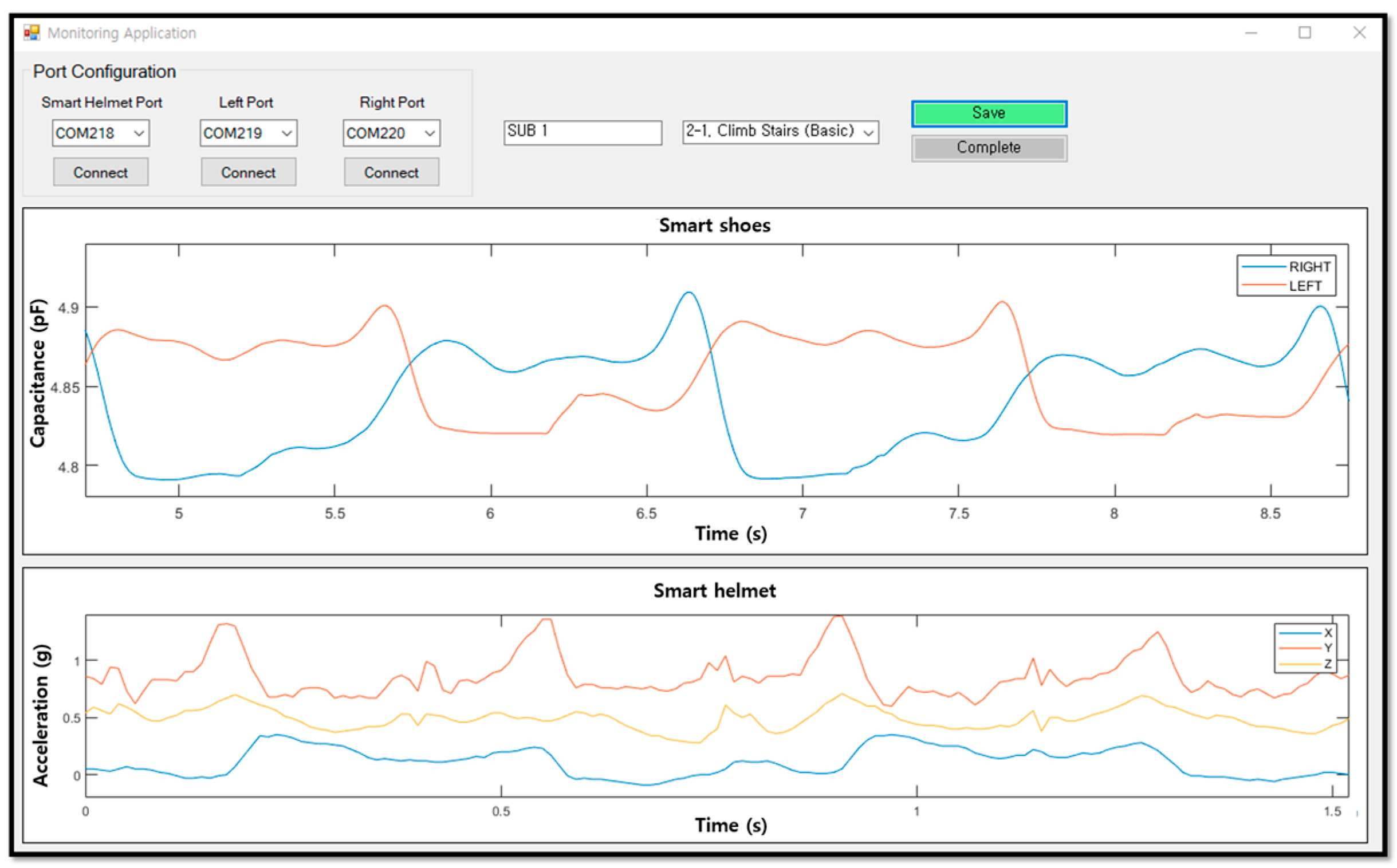
2.1.4. Development of Data Saving and Monitoring Application
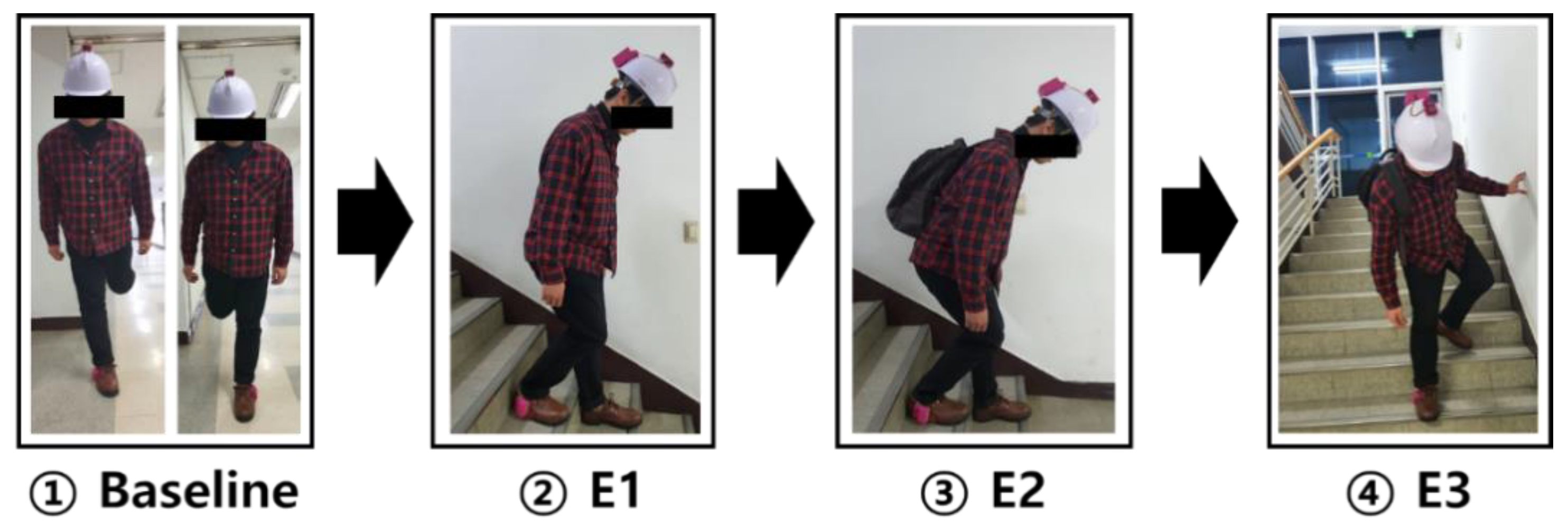
2.2. Stair Descent Simulation of Construction Workers
2.2.1. Subject Characteristics
2.2.2. Experiment Procedure
2.3. Signal Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Whole Body Balance Analysis (Smart Shoes)
2.4.2. Plantar Pressure Distribution Analysis (Smart Shoes)
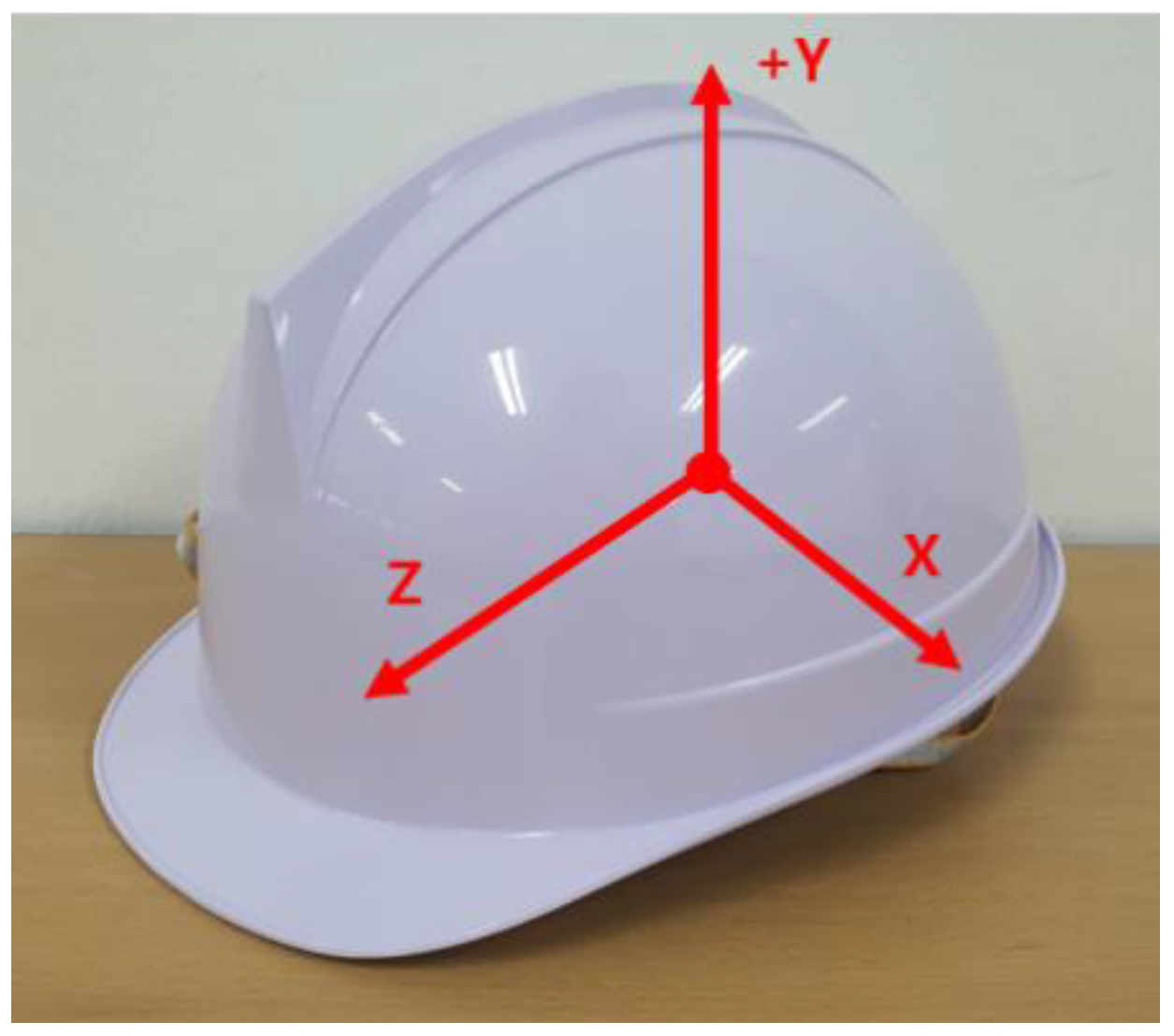
2.4.3. Head Movement Analysis (Smart Helmet)
2.4.4. Smart Helmet and Smart Shoe Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Whole Body Balance Analysis (Smart Shoe)
3.2. Results of Plantar Pressure Distribution Analysis (Smart Shoe)
3.3. Results of Head Movement Analysis (Smart Helmet)
3.4. Results of Smart Helmet and Smart Shoe Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Son, C.B. An Analysis on the Technical Training of Construction Skilled Workers and Its Improvement Measures. J. Korea Inst. Build. Constr. 2019, 19, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yaghmaie, S. Investigation of Fall Accidents in the Construction Industry by Implementation of Design for Safety Concept. Doctoral Dissertation, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.R.; Lee, S.H.; Sun, C.; Jebelli, H.; Yang, K.H.; Choi, B.J. Wearable Sensing Technology Applications in Construction Safety and Health 2019. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 3119007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwu, F.A.; Alabere, I.D.; Douglas, K.E. Prevalence of Falls and Associated Factors among Construction Workers in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Asian J. Med. Health 2019, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasarwanji, M.F.; Mayton, A.G.; Pollard, J. Why Slips, Trips, and Falls Are Still Problem: A Hazard Assessment at Surface Mines. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2019, 63, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmlert, K.; Lundholm, L. Slips, trips and falls in different work groups—With reference to age and from a preventive perspective. Appl. Ergon. 2001, 32, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Lockhart, T.E. Nonfatal occupational injuries associated with slips and falls in the United States 2006. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2006, 36, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.K. Injury Prevention for Healthy & Safe Society; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC): Cheongju, Korea, 2018; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Feng, Y.; Sun, F. Sensor Fusion for Recognition of Activities of Daily Living. Sensors 2018, 18, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Luo, J. Highly Portable, Sensor-Based System for Human Fall Monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.H.; Ahn, C.R.; Vuran, M.C.; Aria, S.S. Semi-supervised near-miss fall detection for ironworkers with a wearable inertial measurement unit. Autom. Constr. 2016, 68, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzeng, R.J.; Fang, Y.C.; Chen, I.C. A feasibility study of using smartphone built-in accelerometers to detect fall portents. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, R.A.; Scanaill, C.N.; McGrath, M. Falls prevention in the home: Challenges for new technologies. Intell. Technol. Bridg. Grey Digit. Divid. 2011, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altman, I.; Wohlwill, J.F. Human Behavior and Environment: Advances in Theory and Research; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gifford, R. Environmental Psychology: Principles and Practice, 4th ed.; Optimal Books: Colville, WA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Light, J.; Cha, S.; Chowdhury, M. Optimizing pressure sensor array data for a smart-shoe fall monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaccour, K.; Assaad, H.A.; Hassani, A.H.; Darazi, R.; Andres, E. Sway analysis and fall prediction method based on spatio-temporal sliding window technique. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbal, F.; Habbal, F.; Nuaimi, A.A.; Shimmari, A.A.; Safi, A.; Abhushuqair, T. PPEs Compliance Technology to Legalize the Automated Monitoring of Safety Standards. In Proceedings of the 36th ISARC, Banff, AB, Canada, 21–24 May 2019; pp. 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzner, J.; Zhang, S.; Teizer, J.; Bargstadt, H.J. A case study on automated safety compliance checking to assist fall protection design and planning in building information models. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2013, 31, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, J.H.; Jang, M.S.; Choi, S.W.; Yoo, H.D.; Lee, E.H. A Study on Smart Helmet to Efficiently Cope with the Operation and Safety of Workers in Industrial Settings. Int. J. Control Autom. 2018, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Wang, C.W.; Min, S.D.; Lee, S.H. Safety Helmet Wearing Management System for Construction Workers Using Three-Axis Accelerometer Sensor. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Gu, Y. An Advanced Deep Learning Approach for Safety Helmet Wearing Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things and IEEE Green Computing and Communications and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing and IEEE Smart Data, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2019; pp. 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, H.; Yin, Q. Building information modeling in combination with real time location systems and sensors for safety performance enhancement. Saf. Sci. 2018, 102, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Kim, Y.; Min, S.D. Soft-Material-Based Smart Insoles for a Gait Monitoring System. Materials 2018, 11, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.W.; Kim, Y.; Shin, H.S.; Min, S.D. Preliminary Clinical Application of Textile Insole Sensor for Hemiparetic Gait Pattern Analysis. Sensors 2019, 19, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, J.; Hoey, J.; Stewart, L.; Zemel, R.S.; Mihailidis, A. Automated detection of unusual events on stairs. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Dominguez, G.S.; Taati, B.; Mihailidis, A. 3D Human Motion Analysis to Detect Abnormal Events on Stairs. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second Joint 3DIM/3DPVT Conference: 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization & Transmission, Zurich, Switzerland, 13–15 October 2012; pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, D.; Johannsen, L.; Hollands, M. Stepping characteristics and Centre of Mass control during stair descent: Effects of age, fall risk and visual factors. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Carter, S. Regional plantar pressure during walking, stair ascent and descent. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeen, S.; Lundquist, K.; Cornwall, M.W.; McPoil, T.G. Plantar pressures during level walking compared with other ambulatory activities. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.F.; Knapik, J.J.; Merullo, D.J. Symptoms during load carrying: Effects of mass and load distribution during a 20-km road march. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1995, 81, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Park, S.H. Effects of Material Position on Postural Stability during Manual Material Handling Tasks. J. Ergon. Soc. Korea 2004, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Li, H. Fall risk assessment of construction workers based on biomechanical gait stability parameters using wearable insole pressure sensor. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 38, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, A.; Ulbrecht, J.S.; Pammer, S.E.; Cavanagh, P.R. In-shoe plantar pressures during activities of daily living: Implications for therapeutic footwear design. Foot Ankle Int. 1996, 17, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, K.S.; Morley, R.E.; Richter, E.J.; Klaesner, J.W.; Mueller, M.J. Foot pressures during level walking are strongly associated with pressures during other ambulatory activities in subjects with diabetic neuropathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldemond, N.A.; Leffers, P.; Sanders, A.P.; Schaper, N.C.; Nieman, F.; Walenkamp, G.H. Daily-life activities and in-shoe forefoot plantar pressure in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.Y. Real-time Activity and Posture Recognition with Combined Acceleration Sensor Data from Smartphone and Wearable Device. J. KIISE Softw. Appl. 2014, 41, 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.M.; Yeh, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, O.K. A real-time fall detection system based on the acceleration sensor of smartphone. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.S.; Kim, C.H. Fall-Detection Algorithm Using Plantar Pressure and Acceleration Data. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.W.; Wu, S.C.; Yu, C.H. Recognition of Direction of Fall by Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2013 26th IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Regina, SK, Canada, 5–8 May 2013; p. 13680673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, A.; Rohr, E.; Orenduff, M.; Shofer, J.; O’Brien, M.; Sangeorzan, B. The effect of walking speed on peak plantar pressure. Foot Ankle Int. 2004, 25, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riener, R.; Rabuffetti, M.; Frigo, C. Stair ascent and descent at different inclinations. Gait Posture 2002, 15, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

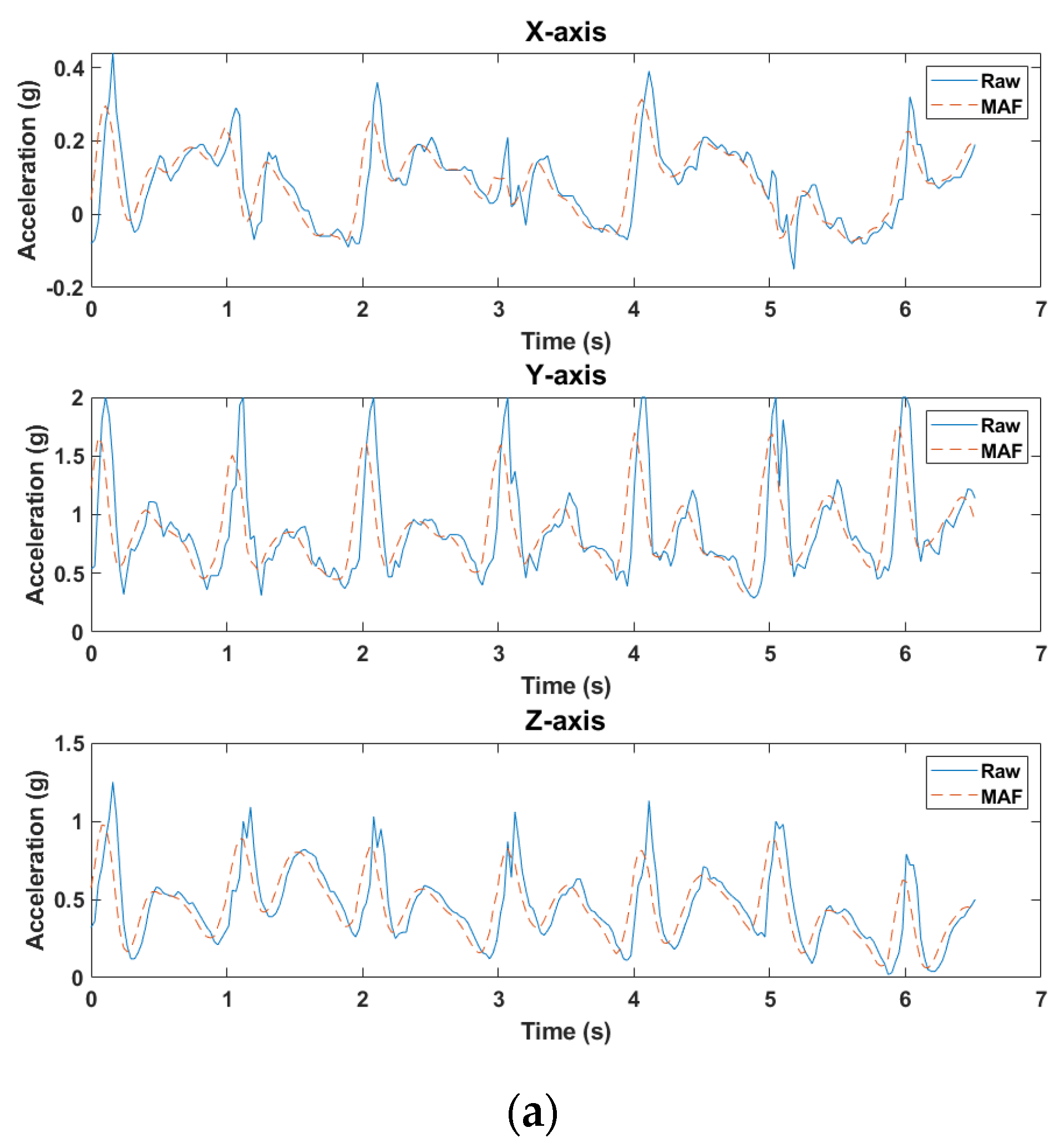
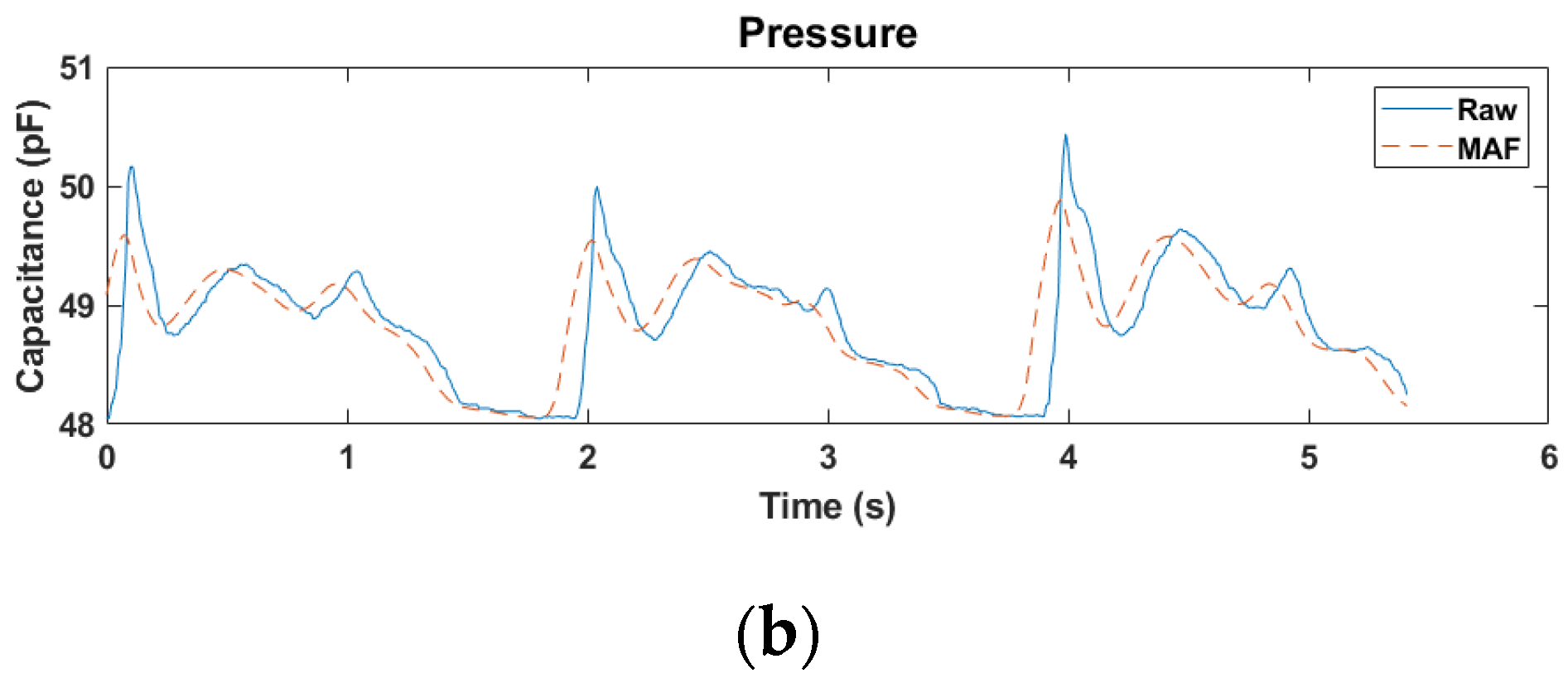
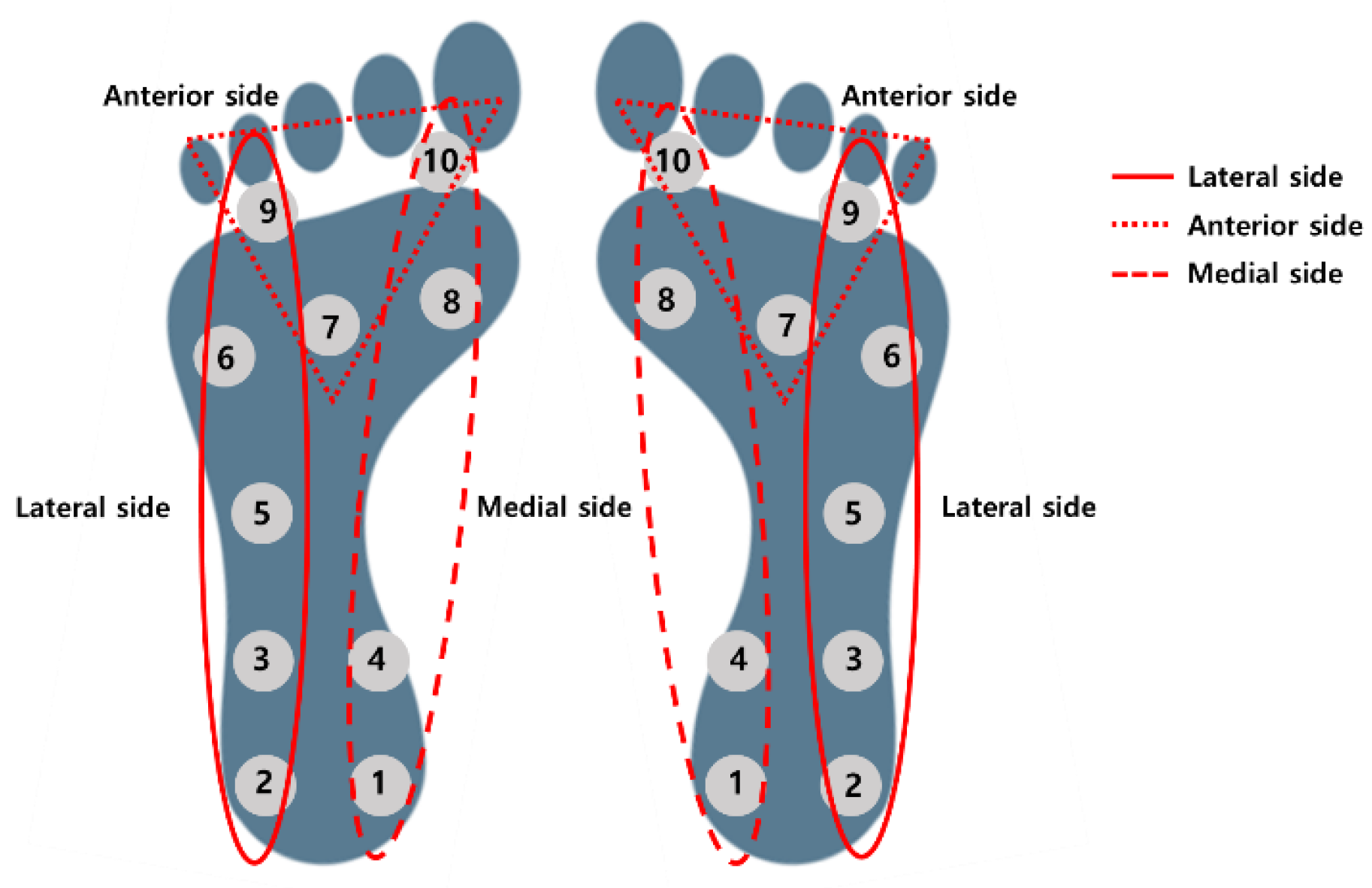



| Subject | Sex | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | Shoe Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 26 | 181 | 73 | 280 |
| 2 | M | 24 | 181 | 93 | 280 |
| 3 | M | 27 | 176 | 84 | 280 |
| 4 | M | 24 | 175 | 74 | 270 |
| 5 | M | 23 | 182 | 83 | 280 |
| 6 | M | 25 | 172 | 79 | 270 |
| 7 | M | 32 | 182 | 92 | 270 |
| 8 | M | 24 | 173 | 76 | 250 |
| 9 | M | 24 | 170 | 60 | 265 |
| 10 | M | 26 | 172 | 69 | 260 |
| AVG | 25.5 | 176.4 | 78.3 | 270.5 | |
| SD | 2.59 | 4.70 | 10.18 | 10.12 |
| E1 | E2 | E3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub No. | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left |
| 1 | 48.41 | 48.64 | 48.55 | 48.71 | 50.71 | 48.62 |
| 2 | 48.63 | 48.82 | 48.82 | 49.01 | 50.11 | 48.85 |
| 3 | 48.40 | 48.65 | 48.56 | 48.73 | 49.65 | 48.62 |
| 4 | 48.45 | 48.65 | 48.54 | 48.81 | 50.50 | 48.75 |
| 5 | 48.54 | 48.68 | 48.63 | 48.84 | 50.77 | 48.60 |
| 6 | 48.67 | 48.89 | 48.83 | 49.00 | 50.24 | 48.86 |
| 7 | 48.33 | 48.90 | 48.39 | 49.05 | 51.10 | 48.85 |
| 8 | 48.63 | 48.90 | 48.71 | 49.06 | 51.10 | 48.87 |
| 9 | 48.15 | 48.49 | 48.32 | 48.63 | 50.98 | 48.49 |
| 10 | 48.30 | 48.84 | 48.42 | 48.97 | 50.47 | 48.77 |
| AVG | 48.45 | 48.75 | 48.58 | 48.88 | 50.56 | 48.73 |
| SD | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.13 |
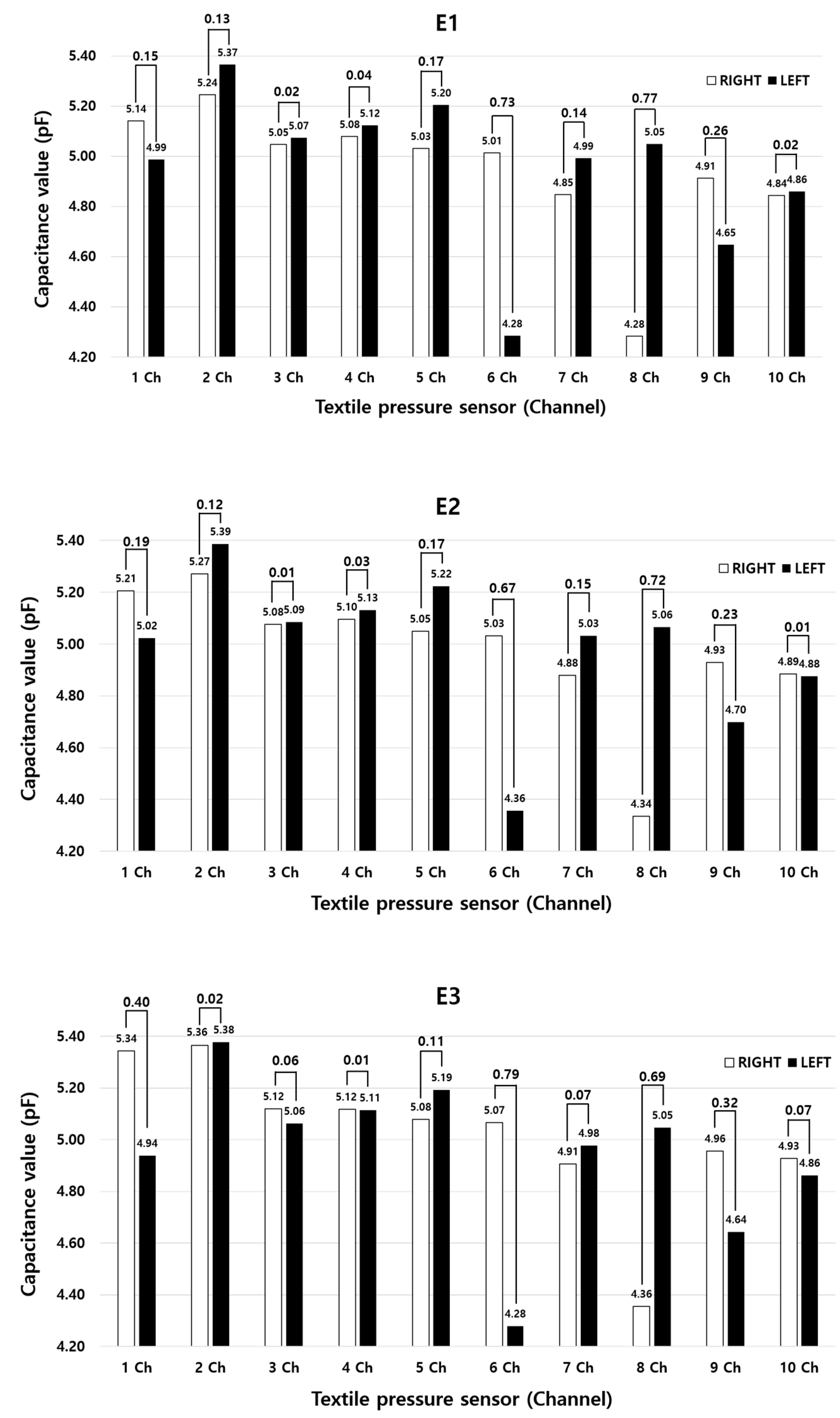
| E1 | E2 | E3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ch. No. | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left |
| 1 | 5.14 | 4.99 | 5.21 | 5.02 | 5.34 | 4.94 |
| 2 | 5.24 | 5.37 | 5.27 | 5.39 | 5.36 | 5.38 |
| 3 | 5.05 | 5.07 | 5.08 | 5.09 | 5.12 | 5.06 |
| 4 | 5.08 | 5.12 | 5.10 | 5.13 | 5.12 | 5.11 |
| 5 | 5.03 | 5.20 | 5.05 | 5.22 | 5.08 | 5.19 |
| 6 | 5.01 | 4.28 | 5.03 | 4.36 | 5.07 | 4.28 |
| 7 | 4.85 | 4.99 | 4.88 | 5.03 | 4.91 | 4.98 |
| 8 | 4.28 | 5.05 | 4.34 | 5.06 | 4.36 | 5.05 |
| 9 | 4.91 | 4.65 | 4.93 | 4.70 | 4.96 | 4.64 |
| 10 | 4.84 | 4.86 | 4.89 | 4.88 | 4.93 | 4.86 |
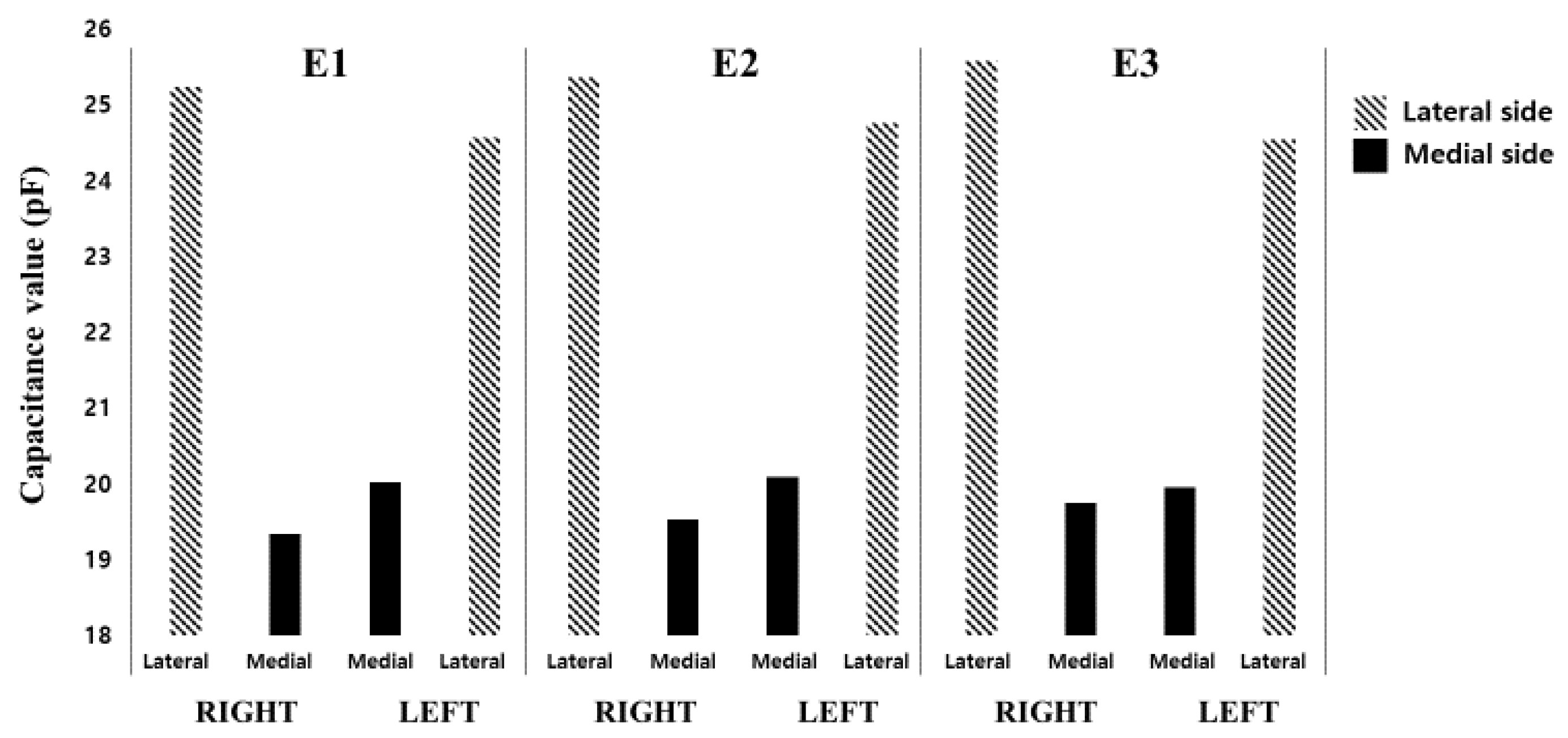
| E1 | E2 | E3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side | Ch. No. | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left |
| Lateral | 2 | 5.24 | 5.37 | 5.27 | 5.39 | 5.36 | 5.38 |
| 3 | 5.05 | 5.07 | 5.08 | 5.09 | 5.12 | 5.06 | |
| 5 | 5.03 | 5.20 | 5.22 | 5.22 | 5.08 | 5.19 | |
| 6 | 5.01 | 4.28 | 4.36 | 4.36 | 5.07 | 4.28 | |
| 9 | 4.91 | 4.65 | 4.93 | 4.70 | 4.96 | 4.64 | |
| Sum | 25.24 | 24.57 | 25.36 | 24.76 | 25.59 | 24.55 | |
| SD | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.15 | 0.44 | |
| Medial | 1 | 5.14 | 4.99 | 5.21 | 5.02 | 5.34 | 4.94 |
| 4 | 5.08 | 5.12 | 5.10 | 5.13 | 5.12 | 5.11 | |
| 8 | 4.28 | 5.05 | 4.34 | 5.06 | 4.36 | 5.05 | |
| 10 | 4.84 | 4.86 | 4.89 | 4.88 | 4.93 | 4.86 | |
| Sum | 19.34 | 20.02 | 19.54 | 20.09 | 19.75 | 19.96 | |
| SD | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.11 | |
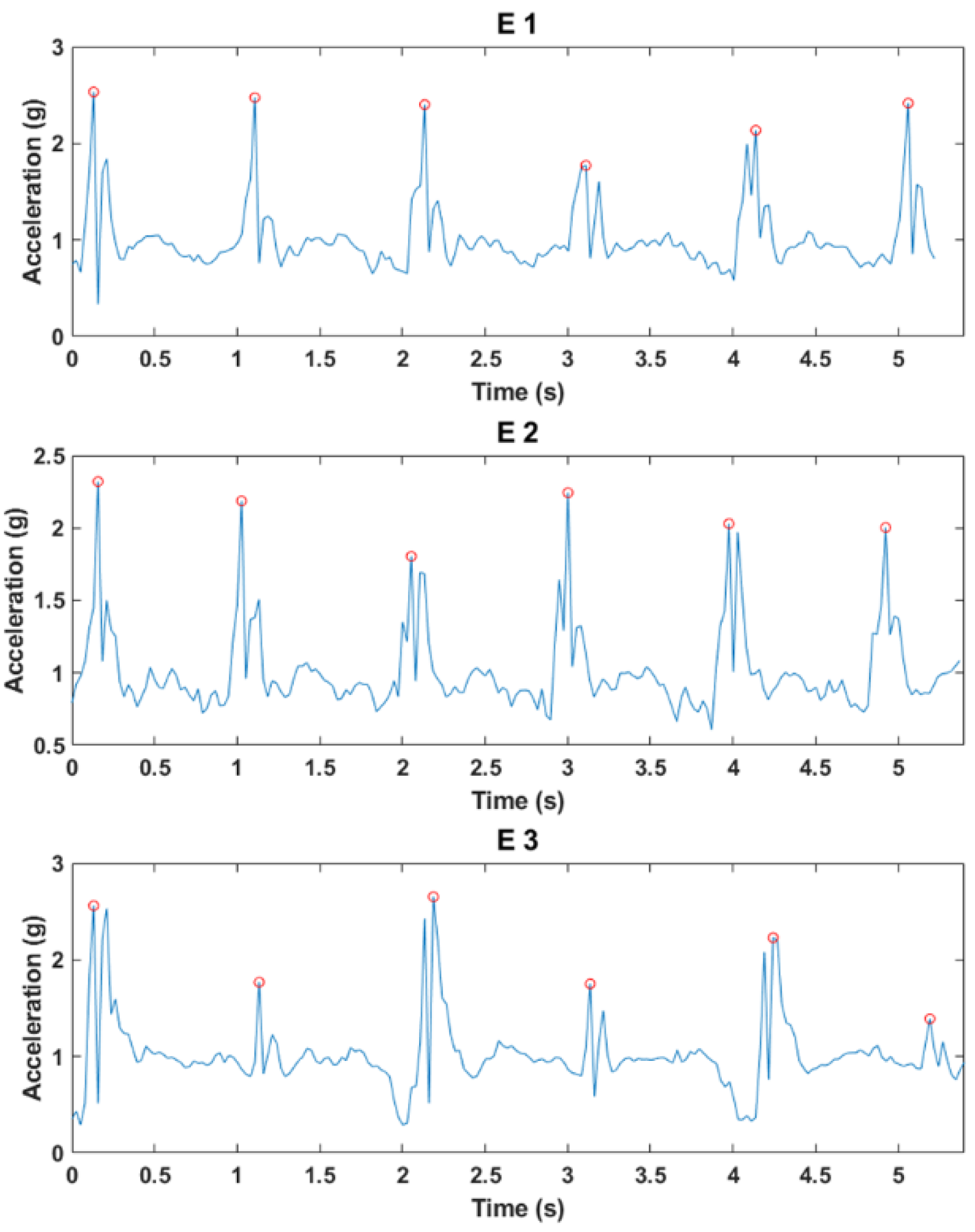
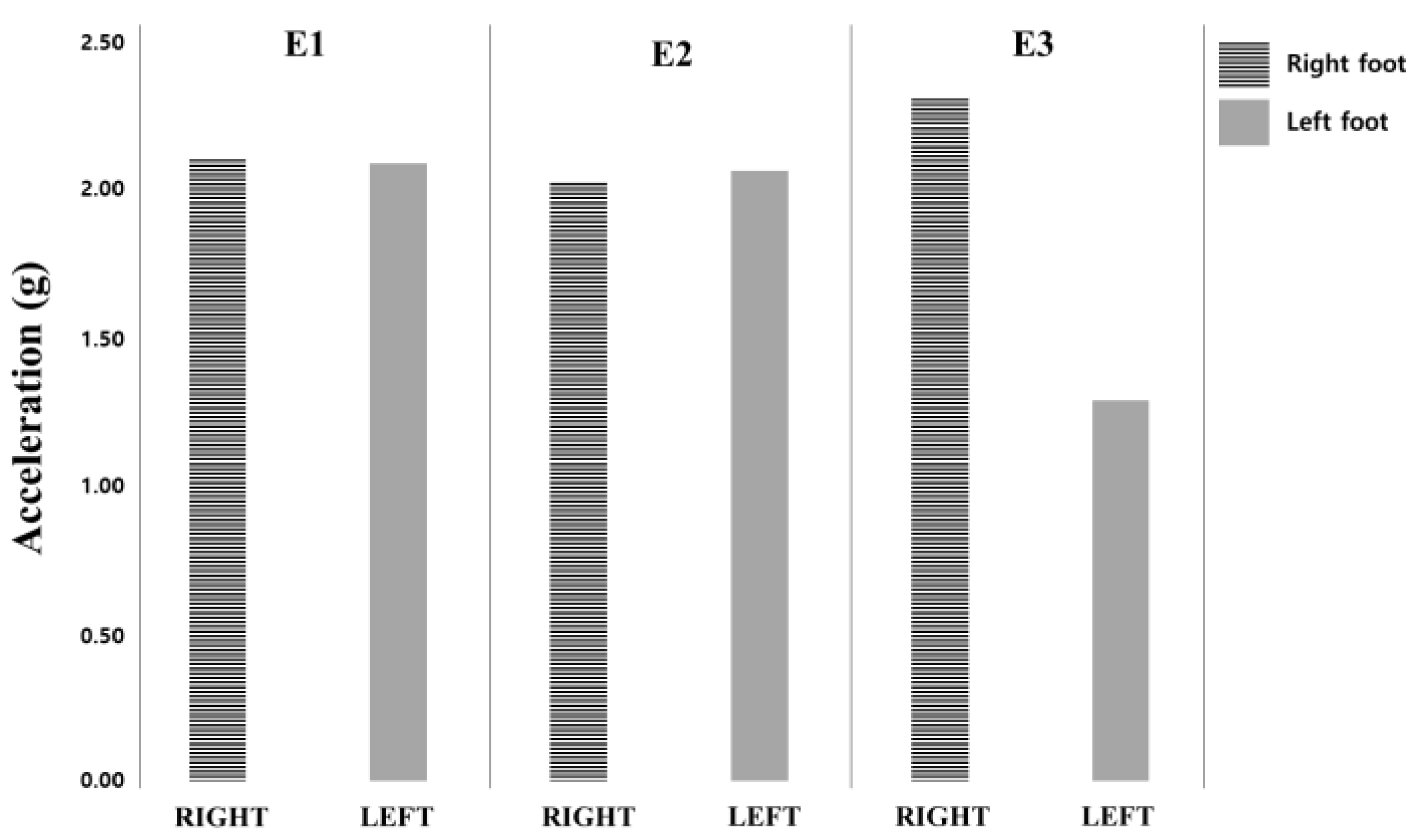
| E1 | E2 | E3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub No. | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left |
| 1 | 2.06 | 2.06 | 2.08 | 2.11 | 2.41 | 1.27 |
| 2 | 2.26 | 2.26 | 2.26 | 2.26 | 2.35 | 1.11 |
| 3 | 2.12 | 1.98 | 1.99 | 1.86 | 2.26 | 1.24 |
| 4 | 2.16 | 1.99 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 2.26 | 1.49 |
| 5 | 2.36 | 2.22 | 2.06 | 2.05 | 2.70 | 1.55 |
| 6 | 2.12 | 2.23 | 2.34 | 2.32 | 2.57 | 1.04 |
| 7 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.31 | 1.40 | 1.65 | 1.36 |
| 8 | 2.33 | 2.35 | 2.31 | 2.35 | 2.40 | 1.19 |
| 9 | 2.13 | 2.12 | 1.89 | 1.97 | 2.26 | 1.13 |
| 10 | 2.03 | 2.22 | 2.03 | 2.37 | 2.29 | 1.47 |
| AVG | 2.10 | 2.09 | 2.02 | 2.06 | 2.31 | 1.29 |
| SD | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.18 |
| Right Foot | Left Foot | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub No. | R2 | p-Value | R2 | p-Value |
| 1 | −0.35 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.17 |
| 2 | −0.17 | 0.00 | −0.15 | 0.03 |
| 3 | −0.23 | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.99 |
| 4 | −0.66 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.82 |
| 5 | −0.38 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| 6 | −0.46 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.48 |
| 7 | −0.53 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.01 |
| 8 | −0.46 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.00 |
| 9 | −0.66 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.53 |
| 10 | −0.60 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.G.; Lee, S.H.; Min, S.D. Smart Helmet and Insole Sensors for Near Fall Incidence Recognition during Descent of Stairs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072262
Wang C, Kim Y, Kim DG, Lee SH, Min SD. Smart Helmet and Insole Sensors for Near Fall Incidence Recognition during Descent of Stairs. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072262
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Changwon, Young Kim, Dae Gyeom Kim, Seung Hyun Lee, and Se Dong Min. 2020. "Smart Helmet and Insole Sensors for Near Fall Incidence Recognition during Descent of Stairs" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072262
APA StyleWang, C., Kim, Y., Kim, D. G., Lee, S. H., & Min, S. D. (2020). Smart Helmet and Insole Sensors for Near Fall Incidence Recognition during Descent of Stairs. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072262








