Topology Optimization for Multipatch Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Problem Definition
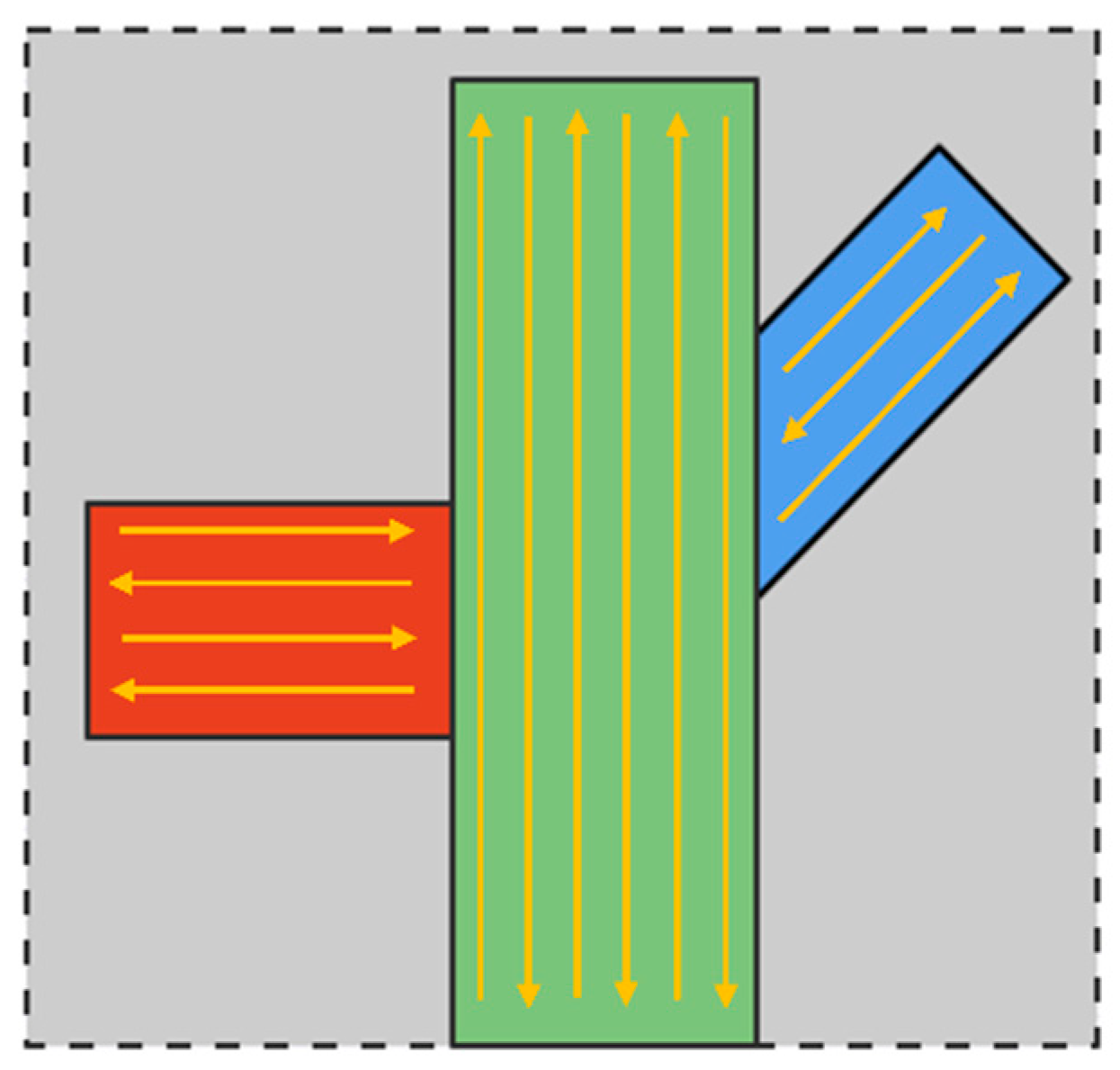
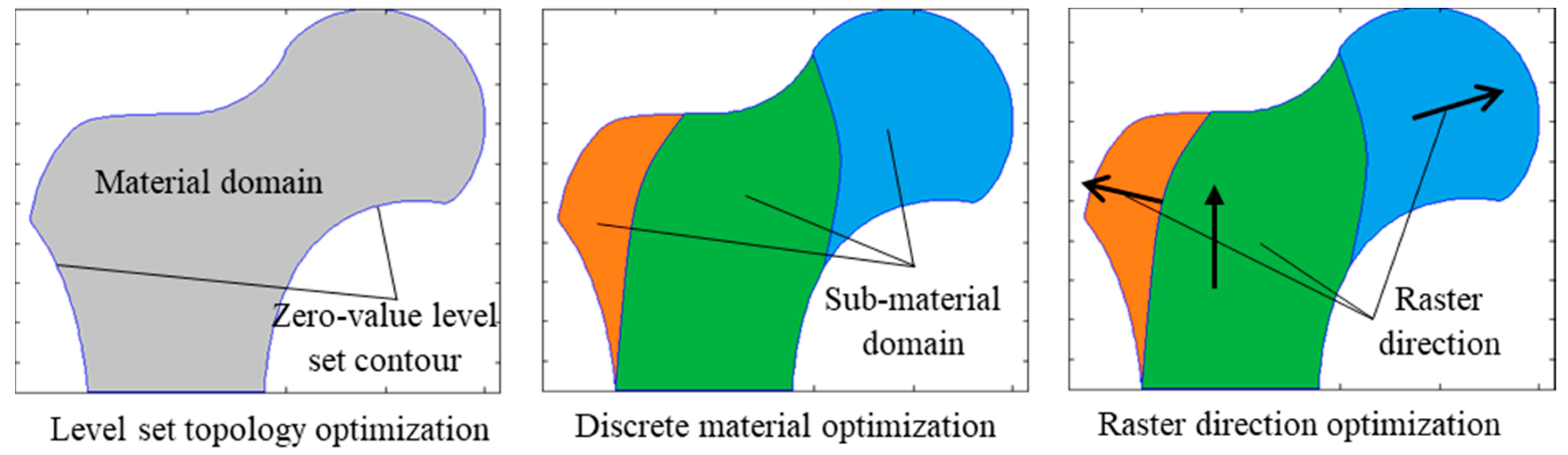
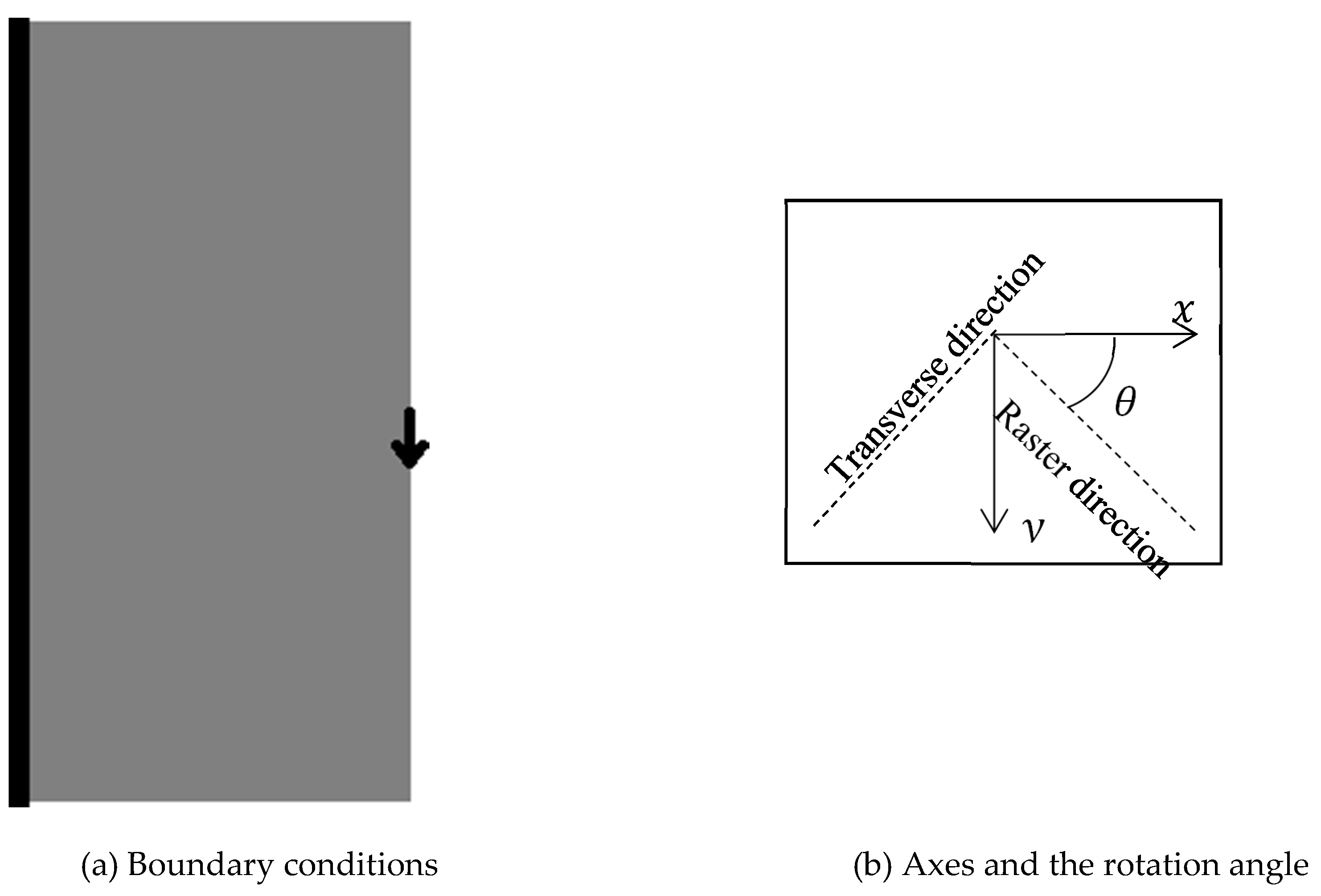
3.1. Design Domain Modeling
3.2. Material Domain Modeling
3.3. Sub-Material Domain Modeling
3.4. The Overall Problem Definition
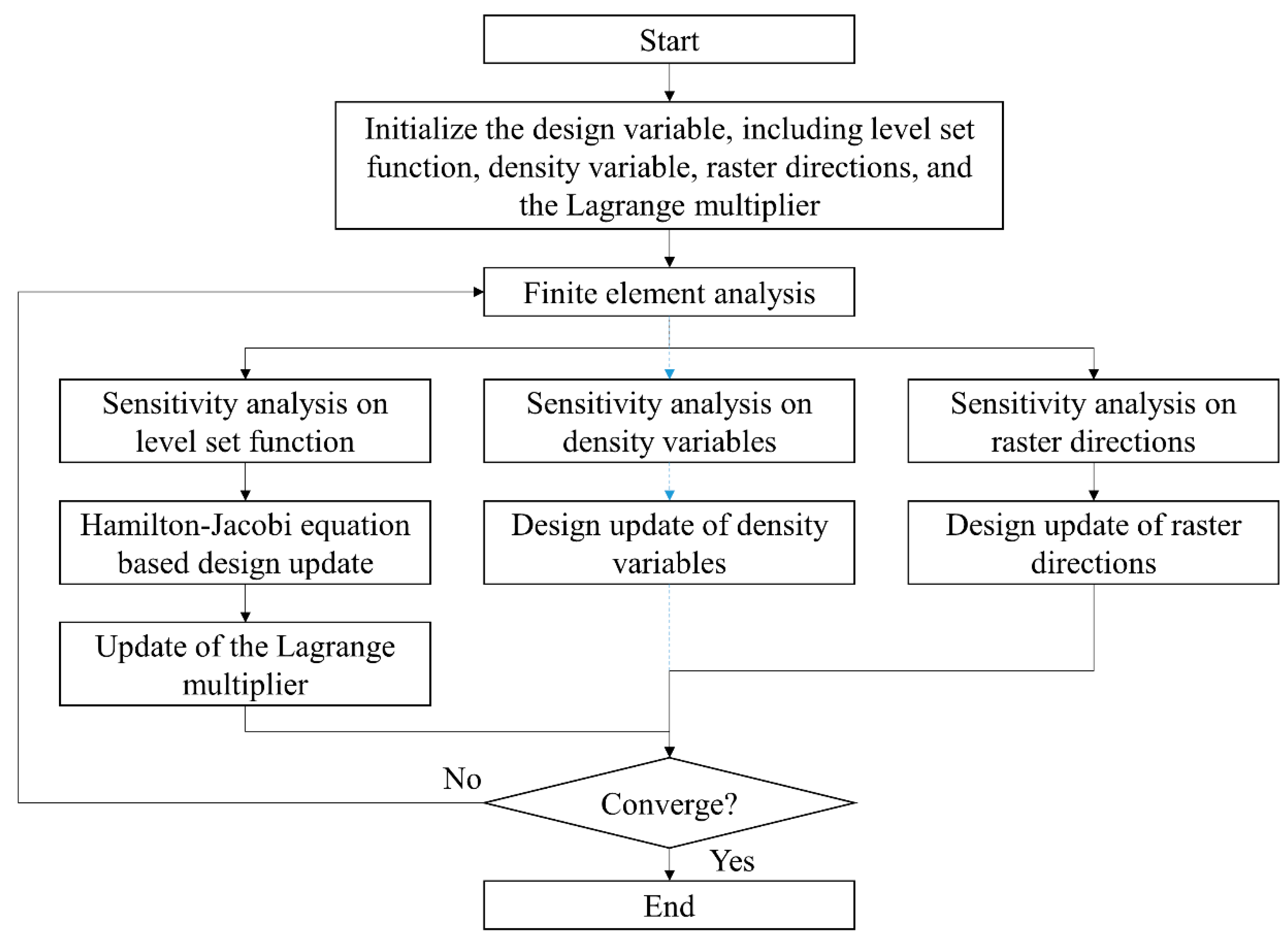
4. Problem Solution
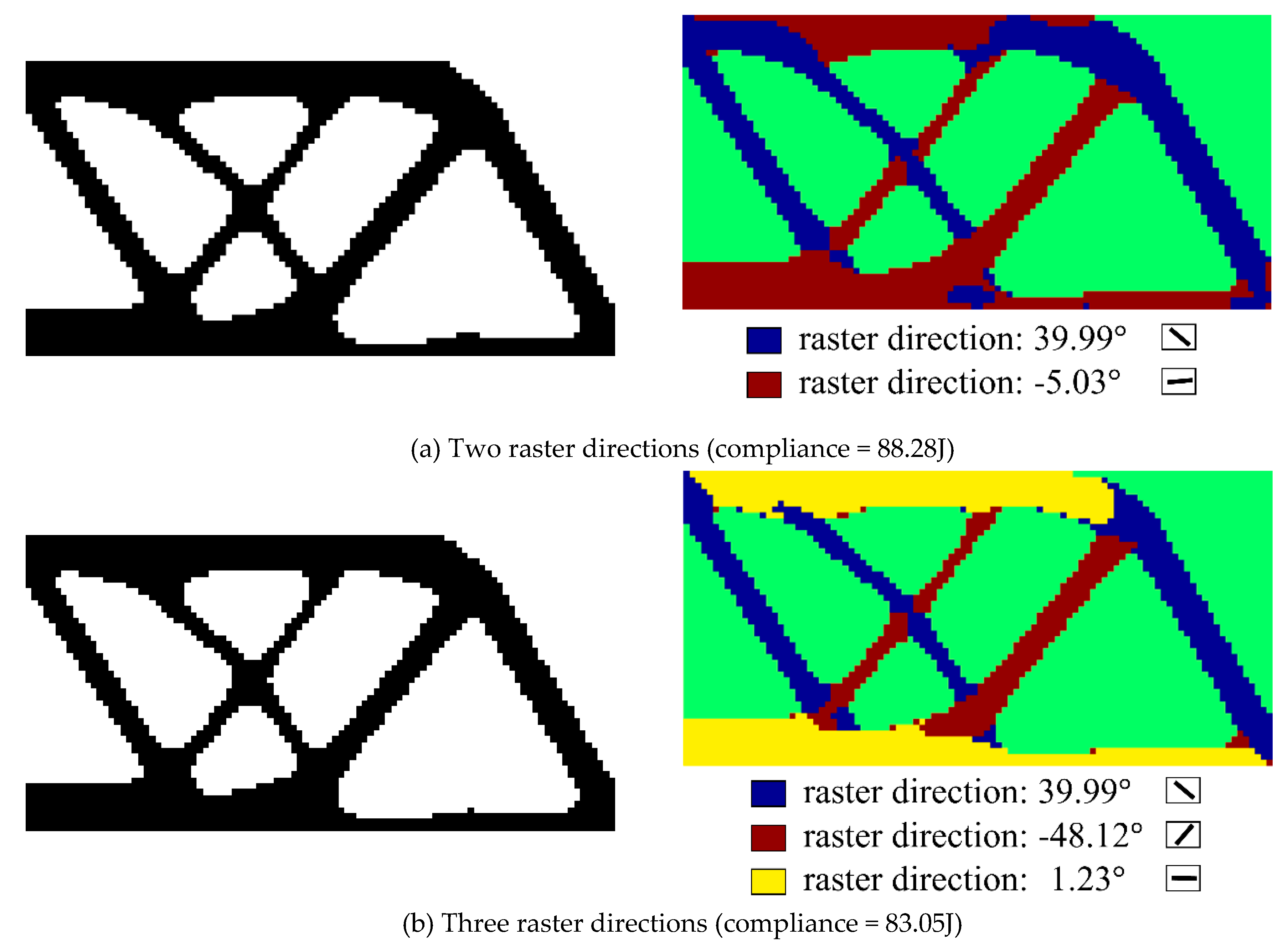
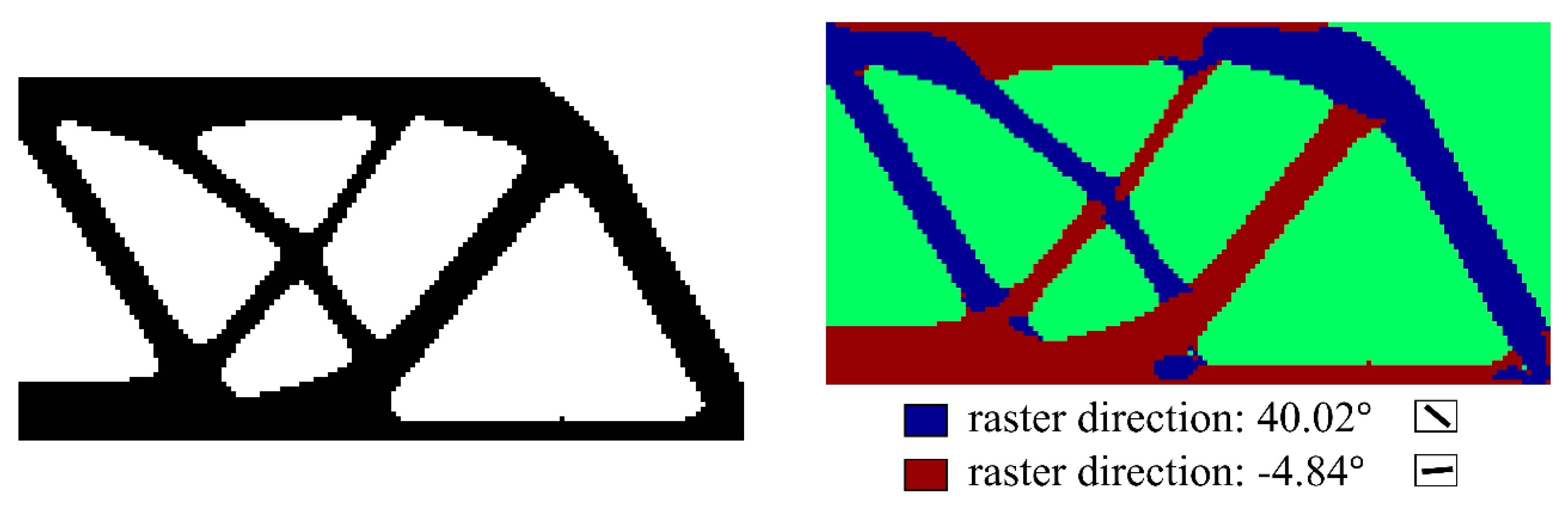
5. Case Studies
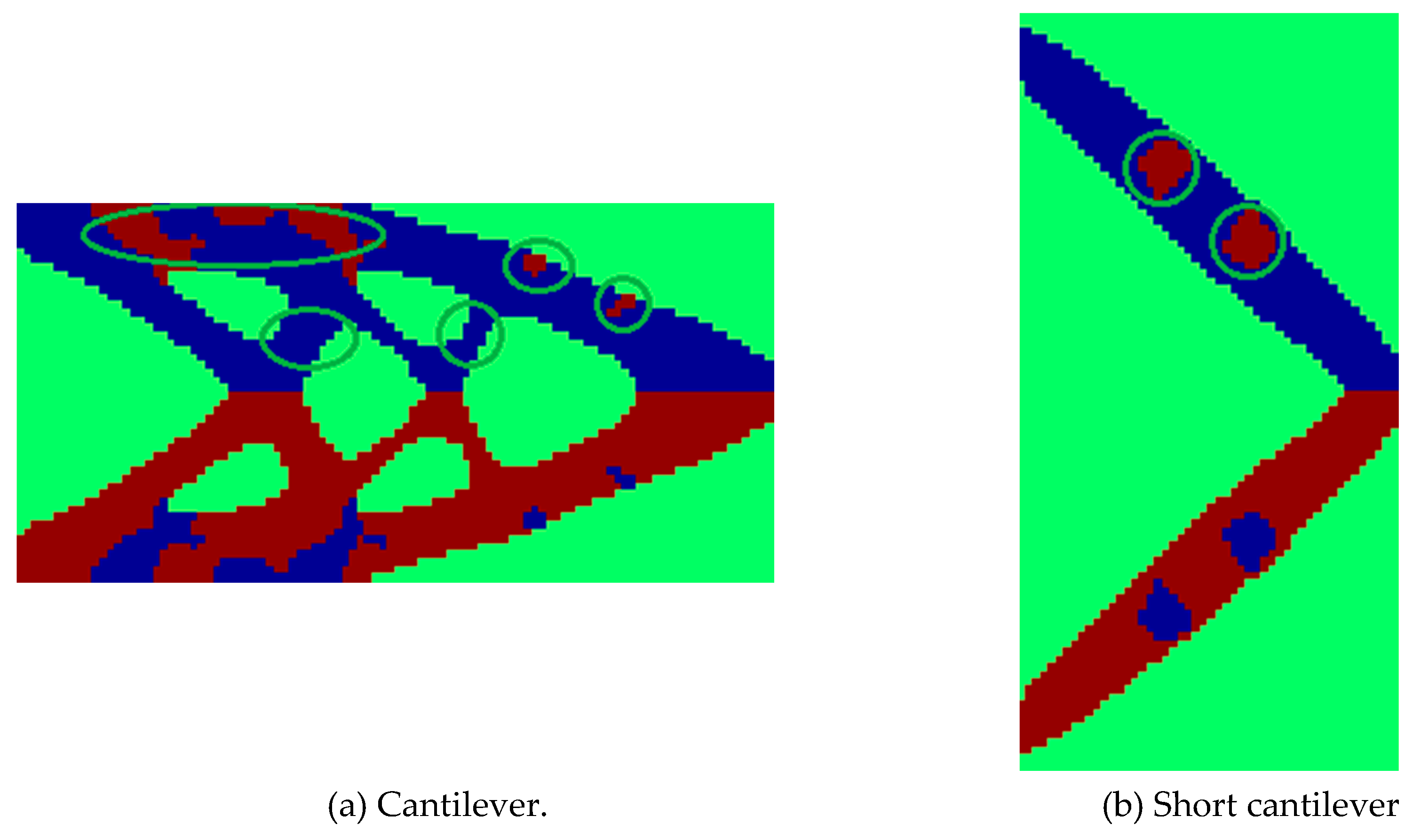
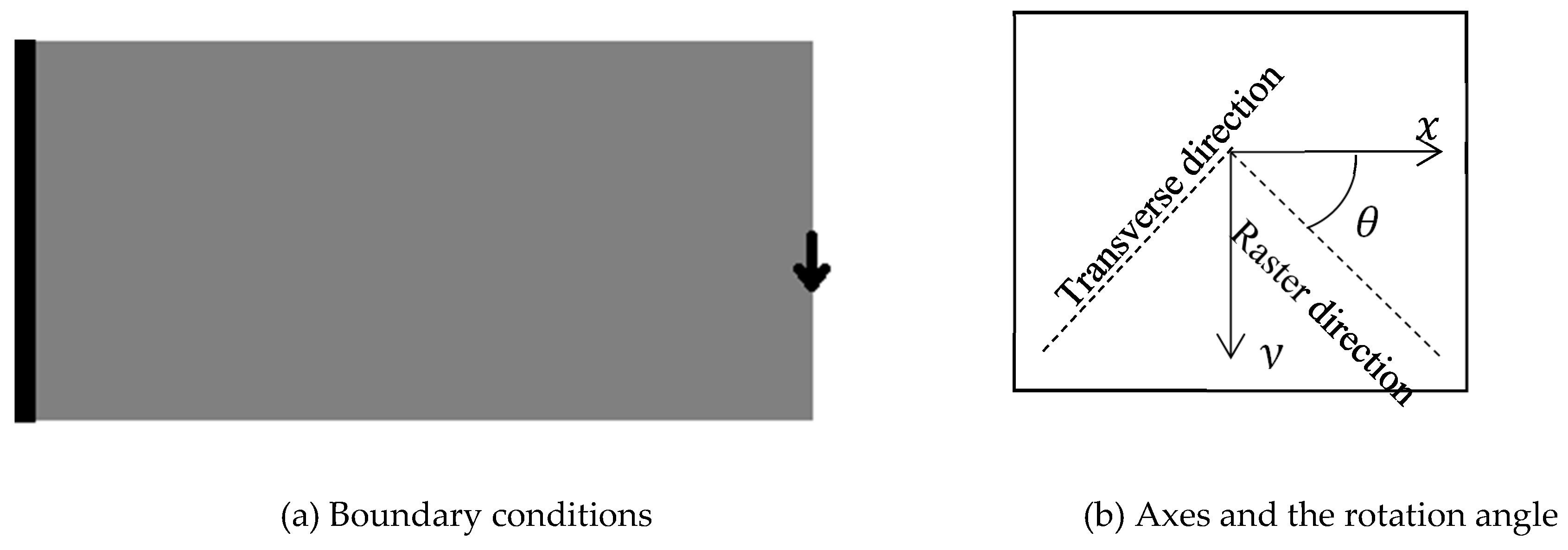
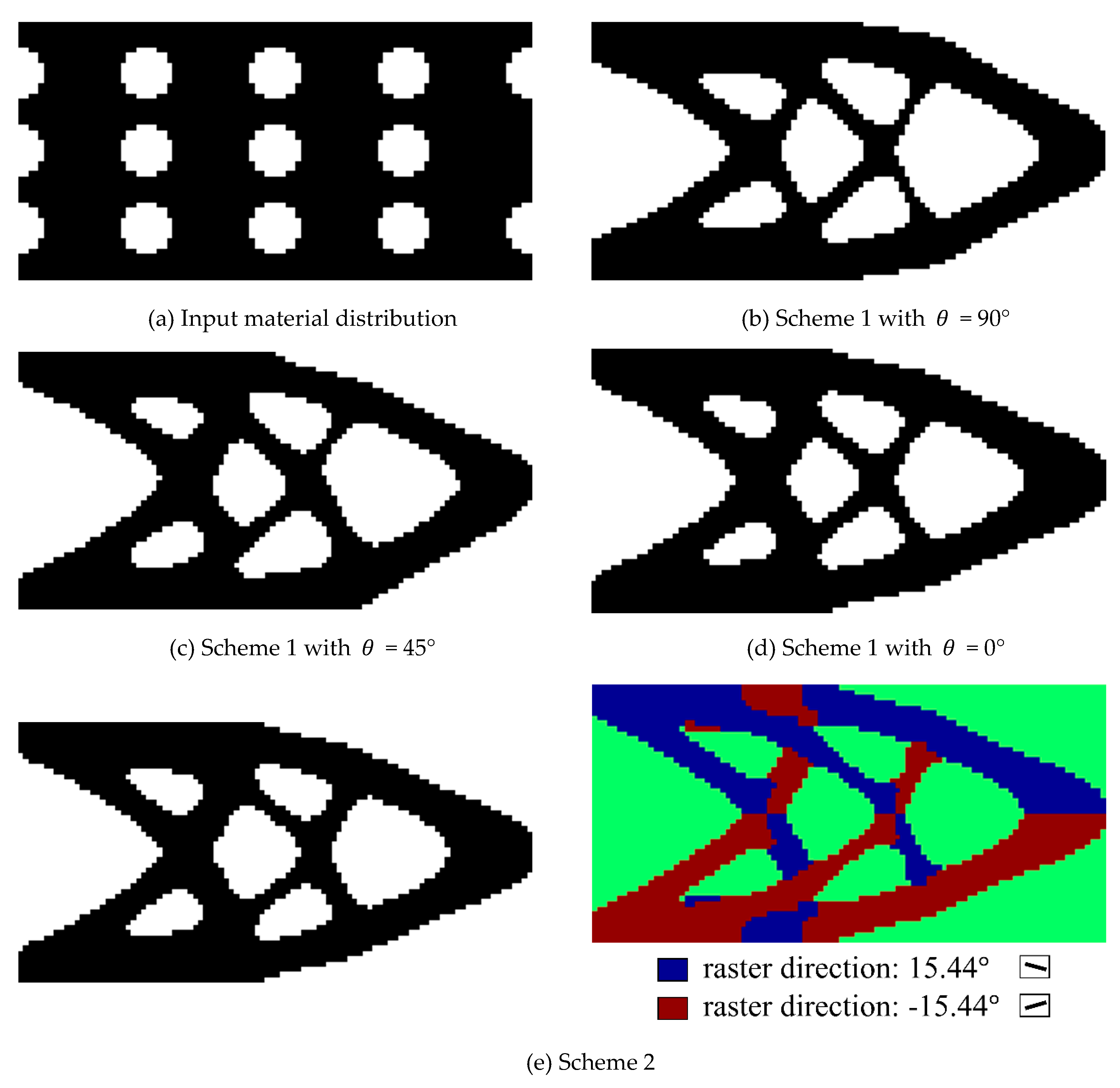
5.1. Cantilever Problem
- (1)
- Topology optimization with a fixed uniraster direction of 90°, 45° or 0°;
- (2)
- Topology optimization with two flexible raster directions starting from ±45°.
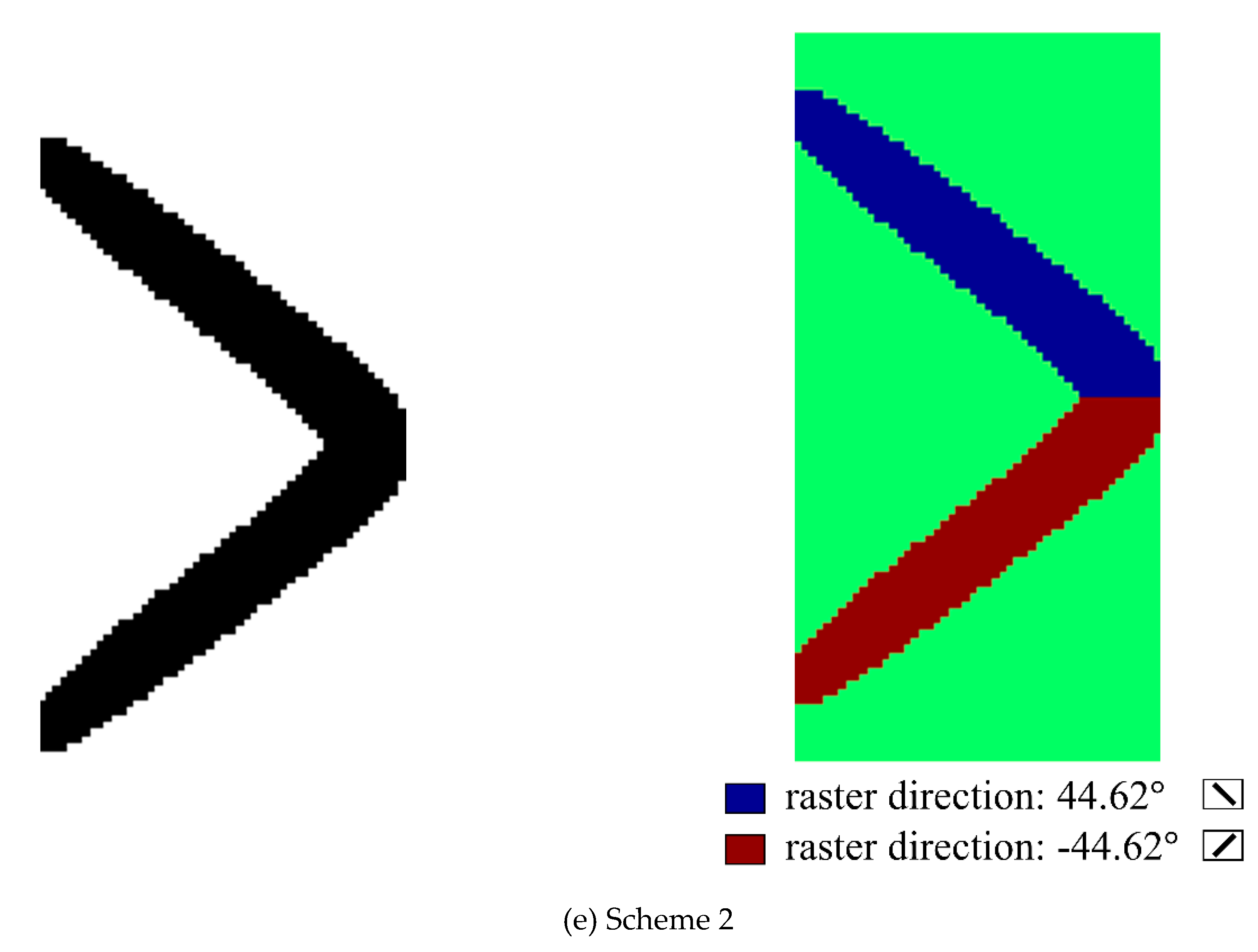
5.2. Short Cantilever Problem
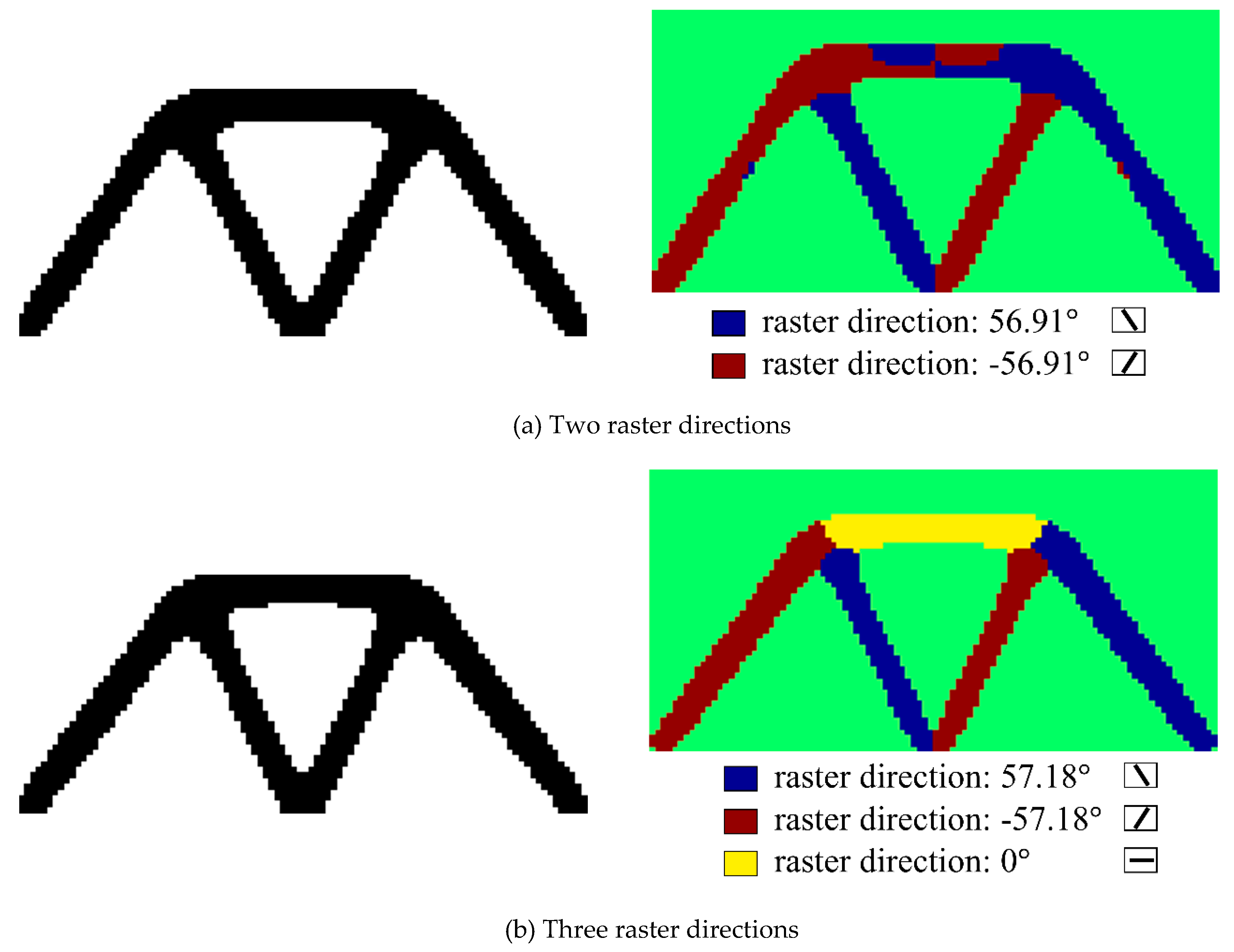
5.3. Michell Structure
5.4. Messerschmidt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) Structure
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ramanujan, D.; Ramani, K.; Chen, Y.; Williams, C.B.; Wang, C.C.L.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Zavattieri, P.D. The status, challenges, and future of additive manufacturing in engineering. Comput. Aided Des. 2015, 69, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gaynor, A.T.; Chen, S.; Kang, Z.; Suresh, K.; Takezawa, A.; Li, L.; Kato, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.C.L.; et al. Current and future trends in topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 57, 2457–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y. A survey of manufacturing oriented topology optimization methods. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 100, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Merli, L.; Torti, F.; Mazur, M.; Brandt, M. Optimal topology for additive manufacture: A method for enabling additive manufacture of support-free optimal structures. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzendehdel, A.M.; Suresh, K. Support structure constrained topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Comput. Aided Des. 2016, 81, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; To, A.C. Deposition path planning-integrated structural topology optimization for 3D additive manufacturing subject to self-support constraint. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 91, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, A.T.; Guest, J.K. Topology optimization considering overhang constraints: Eliminating sacrificial support material in additive manufacturing through design. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 54, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Du, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. Self-supporting structure design in additive manufacturing through explicit topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 323, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Kang, Z. Level set-based topology optimization with overhang constraint: Towards support-free additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 339, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, L. Topology optimization of self-supporting structures with polygon features for additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 334, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y. A new multi-material level set topology optimization method with the length scale control capability. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 329, 444–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Piecewise length scale control for topology optimization with an irregular design domain. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 351, 744–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.R.; Simhambhatla, S. Adopting feature resolution and material distribution constraints into topology optimisation of additive manufacturing components. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2019, 14, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Minimum length scale control in structural topology optimization based on the Moving Morphable Components (MMC) approach. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 311, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, B.S.; Wang, F.; Sigmund, O. Length scale and manufacturability in density-based topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2016, 86, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ahmad, R.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y. Minimum length scale constraints in multi-scale topology optimisation for additive manufacturing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2019, 14, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, E.; Korkmaz, E.; Yay, K.; Ozdoganlar, O.B.; Kara, L.B. Enhancing the structural performance of additively manufactured objects through build orientation optimization. J. Mech. Des. 2015, 137, 111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; To, A.C. Role of anisotropic properties on topology optimization of additive manufactured load bearing structures. Scr. Mater. 2017, 135, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.N.S.; Rolfe, B.; Wu, X.; Yan, W. Effect of stiffness anisotropy on topology optimisation of additively manufactured structures. Eng. Struct. 2018, 171, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, P.; Chen, S.; Zhou, C. An open source framework for integrated additive manufacturing and level-set based topology optimization. ASME J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 17, 041012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegard, T.; Paulino, G.H. Bridging topology optimization and additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2015, 53, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, G.; Yang, M. Lightweight research in engineering: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Topology optimisation using MPBILs and multi-grid ground element. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Toman, J.; Yu, Y.; Biyikli, E.; Kirca, M.; Chmielus, M.; To, A.C. Efficient design-optimization of variable-density hexagonal cellular structure by additive manufacturing: Theory and validation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2015, 137, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Ludwick, S.; Belski, E.; To, A.C. Natural frequency optimization of 3D printed variable-density honeycomb structure via a homogenization-based approach. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 20, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Zou, B.; Shao, W.; Liu, J. Stress-constrained shell-lattice infill structural optimization for additive manufacturing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 15, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, A.; Abdi, M.; Hickman, D.; Ashcroft, I. Strategies for functionally graded lattice structures derived using topology optimisation for additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 19, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gadipudi, V.K.; Salem, D.R. Topology optimization of lightweight lattice structural composites inspired by cuttlefish bone. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X.; To, A.C. Manufacturing cost constrained topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 14, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qureshi, A.; Ahmad, R. A topology optimization method for hybrid subtractive–additive remanufacturing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackett, D.; Ashcroft, I.; Hague, R. Topology optimization for additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.H.; Montero, M.; Odell, D.; Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K. Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling ABS. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2002, 8, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, R.; Badrossamay, M.; Ghaie, A.; Moosavi, H. Topology optimization for fused deposition modeling process. Proc. CIRP 2013, 6, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglund, R.; Smith, D.E. Non-isotropic material distribution topology optimization for fused deposition modeling products. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Hoglund, R.; Smith, D.E. Continuous fiber angle topology optimization for polymer composite deposition additive manufacturing applications. Fibers 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xu, Q.; Hua, H.; Huang, D.; Huang, X. Concurrent topology optimization of structures and orientation of anisotropic materials. Eng. Optim. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H. Concurrent deposition path planning and structural topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Qureshi, A.J.; Ahmad, R. Light-weight shape and topology optimization with hybrid deposition path planning for FDM parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapogny, C.; Estevez, R.; Faure, A.; Michailidis, G. Shape and topology optimization considering anisotropic features induced by additive manufacturing processes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 344, 626–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.H.S.; Bittrich, L.; Nomura, T.; Spickenheuer, A. Cross-section optimization of topologically-optimized variable-axial anisotropic composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hsieh, S.-J.; Ting, C.-C. Modelling and estimation of tensile behaviour of polylactic acid parts manufactured by fused deposition modelling using finite element analysis and knowledge-based library. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Rathee, S. Optimisation of FDM process parameters by Taguchi method for imparting customised properties to components. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zou, B.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, H. A survey of design methods for material extrusion polymer 3D printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Baek, C.; Lee, S.; Ahn, I.S. Anisotropic tensile failure model of rapid prototyping parts—Fused deposition modeling (FDM). Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2003, 17, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, S.H. Measurement of anisotropic compressive strength of rapid prototyping parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 187–188, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.; Haghi, M. Deposition direction-dependent failure criteria for fused deposition modeling polycarbonate. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, N.; Schmidt, R. Cross-sectional structural analysis for 3D printing optimization. SIGGRAPH Asia Tech. Briefs 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzendehdel, A.M.; Rankouhi, B.; Suresh, K. Strength-based topology optimization for anisotropic parts. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 19, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Fedkiw, R. Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces; Applied Mathematical Sciences Book Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 153. [Google Scholar]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, D. A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2003, 192, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, G.; Jouve, F.; Toader, A.-M. Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J. Comput. Phys. 2004, 194, 363–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X. ’Color’ level sets: A multi-phase method for structural topology optimization with multiple materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 469–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X. A level-set based variational method for design and optimization of heterogeneous objects. Comput. Aided Des. 2005, 37, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, N. A multi-material level set-based topology and shape optimization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 283, 1570–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J. A level-set based multi-material topology optimization method using a reaction diffusion equation. Comput. Aided Des. 2016, 73, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, J.; Lund, E. Discrete material optimization of general composite shell structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 62, 2009–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.; Stegmann, J. On structural optimization of composite shell structures using a discrete constitutive parametrization. Wind Energy 2005, 8, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.T.L.; Rodrigues, H.C.; Guedes, J.M.; Hernandes, J.A. Hierarchical optimization of laminated fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2014, 107, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, A.; Fadel, G. Optimizing topology and gradient orthotropic material properties under multiple loads. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| = 90° | = 45° | = 0° | Scheme 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural compliance (J) | 76.67 | 69.91 | 57.94 | 55.47 |
| Compliance reduction compared to the worst case | 0% | 8.82% | 24.43% | 27.65% |
| Optimal raster directions | 90° | 45° | 0° | ±15.44° |
| = 90° | = 45 | = 0° | Scheme 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural compliance (J) | 11.31 | 12.02 | 11.48 | 8.12 |
| Compliance reduction compared to the worst case | 5.91% | 0% | 4.49% | 32.44% |
| Optimal raster directions | 90° | 45° | 0° | ±44.62° |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Hong, H.; Cao, S.; Ahmad, R. Topology Optimization for Multipatch Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030943
Yu H, Hong H, Cao S, Ahmad R. Topology Optimization for Multipatch Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030943
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huangchao, Huajie Hong, Su Cao, and Rafiq Ahmad. 2020. "Topology Optimization for Multipatch Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030943
APA StyleYu, H., Hong, H., Cao, S., & Ahmad, R. (2020). Topology Optimization for Multipatch Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030943






