Abstract
In this paper, leaky Lamb wave radiation from a waveguide plate with finite width is investigated to gain a basic understanding of the radiation characteristics of the plate-type waveguide sensor. Although the leaky Lamb wave behavior has already been theoretically revealed, most studies have only dealt with two dimensional radiations of a single leaky Lamb wave mode in an infinitely wide plate, and the effect of the width modes (that are additionally formed by the lateral sides of the plate) on leaky Lamb wave radiation has not been fully addressed. This work aimed to explain the propagation behavior and characteristics of the Lamb waves induced by the existence of the width modes and to reveal their effects on leaky Lamb wave radiation for the performance improvement of the waveguide sensor. To investigate the effect of the width modes in a waveguide plate with finite width, propagation characteristics of the Lamb waves were analyzed by the semi-analytical finite element (SAFE) method. Then, the Lamb wave radiation was computationally modeled on the basis of the analyzed propagation characteristics and was also experimentally measured for comparison. From the modeled and measured results of the leaky radiation beam, it was found that the width modes could affect leaky Lamb wave radiation with the mode superposition and radiation characteristics were significantly changed depending on the wave phase of the superposed modes on the radiation surface.
1. Introduction
Elastic-guided waves can travel a long distance along the waveguide geometry from a single excitation location. This ability of guided waves not only makes it possible to inspect huge structures effectively, but can also allow remote inspection for hard-to-access structures in harsh environments and underground [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Therefore, guided waves have been widely used in non-destructive testing (NDT) and structural health monitoring (SHM) fields.
There are numerous industrial applications of guided waves; one that maximally uses the advantages of guided waves is waveguide sensor [9,10,11,12,13]. Waveguide sensors are excellent inspection alternatives for special NDT applications because they can perform remote inspection through a long waveguide without any damage to the main probe unit or the inspector under hazardous inspection environments. Hence, waveguide sensors have often been used in the field of power plants; one application example is under-sodium viewing (USV) in a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), which uses liquid sodium as a core coolant. In an SFR, because of the optical opacity of the liquid sodium, USV for the in-vessel structures (including the reactor core) is conducted using the ultrasonic imaging technique. For these USV inspections, immersion sensors have been developed since the early stage of SFR development; however, there are remaining unresolved issues in their development, including thermal and radiation damage to the main actuating part submerged in the high temperature and radioactive liquid sodium [14]. On the other hand, waveguide sensors have been regarded as a promising USV alternative because there is no concern about any damage to the main actuating part.
The waveguide sensors under development can be classified based on the waveguide geometry of a rod or plate. A rod-type waveguide sensor uses a bundle rod and a rolled plate [14,15], whereas a plate-type waveguide sensor uses a plate strip with finite width [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Between these, the plate-type waveguide sensor has been established based on the long distance propagation ability and high radiation efficiency in a fluid of the lowest-order flexural mode of a Lamb wave and its concept for USV was proposed in the early 1980s [16,17]. In recent years, sensor development has resumed [18], with one advanced design concept newly adopting a beryllium coating layer [19]; most recently, USV performance of a 10 m full scale waveguide sensor has been demonstrated in a sodium environment (>200 °C) [20,21], and the underwater performance of ranging inspection for obstacle detection in refueling processes has also been validated [22]. Since its early development stage, however, the plate-type waveguide sensor has had a technical issue caused by the radiation characteristics of leaky Lamb waves. The immersion- and rod-type waveguide sensors generally use longitudinal wave radiation from the axisymmetric radiator; therefore, they have a single axisymmetric main beam and their USV resolutions are not constrained by the scanning direction. On the contrary, the plate-type waveguide sensor uses leaky Lamb wave radiation along the rectangular radiating face and it has a non-axisymmetric radiation beam, which has different radiation characteristics on the vertical and lateral planes (the vertical and lateral planes are on the median and transverse planes with respect to the waveguide plate). Here, the formation and characteristics of the vertical beam are understandable based on previous research on leaky Lamb wave radiation in an infinitely wide plate [23,24,25,26]. However, those of the lateral beam have not been completely explained, and moreover, there is little research that fully addresses the leaky Lamb wave radiation from a plate strip with finite width.
One effort has been made to understand leaky Lamb wave radiation from a plate strip with finite width [27]. In this previous research, characteristics of the leaky radiation beam radiated from the plate strip were acoustically analyzed on two median and lateral planes; however, this research assumed that the velocity distribution of leaky Lamb waves on the aperture was uniform in the width direction. In other words, the effect of the plate width on the leaky Lamb wave radiation was partially studied without full consideration of the propagation characteristics of the leaky Lamb waves in the plate strip.
This paper investigates leaky Lamb wave radiation from a waveguide plate with a finite width to gain a basic understanding of the radiation characteristics of the plate-type waveguide sensor. First, the propagation characteristics of the Lamb wave in the plate strip was evaluated using the semi-analytical finite element (SAFE) method. Then, leaky Lamb wave radiation was computationally modeled on the basis of the analyzed propagation characteristics, and was also measured experimentally for comparison. From this analysis and measurement, the formation and characteristics of the leaky radiation beam radiated from a waveguide plate are three-dimensionally revealed and the design direction for performance improvement of the waveguide sensor is briefly proposed.
2. Lamb Wave Propagation in a Plate Strip with Finite Width
2.1. Semi-Analytical Finite Element(SAFE) Method
To study the leaky Lamb wave radiation from a plate strip with finite width, it is necessary to sufficiently understand the propagation characteristics of the Lamb wave in the plate strip. Figure 1 illustrates the coordinate system of a plate strip with thickness and width ; the plate is infinitely long to ±x direction and the plate material is assumed to be a homogeneous, isotropic, and lossless one. Wave propagation in the plate strip has been analytically studied by many researchers [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36], but most of their analytical studies show limitations of effective frequency and thickness–width ratio by assumptions used in the solution derivation. Fortunately, the semi-analytical finite element (SAFE) method, a numerical method with no limitations of the analytical solutions, has been developed [35,36,37]. Since the SAFE method can calculate dispersion curves for arbitrary cross-section waveguide geometries, such as rails as well as plate strips [35,36,37], it is now prevalent in NDT and SHM fields.
Figure 1.
Coordinate system of a plate strip with finite width.
The SAFE method only constructs the two dimensional finite element (FE) model for the cross-section of the analysis object and the analytical solution of the wave propagation is then applied to the constructed FE model; the cross-section parallel to the yz plane is only modeled using FE and the equation of a traveling wave along the +x direction is applied. The governing equation of the constructed FE system without the external load can be written as follows:
where , and are stiffness matrices, is the mass matrix of the cross section and the displacement vector is given by:
where denotes displacement functions of the cross section. From this eigenvalue equation, the wavenumber can be solved at each frequency and the dispersion curves can be drawn within the interested frequency range. Recently, SAFE methods using commercial Finite Element Method (FEM) software have been introduced, and thereby SAFE modeling has become convenient [38,39]. In this study, to analyze the wave propagation in the plate strip, a modal analysis method under periodic boundary conditions [39] was employed in the commercial FEM software ANSYS (release 2017, ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, PA, USA).
2.2. Dispersion Curves and Wave Structures
Figure 2 shows calculated dispersion curves of Lamb waves in a stainless steel (SS304) plate with 1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width in a vacuum. Note that propagation characteristics in the plate coupled with liquid, such as the wave velocities and structures, are assumed to not be different from those in a vacuum [40]. Specifically, Figure 2a shows the phase velocity dispersion curves, whereas Figure 2b shows the group velocity dispersion curves. As shown in these dispersion curves, in contrast to those in an infinitely wide plate, Lamb waves in a finite width plate have numerous width modes. Therefore, a certain single mode of Lamb waves in the plate strip is named S(m,n) or A(m,n); the first index m is the order of the thickness mode; the second index n is that of the width mode. Furthermore, one can observe that the phase velocity increases and the group velocity decreases as the order of the width mode increases.
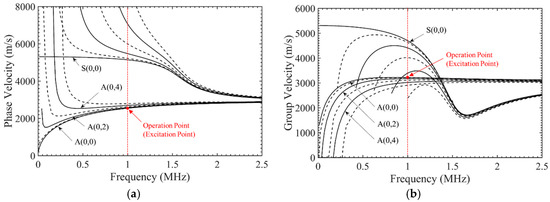
Figure 2.
Dispersion curves of Lamb waves in a SS304 plate with 1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width: (a) phase velocity, (b) group velocity; SS304 plate properties: density = 7800 kg/m³, longitudinal wave velocity = 5800 m/s and shear wave velocity = 3160 m/s; solid line: even order of width mode (symmetric width mode); dashed line: odd order of width mode (anti-symmetric width mode).
The most important observation in the dispersion curves of Figure 2 is that many Lamb wave modes are very close to each other at the operation point of the waveguide sensor, which indicates the difficulty of single mode excitation. In this high modal density area, neighbor width modes from the A(0,1) mode to the A(0,4) mode can have a high possibility of being excited with the lowest-order mode, the A(0,0) mode; the S(m,n) modes are not in our interest because the flexural modes, A(0,n) modes are only used for the high radiation efficiency in the waveguide sensor. In addition, it can be reasonably inferred that the multiple width modes cannot be separated during the short propagation distance because they are not significantly different in group velocities at the operation point.
Each higher-order width mode can be identified in the wave structure results, as shown in Figure 3. The out-of-plane velocity profiles in the width direction change appreciably according to the order of the width mode; they can be described as a combination of the trigonometric and hyperbolic functions [31,32]. Here, the non-flat velocity profile in case of n = 0 is estimated to be caused by the free–free boundary condition and high frequency range. From the dispersion curves and the wave structures, it can be assumed that leaky Lamb wave propagation in the plate strip coupled with liquid might be affected by superposition among the higher-order width modes.
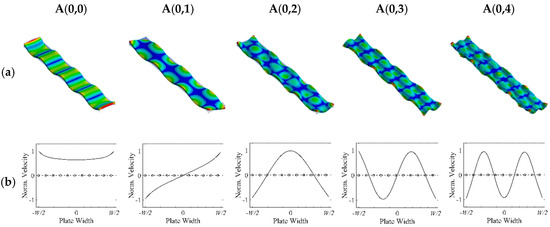
Figure 3.
(a) Wave structures and (b) particle velocity profiles (width direction) of the A(0,n) modes in a SS304 plate with 1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width at 1.0 MHz; the velocity profiles are extracted on the neutral plane (z = 0); solid line: out-of-plane direction (z direction); dashed line: in-plane horizontal direction (y direction); circle markers: in-plane extensional direction (x direction).
3. Leaky Lamb Wave Radiation from a Waveguide Plate with Finite Width
3.1. Rayleigh–Sommerfeld Integral Model
Figure 4 presents a radiation aperture area with length and width . A leaky Lamb wave is propagated along the +x axis and is sequentially radiated into the surrounding liquid (z > 0) from the radiation surface ; the leaky Lamb wave radiation from the radiation surface is limited by in an infinite plate in the x direction. In fact, leaky Lamb wave radiation from the radiation surface at the plate end is used in the practical waveguide sensor. However, the radiation of the backward leaky Lamb wave reflected from the aperture end is not considered in this study; its effect on the main beam generated by the forward wave is assumed to be negligible based on its different radiation angle and diminished energy. An acoustic pressure at a certain point can be defined by the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld integral (RSI) [41]:
where is the liquid density, is the wavenumber in the liquid, and is the velocity distribution on the aperture, given by:
where and are the attenuation coefficient and the wavenumber of the leaky Lamb wave, respectively, and is the velocity profile of a certain width mode in the width direction. Based on this integral equation, the RSI model was constructed as a computational approach; this model is also called the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld numerical integration (RSNI) [42]. The RSI model computes the integral equation (Equation (3)) without any assumptions and approximations such as the far-field approximation; therefore, this model is known to have computation results of high accuracy [43]. In addition, RSI can provide the better computational speed compared with SAFE or FEM approaches, especially for the high-frequency model that requires both small wavelengths and an integration time step [44].
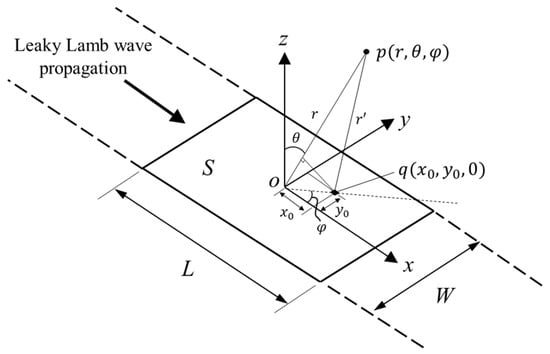
Figure 4.
Coordinate system of radiation aperture area for leaky Lamb wave radiation.
The underwater beam profile of the leaky wave radiated from the unbaffled aperture shown in Figure 4 was calculated using the constructed RSI model. The water domain for calculating the beam profile was predetermined as 90 mm (x) × 50 mm (y) × 90 mm (z) and the total number of grid points was 300 × 167 × 300, with 0.3 mm grid spacing (about 1/5 times smaller than the wavelength of the leaky wave), and 0.5 mm source spacing (about 1/5 times smaller than the wavelength of the leaky Lamb wave). The out-of-plane velocity profiles obtained by the SAFE method were applied to the point sources with the curve-fitting technique. The 3D acoustic field by a certain point source on the aperture was calculated; then, the calculation process was repeated for all point sources. The acoustic field of the leaky wave radiated from the aperture was obtained by integrating the individual calculation results. From the calculated acoustic field, the beam profile was reconstructed by making an envelope for the maximum pressure peaks on the grid points; the beam profile was then normalized by the maximum value in the entire calculation domain. All parameters to calculate the radiation beam profiles of the leaky Lamb wave, such as the phase velocity, were determined on the basis of the dispersion curve results shown in Figure 2a. Other model information is presented in Table 1; the attenuation coefficient of the leaky Lamb wave was adopted from the attenuation dispersion curve in the infinite plate; the attenuation coefficient is strictly different depending on the width mode, but its value at 1.0 MHz is assumed to be equal to that of the fundamental flexural mode in the infinite plate.

Table 1.
Rayleigh–Sommerfeld integral (RSI) model details.
Finally, a 3D beam profile can be analyzed on two independent planes: the vertical and lateral planes. The vertical plane is the median plane (xz plane, φ = 0) with respect to the waveguide plate, and the lateral plane is a lateral cross-sectional plane across the main lobe at the radiation angle. The beam profile on the vertical plane is defined as the vertical beam profile; that on the lateral plane is defined as the lateral beam profile.
3.2. Leaky Radiation Beam Patterns and Beam Profiles
Beam profiles of the A(0,n) mode for n = 0, 1, 2, and 3 are shown in Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. Figure 5a, Figure 6a, Figure 7a and Figure 8a and Figure 5b, Figure 6b, Figure 7b and Figure 8b represent the vertical and lateral beam profile results obtained from the RSI model, respectively.
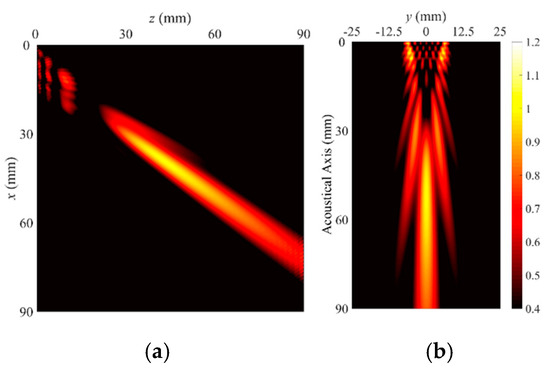
Figure 5.
Radiation patterns and beam profiles of leaky A(0,0) mode Lamb wave, (a) vertical beam profile, and (b) lateral beam profile.
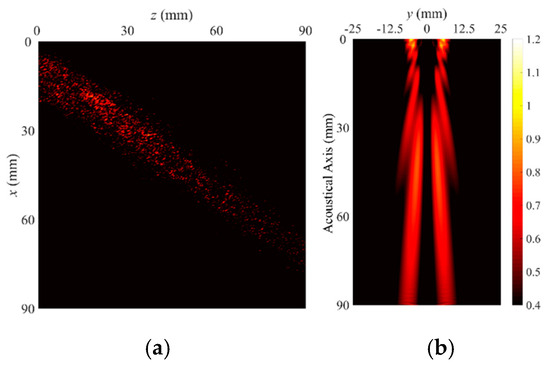
Figure 6.
Radiation patterns and beam profiles of leaky A(0,1) mode Lamb wave, (a) vertical beam profile, and (b) lateral beam profile.
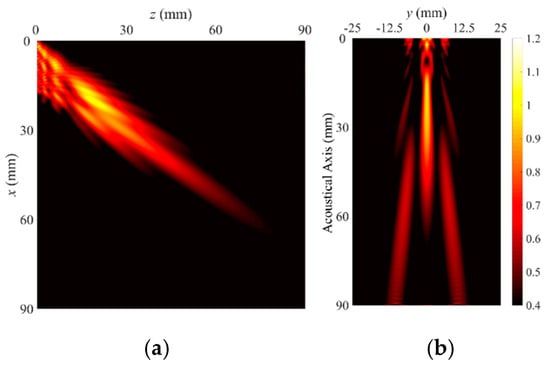
Figure 7.
Radiation patterns and beam profiles of leaky A(0,2) mode Lamb wave, (a) vertical beam profile, and (b) lateral beam profile.
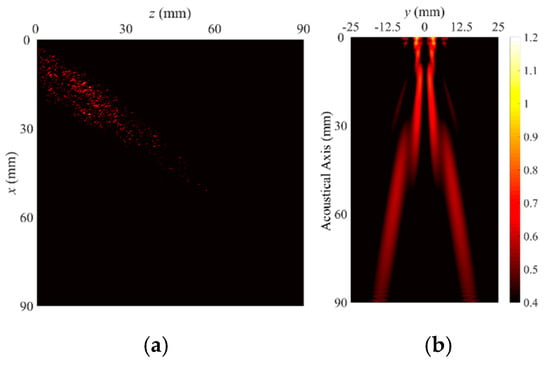
Figure 8.
Radiation patterns and beam profiles of leaky A(0,3) mode Lamb wave, (a) vertical beam profile, and (b) lateral beam profile.
The first trend identified in Figure 5a, Figure 6a, Figure 7a and Figure 8a is that the radiation angles of the vertical beam show no big differences with changes in the width mode because the phase velocities at 1.0 MHz are close to each other; the radiation angles are calculated as 34.0°–35.5° with respect to the z axis.
The second trend is that the leaky radiation beam pattern of the A(0,0) mode has a single main lobe in the far-field as shown in Figure 5b, but the others have split ones as shown in Figure 6b, Figure 7b and Figure 8b, In other words, the A(0,n) mode Lamb waves above n = 1 induce beam splitting on the lateral plane. It is acoustically clear that the beam splitting is caused by the sinusoidal profiles in the width direction on the aperture. Also, the splitting angle increases as the order increases.
The third trend is that the odd order of the width mode has no vertical beam profile at y = 0 (see Figure 6b and Figure 8b) due to the anti-symmetric profile in the width direction, which has a node point at the center of the plate width. As a result, the lowest-order width mode of a Lamb wave in a plate strip provides a single main beam similar to that of a conventional immersion probe, and thus it can be best to solely use the leaky radiation beam of the lowest-order width mode in the waveguide sensor for immersion inspection.
4. Beam Profile Measurements
4.1. Experimental Setup
Figure 9 shows the experimental setup for the measurement of the leaky radiation beam profile radiated from a plate strip in water. The underwater beam profile measurement system consists of an XYZ three-axis scanner, a hydrophone (ONDA HNR-0500, frequency range: 0.25–10 MHz) with a pre-amplifier (ONDA AH-1100, frequency range: 0.005–25 MHz), a waveform generator (Agilent 33521A), a gated amplifier (RITEC GA-2500A), a broadband receiver (RITEC BR-640), a noise suppressor with a 1.0 MHz center frequency (ORBISSYS NS-0017) and a computer with master control software (UTEX WinspectTM). Material and dimensions of the 400 mm long plate strip used in the experiment are the same as those in the RSI model (1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width); also, the aperture size is 18 mm × 15 mm, the same as that in the RSI model. The material of an ultrasonic wedge with 19 mm height and 20 mm width is Lucite (= 2370 m/s); the incidence angle of the wedge is 70° for the generation of the A(0,0) mode Lamb wave at 1.0 MHz. The wedge was mounted with a PZT (lead zirconate titanate) transducer with a 0.5 inch diameter and 1.0 MHz center frequency (GE benchmark series) at three different excitation source positions (d = 300, 350, 400 mm), and the leaky radiation beam was measured for each excitation source position. A four-cycled tone burst signal generated from the waveform generator was input to the transducer with signal amplification by the gated amplifier. The leaky wave radiated from the plate strip was measured by the hydrophone; then, the measured wave signal was transferred to the computer after amplifying and band-pass filtering (from 25 kHz to 5 MHz) by the pre-amplifier, the noise suppressor, and the broadband receiver. Scanning volume size was 90 mm (x) × 50 mm (y) × 90 mm (z), the same as the analysis domain of the RSI model, and scan step was 1 mm. In the post-processing process, a 3D beam profile was reconstructed by mapping the measured 3D matrix data comprising the maximum peak () to the space coordinate; as shown in Figure 9c, the maximum peak () of the gated signal beyond the threshold value was extracted and saved. Finally, the reconstructed beam profile was normalized by the maximum value in the far-field domain.
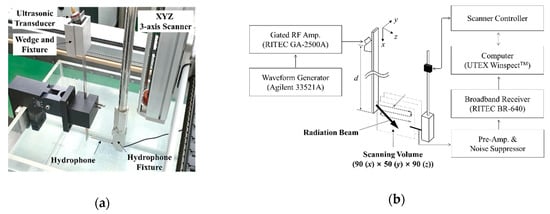
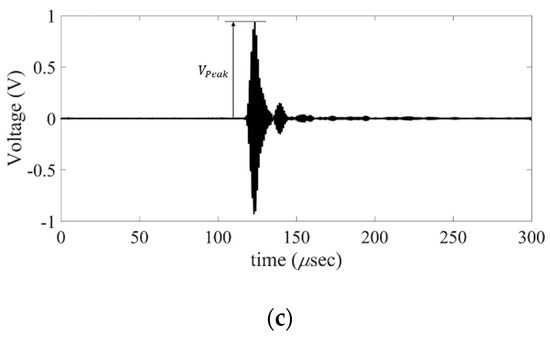
Figure 9.
Experiment for the measurement of the 3D radiation beam profile of a leaky wave radiated from a SS304 plate with 1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width in water, (a) experimental setup and (b) block diagram, and (c) A-scan signal of the leaky wave measured at the center of the radiation surface.
4.2. Measured Beam Profiles and Effects of the Mode Superposition
The measured vertical and lateral beam profiles radiated from the waveguide plate are shown in Figure 10. Without any quantitative evaluations on radiation characteristics, all three measured beam profiles seem to be visually different from those of the A(0,0) mode shown in Figure 5a,b, despite the attempt to excite only the A(0,0) mode, and they show different radiation characteristics depending on the excitation source position. In particular, drastic changes of the lateral beam are noticeable compared with those of the vertical beam; the lateral beams at d = 300 mm and d = 400 mm have a dual main beam, but one at d = 350 mm has a single main beam within the measurement domain. These characteristics cannot be explained by only pure width mode and demonstrate that the leaky radiation beams radiated from the waveguide plate with finite width are affected by the mode superposition of the width modes, as predicted from the dispersion curves of Figure 2.
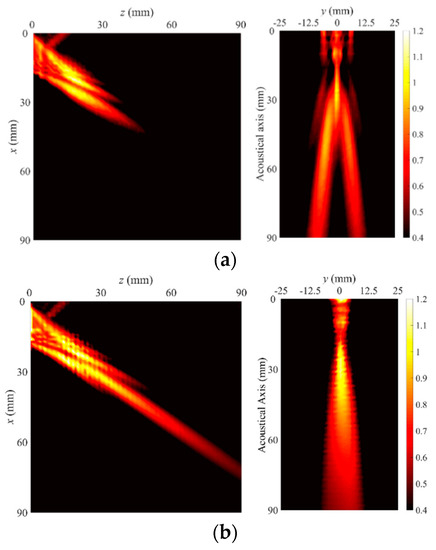
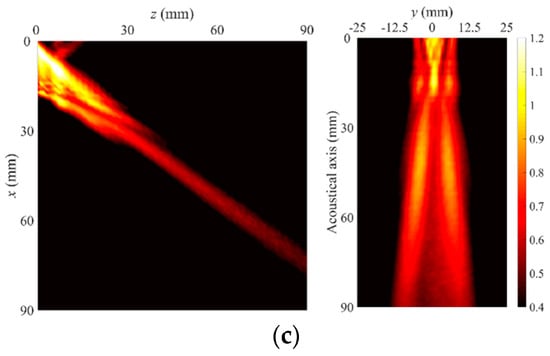
Figure 10.
Measured leaky radiation beam profiles radiated from a SS304 plate (1.5 mm thickness, 15 mm width) with variation of the excitation source position, (a) d = 300 mm, (b) d = 350 mm, and (c) d = 400 mm.
Moreover, the different characteristics changed by the excitation source position are strongly estimated to be affected by the change of the wave phase by phase velocity differences between the superposed modes. Figure 11 shows the wave phase changes on the waveguide plate calculated from the following equation at time , weighting constants a = b = 1, and phase delay constants = = 0:
where and are the normalized velocity distributions of the A(0,0) and A(0,2) modes identified in Figure 3, respectively, and and are the wavenumbers of the A(0,0) and A(0,2) modes, respectively. According to the obtained dispersion curves, the A(0,1) and A(0,2) modes are found to have a high possibility to be excited with the A(0,0) mode. However, only the mode superposition between the A(0,0) mode and the A(0,2) mode was investigated here; the reason why the A(0,1) mode is excluded from the mode superposition is that the anti-symmetric width modes (including the A(0,1) mode) cannot be easily generated by general Lamb wave excitation methods such as the angle–beam method because they have symmetric distribution of the input wave energy in the width direction. It is known that the profile of the input energy in the width direction should match that of the target width mode to be generated [45,46]. The two width modes excited by the high modal density are continually superposed in-phase or out-of-phase with each other during propagation along the waveguide plate. Therefore, from Figure 11, it can be recognized that the superposed modes make the spatial beating due to their differences in phase velocity and the beating on the radiation surface, varied by the excitation source position, results in the change in radiation characteristics.
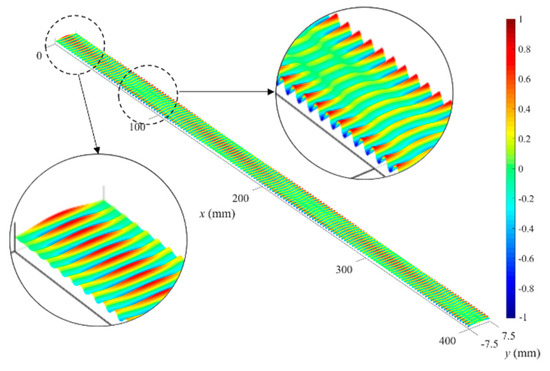
Figure 11.
Change of wave phase on the waveguide plate by the mode superposition between the A(0,0) and A(0,2) modes.
To validate the effect of the spatial beating on the leaky radiation beam, using the constructed RSI model, the leaky radiation beam profiles were simulated with the phase variations of superposed modes on the radiation surface. Figure 12a, Figure 13a and Figure 14a and Figure 12b, Figure 13b and Figure 14b show the wave phase on the radiation surface used in the beam profile calculations of Figure 12c, Figure 13c and Figure 14c and Figure 12d, Figure 13d and Figure 14d; the wave phase on the radiation surface was simulated using Equation (5), including the leaky attenuation coefficient term with adjustment of the phase delay between the superposed modes, and they were presented in case of reasonable quantitative matching with the measurement results as shown in Figure 15 (a representative example of the comparison result). Although the constructed RSI model is a continuous wave model using a single frequency (only the center frequency component of the excitation input is considered), its simulation result shows the good agreement with the experimental one in far-field characteristics and beam pattern.
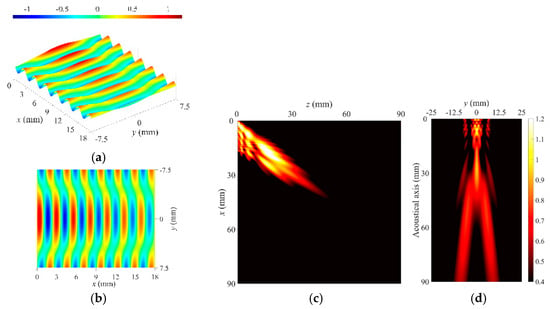
Figure 12.
Simulation #1 of the leaky radiation beam profile based on the wave phase on the radiation surface. (a) Isotropic view of wave phase on radiation surface, (b) top view of wave phase on radiation surface, (c) vertical beam profile, and (d) lateral beam profile.
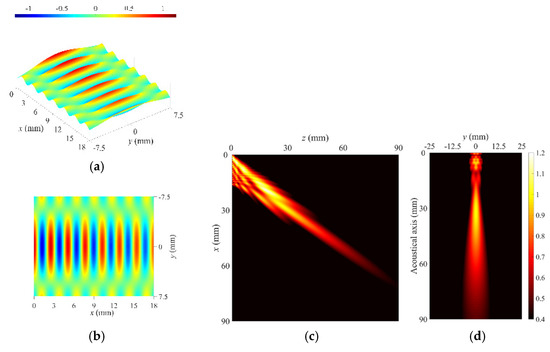
Figure 13.
Simulation #2 of the leaky radiation beam profile based on the wave phase on the radiation surface. (a) Isotropic view of wave phase on radiation surface, (b) top view of wave phase on radiation surface, (c) vertical beam profile, and (d) lateral beam profile.
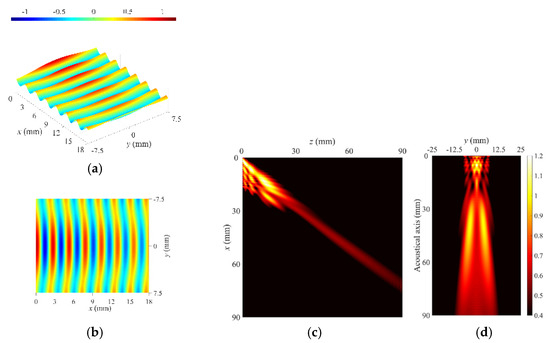
Figure 14.
Simulation #3 of the leaky radiation beam profile based on the wave phase on the radiation surface. (a) Isotropic view of wave phase on radiation surface, (b) top view of wave phase on radiation surface, (c) vertical beam profile, and (d) lateral beam profile.
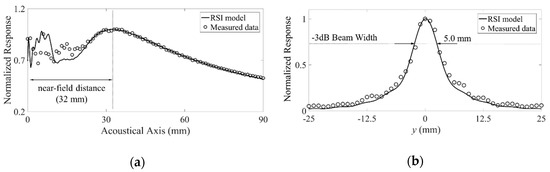
Consequentially, simulation results of the beam profiles describe the fact that the A(0,2) mode affects leaky Lamb wave radiation with the A(0,0) mode in the waveguide plate with finite width, and the change of the wave behavior on the radiation surface caused by the mode superposition and the wave velocity difference results in the change of the radiation characteristics of the leaky radiation beam profile.
5. Discussion and Design Direction for Performance Improvement of the Waveguide Sensor
It seems difficult to completely physically avoid the spatial beating phenomenon and the mode superposition within a short propagation distance because of the high modal density by numerous width modes of the Lamb wave in a waveguide plate with finite width. Therefore, if a single narrow main beam is needed for the application purpose, the position tuning for the excitation source can be recommended for the wave energy concentration at the center in the width direction. Figure 16 shows the measured beam profiles of the leaky Lamb wave excited at d = 330 mm and a clear single main beam can be seen compared with the beam profiles measured for other excitation source positions shown in Figure 10.
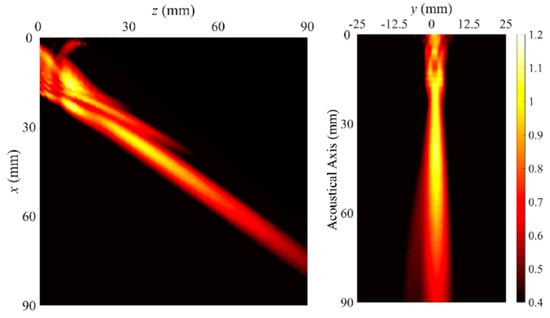
Figure 16.
Measured beam profiles of the leaky Lamb wave excited at d = 330 mm (1.5 mm thickness and 15 mm width, 1.0 MHz center frequency).
In addition, as the plate width increases, the phase velocity curve of the A(0,2) mode converges to that of the A(0,0) mode as shown in Figure 17. This is because the plate strip gets close to the infinitely wide plate with extension of the plate width. Accordingly, unless the plate width is not constrained in the waveguide sensor design, the plate width increment can extend the beating length by a difference in reduction between the A(0,0) and A(0,2) modes in wave velocities, and thereby the effect of the spatial beating on the leaky radiation beam can be reduced.
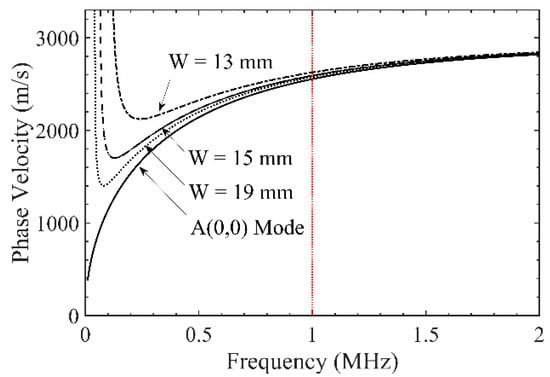
Figure 17.
Phase velocity dispersion curves of the A(0,2) mode in a 1.5 mm thick SS304 plate with variation of the plate width.
Finally, a change in the frequency–thickness product (fh) can be also considered for performance improvement. Figure 18 shows the measured beam profile of the leaky Lamb wave excited at d = 350 mm with fh = 1.5 MHz·mm (1.5 MHz center frequency and 1.0 mm plate thickness), the same as the operational frequency–thickness product in the waveguide sensor (1.0 MHz center frequency and 1.5 mm plate thickness). As the excitation frequency increment makes the wavelength of the leaky Lamb wave short, the width–wavelength ratio is increased. Therefore, the effective plate width can be enlarged without an increment of the physical plate width, although the ultrasonic attenuation is increased and the radiation characteristics are also changed by the frequency increment of the leaky wave.
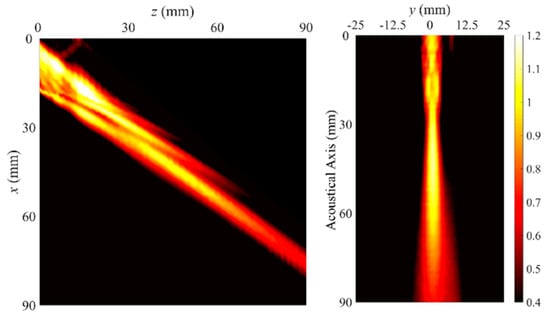
Figure 18.
Measured beam profiles of the leaky Lamb wave excited at d = 350 mm (1.0 mm thickness and 15 mm width, 1.5 MHz center frequency).
As a result, leaky Lamb wave radiation from a waveguide plate with a finite width is affected by the mode superposition of the width modes. For this reason, radiation characteristics of the leaky radiation beam, in particular the lateral beam, are sensitive to the excitation conditions (excitation source position, excitation frequency, etc.). This can be an advantage or disadvantage for the plate-type waveguide sensor. Therefore, according to the application purposes and goals, it will be necessary to properly design and tune the excitation conditions in the plate-type waveguide sensor.
6. Conclusions
This work investigates leaky Lamb wave radiation from a waveguide plate with a finite width with consideration for the width modes of the Lamb wave and their superposition. Dispersion curves obtained using the SAFE method showed that Lamb waves in the plate strip have numerous width modes, in contrast to the case of an infinitely wide plate. These width modes were very close to each other in the dispersion curve, and thus it could be inferred from these results that the multiple width modes were bound to be excited and propagated together by the high modal density. In the beam profile measurement, one could observe that characteristics of the leaky radiation beam from the waveguide plate were noticeably changed with variation of the excitation source position. This characteristic was strongly estimated to be affected by the spatial beating induced by wave velocity differences of the superposed modes. Changes to the wave phase on the waveguide plate were validated by a simple computational result and then the leaky radiation beam profiles were simulated with variation of the wave phase of the superposed modes on the radiation surface. From this simulation, it was demonstrated that leaky Lamb wave radiation from the waveguide plate was affected by superposition of the width modes. In particular, the lateral beam was dominantly influenced by the wave phase on the radiation surface, changed by the excitation source position. Perfect avoidance of the spatial beating caused by the mode superposition of the width modes in the strip-like plate is expected to be physically difficult. Therefore, the excitation conditions, including the excitation frequency and the geometry of the waveguide plate, need to be properly designed for the waveguide sensor using leaky Lamb wave radiation from a waveguide plate with a finite width. Further study is necessary to analyze the radiation characteristics of practical plate-type waveguide sensors based on this preliminary work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: S.-J.P. and Y.-S.J.; investigation: S.-J.P. and Y.-S.J.; SAFE analysis: S.-J.P.; experimental validation: S.-J.P. and Y.-S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-J.P.; writing—review and editing: H.-W.K., and Y.-S.J.; supervision: Y.-S.J.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Nuclear Research & Development Program of the National Research Foundation with a grant funded by the Korea Ministry of Science and ICT.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ditri, J.; Rose, J.L.; Chen, G. Mode selection criteria for defect detection optimization using Lamb waves. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Review of Progress in Quantitative NDE; Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 11, pp. 2109–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Cawley, P.; Alleyne, D.N. The use of Lamb waves for the long range inspection of large structure. Ultrasonics 1996, 34, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleyne, D.N.; Cawley, P. Long range propagation of Lamb waves in chemical plant pipework. Mater. Eval. 1997, 55, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Na, W.-B.; Kundu, T. Underwater pipeline inspection using guided waves. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2002, 124, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Rose, J.L. Ice detection and classification on an aircraft wing with ultrasonic shear horizontal guided waves. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Su, Z.; Cheng, L. Identification of corrosion damage in submerged structures using fundamental anti-symmetric Lamb waves. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Rose, J.L. Goodness dispersion curves for ultrasonic guided wave based SHM: A sample problem in corrosion monitoring. Aeronaut. J. R. Aeronaut. Soc. 2010, 114, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinov, E.; Lowe, M.-J.S.; Cawley, P. Investigation of guided wave propagation and attenuation in pipe buried in sand. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 347, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynnworth, L.C.; Liu, Y.; Umina, J.A. Extensional bundle waveguide techniques for measuring flow of hot fluids. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celga, F.B.; Cawley, P.; Allin, J.; Davies, J. High temperature(>500 °C) wall thickness monitoring using dry-coupled ultrasonic waveguide transducer. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Laws, M.; Ramadas, S.N.; Lynnworth, L.C.; Dixon, S. Parallel strip waveguide for ultrasonic flow measurement in harsh environments. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 62, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Q.; Murayama, R.; Nishino, H. Mode conversion behavior of guided wave in a pipe inspection system based on a long waveguide. Sensors 2016, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Rajagopal, R. In-situ process-and online structural health monitoring of composites using embedded acoustic waveguide sensors. J. Phys. Commun. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.W.; Bond, L.J.; Peters, T.J.; Denslow, K.M.; Posakony, G.J.; Sheen, S.H.; Chien, H.T.; Raptis, A.C. Under-Sodium Viewing: A Review of Ultrasonic Imaging Technology for Liquid Metal Fast Reactors; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Chien, H.; Elmer, T.W.; Lawrence, W.P.; Engel, D.M.; Sheen, S. Development of ultrasonic waveguide techniques for under-sodium viewing. NDT E Int. 2012, 49, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.D.; Deighton, M.O.; Gillespie, A.B.; Pike, R.B. A proposed method for generating and receiving narrow beams of ultrasound in the fast reactor liquid sodium environment. Ultrasonics 1982, 20, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.D.; Barrett, L.M.; McKnight, J.A. Ultrasonic waveguide for use in the sodium coolant of fast reactors. Nucl. Energy 1988, 27, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, Y.-S.; Park, C.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-B. Development of ultrasonic waveguide sensor for under-sodium inspection in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. NDT E Int. 2011, 44, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.-S.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, J.-B.; Kim, J.-Y. Effects of beryllium coating layer on performance of the ultrasonic waveguide sensor. Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Joo, Y.-S.; Park, C.-G.; Kim, J.-B.; Bae, J.-H. Ultrasonic imaging in hot liquid sodium using a plate-type ultrasonic waveguide sensor. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2014, 33, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.-S. Under-sodium viewing techniques in sodium-cooled fast reactors. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2012, 32, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-W.; Joo, Y.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Ultrasonic ranging technique for obstacle monitoring above reactor core in prototype generation IV sodium-cooled fast reactor. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kundu, T. Ultrasonic field modeling in plates immersed in fluid. Int. J. Sol. Struct. 2007, 44, 6013–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Inoue, D. Calculation of leaky Lamb waves with a semi-analytical finite element. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, D.; Hayashi, T. Transient analysis of leaky Lamb waves with a semi-analytical finite element. Ultrasonics 2015, 62, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Z.; Hu, J.; Mao, J.; Lian, G.; Wang, X. Optical visualization of leaky Lamb wave and its application in nondestructive testing. In Proceedings of the 2017 ICU Honolulu Sixth International Congress on Ultrasonics, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–22 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deighton, M.O.; Gillespie, A.-B.; Pike, R.-B.; Watkins, R.-D. Mode conversion of Rayleigh and Lamb waves to compression waves at a metal-liquid interface. Ultrasonics 1981, 19, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, R.W. Dispersion of compressional waves in isotropic rods of rectangular cross section. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1948, 20, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, R.W. The velocity of compressional waves in rods of rectangular cross section. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1950, 22, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D.; Fox, E.A. Vibrations and waves in elastic bars of rectangular cross section. Trans. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1960, 27, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konenkov, Y.K. Plate waves and flexural oscillations of a plate. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1960, 6, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Konenkov, Y.K.; Namukina, N.I.; Tartakovskii, B.D. Investigation of forced flexural vibrations of an elastic strip. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1966, 11, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, W.B. Stress wave propagation in rectangular bars. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1969, 5, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krushynska, A.A.; Meleshko, V.V. Normal waves in elastic bars of rectangular cross section. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Song, W.-J.; Rose, J.L. Guided wave dispersion curves for a bar with an arbitrary cross-section, a rod and rail example. Ultrasonics 2003, 41, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Tanaka, T. Lamb wave propagation in a plate with a finite width. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. A 2006, 72, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukdadi, O.M.; Datta, S.K.; Dunn, M.L. Elastic guided waves in a layered plate with a rectangular cross section. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2002, 124, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakoda, C.; Rose, J.; Shokouhi, P.; Lissenden, C. Using Floquet periodicity to easily calculate dispersion curves and wave structures of homogeneous waveguides. In 44th Annual Review of Progress in Quantitative NDE; Chimenti, D.E., Bond, L.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 37, pp. 020016:1–020016:10. [Google Scholar]
- Groth, E.B.; Iturrioz, I.; Clarke, T.-G.R. The dispersion curve applied in guided wave propagation in prismatic rods. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 15, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlakovic, B.; Lowe, M. DISPERSE: User’s Manual Version 2.0.16B; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2003; pp. 1–209. [Google Scholar]
- Rayleigh, J.W.S. The Theory of Sound; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1945; Volume 2, pp. 1–520. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata, K.; Kono, N. 3-D modelings of an ultrasonic phased array transducer and its radiation properties in solid. In Ultrasonic Waves; Santos, J.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/ultrasonic-waves/3-d-modelings-of-an-ultrasonic-phasedarray-transducer-and-its-radiation-properties-in-solid (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Song, S.-J.; Kim, H.-J. Modeling of radiation beams from ultrasonic transducers in a single medium. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2000, 20, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, T.; Placko, D.; Rahani, E.K.; Yanagita, T.; Dao, C.M. Ultrasonic field modeling: A comparison of analytical, semi-analytical, and numerical techniques. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2010, 57, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Niu, X.; Gan, T.-H.; Kanfoud, J.; Chen, H.-P. A numerical study on the excitation of guided waves in rectangular plates using multiple point sources. Metals 2017, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serey, V.; Quaegebeur, N.; Micheau, P.; Masson, P.; Castaings, M.; Renier, M. Selective generation of ultrasonic guided waves in a bi-dimensional waveguide. SHM 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).