Filter Media-Packed Bed Reactor Fortification with Biochar to Enhance Wastewater Quality
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Filter Materials and Wastewater
2.2. Preparation and Pre-Experiment Analysis of Materials
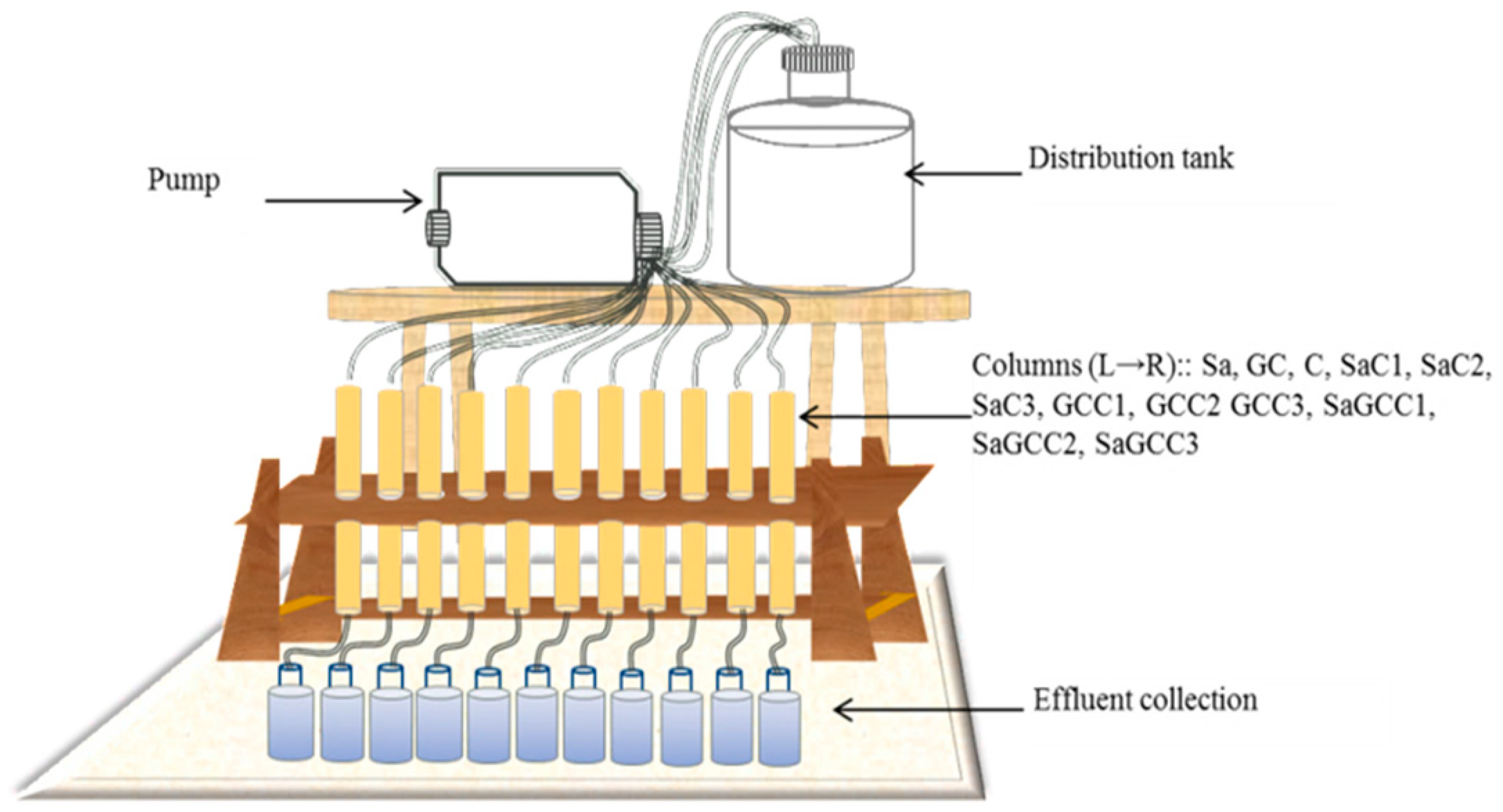
2.3. Preparing and Operating the Packed Bed Reactors (PBR)
2.4. Operating the Columns
2.5. Sampling and Performance Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Filter Characteristics
3.2. Monitored Wastewater Qualities
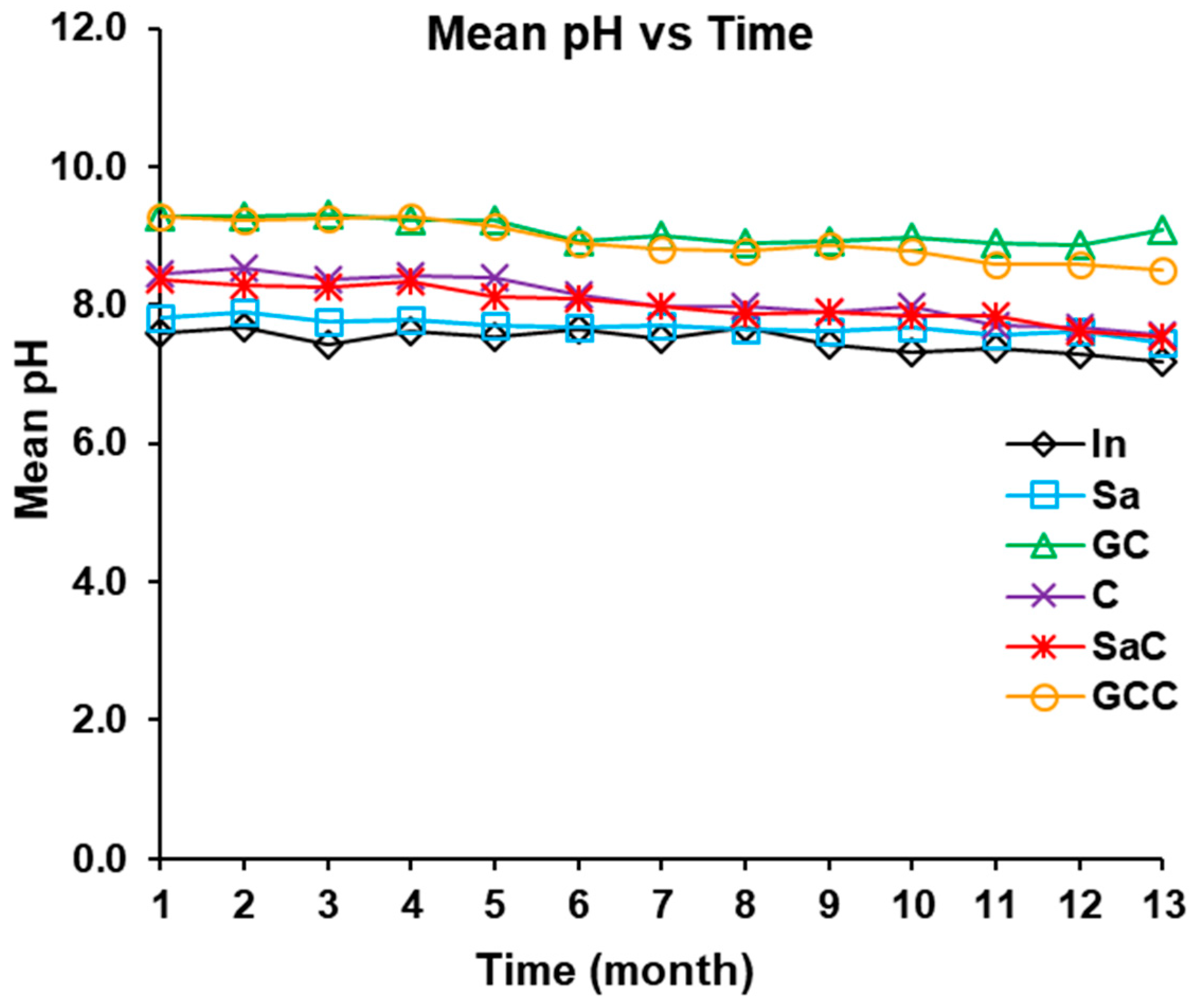
3.2.1. Turbidity and pH
3.2.2. Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) Removal
3.2.3. Filter Efficacy in DOC Removal
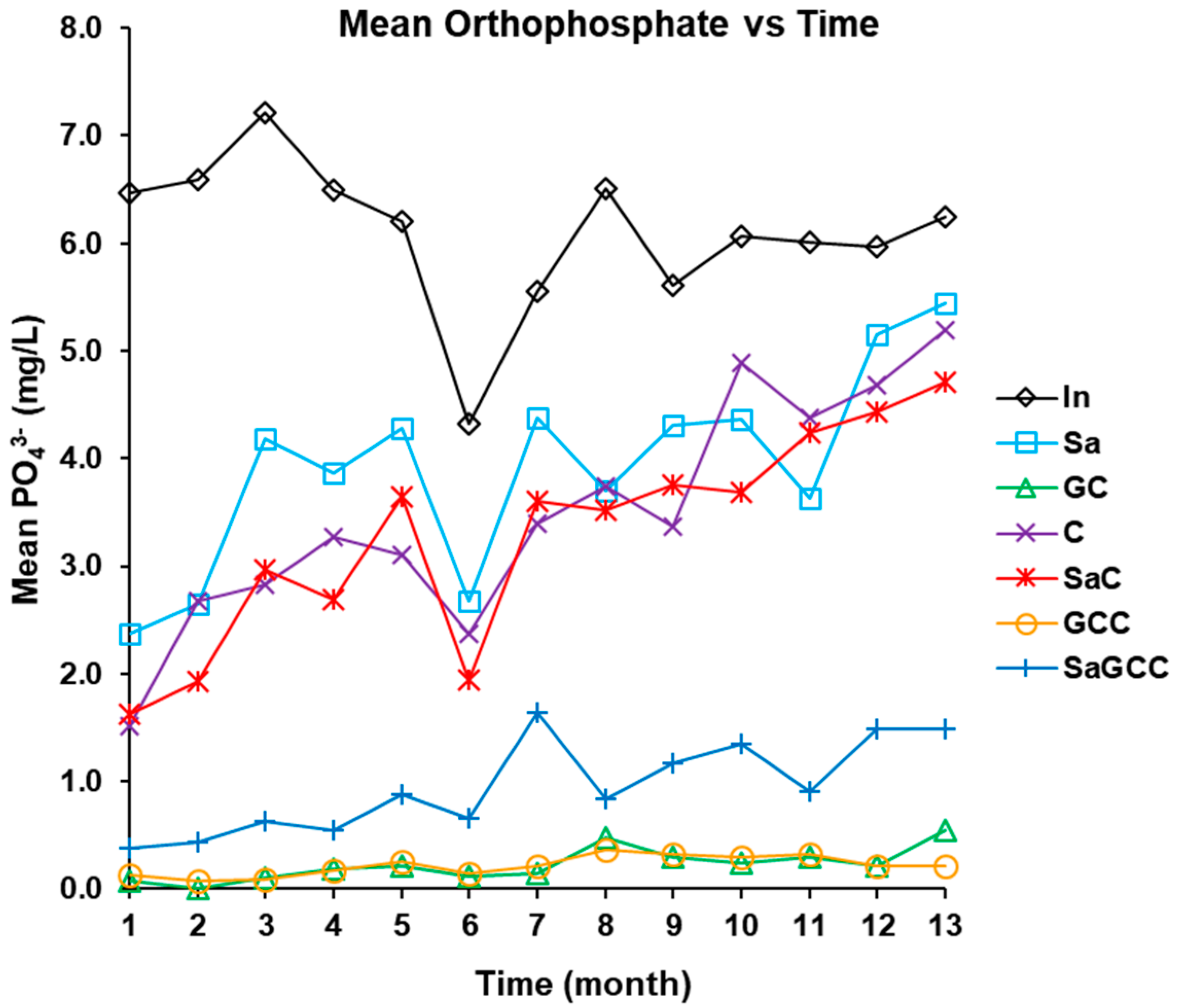
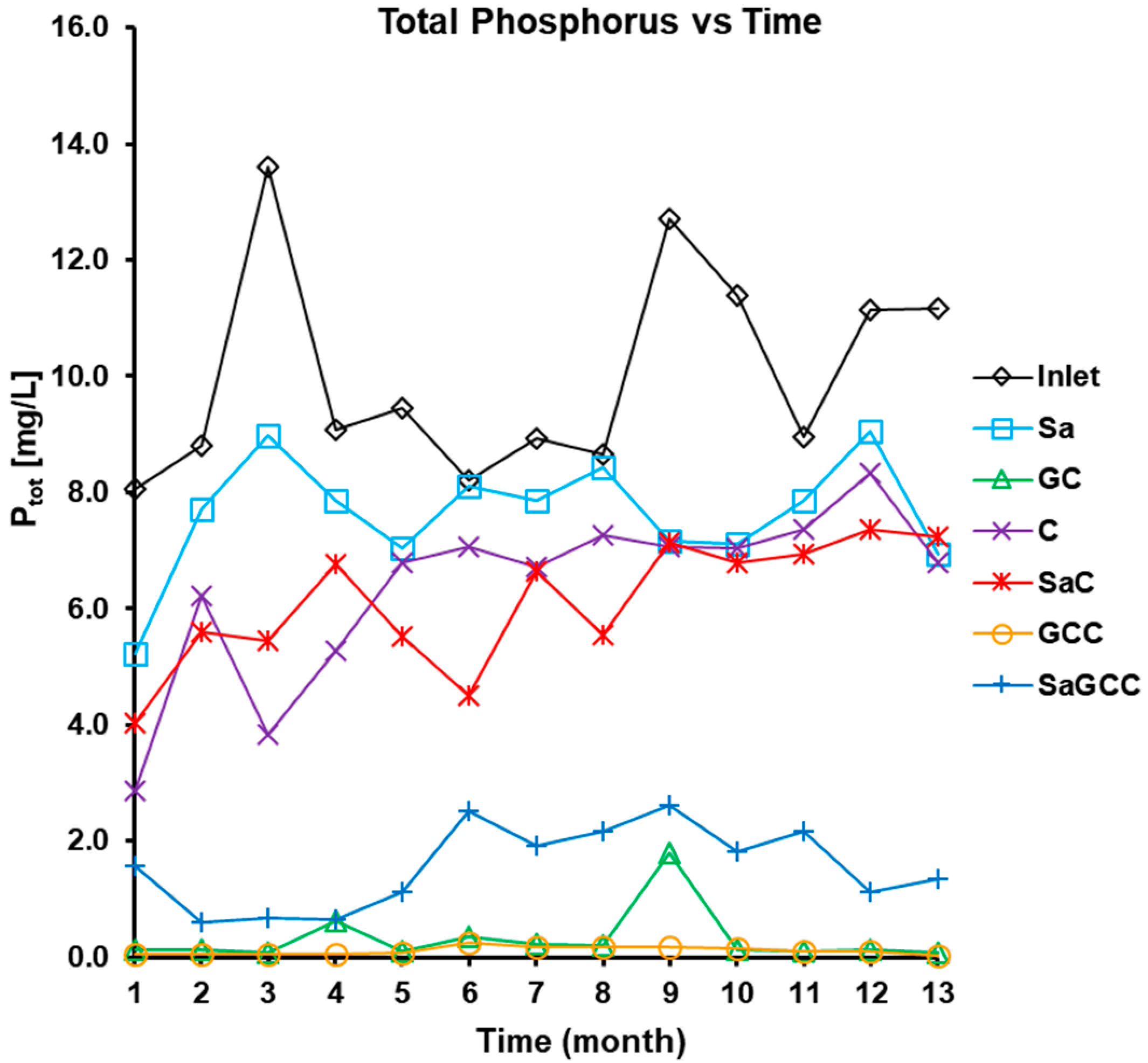
3.2.4. Phosphorus (PO43− and Ptot) Removal
4. Filter Efficacy at P Removal
5. Significance of Fortification with Biochar on DOC and P Removal by Sand
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PBR | Packed bed reactor |
| RF | Reactive filter |
| Sa | Sand |
| C | Biochar |
| GC | Gas concrete |
| GCC | Gas concrete + biochar |
| SaGCC | Sand + gas concrete + biochar |
| STU | Soil treatment units |
| STE | Septic tank effluent |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| P | Phosphorus |
| PO4 | Soluble reactive phosphorus |
| PO43− | Orthophosphate |
| Ptot | Total phosphorus |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| N | Nitrogen |
| Ca | Calcium |
| Al | Aluminum |
| Fe | Iron |
| O2− | Oxides |
| OH− | Hydroxides |
| MgO | Periclase |
| Ca5(PO4)3OH | Calcium hydroxyapatite |
| Ca(OH)2 | Slaked lime |
| SEPA | Swedish Environmental Protection Agency |
| HLR | Hydraulic loading rate |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| GAC | Granulated activated carbon |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| OWT | On-site wastewater treatment |
| PTP | Package treatment plant |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Del Rosario, K.L.; Humphrey, C.P.; Mitra, S.; O’Driscoll, M.A. Nitrogen and carbon dynamics beneath on-site wastewater treatment systems in Pitt County, North Carolina. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Stoate, C. Quantifying the impact of septic tank systems on eutrophication risk in rural headwaters. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, M.A.; Bradbury, K.R.; Alexander, E.C., Jr.; Kolberg, R.J.; Alexander, S.C.; Archer, J.C.; Braatz, L.A.; Forest, B.M.; Green, J.A.; Spencer, S.K. Norovirus outbreak caused by a new septic system in a dolomite aquifer. Groundwater 2011, 49, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, E.; Woessner, W.W.; Benotti, M.J. Pharmaceuticals in on-site wastewater sewage effluent and groundwater. Ground Water 2007, 45, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. The use of constructed wetlands for on-site treatment of domestic wastewater: New Danish guidelines. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, L.; Goonetilleke, A. An investigation into the role of site and soil characteristics in on-site sewage treatment. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eveborn, D.; Kong, D.; Gustafsson, J.P. Wastewater treatment by soil infiltration—Long-term phosphorus removal. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 140–141, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4222–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Miino, M.C.; Baldi, M.; Manzi, S.; Abba, A.; Bertanza, G. Removal of non-ionic and anionic surfactants from laundry wastewater by means of a full-scale wastewater treatment system. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 132, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA. Sweden’s Commitment under the Baltic Sea Action Plan—Proposal for a National Action Plan; Report 6318; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, T.; Afrin, R.; Al Muyeed, A.; Sun, G. Treatment of tannery wastewater in a pilot-scale hybrid constructed wetland system in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-A.; Morel, A.; Tonderski, K. Baffled septic tank with anaerobic filter (BASTAF) and vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland for domestic treatment in Vietnam. IWA Publ. Water Pract. 2010, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistad, A.; Paruch, A.M.; Vråle, L.; Adam, K.; Jenssen, P.D. A high-performance compact filer system treating domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohla, C.; Kõiv, M.; Bavor, H.J.; Chazarenc, F.; Mander, Ü. Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands—A review. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J. Use of industrial wastes as media in constructed wetlands and filter beds—Prospects for removal of phosphate and metals from wastewater streams. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1041–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, I.; Fritsche, J.; Bänninger, D.; Alewell, U.; Sendelov, M.; Hürlimann, H.; Hasselbach, R.; Alewell, C. Improving the treatment efficiency of constructed wetlands with zeolite-containing filter sands. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renman, A.; Renman, G. Long-term phosphate removal by calcium-silicate material polonite in wastewater filtration systems. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søvik, A.K.; Kløve, B. Phosphorus retention processes in shell sand filter systems treating municipal wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilton, A.N.; Elmetri, I.; Drizo, A.; Pratt, S.; Haverkamp, R.G.; Bilby, S.C. Phosphorus removal by an ‘active’ slag filter: A decade of full-scale experience. Water Res. 2006, 40, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ma, L.; Liang, Y.; Gao, B.; Harris, W. Simultaneous immobilization of lead and atrazine in contaminated soils using dairy-manure biochar. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4884–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Clough, T.J.; Sherlock, R.R.; Condron, L.M. A wood based low-temperature biochar captures NH3-N generated from ruminant urine-N, relating its bioavailability. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Xie, T.; Dastgheibi, S. Evaluation of biochar as a potential filter media for the removal of mixed contaminants from urban storm water runoff. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Wnętrzak, R.; Leahy, J.J.; Hayes, M.B.H.; Kwapiński, W.; Hubicki, Z. Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. 2012, 197, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, L.; Sun, K.; Jin, J.; Ro, K.S.; Libra, J.A.; Liu, X.; Xing, B. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic contaminants by biochars derived from maize straw, wood dust and swine manure at different pyrolytic temperatures. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Cantrel, K.B.; Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B. Efficacy of biochar to remove Escherichia coli from stormwater under steady and intermittent flow. Water Res. 2014, 61, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2012, 80, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholoma, E.; Renman, G.; Renman, A. Phosphorus removal from wastewater by field-scale fortified filter beds during a one-year study. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2953–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renman, G.; Renman, A. Sustainable use of crushed autoclaved aerated concrete (CAAC) as a filter medium in wastewater purification. In Proceedings of the WASCON Conference, Gothernburg, Sweden, 30 May–1 June 2012; Available online: http://www.iscowa.org/proceed12/htm/index.htm (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Cucarella, V.; Renman, G. Phosphorus sorption capacity of filter materials used for on-site wastewater treatment determined in batch experiments—A comparative study. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA. Environmental Code Concerning Environmentally Hazardous Activities and Health Protection of Small Sewage Facilities for Household Wastewater; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Achak, M.; Mandi, L.; Ouazzani, N. Removal of organic pollutants and nutrient from olive mill wastewater by a sand filter. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, N.; Ramamurthy, K. Microstructural investigations on aerated concrete. Cement Concrete Res. 2000, 30, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindo, K.; Mizumoto, H.; Sawada, Y.; Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.; Sonoki, T. Physical and chemical characterization of biochars derived from different agricultural residues. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 6613–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.E.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Satrio, J.A.; Brown, R.C. Characterization of biochar from fast pyrolysis and gasification systems. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2009, 28, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Cho, T.-S.; Choi, J.-W. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on physicochemical properties of biochar obtained from the fast pyrolysis of pitch pine (Pinus rigida). Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yargicoglu, E.N.; Sadasivam, B.Y.; Reddy, K.R.; Spokas, K. Physical and chemical characterization of waste wood derived biochars. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmulski, M. pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. IV. Update and new approach. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2009, 337, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverjensky, D.A. Zero-point-of-charge prediction from crystal chemistry and solvation theory. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3123–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Chen, Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Q. Preparations and phosphorus recovery performance of porous calcium-silicate-hydrate. Ceram. Int. 2017, 39, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, C.; Wood, L.; Johnson, J.; Zhu, H.W.; Kaplan, L. Monitoring dissolved organic carbon in surface and drinking waters. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, A.; Samara, C. The fate of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the wastewater treatment process and its importance in the removal of wastewater contaminants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Resour. Int. 2007, 14, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.; Nordqvist, K.; Hedström, A.; Viklander, M. Effect of temperature on the performance of laboratory-scale phosphorus-removing filter beds in on-site wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.W.; Mancl, K.M.; Tuovinen, O.H. Treatment of turkey processing wastewater with sand filtration. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Peters, A.; Trinks, S.; Schonsky, H.; Facklam, M.; Wessolek, G. Impact of biochar and hydrochar addition on water retention and water repellency of sandy soil. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.P.; Renman, A.; Renman, G.; Poll, K. Phosphate removal by mineral-based sorbents for small-scale wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.M.; Comeford, N.; Guerrini, I.A.; Falcão, N.P.S.; Reeves, J.B. Sorption and desorption of phosphate on biochar and biochar-soil mixtures. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Media | pH | ρb (kg/m3) | d (mm) | ø | HRT (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa | 7.4 | 1.70 | 0.1–2.0 (39.8%) 2.0–4.0 (60.2%) | 0.35 | 90–78 |
| GC | 9.1 | 0.66 | 0.1–2.0 (43.4%) 2.0–4.0 (56.6%) | 0.52 | 127–99 |
| C | 8.0 | 0.54 | 0.1–2.0 (46.2%) 2.0–4.0 (53.8%) | 0.47 | 270–108 |
| SaC | 7.8 | n.d | 0.1–4.0 | 0.43 | 105–96 |
| GCC | 8.9 | n.d | 0.1–4.0 | 0.50 | 123–91 |
| Influent | Sa | C | GC | SaC | GCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.1–7.7 (7.5 ± 0.2) | 7.6–8.2 (7.7 ± 0.2) | 7.8–8.7 (8.0 ± 0.4) | 8.9–9.2 (9.1 ± 0.2) | 7.7–8.3 (7.9 ± 0.3) | 8.8–9.1 (8.9 ± 0.2) |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 29–428 (150 ± 210) | 1–3 (2 ± 1) | 1–2 (1 ± 0) | 0–1 (1 ± 0) | 1–2 (1 ± 0) | 0–1 (1 ± 0) |
| PO43− (mg/L) | 5.6–6.9 (6.1 ± 0.8) | 3.6–4.3 (3.9 ± 1.2) | 3.1–3.8 (3.5 ± 1.2) | 0.1–0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) | 2.9–3.6 (3.3 ± 1.1) | 0.2–0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) |
| Ptot (mg/L) | 8.9–10.6 (10.0 ± 1.8) | 6.4–7.4 (7.6. ± 1.0) | 4.5–5.5 (6.4 ± 1.5) | 0.0–0.6 (0.3 ± 0.5) | 10.1–11.0 (6.2 ± 1.0) | 0.1–0.2 (0.1 ± 0.1) |
| DOC (mg/L) | 21.0–32.0 (25.3 ± 2.8) | 10.64–13.46 (12.1 ± 2.3) | 9.12–11.07 (10.1 ± 1.6) | 8.8–11.6 (9.4 ± 2.1) | 9.60–10.78 (10.2 ± 1.0) | 9.3–11.1 (10.0 ± 1.5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kholoma, E.; Renman, A.; Renman, G. Filter Media-Packed Bed Reactor Fortification with Biochar to Enhance Wastewater Quality. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030790
Kholoma E, Renman A, Renman G. Filter Media-Packed Bed Reactor Fortification with Biochar to Enhance Wastewater Quality. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030790
Chicago/Turabian StyleKholoma, Ezekiel, Agnieszka Renman, and Gunno Renman. 2020. "Filter Media-Packed Bed Reactor Fortification with Biochar to Enhance Wastewater Quality" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030790
APA StyleKholoma, E., Renman, A., & Renman, G. (2020). Filter Media-Packed Bed Reactor Fortification with Biochar to Enhance Wastewater Quality. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030790





