The Influences of Acoustic and Pulsed Corona Discharge Coupling Field on Agglomeration of Monodisperse Fine Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
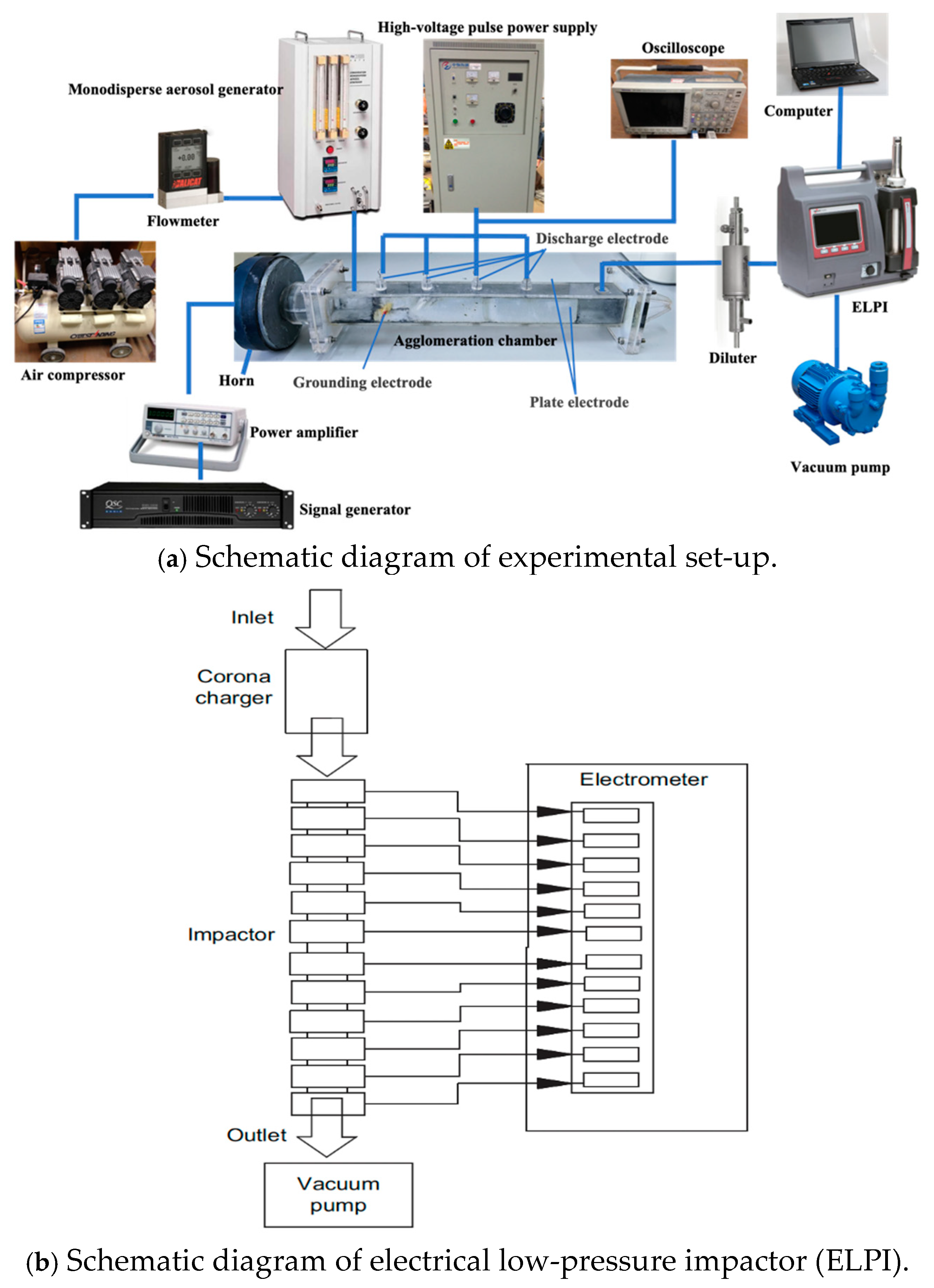
2. Materials and Methods
3. Theoretical Analysis
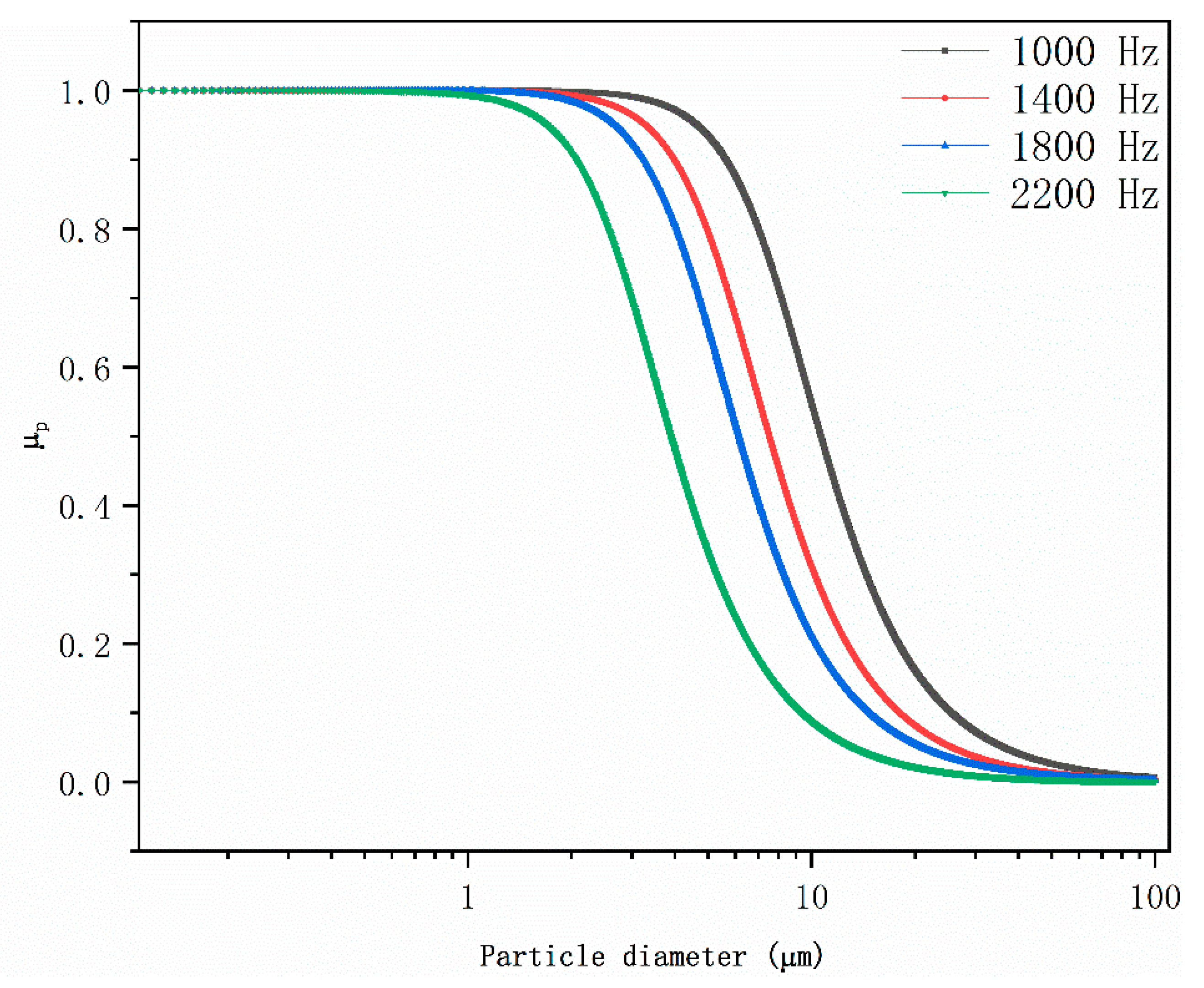
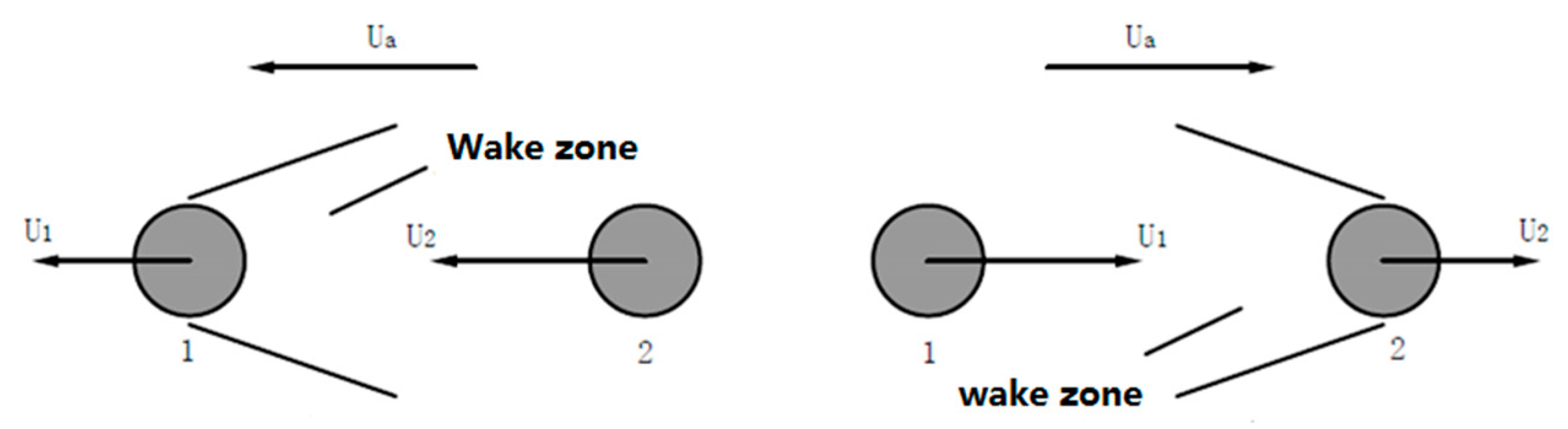
3.1. Acoustic Wave Field
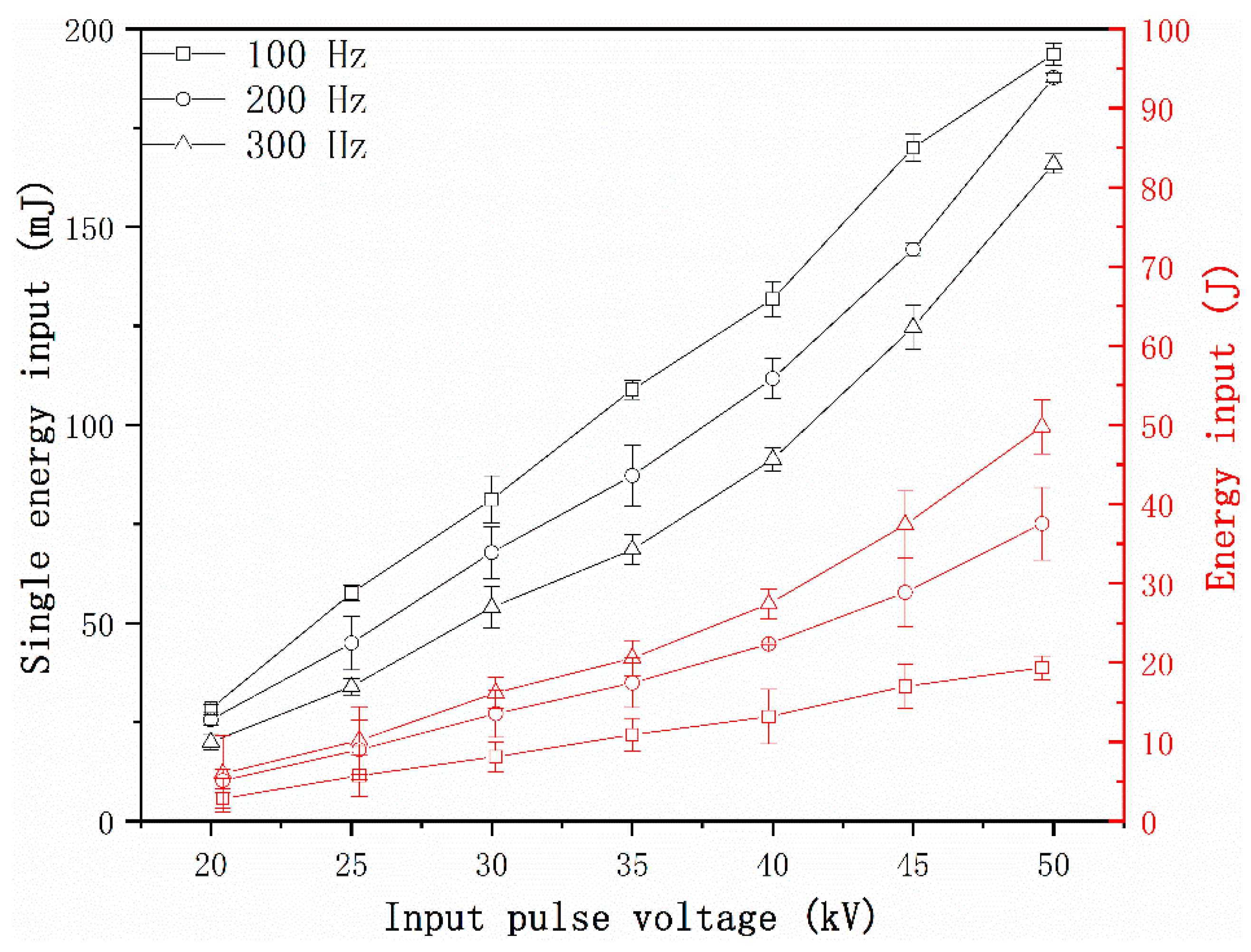
3.2. Pulsed Corona Discharge Field
4. Results and Discussion
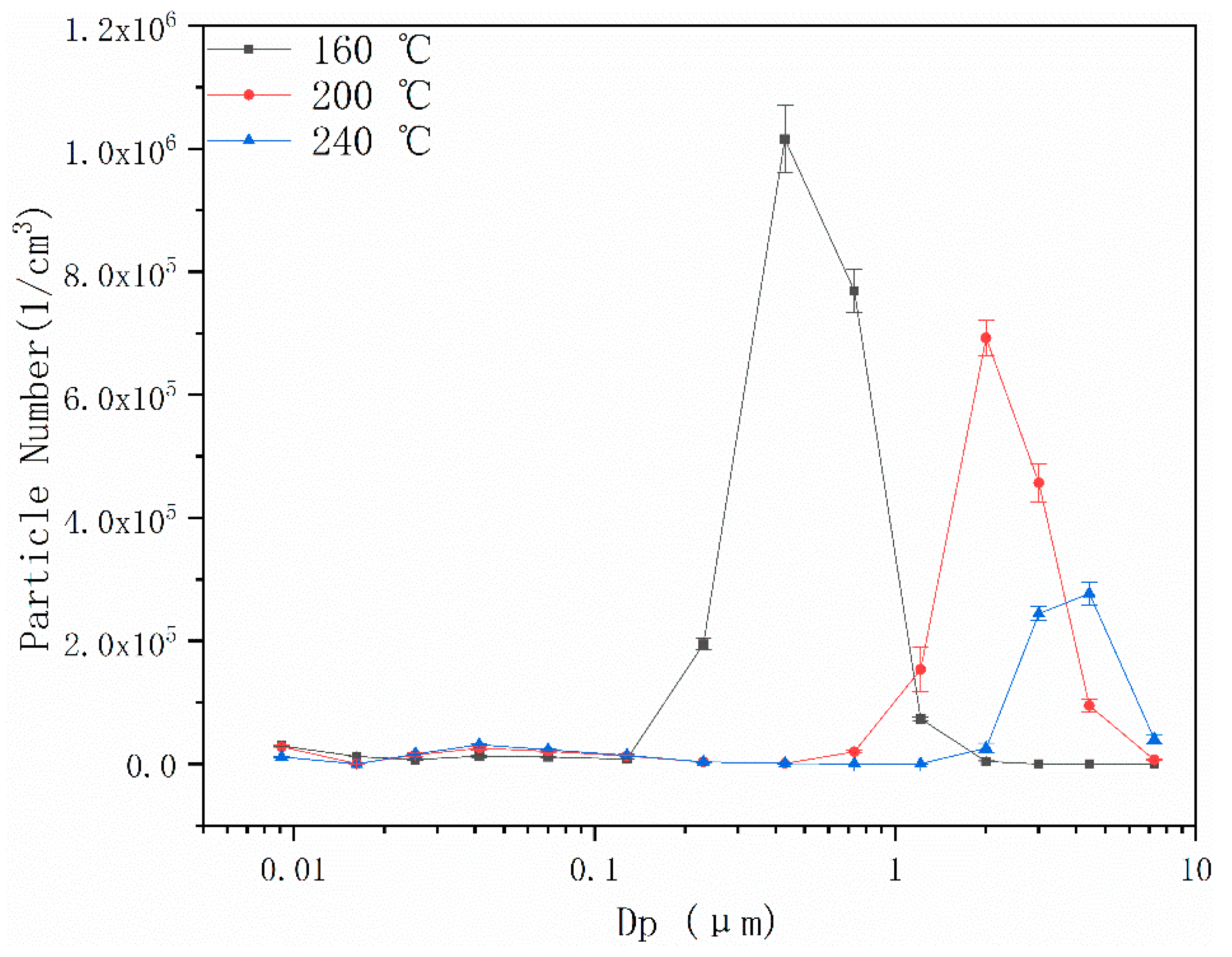
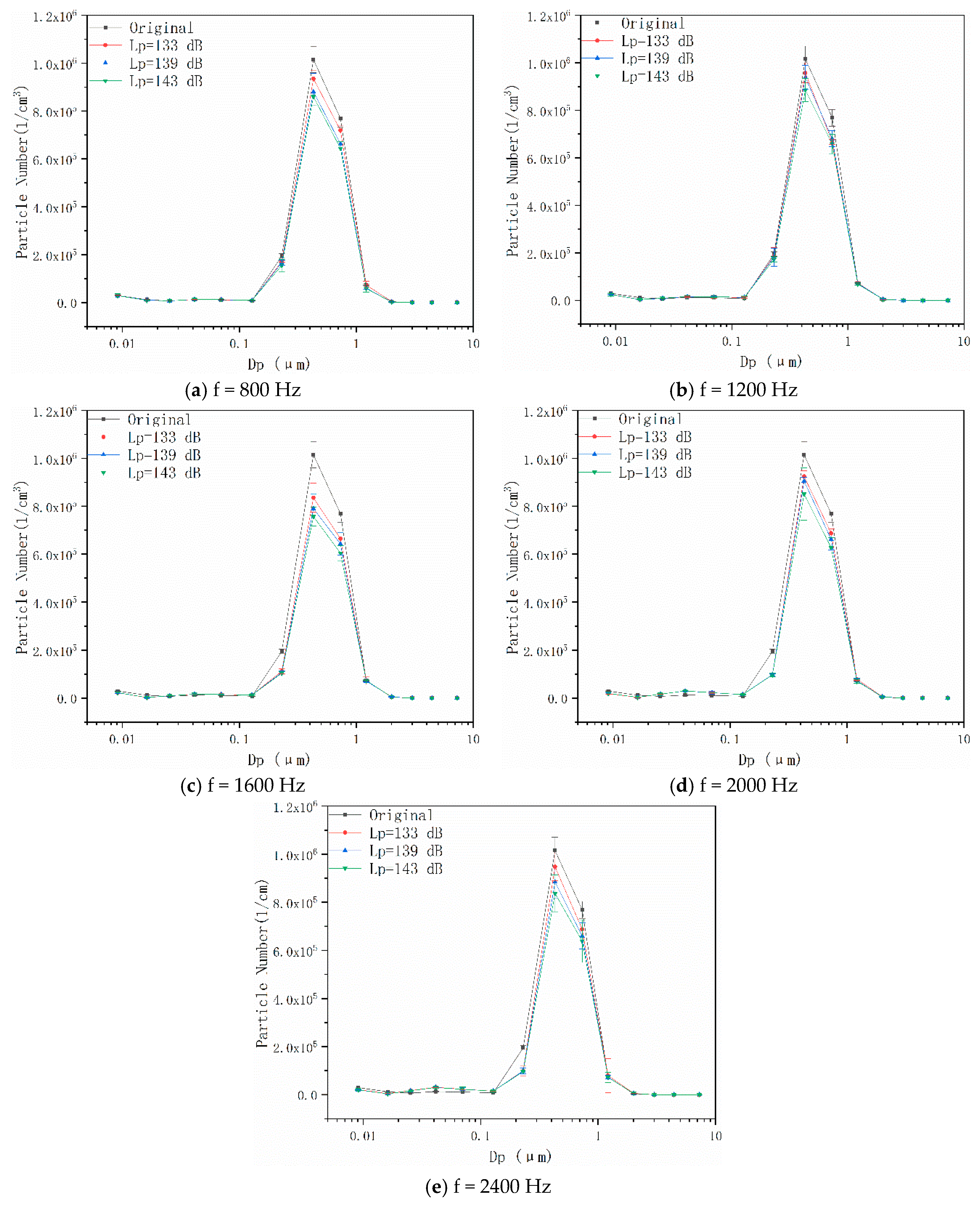
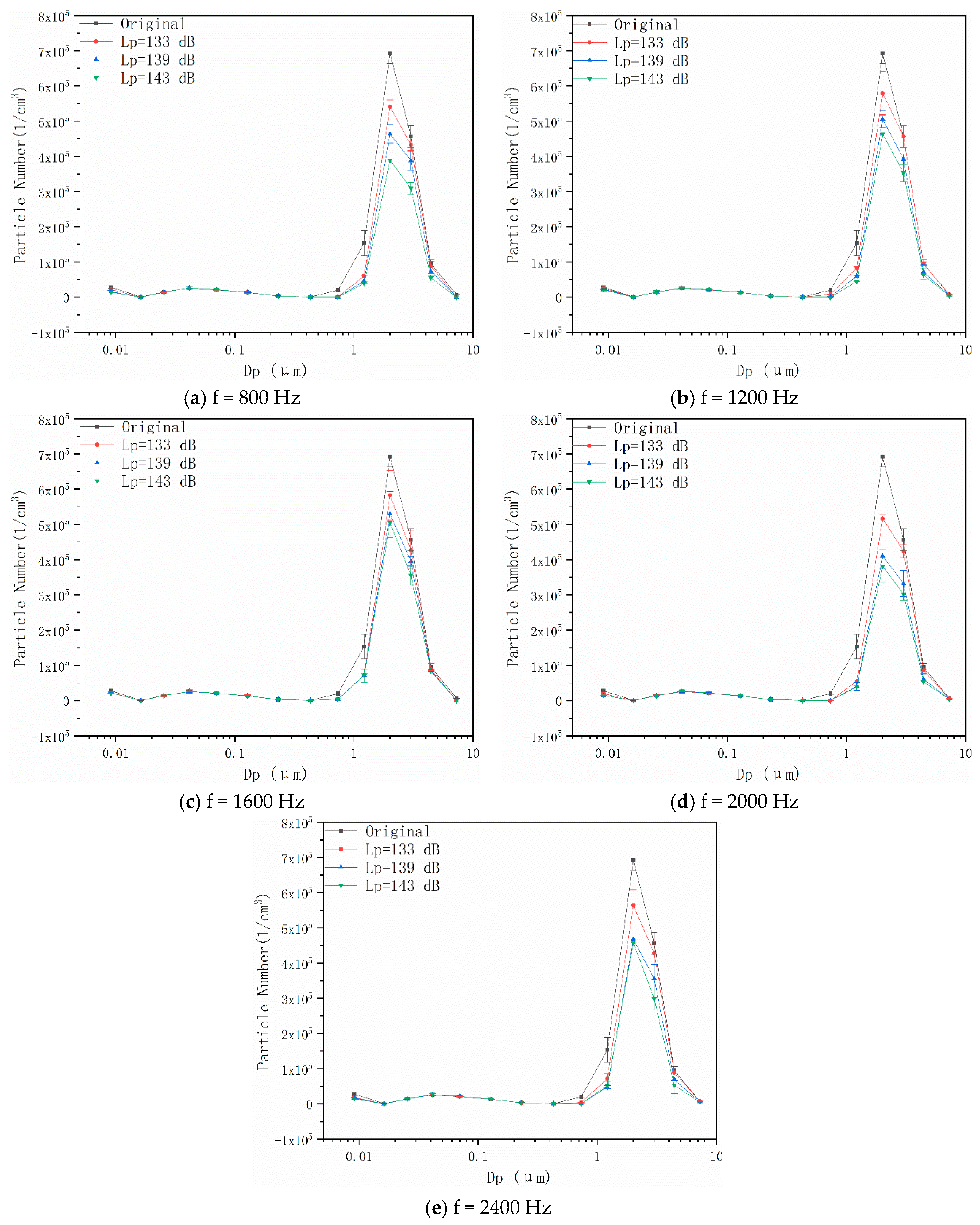
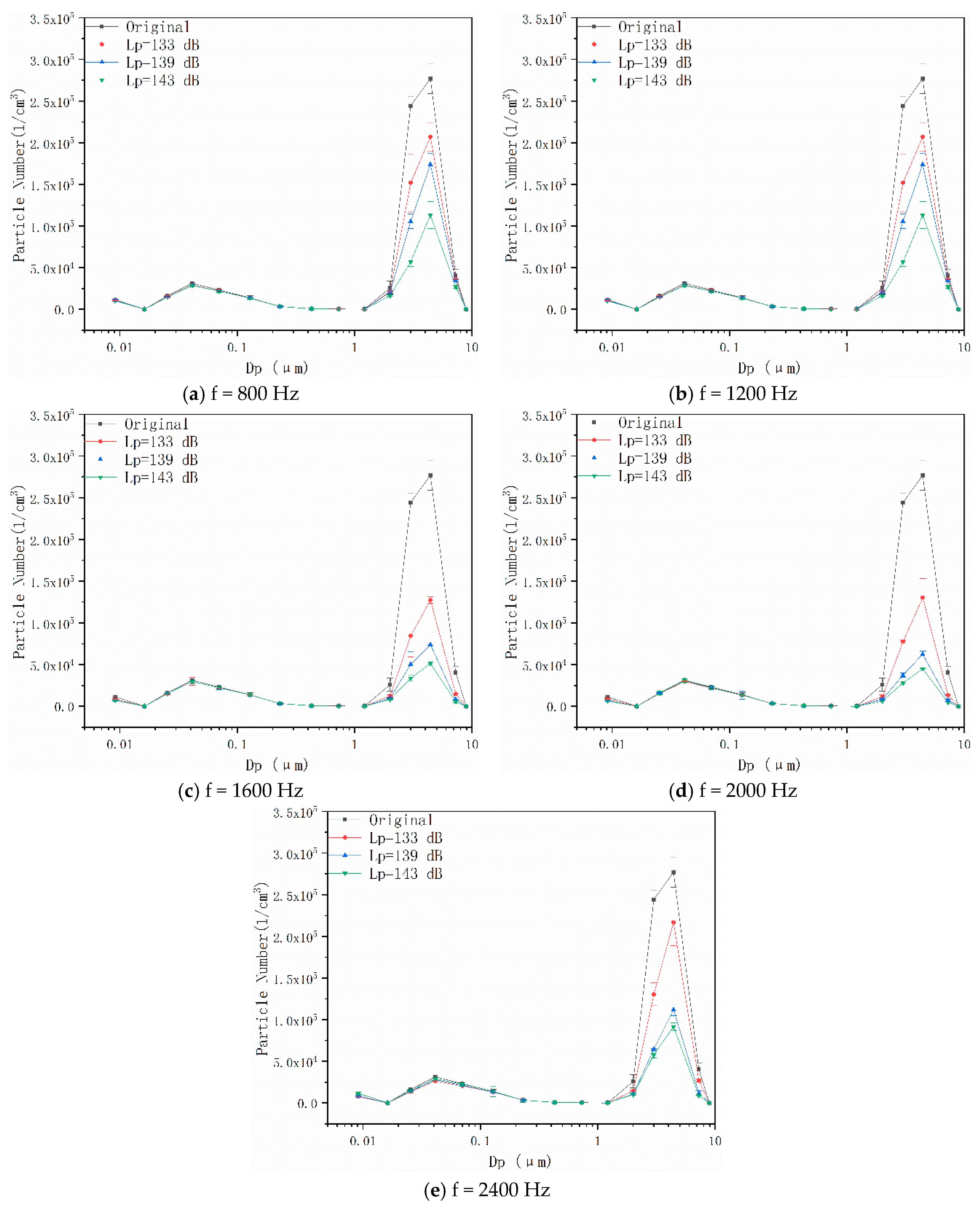
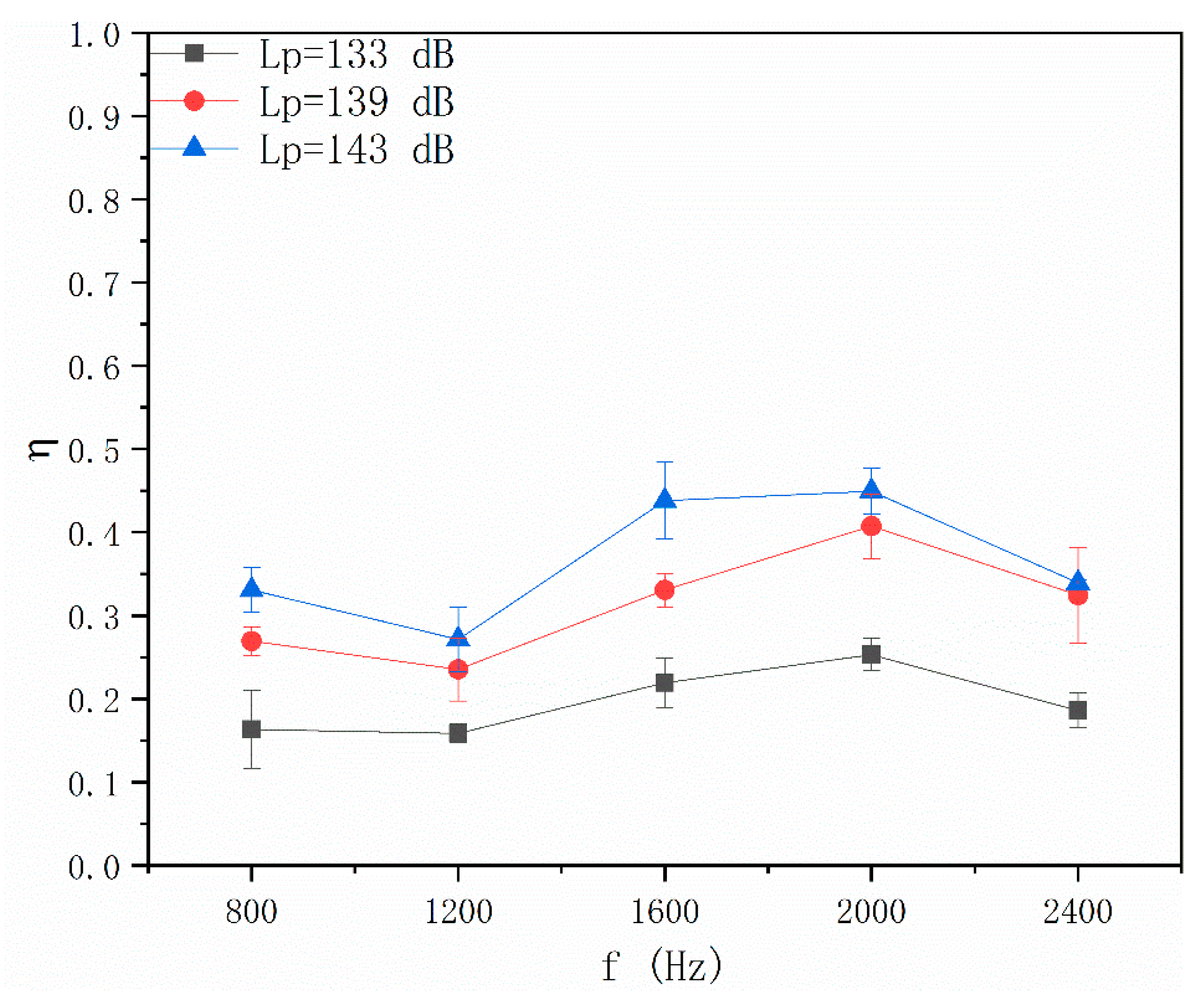
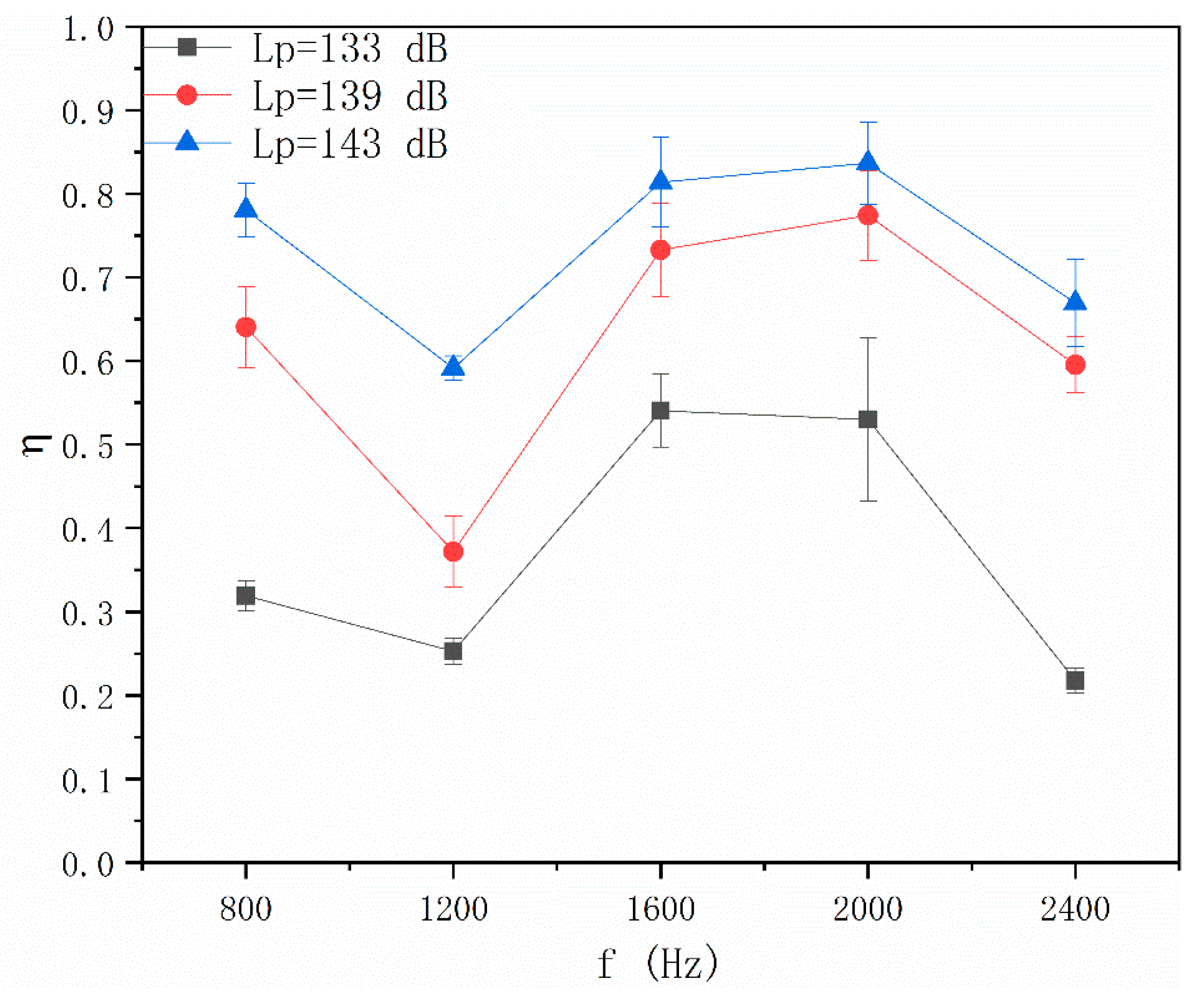
4.1. Effects of Acoustic Wave Field on Particle Number Concentration
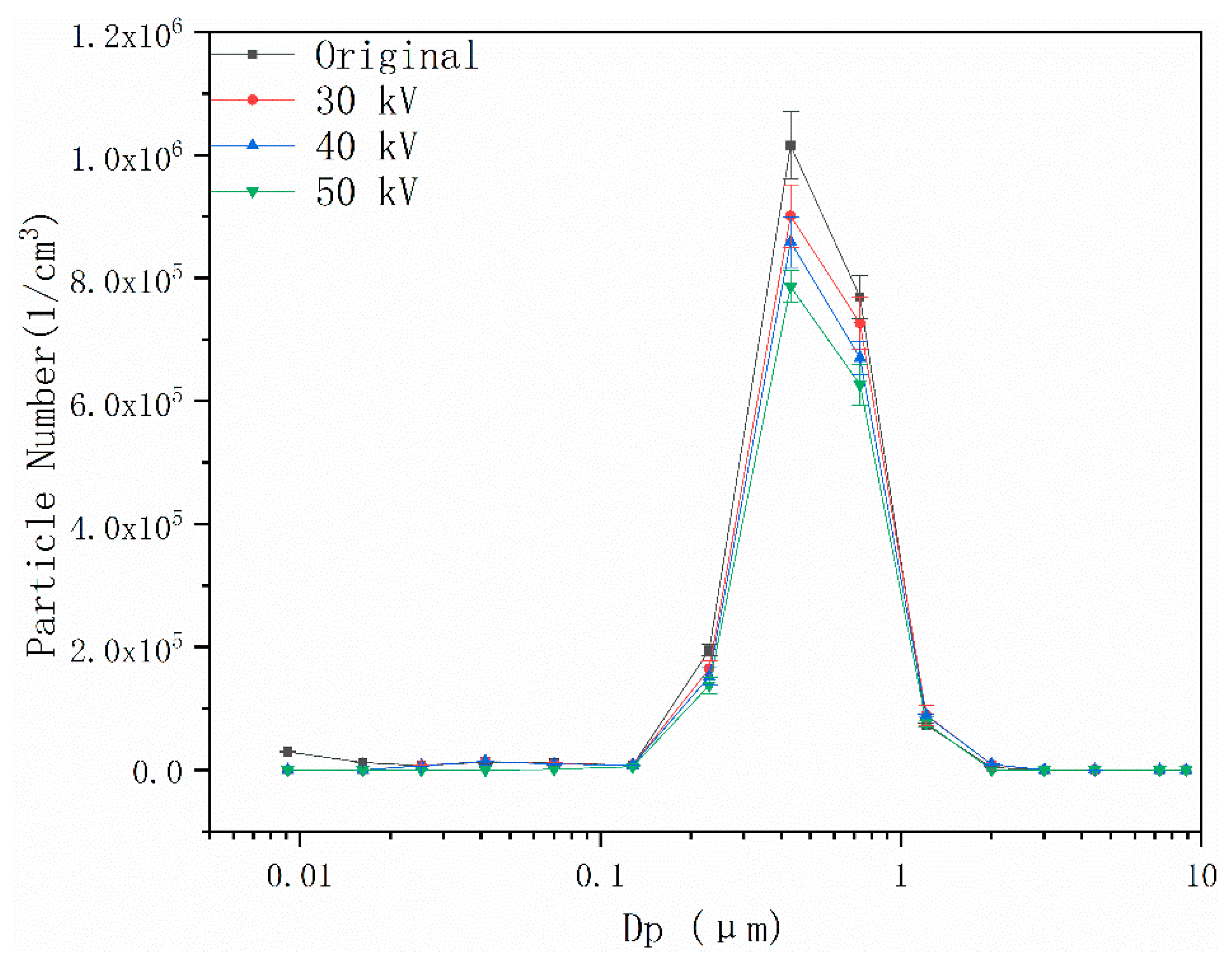
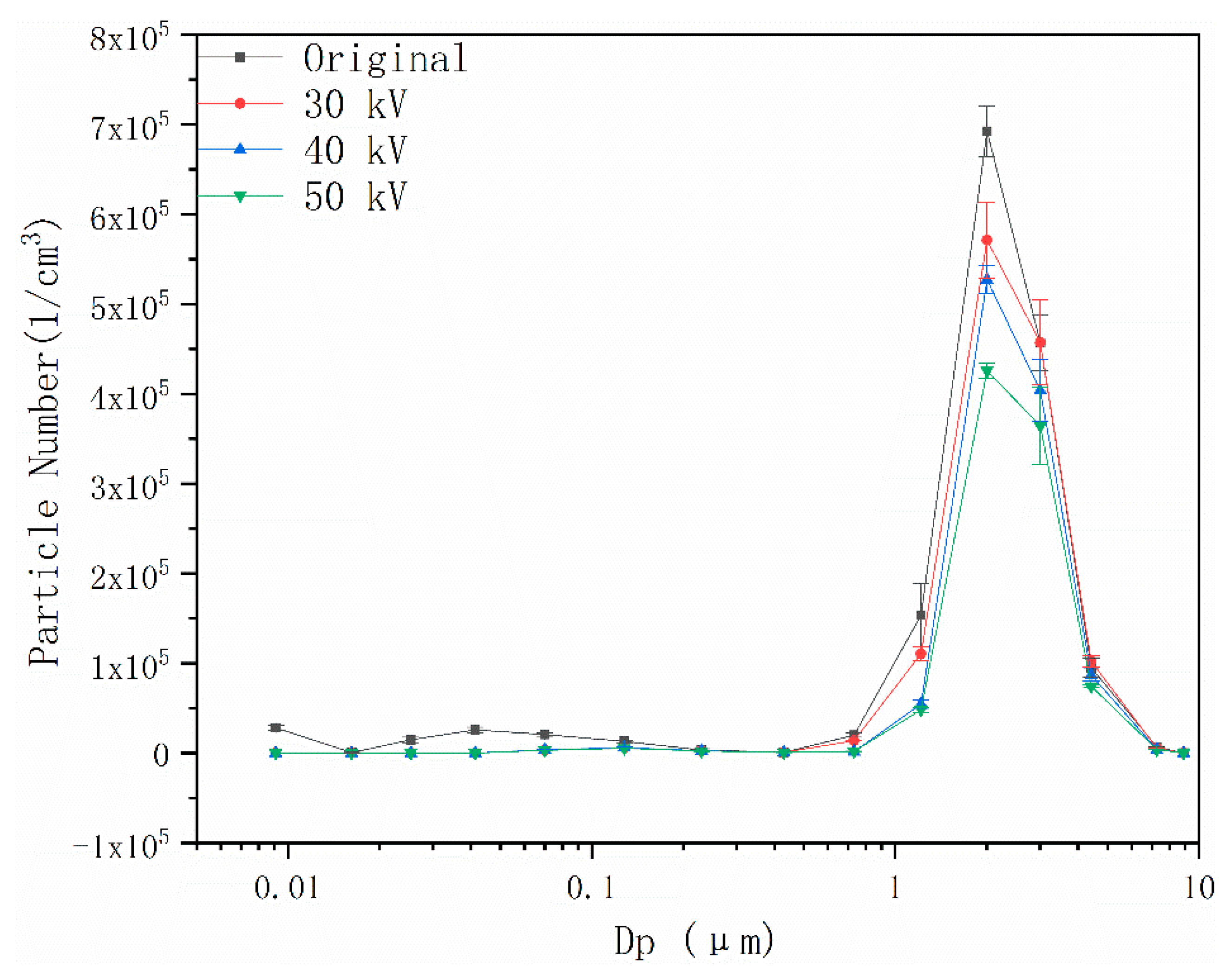
4.2. Effects of Pulsed Corona Discharge Field on Particle Number Concentration
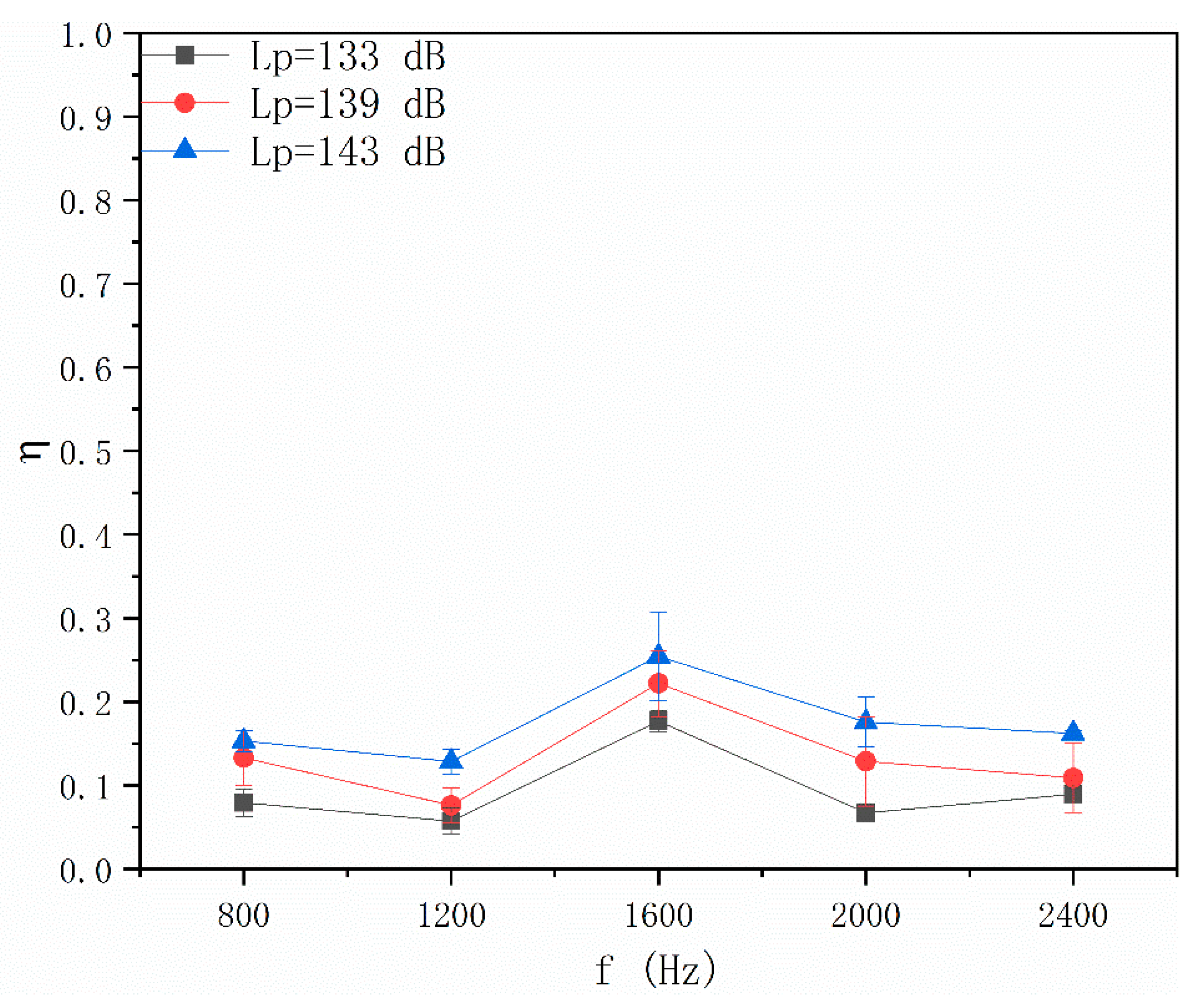
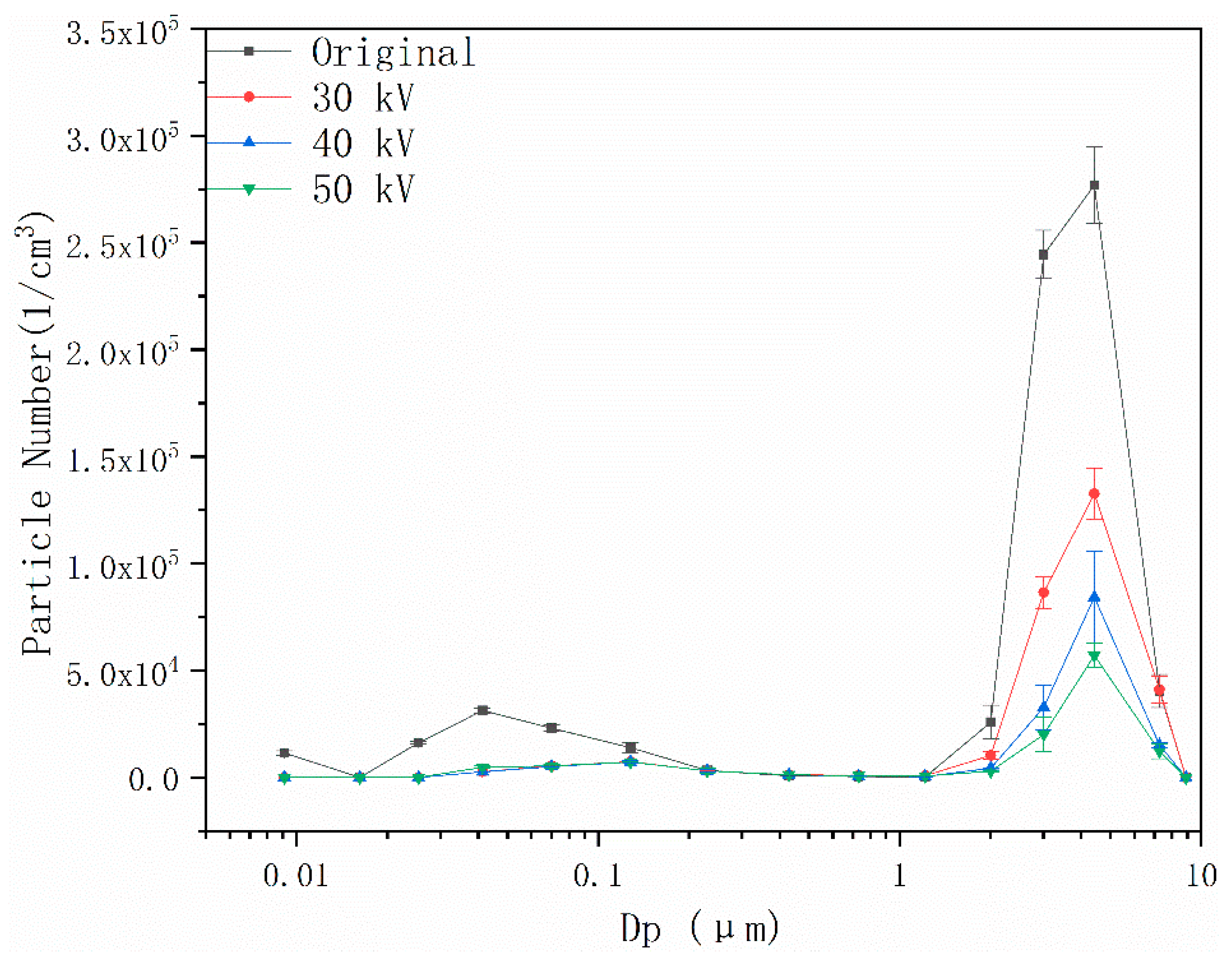
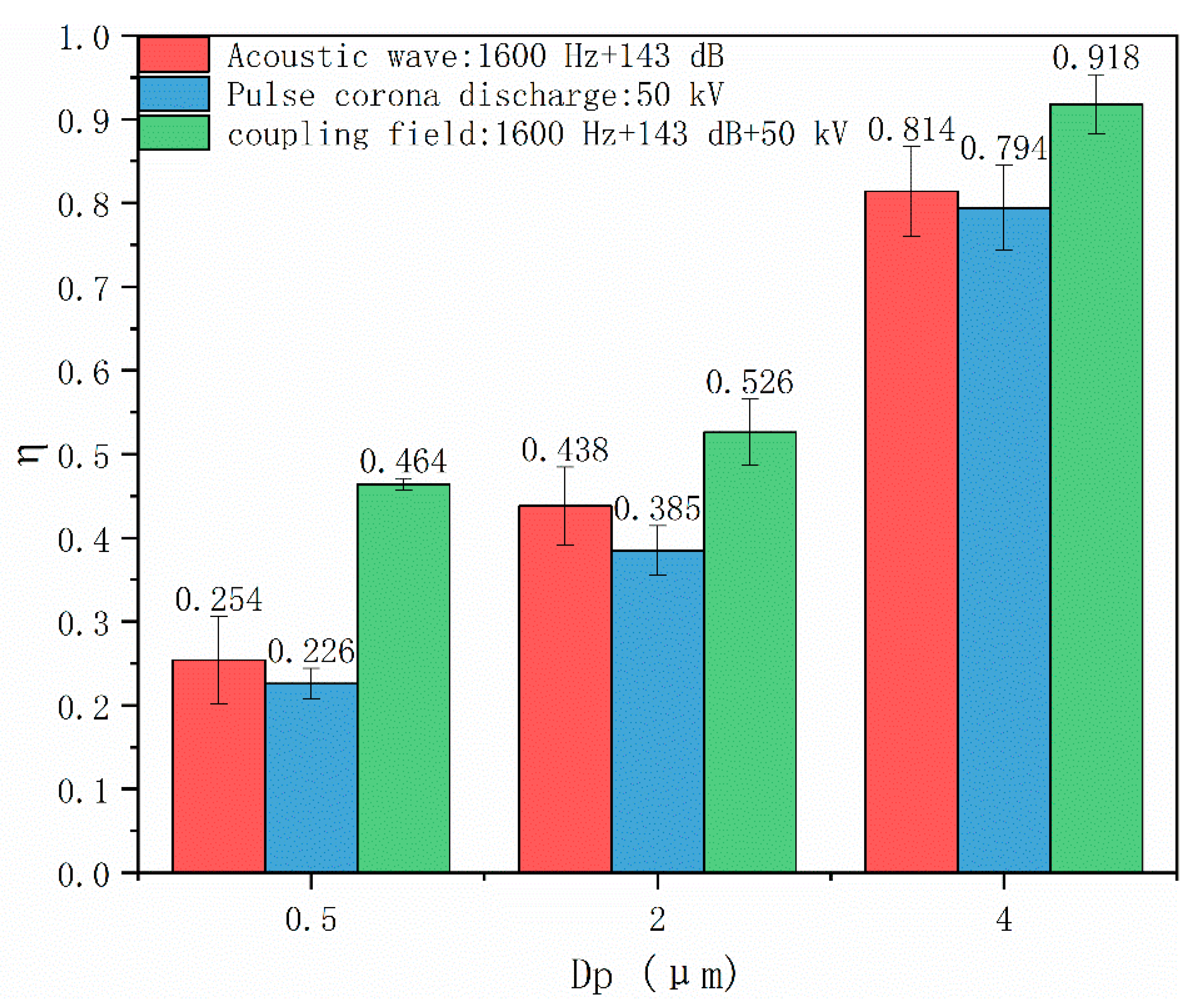
4.3. Effects of Coupling Field on Particle Number Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Wenchang, H.; Minghua, L.; Yong, L.; Shitang, H. A Novel Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Based on Surface Acoustic Wave Technology. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ji, P.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Lin, R. Comprehensive understanding of SO3 effects on synergies among air pollution control devices in ultra-low emission power plants burning high-sulfur coal. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, B. The heaviest particulate air-pollution episodes occurred in northern China in January, 2013: Insights gained from observation. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Yin, S.; Duan, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, S. Pollution characterization, source identification, and health risks of atmospheric-particle-bound heavy metals in PM10 and PM2. 5 at multiple sites in an emerging megacity in the central region of China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczak, B.; Widziewicz-Rzońca, K.; Zioła, N.; Klejnowski, K.; Juda-Rezler, K. Chemical Characteristics of Fine Particulate Matter in Poland in Relation with Data from Selected Rural and Urban Background Stations in Europe. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haikerwal, A.; Akram, M.; Sim, M.R.; Meyer, M.; Abramson, M.J.; Dennekamp, M. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure during a prolonged wildfire period and emergency department visits for asthma. Respirology 2016, 21, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shao, L.; Li, J.; Chang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J. Characteristics of Individual Particles Emitted from an Experimental Burning Chamber with Coal from the Lung Cancer Area of Xuanwei, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Su, T.; Kong, J. Integrated predictor based on decomposition mechanism for PM2.5 long-term prediction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yue, J.; Chen, C.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, M. A Deep Belief Network Combined with Modified Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for PM2.5 Concentration Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-C.; Lin, G.-Y.; Tsai, C.-J. The predictive method for the submicron and nano-sized particle collection efficiency of multipoint-to-plane electrostatic precipitators. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pan, D.; Hong, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, B.; Peng, Z. Removal of sulfuric acid aerosols in desulfurized flue gas by adding moist air. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Fang, M.; He, M.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z. Insights into agglomeration and separation of fly-ash particles in a sound wave field. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5224–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, S.; Ebert, F. Condensational droplet growth as a preconditioning technique for the separation of submicron particles from gases. Chem. Eng. Process. 1995, 34, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.L. Environmental implications of acoustic aerosol agglomeration. Ultrasonics 2000, 38, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Fang, M. Experimental study on improving the efficiency of dust removers by using acoustic agglomeration as pretreatment. Powder Technol. 2016, 289, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsoukas, T. The coagulation rate of charged aerosols in ionized gases. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 187, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Cen, K. Experimental study of acoustic agglomeration of coal-fired fly ash particles at low frequencies. Powder Technol. 2009, 193, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Tao, C.-J.; Cheng, H.-C. Condensation of supersaturated water vapor on charged/neutral nanoparticles of glucose and monosodium glutamate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 255, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.A.; Hoffmann, T.L.; Gallego, J.A. Precise measurements of particle entrainment in a standing-wave acoustic field between 20 and 3500 Hz. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarabia, E.R.-F.; Elvira-Segura, L.; Gonzalez-Gomez, I.; Rodrıguez-Maroto, J.; Munoz-Bueno, R.; Dorronsoro-Areal, J. Investigation of the influence of humidity on the ultrasonic agglomeration of submicron particles in diesel exhausts. Ultrasonics 2003, 41, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Orthogonal design process optimization and single factor analysis for bimodal acoustic agglomeration. Powder Technol. 2011, 210, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Luo, Z.; Bo, W.; Zhao, L.; Gao, X.; Fang, M.; Cen, K. Experimental investigation on charging characteristics and penetration efficiency of PM2. 5 emitted from coal combustion enhanced by positive corona pulsed ESP. J. Electrostat. 2009, 67, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Frequency comparative study of coal-fired fly ash acoustic agglomeration. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Yang, X.; Kim, C.N. Direct simulation of inhalable particle motion and collision in a standing wave field. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Juárez, J.A.; Riera-Franco De Sarabia, E.; RodrÍguez-Corral, G.; Hoffmann, T.L.; Gálvez-Moraleda, J.C.; RodrÍguez-Maroto, J.J.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Bahillo-Ruiz, A.; MartÍn-Espigares, M.; Acha, M. Application of acoustic agglomeration to reduce fine particle emissions from coal combustion plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3843–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochet, R. Lois Charge des Fines Particules (Submicroniques) Etudes Théoriques-Controles Récents Spectre de Particules; Coll. Int. la Physique des Forces Electrostatiques et Leurs Application, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1961; Volume 102, pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, D.; Lu, M.; He, M.; Fang, M.; Cen, K. Agglomeration Kernel of Bipolar Charged Particles in the Presence of External Acoustic and Electric Fields. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.E. Evaluation of the Direct Cost of Sulfur Abatement under the Main Desulfurization Technologies. Energy Sources 1995, 17, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, D.; Lu, M.; Fang, M. Effects of simultaneous acoustic and electric fields on removal of fine particles emitted from coal combustion. Powder Technol. 2015, 281, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T (°C) | 160 | 180 | 200 | 220 | 240 | 260 | 280 |
| Particle Size (μm) | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 4.0 | 6.3 | 8.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, M.; Luo, Z.; Wang, H.; Fang, M. The Influences of Acoustic and Pulsed Corona Discharge Coupling Field on Agglomeration of Monodisperse Fine Particles. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031045
He M, Luo Z, Wang H, Fang M. The Influences of Acoustic and Pulsed Corona Discharge Coupling Field on Agglomeration of Monodisperse Fine Particles. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031045
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Mingchun, Zhongyang Luo, Haolin Wang, and Mengxiang Fang. 2020. "The Influences of Acoustic and Pulsed Corona Discharge Coupling Field on Agglomeration of Monodisperse Fine Particles" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031045
APA StyleHe, M., Luo, Z., Wang, H., & Fang, M. (2020). The Influences of Acoustic and Pulsed Corona Discharge Coupling Field on Agglomeration of Monodisperse Fine Particles. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031045







