Spatial Manipulation of a Supercontinuum Beam for the Study of Vortex Interference Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
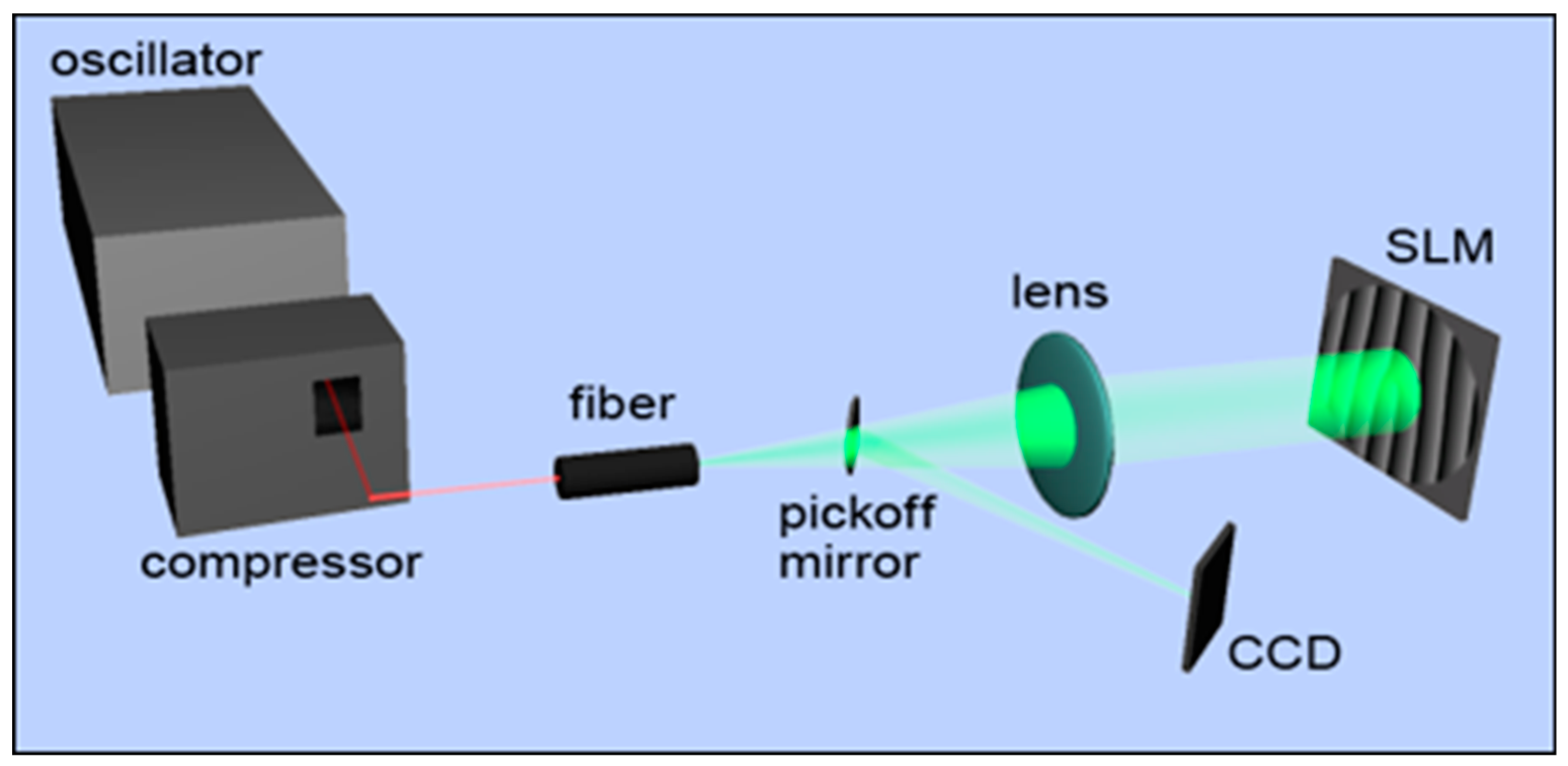
2. Materials and Methods
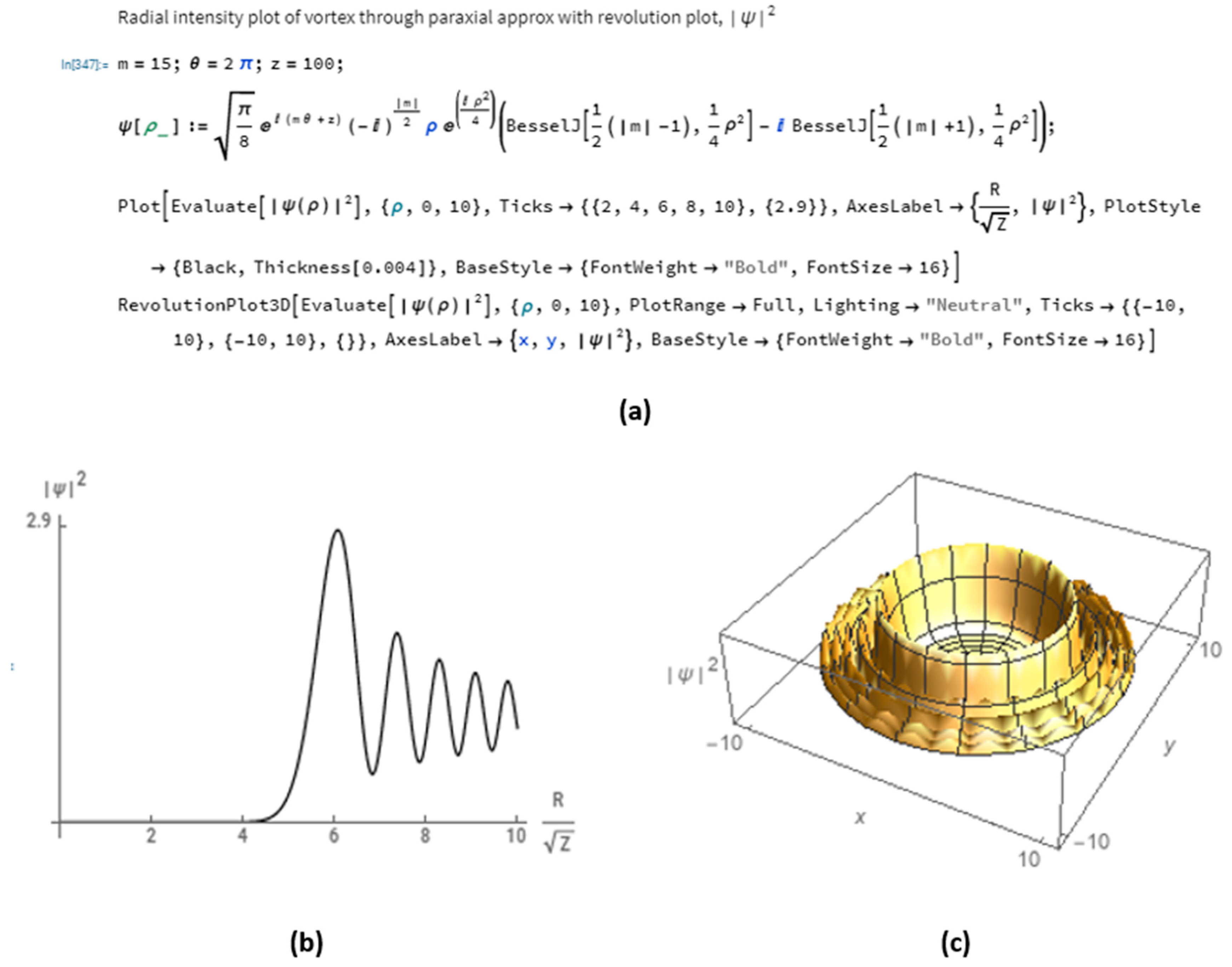
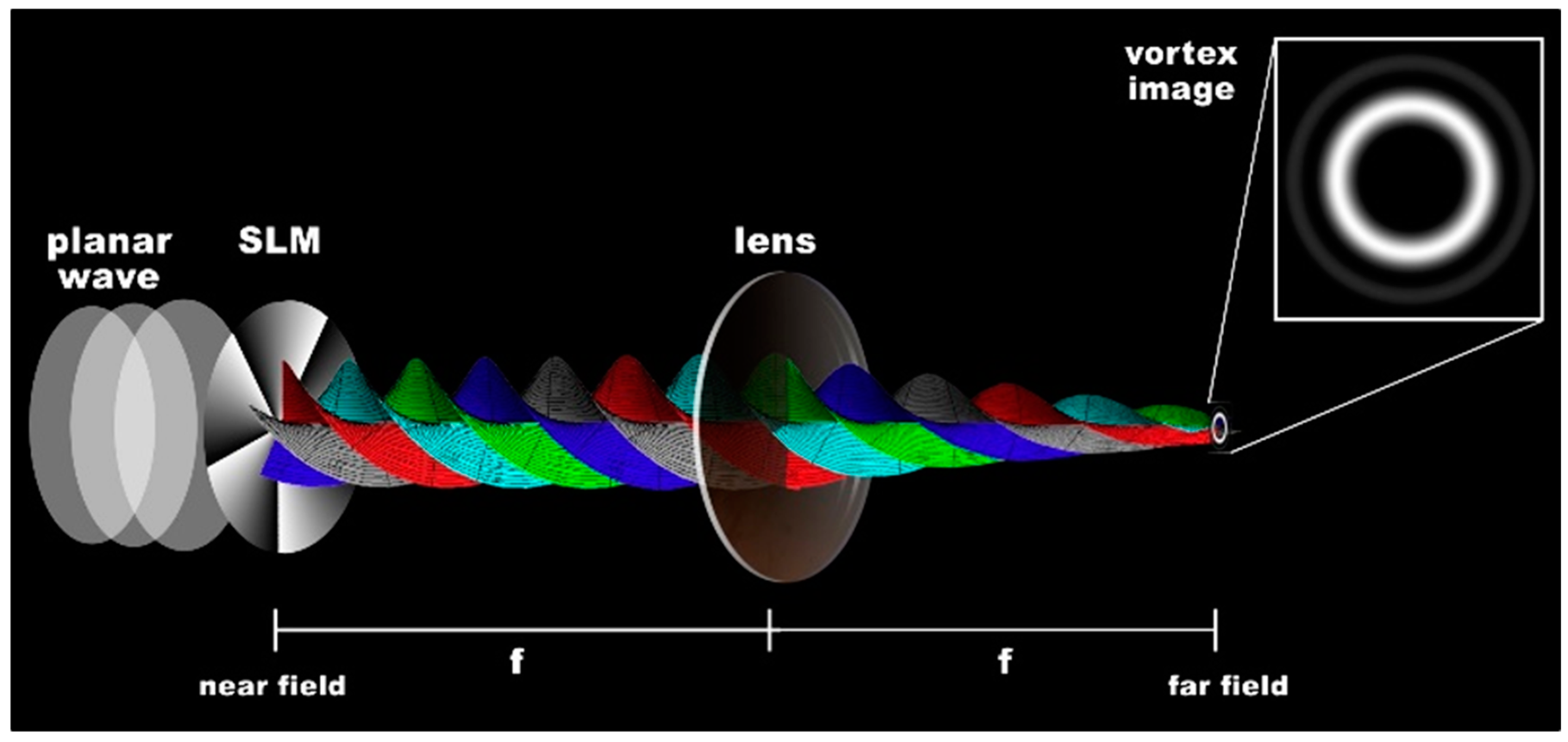
2.1. Analytic Solutions
2.2. Numerical Simulations
2.3. Experimental Setup
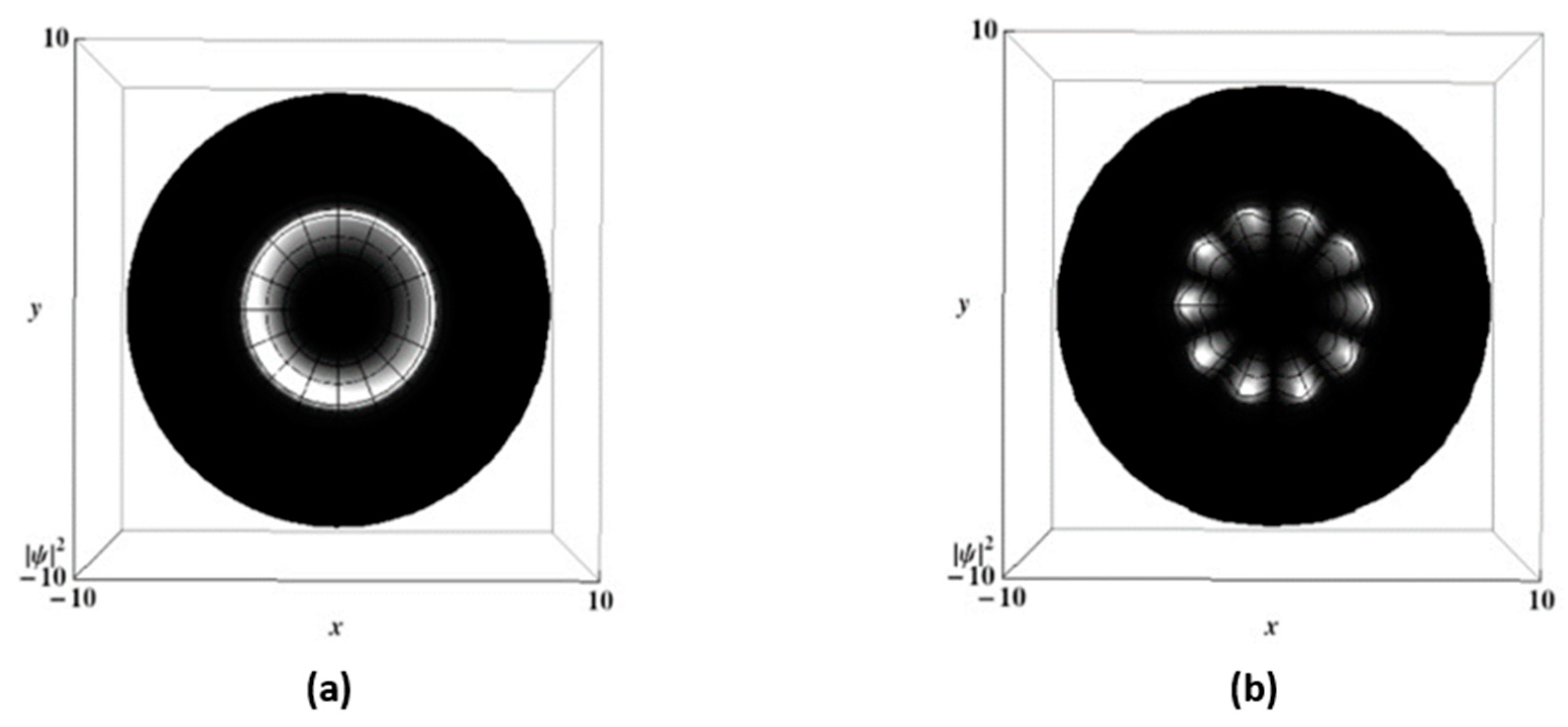
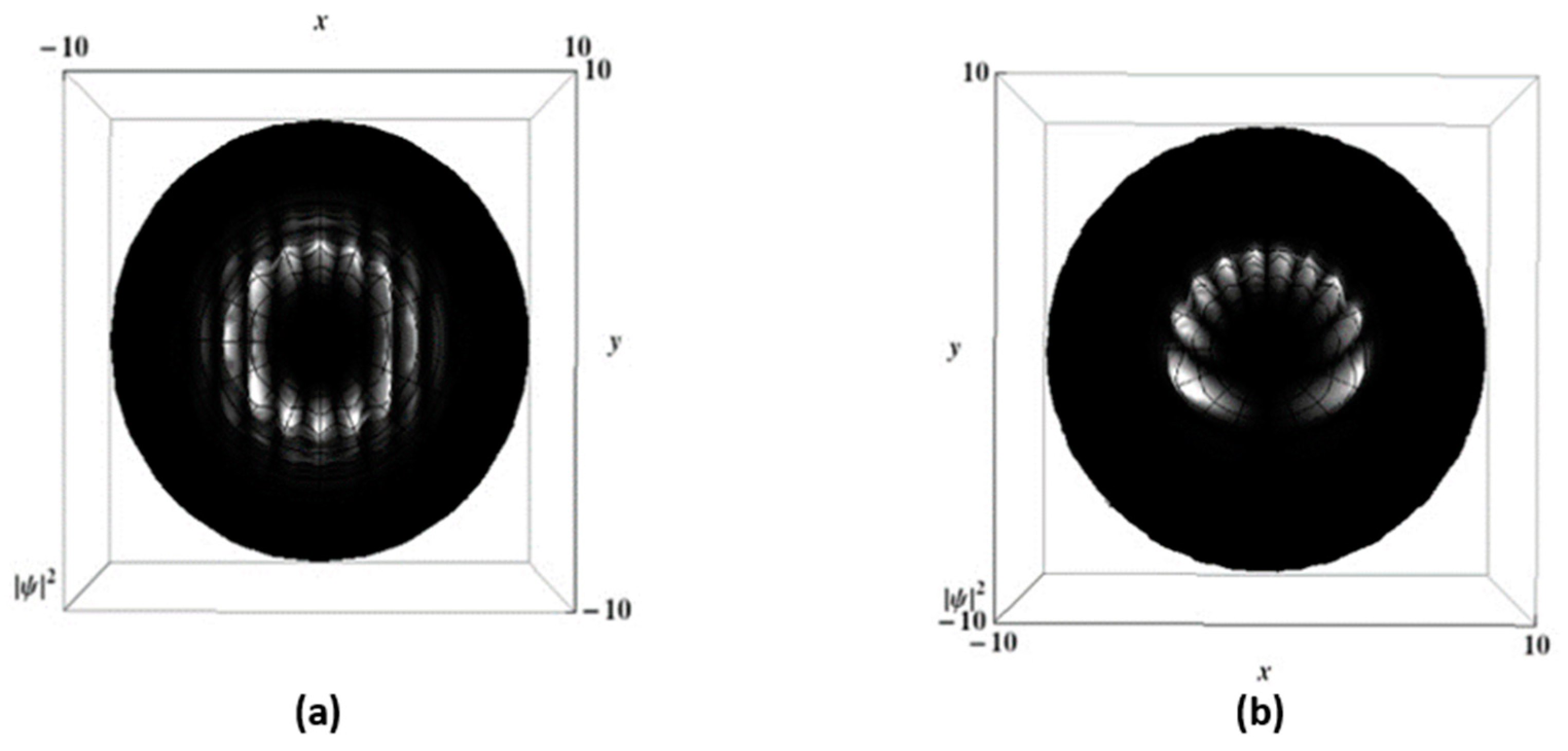
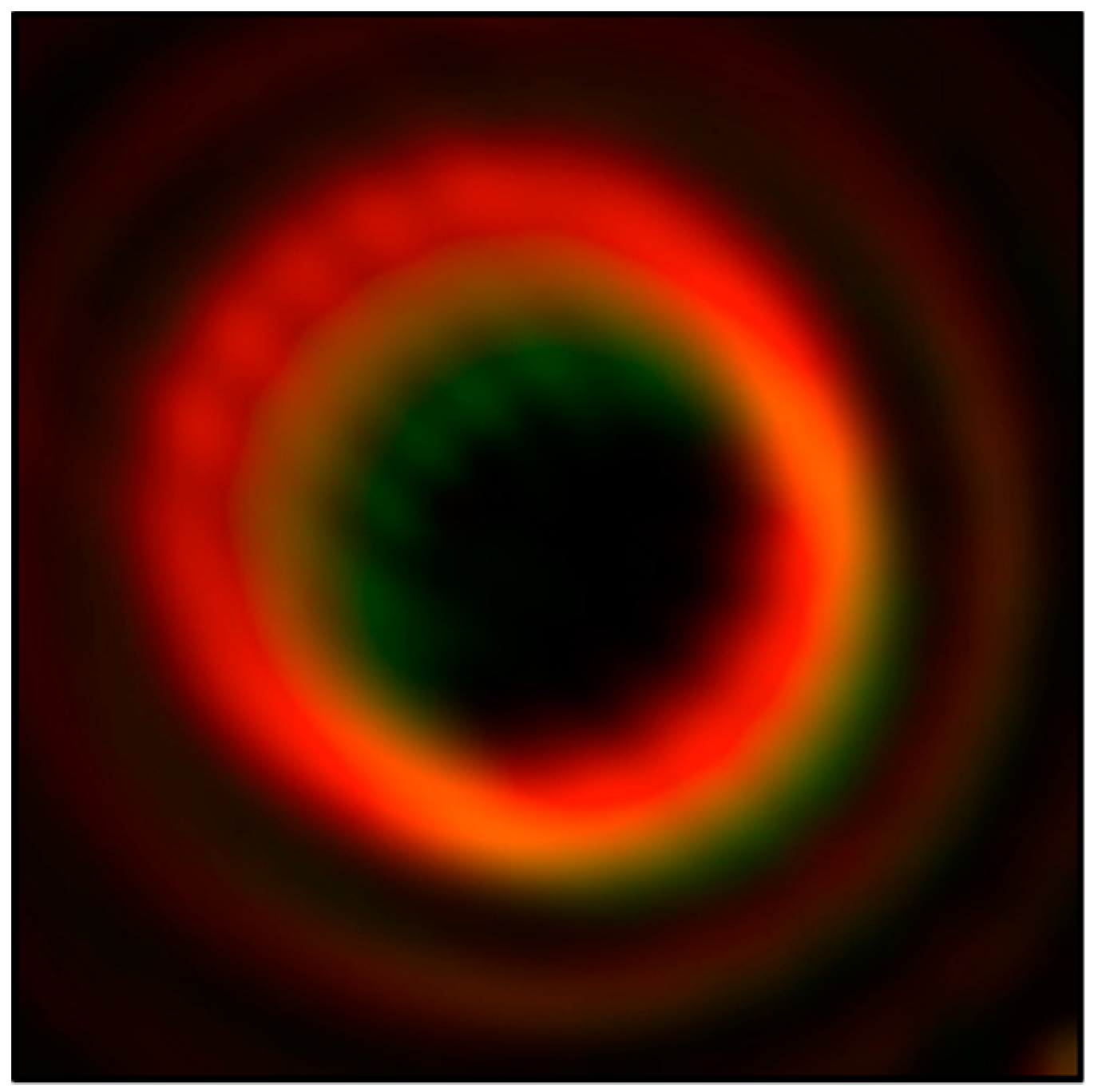
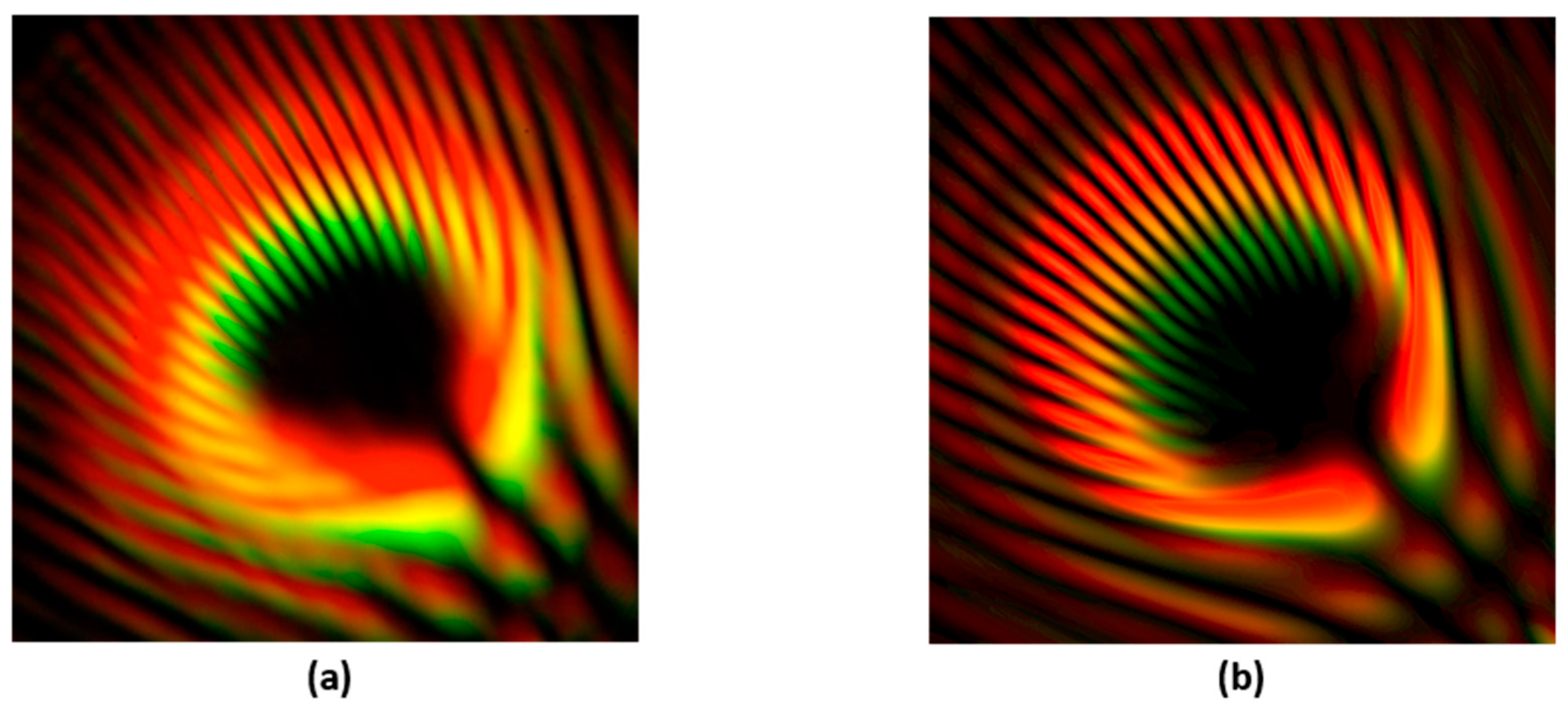
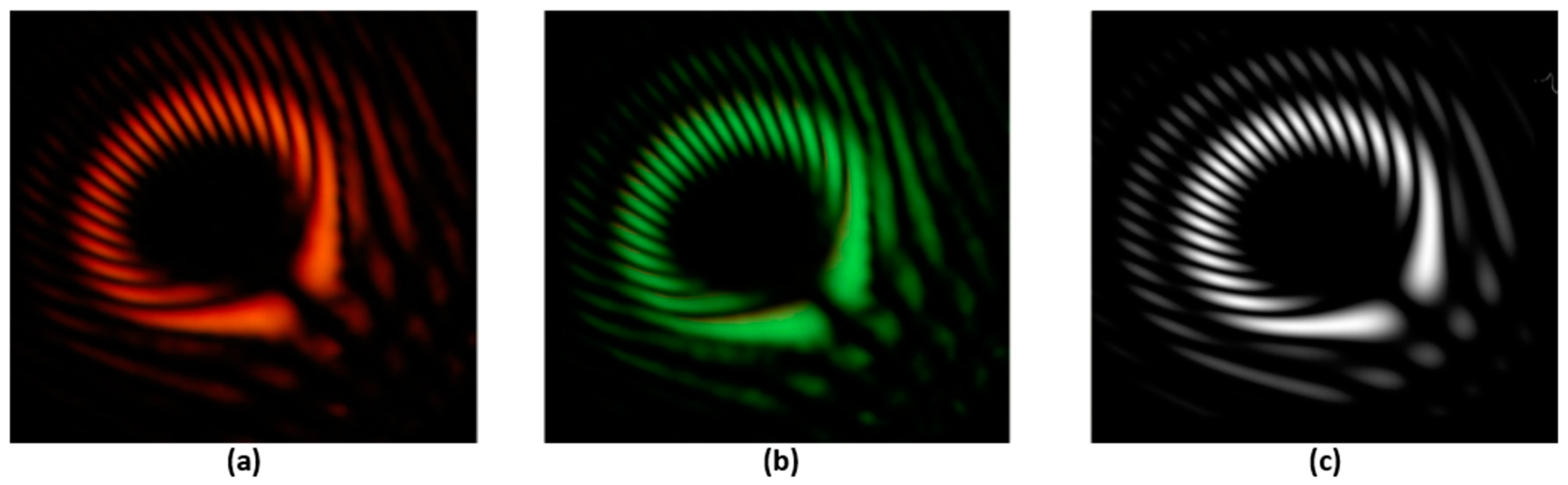
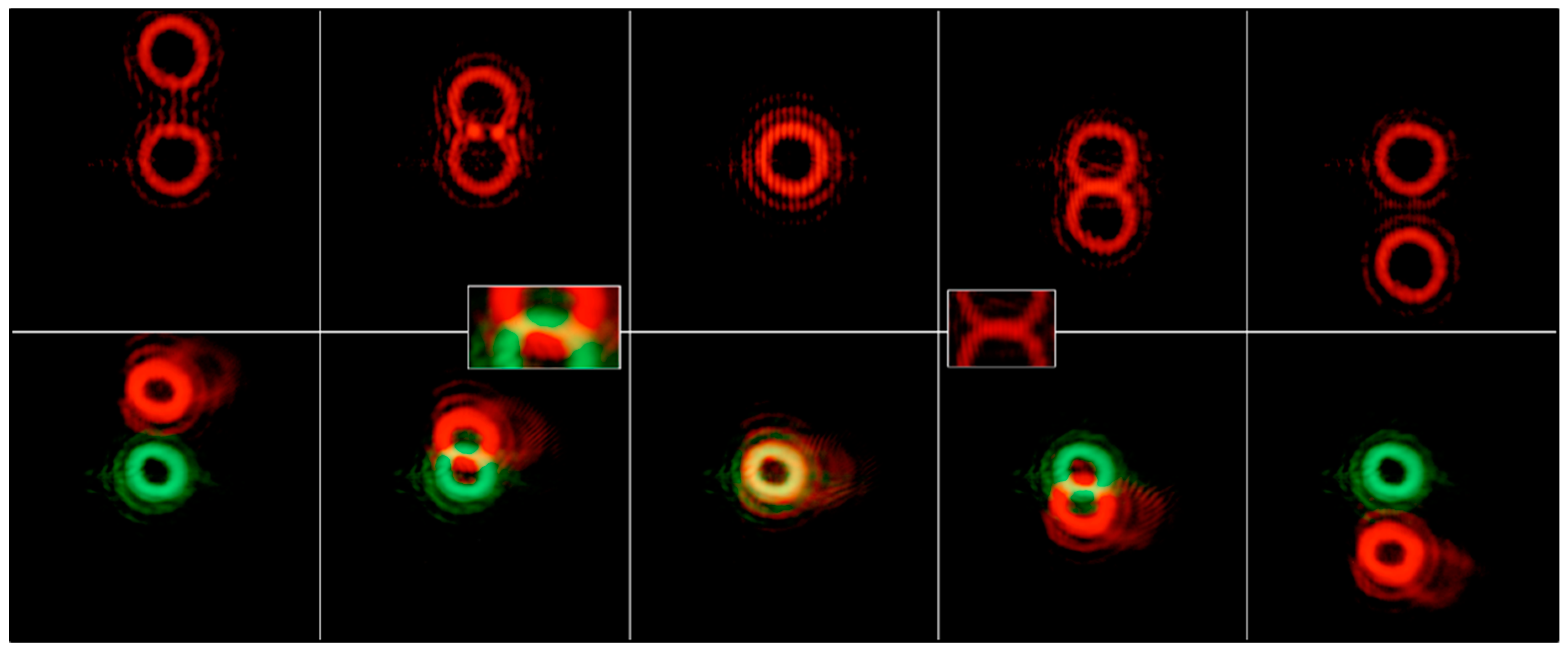
3. Results
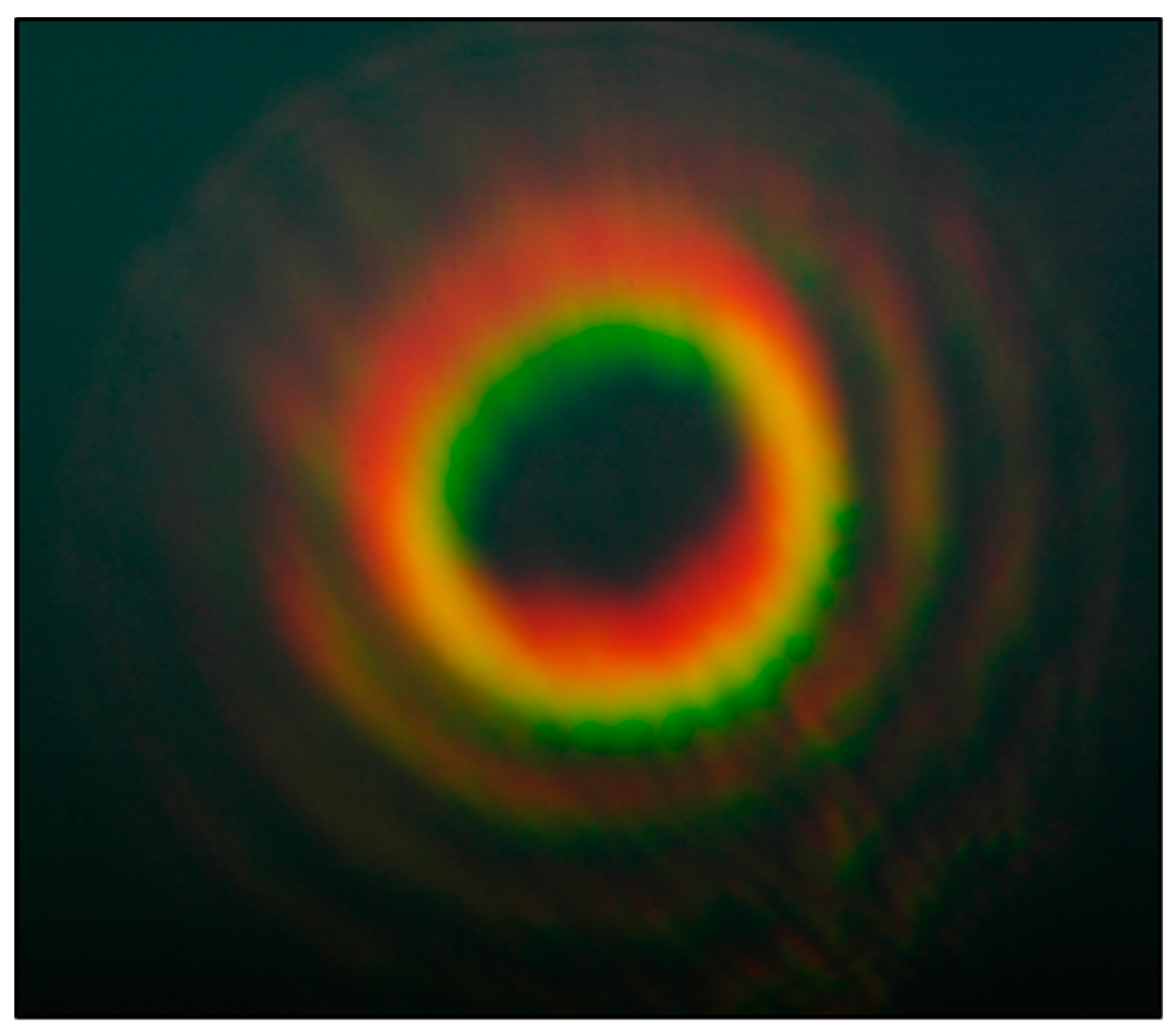
3.1. Multi-Color Vortices
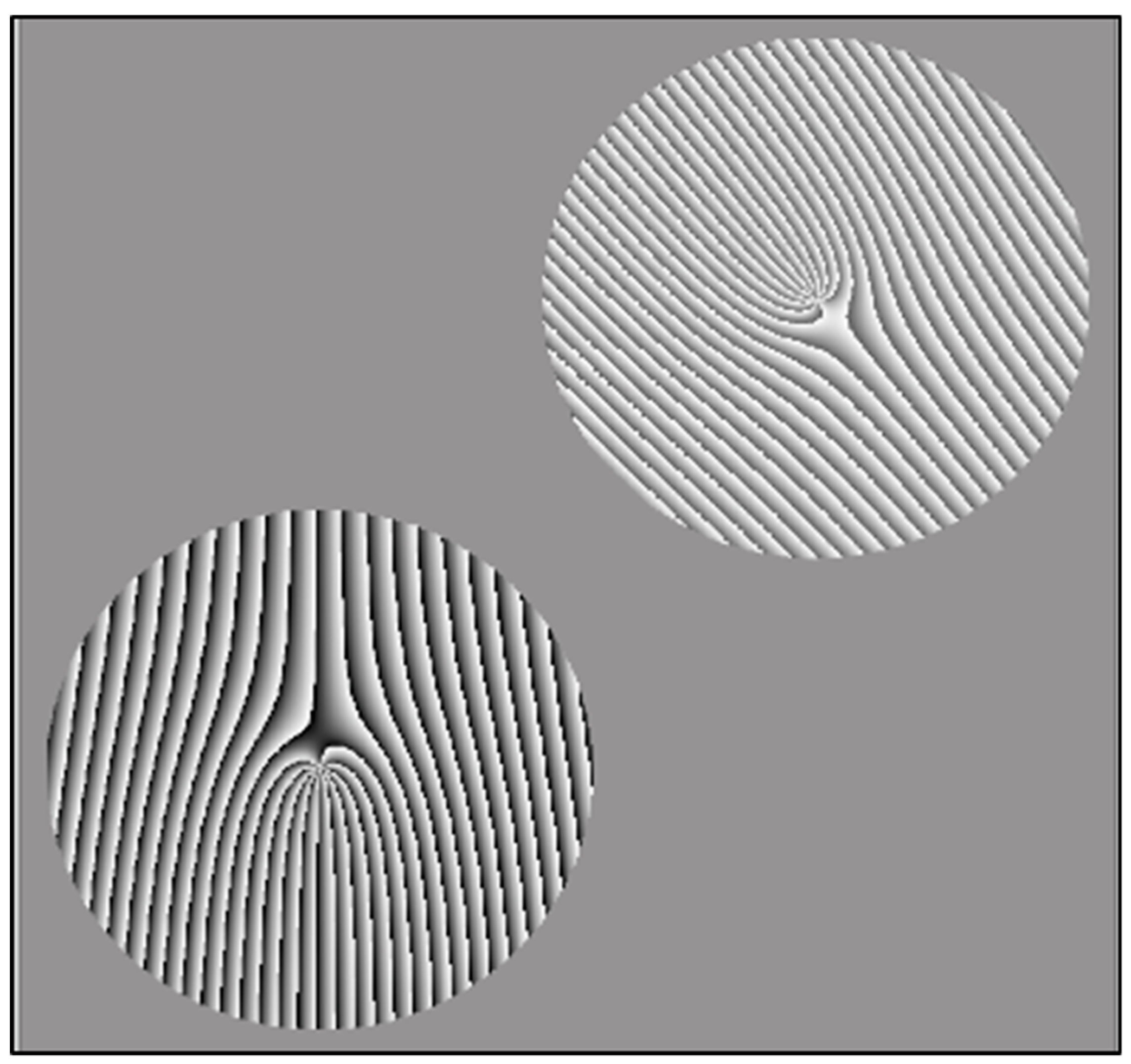
3.2. Vortex Interference
3.3. Color-Tunable Vortices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, Q. Cylindrical vector beams: From mathematical concepts to applications. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2009, 1, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J. A review of multiple optical vortices generation: Methods and applications. Front. Optoelectron. 2019, 12, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.; Beijersbergen, M.W.; Spreeuw, R.J.C.; Woerdman, J.P. Orbital Angular-Momentum of Light and the Transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian Laser Modes. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 8185–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahagan, K.T.; Swartzlander, G.A. Optical vortex trapping of particles. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, C.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, C.; Feng, S.; Nie, S.; Ding, J. Generation of optical vortex array along arbitrary curvilinear arrangement. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 9798–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, A.; Vaziri, A.; Weihs, G.; Zeilinger, A. Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons. Nature 2001, 412, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndagano, B.; Nape, I.; Cox, M.A.; Rosales-Guzman, C.; Forbes, A. Creation and Detection of Vector Vortex Modes for Classical and Quantum Communication. J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 36, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spektor, B.; Normatov, A.; Shamir, J. Singular beam microscopy. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, A78–A87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Trujillo, A.; Anderson, M.E. Surface profilometry using vortex beams generated with a spatial light modulator. Opt. Commun. 2018, 427, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, X.; Polynkin, P. Simultaneously spatially and temporally focused femtosecond vortex beams for laser micromachining. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2018, 35, B16–B19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnatovsky, C.; Shvedov, V.G.; Krolikowski, W.; Rode, A.V. Materials processing with a tightly focused femtosecond laser vortex pulse. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 3417–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidwell, S.C.; Ford, D.H.; Kimura, W.D. Generating radially polarized beams interferometrically. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlyar, V.V.; Almazov, A.A.; Khonina, S.N.; Soifer, V.A.; Elfstrom, H.; Turunen, J. Generation of phase singularity through diffracting a plane or Gaussian beam by a spiral phase plate. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2005, 22, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, I.; Davis, J.A.; Womble-Dahl, T.; Cottrell, D.M. Azimuthal multiple-beam interference effects with combinations of vortex beams. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Chieh, L.; Yasuo, N.; Katsumi, M. Generation of intense femtosecond optical vortex pulses with blazed-phase grating in chirped-pulse amplification system of Ti:sapphire laser. Appl. Phys. B 2016, 122, 280. [Google Scholar]
- Nian, T.; Ling, F.; Min, G. Resolution and contrast enhancement of subtractive second harmonic generation microscopy with a circularly polarized vortex beam. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Kong, L.; Xie, G.; Qin, Z.; Yuan, P.; Qian, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.; Fan, D. Ultraclean femtosecond vortices from a tunable high-order transverse-mode femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2547–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyenko, I.G.; Strohaber, J.; Uiterwaal, C.J. Creation of optical vortices in femtosecond pulses. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 7599–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansinger, P.; Maleshkov, G.; Garanovich, I.L.; Skryabin, D.V.; Neshev, D.N.; Dreischuh, A.; Paulus, G.G. White light generated by femtosecond optical vortex beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2016, 33, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, R.R. The Supercontinuum Laser Source: Fundamentals with Updated References, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 33–183. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, J.; Padgett, M.J. Observation of chromatic effects near a white-light vortex. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.V. Coloured phase singularities. New J. Phys. 2002, 4, 66.1–66.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.V. Optical vortices evolving from helicoidal integer and fractional phase steps. Appl. Opt. 2004, 6, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokizane, Y.; Oka, K.; Morita, R. Supercontinuum optical vortex pulse generation without spatial or topological-charge dispersion. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 14517–14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, K.Y.; Stuti, J.; Hem, C.K. Experimental observation of the effect of generic singularities in polychromatic dark hollow beams. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4966–4969. [Google Scholar]
- Padgett, M.J. Orbital angular momentum 25 years on [Invited]. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 11265–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitry, M.; Doughty, D.C.; Chaloupka, J.L.; Anderson, M.E. Experimental realization of the devil’s vortex Fresnel lens with a programmable spatial light modulator. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 4103–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamatsu Photonics, K.K. SLM Module. In Programmable Phase Modulator; Hamamatsu: Iwata, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ladavac, K.; Grier, D.G. Microoptomechanical pumps assembled and driven by holographic optical vortex arrays. Opt. Exp. 2004, 12, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, M.; Eggeling, C.; Hell, S.W. Analytical description of STED microscopy performance. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 26417–26429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anderson, M.E.; Serrano, A.; Stinson, C.; Talamantes, A.; Miller, N.; Chaloupka, J.L. Spatial Manipulation of a Supercontinuum Beam for the Study of Vortex Interference Effects. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10061966
Anderson ME, Serrano A, Stinson C, Talamantes A, Miller N, Chaloupka JL. Spatial Manipulation of a Supercontinuum Beam for the Study of Vortex Interference Effects. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(6):1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10061966
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnderson, Matthew E., Alejandra Serrano, Cory Stinson, Antonio Talamantes, Nick Miller, and Jan L. Chaloupka. 2020. "Spatial Manipulation of a Supercontinuum Beam for the Study of Vortex Interference Effects" Applied Sciences 10, no. 6: 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10061966
APA StyleAnderson, M. E., Serrano, A., Stinson, C., Talamantes, A., Miller, N., & Chaloupka, J. L. (2020). Spatial Manipulation of a Supercontinuum Beam for the Study of Vortex Interference Effects. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10061966




